e2285f9d464bded19d10ef9450a02301.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

COMESA CLEARING HOUSE MOBILE FINANCIAL SERVICES AND PAYMENT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN COMESA MEMBER COUNTRIES March 2012

AGENDA Ø COMESA AT A GLANCE Ø BACKGROUND TO MFS & PAYMENT SYSTEMS Ø BENEFITS OF MFS & PAYMENT SYSTEMS Ø BASIC CONDITIONS FOR CROSS BORDER MOBILE PAYMENTS Ø PROGRESS Ø REPSS - OBJECTIVES, FEATURES, BENEFITS Ø PAYMENT & SETTLEMENT FLOWS Ø Q&A
COMESA MEMBERSHIP
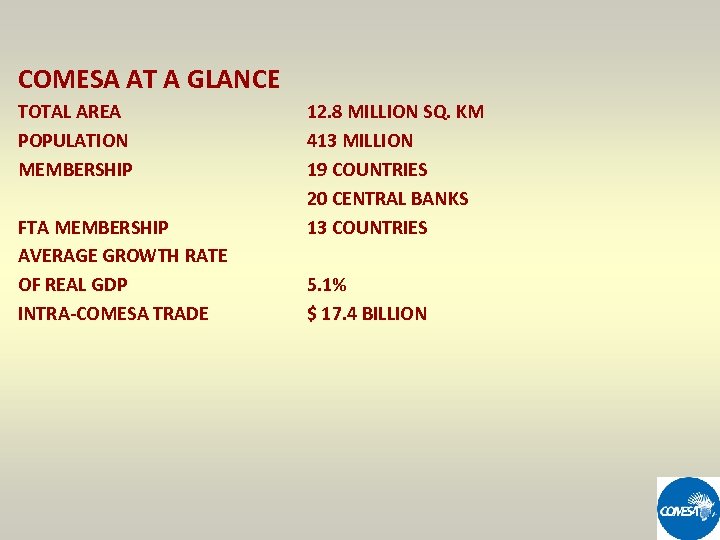
COMESA AT A GLANCE TOTAL AREA POPULATION MEMBERSHIP FTA MEMBERSHIP AVERAGE GROWTH RATE OF REAL GDP INTRA-COMESA TRADE 12. 8 MILLION SQ. KM 413 MILLION 19 COUNTRIES 20 CENTRAL BANKS 13 COUNTRIES 5. 1% $ 17. 4 BILLION

BACKGROUND TO MOBILE FINANCIAL SERVICES & PAYMENT SYSTEMS • ACCESS TO FORMAL FINANCIAL SERVICES LIMITED FOR MOST OF THE WORLD’S POOREST – 2. 5 BILLION DO NOT USE THESE SERVICES • POORER A HOUSEHOLD, STRONGER ITS NEED FOR FINANCIAL SERVICES – SAVINGS, REMITTANCES, CREDIT • MOBILE & RETAIL PAYMENT SYSTEMS IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES LAG BEHIND DEVELOPED COUNTRIES • MOBILE PHONES NOW IN THE HANDS OF BILLIONS, EVEN AT LOW INCOME LEVELS • PRESENTS A GREAT OPPORTUNITY TO GROW THE FORMAL ECONOMY • THIS WOULD UNLOCK EFFICIENCIES IN MANY AREAS OF DEVELOPING ECONOMIES • PAYMENTS SYSTEMS CHANGING FROM PAPER TO ELECTRONIC AT FAST PACE • ELECTRONIC PLATFORMS GROWING • CROSS BORDER PAYMENTS ARE BECOMING SIMPLIFIED

BENEFITS OF MFS • REDUCE RISK FOR FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS • REDUCE OPERATING COSTS • IMPROVE ACCESS TO SERVICES BENEFITS OF PAYMENT SYSTEMS (RETAIL & NATIONAL) • CONVENIENCE – EASY ACCESS TO FUNDS • SAFETY - MORE SECURE THAN CASH • PARTICIPATION IN REGIONAL AND GLOBAL ECONOMY - WIDER REACH • COST EFFECTIVE - REDUCES COSTS OF CHEQUE AND TRADITIONAL BANKING METHODS • RISK REDUCTION - MOVEMENT OF FUNDS IS MONITORED & LIQUIDITY MANAGED • EFFICIENT – FASTER PAYMENTS WITH NOTIFICATIONS

