fcf5714176e5e4fb6529c8ed314b698e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Colonization, biofilm formation and biodegradation of polyethylene by soil bacteria Alex Sivan The Institute for Applied Biosciences and The Department of Biotechnology Engineering, Ben Gurion University, Beer Sheva, Israel Environmental Engineering, 17. 12. 02

Polyethylene for soil mulching In the U. S. ~ ca. 1, 000 Ton/year in agriculture

Polyethylene waste • 25, 000 Ton/year • Makes up to 40% of the plastic waste • Highly flammable; burning releases toxic gases • Pollutes marine and fresh water habitats • Highly recalcitrant; > 400 years for degradation




Control Bacteria


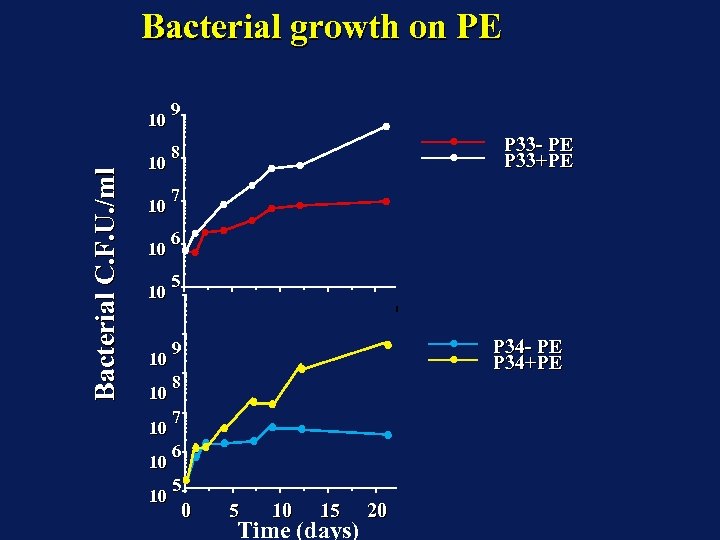
Bacterial growth on PE Bacterial C. F. U. /ml 10 10 10 9 P 33 - PE P 33+PE 8 7 6 5 P 34 - PE P 34+PE 9 8 7 6 5 0 5 10 15 Time (days) 20
