7afa30f16d1b5fed02be42dc70537c18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Cold War Across The Decades 35 More Years of Ideological Conflict
Cold War Across The Decades 35 More Years of Ideological Conflict
 The Cold War 50’s • Race for the H-Bomb -US vs. Soviets in nuclear weapons (arms) race “Brinkmanship” – Threat of mutual destruction to keep the peace. • Covert Actions Begin - US’s CIA conduct secret spy missions to change foreign governments to make them friendly. Middle East – Iran Central America – Guatemala
The Cold War 50’s • Race for the H-Bomb -US vs. Soviets in nuclear weapons (arms) race “Brinkmanship” – Threat of mutual destruction to keep the peace. • Covert Actions Begin - US’s CIA conduct secret spy missions to change foreign governments to make them friendly. Middle East – Iran Central America – Guatemala
 The Cold War 50’s • World Crises Egypt – US faces off vs. Soviets over Suez Canal. Eisenhower Doctrine – US will defend Middle East Hungary – Soviets back less repressive leader so the country remains friendly with them • Space Race Soviets reach space first - Sputnik – 1958 Threat to US was nukes launched in space
The Cold War 50’s • World Crises Egypt – US faces off vs. Soviets over Suez Canal. Eisenhower Doctrine – US will defend Middle East Hungary – Soviets back less repressive leader so the country remains friendly with them • Space Race Soviets reach space first - Sputnik – 1958 Threat to US was nukes launched in space
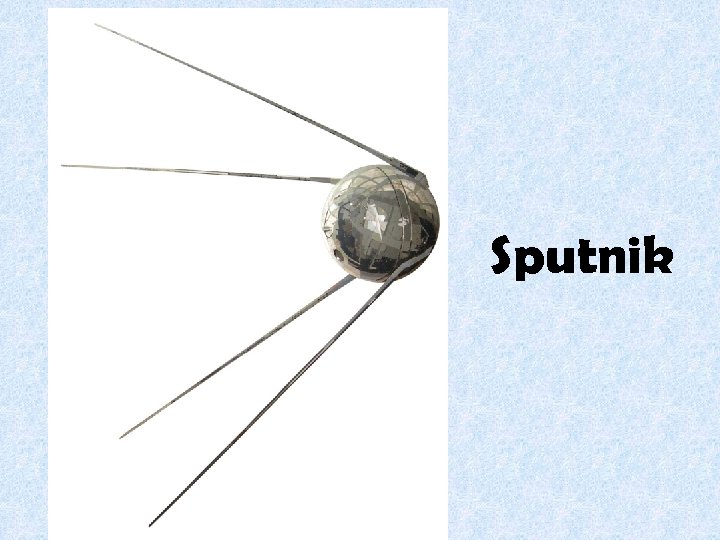 Sputnik
Sputnik
 Leaders Face-Off • Pres. Dwight Eisenhower vs. Nikita Khrushchev • Eisenhower Doctrine US will defend Middle Eastern countries attacked by and all Communist ones. • Khrushchev blasts Eisenhower on May 1960 U-2 Spy plane incident. Eisenhower admits it - CAUGHT - Khrushchev views it as boasting. - Continued bad relations - misunderstandings
Leaders Face-Off • Pres. Dwight Eisenhower vs. Nikita Khrushchev • Eisenhower Doctrine US will defend Middle Eastern countries attacked by and all Communist ones. • Khrushchev blasts Eisenhower on May 1960 U-2 Spy plane incident. Eisenhower admits it - CAUGHT - Khrushchev views it as boasting. - Continued bad relations - misunderstandings
 U-2 Spy Plane
U-2 Spy Plane
 World Leaders’ Status • Basically a tie – US & Soviets were both growing more powerful every year. • Dominant influence in the world could have gone either way in the ‘ 60 s. • Eastern Europe was Communist. Western Europe was Democratic. The Middle East was “up for grabs”. Both sides protected their “backyards” vigorously.
World Leaders’ Status • Basically a tie – US & Soviets were both growing more powerful every year. • Dominant influence in the world could have gone either way in the ‘ 60 s. • Eastern Europe was Communist. Western Europe was Democratic. The Middle East was “up for grabs”. Both sides protected their “backyards” vigorously.
