c440921c5e60623a09293309be2799fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 COM 317 800 Taejin Jung, Ph. D. Week 7: Measurement in PR
COM 317 800 Taejin Jung, Ph. D. Week 7: Measurement in PR
 Measurement l The process of assigning numbers (or labels) to objects, persons, states, or events in accordance with specific rules. l Determining the amount or intensity of some characteristic of interest to the researcher -The way in which information is collected l How we define what we are measuring determines, - How precise we will be in explaining what we have observed - Which analytical tools (statistics) are appropriate for the type of measurement we need
Measurement l The process of assigning numbers (or labels) to objects, persons, states, or events in accordance with specific rules. l Determining the amount or intensity of some characteristic of interest to the researcher -The way in which information is collected l How we define what we are measuring determines, - How precise we will be in explaining what we have observed - Which analytical tools (statistics) are appropriate for the type of measurement we need
 Concepts l Definition l Strengths A term that expresses an abstract idea formed by generalizing from particulars and summarizing related observations. 1. Simplifies research process by combining characteristics or objects into general categories Speech Anxiety – Has characteristics that can be observed, and has related particulars that can form this concept. 2. Facilitates communication among people who have a shared understanding of the terms
Concepts l Definition l Strengths A term that expresses an abstract idea formed by generalizing from particulars and summarizing related observations. 1. Simplifies research process by combining characteristics or objects into general categories Speech Anxiety – Has characteristics that can be observed, and has related particulars that can form this concept. 2. Facilitates communication among people who have a shared understanding of the terms
 Construct l Three distinct characteristics 1. Because it is abstract it cannot be directly observed 2. An abstract notion that is broken down into dimensions represented by lower-level concepts or a combination of concepts 3. It is designed for a particular research purpose so that its exact meaning only relates to the context in which it is found. Ex) Interactivity - Can be with a web page - Can be with a person - Can be mental engagement
Construct l Three distinct characteristics 1. Because it is abstract it cannot be directly observed 2. An abstract notion that is broken down into dimensions represented by lower-level concepts or a combination of concepts 3. It is designed for a particular research purpose so that its exact meaning only relates to the context in which it is found. Ex) Interactivity - Can be with a web page - Can be with a person - Can be mental engagement
 Conceptual & Operational Definitions l Conceptual Definition : A verbal explanation of the meaning of the concept - Media skepticism The degree to which individuals are skeptical toward reality as presented by the mass media. - Brand loyalty The degree to which consumers are consistently loyal to a specific brand. l Operational Definition - Specifies how the concept is to measured - Specific criteria for determining whether (or to what degree) the concept “exists”. - “Quantification” of the concept - Media Skepticism Answers to a five point scale question on the accuracy of news reports - Brand loyalty Out of 10 purchases, the number of times the same brand is purchased
Conceptual & Operational Definitions l Conceptual Definition : A verbal explanation of the meaning of the concept - Media skepticism The degree to which individuals are skeptical toward reality as presented by the mass media. - Brand loyalty The degree to which consumers are consistently loyal to a specific brand. l Operational Definition - Specifies how the concept is to measured - Specific criteria for determining whether (or to what degree) the concept “exists”. - “Quantification” of the concept - Media Skepticism Answers to a five point scale question on the accuracy of news reports - Brand loyalty Out of 10 purchases, the number of times the same brand is purchased
 Media Skepticism l Media skepticism is the degree to which individuals are skeptical toward the reality presented in the mass media. Media skepticism varies across individuals, from those who are mildly skeptical and accept most of what they see and hear in the media to those who completely discount and disbelieve the facts, values, and portrayal of reality in the media. “Please tell me how true each statement is about the media. Is it “very true (1)”, “not very true (2)”, or “not at all true (3)”? ” 1. The program was not very accurate in its portrayal of the problem. 2. Most of the story was staged for entertainment purposes. 3. The presentation was slanted and unfair.
Media Skepticism l Media skepticism is the degree to which individuals are skeptical toward the reality presented in the mass media. Media skepticism varies across individuals, from those who are mildly skeptical and accept most of what they see and hear in the media to those who completely discount and disbelieve the facts, values, and portrayal of reality in the media. “Please tell me how true each statement is about the media. Is it “very true (1)”, “not very true (2)”, or “not at all true (3)”? ” 1. The program was not very accurate in its portrayal of the problem. 2. Most of the story was staged for entertainment purposes. 3. The presentation was slanted and unfair.
