facafc576a9cf3b3bf37d570e10e4234.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

COMBATING WATER CRISIS Challenges & Opportunities Mushtaq Ahmad Gill (T. I. ) Executive Director South Asian Conservation Agriculture Network (SACAN) http: //www. sacanasia. org

PAKISTAN’S AGRICULTURE CHALLENGES • Low agricultural productivity • Increasing population pressure • Dwindling land for agriculture • Shrinking water resources • Limiting/diminishing energy resources ü Shortage of electricity ü High cost of diesel • High water losses in irrigation system • Over exploitation of groundwater

WATER CRISIS IN PAKISTAN (AFTER INDUS WATER TREATY- 1961) Ø Deprivation from water of eastern rivers (20 MAF) Ø Water logging, salinity & sodicity Ø Increase in domestic and industrial requirement Ø Deterioration of groundwater quality Ø Increase in demand of irrigation water Ø Persistent drought
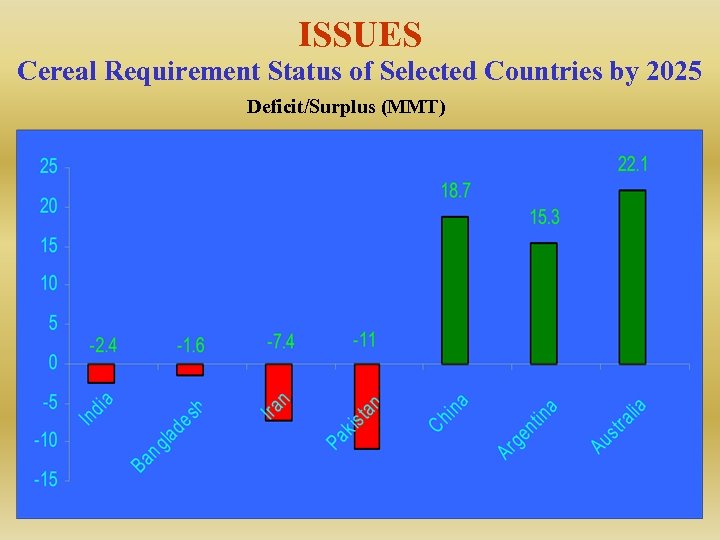
ISSUES Cereal Requirement Status of Selected Countries by 2025 Deficit/Surplus (MMT)
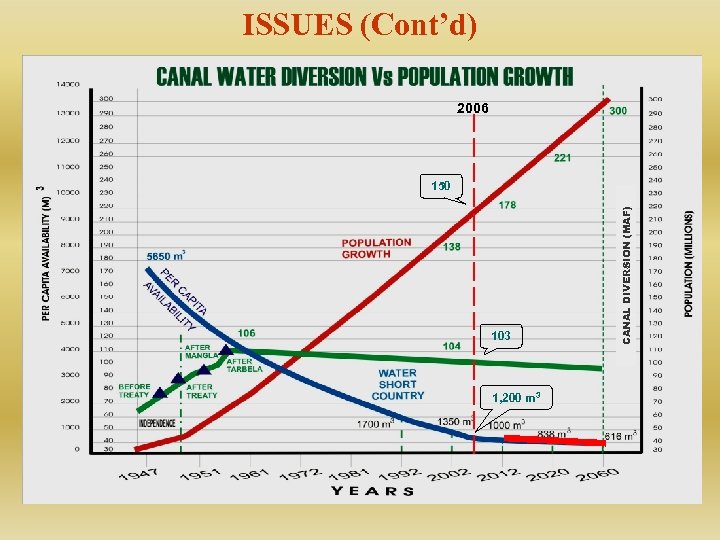
ISSUES (Cont’d) 2006 103 1, 200 m 3 CANAL DIVERSION (MAF) 150
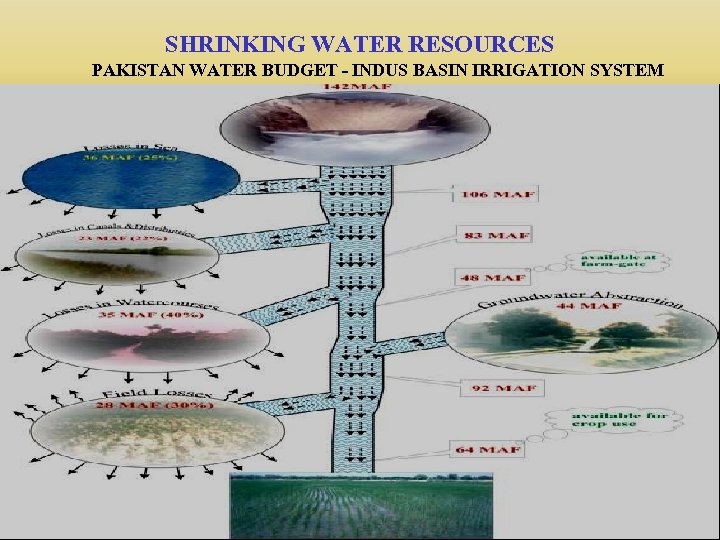
SHRINKING WATER RESOURCES PAKISTAN WATER BUDGET - INDUS BASIN IRRIGATION SYSTEM
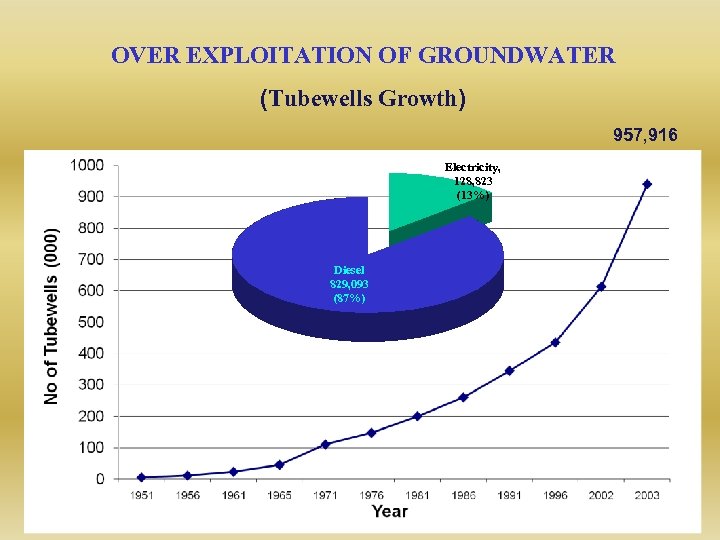
OVER EXPLOITATION OF GROUNDWATER (Tubewells Growth) 957, 916 Electricity, 128, 823 (13%) Diesel 829, 093 (87%)