 The Cold War 60’s • Kennedy vs. Khrushchev - Hard Line vs. Soviets - Big conventional army would allow “Flexible Response” - Rise of Military/Industrial Complex • Problems in Cuba, Berlin again & S/E Asia again - Communist Fidel Castro revolts in Cuba - Seeks aid from Soviets - Bay of Pigs Attempts to Overthrow Castro - Failed
The Cold War 60’s • Kennedy vs. Khrushchev - Hard Line vs. Soviets - Big conventional army would allow “Flexible Response” - Rise of Military/Industrial Complex • Problems in Cuba, Berlin again & S/E Asia again - Communist Fidel Castro revolts in Cuba - Seeks aid from Soviets - Bay of Pigs Attempts to Overthrow Castro - Failed
 Cuban Missile Crisis • 1962 - Soviet Aid to Cuba expands nuclear missiles & advisors arrive and build launch pads. - U-2 Spy planes take photos - US blockades Cuba w/ships & subs - Prepares 200, 000 man invasion force in Florida. - Khrushchev orders Soviet ships on the way, stopped. -Agrees to bring missiles home if US doesn’t invade.
Cuban Missile Crisis • 1962 - Soviet Aid to Cuba expands nuclear missiles & advisors arrive and build launch pads. - U-2 Spy planes take photos - US blockades Cuba w/ships & subs - Prepares 200, 000 man invasion force in Florida. - Khrushchev orders Soviet ships on the way, stopped. -Agrees to bring missiles home if US doesn’t invade.

 Progress From Crisis • “Hot Line” between Kremlin and White House – a direct phone line - so leaders can talk before crises escalate. • Limited Test Ban Treaty – Forbids nuclear testing in the atmosphere. • But as our “backyard crises” eased, a new threat arose in Southeast Asia…Vietnam.
Progress From Crisis • “Hot Line” between Kremlin and White House – a direct phone line - so leaders can talk before crises escalate. • Limited Test Ban Treaty – Forbids nuclear testing in the atmosphere. • But as our “backyard crises” eased, a new threat arose in Southeast Asia…Vietnam.
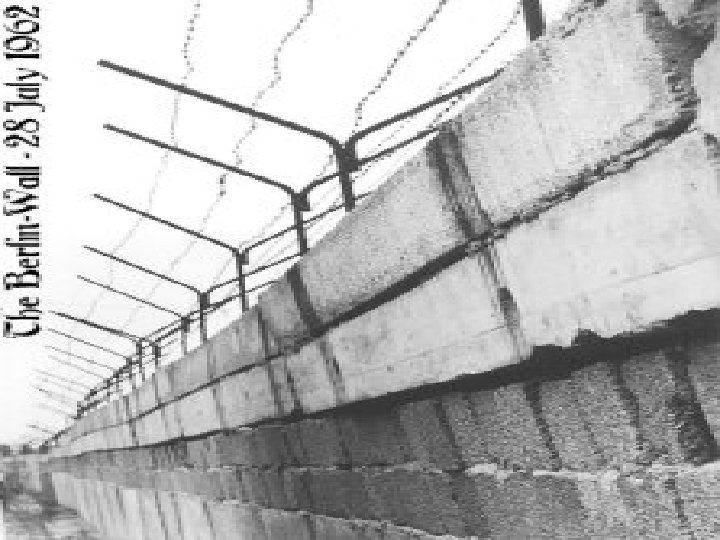
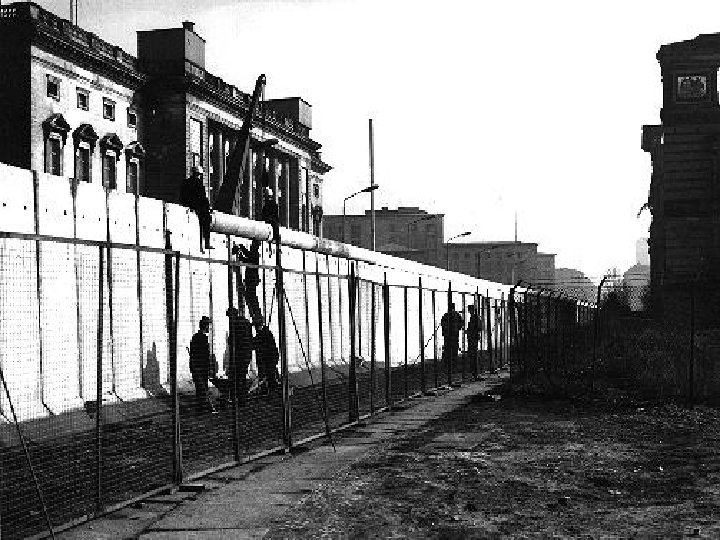
 Berlin Crisis • Since Marshall Plan & Berlin Airlift, West Germany prospered & East Germany failed • 3 Million East Germans fled to the West. - Lost educated people who could help - Bad PR for the Communists - Khrushchev tries to get Germans to agree to seal out the Western nations. Kennedy resists - 1961 – Berlin Wall built to keep E. Germans in
Berlin Crisis • Since Marshall Plan & Berlin Airlift, West Germany prospered & East Germany failed • 3 Million East Germans fled to the West. - Lost educated people who could help - Bad PR for the Communists - Khrushchev tries to get Germans to agree to seal out the Western nations. Kennedy resists - 1961 – Berlin Wall built to keep E. Germans in
