e42fad05257cff7deff8841ea89e00fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

- Collaborative report writing Bridging the divide between formal and informal learning Richard Walker & Wayne Britcliffe E-Learning Development Team, University of York Durham Blackboard Users’ Conference 2007
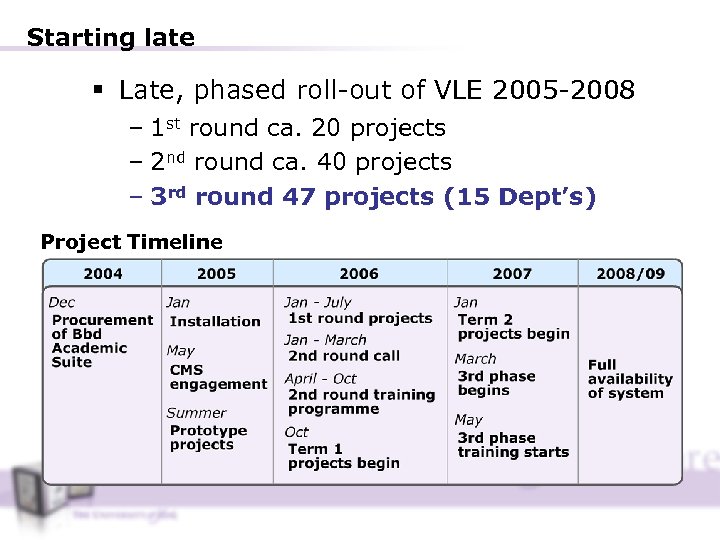
Starting late § Late, phased roll-out of VLE 2005 -2008 – 1 st round ca. 20 projects – 2 nd round ca. 40 projects – 3 rd round 47 projects (15 Dept’s) Project Timeline
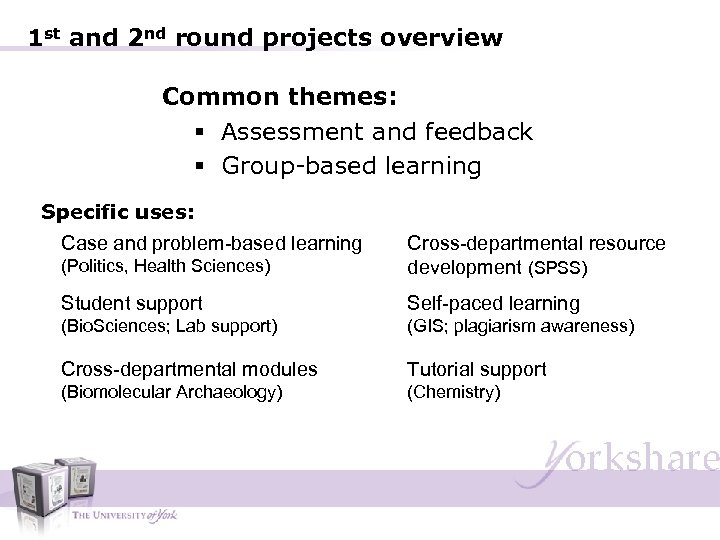
1 st and 2 nd round projects overview Common themes: § Assessment and feedback § Group-based learning Specific uses: Case and problem-based learning (Politics, Health Sciences) Cross-departmental resource development (SPSS) Student support Self-paced learning (Bio. Sciences; Lab support) (GIS; plagiarism awareness) Cross-departmental modules Tutorial support (Biomolecular Archaeology) (Chemistry)
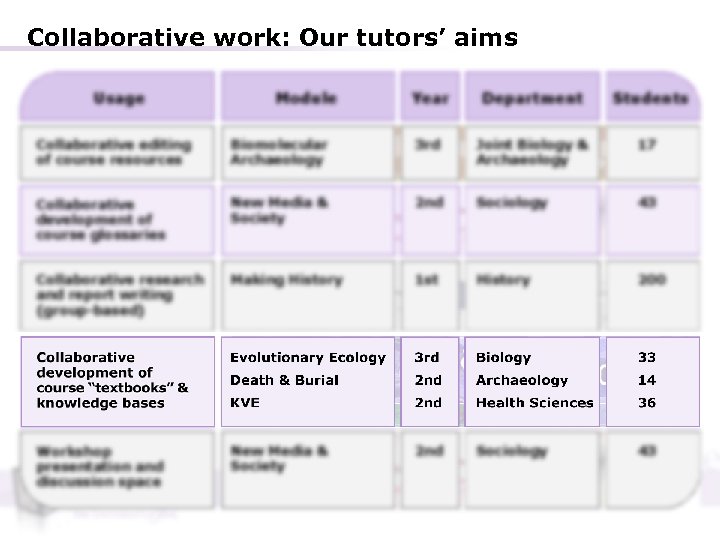
Collaborative work: Our tutors’ aims

Drivers for Course Redesign § Challenging subject areas: – fast moving § Challenging subject areas: – no authoritative textbook § – fast moving Conceptual problems with research literature: – Poor research / critical reading in – no authoritative textbook preparation for module exam – Narrow knowledge base § Unstructured problems § Conceptual study time with research literature: – focus on individual reading activities – Poor research / critical reading in preparation for course textbook / shared § Develop online module exam research knowledge base – Narrow resources § Structured research activities through weekly tasks § Unstructured study time – Critical reading & research – focus on individual reading activities – Writing up & summarising research findings – Knowledge sharing (within and across groups)
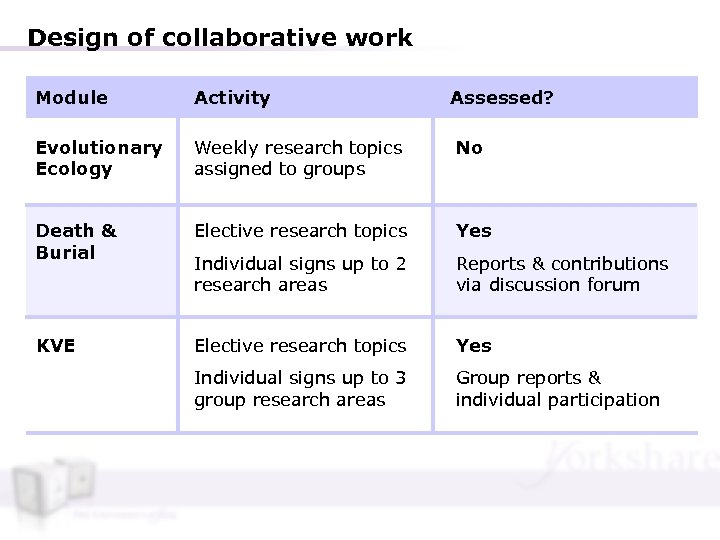