OPTION q Productivity Enhancement in Canal and Non-Canal Command areas (marginal land water conditions)and desert and semi desert areas through Water Saving Technologies and Practices in order to: q foster sustainable food security q improve livelihoods q reduce poverty q environment friendly agriculture

Water Saving Technologies ( For Desert and Arid Agriculture)
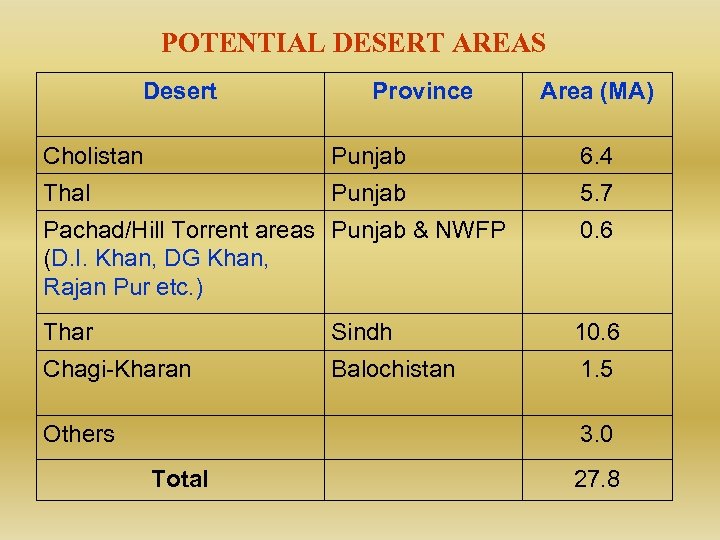
POTENTIAL DESERT AREAS Desert Province Area (MA) Cholistan Punjab 6. 4 Thal Punjab 5. 7 Pachad/Hill Torrent areas Punjab & NWFP (D. I. Khan, DG Khan, Rajan Pur etc. ) 0. 6 Thar Sindh 10. 6 Chagi-Kharan Balochistan 1. 5 Others 3. 0 Total 27. 8

