24a84d5e74eb631e5fe2b6667ceba745.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 • Cold War – define; how long did it last • Truman Doctrine – define; which countries were immediately affected; how much money did they receive • Marshall Plan – define; include goal • Division of Germany – 1948; Stalin’s reaction to West Berlin • Berlin Airlift – define; explain what happened and why • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – define; significance to the US
• Cold War – define; how long did it last • Truman Doctrine – define; which countries were immediately affected; how much money did they receive • Marshall Plan – define; include goal • Division of Germany – 1948; Stalin’s reaction to West Berlin • Berlin Airlift – define; explain what happened and why • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – define; significance to the US
 Chapter 26, Section 2 The Cold War Heats Up
Chapter 26, Section 2 The Cold War Heats Up
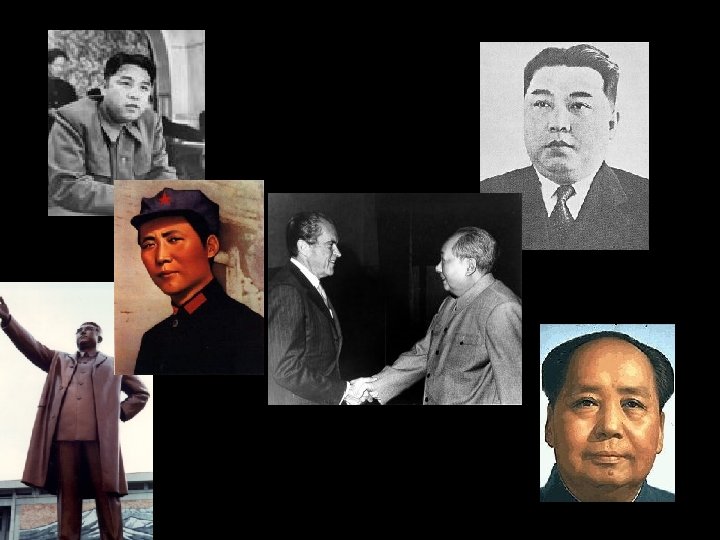
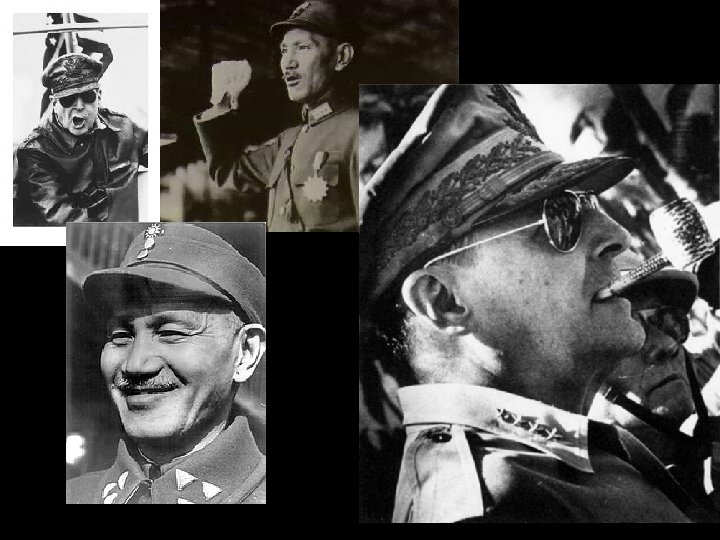
 China Falls to Communism • • • Chiang Kai-shek: Nationalist leader of China supported by the US Mao Zedong: Communist rebel leader supported by the Soviet Union They had joined forces during World War II to fight against the Japanese in China As soon as World War II was over, the civil war between the two leaders began again Truman sent over $2 billion to help the Nationalists since he refused to send US military over there The money wasn’t enough to save the Nationalists – they fled to Taiwan The Communists ruled mainland China establishing a new government called the People’s Republic of China (the US refused to accept this as China’s true government, so we only dealt with Taiwan) Containment had failed in China! Everyone either blamed Truman or started to think Communists were infiltrating the US government (the Second Red Scare is about to begin)
China Falls to Communism • • • Chiang Kai-shek: Nationalist leader of China supported by the US Mao Zedong: Communist rebel leader supported by the Soviet Union They had joined forces during World War II to fight against the Japanese in China As soon as World War II was over, the civil war between the two leaders began again Truman sent over $2 billion to help the Nationalists since he refused to send US military over there The money wasn’t enough to save the Nationalists – they fled to Taiwan The Communists ruled mainland China establishing a new government called the People’s Republic of China (the US refused to accept this as China’s true government, so we only dealt with Taiwan) Containment had failed in China! Everyone either blamed Truman or started to think Communists were infiltrating the US government (the Second Red Scare is about to begin)
 The Korean War 1950 - 1953