Design of collaborative work Module Activity Assessed? Evolutionary Ecology Weekly research topics assigned to groups No Death & Burial Elective research topics Yes Individual signs up to 2 research areas Reports & contributions via discussion forum KVE Elective research topics Yes Individual signs up to 3 group research areas Group reports & individual participation

Interaction matrix – Evolutionary Ecology Wiki interaction options Note that an instructor always has view, edit and commenting privileges to all wikis No Groups Instructor Single wiki for the whole module that only an instructor can edit. Students can view the wiki but not make changes. Commenting can be on/off. Groups Evolutionary Ecology Private Groups Open Groups Plenary wiki: viewable to all Each group has atextbook) Each group has a wiki (course wiki that only an instructor can edit. that only an instructor Commenting can be on/off. Other groups can’t view the wiki. can edit. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Single wiki for the whole module. Single wiki per group. Only students in that group can edit the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. All students can view the wiki. Students can Ecology Evolutionary edit the wiki. can edit and view the wiki. Group wikis (x 8) viewable to group members only (drafting report) Each (x 8) viewable to group student Group blogsstudent has their own Eachthat onlyhas their own wiki that only they can edit. wiki the student can edit. members onlycan only view their Students (information own wiki. Students in the same group sharing/organisation) can view each other’s wiki. Commenting can be on/off Students (for instructor and student to use). Commenting can be on/off. Each student has their own wiki that only they can edit. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Private communication tools: optional Adapted from Andrew Fisher, Barking College, ALT-C 2006
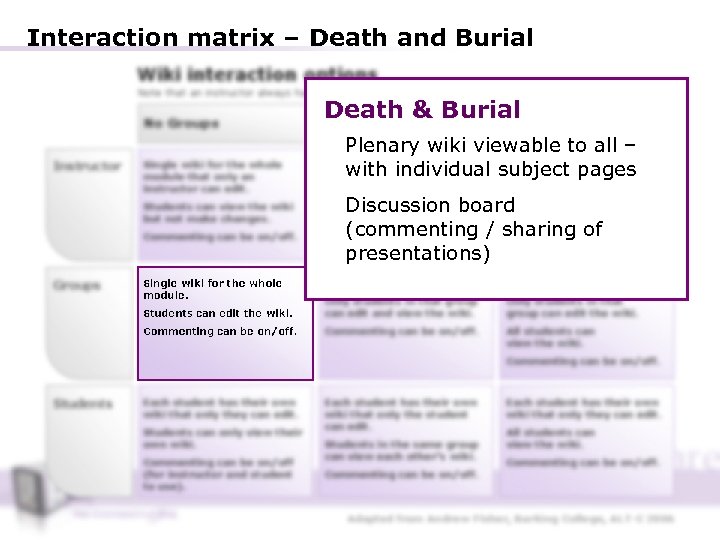