POTENTIAL DESERT AREAS Challenges and Issues § § § Scarcity of irrigation water High cost of development of irrigation schemes Colossal loss of land due Water and Wind erosion Undulated topography Limited infrastructural facilities Heavy farm machinery requirements for traditional cultivation

DEVELOPMENT OF DESERT AGRICULTURE SUCCESS STORIES Desert Crops Grown Ghobi Desert, China Cotton & Tomato Sanai Desert, Israel/Egypt Fruits & Vegetables Alien Desert, UAE Fruits, Vegetables, Fodder Rajistan Desert, India Fruits, Vegetables, Oil Seeds Dasht-e-Kavir & Qir Qazim, Iran High Value Crops

CHALLENGES AND ISSUES § § § Scarcity of irrigation water High cost of development of irrigation schemes Colossal loss of land due water and wind erosion Undulated topography Prevailing poverty Limited infrastructural facilities Frequent weather/climate changes Heavy farm machinery requirements for cultivation Scattered and small holdings Shortage of skilled and unskilled labour Poor access to inputs

DEVELOPMENT OPTIONS § Supply of canal water to the desert/semi-desert areas § Establishment of mini dams, check dams, dugwells, lift irrigation schemes etc. § Construction and renovation of water storage ponds, underground tanks (Kunds), and Tobas by use of cost effective lining/layering materials (e. g. HDPE/plastic sheets etc. ) § Adoption of Resource Conservation Technology § Use of alternative energy sources (solar and wind) powered pumps for conveyance of water from water storage tanks to fields by use of drip/sprinkler and Flexible Gated Pipes § Management of groundwater by treated, cyclic and conjunctive use

Ongoing Development Strategies • Construction of Large and Small Dams • Construction of New Canal Systems – Greater Thal Canal (GTC) - Punjab – Katchi Canal - Balochistan – Rainee Canal - Sindh – Chasma Right Bank Canal (CRBC) - KPK

