4eed81dd1270c2f3d3d49450134a9369.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Colonization and Settlement of America
Colonization and Settlement of America
 Reasons for Exploration • Expanding populations—needed more space • Trade increased – merchants wanted access to Asia – spices, silk, porcelain • Three G’s—in this order • 1. Gold *any riches (gold, silver, resources) Most important to most explorers • 2. God *to convert natives • 3. Glory *to make a name for themselves
Reasons for Exploration • Expanding populations—needed more space • Trade increased – merchants wanted access to Asia – spices, silk, porcelain • Three G’s—in this order • 1. Gold *any riches (gold, silver, resources) Most important to most explorers • 2. God *to convert natives • 3. Glory *to make a name for themselves
 • First European explorers to reach the Americas were Vikings – Leif Eriksson – Canada – around 1000 A. D. • Christopher Columbus – Caribbean 1492 A. D. • Spain is first European country to permanently colonize the New World • Amerigo Vespucci—first European to map North and South America (1501) • Natives were treated poorly – Plantation System – used for agricultural (sugar cane) and mining work (gold and silver)
• First European explorers to reach the Americas were Vikings – Leif Eriksson – Canada – around 1000 A. D. • Christopher Columbus – Caribbean 1492 A. D. • Spain is first European country to permanently colonize the New World • Amerigo Vespucci—first European to map North and South America (1501) • Natives were treated poorly – Plantation System – used for agricultural (sugar cane) and mining work (gold and silver)

 Smallpox Victim Native populations were devastated by disease
Smallpox Victim Native populations were devastated by disease
 Leif Eriksson sights land Christopher Columbus Amerigo Vespucci
Leif Eriksson sights land Christopher Columbus Amerigo Vespucci
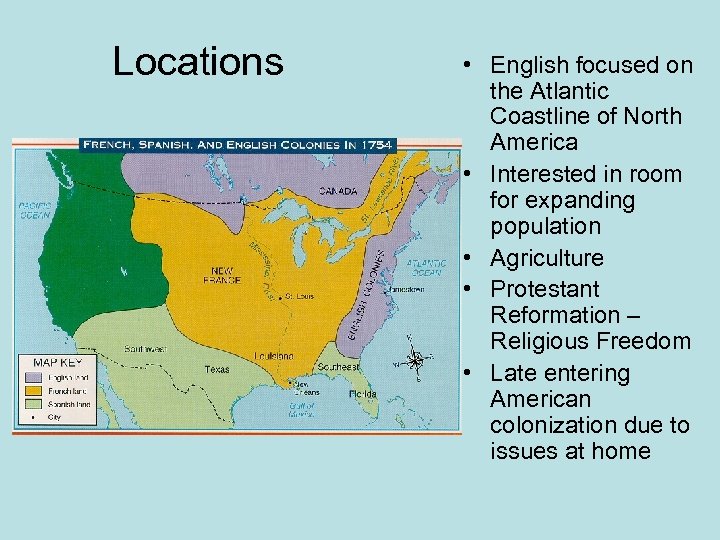 Locations • English focused on the Atlantic Coastline of North America • Interested in room for expanding population • Agriculture • Protestant Reformation – Religious Freedom • Late entering American colonization due to issues at home