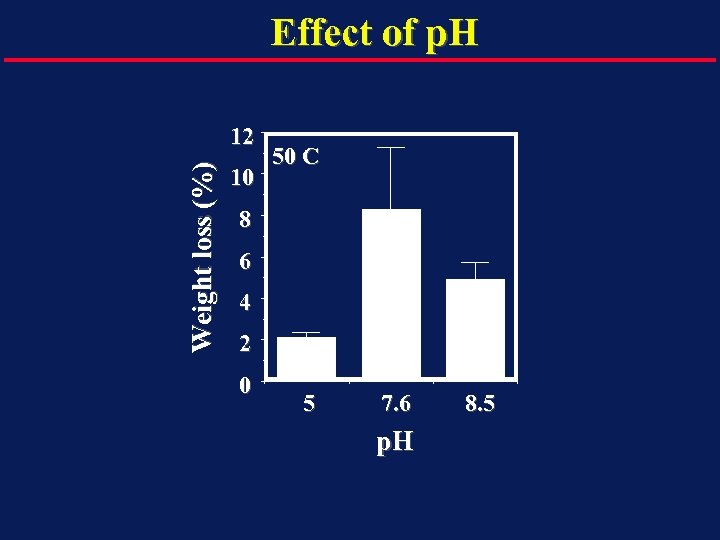
Effect of p. H Weight loss (%) 12 10 50 C 8 6 4 2 0 5 7. 6 p. H 8. 5

Biofilm on polyethylene



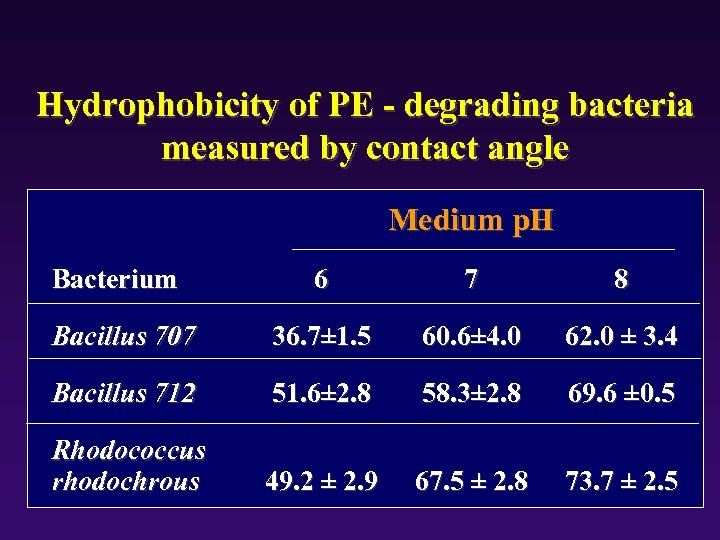
Hydrophobicity of PE - degrading bacteria measured by contact angle Medium p. H Bacterium 6 7 8 Bacillus 707 36. 7± 1. 5 60. 6± 4. 0 62. 0 ± 3. 4 Bacillus 712 51. 6± 2. 8 58. 3± 2. 8 69. 6 ± 0. 5 Rhodococcus rhodochrous 49. 2 ± 2. 9 67. 5 ± 2. 8 73. 7 ± 2. 5
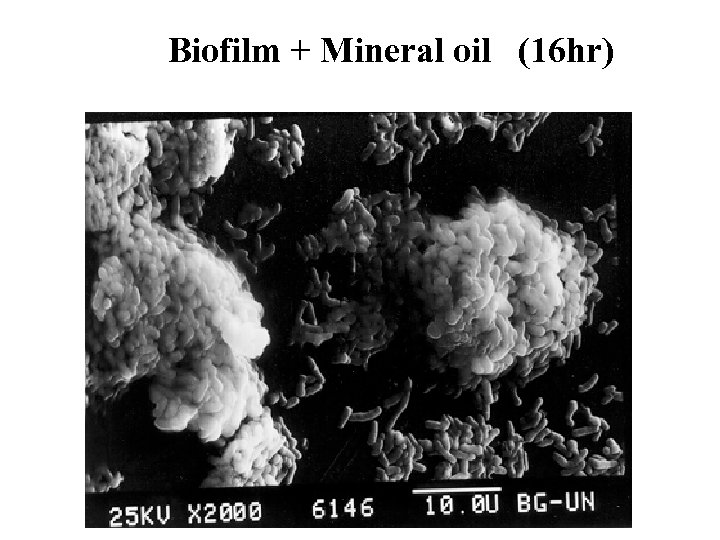



Biofilm + Mineral oil (16 hr)
Biofilm + Mineral oil (7 days)

Mix C 30 Effect of an anionic surfactant and mineral oil on biofilm formation on polyethylene * Biofilm density index: 0 = No biofilm; 4 = Dense biofim
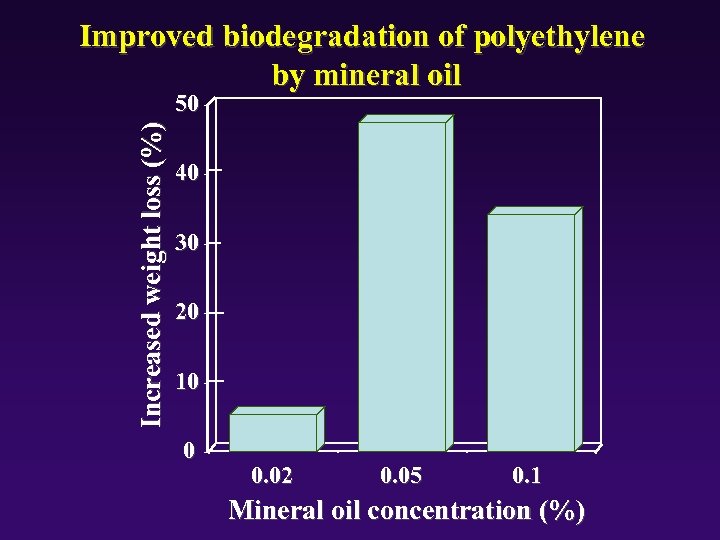
