8bbfe87c9f6c95100bee78bc2f332321.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
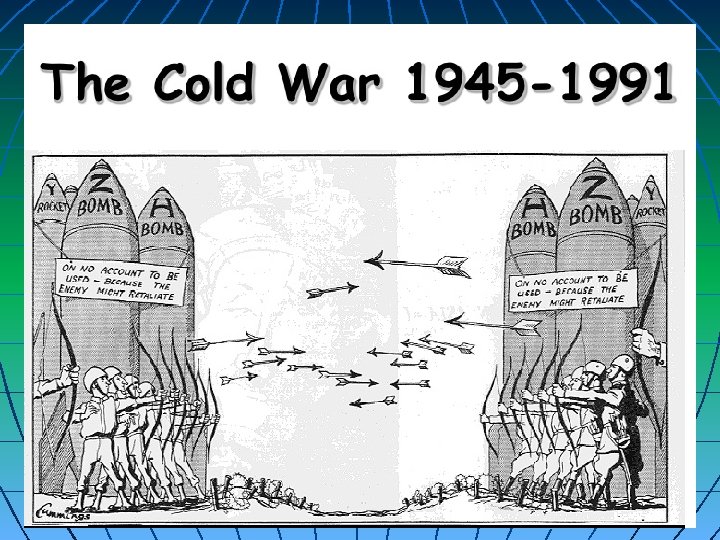

Cold War Definition: The antagonism between the United States and the Soviet Union using third party nations to do the fighting. 1945 -1991
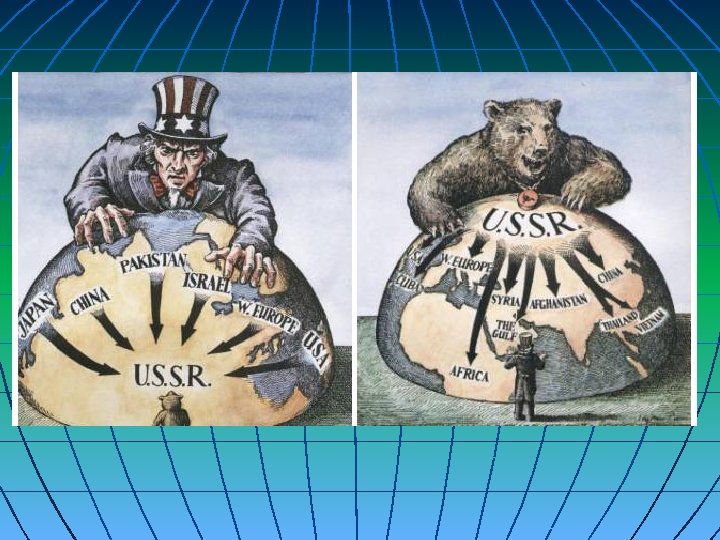

Dissent after WW II n n Soviets wanted reparations U. S. feared it would end up having to fund the Soviet recovery Decision made to partition Germany Russia has control of valuable industrial eastern part of Germany

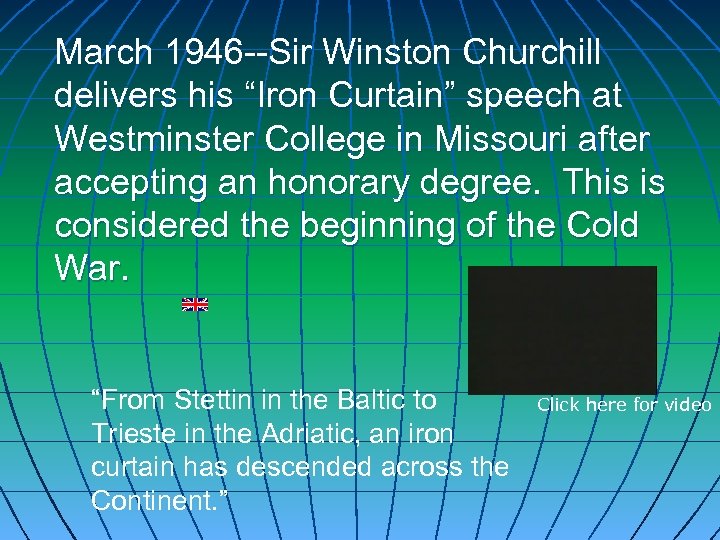
March 1946 --Sir Winston Churchill delivers his “Iron Curtain” speech at Westminster College in Missouri after accepting an honorary degree. This is considered the beginning of the Cold War. “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. ” Click here for video

The “Doomsday Clock” appears for the first time on the cover of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. The hands of the Doomsday Clock, a symbol of nuclear danger, move closer to midnight as world tensions increase or farther from midnight as tensions ease.