Locations • English focused on the Atlantic Coastline of North America • Interested in room for expanding population • Agriculture • Protestant Reformation – Religious Freedom • Late entering American colonization due to issues at home
 Roanoke Voyages • English made 3 voyages to the Outer Banks of North Carolina (1584, 1585, 1587); organized by Sir Walter Raleigh (NC capital named for him) • 1 st voyage—named land Virginia • 2 nd voyage—found Chesapeake Bay, attempt to create military settlement, ended in violence with local natives • 3 rd voyage—The Lost Colony—a colony of men, women, and children led by John White; do not know what happened to them
Roanoke Voyages • English made 3 voyages to the Outer Banks of North Carolina (1584, 1585, 1587); organized by Sir Walter Raleigh (NC capital named for him) • 1 st voyage—named land Virginia • 2 nd voyage—found Chesapeake Bay, attempt to create military settlement, ended in violence with local natives • 3 rd voyage—The Lost Colony—a colony of men, women, and children led by John White; do not know what happened to them
 Jamestown • 1 st permanent English settlement – Virginia in 1607 • John Smith (military leader), John Rolfe (tobacco), Pocahontas (married Rolfe, not Smith) • Colony almost did not survive – bad location • 1608 – Starving Time • 1619 (a big year): House of Burgess (1 st representative assembly), English women arrive, Africans brought as Indentured Servants
Jamestown • 1 st permanent English settlement – Virginia in 1607 • John Smith (military leader), John Rolfe (tobacco), Pocahontas (married Rolfe, not Smith) • Colony almost did not survive – bad location • 1608 – Starving Time • 1619 (a big year): House of Burgess (1 st representative assembly), English women arrive, Africans brought as Indentured Servants
 John Rolfe marries Pocahontas John Smith Pocahontas
John Rolfe marries Pocahontas John Smith Pocahontas
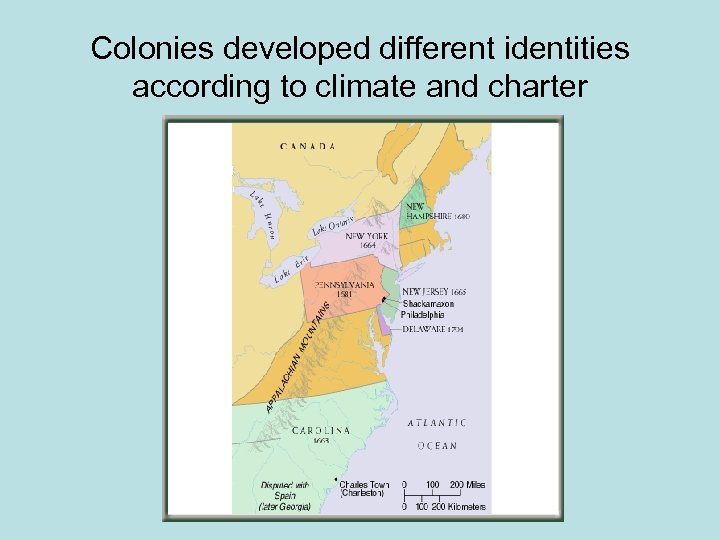 Colonies developed different identities according to climate and charter
Colonies developed different identities according to climate and charter
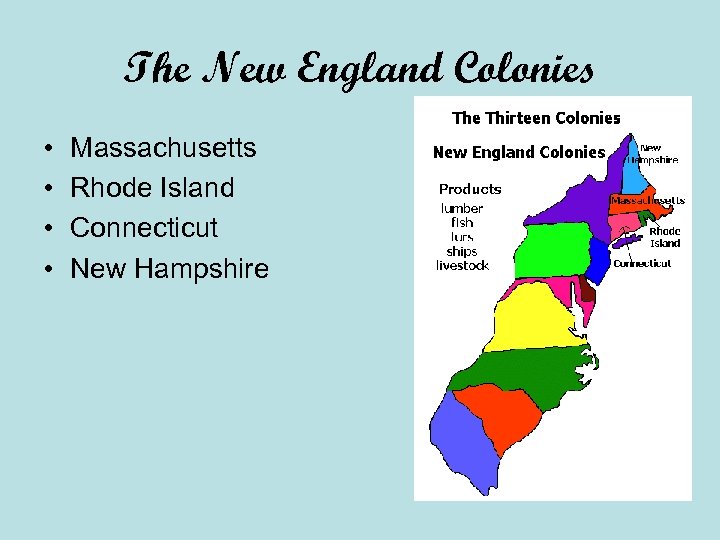 The New England Colonies • • Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut New Hampshire
The New England Colonies • • Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut New Hampshire
