0d71510b147da67925e26ab2848294b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Cold War Quiz 1. Define “Cold War” 2. Define Communism 3. Define Capitalism 4. What is the United Nations? 8. What was the “Warsaw Pact”? 9. What foreign country supported North Korea in the Korean War? 10. Who built the Berlin Wall? 5. What was the “Arms Race”? 6. What was the “Space Race”? 7. What was “Containment”? 13. What is “Perestroika”? What was “Brinkmanship”? 15. Name two countries that are still Communist today 8. 11. Who won the Vietnam War? 12. What is “Détente”? 14. How did the Cold War end?
Cold War Quiz 1. Define “Cold War” 2. Define Communism 3. Define Capitalism 4. What is the United Nations? 8. What was the “Warsaw Pact”? 9. What foreign country supported North Korea in the Korean War? 10. Who built the Berlin Wall? 5. What was the “Arms Race”? 6. What was the “Space Race”? 7. What was “Containment”? 13. What is “Perestroika”? What was “Brinkmanship”? 15. Name two countries that are still Communist today 8. 11. Who won the Vietnam War? 12. What is “Détente”? 14. How did the Cold War end?
 Unit 6 The World Since 1945 The Cold War Ch. 17/1 Ch. 19/3 Middle East Ch. 18/4 African De-Colonization Ch. 18/3 Ch. 19/2
Unit 6 The World Since 1945 The Cold War Ch. 17/1 Ch. 19/3 Middle East Ch. 18/4 African De-Colonization Ch. 18/3 Ch. 19/2
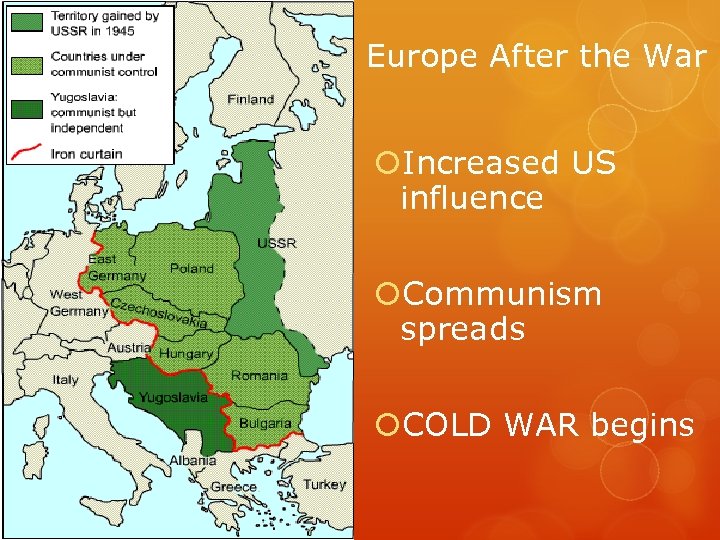 Europe After the War Increased US influence Communism spreads COLD WAR begins
Europe After the War Increased US influence Communism spreads COLD WAR begins
 The Cold War An ideological conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union in which neither nation directly confronted the other on the battlefield Capitalism Communism
The Cold War An ideological conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union in which neither nation directly confronted the other on the battlefield Capitalism Communism
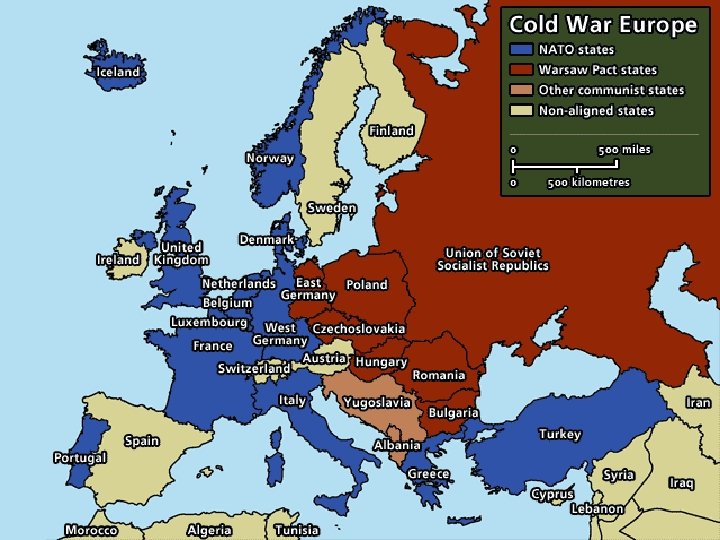
 United Nations, NATO and the Warsaw Pact The New Alliance System? United Nations Replaces League of Nations NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military Alliance btwn US, other Western powers to protect against a Soviet attack Warsaw Pact military alliance btwn Soviet satellite nations to protect against Capitalist attack Creates a “buffer zone”
United Nations, NATO and the Warsaw Pact The New Alliance System? United Nations Replaces League of Nations NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military Alliance btwn US, other Western powers to protect against a Soviet attack Warsaw Pact military alliance btwn Soviet satellite nations to protect against Capitalist attack Creates a “buffer zone”