Improved biodegradation of polyethylene by mineral oil Increased weight loss (%) 50 40 30 20 10 0 0. 02 0. 05 0. 1 Mineral oil concentration (%)

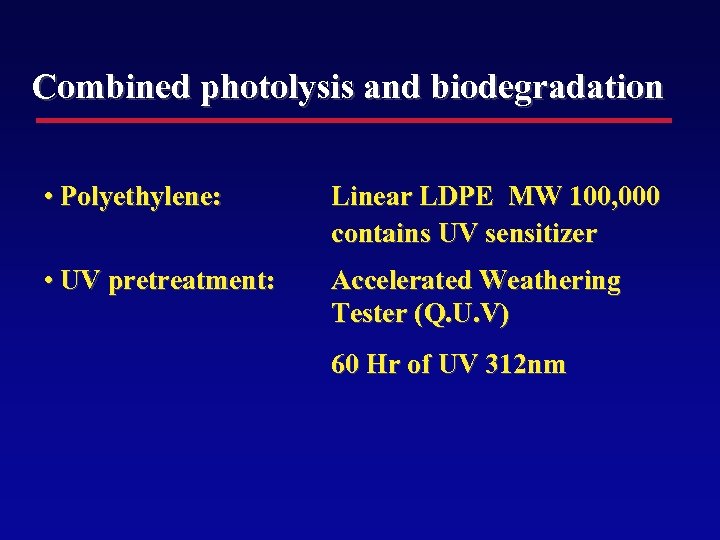
Combined photolysis and biodegradation • Polyethylene: Linear LDPE MW 100, 000 contains UV sensitizer • UV pretreatment: Accelerated Weathering Tester (Q. U. V) 60 Hr of UV 312 nm
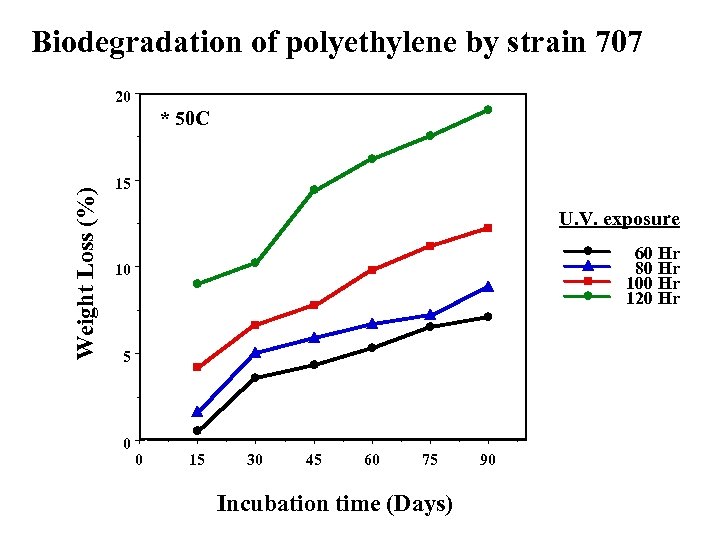
Biodegradation of polyethylene by strain 707 20 Weight Loss (%) * 50 C 15 U. V. exposure 60 Hr 80 Hr 100 Hr 120 Hr 10 5 0 0 15 30 45 60 75 Incubation time (Days) 90
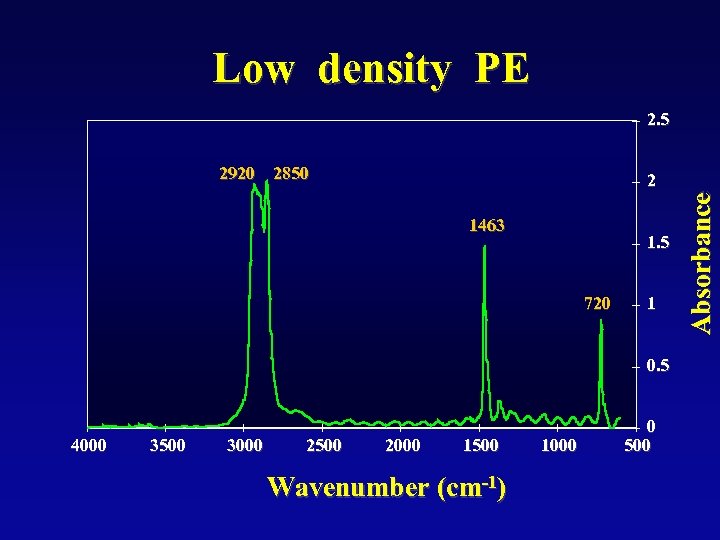
Low density PE 2. 5 2920 2850 1463 1. 5 720 1 0. 5 4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 0 500 Absorbance 2
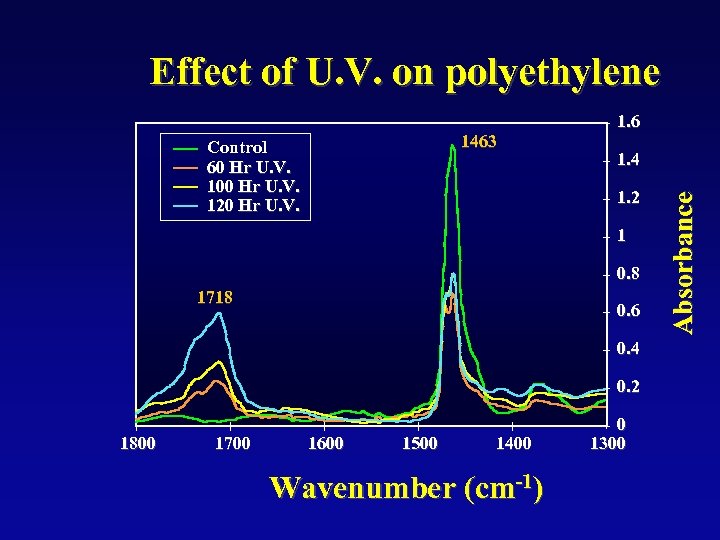