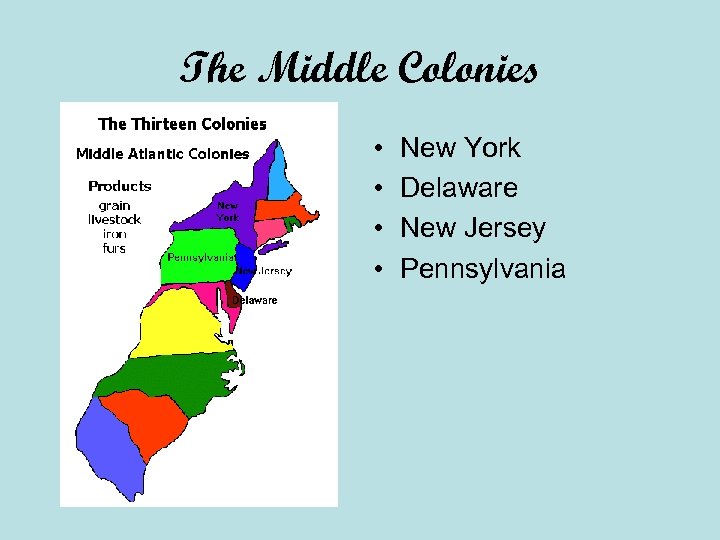 The Middle Colonies • • New York Delaware New Jersey Pennsylvania
The Middle Colonies • • New York Delaware New Jersey Pennsylvania
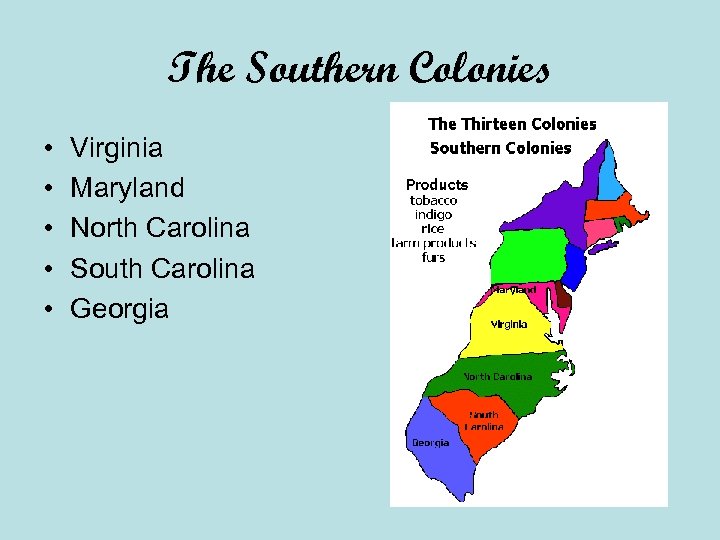 The Southern Colonies • • • Virginia Maryland North Carolina South Carolina Georgia
The Southern Colonies • • • Virginia Maryland North Carolina South Carolina Georgia
 English Colonies • Split into three regions • New England (MA, NH, RI, CN) – settled by many people seeking religious freedom –Economy was based on fishing, lumbering, and shipbuilding • Middle Colonies (NY, NJ, PA, DE) ––More of a mix coming for religious freedom and economic opportunities – more diverse backgrounds
English Colonies • Split into three regions • New England (MA, NH, RI, CN) – settled by many people seeking religious freedom –Economy was based on fishing, lumbering, and shipbuilding • Middle Colonies (NY, NJ, PA, DE) ––More of a mix coming for religious freedom and economic opportunities – more diverse backgrounds
 13 Colonies • Southern Colonies –(MD, VA, NC, SC, GA) mostly came for economic opportunities • Economy was based on agriculture – Tobacco, Cotton, Rice, Indigo • Georgia – place for debtors and poor to live
13 Colonies • Southern Colonies –(MD, VA, NC, SC, GA) mostly came for economic opportunities • Economy was based on agriculture – Tobacco, Cotton, Rice, Indigo • Georgia – place for debtors and poor to live
 Immigrant Groups of the 13 colonies • New England • Pilgrims - Settled in Massachusetts in 1620 – Plymouth • Puritans - Settled in Massachusetts in 1630 – Boston • Wanted religious freedom • Middle Colonies • Catholics • Quakers –William Penn • More tolerant
Immigrant Groups of the 13 colonies • New England • Pilgrims - Settled in Massachusetts in 1620 – Plymouth • Puritans - Settled in Massachusetts in 1630 – Boston • Wanted religious freedom • Middle Colonies • Catholics • Quakers –William Penn • More tolerant
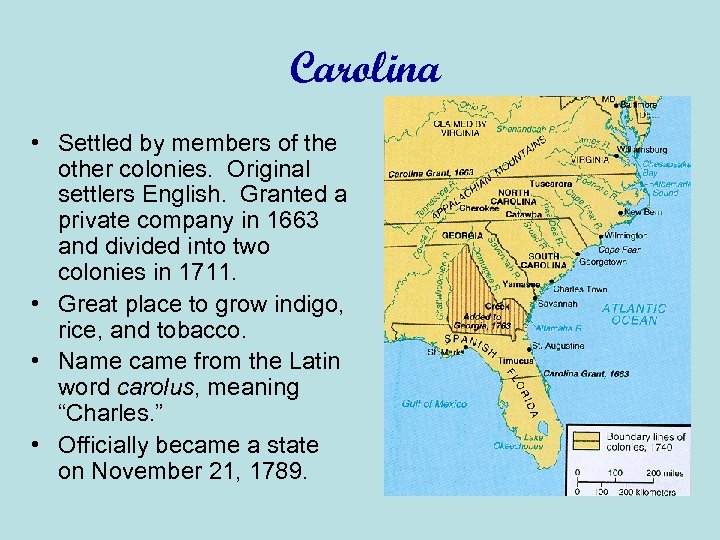 Carolina • Settled by members of the other colonies. Original settlers English. Granted a private company in 1663 and divided into two colonies in 1711. • Great place to grow indigo, rice, and tobacco. • Name came from the Latin word carolus, meaning “Charles. ” • Officially became a state on November 21, 1789.
