26170_coherent sources.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Coherent Sources
Coherent Sources
 Wavefront splitting Interferometer
Wavefront splitting Interferometer
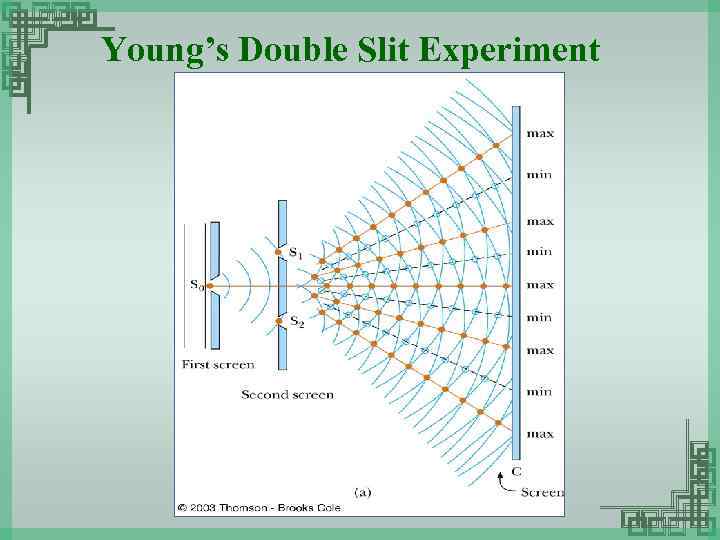 Young’s Double Slit Experiment
Young’s Double Slit Experiment
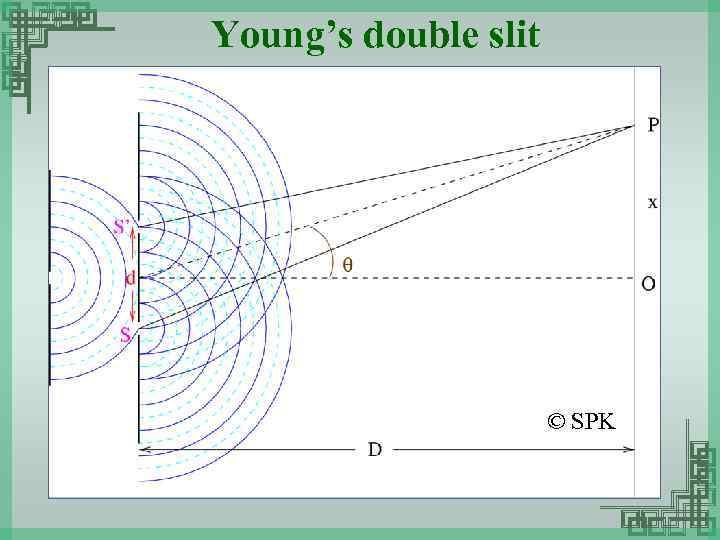 Young’s double slit © SPK
Young’s double slit © SPK
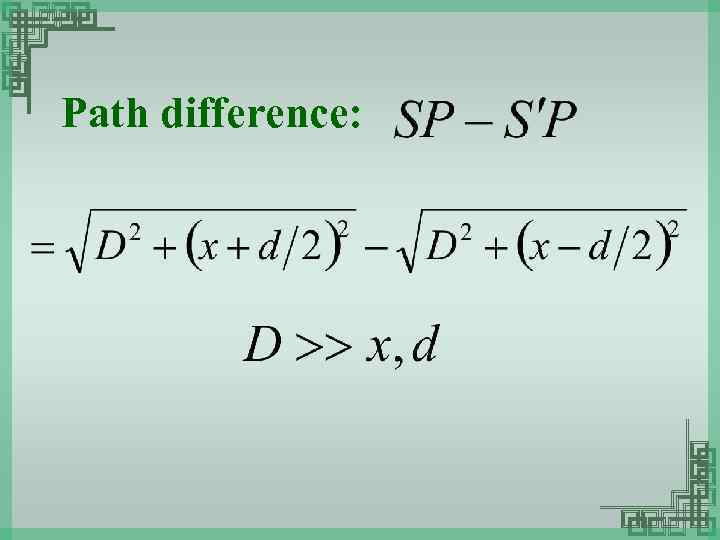 Path difference:
Path difference:
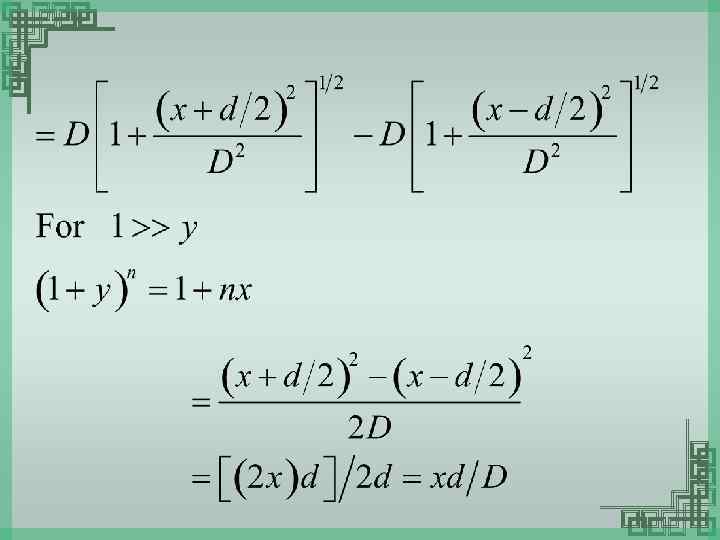
 For a bright fringe, For a dark fringe, m: any integer
For a bright fringe, For a dark fringe, m: any integer
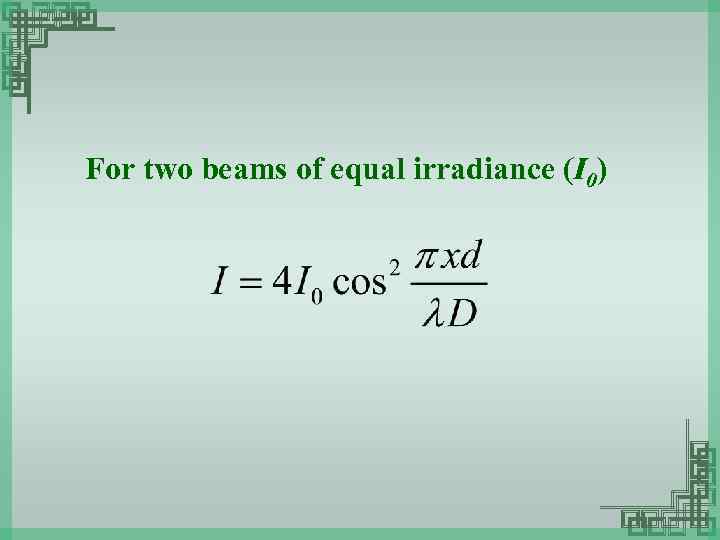 For two beams of equal irradiance (I 0)