 Building Berlin Wall
Building Berlin Wall



 Domino Theory & SE Asia • Mao Zedong’s Communist Ideology spreads to Vietnam. • Ho Chi Minh leads North Viet Nam to unite with the South under Communism. • US aids the South
Domino Theory & SE Asia • Mao Zedong’s Communist Ideology spreads to Vietnam. • Ho Chi Minh leads North Viet Nam to unite with the South under Communism. • US aids the South
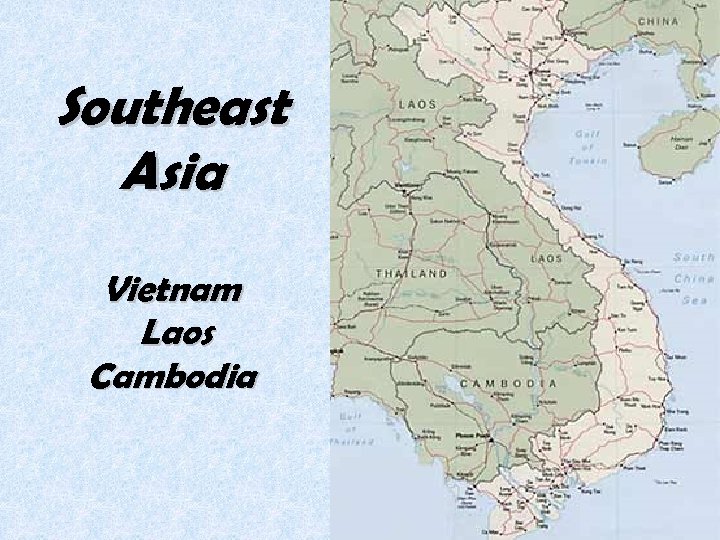 Southeast Asia Vietnam Laos Cambodia
Southeast Asia Vietnam Laos Cambodia
 Containing Communism in Southeast Asia • French occupied the area until 1954, when the Viet Minh drove them out. Eisenhower aided the non-communist south after French. • In 1961 Kennedy continued military aid to South amidst a civil war vs. North Vietnam • 1965 President Johnson, Kennedy’s successor vows contain Communism & not to “…lose Southeast Asia. ”
Containing Communism in Southeast Asia • French occupied the area until 1954, when the Viet Minh drove them out. Eisenhower aided the non-communist south after French. • In 1961 Kennedy continued military aid to South amidst a civil war vs. North Vietnam • 1965 President Johnson, Kennedy’s successor vows contain Communism & not to “…lose Southeast Asia. ”

 President Lyndon Baines Johnson Assumes presidency on November 22, 1963, the day President Kennedy was shot.
President Lyndon Baines Johnson Assumes presidency on November 22, 1963, the day President Kennedy was shot.
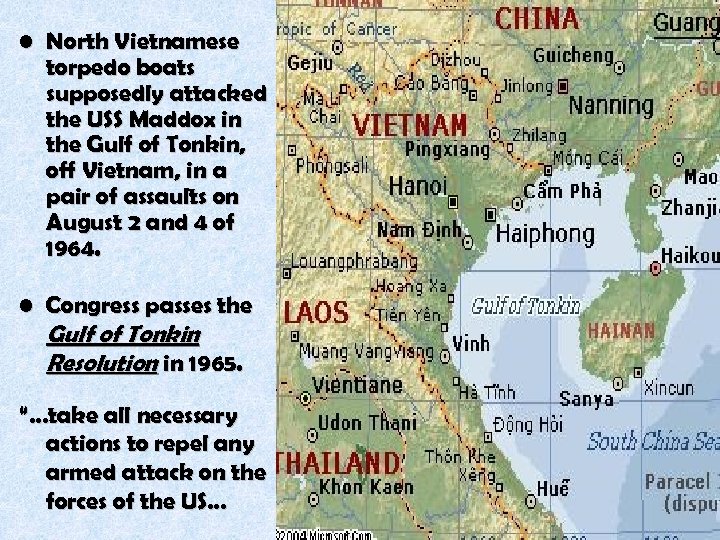 • North Vietnamese torpedo boats supposedly attacked the USS Maddox in the Gulf of Tonkin, off Vietnam, in a pair of assaults on August 2 and 4 of 1964. • Congress passes the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution in 1965. “…take all necessary actions to repel any armed attack on the forces of the US…
• North Vietnamese torpedo boats supposedly attacked the USS Maddox in the Gulf of Tonkin, off Vietnam, in a pair of assaults on August 2 and 4 of 1964. • Congress passes the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution in 1965. “…take all necessary actions to repel any armed attack on the forces of the US…
 Pres. Richard Nixon • NVA’s “Tet” offensive changes the war – 1968 - North Vietnam takes command. • Ends the war in Vietnam through policy of “Vietnamization” – turning over the war to the people of South Vietnam. • 1969 – First troops come home • 1972 – South cannot fight off the North &…
