e6212ce5336129589032112849102ab8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Cold war course • • Natalia Tsvetkova Professor American studies dep. tsvetkoffa@mail. ru
Cold war course • • Natalia Tsvetkova Professor American studies dep. tsvetkoffa@mail. ru
 The aim of the course Problem: • There a lots of stories about this event (cold war); • All stories are based on some selected documents, and every author tries to find surprising things using his (her) personal interpretations, so Solution: • To write own story of the Cold War using selected documents • The course will be a combination of my lectures (my story of cold war) and your analysis of documents + reading • Result: you will tell your own story.
The aim of the course Problem: • There a lots of stories about this event (cold war); • All stories are based on some selected documents, and every author tries to find surprising things using his (her) personal interpretations, so Solution: • To write own story of the Cold War using selected documents • The course will be a combination of my lectures (my story of cold war) and your analysis of documents + reading • Result: you will tell your own story.
 Requirements and Assesment (Active students are free from final exam) No papers 6 credits: • Reading and analysis of documents • Participation in discussions and presentations • Final exam (1 document for analysis) 4 credits or 2 credits: • a passive participation • 1 question for a final exam
Requirements and Assesment (Active students are free from final exam) No papers 6 credits: • Reading and analysis of documents • Participation in discussions and presentations • Final exam (1 document for analysis) 4 credits or 2 credits: • a passive participation • 1 question for a final exam
 General History of the Cold War Overview of Cold War events
General History of the Cold War Overview of Cold War events
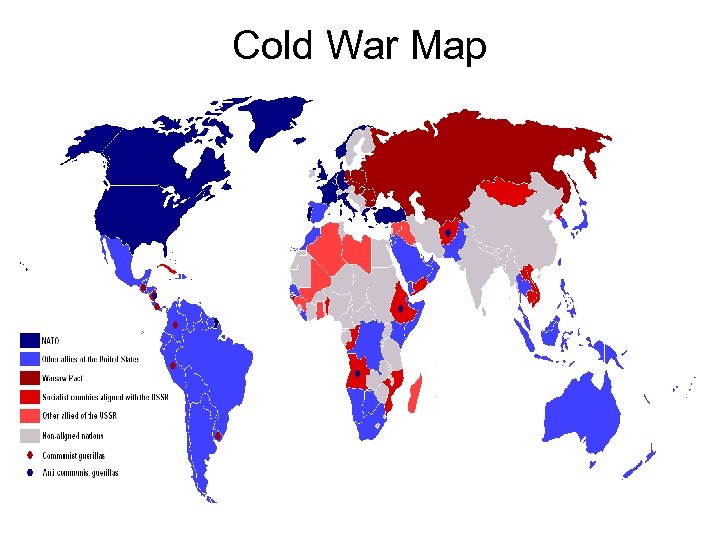 Cold War Map
Cold War Map
 Periods of the Cold War are relative to the periods of American foreign policy Russians do not elaborate their own 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) the period of the pre-Cold War, 1945– 47, the containment period, 1947– 54, the flexible response, 1954– 1969, the period of Détente 1969– 1979, the collapse of the communist in the countries of Eastern Europe and in the Soviet Union, 1980 s– 1990, and the aftermath of the Cold War, 1990– 1992
Periods of the Cold War are relative to the periods of American foreign policy Russians do not elaborate their own 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) the period of the pre-Cold War, 1945– 47, the containment period, 1947– 54, the flexible response, 1954– 1969, the period of Détente 1969– 1979, the collapse of the communist in the countries of Eastern Europe and in the Soviet Union, 1980 s– 1990, and the aftermath of the Cold War, 1990– 1992
 The pre-cold war, 1945– 47 1) 1943 Teheran and 1945 Yalta Conferences: Franklin Roosevelt, Winston Churchill and Joseph Stalin • shaped the spheres of influence in Europe in regard to the real presence of the Soviet troops in countries of the region. • An agreement on free elections in occupied countries 2) The death of F. Roosevelt and new president H. Truman insisted on Soviet obligations to arrange free elections in client countries:
The pre-cold war, 1945– 47 1) 1943 Teheran and 1945 Yalta Conferences: Franklin Roosevelt, Winston Churchill and Joseph Stalin • shaped the spheres of influence in Europe in regard to the real presence of the Soviet troops in countries of the region. • An agreement on free elections in occupied countries 2) The death of F. Roosevelt and new president H. Truman insisted on Soviet obligations to arrange free elections in client countries:
