9f2a3f45ca4050070c8752d35125399b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Common Anomaly Detection Platform Tony Xing Senior Product Manager @ Microsoft
Common Anomaly Detection Platform Tony Xing Senior Product Manager @ Microsoft
 Bio § Senior Product Manager of Shared Data team @ Microsoft - Data quality and anomaly detection - NRT datasets - Data Ingestion § Senior Product Manager of Skype Data team @ Microsoft - Real time analytics - Anomaly detection - Cross platform SDKs
Bio § Senior Product Manager of Shared Data team @ Microsoft - Data quality and anomaly detection - NRT datasets - Data Ingestion § Senior Product Manager of Skype Data team @ Microsoft - Real time analytics - Anomaly detection - Cross platform SDKs
 Agenda § Context § Anomaly detection 101 § Problem statement § Design principles § How it works § Algorithms § Challenges and future work
Agenda § Context § Anomaly detection 101 § Problem statement § Design principles § How it works § Algorithms § Challenges and future work

 Shared Data
Shared Data
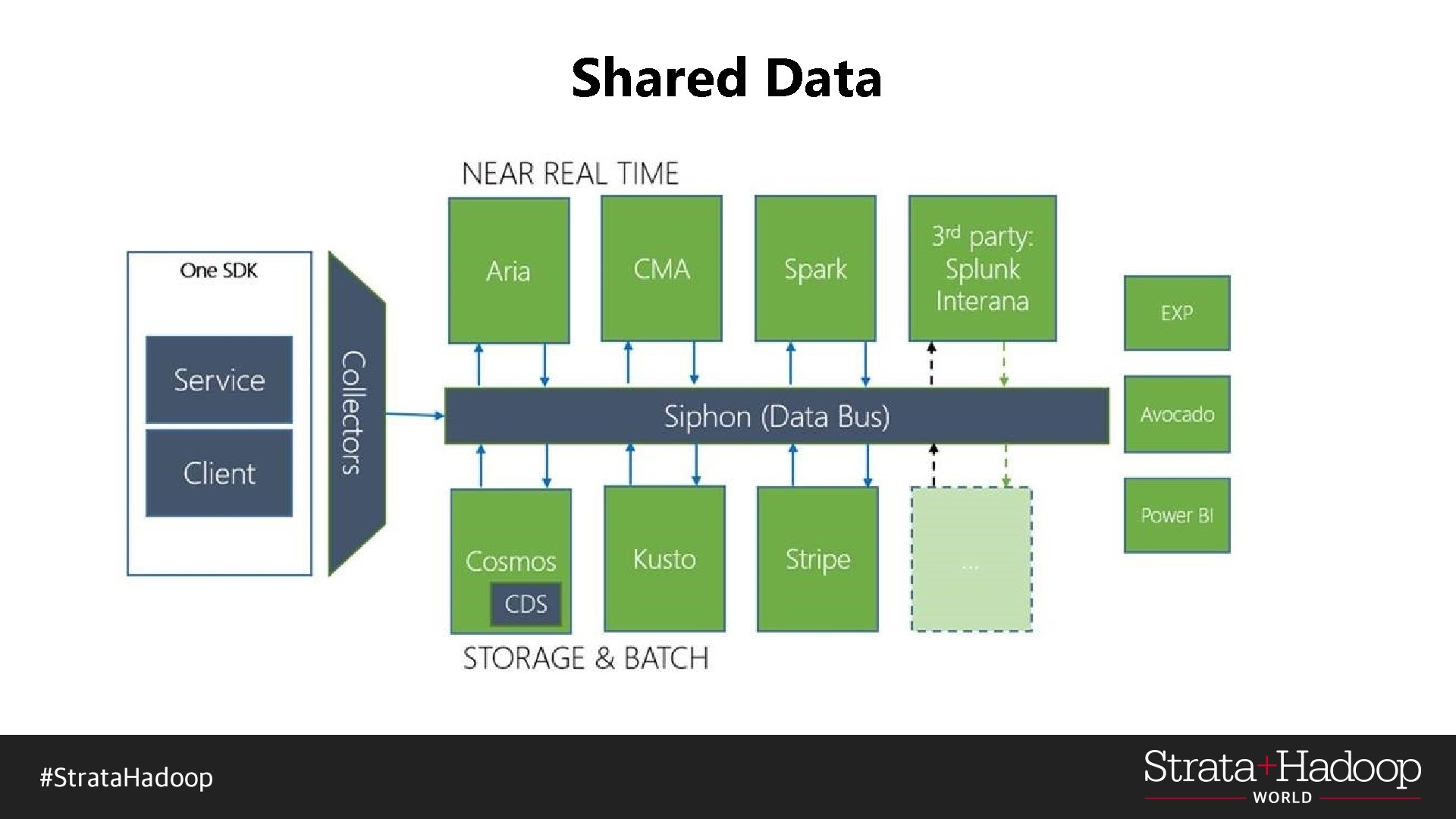 Shared Data