For two beams of equal irradiance (I 0)
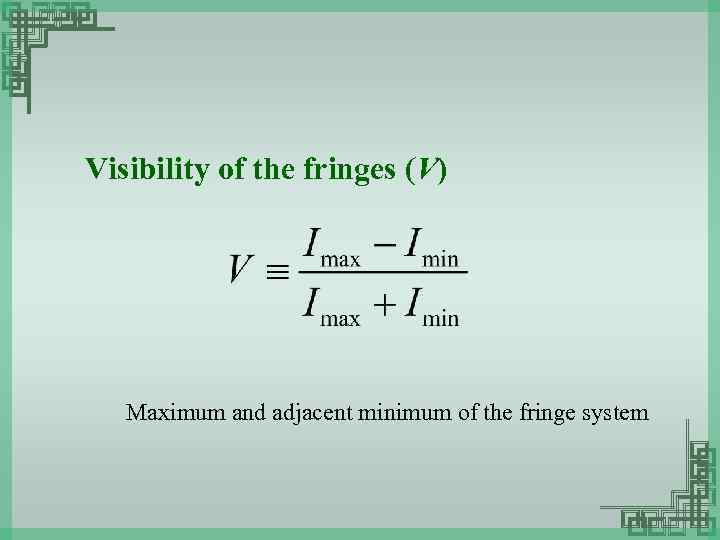 Visibility of the fringes (V) Maximum and adjacent minimum of the fringe system
Visibility of the fringes (V) Maximum and adjacent minimum of the fringe system
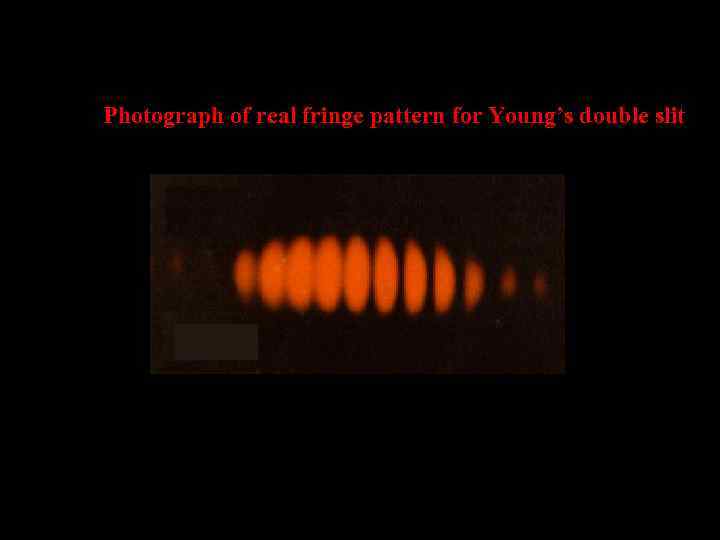 Photograph of real fringe pattern for Young’s double slit
Photograph of real fringe pattern for Young’s double slit
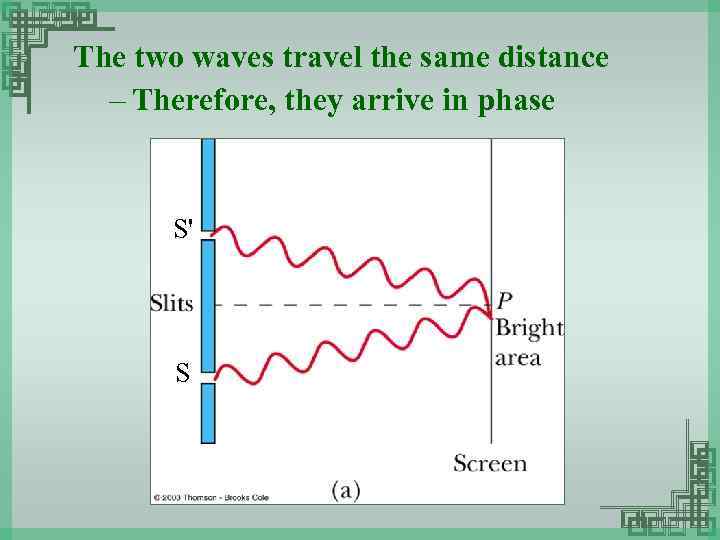 The two waves travel the same distance – Therefore, they arrive in phase S' S
The two waves travel the same distance – Therefore, they arrive in phase S' S