Pres. Richard Nixon • NVA’s “Tet” offensive changes the war – 1968 - North Vietnam takes command. • Ends the war in Vietnam through policy of “Vietnamization” – turning over the war to the people of South Vietnam. • 1969 – First troops come home • 1972 – South cannot fight off the North &…
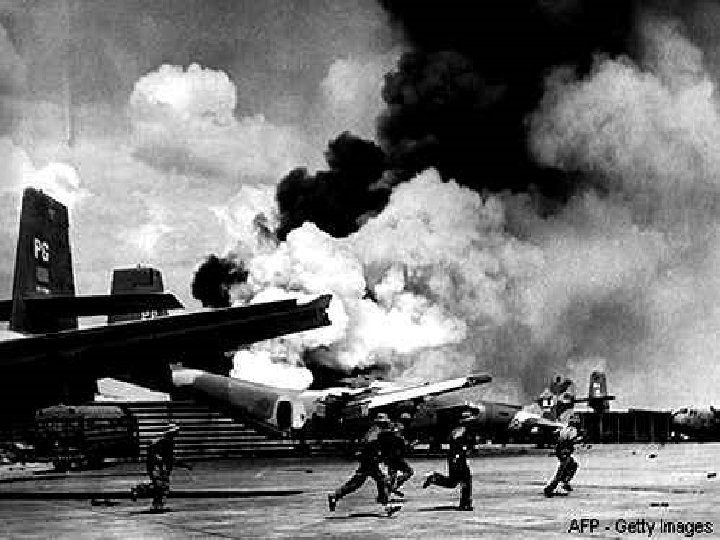 Saigon Falls to Viet Cong • On the last day of the Vietnam War… • When Saigon fell to the North Vietnamese Army…
Saigon Falls to Viet Cong • On the last day of the Vietnam War… • When Saigon fell to the North Vietnamese Army…
 The Fall of Saigon South Vietnamse civilians try to climb the wall of the U. S. Embassy In a desperate bid to board one of the last evacuation flights out of Saigon. August 29, 1975
The Fall of Saigon South Vietnamse civilians try to climb the wall of the U. S. Embassy In a desperate bid to board one of the last evacuation flights out of Saigon. August 29, 1975
 Ideological Changes After Vietnam • Nixon sees the problems of intervention. • Changes the “approach” toward the Soviets and the Chinese Communists. • Seeks to ‘engage’ enemies • “Keep friends close & enemies closer. ”
Ideological Changes After Vietnam • Nixon sees the problems of intervention. • Changes the “approach” toward the Soviets and the Chinese Communists. • Seeks to ‘engage’ enemies • “Keep friends close & enemies closer. ”
 Cold War in the 70 s • Nixon, Kissinger and “Realpolitik” -Be practical in negotiations with nations. -Evaluate the power of nations & ignore them if they are weak. -Confront strong nations, recognize strength, negotiate and engage militarily
Cold War in the 70 s • Nixon, Kissinger and “Realpolitik” -Be practical in negotiations with nations. -Evaluate the power of nations & ignore them if they are weak. -Confront strong nations, recognize strength, negotiate and engage militarily
 China and Russia • Successfully opened relations with Communist China for the first time since the Cold War began - Agrees that Taiwan is part of mainland China. - SALT I Treaty with Soviets Limit Numbers of ICBMs - Cold War still on, but now begins to engage rivals. - Sets stage for SALT II talks to further reduce nukes
China and Russia • Successfully opened relations with Communist China for the first time since the Cold War began - Agrees that Taiwan is part of mainland China. - SALT I Treaty with Soviets Limit Numbers of ICBMs - Cold War still on, but now begins to engage rivals. - Sets stage for SALT II talks to further reduce nukes
 Nixon the Diplomat With Zhao En Lai With Leonid Breznhev Détente – Be in contact with enemies to better understand them. Tries to ease Cold War tensions.