Shared Data

 What is Anomaly Detection § Anomaly detection is the identification of items, events or observations which do not conform to an expected pattern or other items in a dataset § Widely used in - System health monitoring - Business metric monitoring - Application performance monitoring § “My current value is not what it should be as of right now”
What is Anomaly Detection § Anomaly detection is the identification of items, events or observations which do not conform to an expected pattern or other items in a dataset § Widely used in - System health monitoring - Business metric monitoring - Application performance monitoring § “My current value is not what it should be as of right now”
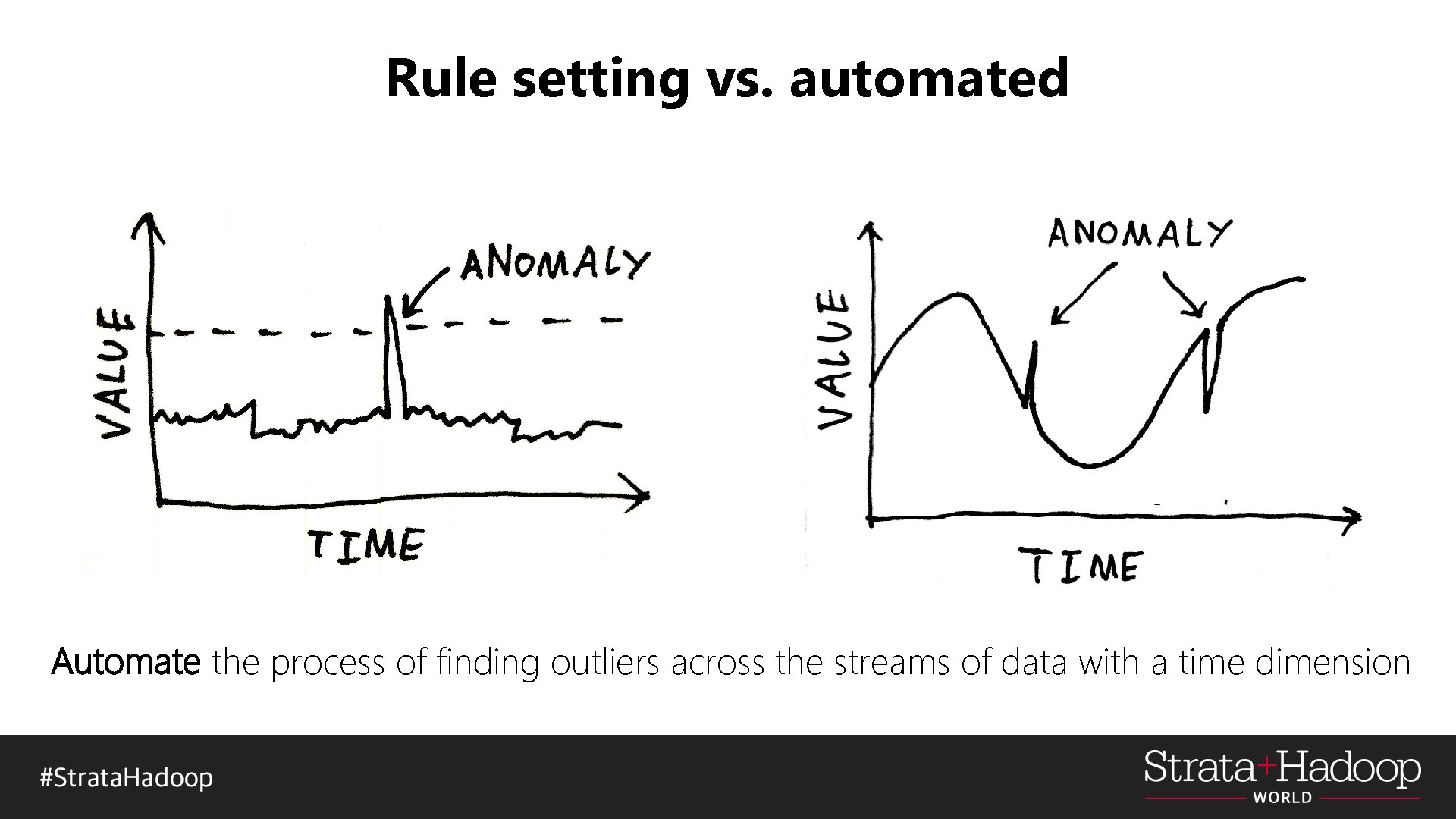 Rule setting vs. automated Automate the process of finding outliers across the streams of data with a time dimension
Rule setting vs. automated Automate the process of finding outliers across the streams of data with a time dimension