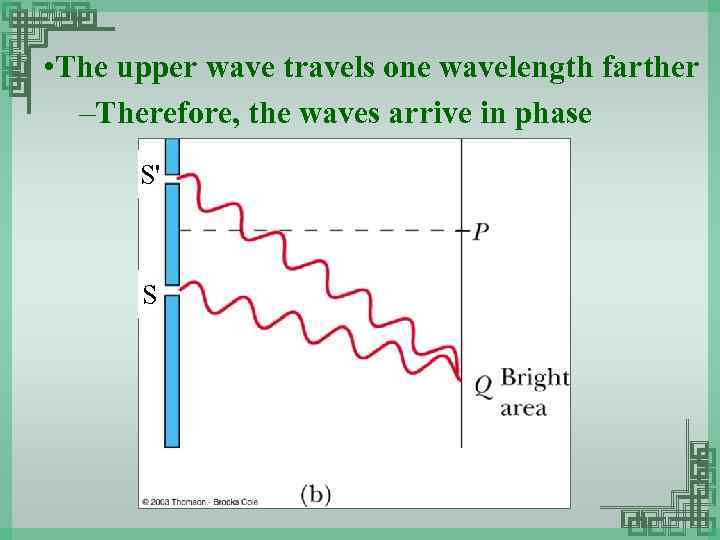 • The upper wave travels one wavelength farther –Therefore, the waves arrive in phase S' S
• The upper wave travels one wavelength farther –Therefore, the waves arrive in phase S' S
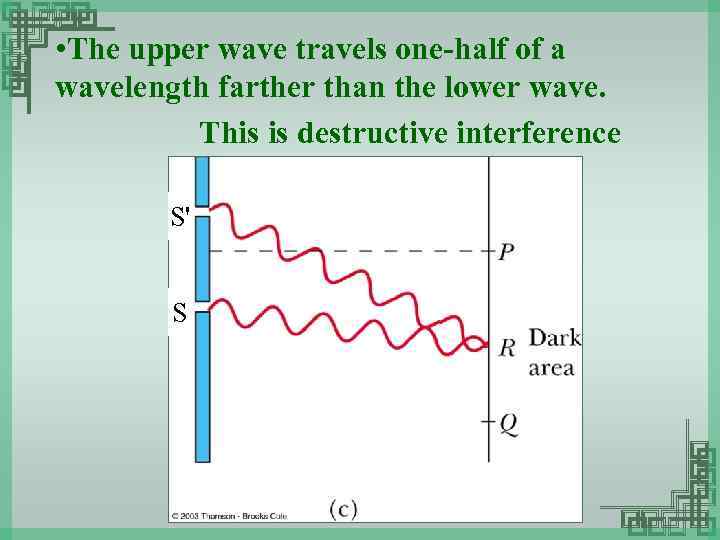 • The upper wave travels one-half of a wavelength farther than the lower wave. This is destructive interference S' S
• The upper wave travels one-half of a wavelength farther than the lower wave. This is destructive interference S' S
 Uses for Young’s Double Slit Experiment • Young’s Double Slit Experiment provides a method for measuring wavelength of the light • This experiment gave the wave model of light a great deal of credibility.
