28f07379ecb898560d6d6e65853f78e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Commission Meeting July 25, 2012
Commission Meeting July 25, 2012
 Innovation Platform Program Fiscal Year 2012
Innovation Platform Program Fiscal Year 2012
 Purpose To link the development and innovation capabilities and capacities of an already established Innovation Platform and all its resources at an Ohio college or university or not-for-profit research institution to specific late stage development and innovation needs of Ohio companies Innovation Platform – an already existing capacity that incorporates unique technology capabilities and strengths, talent, equipment, facilities, engaged industry partners, a track record of research commercialization and innovation, intellectual property, and other resources in a particular technology area that collectively can serve as a vehicle for significant, industry-defined and directed opportunities through the development and commercialization of new products and innovations
Purpose To link the development and innovation capabilities and capacities of an already established Innovation Platform and all its resources at an Ohio college or university or not-for-profit research institution to specific late stage development and innovation needs of Ohio companies Innovation Platform – an already existing capacity that incorporates unique technology capabilities and strengths, talent, equipment, facilities, engaged industry partners, a track record of research commercialization and innovation, intellectual property, and other resources in a particular technology area that collectively can serve as a vehicle for significant, industry-defined and directed opportunities through the development and commercialization of new products and innovations
 FY 2012 Proposals • 37 proposals submitted • 35 proposals passed Development’s administrative review • Proposals based in one or more 8 technology areas: - Advanced Materials (13) - Fuel Cells & Energy Storage (7) - Software Applications for business and healthcare (3) - Situational Awareness and Surveillance Systems (3) - Aeropropulsion Power Management (3) Medical Technology (14) Sensing & Automation Technologies (6) Solar Photovoltaics (3)
FY 2012 Proposals • 37 proposals submitted • 35 proposals passed Development’s administrative review • Proposals based in one or more 8 technology areas: - Advanced Materials (13) - Fuel Cells & Energy Storage (7) - Software Applications for business and healthcare (3) - Situational Awareness and Surveillance Systems (3) - Aeropropulsion Power Management (3) Medical Technology (14) Sensing & Automation Technologies (6) Solar Photovoltaics (3)
 Program Basics • Lead Applicants = Ohio colleges or universities or an Ohio not-for-profit public or private research institution. Proposals must include collaboration with at least two or more Ohio for-profit companies. • Funding = $18 million available (FY 12); Award range of $1 – $3 million • External Evaluator = National Academies of Science (NAS)
Program Basics • Lead Applicants = Ohio colleges or universities or an Ohio not-for-profit public or private research institution. Proposals must include collaboration with at least two or more Ohio for-profit companies. • Funding = $18 million available (FY 12); Award range of $1 – $3 million • External Evaluator = National Academies of Science (NAS)
 Review of Proposals to Ohio’s Third Frontier Program, 2012 -2013: Innovation Platform Program (IPP) 2012 The National Academies July 25, 2012
Review of Proposals to Ohio’s Third Frontier Program, 2012 -2013: Innovation Platform Program (IPP) 2012 The National Academies July 25, 2012
 The National Academies • The National Academies bring together committees of experts in all areas of scientific and technological endeavors. These experts serve on a volunteer basis to address critical national issues. • The National Research Council, which operates under the auspices of the National Academies, is committed to providing elected leaders, policy makers, and the public with expert advice based on sound scientific evidence. 7
The National Academies • The National Academies bring together committees of experts in all areas of scientific and technological endeavors. These experts serve on a volunteer basis to address critical national issues. • The National Research Council, which operates under the auspices of the National Academies, is committed to providing elected leaders, policy makers, and the public with expert advice based on sound scientific evidence. 7
 Committee Membership • Committee of 23 includes: – Working engineers, scientists, academics, investors, and businessmen and women – 3 are elected members of the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) – 2 are elected members of the National Academy of Science (NAS) – 3 financial analysts – 5 Presidents or CEOs, 1 Vice President, and 1 Executive Director of private (for profit) companies – Geographically diverse: members are from all over the United States; – 17 previously served on NRC Committees to review proposals for Ohio 8
Committee Membership • Committee of 23 includes: – Working engineers, scientists, academics, investors, and businessmen and women – 3 are elected members of the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) – 2 are elected members of the National Academy of Science (NAS) – 3 financial analysts – 5 Presidents or CEOs, 1 Vice President, and 1 Executive Director of private (for profit) companies – Geographically diverse: members are from all over the United States; – 17 previously served on NRC Committees to review proposals for Ohio 8