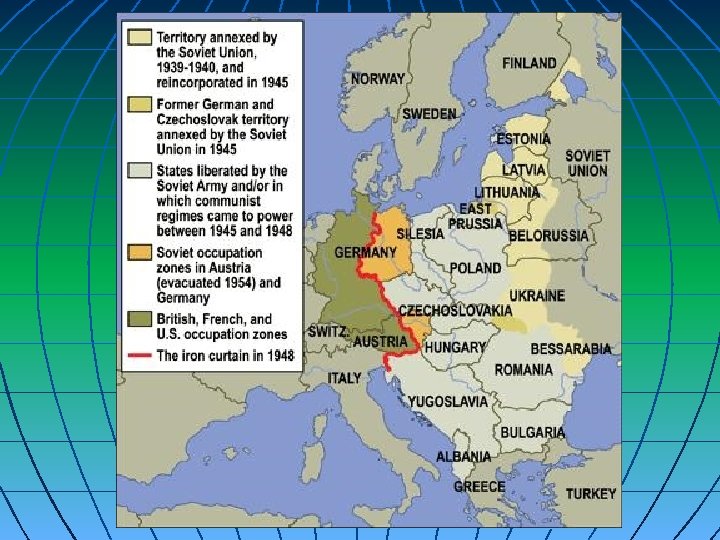
The Truman Doctrine was announced in 1947 to “contain” Communism, starting in Greece. n Post-WWII--"In Eastern Europe, the Soviets gradually took over the countries they had liberated, Poland, East Germany, Hungary, Eastern Austria, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Albania and Romania all became part of the Soviet Block" Click here for video Soviet Union

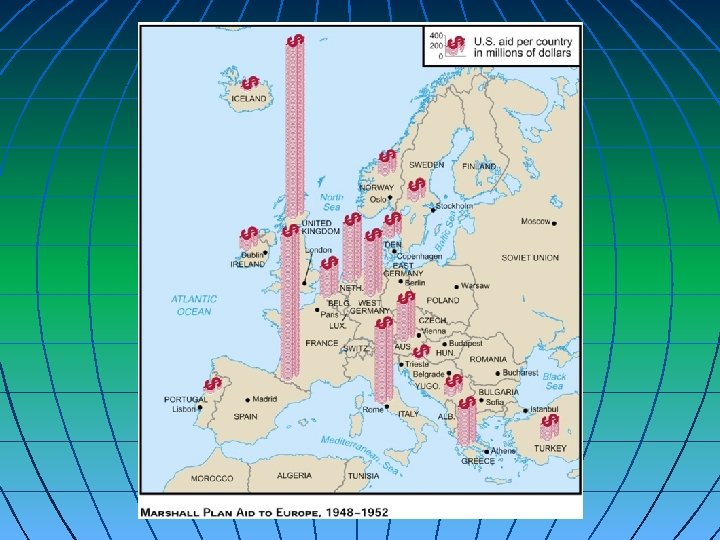
The Marshall Plan: June 1947 n n Secretary of State, George Marshall noted that the nations of Europe were in dire need of investment in order to recover from the war. Marshall proposed loans The Soviet leader forbade any of the eastern European countries to participate, but the western European nations were enthusiastic. The Marshall Plan was a life saver for Europe. Over the next four years, about $13 Billion went overseas. It was used for repairs to highways, port facilities, bridges, and railroads and for getting factories back into production. " Dollar Diplomacy! President Harry S. Truman and General George C. Marshall.


n n UFO sightings will contribute to Cold War hysteria when some sightings are attributed to over-flights by the USSR. NATO and the Warsaw Pact form the military alliance “balance of power” in Europe. ?