Uses for Young’s Double Slit Experiment • Young’s Double Slit Experiment provides a method for measuring wavelength of the light • This experiment gave the wave model of light a great deal of credibility.
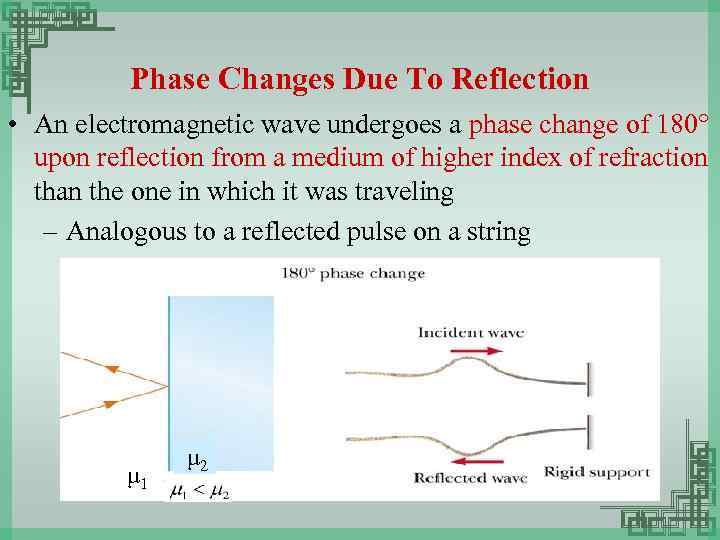 Phase Changes Due To Reflection • An electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 180° upon reflection from a medium of higher index of refraction than the one in which it was traveling – Analogous to a reflected pulse on a string μ 1 μ 2
Phase Changes Due To Reflection • An electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 180° upon reflection from a medium of higher index of refraction than the one in which it was traveling – Analogous to a reflected pulse on a string μ 1 μ 2
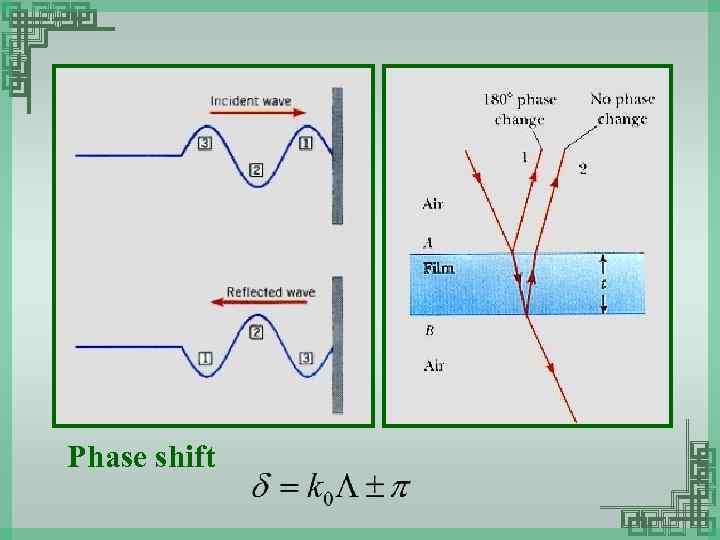 Phase shift
Phase shift
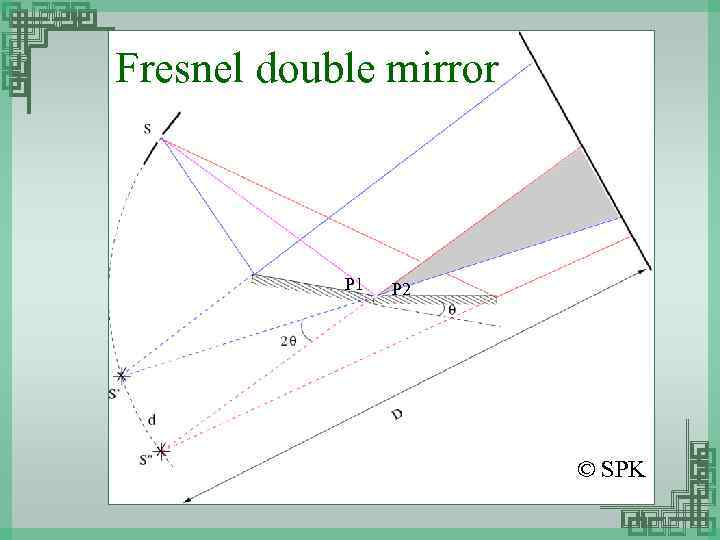 Fresnel double mirror P 1 P 2 © SPK
Fresnel double mirror P 1 P 2 © SPK
 Problem In a Fresnel mirror the angle between the mirrors a=12’. The distance r= 10 cm and b=130 cm. Find (a) The fringe width on the screen and the number of possible maxima. (b) the shift of the interference pattern on the screen when the slit S is displaced by dl=1 mm along the arc of radius r about the center O. (c) The maximum width of the source slit at which the fringe pattern on the screen can still be observed sufficiently sharp.