 IPP Evaluation Criteria Technical Merit & Plan • Can the technical challenges be • met? Are novel concepts, approaches or methods employed? Performance Goals • Will the project have an impact on Ohio in three or more of the following areas? 1) job creation 2) personal wealth 3) new sales of products 4) company creation or attraction 5) follow-on investment 6) talent recruitment and 7) enhanced Ohio, national, and/or international recognition Commercialization Strategy • Does the team understand the total • • • resource requirements for achieving market entry? What is the specific value proposition of the proposed approach? Has the Innovation Platform already achieved at least proof of principle? How closely matched is the project with the existing or emerging supply chain’s capabilities? Experience and Qualifications • Is leadership demonstrated in all • critical phases of the proposal? Does the applicant team have the relevant experience to perform the work involved? 9
IPP Evaluation Criteria Technical Merit & Plan • Can the technical challenges be • met? Are novel concepts, approaches or methods employed? Performance Goals • Will the project have an impact on Ohio in three or more of the following areas? 1) job creation 2) personal wealth 3) new sales of products 4) company creation or attraction 5) follow-on investment 6) talent recruitment and 7) enhanced Ohio, national, and/or international recognition Commercialization Strategy • Does the team understand the total • • • resource requirements for achieving market entry? What is the specific value proposition of the proposed approach? Has the Innovation Platform already achieved at least proof of principle? How closely matched is the project with the existing or emerging supply chain’s capabilities? Experience and Qualifications • Is leadership demonstrated in all • critical phases of the proposal? Does the applicant team have the relevant experience to perform the work involved? 9
 IPP Evaluation Criteria Budget & Cost Share • Budget: – Is the budget justified and adequate? • Cost Share: – Is the cost share necessary and reasonable? – Does the cost share represent a specific new commitment, and is it in the form of cash? – Is the cost share being used directly in support of the Innovation Platform? – Is the cost share firmly committed, with no contingencies or conditions, from known sources and available to the Innovation Platform at the time of Proposal submittal? • Does the proposal contain sufficiently detailed commitment letters, including an explanation of cost share commitment? 10
IPP Evaluation Criteria Budget & Cost Share • Budget: – Is the budget justified and adequate? • Cost Share: – Is the cost share necessary and reasonable? – Does the cost share represent a specific new commitment, and is it in the form of cash? – Is the cost share being used directly in support of the Innovation Platform? – Is the cost share firmly committed, with no contingencies or conditions, from known sources and available to the Innovation Platform at the time of Proposal submittal? • Does the proposal contain sufficiently detailed commitment letters, including an explanation of cost share commitment? 10
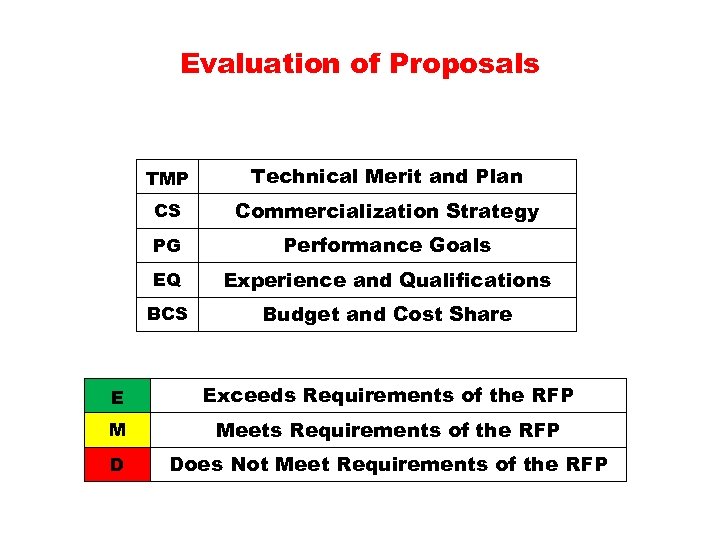 Evaluation of Proposals TMP Technical Merit and Plan CS Commercialization Strategy PG Performance Goals EQ Experience and Qualifications BCS Budget and Cost Share E Exceeds Requirements of the RFP M Meets Requirements of the RFP D Does Not Meet Requirements of the RFP
Evaluation of Proposals TMP Technical Merit and Plan CS Commercialization Strategy PG Performance Goals EQ Experience and Qualifications BCS Budget and Cost Share E Exceeds Requirements of the RFP M Meets Requirements of the RFP D Does Not Meet Requirements of the RFP
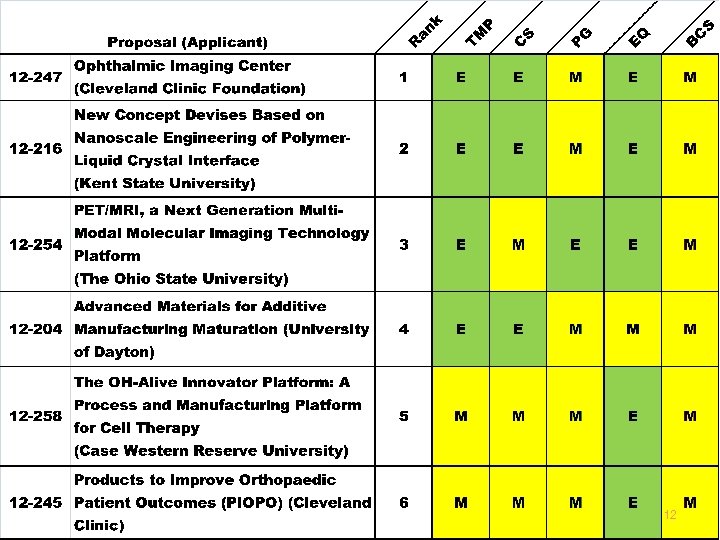 12
12
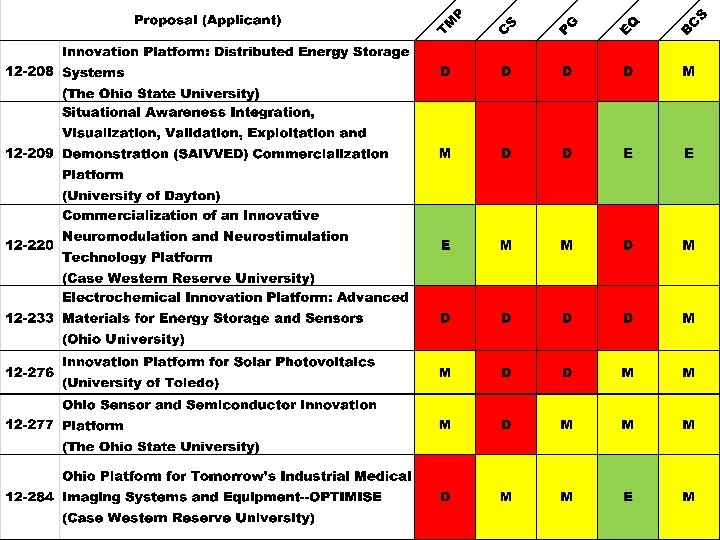 13
13
 Recommended Proposals
Recommended Proposals
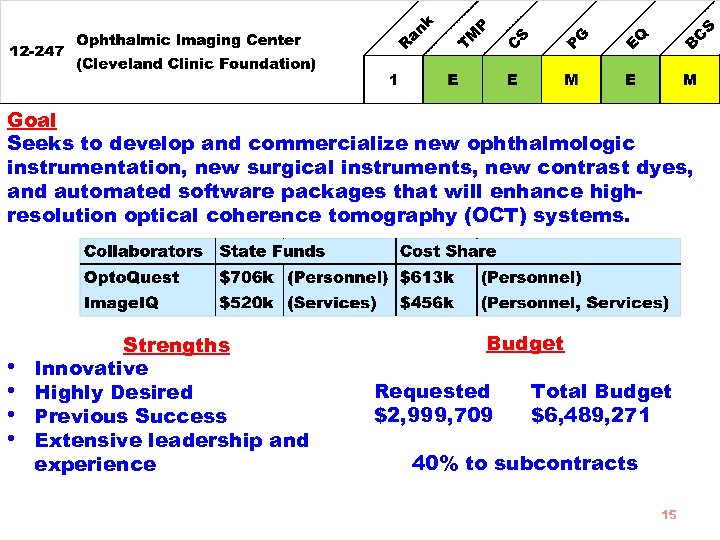 Goal Seeks to develop and commercialize new ophthalmologic instrumentation, new surgical instruments, new contrast dyes, and automated software packages that will enhance highresolution optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems. • • Strengths Innovative Highly Desired Previous Success Extensive leadership and experience Budget Requested $2, 999, 709 Total Budget $6, 489, 271 40% to subcontracts 15
Goal Seeks to develop and commercialize new ophthalmologic instrumentation, new surgical instruments, new contrast dyes, and automated software packages that will enhance highresolution optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems. • • Strengths Innovative Highly Desired Previous Success Extensive leadership and experience Budget Requested $2, 999, 709 Total Budget $6, 489, 271 40% to subcontracts 15
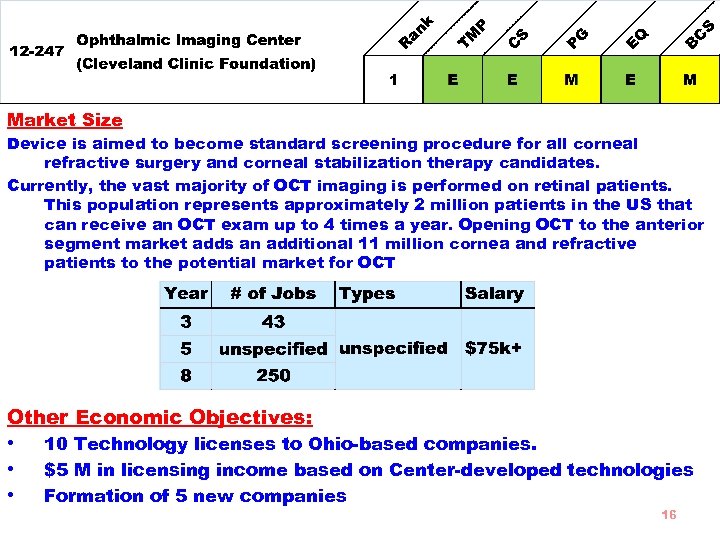 Market Size Device is aimed to become standard screening procedure for all corneal refractive surgery and corneal stabilization therapy candidates. Currently, the vast majority of OCT imaging is performed on retinal patients. This population represents approximately 2 million patients in the US that can receive an OCT exam up to 4 times a year. Opening OCT to the anterior segment market adds an additional 11 million cornea and refractive patients to the potential market for OCT Other Economic Objectives: • • • 10 Technology licenses to Ohio-based companies. $5 M in licensing income based on Center-developed technologies Formation of 5 new companies 16
