e7cc38412ff23667a9485f6be88ae6a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 COLD WAR Foreign and domestic tensions and issues
COLD WAR Foreign and domestic tensions and issues
 Cold War, 1945 -1991 n A series of conflicts, compromises, and competitions between the capitalist US and the communist Soviet Union to influence other countries into allying with one side or the other
Cold War, 1945 -1991 n A series of conflicts, compromises, and competitions between the capitalist US and the communist Soviet Union to influence other countries into allying with one side or the other
 Atomic Energy Act, 1946 n Created the Atomic Energy Commission to oversee nuclear weapons research and to promote peacetime use of atomic energy
Atomic Energy Act, 1946 n Created the Atomic Energy Commission to oversee nuclear weapons research and to promote peacetime use of atomic energy
 containment n Trying to restrict the expansion of Soviet communism
containment n Trying to restrict the expansion of Soviet communism
 Truman Doctrine, 1947 n Policy of supporting people who are resisting attempted conquest by armed minorities or by outside pressures
Truman Doctrine, 1947 n Policy of supporting people who are resisting attempted conquest by armed minorities or by outside pressures
 CIA n n Central Intelligence Agency Created in 1947 Gathers information secretly Still active today
CIA n n Central Intelligence Agency Created in 1947 Gathers information secretly Still active today
 Marshall Plan, 1948 n European Recovery Program in which the US provided billions of dollars in economic aid for Europe to prevent the spread of communism
Marshall Plan, 1948 n European Recovery Program in which the US provided billions of dollars in economic aid for Europe to prevent the spread of communism
 Berlin Airlift, June 1948 -May 1949 n n n US, England, and France planned to combine their German zones SU was angry and blocked all entry into Berlin Western leaders airlifted food and supplies to Berlin for 10 months
Berlin Airlift, June 1948 -May 1949 n n n US, England, and France planned to combine their German zones SU was angry and blocked all entry into Berlin Western leaders airlifted food and supplies to Berlin for 10 months

 NATO, 1949 n n n North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military alliance originally formed by democratic nations Now includes some former Soviet bloc nations
NATO, 1949 n n n North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military alliance originally formed by democratic nations Now includes some former Soviet bloc nations
 China becomes Communist under Mao Zedong in 1949
China becomes Communist under Mao Zedong in 1949
 brinksmanship n n Using the threat of massive military retaliation going to the brink of war in order to stop communism from spreading
brinksmanship n n Using the threat of massive military retaliation going to the brink of war in order to stop communism from spreading
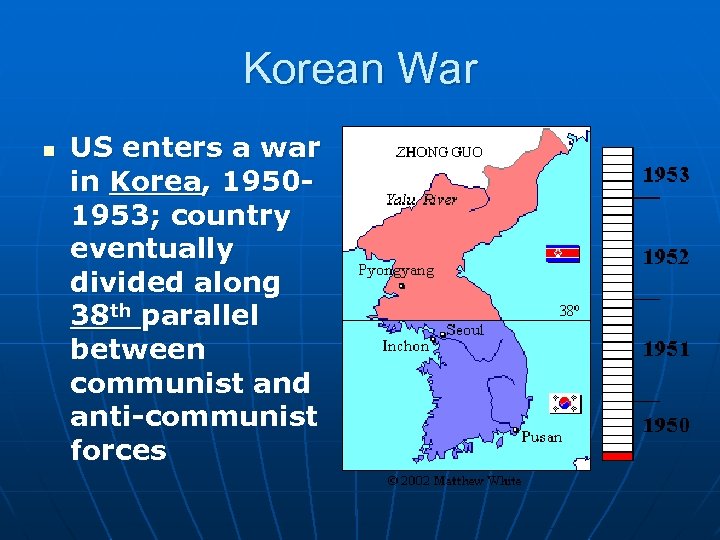 Korean War n US enters a war in Korea, 19501953; country eventually divided along 38 th parallel between communist and anti-communist forces
Korean War n US enters a war in Korea, 19501953; country eventually divided along 38 th parallel between communist and anti-communist forces
 U-2 incident, 1960 n n Francis Gary Powers was shot down by the SU while spying Heightened tensions between the US and SU
U-2 incident, 1960 n n Francis Gary Powers was shot down by the SU while spying Heightened tensions between the US and SU
 Meanwhile… On the Home Front…
Meanwhile… On the Home Front…
 House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) n Investigated people who might be against the government, particularly communists
House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) n Investigated people who might be against the government, particularly communists
 Hollywood Ten, 1947 n People in Hollywood who refused to testify before HUAC and were jailed and later blacklisted
Hollywood Ten, 1947 n People in Hollywood who refused to testify before HUAC and were jailed and later blacklisted
 Internal Security Act, 1950 n n Communist Party members must register with the government Strict controls on immigrants suspected of being communists
Internal Security Act, 1950 n n Communist Party members must register with the government Strict controls on immigrants suspected of being communists
 Joseph Mc. Carthy, 1950 n n Claimed he had a list of supposed communists in the State Department Ruined many careers
Joseph Mc. Carthy, 1950 n n Claimed he had a list of supposed communists in the State Department Ruined many careers
 Hydrogen bomb 1952 (US), 1953 (SU) n n Much more powerful than the atomic bomb First test vaporized an entire island
Hydrogen bomb 1952 (US), 1953 (SU) n n Much more powerful than the atomic bomb First test vaporized an entire island
 Alger Hiss, Julius and Ethel Rosenberg n n Hiss—jailed in 1950 for supposedly being a Soviet spy and lying under oath Rosenbergs— executed in 1953 for selling secrets to the Soviets
Alger Hiss, Julius and Ethel Rosenberg n n Hiss—jailed in 1950 for supposedly being a Soviet spy and lying under oath Rosenbergs— executed in 1953 for selling secrets to the Soviets
 Sputnik, 1957 n n n First satellite launched into space By Soviet Union Heightened the space race
Sputnik, 1957 n n n First satellite launched into space By Soviet Union Heightened the space race
 National Defense Education Act n n Passed in 1958 in response to Sputnik Money for training in science, math and languages
National Defense Education Act n n Passed in 1958 in response to Sputnik Money for training in science, math and languages
 NASA n n Established in 1958 National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NASA n n Established in 1958 National Aeronautics and Space Administration

 Other notable Cold War events n n n n Castro comes to power in Cuba, 1959 Bay of Pigs invasion, 1961 Berlin Wall, 1961 -1989 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 Strategic Arms Limitation Talks, 1972 Glasnost, perestroika; “tear down this wall”—Reagan to Gorbachev Fall of Berlin Wall, 1989; Fall of the Soviet Union, 1991
Other notable Cold War events n n n n Castro comes to power in Cuba, 1959 Bay of Pigs invasion, 1961 Berlin Wall, 1961 -1989 Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 Strategic Arms Limitation Talks, 1972 Glasnost, perestroika; “tear down this wall”—Reagan to Gorbachev Fall of Berlin Wall, 1989; Fall of the Soviet Union, 1991