Problem In a Fresnel mirror the angle between the mirrors a=12’. The distance r= 10 cm and b=130 cm. Find (a) The fringe width on the screen and the number of possible maxima. (b) the shift of the interference pattern on the screen when the slit S is displaced by dl=1 mm along the arc of radius r about the center O. (c) The maximum width of the source slit at which the fringe pattern on the screen can still be observed sufficiently sharp.
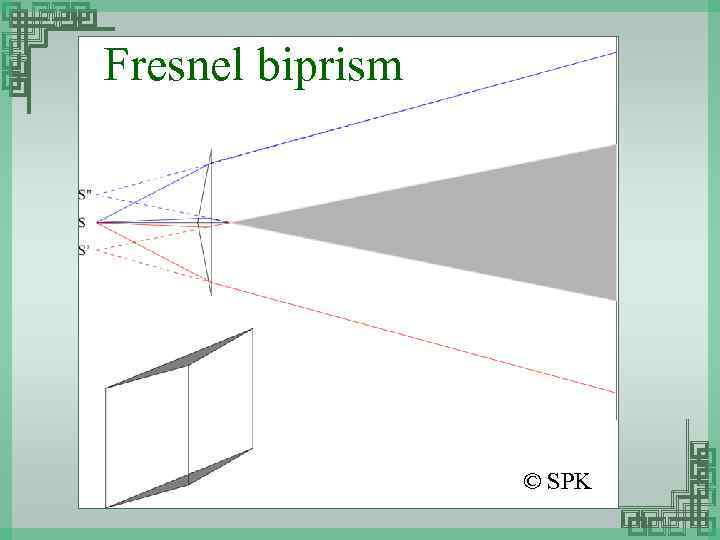 Fresnel biprism © SPK
Fresnel biprism © SPK
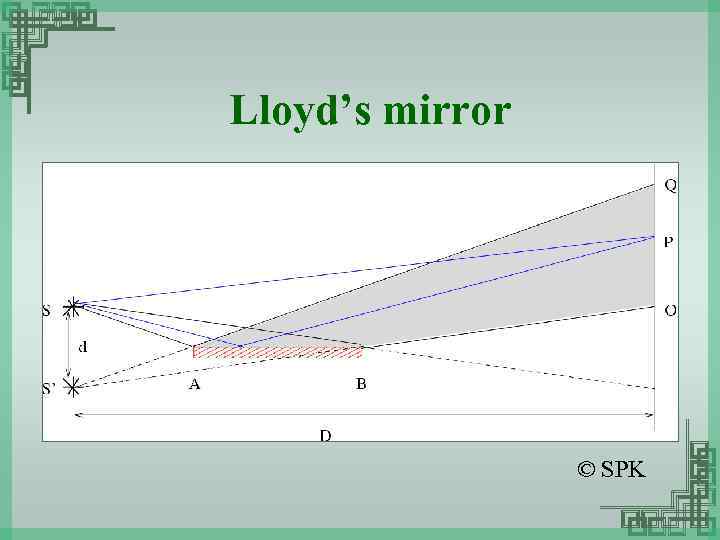 Lloyd’s mirror © SPK
Lloyd’s mirror © SPK
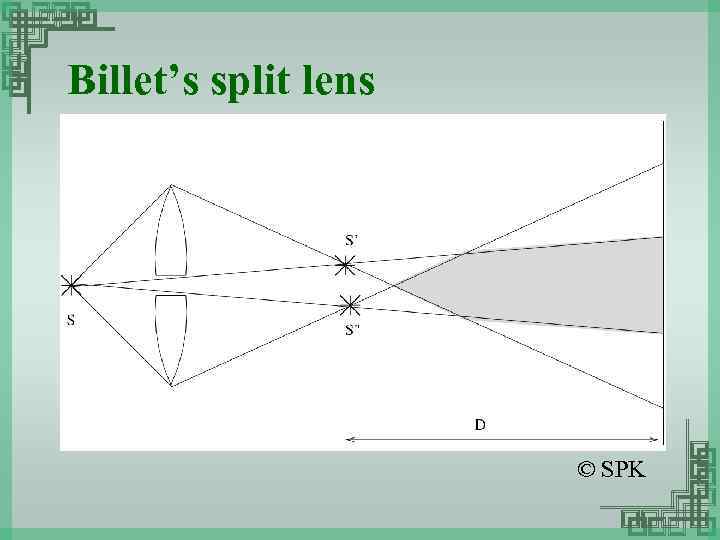 Billet’s split lens © SPK