Market Size Device is aimed to become standard screening procedure for all corneal refractive surgery and corneal stabilization therapy candidates. Currently, the vast majority of OCT imaging is performed on retinal patients. This population represents approximately 2 million patients in the US that can receive an OCT exam up to 4 times a year. Opening OCT to the anterior segment market adds an additional 11 million cornea and refractive patients to the potential market for OCT Other Economic Objectives: • • • 10 Technology licenses to Ohio-based companies. $5 M in licensing income based on Center-developed technologies Formation of 5 new companies 16
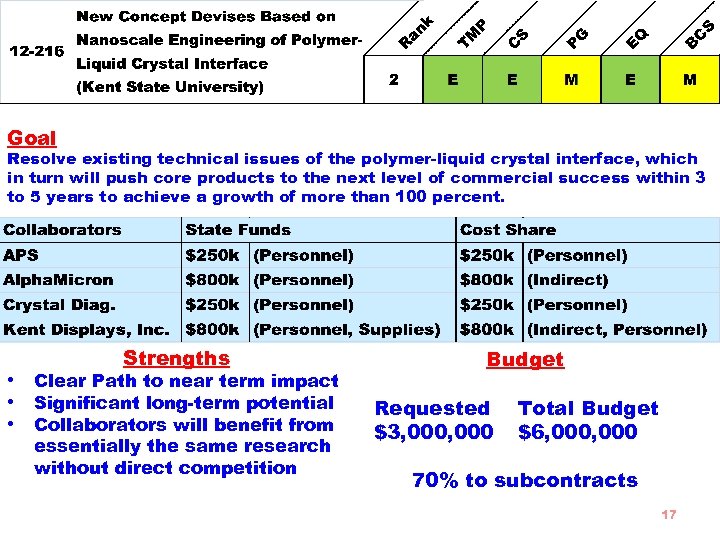 Goal Resolve existing technical issues of the polymer-liquid crystal interface, which in turn will push core products to the next level of commercial success within 3 to 5 years to achieve a growth of more than 100 percent. Strengths • Clear Path to near term impact • Significant long-term potential • Collaborators will benefit from essentially the same research without direct competition Budget Requested $3, 000 Total Budget $6, 000 70% to subcontracts 17
Goal Resolve existing technical issues of the polymer-liquid crystal interface, which in turn will push core products to the next level of commercial success within 3 to 5 years to achieve a growth of more than 100 percent. Strengths • Clear Path to near term impact • Significant long-term potential • Collaborators will benefit from essentially the same research without direct competition Budget Requested $3, 000 Total Budget $6, 000 70% to subcontracts 17
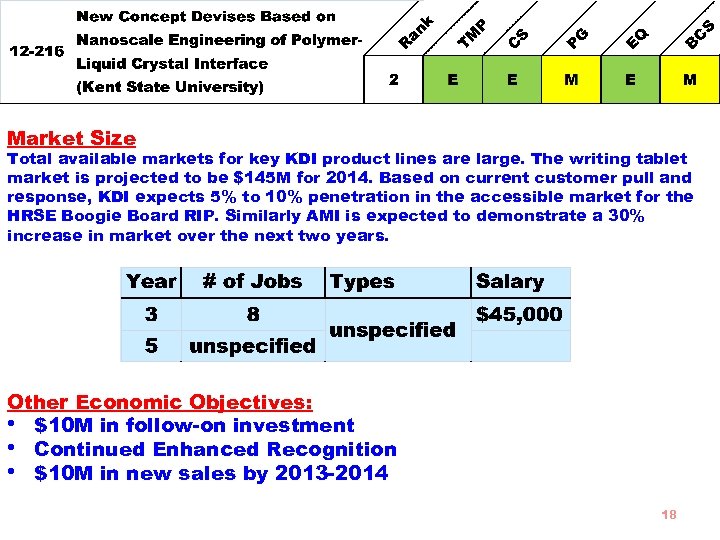 Market Size Total available markets for key KDI product lines are large. The writing tablet market is projected to be $145 M for 2014. Based on current customer pull and response, KDI expects 5% to 10% penetration in the accessible market for the HRSE Boogie Board RIP. Similarly AMI is expected to demonstrate a 30% increase in market over the next two years. Other Economic Objectives: • $10 M in follow-on investment • Continued Enhanced Recognition • $10 M in new sales by 2013 -2014 18
Market Size Total available markets for key KDI product lines are large. The writing tablet market is projected to be $145 M for 2014. Based on current customer pull and response, KDI expects 5% to 10% penetration in the accessible market for the HRSE Boogie Board RIP. Similarly AMI is expected to demonstrate a 30% increase in market over the next two years. Other Economic Objectives: • $10 M in follow-on investment • Continued Enhanced Recognition • $10 M in new sales by 2013 -2014 18
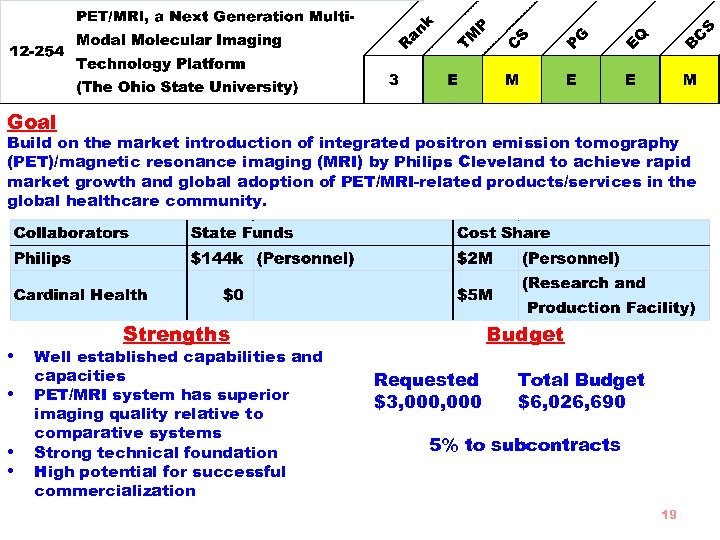 Goal Build on the market introduction of integrated positron emission tomography (PET)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by Philips Cleveland to achieve rapid market growth and global adoption of PET/MRI-related products/services in the global healthcare community. • • Strengths Well established capabilities and capacities PET/MRI system has superior imaging quality relative to comparative systems Strong technical foundation High potential for successful commercialization Budget Requested $3, 000 Total Budget $6, 026, 690 5% to subcontracts 19
Goal Build on the market introduction of integrated positron emission tomography (PET)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by Philips Cleveland to achieve rapid market growth and global adoption of PET/MRI-related products/services in the global healthcare community. • • Strengths Well established capabilities and capacities PET/MRI system has superior imaging quality relative to comparative systems Strong technical foundation High potential for successful commercialization Budget Requested $3, 000 Total Budget $6, 026, 690 5% to subcontracts 19
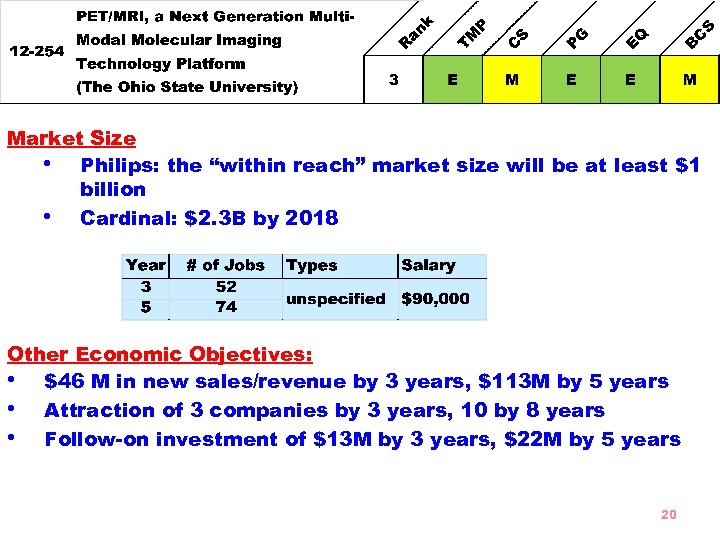 Market Size • Philips: the “within reach” market size will be at least $1 billion • Cardinal: $2. 3 B by 2018 Other Economic Objectives: • $46 M in new sales/revenue by 3 years, $113 M by 5 years • Attraction of 3 companies by 3 years, 10 by 8 years • Follow-on investment of $13 M by 3 years, $22 M by 5 years 20
Market Size • Philips: the “within reach” market size will be at least $1 billion • Cardinal: $2. 3 B by 2018 Other Economic Objectives: • $46 M in new sales/revenue by 3 years, $113 M by 5 years • Attraction of 3 companies by 3 years, 10 by 8 years • Follow-on investment of $13 M by 3 years, $22 M by 5 years 20
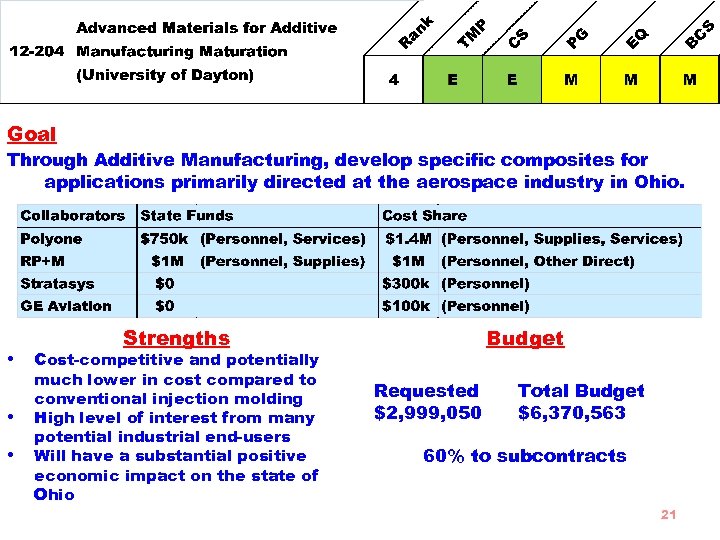 Goal Through Additive Manufacturing, develop specific composites for applications primarily directed at the aerospace industry in Ohio. • • • Strengths Cost-competitive and potentially much lower in cost compared to conventional injection molding High level of interest from many potential industrial end-users Will have a substantial positive economic impact on the state of Ohio Budget Requested $2, 999, 050 Total Budget $6, 370, 563 60% to subcontracts 21
Goal Through Additive Manufacturing, develop specific composites for applications primarily directed at the aerospace industry in Ohio. • • • Strengths Cost-competitive and potentially much lower in cost compared to conventional injection molding High level of interest from many potential industrial end-users Will have a substantial positive economic impact on the state of Ohio Budget Requested $2, 999, 050 Total Budget $6, 370, 563 60% to subcontracts 21