 Problem Statement § Manual rule setting is impossible for large number of time series § Single AD algorithm can not fit all signal types § Precision vs. recall § Analysis and diagnostics when issues happen § Near real time detection § Scalable § Customers needs flexibility in plugging in different sources
Problem Statement § Manual rule setting is impossible for large number of time series § Single AD algorithm can not fit all signal types § Precision vs. recall § Analysis and diagnostics when issues happen § Near real time detection § Scalable § Customers needs flexibility in plugging in different sources
 What is CAP § One stop shop for metric monitoring, analysis and diagnostics § Key capabilities Automation: Full automation from creating rules to detection without human intervention Extensibility: Can plug in new data sources and anomaly detection algorithms. Scalability & real time: linear scale out Azure service Finer Granularity: support time series AD in hour/minute level REST APIs: REST APIs available for all operations. Allow easy integration into other product experience Algorithm tuning: allow easier tuning of algorithm
What is CAP § One stop shop for metric monitoring, analysis and diagnostics § Key capabilities Automation: Full automation from creating rules to detection without human intervention Extensibility: Can plug in new data sources and anomaly detection algorithms. Scalability & real time: linear scale out Azure service Finer Granularity: support time series AD in hour/minute level REST APIs: REST APIs available for all operations. Allow easy integration into other product experience Algorithm tuning: allow easier tuning of algorithm
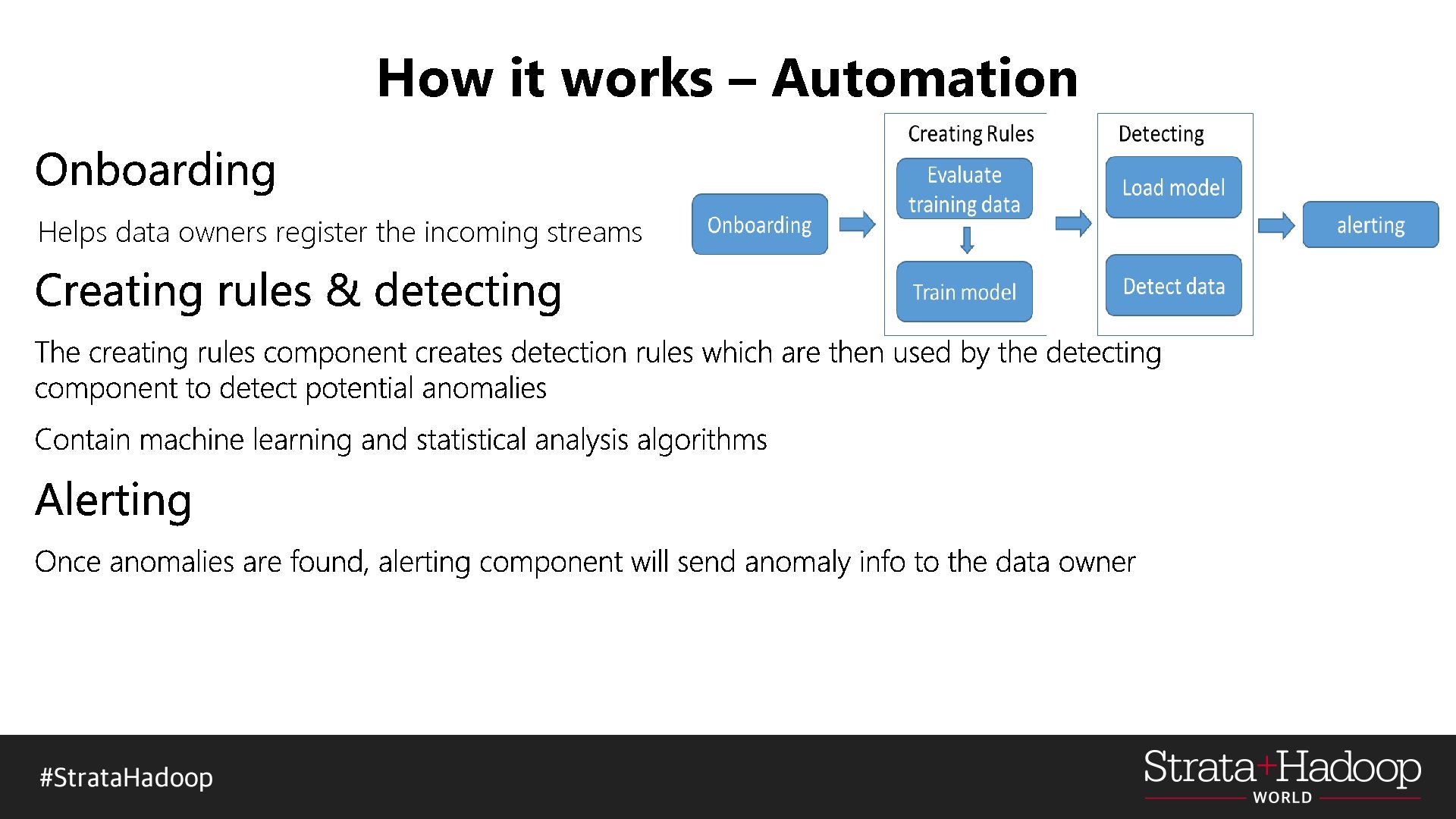 How it works – Automation Helps data owners register the incoming streams
How it works – Automation Helps data owners register the incoming streams
 How it works - Extensibility § Defined a generic interface of training and detection § Each algorithm provider would implement per defined interface § For example for each data point, we expect following from algorithm providers - Whether it is an anomaly - What is the predicted/expected value by algorithm - What is the suggested lower bound - What is the suggested upper bound - Confidence level - …