Billet’s split lens © SPK
 Wavefront splitting interferometers • Young’s double slit • Fresnel double mirror • Fresnel double prism • Lloyd’s mirror
Wavefront splitting interferometers • Young’s double slit • Fresnel double mirror • Fresnel double prism • Lloyd’s mirror
 Division of Amplitude
Division of Amplitude
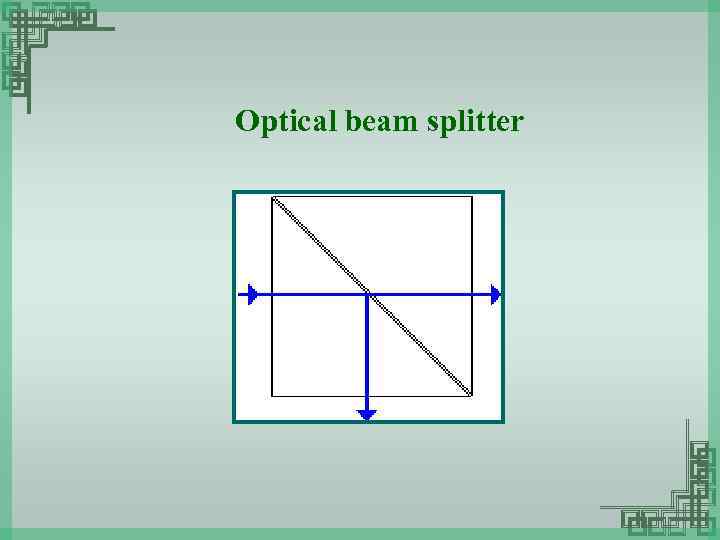 Optical beam splitter
Optical beam splitter
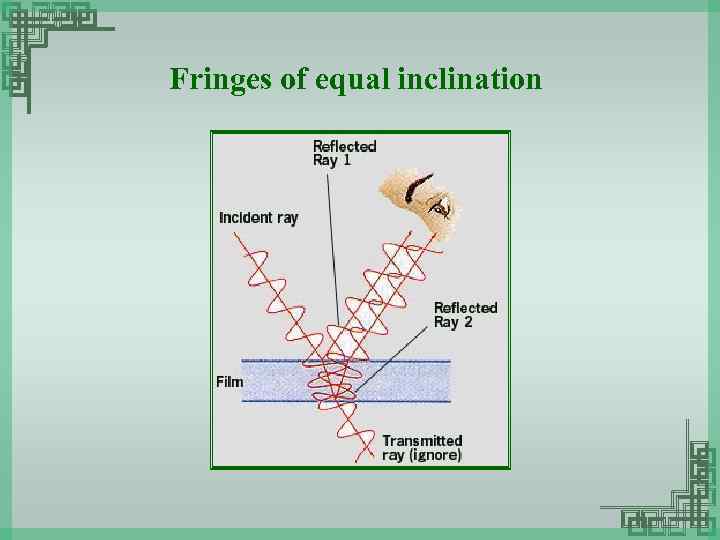 Fringes of equal inclination
Fringes of equal inclination
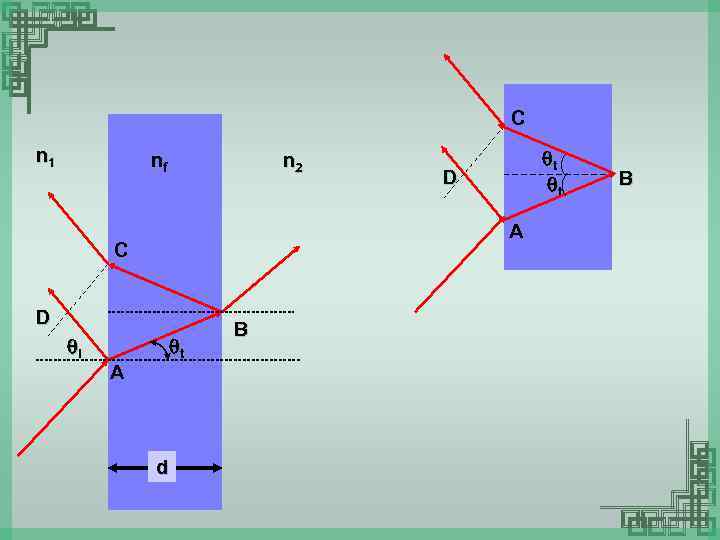 C n 1 nf n 2 D A C D i t t t A d B B
C n 1 nf n 2 D A C D i t t t A d B B