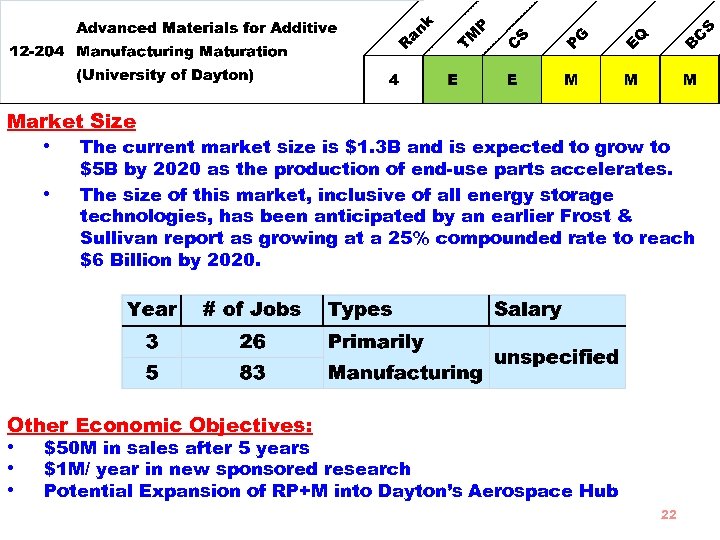 Market Size • • The current market size is $1. 3 B and is expected to grow to $5 B by 2020 as the production of end-use parts accelerates. The size of this market, inclusive of all energy storage technologies, has been anticipated by an earlier Frost & Sullivan report as growing at a 25% compounded rate to reach $6 Billion by 2020. Other Economic Objectives: • • • $50 M in sales after 5 years $1 M/ year in new sponsored research Potential Expansion of RP+M into Dayton’s Aerospace Hub 22
Market Size • • The current market size is $1. 3 B and is expected to grow to $5 B by 2020 as the production of end-use parts accelerates. The size of this market, inclusive of all energy storage technologies, has been anticipated by an earlier Frost & Sullivan report as growing at a 25% compounded rate to reach $6 Billion by 2020. Other Economic Objectives: • • • $50 M in sales after 5 years $1 M/ year in new sponsored research Potential Expansion of RP+M into Dayton’s Aerospace Hub 22
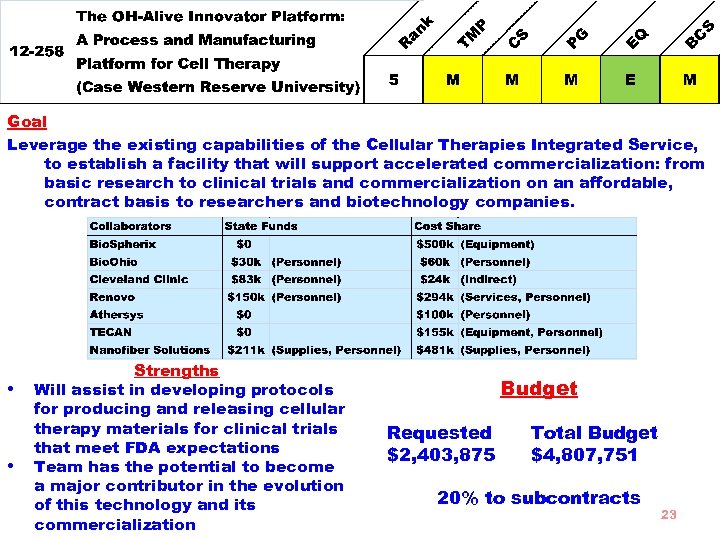 Goal Leverage the existing capabilities of the Cellular Therapies Integrated Service, to establish a facility that will support accelerated commercialization: from basic research to clinical trials and commercialization on an affordable, contract basis to researchers and biotechnology companies. • • Strengths Will assist in developing protocols for producing and releasing cellular therapy materials for clinical trials that meet FDA expectations Team has the potential to become a major contributor in the evolution of this technology and its commercialization Budget Requested $2, 403, 875 Total Budget $4, 807, 751 20% to subcontracts 23
Goal Leverage the existing capabilities of the Cellular Therapies Integrated Service, to establish a facility that will support accelerated commercialization: from basic research to clinical trials and commercialization on an affordable, contract basis to researchers and biotechnology companies. • • Strengths Will assist in developing protocols for producing and releasing cellular therapy materials for clinical trials that meet FDA expectations Team has the potential to become a major contributor in the evolution of this technology and its commercialization Budget Requested $2, 403, 875 Total Budget $4, 807, 751 20% to subcontracts 23
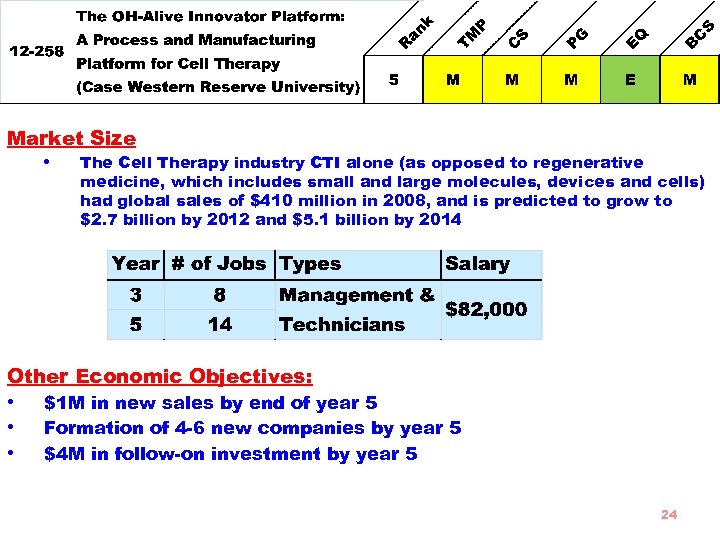 Market Size • The Cell Therapy industry CTI alone (as opposed to regenerative medicine, which includes small and large molecules, devices and cells) had global sales of $410 million in 2008, and is predicted to grow to $2. 7 billion by 2012 and $5. 1 billion by 2014 Other Economic Objectives: • • • $1 M in new sales by end of year 5 Formation of 4 -6 new companies by year 5 $4 M in follow-on investment by year 5 24
Market Size • The Cell Therapy industry CTI alone (as opposed to regenerative medicine, which includes small and large molecules, devices and cells) had global sales of $410 million in 2008, and is predicted to grow to $2. 7 billion by 2012 and $5. 1 billion by 2014 Other Economic Objectives: • • • $1 M in new sales by end of year 5 Formation of 4 -6 new companies by year 5 $4 M in follow-on investment by year 5 24
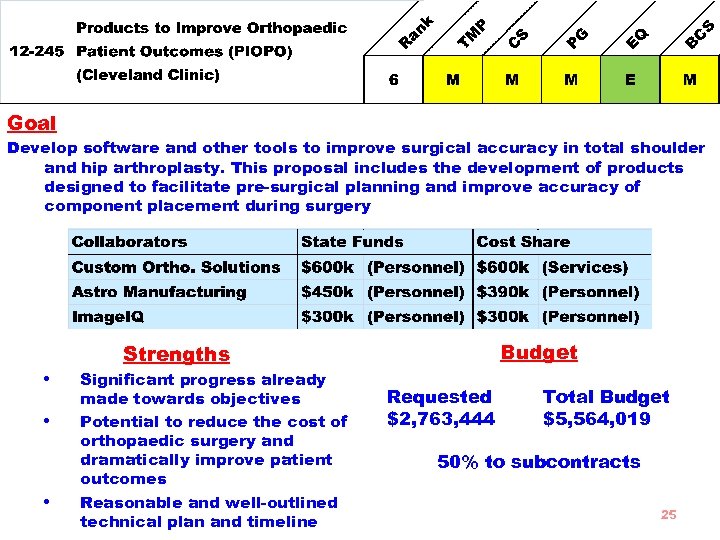 Goal Develop software and other tools to improve surgical accuracy in total shoulder and hip arthroplasty. This proposal includes the development of products designed to facilitate pre-surgical planning and improve accuracy of component placement during surgery Budget Strengths • • • Significant progress already made towards objectives Potential to reduce the cost of orthopaedic surgery and dramatically improve patient outcomes Reasonable and well-outlined technical plan and timeline Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 50% to subcontracts 25
Goal Develop software and other tools to improve surgical accuracy in total shoulder and hip arthroplasty. This proposal includes the development of products designed to facilitate pre-surgical planning and improve accuracy of component placement during surgery Budget Strengths • • • Significant progress already made towards objectives Potential to reduce the cost of orthopaedic surgery and dramatically improve patient outcomes Reasonable and well-outlined technical plan and timeline Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 50% to subcontracts 25
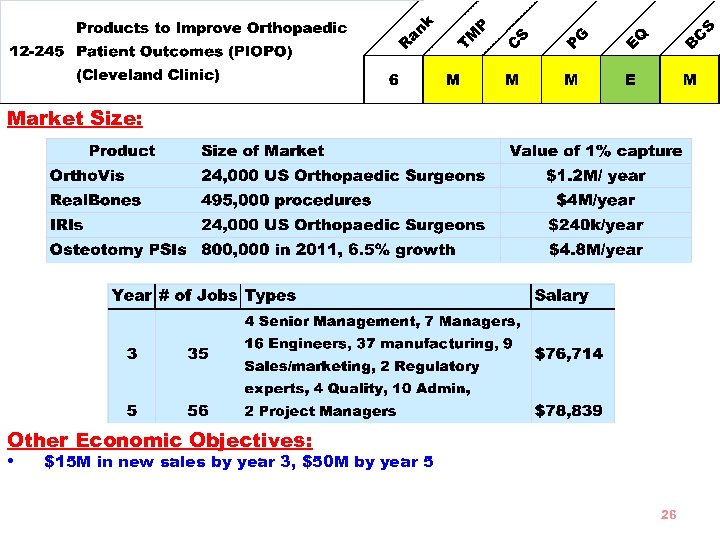 Market Size: Other Economic Objectives: • $15 M in new sales by year 3, $50 M by year 5 26
Market Size: Other Economic Objectives: • $15 M in new sales by year 3, $50 M by year 5 26
 Final Remarks • Total state funds requested by the 6 proposals: $17, 166, 078 • The remaining 29 proposals, when ranked against the RFP’s criteria and requirements, scored significantly lower than the recommended 6 Thank You! The National Academies would like to thank the State of Ohio for placing its trust in our process and in our outstanding volunteer committee members. 27
Final Remarks • Total state funds requested by the 6 proposals: $17, 166, 078 • The remaining 29 proposals, when ranked against the RFP’s criteria and requirements, scored significantly lower than the recommended 6 Thank You! The National Academies would like to thank the State of Ohio for placing its trust in our process and in our outstanding volunteer committee members. 27
 QUESTIONS?
QUESTIONS?