BASIC CONDITIONS FOR CROSS BORDER PAYMENTS Ø REGULATORY PROPORTIONALITY • blend of different regulatory boundaries to allow a framework that provides room for innovation and safeguards against risks • legal act to address standard payment system issues • regulations, guidelines to address specific aspects • proportionate regulations for payment service providers • enable non-bank players to offer payment services Ø MARKET COMPETITIVENESS • both the financial service sector and other related service providers need to offer cost effective solutions to encourage use of mobile payments Ø END-USER ACCESS • consumers must have a basic understanding of financial issues and no cultural or structural impediments to financial access. Thus financial literacy, financial empowerment and mobile penetration are key

BASIC CONDITIONS FOR CROSS BORDER PAYMENTS Ø MARKET CATALYSTS • Government usage of mobile payments will provide certainty to private sector players to also use this channel • Increased demand for retail cross border trade promotes use of mobile payments • Robust data collection and monitoring points to areas where more effort will be channelled to promote cross border mobile payments Ø ICT INFRASTRUCTURE • Heavy investment in modern technology to attain interoperability, security and easy customisation of technology • Fosters creation of national payment networks • Fair and transparent access criteria for using infrastructure • Ensures cross network acceptance of payment instruments

PROGRESS ACHIEVED Ø COMESA REGION HAS MADE STRIDES IN ACHIEVING - Greater mobile financial service use; - Liberalized financial sector; and - Flow of trade and services across its borders Ø THIS HAS BEEN ACHIEVED THROUGH PROMOTING ENABLERS SUCH AS: - Consumer protection - Legal framework - Infrastructure - Risk management
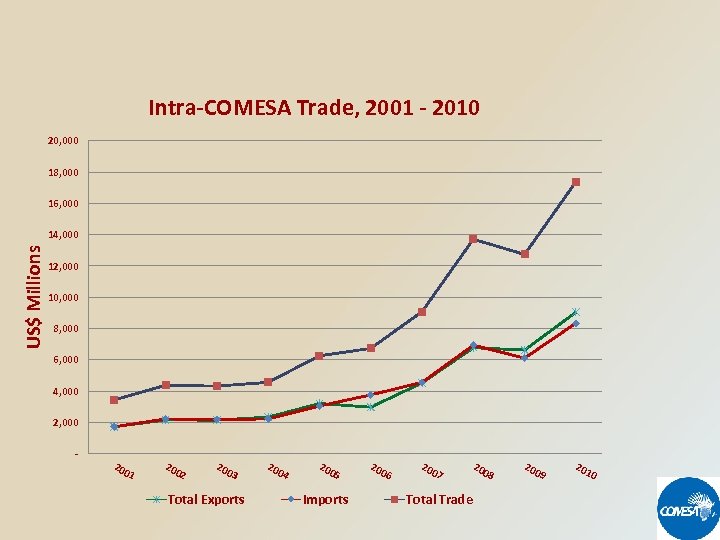
Intra-COMESA Trade, 2001 - 2010 20, 000 18, 000 16, 000 US$ Millions 14, 000 12, 000 10, 000 8, 000 6, 000 4, 000 2, 000 - 200 1 200 2 200 3 Total Exports 200 4 200 5 Imports 200 6 200 7 200 Total Trade 8 200 9 201 0
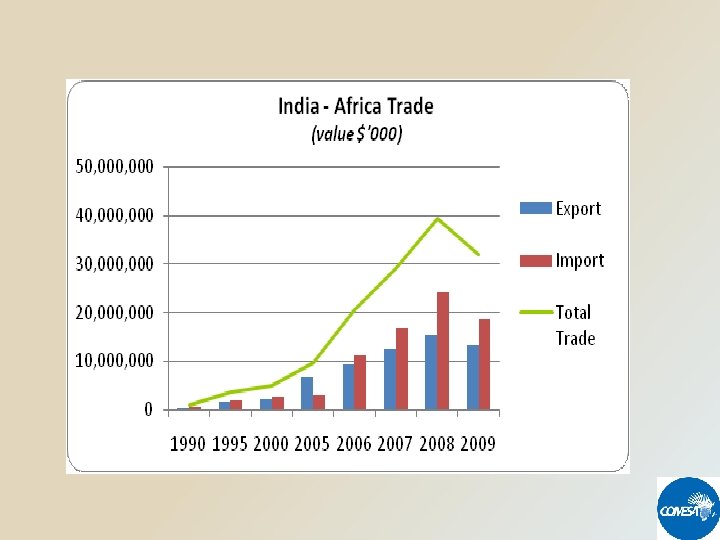
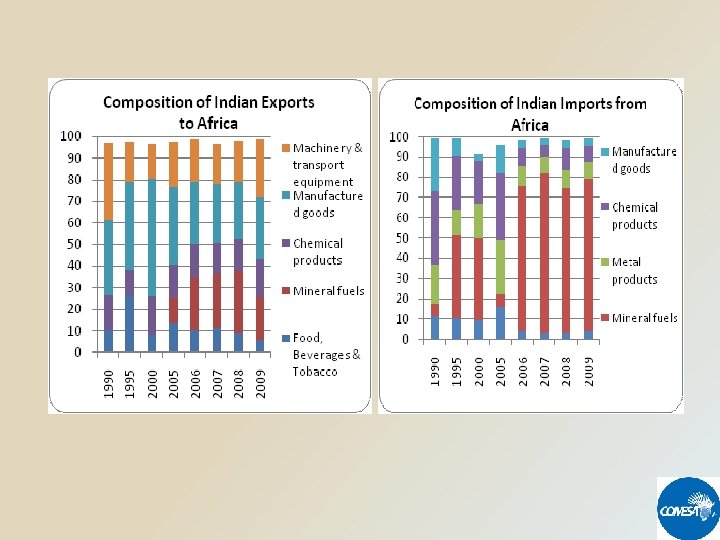
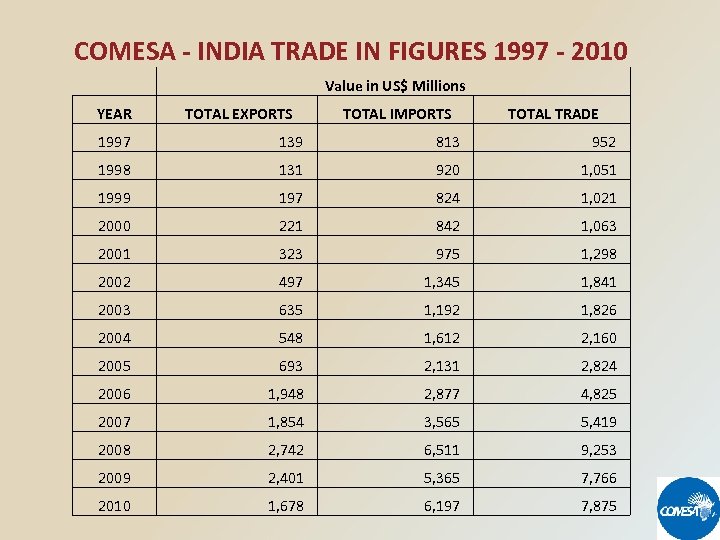
COMESA - INDIA TRADE IN FIGURES 1997 - 2010 Value in US$ Millions YEAR TOTAL EXPORTS TOTAL IMPORTS TOTAL TRADE 1997 139 813 952 1998 131 920 1, 051 1999 197 824 1, 021 2000 221 842 1, 063 2001 323 975 1, 298 2002 497 1, 345 1, 841 2003 635 1, 192 1, 826 2004 548 1, 612 2, 160 2005 693 2, 131 2, 824 2006 1, 948 2, 877 4, 825 2007 1, 854 3, 565 5, 419 2008 2, 742 6, 511 9, 253 2009 2, 401 5, 365 7, 766 2010 1, 678 6, 197 7, 875
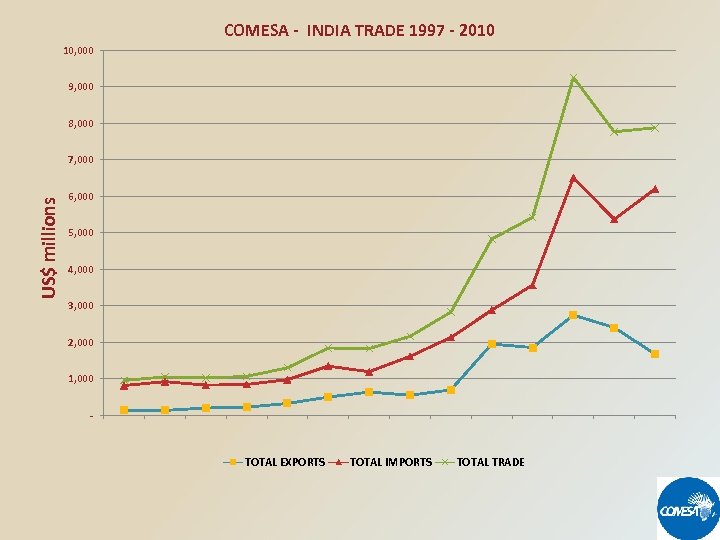
COMESA - INDIA TRADE 1997 - 2010 10, 000 9, 000 8, 000 US$ millions 7, 000 6, 000 5, 000 4, 000 3, 000 2, 000 1, 000 - TOTAL EXPORTS TOTAL IMPORTS TOTAL TRADE