 The pre-cold war, 1945– 47 4) Potsdam conference, July and August 1945: German question: to be unified or not, how to govern it by 4 Zonal Administrations, and how meet reparation demands of the Soviet Union. 5) Stalin’s rejection to insert democratic parties in governments of the countries in Eastern Europe + his rejection to leave Iran+ Kennan diplomatic reports from Moscow, winter 1946 >> U. S. policy was to be more tough with Russians and
The pre-cold war, 1945– 47 4) Potsdam conference, July and August 1945: German question: to be unified or not, how to govern it by 4 Zonal Administrations, and how meet reparation demands of the Soviet Union. 5) Stalin’s rejection to insert democratic parties in governments of the countries in Eastern Europe + his rejection to leave Iran+ Kennan diplomatic reports from Moscow, winter 1946 >> U. S. policy was to be more tough with Russians and
 The containment, 1947– 54 1) East and West coalitions fell into place: Stalin establish strong international movement of communists (Cominform)>> 2) Communists took the political power in Eastern European countries >> Truman doctrine and Marshall plan, 1947 was to save the part of Europe 3) Germany was not unified and Berlin Airlift of 1948– 49: a Soviet test of American aims concerning the Soviet Union (map) 4) communists under Mao Zedong defeated Chinese nationalists led by Chiang Kai-shek >> Mao formed a communist People’s Republic of China on October 1, 1949
The containment, 1947– 54 1) East and West coalitions fell into place: Stalin establish strong international movement of communists (Cominform)>> 2) Communists took the political power in Eastern European countries >> Truman doctrine and Marshall plan, 1947 was to save the part of Europe 3) Germany was not unified and Berlin Airlift of 1948– 49: a Soviet test of American aims concerning the Soviet Union (map) 4) communists under Mao Zedong defeated Chinese nationalists led by Chiang Kai-shek >> Mao formed a communist People’s Republic of China on October 1, 1949
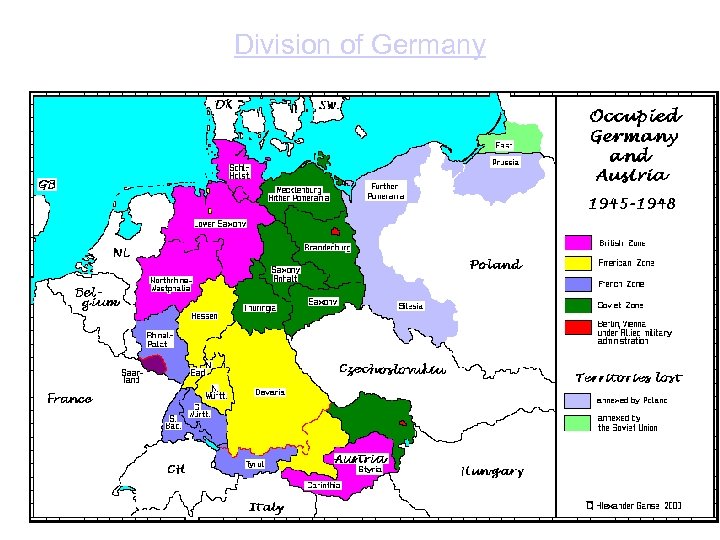 Division of Germany
Division of Germany
 containment, 1947– 54 5) 1950 -1953 – Korean War >> a unstable pacific region 6) India received its independence from Great Britain in 1947 and was broken into two nations: Muslim Pakistan and Hindu India >> wars between them were started + 7) Conflict between Jewish state and Arab world in middle East after withdrawal of the Great Britain. 8) Russians are ready for world expansion >> American containment strategy, 1951
containment, 1947– 54 5) 1950 -1953 – Korean War >> a unstable pacific region 6) India received its independence from Great Britain in 1947 and was broken into two nations: Muslim Pakistan and Hindu India >> wars between them were started + 7) Conflict between Jewish state and Arab world in middle East after withdrawal of the Great Britain. 8) Russians are ready for world expansion >> American containment strategy, 1951
 The period of the flexible response, 1954– 1969 1) Eisenhower –Khrushchev: massive rolling back of each other; 2) Vietnam, 1954 -1973: Ho Chi Minh defeated the French army>>Geneva Peace Accords called for the temporary creation of North and South Vietnam; 3) Revolts in Germany (1953), Hungary (1956) and Czechoslovakia (1968) and cool position of the USA>> the stability of European confrontation; 4) Developing world as a new border of the Cold War, since the end 1950 s.