How it works - Extensibility § Defined a generic interface of training and detection § Each algorithm provider would implement per defined interface § For example for each data point, we expect following from algorithm providers - Whether it is an anomaly - What is the predicted/expected value by algorithm - What is the suggested lower bound - What is the suggested upper bound - Confidence level - …
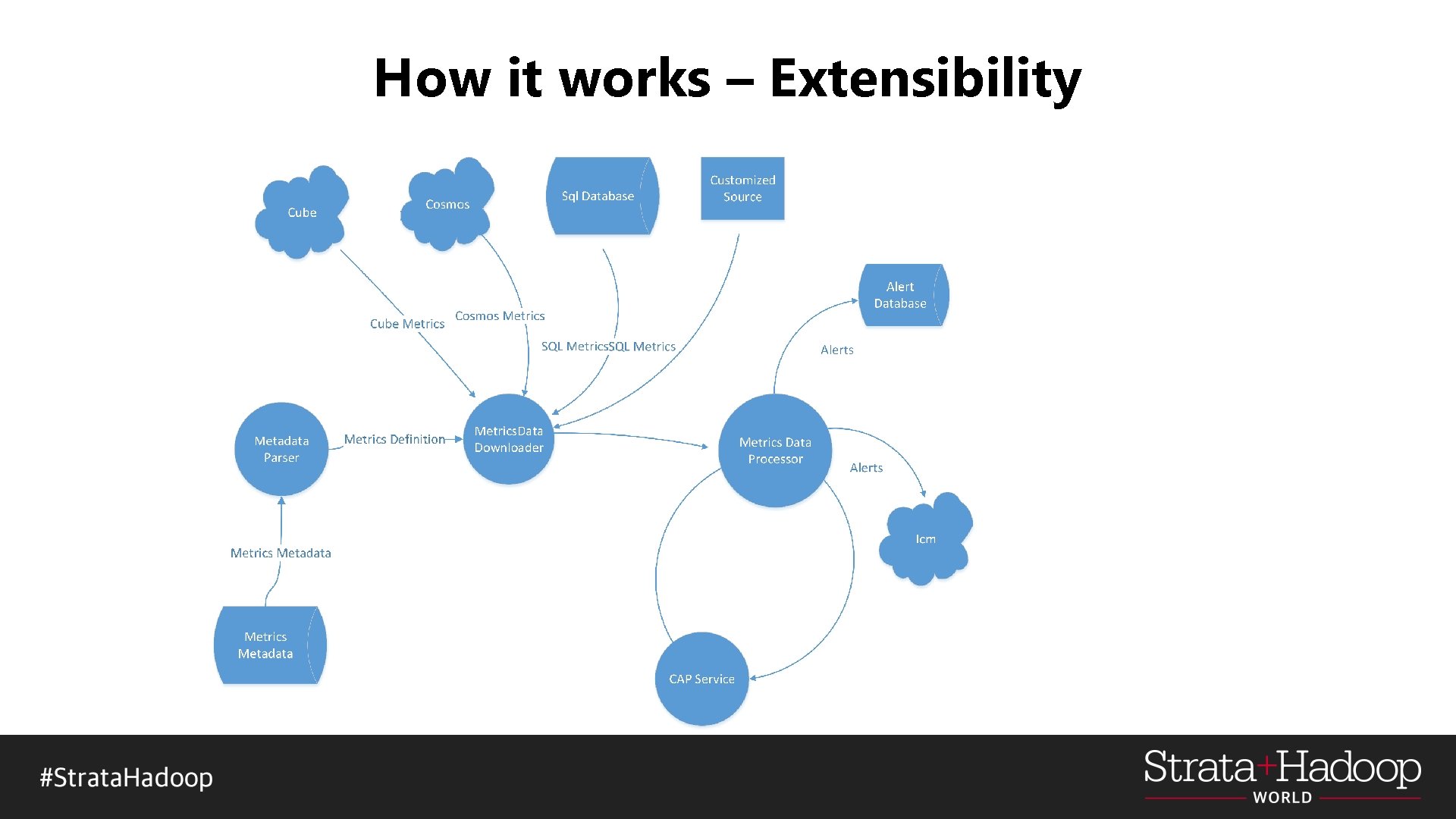 How it works – Extensibility
How it works – Extensibility
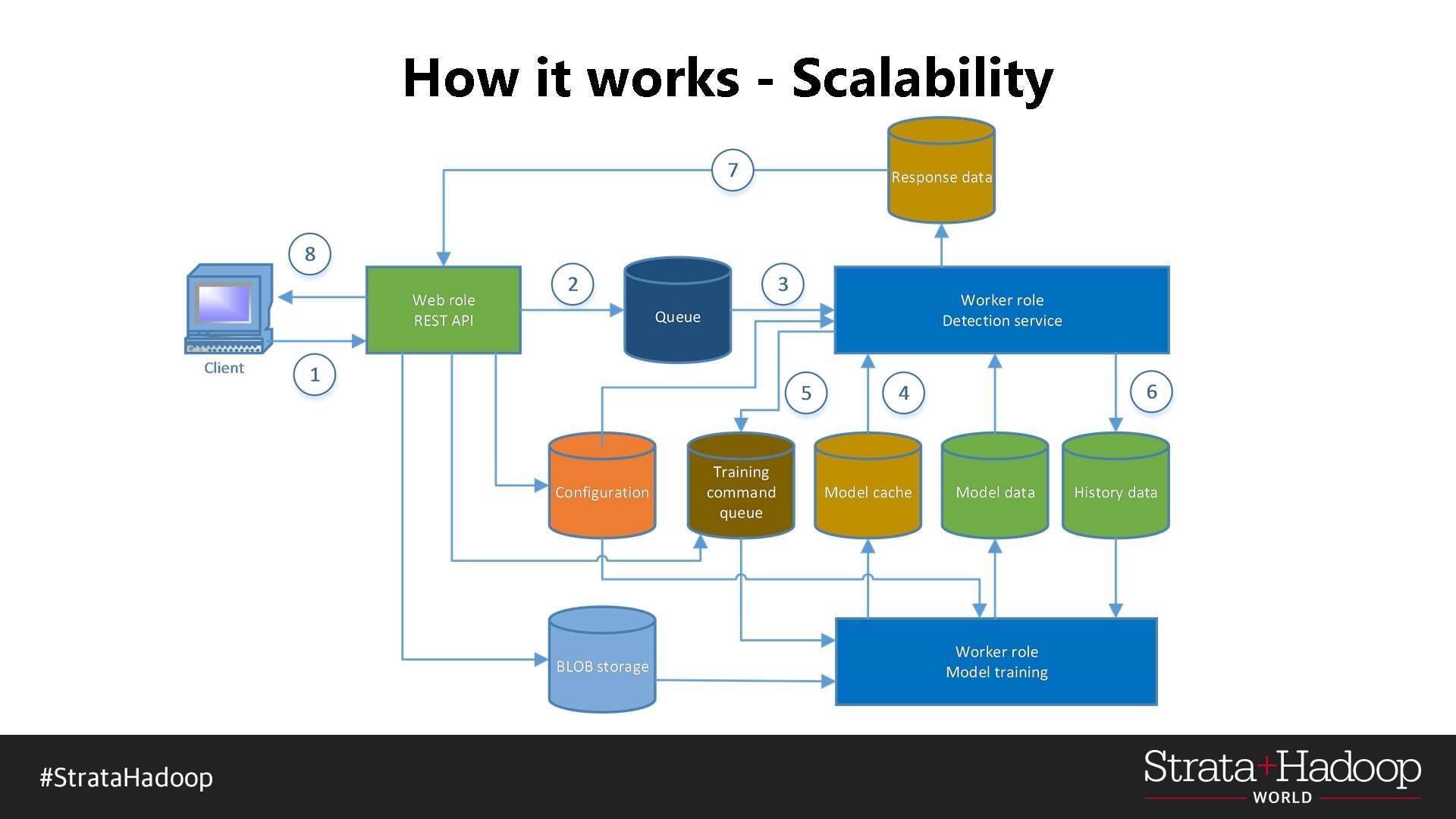 How it works - Scalability
How it works - Scalability

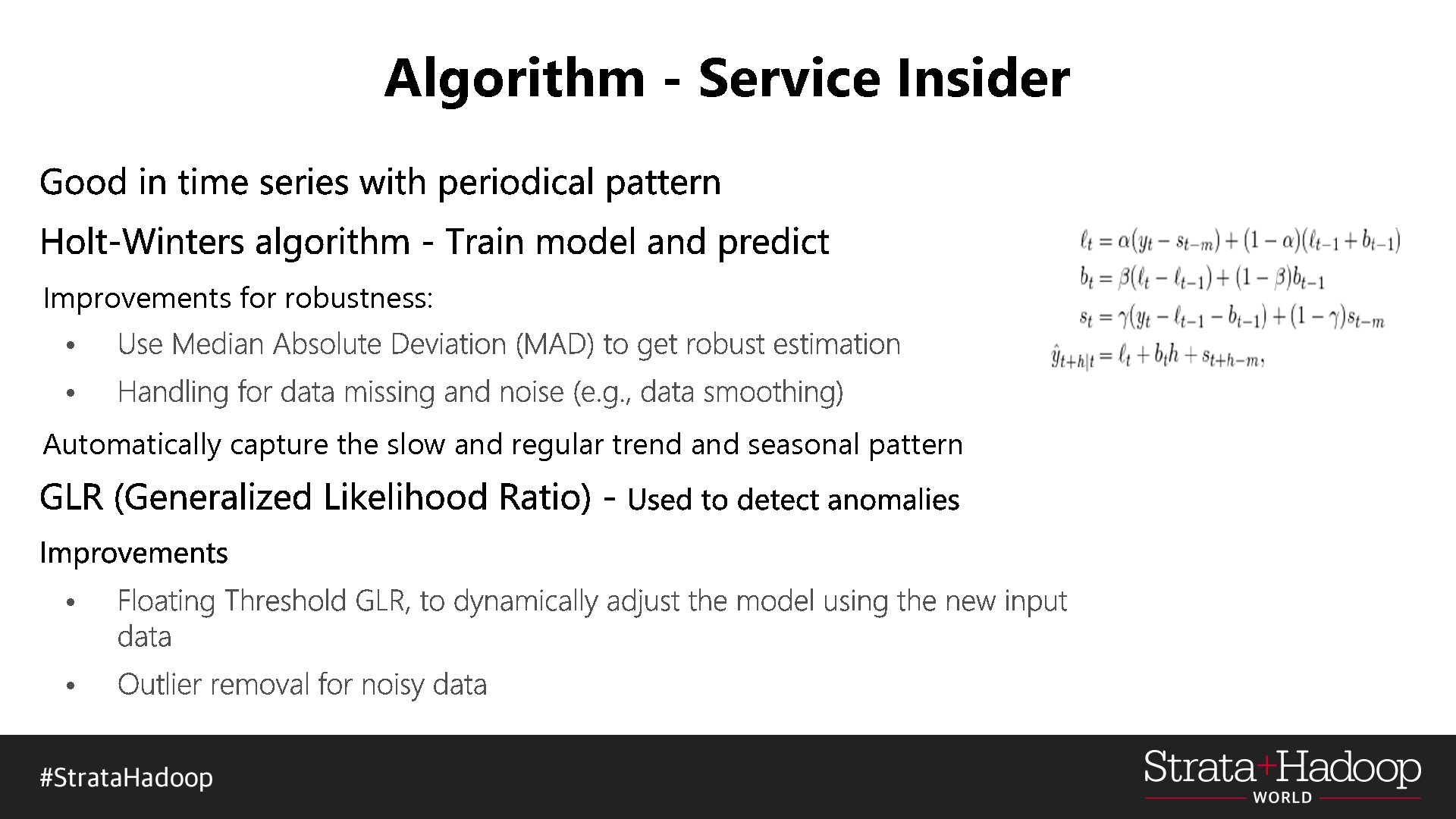 Algorithm - Service Insider Improvements for robustness: • • Automatically capture the slow and regular trend and seasonal pattern • •
Algorithm - Service Insider Improvements for robustness: • • Automatically capture the slow and regular trend and seasonal pattern • •
 Other Improvements § § §
Other Improvements § § §