 Brand Loyalty l Brand loyalty consists of a consumer's commitment to repurchase the brand can be demonstrated by repeated buying of a product or service or other positive behaviors such as word of mouth advocacy Measurement items 1. 2. 3. 4. I am happy about decision to buy the ____. The ___ provides me superior service quality as compared to any other brands. I like ___ more than any other brand. I intend to continue use ___.
Brand Loyalty l Brand loyalty consists of a consumer's commitment to repurchase the brand can be demonstrated by repeated buying of a product or service or other positive behaviors such as word of mouth advocacy Measurement items 1. 2. 3. 4. I am happy about decision to buy the ____. The ___ provides me superior service quality as compared to any other brands. I like ___ more than any other brand. I intend to continue use ___.
 Criteria for Measurements l A good measure should be: - Valid - Reliable - Sensitive l Validity exists when: - “testing for the right thing” - A valid measure actually measures what it was intended to measure
Criteria for Measurements l A good measure should be: - Valid - Reliable - Sensitive l Validity exists when: - “testing for the right thing” - A valid measure actually measures what it was intended to measure
 Criteria for Measurements l Reliability exists when… l - Repeated measures provide consistent results - Similar results obtained over time and situations l Two types of reliability - Repeatability - stability over time using the same subjects - Internal consistency - similar results on multiple items/attributes which are intended to measure the same concept Reliability and Validity - A reliable measure is not necessarily valid - By definition, to be valid, a measure must be reliable. l Sensitivity exists when: - A measure can accurately capture variability in responses - A range of scores is possible
Criteria for Measurements l Reliability exists when… l - Repeated measures provide consistent results - Similar results obtained over time and situations l Two types of reliability - Repeatability - stability over time using the same subjects - Internal consistency - similar results on multiple items/attributes which are intended to measure the same concept Reliability and Validity - A reliable measure is not necessarily valid - By definition, to be valid, a measure must be reliable. l Sensitivity exists when: - A measure can accurately capture variability in responses - A range of scores is possible
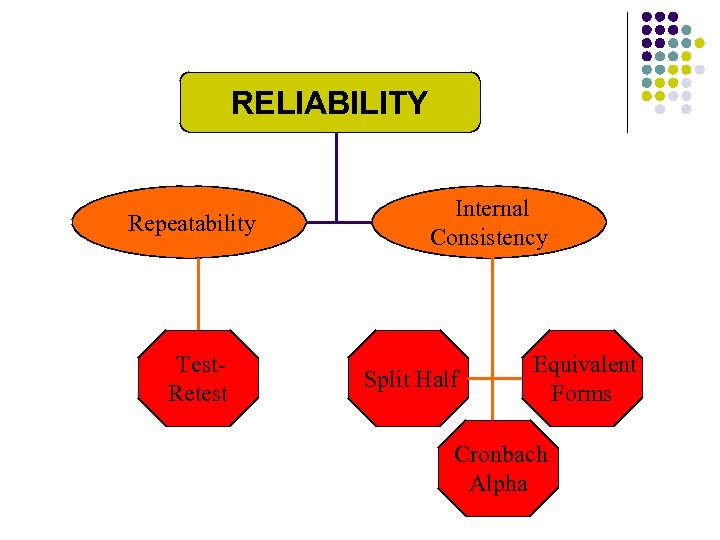 RELIABILITY Repeatability Test. Retest Internal Consistency Split Half Equivalent Forms Cronbach Alpha
RELIABILITY Repeatability Test. Retest Internal Consistency Split Half Equivalent Forms Cronbach Alpha
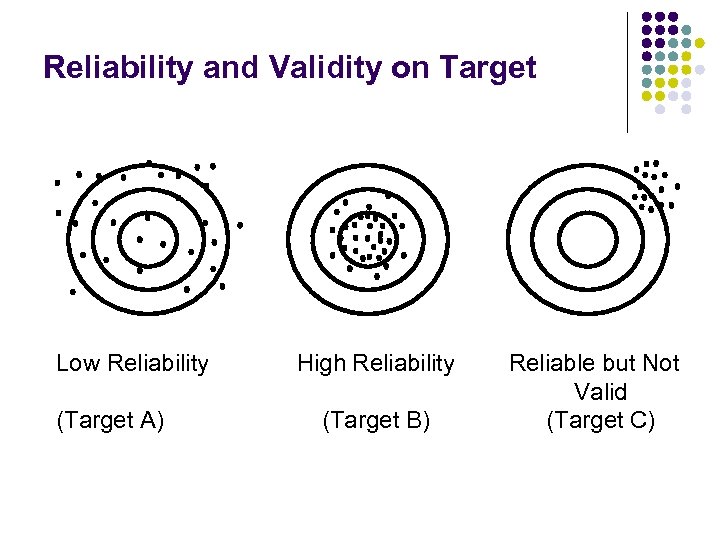 Reliability and Validity on Target Low Reliability (Target A) High Reliability (Target B) Reliable but Not Valid (Target C)
Reliability and Validity on Target Low Reliability (Target A) High Reliability (Target B) Reliable but Not Valid (Target C)
 Levels of Measurement l Nominal Scale - Each object is assigned a label - The labels have no “quantifiable” value - Things are given “names” l Ordinal Scale - Items are ranked order - Order is indicated but degree of differences between places is not Indicated l Importance of Measurement Levels - The level of scale determines the information you will receive - Determines what you can and can not say Interval Scale - Measures distance in equal intervals from an arbitrary starting point. l l Ratio Scale - Assign absolute rather than relative quantities - Numeric zero exists - Determines the type of statistics that can be used.