Berlin Airlift 1948

Proxy War - Korea n 25 June 1950 --North Korea invades South Korea. UN forces, led by the US, drive the North Koreans back. Feeling threatened, Chinese Communist troops join the war. The Korean war will run until 1953, when an uneasy truce will begin; and is still holding today. Click here for video

Click here for video n n n March 1951 --Julius and Ethel Rosenberg are convicted of espionage for selling nuclear secrets to the Soviet Union. June 1953 --Julius and Ethel Rosenberg are executed at Sing Prison. They are the first American civilians to be executed for espionage under the Espionage Act of 1917. Papers released after the fall of communism indicate that Ethel was innocent.

Arms race n n As the rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union grew in the late 1940 s and into the 50 s, both countries began to rebuild their military forces The 1950 budget had allocated $13 billion for military spending (about one-third of the national budget), the 1951 budget, dedicated $60 billion for defense (about two-thirds of the national budget)
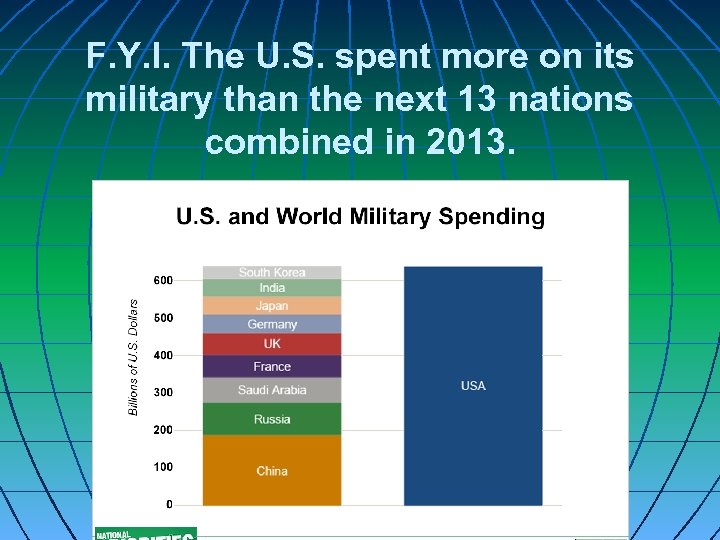
F. Y. I. The U. S. spent more on its military than the next 13 nations combined in 2013.

The “H” bomb n n n October 1952 --The UK announces its first test of a fission weapon. Code named Hurricane, it has a yield of 25 kilotons. The UK announces it will coordinate its nuclear weapons with the US’s. The next year the Soviets test theirs Click here for video

n March 1953 --Josef Stalin dies. One of the most hated and feared men of the twentieth century, Stalin is generally credited with causing more deaths (up to 50 million) in the former USSR than did the invading German forces in World War II (20 million). New Premier, Khrushchev will begin de-Stalinization. Click here for video

Mc. Carthyism, or the Red Scare o de vi r e fo er k h n 1953 --Charlie Chaplin, suspected of being a Communist, is denied entry into the US. Robert Oppenheimer, scientific director during the war-time Manhattan Project, is accused of harboring Communist sympathies. ic n Joseph Mc. Carthy looks for communists in America Cl n

Proxy war Vietnam n n May 1954 --Having been soundly beaten at Dien Bien Phu, the French seek an end to the fighting and soon withdraw from Indochina. Vietnam is divided. US will send forces from 1954 -1973. Click here for video French troops parachute into Dien Bien Phu in November 1953 The battle of Dien Bien Phu lasted from March until early May 1954 Captured French soldiers are led to a camp 435 miles (700 km) north of Dien Bien Phu May 7, 1954