Carolina • Settled by members of the other colonies. Original settlers English. Granted a private company in 1663 and divided into two colonies in 1711. • Great place to grow indigo, rice, and tobacco. • Name came from the Latin word carolus, meaning “Charles. ” • Officially became a state on November 21, 1789.
 • Lords Proprietors – 8 noble supporters of Charles II, awarded Carolina in return for their support – 1663 • 1706 – Bath – first NC town • 1710 – New Bern founded – became 1 st capital of NC • Three regions • 1. Coastal Plain in east • 2. Piedmont in central • 3. Mountains in west
• Lords Proprietors – 8 noble supporters of Charles II, awarded Carolina in return for their support – 1663 • 1706 – Bath – first NC town • 1710 – New Bern founded – became 1 st capital of NC • Three regions • 1. Coastal Plain in east • 2. Piedmont in central • 3. Mountains in west
 • • • New Immigration NC becomes royal colony in 1728. New settlers 1. Scots-Irish – settled in east 2. Highland Scots – settled in east 3. Germans and Moravians –settled in Piedmont – backcountry Great Wagon Road Moravians – name their land Wachovia 1766 – establish the towns of Bethabara and Salem 4. Africans – brought as slaves – fewer than many other southern colonies
• • • New Immigration NC becomes royal colony in 1728. New settlers 1. Scots-Irish – settled in east 2. Highland Scots – settled in east 3. Germans and Moravians –settled in Piedmont – backcountry Great Wagon Road Moravians – name their land Wachovia 1766 – establish the towns of Bethabara and Salem 4. Africans – brought as slaves – fewer than many other southern colonies
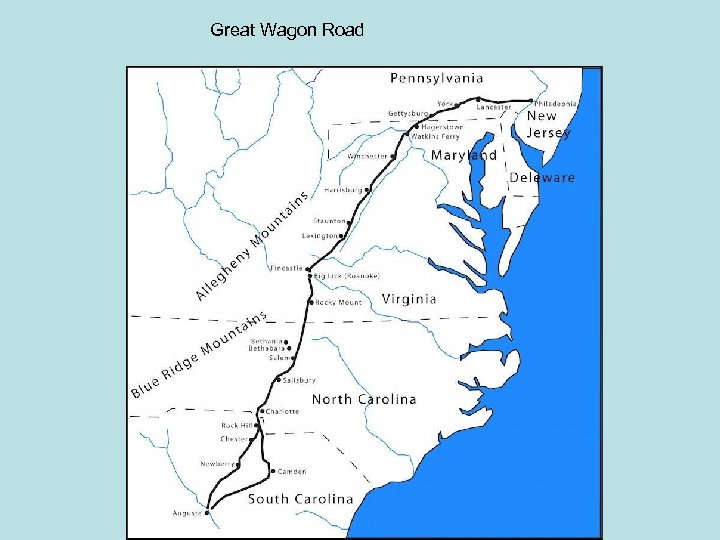 Great Wagon Road
Great Wagon Road
 Economy/Social Structure • Economy – North Carolina was mostly agricultural. • Cash Crops – Tobacco, Rice, and Indigo • Naval Stores – tar, pitch, turpentine • Trade was difficult due to NC’s lack of roads and difficult waterways. • Social Classes • 1. Gentry – rich planters, doctors, lawyers • 2. Artisans – craftsmen – blacksmith, cobblers • 3. Small Farmers – Yeomen – biggest group