 Interviewees Not Recommended
Interviewees Not Recommended
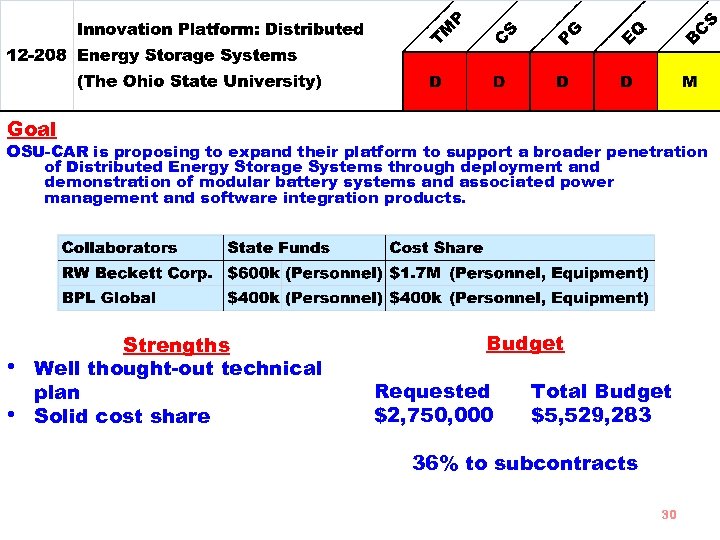 Goal OSU-CAR is proposing to expand their platform to support a broader penetration of Distributed Energy Storage Systems through deployment and demonstration of modular battery systems and associated power management and software integration products. • • Strengths Well thought-out technical plan Solid cost share Budget Requested $2, 750, 000 Total Budget $5, 529, 283 36% to subcontracts 30
Goal OSU-CAR is proposing to expand their platform to support a broader penetration of Distributed Energy Storage Systems through deployment and demonstration of modular battery systems and associated power management and software integration products. • • Strengths Well thought-out technical plan Solid cost share Budget Requested $2, 750, 000 Total Budget $5, 529, 283 36% to subcontracts 30
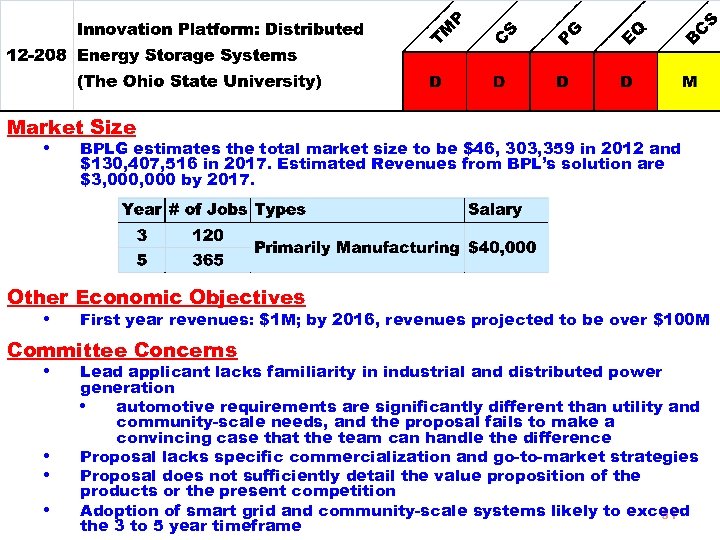 Market Size • BPLG estimates the total market size to be $46, 303, 359 in 2012 and $130, 407, 516 in 2017. Estimated Revenues from BPL’s solution are $3, 000 by 2017. Other Economic Objectives • First year revenues: $1 M; by 2016, revenues projected to be over $100 M Committee Concerns • Lead applicant lacks familiarity in industrial and distributed power • • • generation • automotive requirements are significantly different than utility and community-scale needs, and the proposal fails to make a convincing case that the team can handle the difference Proposal lacks specific commercialization and go-to-market strategies Proposal does not sufficiently detail the value proposition of the products or the present competition Adoption of smart grid and community-scale systems likely to exceed 31 the 3 to 5 year timeframe
Market Size • BPLG estimates the total market size to be $46, 303, 359 in 2012 and $130, 407, 516 in 2017. Estimated Revenues from BPL’s solution are $3, 000 by 2017. Other Economic Objectives • First year revenues: $1 M; by 2016, revenues projected to be over $100 M Committee Concerns • Lead applicant lacks familiarity in industrial and distributed power • • • generation • automotive requirements are significantly different than utility and community-scale needs, and the proposal fails to make a convincing case that the team can handle the difference Proposal lacks specific commercialization and go-to-market strategies Proposal does not sufficiently detail the value proposition of the products or the present competition Adoption of smart grid and community-scale systems likely to exceed 31 the 3 to 5 year timeframe
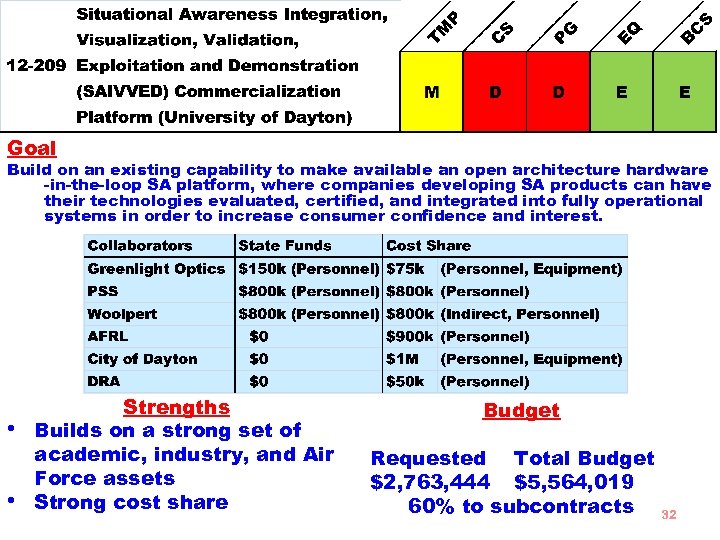 Goal Build on an existing capability to make available an open architecture hardware -in-the-loop SA platform, where companies developing SA products can have their technologies evaluated, certified, and integrated into fully operational systems in order to increase consumer confidence and interest. • • Strengths Builds on a strong set of academic, industry, and Air Force assets Strong cost share Budget Requested Total Budget $2, 763, 444 $5, 564, 019 60% to subcontracts 32
Goal Build on an existing capability to make available an open architecture hardware -in-the-loop SA platform, where companies developing SA products can have their technologies evaluated, certified, and integrated into fully operational systems in order to increase consumer confidence and interest. • • Strengths Builds on a strong set of academic, industry, and Air Force assets Strong cost share Budget Requested Total Budget $2, 763, 444 $5, 564, 019 60% to subcontracts 32
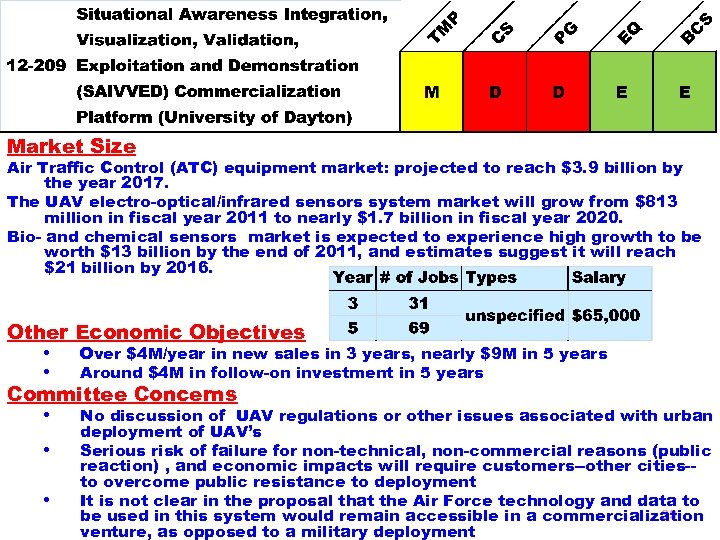 Market Size Air Traffic Control (ATC) equipment market: projected to reach $3. 9 billion by the year 2017. The UAV electro-optical/infrared sensors system market will grow from $813 million in fiscal year 2011 to nearly $1. 7 billion in fiscal year 2020. Bio- and chemical sensors market is expected to experience high growth to be worth $13 billion by the end of 2011, and estimates suggest it will reach $21 billion by 2016. Other Economic Objectives • Over $4 M/year in new sales in 3 years, nearly $9 M in 5 years • Around $4 M in follow-on investment in 5 years Committee Concerns • No discussion of UAV regulations or other issues associated with urban • • deployment of UAV’s Serious risk of failure for non-technical, non-commercial reasons (public reaction) , and economic impacts will require customers--other cities-to overcome public resistance to deployment It is not clear in the proposal that the Air Force technology and data to 33 be used in this system would remain accessible in a commercialization venture, as opposed to a military deployment
Market Size Air Traffic Control (ATC) equipment market: projected to reach $3. 9 billion by the year 2017. The UAV electro-optical/infrared sensors system market will grow from $813 million in fiscal year 2011 to nearly $1. 7 billion in fiscal year 2020. Bio- and chemical sensors market is expected to experience high growth to be worth $13 billion by the end of 2011, and estimates suggest it will reach $21 billion by 2016. Other Economic Objectives • Over $4 M/year in new sales in 3 years, nearly $9 M in 5 years • Around $4 M in follow-on investment in 5 years Committee Concerns • No discussion of UAV regulations or other issues associated with urban • • deployment of UAV’s Serious risk of failure for non-technical, non-commercial reasons (public reaction) , and economic impacts will require customers--other cities-to overcome public resistance to deployment It is not clear in the proposal that the Air Force technology and data to 33 be used in this system would remain accessible in a commercialization venture, as opposed to a military deployment
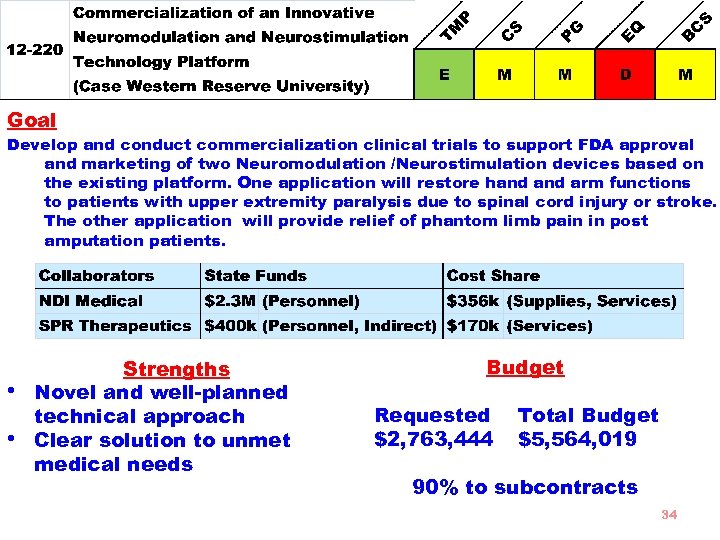 Goal Develop and conduct commercialization clinical trials to support FDA approval and marketing of two Neuromodulation /Neurostimulation devices based on the existing platform. One application will restore hand arm functions to patients with upper extremity paralysis due to spinal cord injury or stroke. The other application will provide relief of phantom limb pain in post amputation patients. • • Strengths Novel and well-planned technical approach Clear solution to unmet medical needs Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 90% to subcontracts 34
Goal Develop and conduct commercialization clinical trials to support FDA approval and marketing of two Neuromodulation /Neurostimulation devices based on the existing platform. One application will restore hand arm functions to patients with upper extremity paralysis due to spinal cord injury or stroke. The other application will provide relief of phantom limb pain in post amputation patients. • • Strengths Novel and well-planned technical approach Clear solution to unmet medical needs Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 90% to subcontracts 34