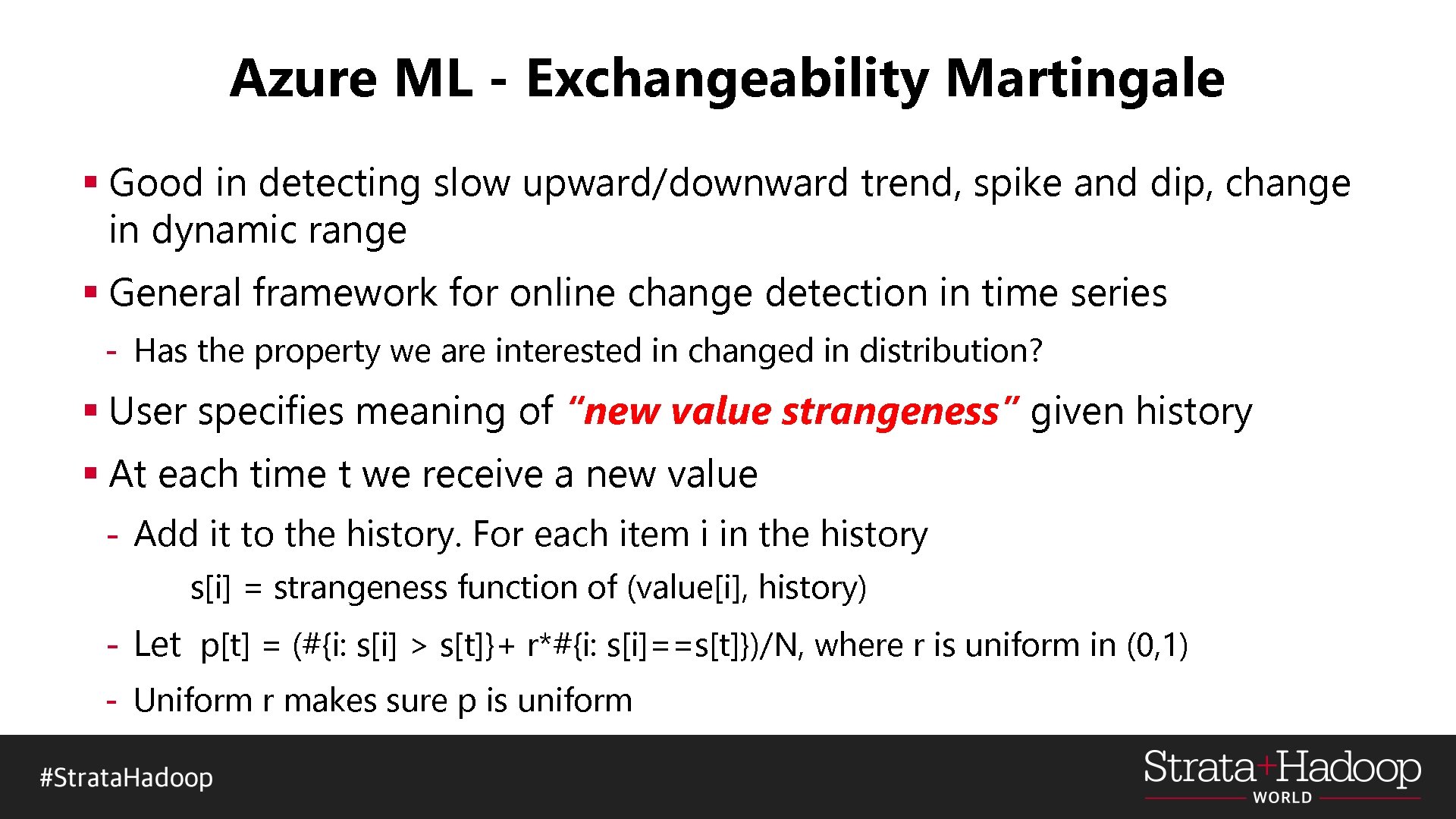 Azure ML - Exchangeability Martingale § Good in detecting slow upward/downward trend, spike and dip, change in dynamic range § General framework for online change detection in time series - Has the property we are interested in changed in distribution? § User specifies meaning of “new value strangeness” given history § At each time t we receive a new value - Add it to the history. For each item i in the history s[i] = strangeness function of (value[i], history) - Let p[t] = (#{i: s[i] > s[t]}+ r*#{i: s[i]==s[t]})/N, where r is uniform in (0, 1) - Uniform r makes sure p is uniform
Azure ML - Exchangeability Martingale § Good in detecting slow upward/downward trend, spike and dip, change in dynamic range § General framework for online change detection in time series - Has the property we are interested in changed in distribution? § User specifies meaning of “new value strangeness” given history § At each time t we receive a new value - Add it to the history. For each item i in the history s[i] = strangeness function of (value[i], history) - Let p[t] = (#{i: s[i] > s[t]}+ r*#{i: s[i]==s[t]})/N, where r is uniform in (0, 1) - Uniform r makes sure p is uniform