Effect of U. V. on polyethylene 1. 4 1. 2 1 0. 8 1718 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 1800 1700 1600 1500 1400 Wavenumber (cm-1) 0 1300 Absorbance 1463 Control 60 Hr U. V. 100 Hr U. V. 120 Hr U. V. 1. 6
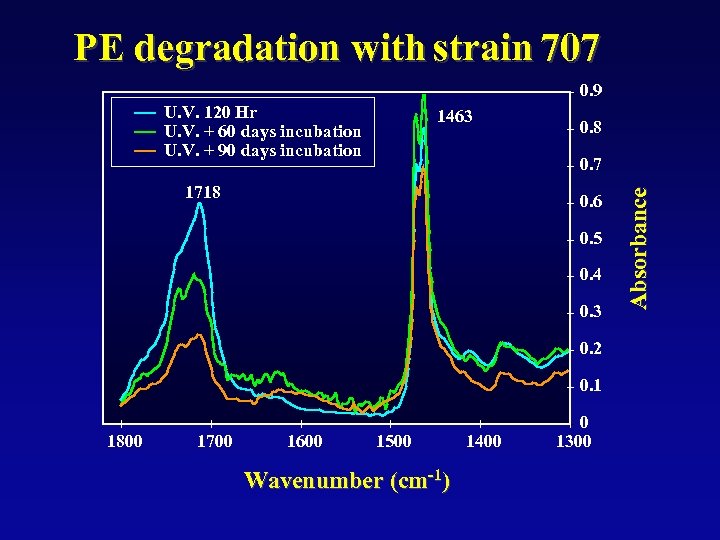
PE degradation with strain 707 0. 9 U. V. 120 Hr U. V. + 60 days incubation U. V. + 90 days incubation 1463 0. 8 1718 0. 6 0. 5 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 1800 1700 1600 1500 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1400 0 1300 Absorbance 0. 7
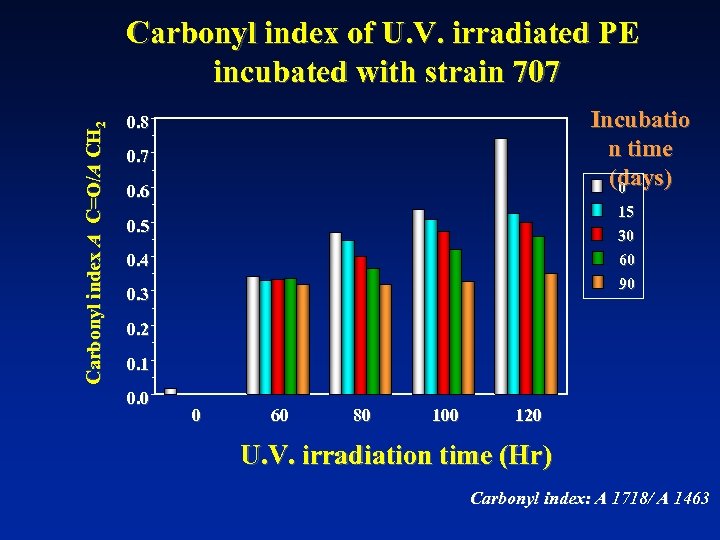
Carbonyl index A C=O/A CH 2 Carbonyl index of U. V. irradiated PE incubated with strain 707 Incubatio n time (days) 0 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 15 30 0. 5 0. 