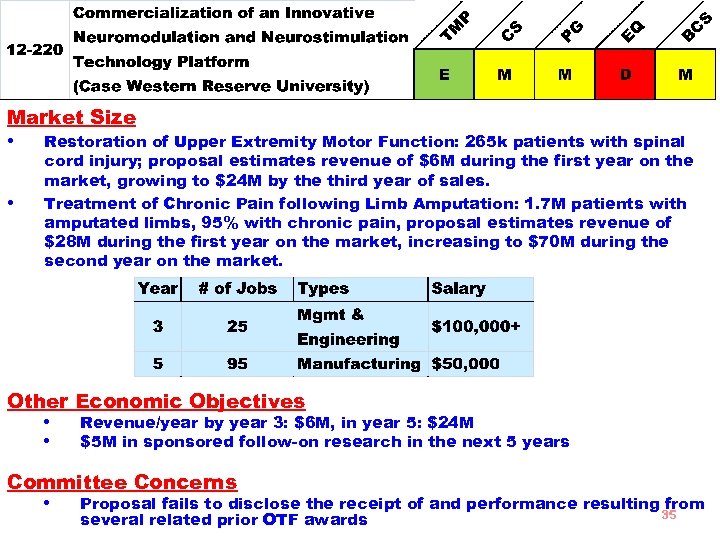 Market Size • Restoration of Upper Extremity Motor Function: 265 k patients with spinal • cord injury; proposal estimates revenue of $6 M during the first year on the market, growing to $24 M by the third year of sales. Treatment of Chronic Pain following Limb Amputation: 1. 7 M patients with amputated limbs, 95% with chronic pain, proposal estimates revenue of $28 M during the first year on the market, increasing to $70 M during the second year on the market. Other Economic Objectives • Revenue/year by year 3: $6 M, in year 5: $24 M • $5 M in sponsored follow-on research in the next 5 years Committee Concerns • Proposal fails to disclose the receipt of and performance resulting from 35 several related prior OTF awards
Market Size • Restoration of Upper Extremity Motor Function: 265 k patients with spinal • cord injury; proposal estimates revenue of $6 M during the first year on the market, growing to $24 M by the third year of sales. Treatment of Chronic Pain following Limb Amputation: 1. 7 M patients with amputated limbs, 95% with chronic pain, proposal estimates revenue of $28 M during the first year on the market, increasing to $70 M during the second year on the market. Other Economic Objectives • Revenue/year by year 3: $6 M, in year 5: $24 M • $5 M in sponsored follow-on research in the next 5 years Committee Concerns • Proposal fails to disclose the receipt of and performance resulting from 35 several related prior OTF awards
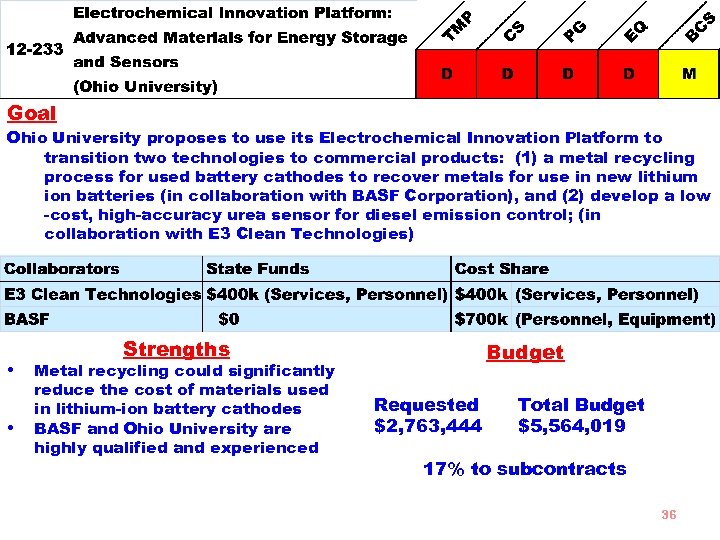 Goal Ohio University proposes to use its Electrochemical Innovation Platform to transition two technologies to commercial products: (1) a metal recycling process for used battery cathodes to recover metals for use in new lithium ion batteries (in collaboration with BASF Corporation), and (2) develop a low -cost, high-accuracy urea sensor for diesel emission control; (in collaboration with E 3 Clean Technologies) • • Strengths Metal recycling could significantly reduce the cost of materials used in lithium-ion battery cathodes BASF and Ohio University are highly qualified and experienced Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 17% to subcontracts 36
Goal Ohio University proposes to use its Electrochemical Innovation Platform to transition two technologies to commercial products: (1) a metal recycling process for used battery cathodes to recover metals for use in new lithium ion batteries (in collaboration with BASF Corporation), and (2) develop a low -cost, high-accuracy urea sensor for diesel emission control; (in collaboration with E 3 Clean Technologies) • • Strengths Metal recycling could significantly reduce the cost of materials used in lithium-ion battery cathodes BASF and Ohio University are highly qualified and experienced Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 17% to subcontracts 36
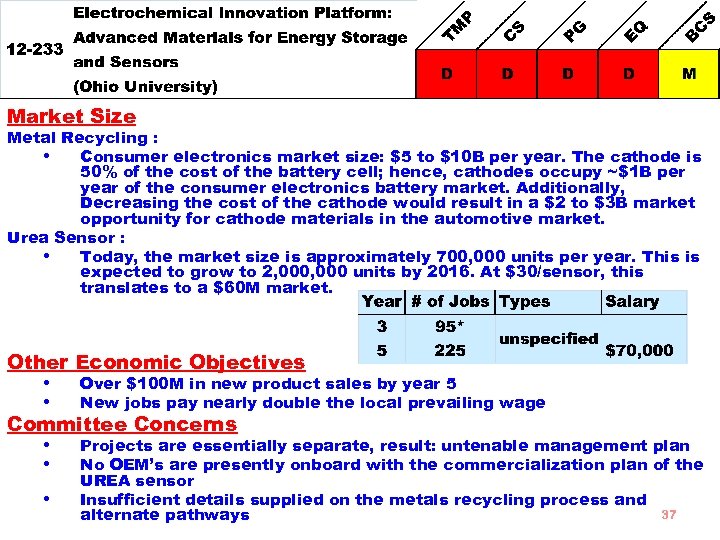 Market Size Metal Recycling : • Consumer electronics market size: $5 to $10 B per year. The cathode is 50% of the cost of the battery cell; hence, cathodes occupy ~$1 B per year of the consumer electronics battery market. Additionally, Decreasing the cost of the cathode would result in a $2 to $3 B market opportunity for cathode materials in the automotive market. Urea Sensor : • Today, the market size is approximately 700, 000 units per year. This is expected to grow to 2, 000 units by 2016. At $30/sensor, this translates to a $60 M market. Other Economic Objectives • Over $100 M in new product sales by year 5 • New jobs pay nearly double the local prevailing wage Committee Concerns • Projects are essentially separate, result: untenable management plan • No OEM’s are presently onboard with the commercialization plan of the • UREA sensor Insufficient details supplied on the metals recycling process and alternate pathways 37
Market Size Metal Recycling : • Consumer electronics market size: $5 to $10 B per year. The cathode is 50% of the cost of the battery cell; hence, cathodes occupy ~$1 B per year of the consumer electronics battery market. Additionally, Decreasing the cost of the cathode would result in a $2 to $3 B market opportunity for cathode materials in the automotive market. Urea Sensor : • Today, the market size is approximately 700, 000 units per year. This is expected to grow to 2, 000 units by 2016. At $30/sensor, this translates to a $60 M market. Other Economic Objectives • Over $100 M in new product sales by year 5 • New jobs pay nearly double the local prevailing wage Committee Concerns • Projects are essentially separate, result: untenable management plan • No OEM’s are presently onboard with the commercialization plan of the • UREA sensor Insufficient details supplied on the metals recycling process and alternate pathways 37
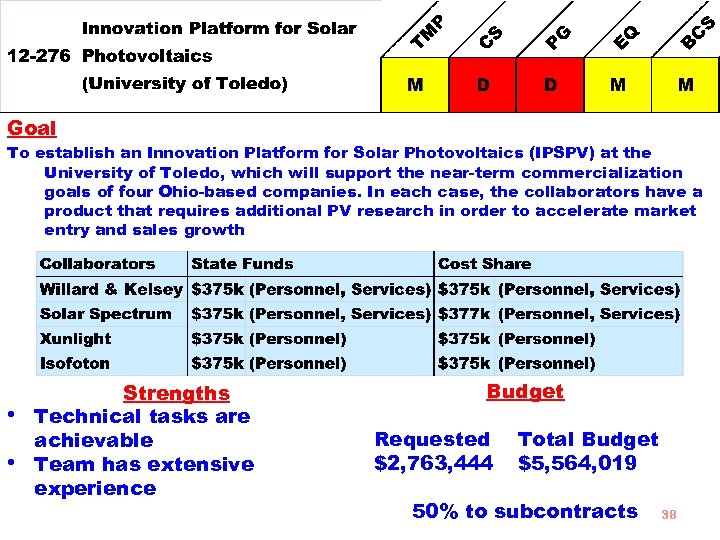 Goal To establish an Innovation Platform for Solar Photovoltaics (IPSPV) at the University of Toledo, which will support the near-term commercialization goals of four Ohio-based companies. In each case, the collaborators have a product that requires additional PV research in order to accelerate market entry and sales growth • • Strengths Technical tasks are achievable Team has extensive experience Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 50% to subcontracts 38
Goal To establish an Innovation Platform for Solar Photovoltaics (IPSPV) at the University of Toledo, which will support the near-term commercialization goals of four Ohio-based companies. In each case, the collaborators have a product that requires additional PV research in order to accelerate market entry and sales growth • • Strengths Technical tasks are achievable Team has extensive experience Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 50% to subcontracts 38
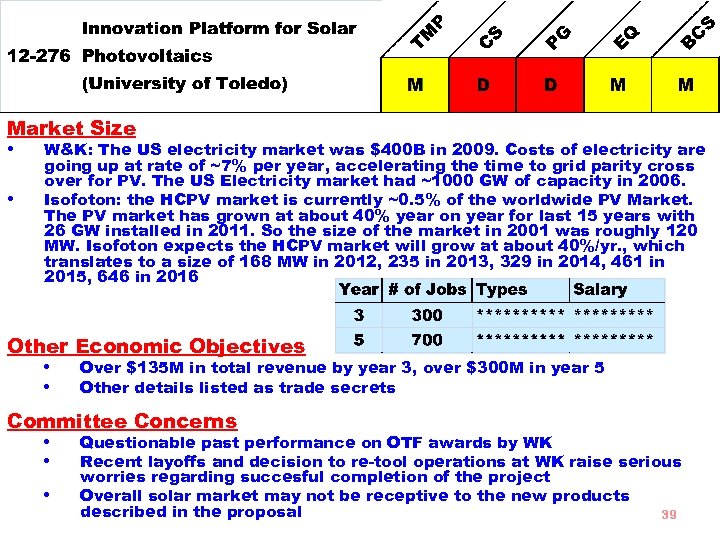 Market Size • W&K: The US electricity market was $400 B in 2009. Costs of electricity are • going up at rate of ~7% per year, accelerating the time to grid parity cross over for PV. The US Electricity market had ~1000 GW of capacity in 2006. Isofoton: the HCPV market is currently ~0. 5% of the worldwide PV Market. The PV market has grown at about 40% year on year for last 15 years with 26 GW installed in 2011. So the size of the market in 2001 was roughly 120 MW. Isofoton expects the HCPV market will grow at about 40%/yr. , which translates to a size of 168 MW in 2012, 235 in 2013, 329 in 2014, 461 in 2015, 646 in 2016 Other Economic Objectives • Over $135 M in total revenue by year 3, over $300 M in year 5 • Other details listed as trade secrets Committee Concerns • Questionable past performance on OTF awards by WK • Recent layoffs and decision to re-tool operations at WK raise serious • worries regarding succesful completion of the project Overall solar market may not be receptive to the new products described in the proposal 39