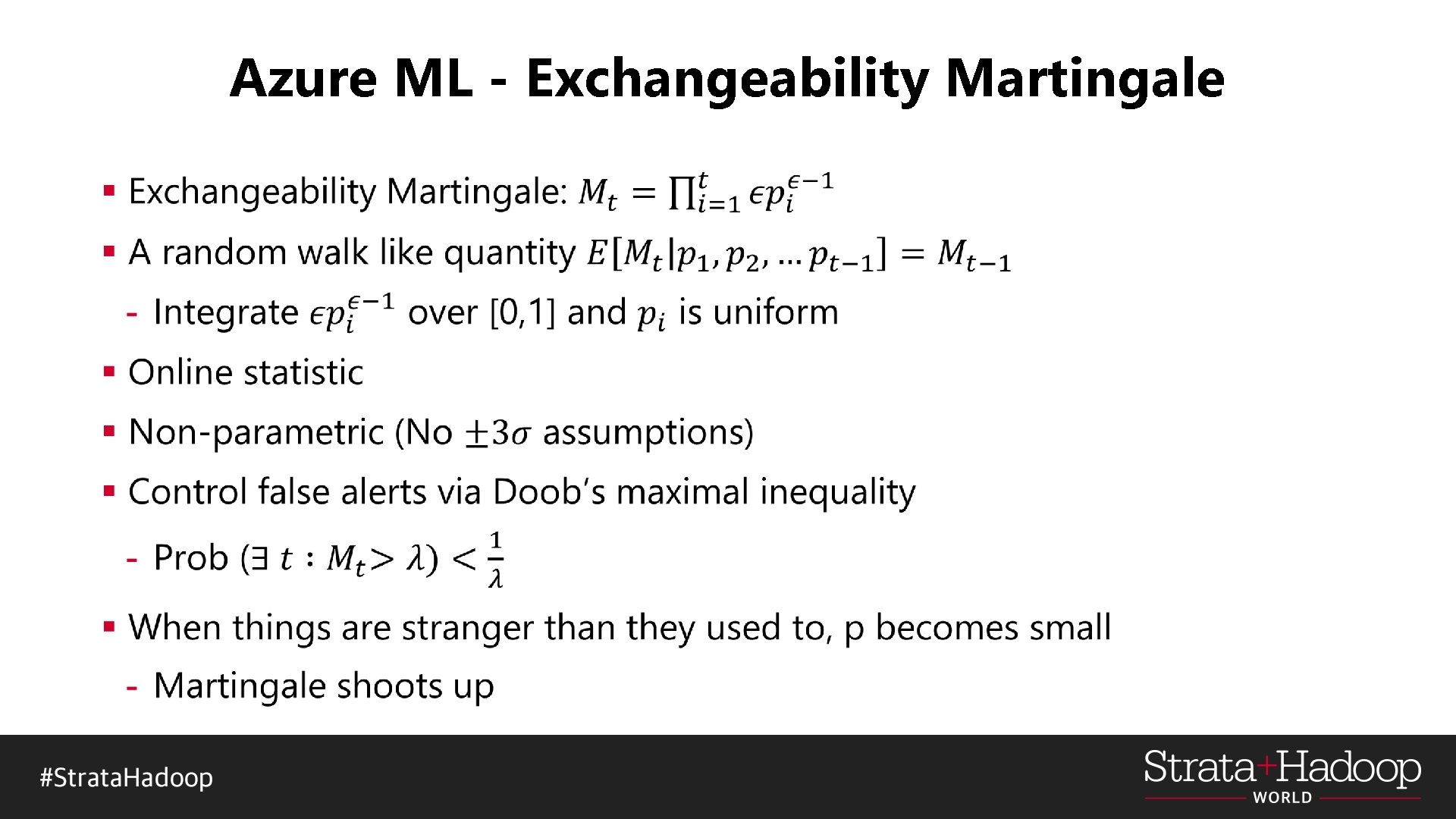 Azure ML - Exchangeability Martingale
Azure ML - Exchangeability Martingale
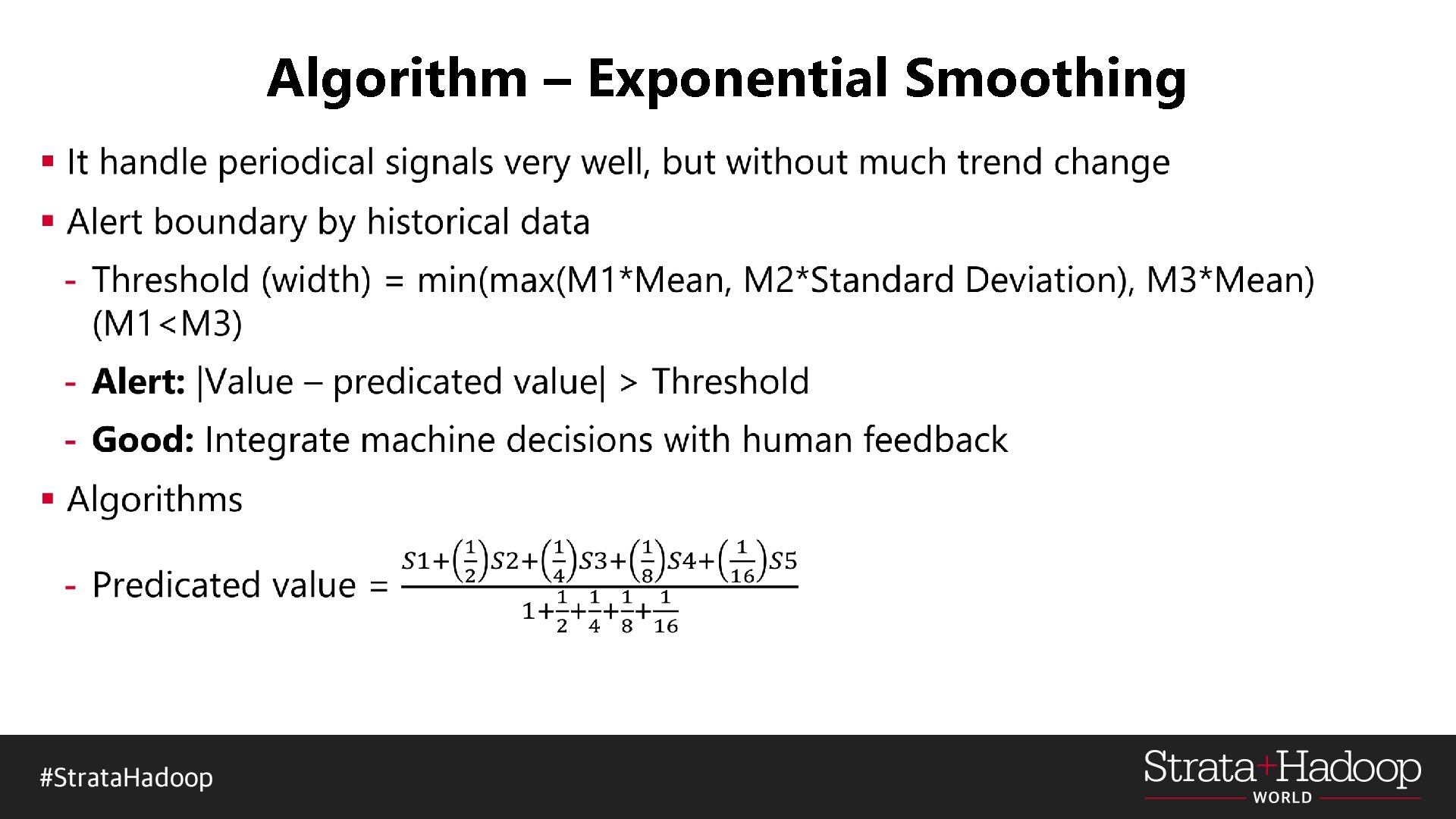 Algorithm – Exponential Smoothing §
Algorithm – Exponential Smoothing §
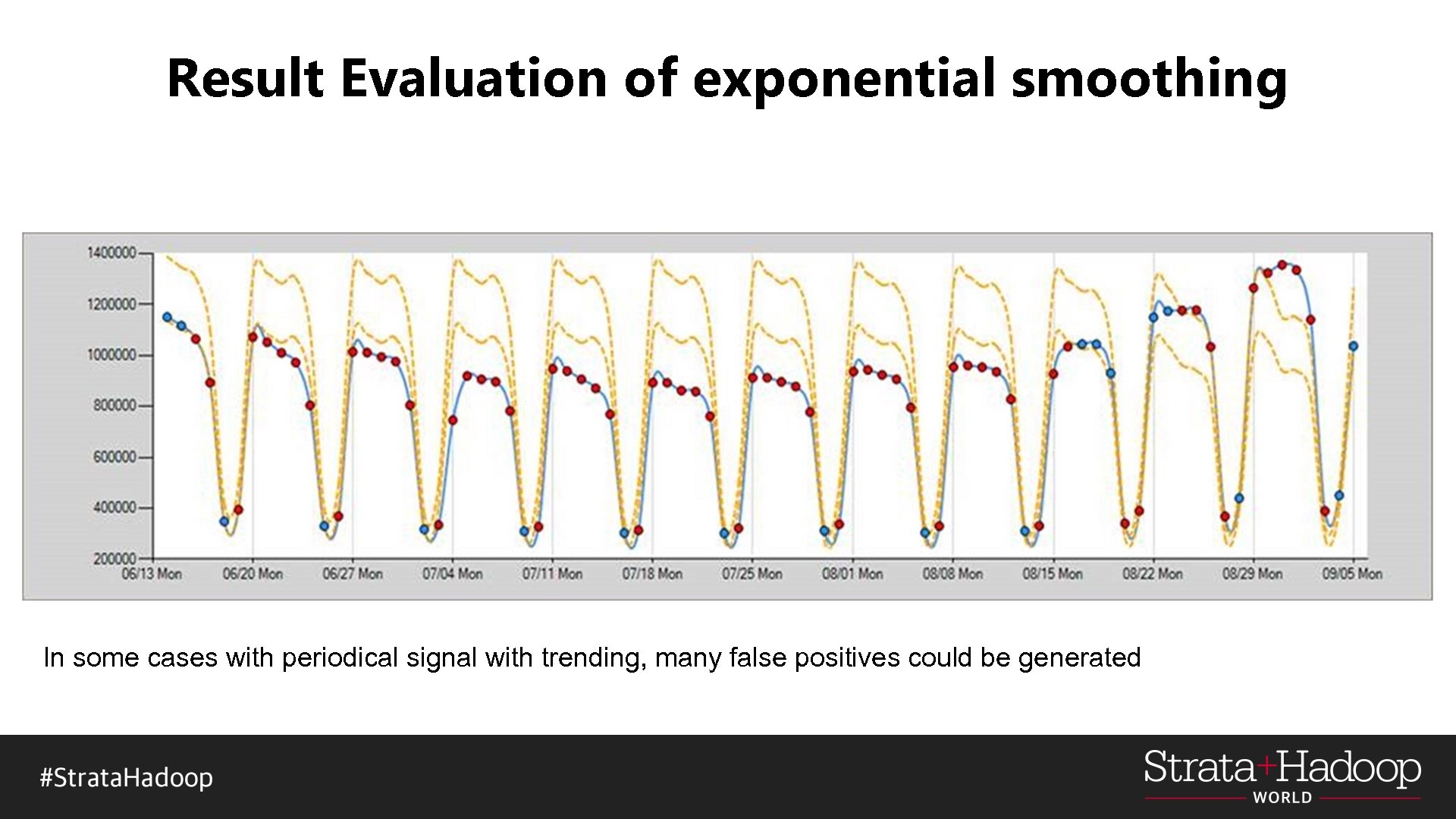 Result Evaluation of exponential smoothing In some cases with periodical signal with trending, many false positives could be generated
Result Evaluation of exponential smoothing In some cases with periodical signal with trending, many false positives could be generated
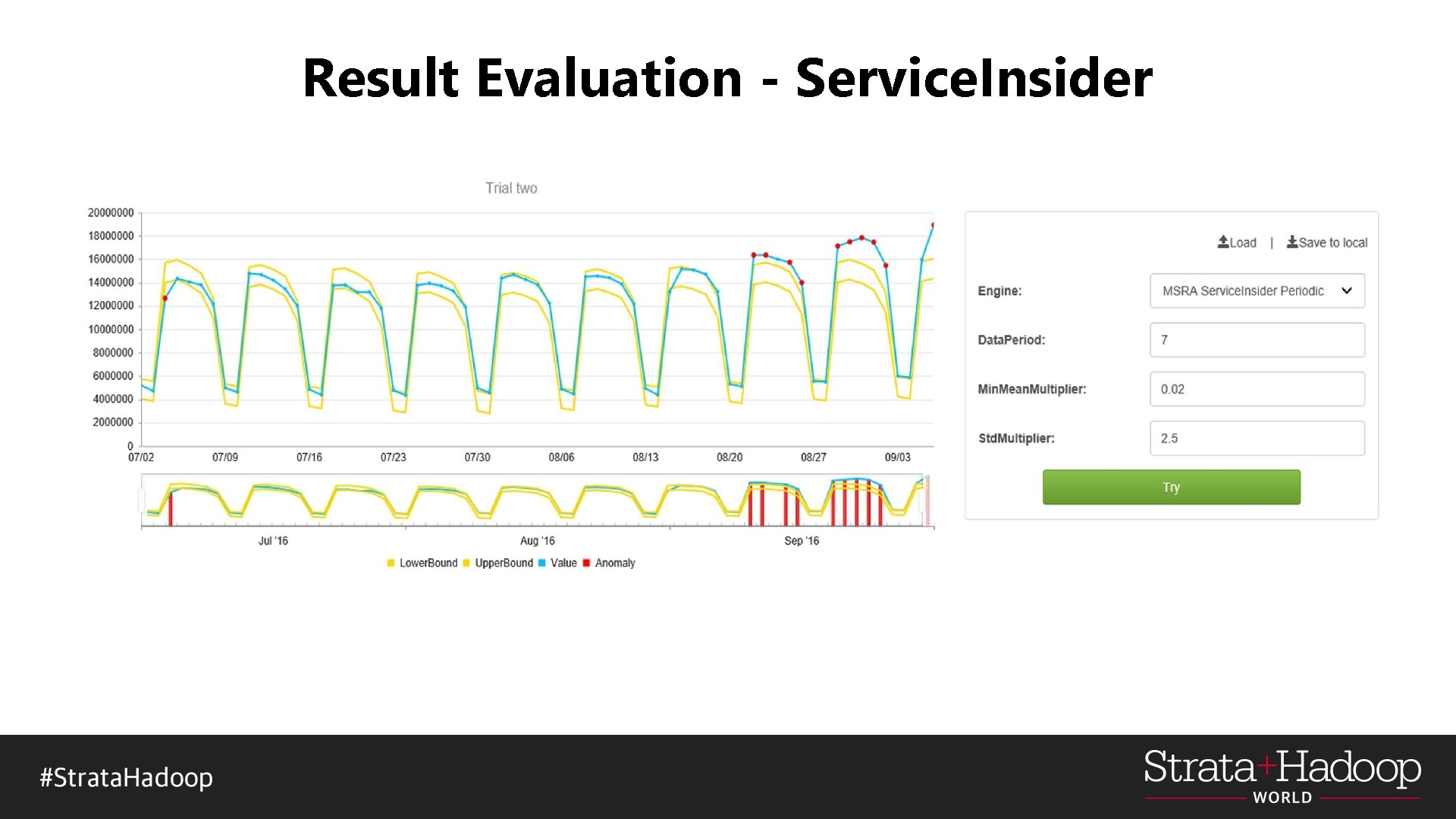 Result Evaluation - Service. Insider
Result Evaluation - Service. Insider
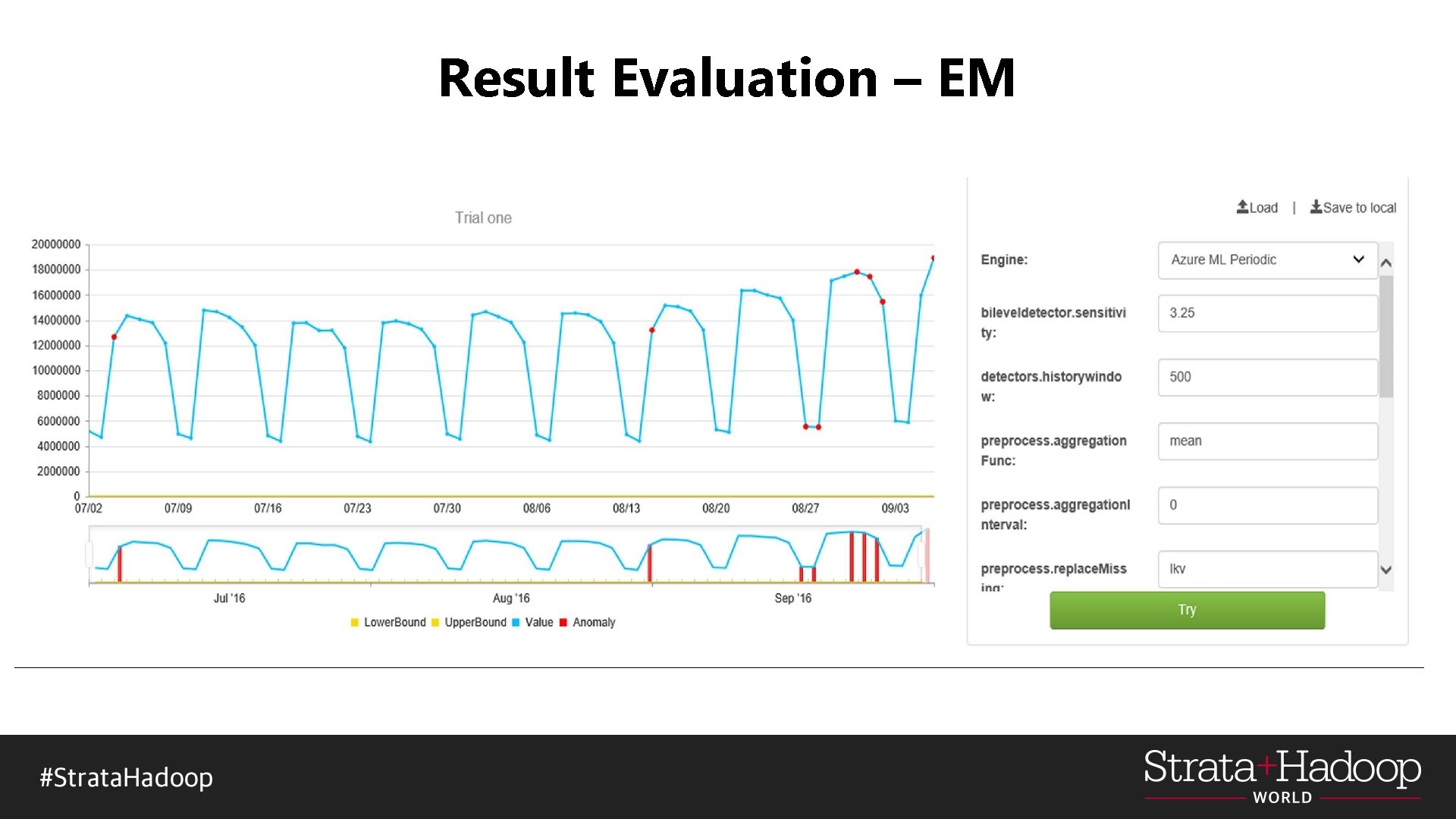 Result Evaluation – EM
Result Evaluation – EM
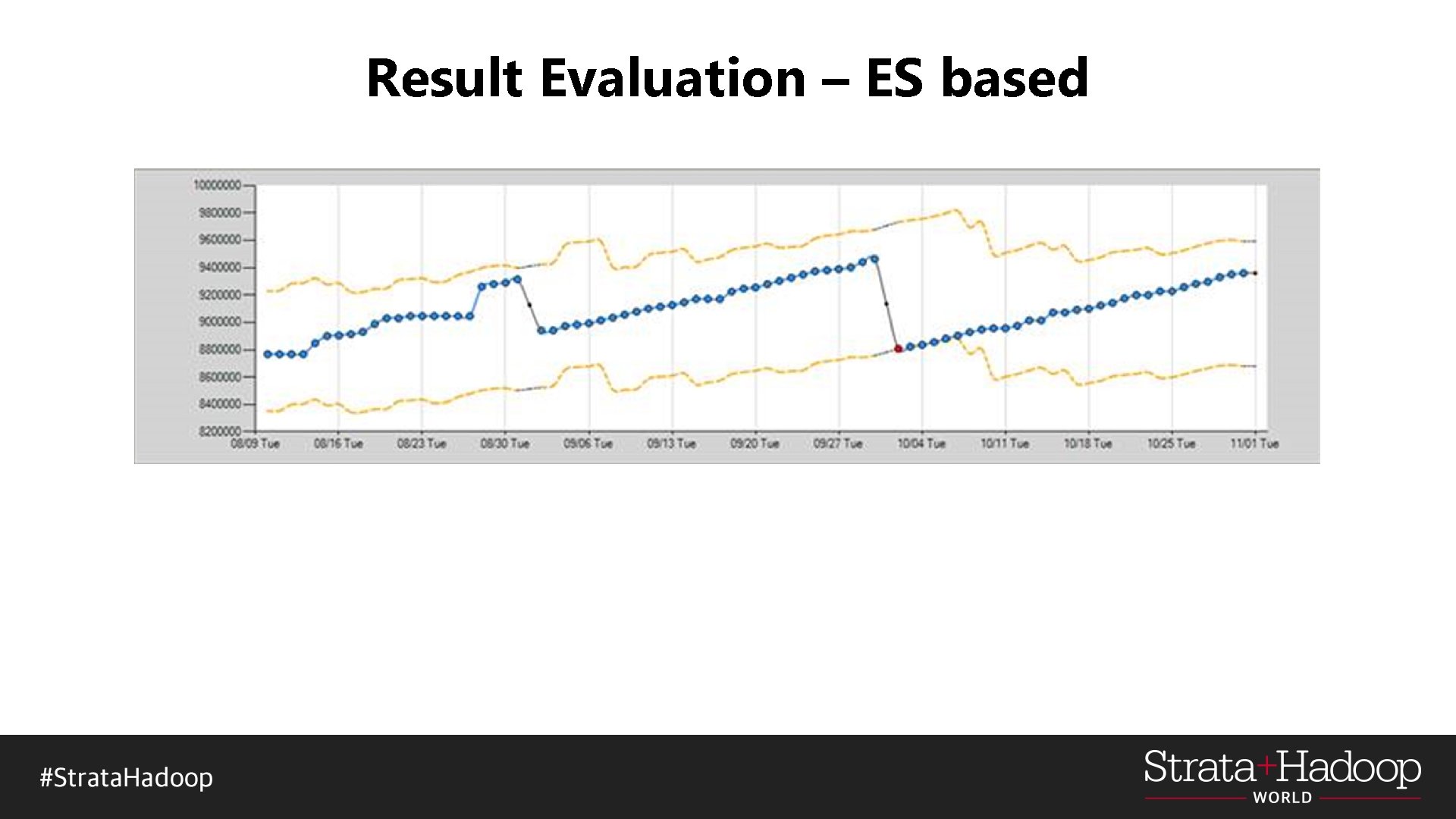 Result Evaluation – ES based
Result Evaluation – ES based
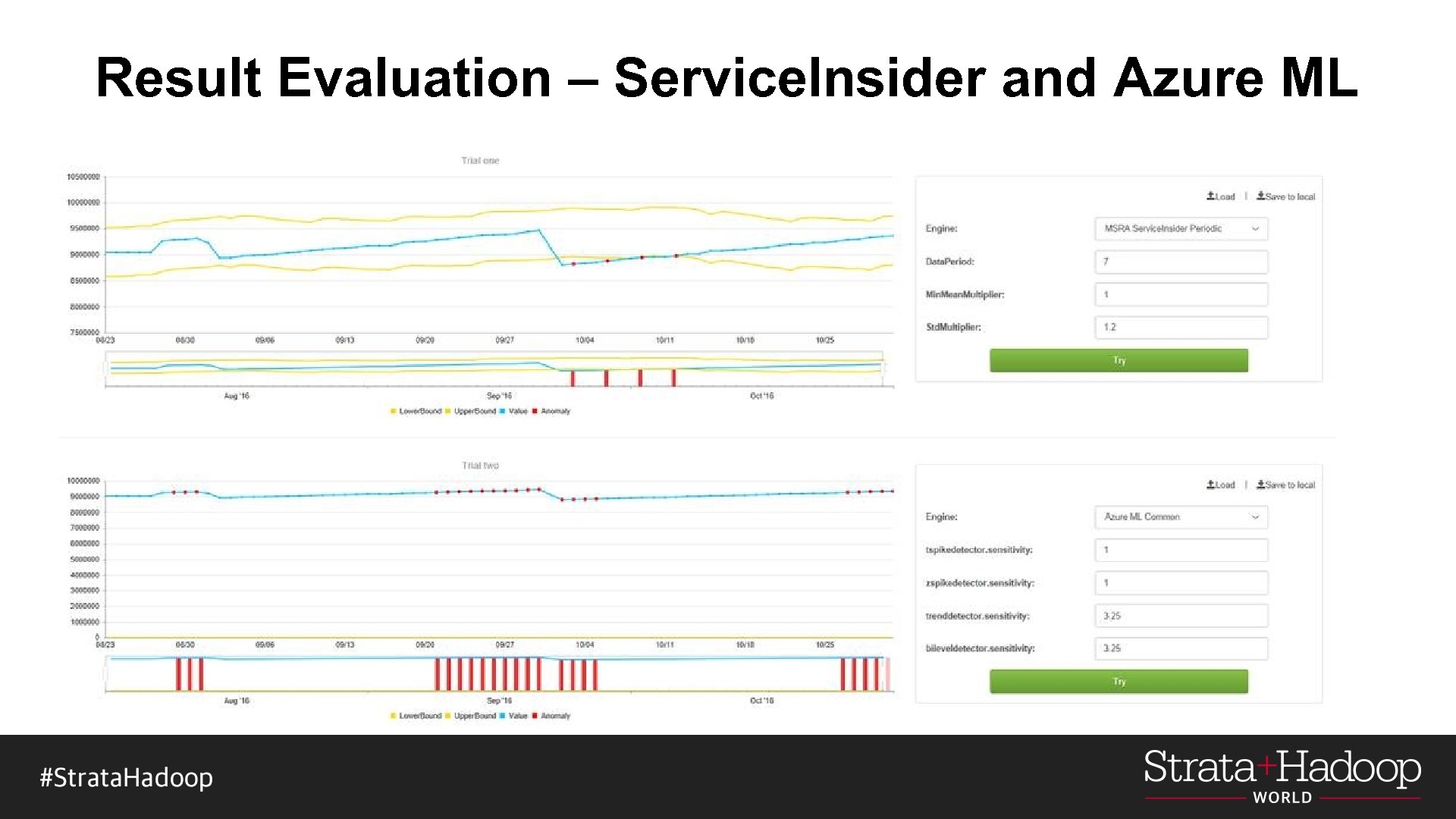 Result Evaluation – Service. Insider and Azure ML
Result Evaluation – Service. Insider and Azure ML
 Challenges and Future Work § Real time vs. accuracy § Automated handling of data pattern change § Easy tuning or usage of different algorithms