The Korean War 1950 - 1953
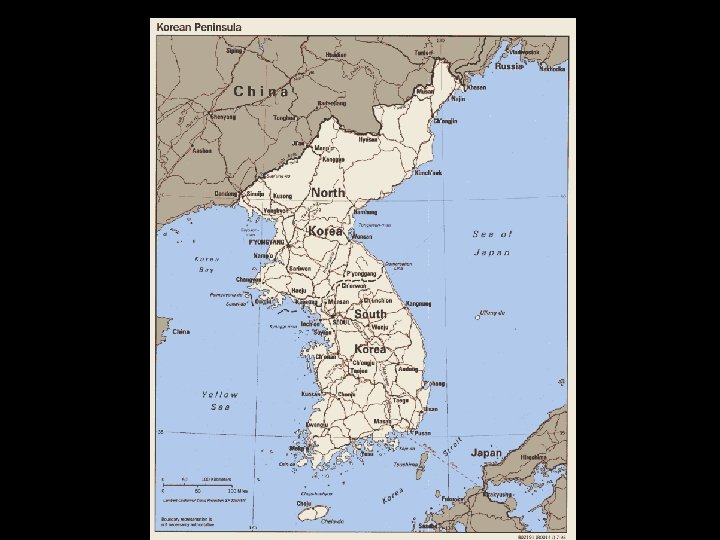


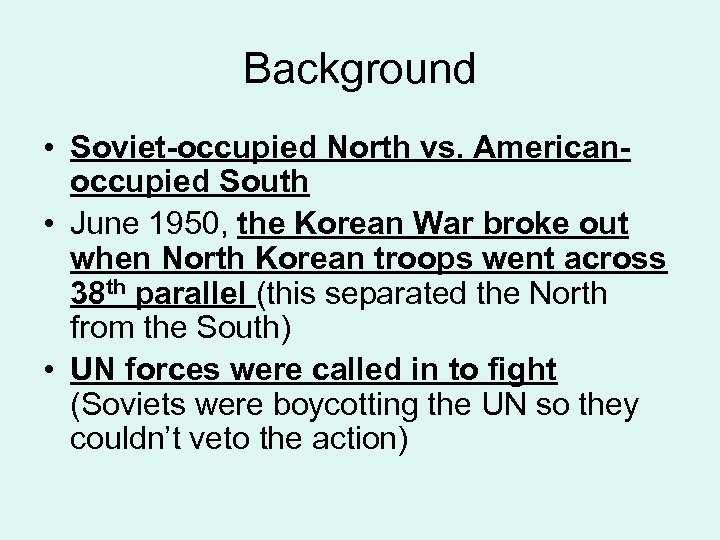 Background • Soviet-occupied North vs. Americanoccupied South • June 1950, the Korean War broke out when North Korean troops went across 38 th parallel (this separated the North from the South) • UN forces were called in to fight (Soviets were boycotting the UN so they couldn’t veto the action)
Background • Soviet-occupied North vs. Americanoccupied South • June 1950, the Korean War broke out when North Korean troops went across 38 th parallel (this separated the North from the South) • UN forces were called in to fight (Soviets were boycotting the UN so they couldn’t veto the action)
 Douglas Mac. Arthur • Strong anti-Communist • Truman’s choice to lead UN forces in Korea • Many viewed him as too ambitious • He believed FDR and Truman were too soft on Communism • He wanted to use the atomic bomb in the war to defeat China, but was refused
Douglas Mac. Arthur • Strong anti-Communist • Truman’s choice to lead UN forces in Korea • Many viewed him as too ambitious • He believed FDR and Truman were too soft on Communism • He wanted to use the atomic bomb in the war to defeat China, but was refused
 • Mac. Arthur attacked enemy supply lines from the back • The North Koreans were then caught between UN forces in the north and south, and with their supplies cut-off, fled across the 38 th parallel • UN troops pursued them northward • Chinese communists get scared when they hear that American and South Korean leaders talked about reuniting Korea under Southern Korean control • UN troops approach North Korea’s border with China
• Mac. Arthur attacked enemy supply lines from the back • The North Koreans were then caught between UN forces in the north and south, and with their supplies cut-off, fled across the 38 th parallel • UN troops pursued them northward • Chinese communists get scared when they hear that American and South Korean leaders talked about reuniting Korea under Southern Korean control • UN troops approach North Korea’s border with China
 • Mac. Arthur ignored warnings by the Chinese • Chinese and North Koreans pushed UN forces back into South Korea • Mac. Arthur wanted the Chinese opposition forces of Chiang Kai-shek to return to the mainland attack the Chinese Communists • Truman refused this fearing that it would lead to war in Asia
• Mac. Arthur ignored warnings by the Chinese • Chinese and North Koreans pushed UN forces back into South Korea • Mac. Arthur wanted the Chinese opposition forces of Chiang Kai-shek to return to the mainland attack the Chinese Communists • Truman refused this fearing that it would lead to war in Asia
 • Mac. Arthur is so upset at Truman that he sends a letter to the House Minority Leader attacking the President’s policies • Truman found out about this and fired Mac. Arthur for insubordination