Market Size • W&K: The US electricity market was $400 B in 2009. Costs of electricity are • going up at rate of ~7% per year, accelerating the time to grid parity cross over for PV. The US Electricity market had ~1000 GW of capacity in 2006. Isofoton: the HCPV market is currently ~0. 5% of the worldwide PV Market. The PV market has grown at about 40% year on year for last 15 years with 26 GW installed in 2011. So the size of the market in 2001 was roughly 120 MW. Isofoton expects the HCPV market will grow at about 40%/yr. , which translates to a size of 168 MW in 2012, 235 in 2013, 329 in 2014, 461 in 2015, 646 in 2016 Other Economic Objectives • Over $135 M in total revenue by year 3, over $300 M in year 5 • Other details listed as trade secrets Committee Concerns • Questionable past performance on OTF awards by WK • Recent layoffs and decision to re-tool operations at WK raise serious • worries regarding succesful completion of the project Overall solar market may not be receptive to the new products described in the proposal 39
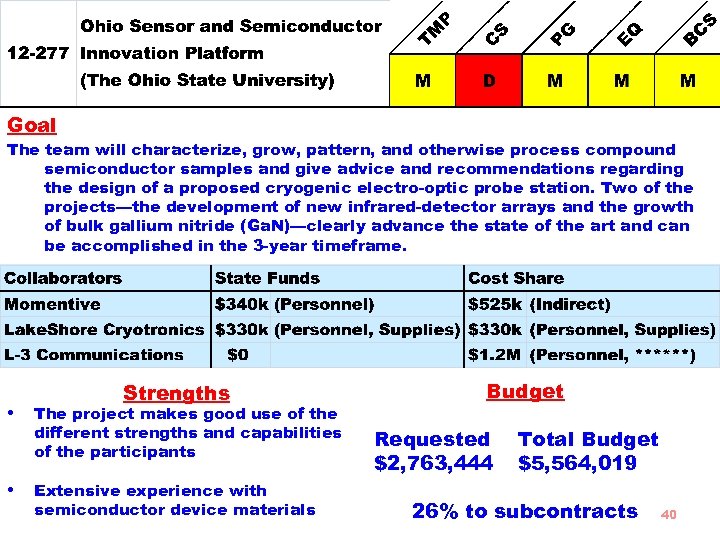 Goal The team will characterize, grow, pattern, and otherwise process compound semiconductor samples and give advice and recommendations regarding the design of a proposed cryogenic electro-optic probe station. Two of the projects—the development of new infrared-detector arrays and the growth of bulk gallium nitride (Ga. N)—clearly advance the state of the art and can be accomplished in the 3 -year timeframe. • • Strengths The project makes good use of the different strengths and capabilities of the participants Extensive experience with semiconductor device materials Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 26% to subcontracts 40
Goal The team will characterize, grow, pattern, and otherwise process compound semiconductor samples and give advice and recommendations regarding the design of a proposed cryogenic electro-optic probe station. Two of the projects—the development of new infrared-detector arrays and the growth of bulk gallium nitride (Ga. N)—clearly advance the state of the art and can be accomplished in the 3 -year timeframe. • • Strengths The project makes good use of the different strengths and capabilities of the participants Extensive experience with semiconductor device materials Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 26% to subcontracts 40
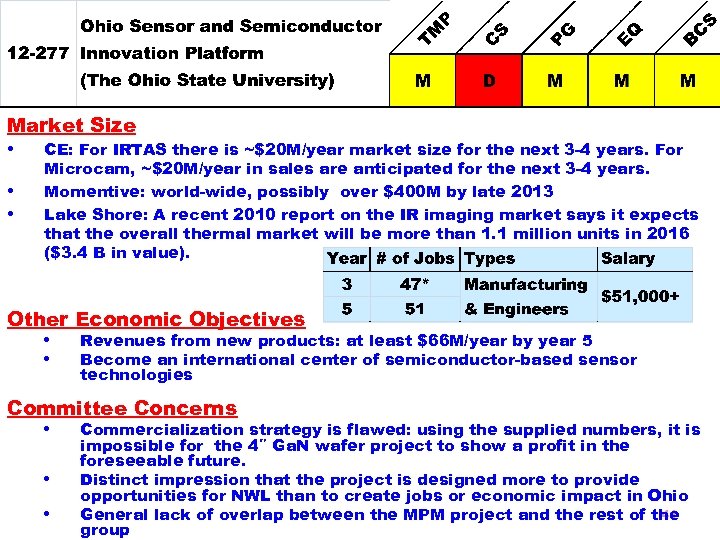 Market Size • CE: For IRTAS there is ~$20 M/year market size for the next 3 -4 years. For • • Microcam, ~$20 M/year in sales are anticipated for the next 3 -4 years. Momentive: world-wide, possibly over $400 M by late 2013 Lake Shore: A recent 2010 report on the IR imaging market says it expects that the overall thermal market will be more than 1. 1 million units in 2016 ($3. 4 B in value). Other Economic Objectives • Revenues from new products: at least $66 M/year by year 5 • Become an international center of semiconductor-based sensor technologies Committee Concerns • Commercialization strategy is flawed: using the supplied numbers, it is • • impossible for the 4″ Ga. N wafer project to show a profit in the foreseeable future. Distinct impression that the project is designed more to provide opportunities for NWL than to create jobs or economic impact in Ohio 41 General lack of overlap between the MPM project and the rest of the group
Market Size • CE: For IRTAS there is ~$20 M/year market size for the next 3 -4 years. For • • Microcam, ~$20 M/year in sales are anticipated for the next 3 -4 years. Momentive: world-wide, possibly over $400 M by late 2013 Lake Shore: A recent 2010 report on the IR imaging market says it expects that the overall thermal market will be more than 1. 1 million units in 2016 ($3. 4 B in value). Other Economic Objectives • Revenues from new products: at least $66 M/year by year 5 • Become an international center of semiconductor-based sensor technologies Committee Concerns • Commercialization strategy is flawed: using the supplied numbers, it is • • impossible for the 4″ Ga. N wafer project to show a profit in the foreseeable future. Distinct impression that the project is designed more to provide opportunities for NWL than to create jobs or economic impact in Ohio 41 General lack of overlap between the MPM project and the rest of the group
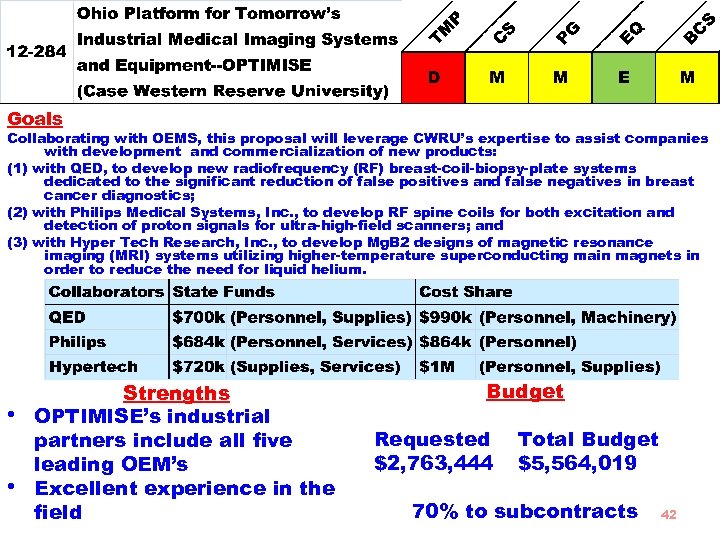 Goals Collaborating with OEMS, this proposal will leverage CWRU’s expertise to assist companies with development and commercialization of new products: (1) with QED, to develop new radiofrequency (RF) breast-coil-biopsy-plate systems dedicated to the significant reduction of false positives and false negatives in breast cancer diagnostics; (2) with Philips Medical Systems, Inc. , to develop RF spine coils for both excitation and detection of proton signals for ultra-high-field scanners; and (3) with Hyper Tech Research, Inc. , to develop Mg. B 2 designs of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems utilizing higher-temperature superconducting main magnets in order to reduce the need for liquid helium. • • Strengths OPTIMISE’s industrial partners include all five leading OEM’s Excellent experience in the field Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 70% to subcontracts 42
Goals Collaborating with OEMS, this proposal will leverage CWRU’s expertise to assist companies with development and commercialization of new products: (1) with QED, to develop new radiofrequency (RF) breast-coil-biopsy-plate systems dedicated to the significant reduction of false positives and false negatives in breast cancer diagnostics; (2) with Philips Medical Systems, Inc. , to develop RF spine coils for both excitation and detection of proton signals for ultra-high-field scanners; and (3) with Hyper Tech Research, Inc. , to develop Mg. B 2 designs of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems utilizing higher-temperature superconducting main magnets in order to reduce the need for liquid helium. • • Strengths OPTIMISE’s industrial partners include all five leading OEM’s Excellent experience in the field Budget Requested $2, 763, 444 Total Budget $5, 564, 019 70% to subcontracts 42
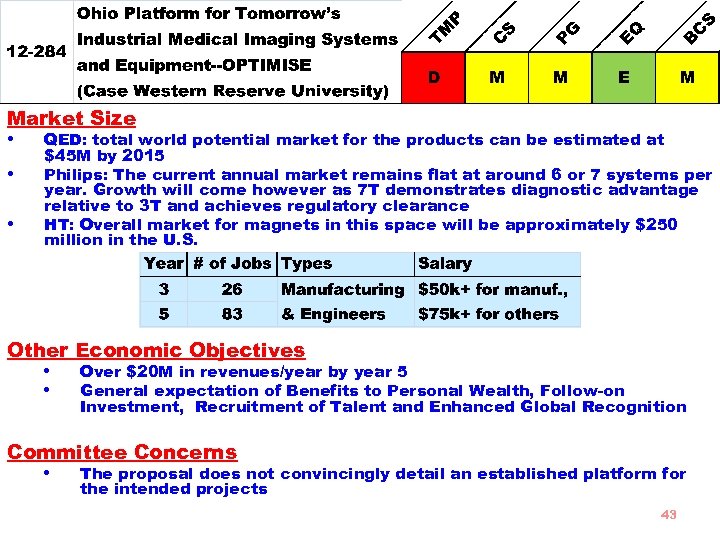 Market Size • QED: total world potential market for the products can be estimated at • • $45 M by 2015 Philips: The current annual market remains flat at around 6 or 7 systems per year. Growth will come however as 7 T demonstrates diagnostic advantage relative to 3 T and achieves regulatory clearance HT: Overall market for magnets in this space will be approximately $250 million in the U. S. Other Economic Objectives • Over $20 M in revenues/year by year 5 • General expectation of Benefits to Personal Wealth, Follow-on Investment, Recruitment of Talent and Enhanced Global Recognition Committee Concerns • The proposal does not convincingly detail an established platform for the intended projects 43
Market Size • QED: total world potential market for the products can be estimated at • • $45 M by 2015 Philips: The current annual market remains flat at around 6 or 7 systems per year. Growth will come however as 7 T demonstrates diagnostic advantage relative to 3 T and achieves regulatory clearance HT: Overall market for magnets in this space will be approximately $250 million in the U. S. Other Economic Objectives • Over $20 M in revenues/year by year 5 • General expectation of Benefits to Personal Wealth, Follow-on Investment, Recruitment of Talent and Enhanced Global Recognition Committee Concerns • The proposal does not convincingly detail an established platform for the intended projects 43