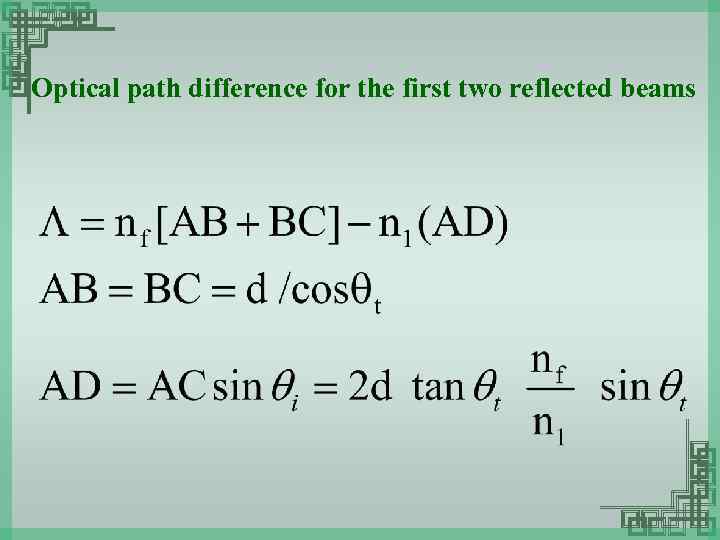 Optical path difference for the first two reflected beams
Optical path difference for the first two reflected beams
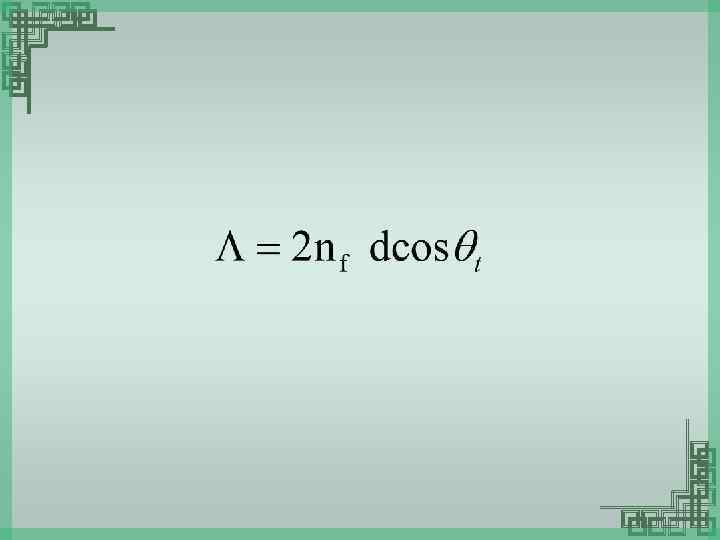
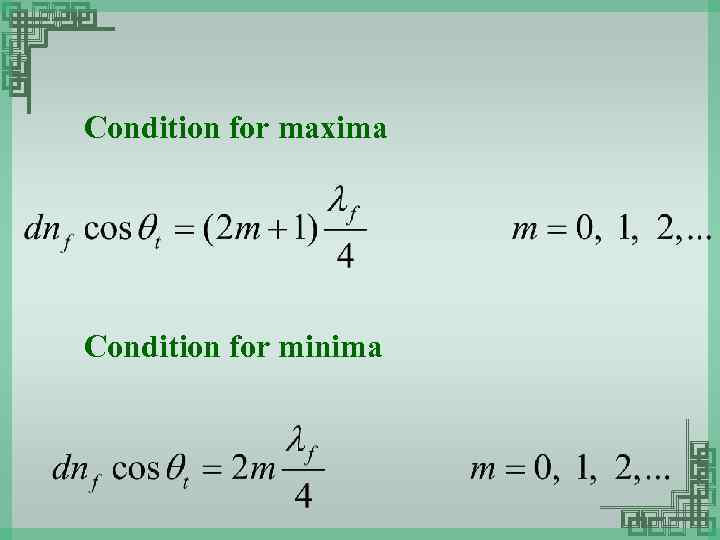 Condition for maxima Condition for minima
Condition for maxima Condition for minima
 Fringes of equal thickness Constant height contour of a topographial map
Fringes of equal thickness Constant height contour of a topographial map
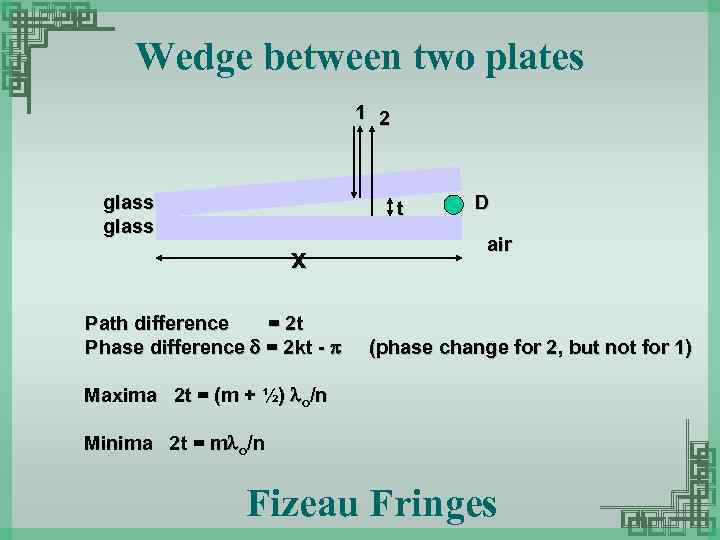 Wedge between two plates 1 2 glass t x Path difference = 2 t Phase difference = 2 kt - D air (phase change for 2, but not for 1) Maxima 2 t = (m + ½) o/n Minima 2 t = m o/n Fizeau Fringes
