90c5a87cd69de739ba28c12e0f900bc8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Colored Prosthetic Skin Anika Lohrentz, Alice Tang, Rexxi Prasasya, Chou Mai William Murphy – Advisor Greg Gion - Client
Colored Prosthetic Skin Anika Lohrentz, Alice Tang, Rexxi Prasasya, Chou Mai William Murphy – Advisor Greg Gion - Client
 Outline Background Problem Statement Competition Design Requirements Design Proposals Design Evaluations Future Work
Outline Background Problem Statement Competition Design Requirements Design Proposals Design Evaluations Future Work
 Background Prosthetic skin: covers amputations and large wounds Client’s Method Hand-paint mold Fill mold with silicone Cure silicone in oven Add external layer of color
Background Prosthetic skin: covers amputations and large wounds Client’s Method Hand-paint mold Fill mold with silicone Cure silicone in oven Add external layer of color
 Problem Statement Skin prosthetics colored manually Costs time, money, energy Goal: systematic method to mass-produce skin color http: //www. prostheticskin. org/handprostheses 2. htm
Problem Statement Skin prosthetics colored manually Costs time, money, energy Goal: systematic method to mass-produce skin color http: //www. prostheticskin. org/handprostheses 2. htm
 Competition Rapid Prototyping Utilizes CAD generated image Time efficient for patients Skin texture not completely precise Color not yet explored www. newscientist. com
Competition Rapid Prototyping Utilizes CAD generated image Time efficient for patients Skin texture not completely precise Color not yet explored www. newscientist. com
 Design Requirements Pigments adhere to substrate Substrate- silicone, polyurethane, TPE Pigment- primary colors Safety- non-toxic and hypoallergenic Operation by one person Cost- under $500
Design Requirements Pigments adhere to substrate Substrate- silicone, polyurethane, TPE Pigment- primary colors Safety- non-toxic and hypoallergenic Operation by one person Cost- under $500
 Design Proposals Pad Printing Laser Printing Lithography Inkjet Printing
Design Proposals Pad Printing Laser Printing Lithography Inkjet Printing
 Design 1: Pad Printing Three main components Cliché – etched plate with design Silicone pad Ink Uses applied force – transfer ink www. masona. co. uk/content/printing. htm
Design 1: Pad Printing Three main components Cliché – etched plate with design Silicone pad Ink Uses applied force – transfer ink www. masona. co. uk/content/printing. htm