COMESA TOP TWENTY IMPORTS FROM INDIA IN 2010 Rank Products Value (US$ millions) 1 Petroleum oils and oils obtained from bituminous minerals (excl. crude… 1, 406 2 Medicaments consisting of mixed or unmixed products for therapeutic or. . . 418 3 Boneless, frozen meat of bovine animals 287 4 Transmission apparatus incorporating reception apparatus, for radio-te. . . 143 5 Motor-cycles with reciprocating internal combustion piston engine cyli. . . 133 6 Floor coverings of polymers of vinyl chloride, whether or not self-adh. . . 76 7 Flat-rolled products of iron or non-alloy steel, of a width >= 600 mm, . . . 71 8 Single cotton yarn other than sewing thread of combed fibres, containi. . . 68 9 Transformers, other than liquid dielectric, having a power handling ca. . . 49 10 Flat-rolled products of iron or steel, of a width >= 600 mm, cold-roll. . . 37 11 Paper and paperboard, uncoated, in rolls or sheets as specified in not. . . 35 12 Motor cars and other motor vehicles principally designed for the trans. . . 32 13 Synthetic filament yarn, incl. synthetic monofilament of < 67 decitex, . . . 32 14 Cement clinkers 32 15 Structures and parts of structures, of iron or steel, n. e. s. (excl. br. . . 32 16 Semi-milled or wholly milled rice 31 17 Co-axial cable and other co-axial electric conductors, insulated 30 18 Tractors (excl. those of heading no 8709, pedestrian-controlled tracto. . . 28 19 Printed books, brochures and similar printed matter (excl. those in lo. . . 28 20 Polyethylene terephthalate, in primary forms 27

COMESA TOP 20 EXPORTS TO INDIA IN 2010 Rank Products Value (US$ millions) 1 Petroleum oils and oils obtained from bituminous minerals, crude 1, 011 2 Cotton, neither carded nor combed 110 3 Coke and semi-coke of coal, of lignite or of peat, whether or not aggl. . . 50 4 Commercial ammonium carbonate and other ammonium carbonates 31 5 Anhydrous ammonia 31 6 Natural calcium phosphates, natural aluminium calcium phosphates and p. . . 24 7 Leather of whole hides of bovine animals, with a surface area of =< 2. . 21 8 Diamonds, unsorted 16 9 Black fermented tea and partly fermented tea, whether or not flavoured. . . 14 10 Dried, shelled peas pisum sativum, whether or not skinned or split 14 11 Dried, shelled leguminous vegetables, whether or not skinned or split. . . 13 12 Natural gas, liquefied 13 13 Natural calcium phosphates, natural aluminium calcium phosphates and p. . . 10 14 Alfalfa seed for sowing 10 15 Sheep or lambskin leather, without wool on, prepared after tanning, in. . . 10 16 Articles of asphalt or similar materials, e. g. petroleum bitumen or co. . . 9 17 Medicaments consisting of mixed or unmixed products for therapeutic or 9 18 Dried, shelled kidney beans phaseolus vulgaris, whether or not skinn. . . 8 19 Precious stones and semi-precious stones, unworked or simply sawn or r. . . 8 20 Waste and scrap, of copper (excl. ingots or other similar unwrought sh. . . 7

REGIONAL PAYMENT AND SETTLEMENT SYSTEM (REPSS) • REPSS IS A MULTILATERAL NETTING SYSTEM WITH END-OF-DAY SETTLEMENT • ALLOWS FOR SETTLEMENT IN A MULTICURRENCY ENVIRONMENT • TRANSACTIONS ARE SETTLED AT SPOT T+0 VALUE T+1 • A SINGLE CURRENCY (US$ OR EURO) IS USED FOR NET SETTLEMENT; • A SINGLE NOSTRO CORRESPONDENT FOR THE NET SETTLEMENT CURRENCY; • THE COMESA CLEARING HOUSE (CCH) ACTS AS AGENT OF CENTRAL BANKS