Non-Alignment n n n Bandung Conference Neutral (not really) Led by Indonesia and India Played both sides Communist Yugoslavia (led by Marshall Tito) took a course independent of the USSR. Click here for video
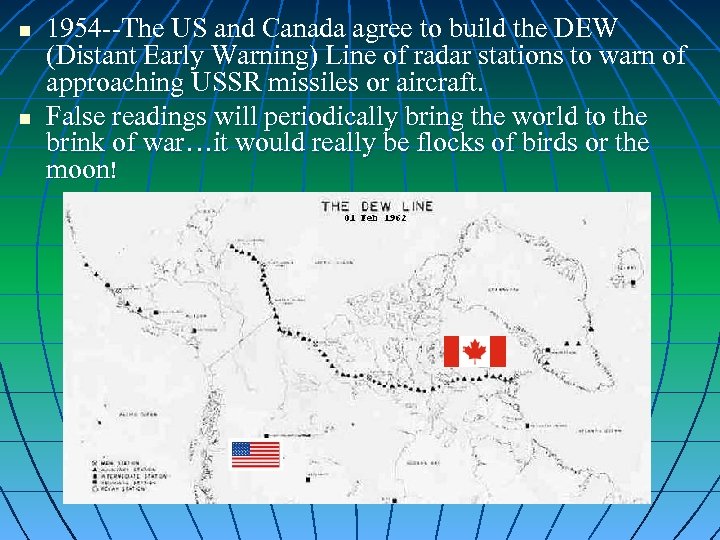
n n 1954 --The US and Canada agree to build the DEW (Distant Early Warning) Line of radar stations to warn of approaching USSR missiles or aircraft. False readings will periodically bring the world to the brink of war…it would really be flocks of birds or the moon!

Missiles n n 1956 --The Atlas missile, one of America's first ICBMs (Intercontinental Ballastic Missile), is designed. American launched rockets can now hit the USSR. Click here for video

Submarines, the perfect weapons n 1956 --The US develops the Polaris missile, which can be launched from a submerged submarine. Click here for video

Hungarian Tragedy n October 1956 --Soviet tanks put down attempts at Democratic reform in Hungary. They thought de-Stalinization meant freedom. d pie cu -oc he e pr in t is. S. crisis U The h the Wit z. e Su Click here for video

sn Di la ey. ou r Y fo nd November 1956 -At a reception in the Kremlin, Soviet premier Nikita Khrushchev tells ambassadors from the West, "History is on our side. We will bury you!" No n

n n ide r v fo re he n ck n October 1957 --The USSR launches Sputnik. The US is taken by surprise. November 1957 --USSR launches a dog, Laika, into orbit. US Shocked to find its students behind in math and science! Education system will move to catch up. Cli n o Space Race Begins

n 1958 --The United States weighed a plan to detonate a nuclear bomb on the moon as a show of military and technical strength!

n n April 1961 -Yuri Gagarin successfully orbited the Earth -the first man to make a successful space flight“ May 1961 --President Kennedy announced the ambitious goal of sending an American safely to the Moon before the end of the decade.

Sci-Fi Movies are really about the Cold War Aliens = Soviets Zombies = communists
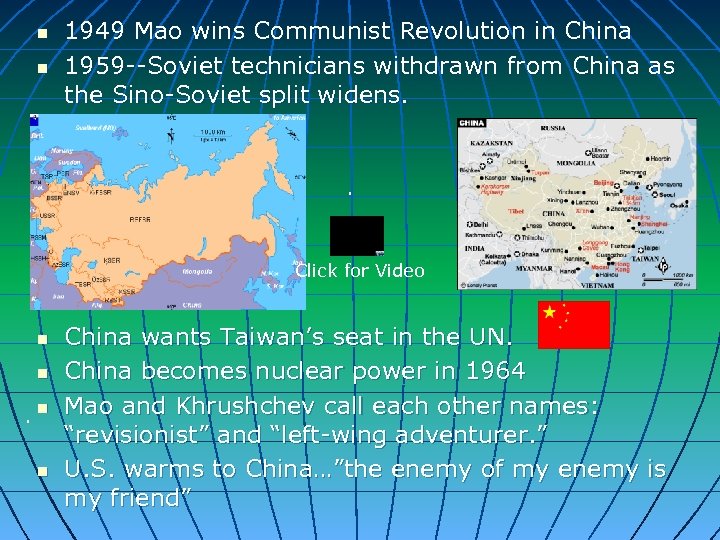
n n 1949 Mao wins Communist Revolution in China 1959 --Soviet technicians withdrawn from China as the Sino-Soviet split widens. . Click for Video n n China wants Taiwan’s seat in the UN. China becomes nuclear power in 1964 Mao and Khrushchev call each other names: “revisionist” and “left-wing adventurer. ” U. S. warms to China…”the enemy of my enemy is my friend”

n n 1959 -US Vice President Richard Nixon, in Moscow to open a US lifestyle exhibit, engages Soviet premier Nikita Khrushchev in an impromptu debate in front of a model kitchen. The so-called "kitchen debate, " in which Nixon extols the American standard of living, is highly publicized