 Design 1: Pros and Cons Pros Cons User-friendly Uses solvent based-ink Versatile Substrate – higher Variety of ink colors Easy to modify surface energy than silicone pad Thin ink
Design 1: Pros and Cons Pros Cons User-friendly Uses solvent based-ink Versatile Substrate – higher Variety of ink colors Easy to modify surface energy than silicone pad Thin ink
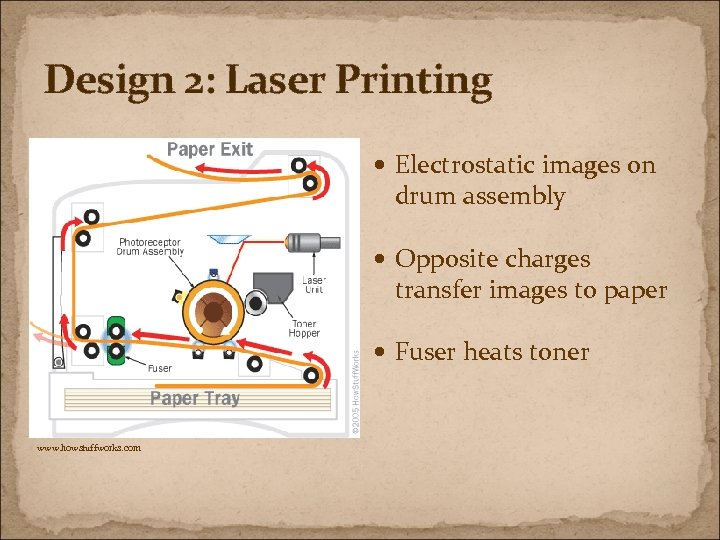 Design 2: Laser Printing Electrostatic images on drum assembly Opposite charges transfer images to paper Fuser heats toner www. howstuffworks. com
Design 2: Laser Printing Electrostatic images on drum assembly Opposite charges transfer images to paper Fuser heats toner www. howstuffworks. com
 Design 2: Pros and Cons Pros Cons High speed High fuser temperature – Highly detailed and precise Toner binds to substrate above 2000 C Routine maintenance Expensive technology
Design 2: Pros and Cons Pros Cons High speed High fuser temperature – Highly detailed and precise Toner binds to substrate above 2000 C Routine maintenance Expensive technology
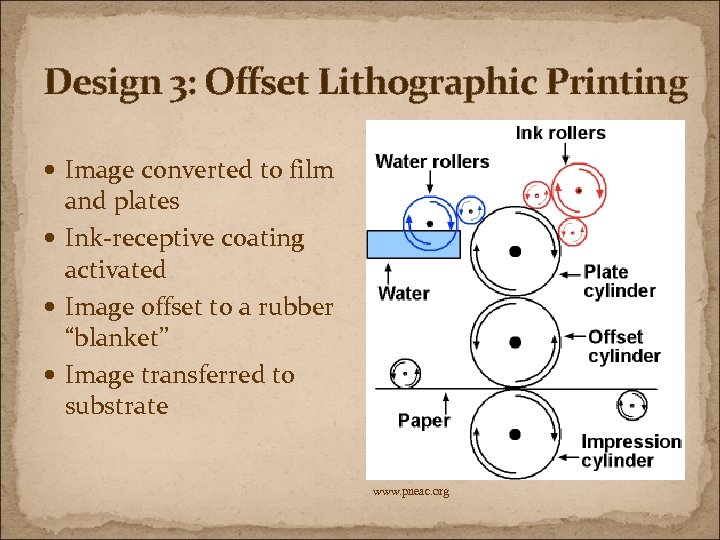 Design 3: Offset Lithographic Printing Image converted to film and plates Ink-receptive coating activated Image offset to a rubber “blanket” Image transferred to substrate www. pneac. org
Design 3: Offset Lithographic Printing Image converted to film and plates Ink-receptive coating activated Image offset to a rubber “blanket” Image transferred to substrate www. pneac. org
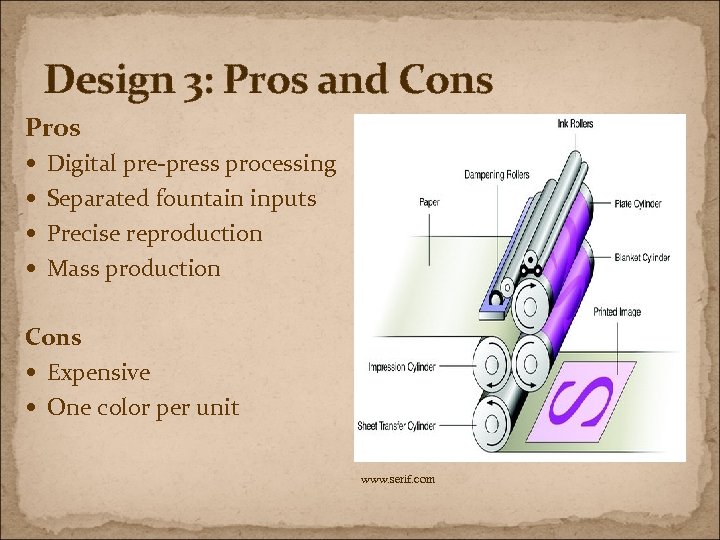 Design 3: Pros and Cons Pros Digital pre-press processing Separated fountain inputs Precise reproduction Mass production Cons Expensive One color per unit www. serif. com
Design 3: Pros and Cons Pros Digital pre-press processing Separated fountain inputs Precise reproduction Mass production Cons Expensive One color per unit www. serif. com
 Design 4: Inkjet Printing Resistor or piezoelectric heater warms ink Ink drops onto surface of paper Plate feed printer for flat surfaces http: //www. thetechgeek. com/images/product_photos/03 -C 589011 -EP. jpg
Design 4: Inkjet Printing Resistor or piezoelectric heater warms ink Ink drops onto surface of paper Plate feed printer for flat surfaces http: //www. thetechgeek. com/images/product_photos/03 -C 589011 -EP. jpg