The period of the flexible response, 1954– 1969 1) Eisenhower –Khrushchev: massive rolling back of each other; 2) Vietnam, 1954 -1973: Ho Chi Minh defeated the French army>>Geneva Peace Accords called for the temporary creation of North and South Vietnam; 3) Revolts in Germany (1953), Hungary (1956) and Czechoslovakia (1968) and cool position of the USA>> the stability of European confrontation; 4) Developing world as a new border of the Cold War, since the end 1950 s.
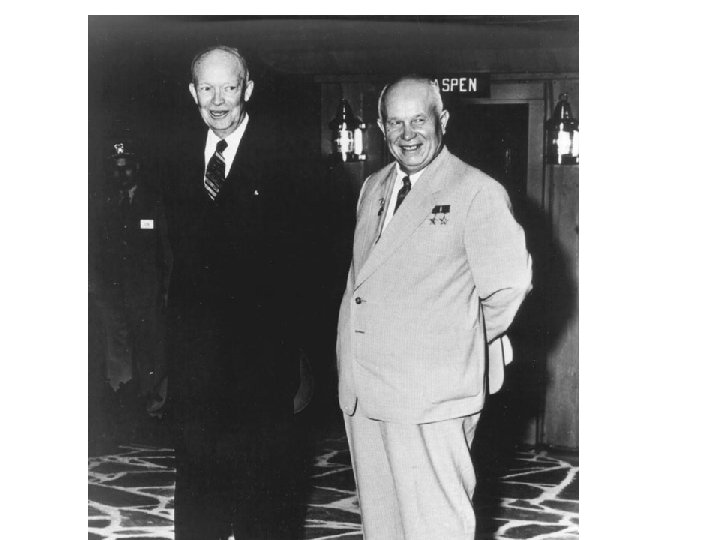

 The period of the flexible response, 1954– 1969 6) Outer space: Soviet satellite, 1957 Gagarin, 1961 and atom 7) new Berlin and Cuba crises, 1961 -1962 >> and idea of a peaceful coexistence and détente was discussed in both Moscow and Washington; 8) Six Day War between Israel and Arab states, 1967 >> the Soviet and American allies in the region became clear (until the end 1970 s): Egypt+Syria= the Soviet Union, Israel =the United States
The period of the flexible response, 1954– 1969 6) Outer space: Soviet satellite, 1957 Gagarin, 1961 and atom 7) new Berlin and Cuba crises, 1961 -1962 >> and idea of a peaceful coexistence and détente was discussed in both Moscow and Washington; 8) Six Day War between Israel and Arab states, 1967 >> the Soviet and American allies in the region became clear (until the end 1970 s): Egypt+Syria= the Soviet Union, Israel =the United States
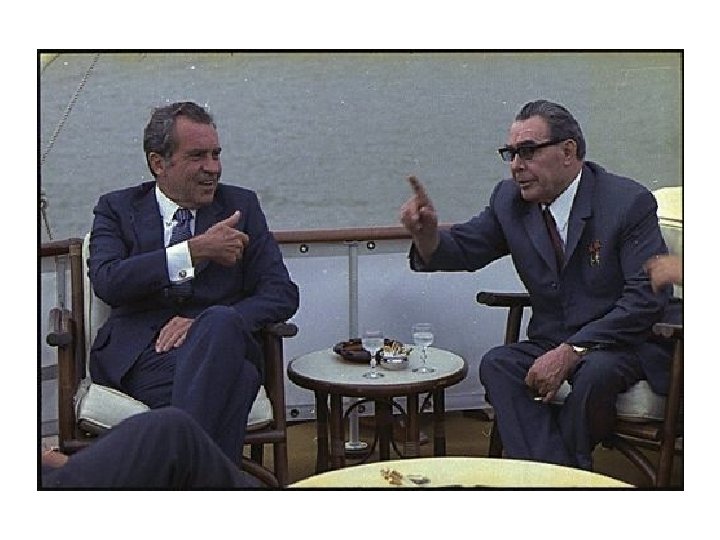
 Détente, until 1979 1) Pragmatic approach to Cold War politics by Nixon and Henry Kissinger: ideology was put aside; • West recognition of Soviet influence in Europe, • American alliance with China and • West evolutionary pressure on the Soviet Union policy in the area of human rights. • Ostpolitik, initiated by W. Brandt: to establish friendly relations with East Block 2) Helsinki Summit, 1975: the West gained a possibility to communicate with human rights activists and with dissidents in E. Europe and in the Soviet Union. 3) The end of 1970 s: the Soviet invasion in Afghanistan and the denial of the U. S. Congress to ratify a treaty on the reduction of nuclear weapons
Détente, until 1979 1) Pragmatic approach to Cold War politics by Nixon and Henry Kissinger: ideology was put aside; • West recognition of Soviet influence in Europe, • American alliance with China and • West evolutionary pressure on the Soviet Union policy in the area of human rights. • Ostpolitik, initiated by W. Brandt: to establish friendly relations with East Block 2) Helsinki Summit, 1975: the West gained a possibility to communicate with human rights activists and with dissidents in E. Europe and in the Soviet Union. 3) The end of 1970 s: the Soviet invasion in Afghanistan and the denial of the U. S. Congress to ratify a treaty on the reduction of nuclear weapons

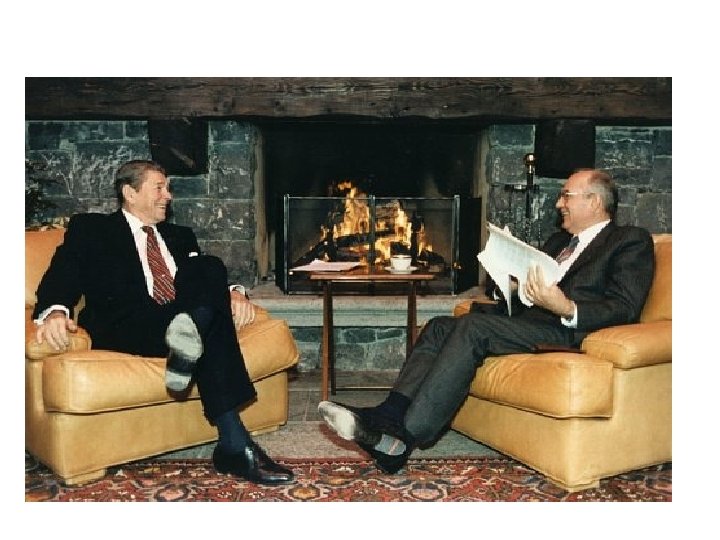