4 60 90 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0. 0 0 60 80 100 120 U. V. irradiation time (Hr) Carbonyl index: A 1718/ A 1463
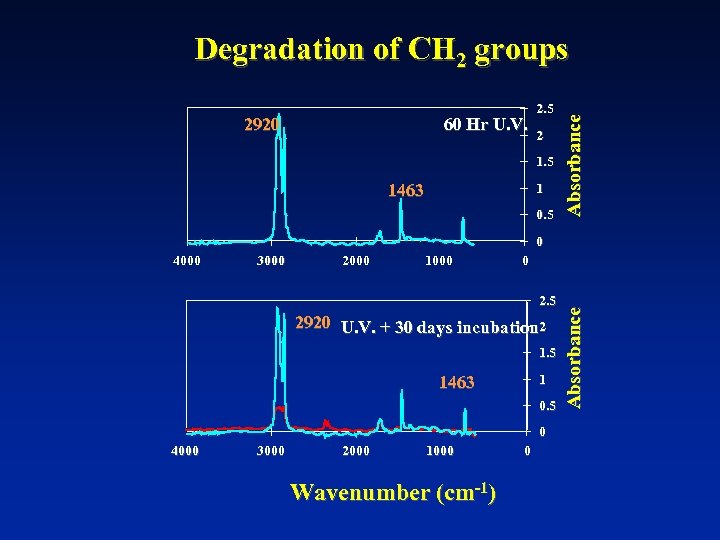
60 Hr U. V. 2920 2. 5 2 1. 5 1463 1 0. 5 Absorbance Degradation of CH 2 groups 0 3000 2000 1000 0 2. 5 2920 U. V. + 30 days incubation 2 1. 5 1 1463 0. 5 0 4000 3000 2000 1000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 0 Absorbance 4000
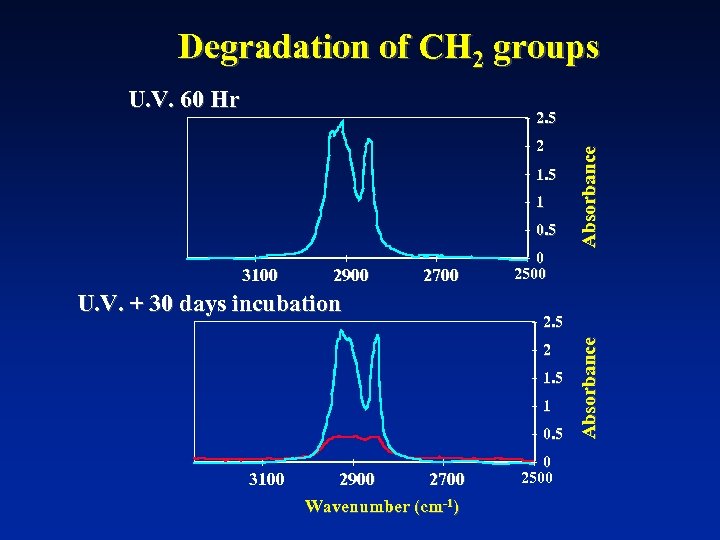
Degradation of CH 2 groups U. V. 60 Hr 2 1. 5 1 0. 5 2900 2700 U. V. + 30 days incubation 0 2500 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 0. 5 3100 2900 2700 Wavenumber (cm-1) 0 2500 Absorbance 3100 Absorbance 2. 5
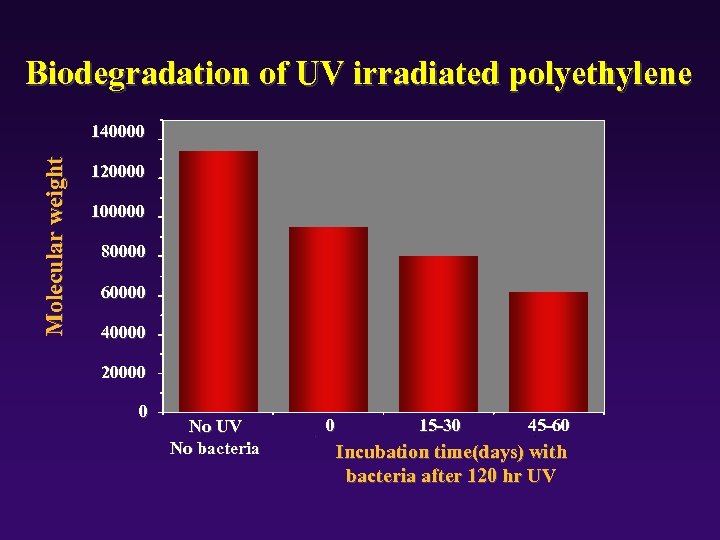