Levels of Measurement l Nominal Scale - Each object is assigned a label - The labels have no “quantifiable” value - Things are given “names” l Ordinal Scale - Items are ranked order - Order is indicated but degree of differences between places is not Indicated l Importance of Measurement Levels - The level of scale determines the information you will receive - Determines what you can and can not say Interval Scale - Measures distance in equal intervals from an arbitrary starting point. l l Ratio Scale - Assign absolute rather than relative quantities - Numeric zero exists - Determines the type of statistics that can be used.
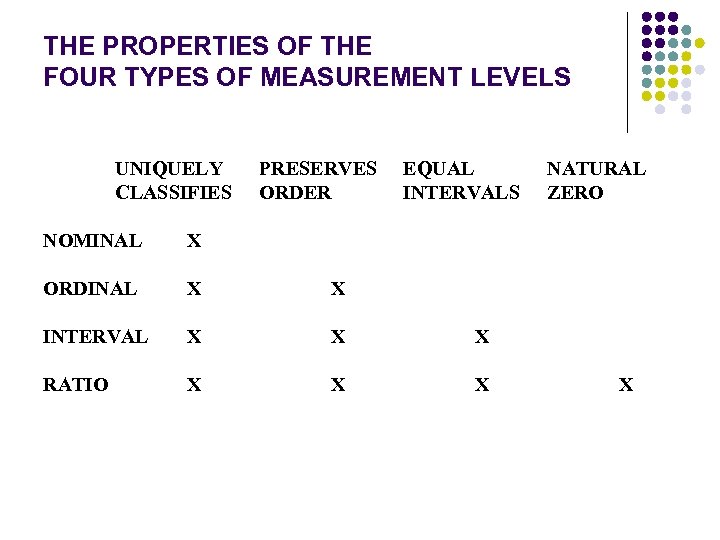 THE PROPERTIES OF THE FOUR TYPES OF MEASUREMENT LEVELS UNIQUELY CLASSIFIES PRESERVES ORDER EQUAL INTERVALS NOMINAL X ORDINAL X X INTERVAL X X X RATIO X X X NATURAL ZERO X
THE PROPERTIES OF THE FOUR TYPES OF MEASUREMENT LEVELS UNIQUELY CLASSIFIES PRESERVES ORDER EQUAL INTERVALS NOMINAL X ORDINAL X X INTERVAL X X X RATIO X X X NATURAL ZERO X
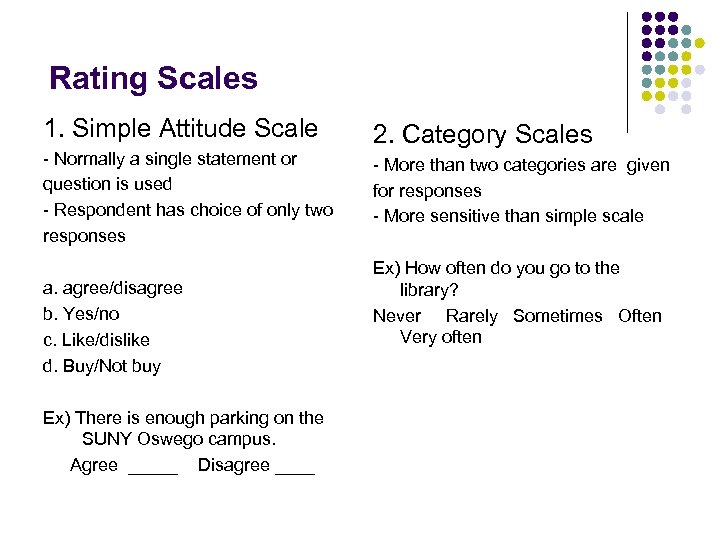 Rating Scales 1. Simple Attitude Scale - Normally a single statement or question is used - Respondent has choice of only two responses a. agree/disagree b. Yes/no c. Like/dislike d. Buy/Not buy Ex) There is enough parking on the SUNY Oswego campus. Agree _____ Disagree ____ 2. Category Scales - More than two categories are given for responses - More sensitive than simple scale Ex) How often do you go to the library? Never Rarely Sometimes Often Very often
Rating Scales 1. Simple Attitude Scale - Normally a single statement or question is used - Respondent has choice of only two responses a. agree/disagree b. Yes/no c. Like/dislike d. Buy/Not buy Ex) There is enough parking on the SUNY Oswego campus. Agree _____ Disagree ____ 2. Category Scales - More than two categories are given for responses - More sensitive than simple scale Ex) How often do you go to the library? Never Rarely Sometimes Often Very often
 Likert Scale l l Usually a five point scale, can be 3 or 7 Most common options on the scale are strongly agree to strongly disagree In analysis each option is assigned a value Usually a large number of questions are used and are “summed” to get an overall response - index