Interaction matrix – Death and Burial Wiki interaction options Note that an instructor always has view, edit and commenting privileges to all wikis No Groups Instructor Single wiki for the whole module that only an instructor can edit. Students can view the wiki but not make changes. Commenting can be on/off. Groups Single wiki for the whole module. Death & Burial Groups Private Groups Open Plenary wiki viewable to all – Each group with individual subject has a wiki pages that only an instructor Each group has a wiki that only an instructor can edit. Commenting can be on/off. can edit. All Discussion board students can view the wiki. (commenting / sharing can be Commenting of presentations) on/off. Other groups can’t view the wiki. Single wiki per group. Students can edit the wiki. Only students in that group can edit and view the wiki. Only students in that group can edit the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Students Each student has their own wiki that only they can edit. Students can only view their own wiki. Commenting can be on/off (for instructor and student to use). Each student has their own wiki that only the student can edit. Students in the same group can view each other’s wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Each student has their own wiki that only they can edit. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Adapted from Andrew Fisher, Barking College, ALT-C 2006
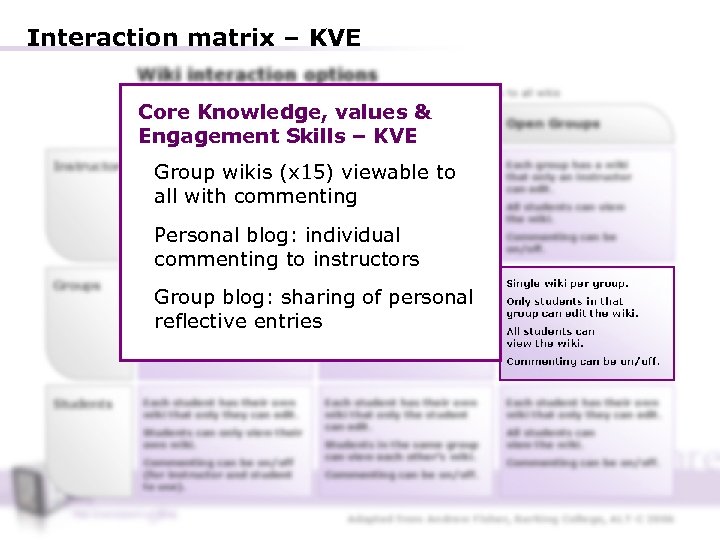
Interaction matrix – KVE Wiki interaction options Note that an instructor always has view, edit and commenting privileges to all wikis Core Knowledge, Private Groups values & No Groups Engagement Skills – KVE Instructor Single wiki for the whole module that only an instructor can edit. Each group has a wiki that Group wikis (x 15) viewablecan edit. only an instructor to Commenting can be on/off. all with commenting Students can view the wiki but not make changes. Other groups can’t view the wiki. Personal blog: individual commenting to instructors Commenting can be on/off. Groups Single wiki for the whole module. Single wiki per group. Group blog: sharingstudents in that group Only of personal can edit and view the wiki. reflective entries Commenting can be on/off. Students can edit the wiki. Open Groups Each group has a wiki that only an instructor can edit. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Single wiki per group. Only students in that group can edit the wiki. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Students Each student has their own wiki that only they can edit. Students can only view their own wiki. Commenting can be on/off (for instructor and student to use). Each student has their own wiki that only the student can edit. Students in the same group can view each other’s wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Each student has their own wiki that only they can edit. All students can view the wiki. Commenting can be on/off. Adapted from Andrew Fisher, Barking College, ALT-C 2006
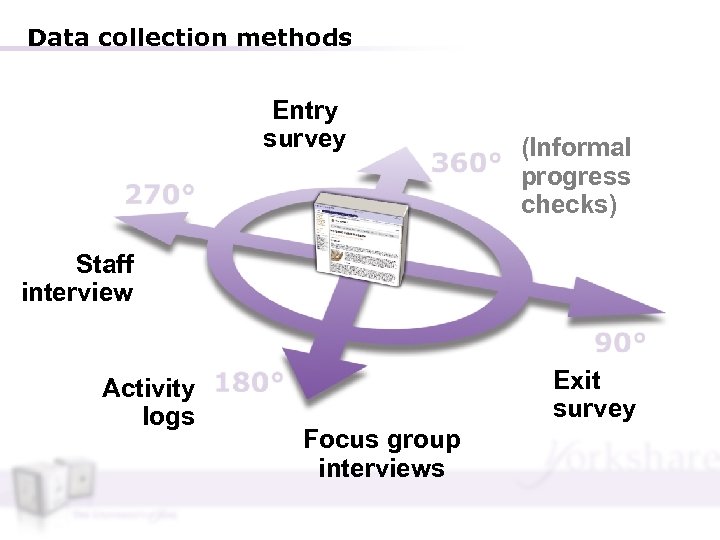
Data collection methods Entry survey (Informal progress checks) Staff interview Activity logs Exit survey Focus group interviews
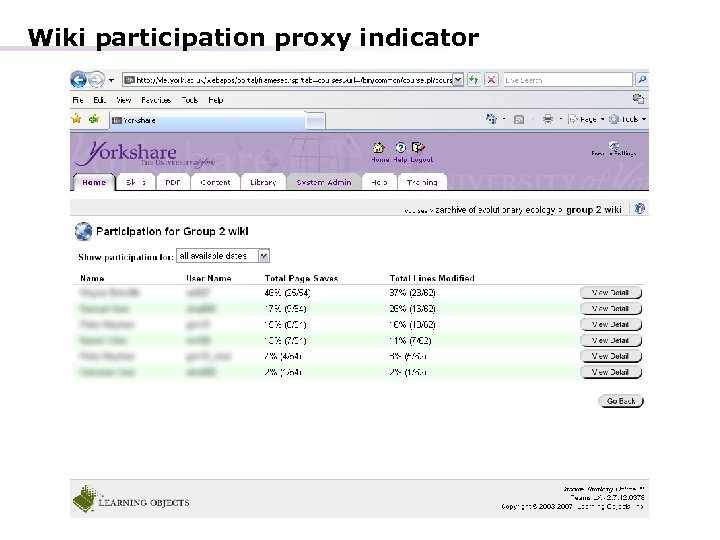
Wiki participation proxy indicator
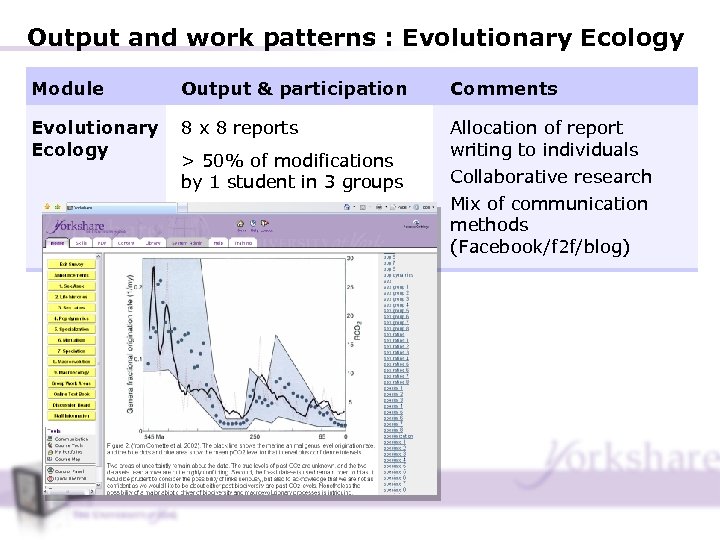
Output and work patterns : Evolutionary Ecology Module Output & participation Comments Evolutionary Ecology 8 x 8 reports Allocation of report writing to individuals Collaborative research > 50% of modifications by 1 student in 3 groups Mix of communication methods (Facebook/f 2 f/blog)
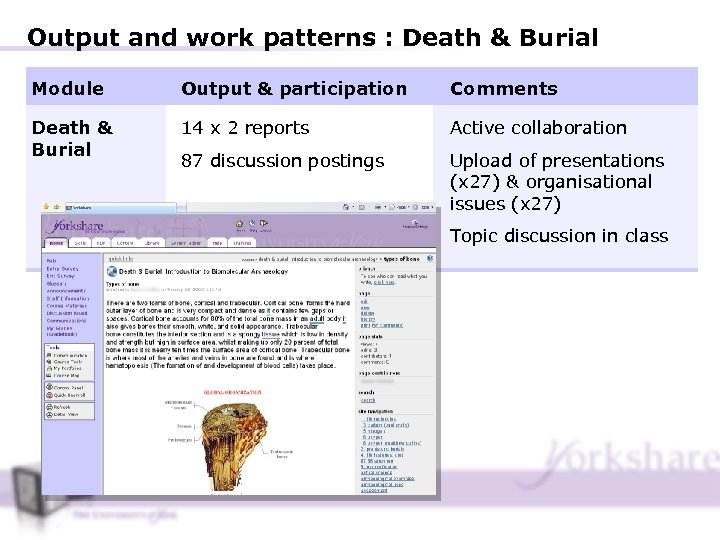
Output and work patterns : Death & Burial Module Output & participation Comments Death & Burial 14 x 2 reports Active collaboration 87 discussion postings Upload of presentations (x 27) & organisational issues (x 27) Topic discussion in class
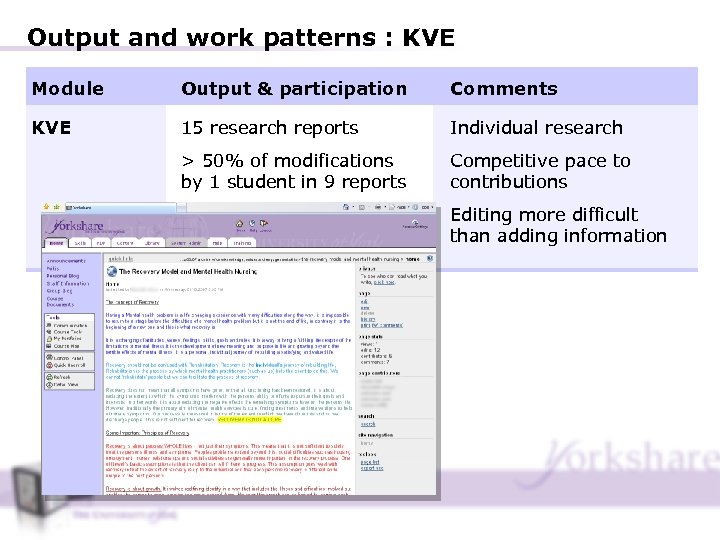
Output and work patterns : KVE Module Output & participation Comments KVE 15 research reports Individual research > 50% of modifications by 1 student in 9 reports Competitive pace to contributions Editing more difficult than adding information