Economy/Social Structure • Economy – North Carolina was mostly agricultural. • Cash Crops – Tobacco, Rice, and Indigo • Naval Stores – tar, pitch, turpentine • Trade was difficult due to NC’s lack of roads and difficult waterways. • Social Classes • 1. Gentry – rich planters, doctors, lawyers • 2. Artisans – craftsmen – blacksmith, cobblers • 3. Small Farmers – Yeomen – biggest group
 • 4. Indentured Servants – poor people who bought their passage to America with their service. • 5. Slaves/Indians • Triangle Trade – three-part voyage • A. Europe to Africa – manufactured trade goods • B. Africa to America (Middle Passage)- slaves • C. America to Europe – raw materials (lumber, cotton, tobacco) • Growing conflict between Eastern and Western NC over taxes and political power.
• 4. Indentured Servants – poor people who bought their passage to America with their service. • 5. Slaves/Indians • Triangle Trade – three-part voyage • A. Europe to Africa – manufactured trade goods • B. Africa to America (Middle Passage)- slaves • C. America to Europe – raw materials (lumber, cotton, tobacco) • Growing conflict between Eastern and Western NC over taxes and political power.
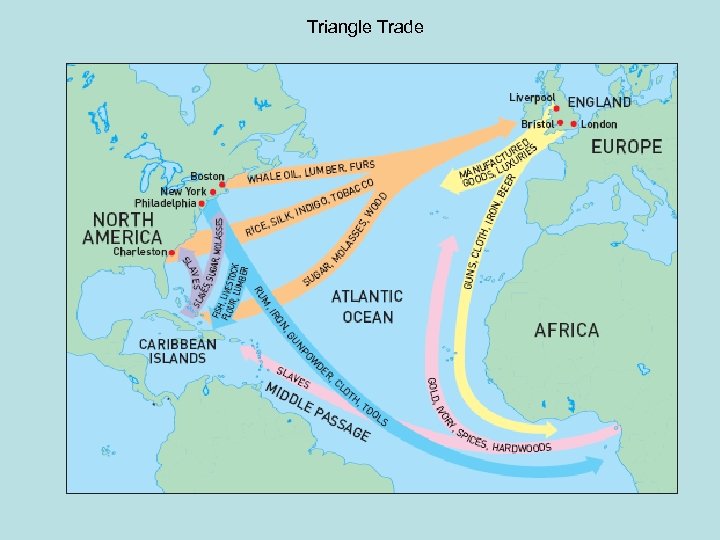 Triangle Trade
Triangle Trade

 Early Government in the Colonies • English Bill of Rights – limited King’s power; gave representative government (Parliament) more power • Representative Government – the people elect representatives to speak for them in government • Mayflower Compact – first attempt at selfgovernment in the English colonies • Town meetings – first form of American government in which all free men could participate
Early Government in the Colonies • English Bill of Rights – limited King’s power; gave representative government (Parliament) more power • Representative Government – the people elect representatives to speak for them in government • Mayflower Compact – first attempt at selfgovernment in the English colonies • Town meetings – first form of American government in which all free men could participate
 • House of Burgess – first representative government in America • Proprietary colony – privately-owned colony • Royal colony – government-run colony
• House of Burgess – first representative government in America • Proprietary colony – privately-owned colony • Royal colony – government-run colony