Likert Scale l l Usually a five point scale, can be 3 or 7 Most common options on the scale are strongly agree to strongly disagree In analysis each option is assigned a value Usually a large number of questions are used and are “summed” to get an overall response - index
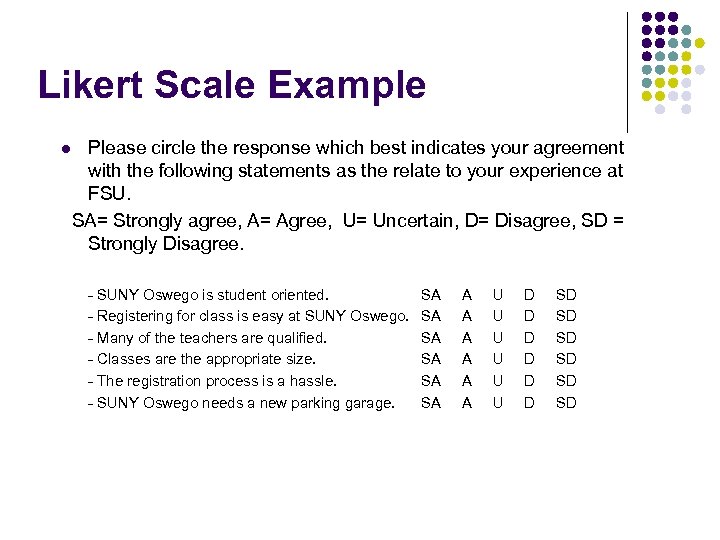 Likert Scale Example l Please circle the response which best indicates your agreement with the following statements as the relate to your experience at FSU. SA= Strongly agree, A= Agree, U= Uncertain, D= Disagree, SD = Strongly Disagree. - SUNY Oswego is student oriented. - Registering for class is easy at SUNY Oswego. - Many of the teachers are qualified. - Classes are the appropriate size. - The registration process is a hassle. - SUNY Oswego needs a new parking garage. SA SA SA A A A U U U D D D SD SD SD
Likert Scale Example l Please circle the response which best indicates your agreement with the following statements as the relate to your experience at FSU. SA= Strongly agree, A= Agree, U= Uncertain, D= Disagree, SD = Strongly Disagree. - SUNY Oswego is student oriented. - Registering for class is easy at SUNY Oswego. - Many of the teachers are qualified. - Classes are the appropriate size. - The registration process is a hassle. - SUNY Oswego needs a new parking garage. SA SA SA A A A U U U D D D SD SD SD
 Semantic Differential l A series of attitude scales - Uses bipolar (opposite) adjectives - “Semantic” spaces are used for response options - Normally has seven possible positions - Weights are assigned for analysis l The text book for this class is: Boring __: __: __: __Interesting Up to date__: __: __: __Dated Hard to read__: __: __: __Easy to read Theoretical __: __: __: __ Managerial
Semantic Differential l A series of attitude scales - Uses bipolar (opposite) adjectives - “Semantic” spaces are used for response options - Normally has seven possible positions - Weights are assigned for analysis l The text book for this class is: Boring __: __: __: __Interesting Up to date__: __: __: __Dated Hard to read__: __: __: __Easy to read Theoretical __: __: __: __ Managerial