 Cold War in the 50’s and 60’s Korea and Vietnam – Examples of Containment, Brinksmanship and Domino Effect The Berlin Wall Bay of Pigs Cuban Missile Crisis Space Race Arms Race
Cold War in the 50’s and 60’s Korea and Vietnam – Examples of Containment, Brinksmanship and Domino Effect The Berlin Wall Bay of Pigs Cuban Missile Crisis Space Race Arms Race
 Cold War in the 70’s and 80’s Many reforms to limit nuclear weapons Nixon & Reagan Détente: A lessening of tensions Mikhail Gorbachev – Soviet Premiere attempts political and economic reforms Glasnost: “Openness” between US & USSR Perestroika: Economic restructuring of Soviet system
Cold War in the 70’s and 80’s Many reforms to limit nuclear weapons Nixon & Reagan Détente: A lessening of tensions Mikhail Gorbachev – Soviet Premiere attempts political and economic reforms Glasnost: “Openness” between US & USSR Perestroika: Economic restructuring of Soviet system
 End of the Cold War European Union (EU) stimulates economic growth of participating countries (the Euro) Collapse of Communist gov’ts in Eastern Europe Fall of Berlin Wall (1989) – the symbolic end to Cold War Today? Russia? China? Cuba? Vietnam? Korea?
End of the Cold War European Union (EU) stimulates economic growth of participating countries (the Euro) Collapse of Communist gov’ts in Eastern Europe Fall of Berlin Wall (1989) – the symbolic end to Cold War Today? Russia? China? Cuba? Vietnam? Korea?
 Problems in Newly Independent Countries After WW 2 Africa, South America and Asia § Weak, corrupt governments § Militant Regimes § Poor economy § Land disputes § Cultural differences All these problems lead to instability and conflict
Problems in Newly Independent Countries After WW 2 Africa, South America and Asia § Weak, corrupt governments § Militant Regimes § Poor economy § Land disputes § Cultural differences All these problems lead to instability and conflict
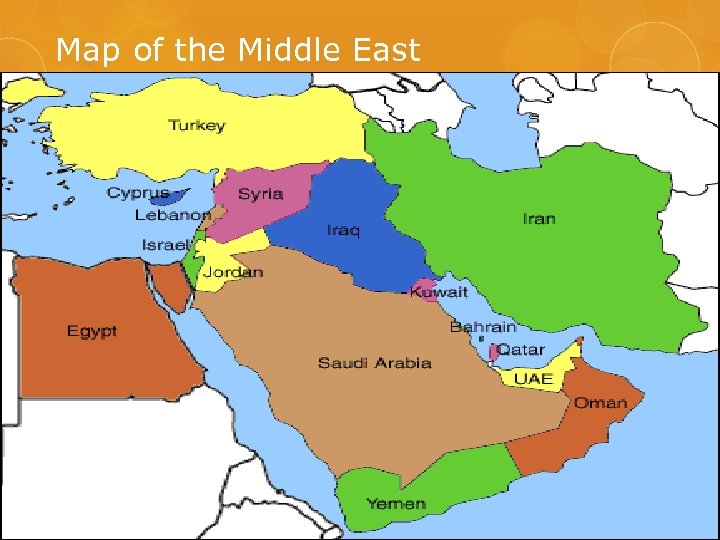 Map of the Middle East
Map of the Middle East
 The Middle East – Israel/Palestine Balfour Declaration – 1917 – Zionist Movement called for a Jewish Homeland Read…. Following WW 2 Israel’s population doubled…Why? Formation of Israel (1948) – split Palestine Jews and Palestinians both have religious and historic ties to the region Still a “hot spot” today
The Middle East – Israel/Palestine Balfour Declaration – 1917 – Zionist Movement called for a Jewish Homeland Read…. Following WW 2 Israel’s population doubled…Why? Formation of Israel (1948) – split Palestine Jews and Palestinians both have religious and historic ties to the region Still a “hot spot” today
 African De-Colonization Many African nations gained their independence from European powers following World War 2 (see map) Why do you think this is? Problems facing these new countries?