 Design 4: Pros and Cons Pros Cons Inexpensive Less innovative design Simple design Color adheres to surface Materials easy to obtain only
Design 4: Pros and Cons Pros Cons Inexpensive Less innovative design Simple design Color adheres to surface Materials easy to obtain only
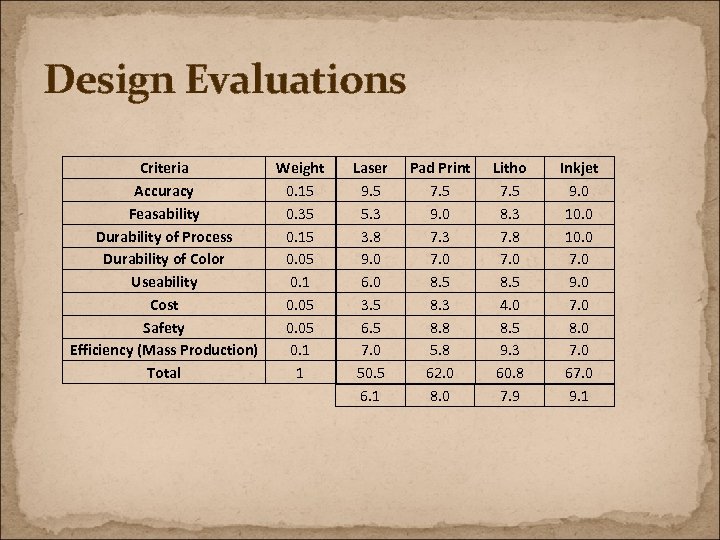 Design Evaluations Criteria Accuracy Feasability Durability of Process Durability of Color Useability Cost Safety Efficiency (Mass Production) Total Weight 0. 15 0. 35 0. 15 0. 05 0. 1 1 Laser 9. 5 5. 3 3. 8 9. 0 6. 0 3. 5 6. 5 7. 0 50. 5 6. 1 Pad Print 7. 5 9. 0 7. 3 7. 0 8. 5 8. 3 8. 8 5. 8 62. 0 8. 0 Litho 7. 5 8. 3 7. 8 7. 0 8. 5 4. 0 8. 5 9. 3 60. 8 7. 9 Inkjet 9. 0 10. 0 7. 0 9. 0 7. 0 8. 0 7. 0 67. 0 9. 1
Design Evaluations Criteria Accuracy Feasability Durability of Process Durability of Color Useability Cost Safety Efficiency (Mass Production) Total Weight 0. 15 0. 35 0. 15 0. 05 0. 1 1 Laser 9. 5 5. 3 3. 8 9. 0 6. 0 3. 5 6. 5 7. 0 50. 5 6. 1 Pad Print 7. 5 9. 0 7. 3 7. 0 8. 5 8. 3 8. 8 5. 8 62. 0 8. 0 Litho 7. 5 8. 3 7. 8 7. 0 8. 5 4. 0 8. 5 9. 3 60. 8 7. 9 Inkjet 9. 0 10. 0 7. 0 9. 0 7. 0 8. 0 7. 0 67. 0 9. 1
 Future Work Obtain materials for Inkjet Printing process Plate feed printer Compatible pigment Plasma-treatment setup Coating material for printer – nonstick Silicone Build and test process Upscale process for mass production
Future Work Obtain materials for Inkjet Printing process Plate feed printer Compatible pigment Plasma-treatment setup Coating material for printer – nonstick Silicone Build and test process Upscale process for mass production
 References “Printing Process Description: Lithography. ” Printers’ National Environmental Assistance Center. 2007. www. pneac. org “Copying Wrinkles for Better Prosthetic. ” New. Scientists Blog. Jan 2007. www. newscientist. com “Offset printing. ” MM-Packaging. 2007. www. mm-packagin. com “Offset Lithography. ” Serif Printing Resource. 2007. www. serif. com “How Laser Printer Works. ” Tom Harris. 2007. www. howstuffworks. com
References “Printing Process Description: Lithography. ” Printers’ National Environmental Assistance Center. 2007. www. pneac. org “Copying Wrinkles for Better Prosthetic. ” New. Scientists Blog. Jan 2007. www. newscientist. com “Offset printing. ” MM-Packaging. 2007. www. mm-packagin. com “Offset Lithography. ” Serif Printing Resource. 2007. www. serif. com “How Laser Printer Works. ” Tom Harris. 2007. www. howstuffworks. com