Click here for video n n n February 1960 --France tests its first fission weapon at Reganne, Algeria. France withdraws from NATO and follows and independent course. France wants to be seen as a world power.

n August 1961 --The USSR begins building the Berlin Wall. Click here for video

Cuba n n n Bay of Pigs 1961 - attempted invasion October, 1962 --Cuban missile crisis. The world teeters on the brink of nuclear war for a period of 5 days. Soviets back down, US agrees not to invade Cuba and to remove missiles from Turkey. Click here for video

Results of Crisis n n October 1963 --The Limited Test Ban Treaty, which bans atmospheric nuclear testing, goes into effect. 1963 --The hotline is established between the US and the USSR. Détente: reduction of hostility June 1963 --US President John F. Kennedy gives his "Ich bin ein Berliner" speech in divided Berlin.

Instability in the Soviet Union n n 1964 --Krushchev is deposed by Brezhnev Doctrine: The USSR will invade socialist governments that are threatened.

Détente: Relaxation of Tension n n n Brezhnev felt that the economic burden of the nuclear arms race was unsustainable. The American economy was also in financial trouble as the Vietnam War drained government finances at the same time as Lyndon Johnson sought to expand the government welfare state. Soviet thinkers also felt that a less aggressive policy could potentially detach the Western Europeans from their American ally. Worsening relations with the People's Republic of China, leading to the Sino-Soviet Split, had caused great concern in the Soviet Union. Rough parity had been achieved in stockpiling nuclear weapons with a clear capability of mutually assured destruction (MAD). Brezhnev and Nixon each hoped improved relations would boost their domestic popularity and secure their power.

Attempts to Disarm n n n 1960 s US & USSR working on antiballistic missile systems. 1969: SALT (Strategic Arms Limitation Talks) negotiations begin in Helsinki, Finland. See article for details on goals. 1972 Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty signed; ends ABM development May 26, 1972 Brezhnev and Nixon sign SALT Treaty. 1972 the five-year SALT Interim Agreement freezes the number of ballistic missile launchers at 1972 levels. 1973 Brezhnev signs Agreement on Prevention of Nuclear War with the US.

n January 1966 --A US B-52 bomber carrying four one megaton H-bombs collides with a KC-135 tanker over Palomares, Spain. As both aircraft disintegrate in flight, the Hbombs fall free. One lands in the Mediterranean Sea, three land in the village of Palomares. After an 80 -day search, the last H-bomb is recovered from the ocean depths a half mile below the surface

Brezhnev Doctrine carried out for the first time. Click here for video

n 1968 --More than 100 nations ratify the Nuclear Non. Proliferation Treaty; holdouts include Israel, India, Pakistan, South Africa, Argentina, and Brazil.

n 1979 --Embarking on their own version of Vietnam, the USSR sends tanks, troops, aircraft to Afghanistan to support a faltering Marxist government. The US and many Muslim states would support Afghan rebels who would fight for religious reasons as well as nationalistic reasons.

Collapse of Communism!

The Soviet Union’s Final “Czar” n 1987 Gorbachev campaigns: glasnost & perestroika (openness and restructuring) n WHY Communism Collapses? • Cost of arms race • Failure of planned economy • Repression • Power of Nationalism

Click here for video Communism: Instability and Collapse n n n 1989 Demonstrations in Tiananmen Square. China resists change (army support) Solidarity party wins overwhelming electoral victory in Poland East Germans begin to escape to West Germany through Hungary Berlin Wall falls Nov. 1989 Romania votes out Communist rule (Ceausescu goes violently) Hungary and Czechoslovakia vote Communist out, they leave peacefully (velvet Revolution compared to Prague Spring)

n n 1990 Reunification of Germany Lech Walesa democratically elected president of Poland

Aftermath of Collapse of Communism n n n Warsaw Pact nations join NATO Com. nations join the EU (May 1, 2004) Albania votes Communists back into power…. . wants stability China and Vietnam relax command economy and allow limited capitalism, remain one party-states North Korea is the only Communist nation Germans will prosecute some Communist leaders
8bbfe87c9f6c95100bee78bc2f332321.ppt