African De-Colonization Many African nations gained their independence from European powers following World War 2 (see map) Why do you think this is? Problems facing these new countries?
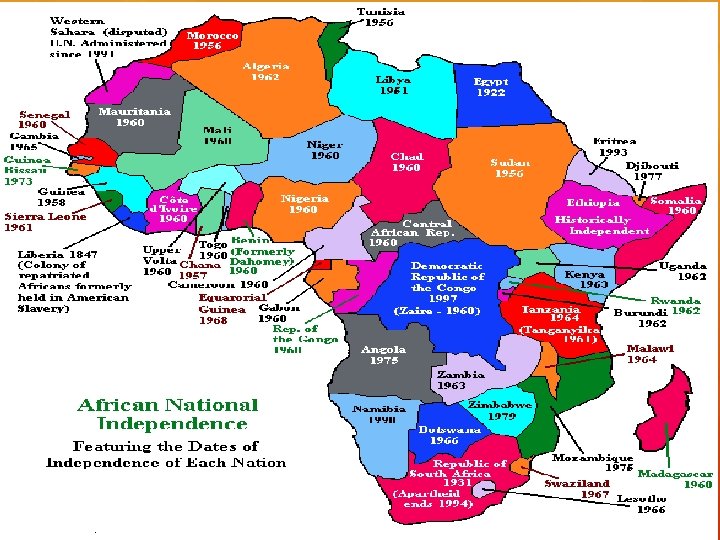 African Independence t. Decolonization – after 1946 t. Third World Countries tthe underdeveloped nations of the world, esp. those with widespread poverty. tthe group of developing nations, esp. of Asia and Africa
African Independence t. Decolonization – after 1946 t. Third World Countries tthe underdeveloped nations of the world, esp. those with widespread poverty. tthe group of developing nations, esp. of Asia and Africa
 Rwandan Genocide Rwanda 1994 Hutus v Tutsis Indirectly caused by Imperialism Cultural/Tribal clashes 800, 000 to 1, 000 dead in three months “Never again”?
Rwandan Genocide Rwanda 1994 Hutus v Tutsis Indirectly caused by Imperialism Cultural/Tribal clashes 800, 000 to 1, 000 dead in three months “Never again”?
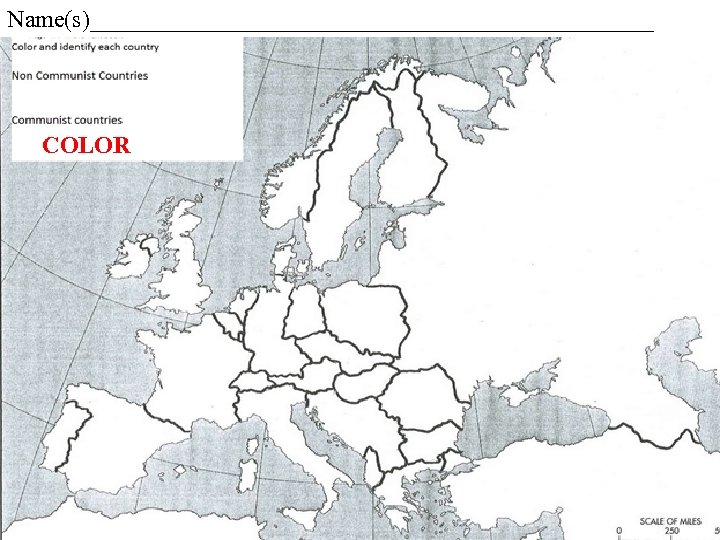 Name(s)________________________ COLOR
Name(s)________________________ COLOR
 Post WW 2 Map Quiz – 15 pts Identify the countries and color the COMMUNIST -based countries. 1 pt each – get both parts right! East Germany West Germany France Spain Poland Finland Turkey Italy Hungary Yugoslavia Bulgaria Czechoslovakia Greece Austria USSR EXTRA – Name the largest Communist country in the world today
Post WW 2 Map Quiz – 15 pts Identify the countries and color the COMMUNIST -based countries. 1 pt each – get both parts right! East Germany West Germany France Spain Poland Finland Turkey Italy Hungary Yugoslavia Bulgaria Czechoslovakia Greece Austria USSR EXTRA – Name the largest Communist country in the world today