Challenges and Future Work § Real time vs. accuracy § Automated handling of data pattern change § Easy tuning or usage of different algorithms
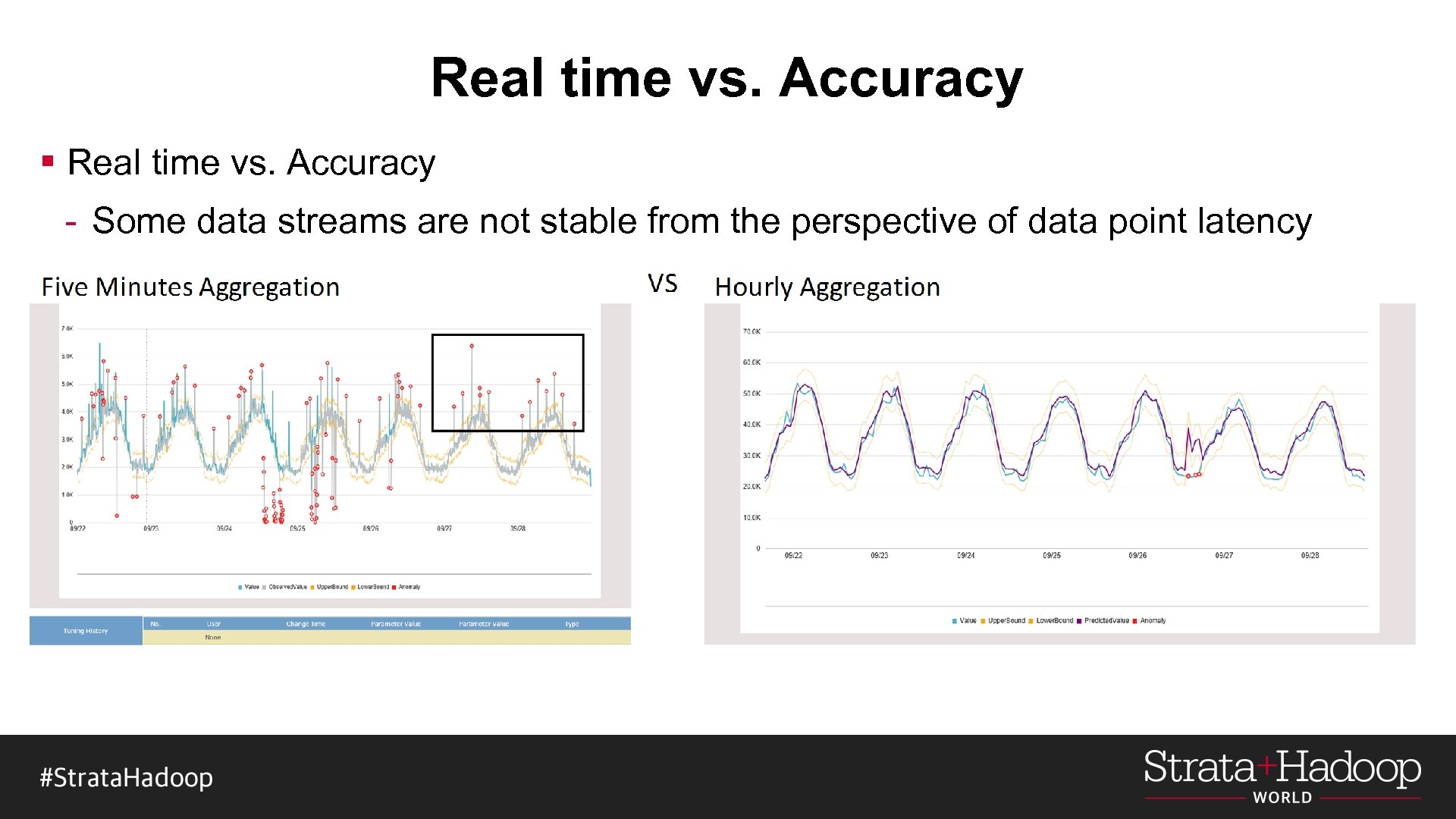 Real time vs. Accuracy § Real time vs. Accuracy - Some data streams are not stable from the perspective of data point latency
Real time vs. Accuracy § Real time vs. Accuracy - Some data streams are not stable from the perspective of data point latency
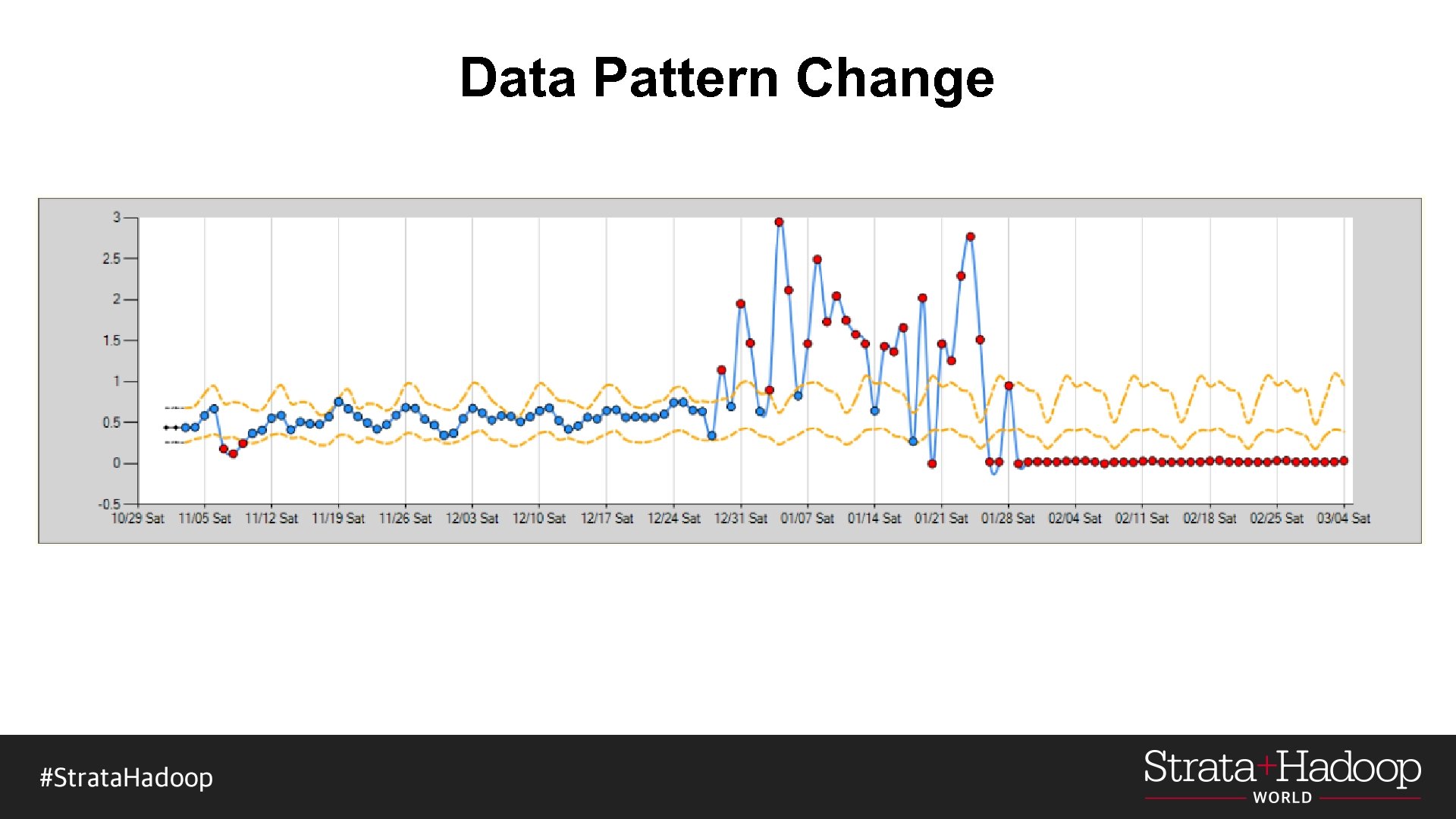 Data Pattern Change
Data Pattern Change
 Easy Tuning § Tuning the algorithm parameters to achieve right detection precision and recall is a pain to the users - Service insider 2 parameters - EM based: 7 parameters - ES based: 3 parameters § Creative UI to hide those details § Do without human tuning at all!
Easy Tuning § Tuning the algorithm parameters to achieve right detection precision and recall is a pain to the users - Service insider 2 parameters - EM based: 7 parameters - ES based: 3 parameters § Creative UI to hide those details § Do without human tuning at all!