REPSS Objectives Ø STIMULATE ECONOMIC GROWTH THROUGH AN INCREASE OF INTRAREGIONAL TRADE Ø REDUCE COST AND DURATION OF CROSS BORDER TRANSACTIONS Ø HOMEGROWN SOLUTION, TO BE OPERATED BY THE COMESA COUNTRIES Ø SYSTEM TO BE RELIABLE, SECURE AND PREDICTABLE Ø LOW INVESTMENT AND OPERATIONAL COSTS Ø SETTLEMENT IN HARD CURRENCIES ($, €)

REPSS FEATURES • SYSTEM IS CENTRALLY LOCATED • LOCAL BANKS TO ACCESS SYSTEM THROUGH CENTRAL BANKS • PAYMENT SYSTEM LINKING CENTRAL BANKS • PAYMENTS TO BE EFFECTED THROUGH CLEARING (NOT REAL TIME) • PRINCIPLE OF CREDIT PUSH (PRE-FUNDED ACCOUNT) • COMPLIANT WITH BIS CORE PRINCIPLES

BENEFITS Ø REDUCES NUMBER OF SETTLEMENT TRANSACTIONS Ø REDUCES FOREIGN CORRESPONDENT BANKING CHARGES Ø REDUCES COST OF INTRA-REGIONAL TRADE Ø REDUCES SETTLEMENT TIME PERIOD Ø GUARANTEES PROMPT PAYMENT TO EXPORTER Ø BUILDS TRUST AMONG TRADERS Ø SETTLEMENT FINALITY Ø LEVELS PLAYING FIELD FOR COMMERCIAL BANKS Ø EVENTUALLY ALLOWS TRADE ON OPEN ACCOUNT

PAYMENT & SETTLEMENT FLOWS
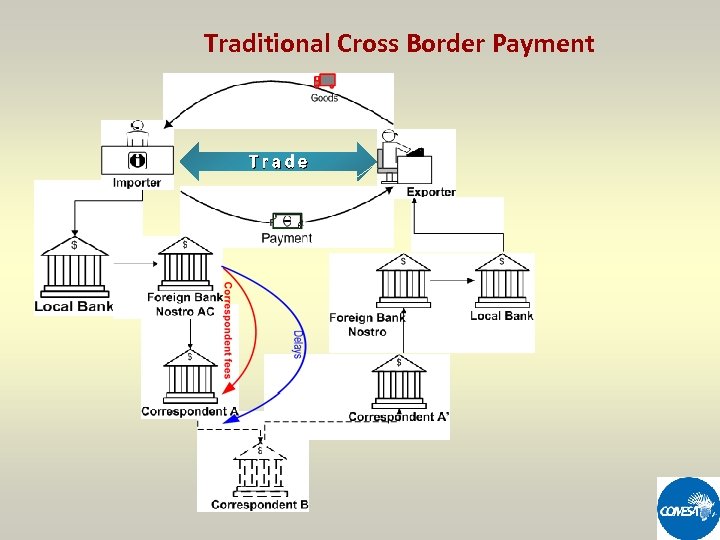
Traditional Cross Border Payment Trade
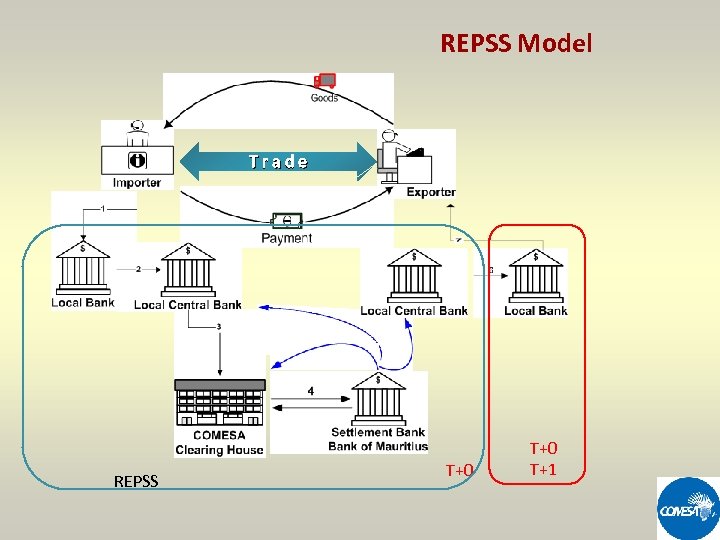
REPSS Model Trade REPSS T+0 T+1

Q&A
e2285f9d464bded19d10ef9450a02301.ppt