Observations on the group work § Wikis viewed as spaces for presentation of work – not drafting & negotiation § Formal spaces for information sharing & completed work – Informal spaces for social messaging § Text negotiation challenging – “Contribute first before you edit someone else’s work” § Learning competencies – Skills to synthesis & condense, rather than add information – Ownership of contributions & willingness to edit work of others – Peer review & feedback

Lessons Learned Design § Module leader must be clear on: – How to use wikis – Targeted learning behaviour; how tool will be used – Participation drivers (assessment & accountability) Induction § Purpose of wiki / incentives to contribute / ownership issues must be addressed § Modelling of course tasks and targeted learning behaviour – building confidence & addressing technical & learning competencies § ‘Wikiquette’: how to contribute / frequency of contributions / group roles / self-regulation & ownership issues.

Lessons Learned Supporting § Just In Time instructions; technical support § Monitoring of on-line work / on-going evaluation & accountability – “little and often” § Wiki-in-progress class discussion Interlinking & Summing up § Class presentations on wiki work (peer accountability) § Acknowledging and summarising on-line contributions § Making explicit learning outcomes from class-based and virtual activities

Case Studies (http: //vlesupport. york. ac. uk) § Case Study Overview – – – – Background Description of approach Learning activities & tools Student profile Experience with computers for learning Expectations towards the VLE Outcomes of the pilot Activity statistics Focus group feedback Exit survey feedback Instructor and tutors’ feedback Student skills required & developed Staff skills required & developed Actions for further development

Questions
e42fad05257cff7deff8841ea89e00fa.ppt