Nixon the Diplomat With Zhao En Lai With Leonid Breznhev Détente – Be in contact with enemies to better understand them. Tries to ease Cold War tensions.
 To Whose Advantage was Détente? • Soviet View of Détente is contact to delay agreements until they achieve their goal of expanding Communism worldwide. • American View of Détente is contact to look for Soviet weaknesses so as to gain agreements that allow democratically elected governments to exist.
To Whose Advantage was Détente? • Soviet View of Détente is contact to delay agreements until they achieve their goal of expanding Communism worldwide. • American View of Détente is contact to look for Soviet weaknesses so as to gain agreements that allow democratically elected governments to exist.
 President Carter • Hard line on human rights set détente back 4 years - Rejected “Realpolitik” - Soviet dissidents mistreated - Salt II stalled when Soviets invaded Afghanistan in 1979 - Boycotts Moscow Olympics
President Carter • Hard line on human rights set détente back 4 years - Rejected “Realpolitik” - Soviet dissidents mistreated - Salt II stalled when Soviets invaded Afghanistan in 1979 - Boycotts Moscow Olympics
 Carter’s Great Success Camp David Accords • Since 1948 Jews and Arabs have fought over the land known as Palestine. Both claim it as their birthright. • President Carter and Henry Kissinger’s efforts - “Shuttle Diplomacy” - brokered an agreement, signed at Camp David, Maryland. Anwar Sadat, President Carter and Menachem Begin
Carter’s Great Success Camp David Accords • Since 1948 Jews and Arabs have fought over the land known as Palestine. Both claim it as their birthright. • President Carter and Henry Kissinger’s efforts - “Shuttle Diplomacy” - brokered an agreement, signed at Camp David, Maryland. Anwar Sadat, President Carter and Menachem Begin
 Carter’s Great Failure • Iran Hostage Crisis 1979 – Islamic Revolution led by Ayatollah Khomeini • Demands former ruler, Shah be returned • Takes US Embassy and 52 Americans – holds them for 444 days
Carter’s Great Failure • Iran Hostage Crisis 1979 – Islamic Revolution led by Ayatollah Khomeini • Demands former ruler, Shah be returned • Takes US Embassy and 52 Americans – holds them for 444 days
 Ronald Reagan – The Ultimate Cold Warrior • Increases military spending – revives two old weapons systems – MX missile & B-1 Bomber. • Sees an opportunity to reopen détente with the Soviets – based on military strength. • Reverses Carter’s policies fights communism.
Ronald Reagan – The Ultimate Cold Warrior • Increases military spending – revives two old weapons systems – MX missile & B-1 Bomber. • Sees an opportunity to reopen détente with the Soviets – based on military strength. • Reverses Carter’s policies fights communism.
 Cold War in Central America • Nicaraguan Sandinistas - Communists according to Reagan, overthrow US backed government. - Contras – based in Honduras, resist Sandinistas with US aid • Granada – Reagan sends troops to stop a Cuba friendly gov’t. from taking over & protect US Medical students there.
Cold War in Central America • Nicaraguan Sandinistas - Communists according to Reagan, overthrow US backed government. - Contras – based in Honduras, resist Sandinistas with US aid • Granada – Reagan sends troops to stop a Cuba friendly gov’t. from taking over & protect US Medical students there.
 Reagan’s Detente • Convinces Europe not to help build Soviet pipeline – would have enabled Soviets to fund their expansion. • “Outspends” the Soviets – Their economy collapses • Strategic Defense Initiative – (Star Wars) A missile System to destroy incoming ICBM’s • INF (Intermediate Range Nuclear Forces) Treaty – Drops 2 types of nuclear weapons from the arsenals of US & Soviet Union – Allows inspections!
Reagan’s Detente • Convinces Europe not to help build Soviet pipeline – would have enabled Soviets to fund their expansion. • “Outspends” the Soviets – Their economy collapses • Strategic Defense Initiative – (Star Wars) A missile System to destroy incoming ICBM’s • INF (Intermediate Range Nuclear Forces) Treaty – Drops 2 types of nuclear weapons from the arsenals of US & Soviet Union – Allows inspections!
 Reagan & Gorbachev • Reagan’s stand resulted in Soviets’ not being able to “spend” with us. • Gorbachev makes changes to Soviet society and economy – Perestroika - Glasnost • Berlin Wall Comes down (November 1989 under 1 st President Bush • Cold War Ends
Reagan & Gorbachev • Reagan’s stand resulted in Soviets’ not being able to “spend” with us. • Gorbachev makes changes to Soviet society and economy – Perestroika - Glasnost • Berlin Wall Comes down (November 1989 under 1 st President Bush • Cold War Ends