 Committee Membership • Committee members were recruited based on technical expertise as well as experience with business practices, technology transfer, venture capital, and economic development. • Bias and Conflict of Interest – Potential members reviewed full list of participating institutions and collaborators before nomination – After nomination, each member completed bias and conflict forms which were reviewed by NRC staff and discussed by the committee 44
Committee Membership • Committee members were recruited based on technical expertise as well as experience with business practices, technology transfer, venture capital, and economic development. • Bias and Conflict of Interest – Potential members reviewed full list of participating institutions and collaborators before nomination – After nomination, each member completed bias and conflict forms which were reviewed by NRC staff and discussed by the committee 44
 Committee Membership T. S. Sudarshan, Chair CEO and President, Materials Modification, Inc. Viola L. Acoff Head and Professor, Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Univ. of Alabama Catherine G. Ambrose Associate Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery, Univ. of Texas David E. Aspnes (NAS) Distinguished University Professor, Dept. of Physics, North Carolina State Univ. Paul A. Erickson Associate Professor, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, UC Davis Bruce Gitter Senior principle scientist and manager of nuclear medicine imaging, Covance Laboratories, Inc. Jahan K. Jewayni Independent Wealth Management Consultant Matt Jones Partner, Nth Power Carol Cherkis Mohammad A. Karim David E. Crow (NAE) Chester Kolodziej Life Sciences Industry Consultant, New. Cap Partners Senior VP, Pratt and Whitney (ret) and professor emeritus of mechanical engineering at the Univ. of Connecticut Vice President for Research Old Dominion University Executive Director, Freedom Field Renewable Energy, Inc 45
Committee Membership T. S. Sudarshan, Chair CEO and President, Materials Modification, Inc. Viola L. Acoff Head and Professor, Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Univ. of Alabama Catherine G. Ambrose Associate Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery, Univ. of Texas David E. Aspnes (NAS) Distinguished University Professor, Dept. of Physics, North Carolina State Univ. Paul A. Erickson Associate Professor, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, UC Davis Bruce Gitter Senior principle scientist and manager of nuclear medicine imaging, Covance Laboratories, Inc. Jahan K. Jewayni Independent Wealth Management Consultant Matt Jones Partner, Nth Power Carol Cherkis Mohammad A. Karim David E. Crow (NAE) Chester Kolodziej Life Sciences Industry Consultant, New. Cap Partners Senior VP, Pratt and Whitney (ret) and professor emeritus of mechanical engineering at the Univ. of Connecticut Vice President for Research Old Dominion University Executive Director, Freedom Field Renewable Energy, Inc 45
 Committee Membership Laura Mazzola Vice President of Global Health Products, Wave 80 Biosciences Trent Molter Associate Research Professor and Business Development Officer, Center for Clean Energy Engineering, Univ. of Connecticut C. Bradley Moore (NAS) Professor of Chemistry Emeritus at Univ. of California, Berkeley Nabil Nasr Director, Center for Integrated Manufacturing Studies, Rochester Institute of Technology Arthur L. Patterson President and CEO, CMC, LLC Shalini Prasad Professor of bioengineering at Univ. of Texas, Dallas Lloyd M. Robeson (NAE) Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, Lehigh Univ. and Principle Research Associate, Air Products and Chemicals (ret) Subhash C. Singhal (NAE) Independent Consultant and Battelle Fellow Emeritus, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Norman A. Wereley Professor and Associate Chair of Aerospace Engineering, Univ. of Maryland Jim Wheeler Senior Vice President of Economic Competitiveness Policy and Research, Thomas P. Miller and Associates Raul E. Zavaleta CEO, Indigo Bio. Systems, Inc. 46
Committee Membership Laura Mazzola Vice President of Global Health Products, Wave 80 Biosciences Trent Molter Associate Research Professor and Business Development Officer, Center for Clean Energy Engineering, Univ. of Connecticut C. Bradley Moore (NAS) Professor of Chemistry Emeritus at Univ. of California, Berkeley Nabil Nasr Director, Center for Integrated Manufacturing Studies, Rochester Institute of Technology Arthur L. Patterson President and CEO, CMC, LLC Shalini Prasad Professor of bioengineering at Univ. of Texas, Dallas Lloyd M. Robeson (NAE) Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, Lehigh Univ. and Principle Research Associate, Air Products and Chemicals (ret) Subhash C. Singhal (NAE) Independent Consultant and Battelle Fellow Emeritus, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Norman A. Wereley Professor and Associate Chair of Aerospace Engineering, Univ. of Maryland Jim Wheeler Senior Vice President of Economic Competitiveness Policy and Research, Thomas P. Miller and Associates Raul E. Zavaleta CEO, Indigo Bio. Systems, Inc. 46
 Committee Process First meeting: April 19 -20, 2012 • ODOD Presentation on IPP • Extensive discussion on all proposals • Through consensus, selected 13 proposals for future interviews Between meetings, committee members continued in-depth evaluation of the 13 interviewees, including examination of their financial and technical viability Second meeting: May 30 -June 1, 2012 • Held 13 interviews • Each 50 minute session was conducted in true “interview” format • After Interviews, held a final dialogue with ODOD staff: • – Prior performance of interviewees on prior OTF grants – Requirements and objectives of the IPP Through consensus, committee determined which proposals best satisfied the requirements of the RFP and their respective rank-order 47
Committee Process First meeting: April 19 -20, 2012 • ODOD Presentation on IPP • Extensive discussion on all proposals • Through consensus, selected 13 proposals for future interviews Between meetings, committee members continued in-depth evaluation of the 13 interviewees, including examination of their financial and technical viability Second meeting: May 30 -June 1, 2012 • Held 13 interviews • Each 50 minute session was conducted in true “interview” format • After Interviews, held a final dialogue with ODOD staff: • – Prior performance of interviewees on prior OTF grants – Requirements and objectives of the IPP Through consensus, committee determined which proposals best satisfied the requirements of the RFP and their respective rank-order 47