GREATER THAL CANAL PROJECT

MAIN CANAL HEAD REGULATOR

MAIN CANAL

NURPUR Dy OF PHASE - I

TEMPORARY PIPE OUTLET
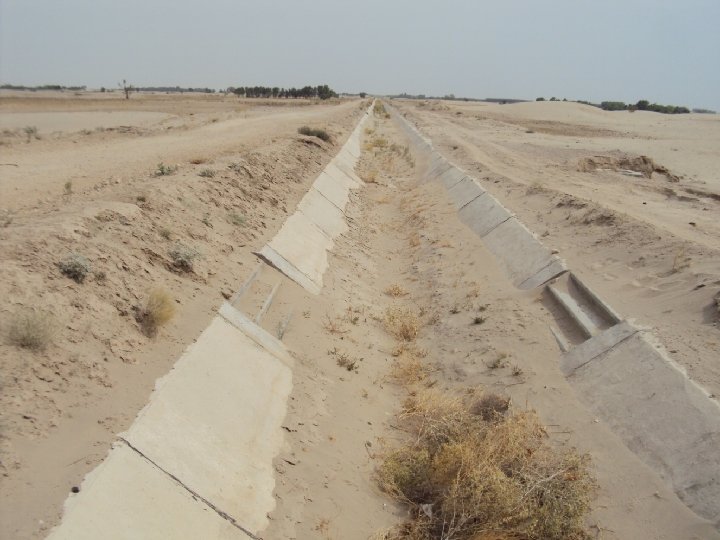
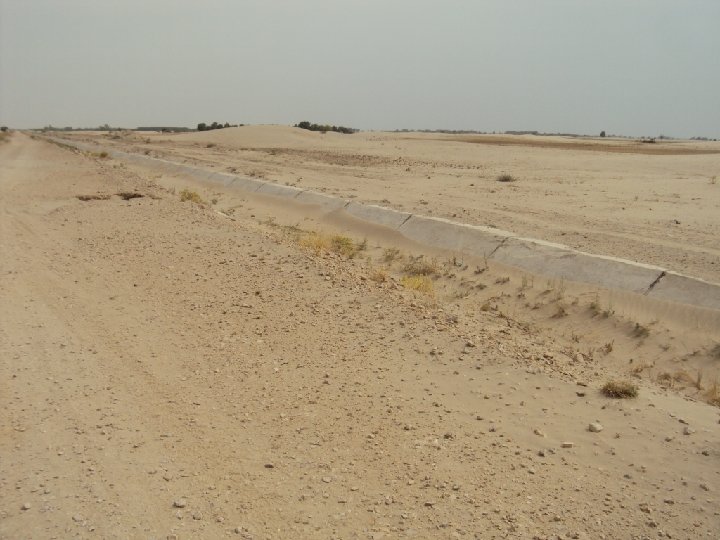
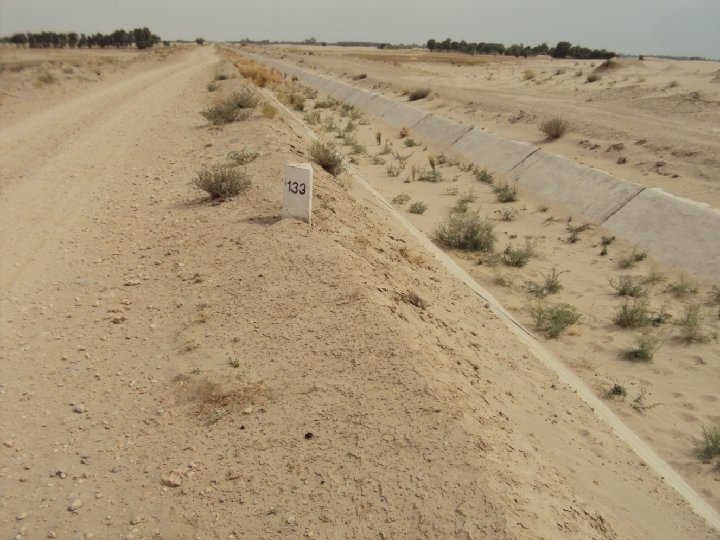
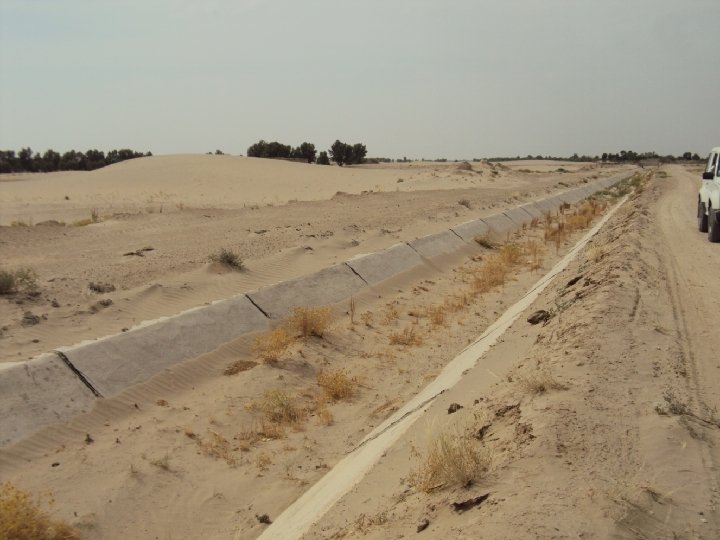





WAY FORWARD • National Water Policy • Provincial Water Visions in Accordance with Post IWT Scenario 1961 – Indus Water Apportionment Accord 1991 (CBM’s) • Creation of Think tank ( Planning Commission, HEC, Universities, PEC, PSAE) for Water Resources Development and Management

WAY FORWARD (Cont’d) § Desert areas may be developed following the models of Alien (UAE), Sanai (Israel/Egypt), Ghobi (China), Rajasthan (India), and Dasht-e. Kavir (Iran) § Feasibility study and preparation of development projects for Conservation Agriculture may be carried-out through involvement of private sector (consultants/companies e. g. PSAE, SACAN etc. ) § A body on the pattern of Thal Development Authority and Arid Land Development Authority, India may be constituted under the Supervision of Prime Minister at federal and CMs at provincial levels. § A project for development of 50, 000 acres at Head, Tail and Middle of Thal desert, with main focus on GTC area, may be launched § Outsource the project implementation to the private sector following the example of Rajistan Development in India with full support from public sector

Resource Conserved Is A Resource Generated http: //www. sacanasia. org THANKS
facafc576a9cf3b3bf37d570e10e4234.ppt