Biodegradation of UV irradiated polyethylene Molecular weight 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 No UV No bacteria 1 2 0 15 -30 3 45 -60 4 Incubation time(days) with bacteria after 120 hr UV
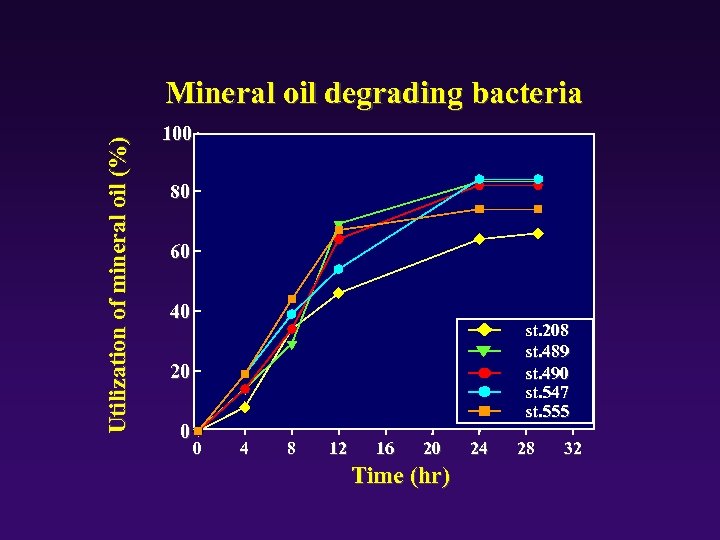
Utilization of mineral oil (%) Mineral oil degrading bacteria 100 80 60 40 st. 208 st. 489 st. 490 st. 547 st. 555 20 0 0 4 8 12 16 20 Time (hr) 24 28 32
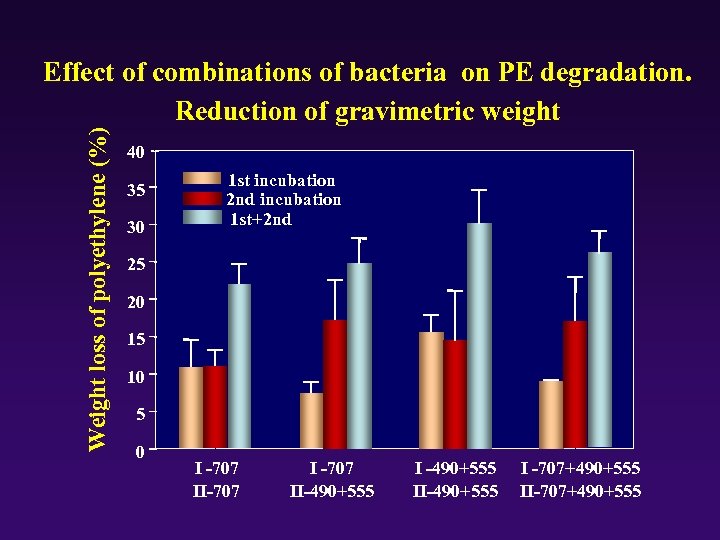
Weight loss of polyethylene (%) Effect of combinations of bacteria on PE degradation. Reduction of gravimetric weight 40 35 30 1 st incubation 2 nd incubation 1 st+2 nd 25 20 15 10 5 0 I -707 II-707 II-490+555 II-490+555 I -707+490+555 II-707+490+555
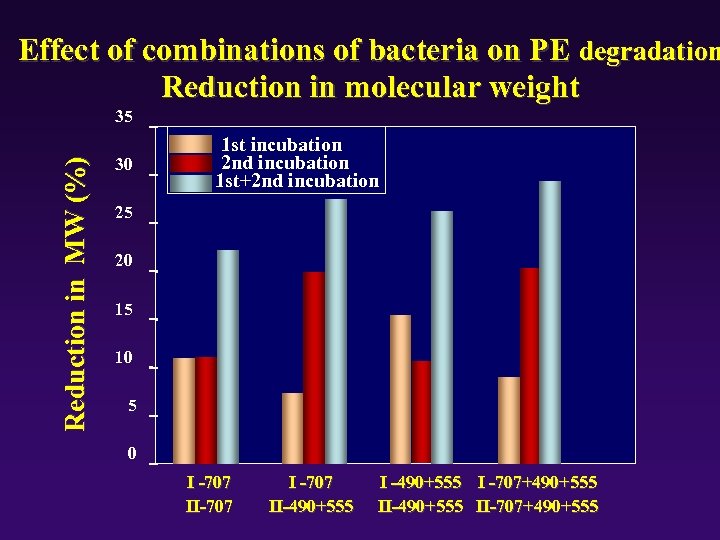
Effect of combinations of bacteria on PE degradation Reduction in molecular weight Reduction in MW (%) 35 30 1 st incubation 2 nd incubation 1 st+2 nd incubation 25 20 15 10 5 0 I -707 II-707 II-490+555 I -707+490+555 II-707+490+555
Summary • Enrichment cultures gave rise to bacterial strains that could utilize PE as a sole carbon and energy source • Maximal biodegradation (up to 30%) was obtained after two-steps incubation with combined cultures • PE degrading bacteria are hydrophobic and form a biofilm on the PE surface • Mineral oil enhances biofilm formation and PE biodegradation • The degrading bacteria utilize carbonyl residues in the PE which are formed during UV irradiation • Combination of UV photolysis and biodegradation showed a synergistic effect

Collaborators Irit Gilan Deborah Bitty Dr. Valentina Pavlov Dr. Mark Karpassas Prof. Shimona Geresh
fcf5714176e5e4fb6529c8ed314b698e.ppt