• Mac. Arthur is so upset at Truman that he sends a letter to the House Minority Leader attacking the President’s policies • Truman found out about this and fired Mac. Arthur for insubordination
 • With Mac. Arthur gone, Truman was able to keep the war limited, but it still lasted into the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower • A truce was signed in 1953, leaving Korea divided at almost the same place as before the war, near the 38 th parallel
• With Mac. Arthur gone, Truman was able to keep the war limited, but it still lasted into the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower • A truce was signed in 1953, leaving Korea divided at almost the same place as before the war, near the 38 th parallel
 Effects of the War • 54, 000 Americans were killed and 103, 000 wounded • Many began to question the government’s efforts to stop communism • On the positive, containment occurred without using nuclear warfare; US troops were now fully integrated • On the negative, returning troops were not wellreceived; huge increase in military spending; US accepted demands of permanent mobilization; military industrial complex began in which military is linked to the corporate and scientific communities • It was still a grim foreshadowing of the American public’s response to the encroaching Vietnam conflict
Effects of the War • 54, 000 Americans were killed and 103, 000 wounded • Many began to question the government’s efforts to stop communism • On the positive, containment occurred without using nuclear warfare; US troops were now fully integrated • On the negative, returning troops were not wellreceived; huge increase in military spending; US accepted demands of permanent mobilization; military industrial complex began in which military is linked to the corporate and scientific communities • It was still a grim foreshadowing of the American public’s response to the encroaching Vietnam conflict
 The Cold War At Home pages 822 - 827 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) Hollywood Ten/blacklist The Mc. Carran Act Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Joseph Mc. Carthyism Mc. Carthy’s claim on the State Department and the Democratic Party What led to Mc. Carthy’s downfall? Two examples of how the fear of communism caused near hysteria.
The Cold War At Home pages 822 - 827 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) Hollywood Ten/blacklist The Mc. Carran Act Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Joseph Mc. Carthyism Mc. Carthy’s claim on the State Department and the Democratic Party What led to Mc. Carthy’s downfall? Two examples of how the fear of communism caused near hysteria.