 Collapse of communism, 1980 s– 1990 1) 2) 3) Afghanistan (the invasion of the Soviet Union) and Ronald Reagan approach to the Soviet Union (dissidents, economic sanctions and Strategic Defense Initiative in 1983) made the Cold War to be similar its initial phase and undermined the power of the Soviet Union; Gorbochev decided to talk with Regan, 1985 -1987; Inside reforms in Russia gave impetus for revolution in the Eastern European countries, 1989 -1990: 1) 2) 3) Poland Hungary- free elections, October 1989 Bulgaria and Czechoslovakia, November 1989 German reunification, 1990
Collapse of communism, 1980 s– 1990 1) 2) 3) Afghanistan (the invasion of the Soviet Union) and Ronald Reagan approach to the Soviet Union (dissidents, economic sanctions and Strategic Defense Initiative in 1983) made the Cold War to be similar its initial phase and undermined the power of the Soviet Union; Gorbochev decided to talk with Regan, 1985 -1987; Inside reforms in Russia gave impetus for revolution in the Eastern European countries, 1989 -1990: 1) 2) 3) Poland Hungary- free elections, October 1989 Bulgaria and Czechoslovakia, November 1989 German reunification, 1990

 Collapse of communism, 1980– 1990 4) Officially the Cold War was ended in September 1990: Great Britain, the U. S. , and the Soviet Union signed a peace treaty with East and West Germany: • the withdrawal of the Soviet Army and admit the unification of Germany; + 5) On November 1990 - the nonaggression agreement between member of NATO and the Warsaw Pact. • George Bush said that “We closed the chapter of history. The Cold War is over”.
Collapse of communism, 1980– 1990 4) Officially the Cold War was ended in September 1990: Great Britain, the U. S. , and the Soviet Union signed a peace treaty with East and West Germany: • the withdrawal of the Soviet Army and admit the unification of Germany; + 5) On November 1990 - the nonaggression agreement between member of NATO and the Warsaw Pact. • George Bush said that “We closed the chapter of history. The Cold War is over”.
 The aftermath of the Cold War, 1990 -1992 1) 2) 3) A process of dissolution of the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia >> era of nationalistic and religious conflicts; The U. S. and Russia weakened the ties with radical groups in different parts of the world >> New ideologies are determining of international relations system: Islam fundamentalism as the substitution of communism.
The aftermath of the Cold War, 1990 -1992 1) 2) 3) A process of dissolution of the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia >> era of nationalistic and religious conflicts; The U. S. and Russia weakened the ties with radical groups in different parts of the world >> New ideologies are determining of international relations system: Islam fundamentalism as the substitution of communism.