Wedge between two plates 1 2 glass t x Path difference = 2 t Phase difference = 2 kt - D air (phase change for 2, but not for 1) Maxima 2 t = (m + ½) o/n Minima 2 t = m o/n Fizeau Fringes
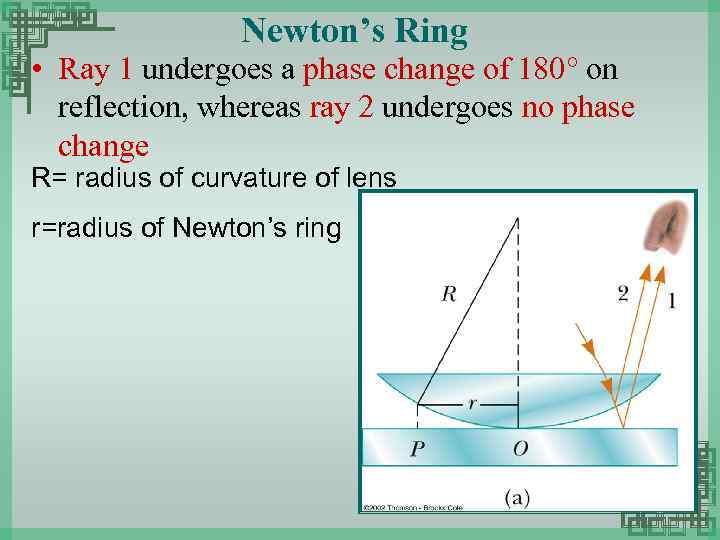 Newton’s Ring • Ray 1 undergoes a phase change of 180 on reflection, whereas ray 2 undergoes no phase change R= radius of curvature of lens r=radius of Newton’s ring
Newton’s Ring • Ray 1 undergoes a phase change of 180 on reflection, whereas ray 2 undergoes no phase change R= radius of curvature of lens r=radius of Newton’s ring
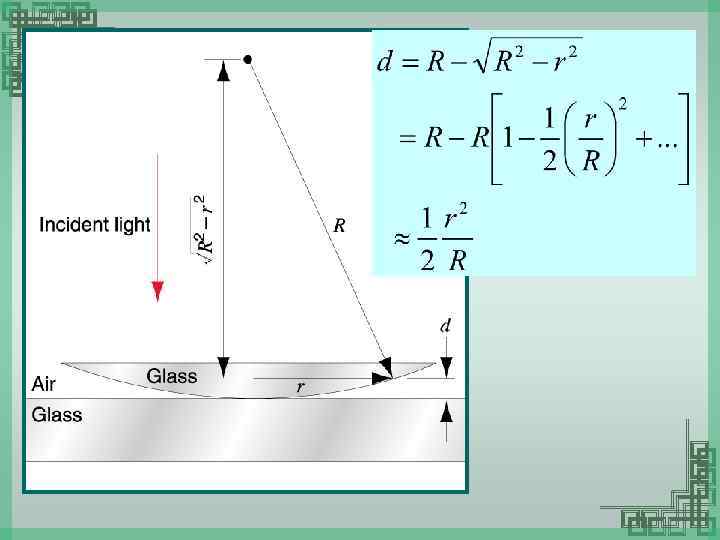

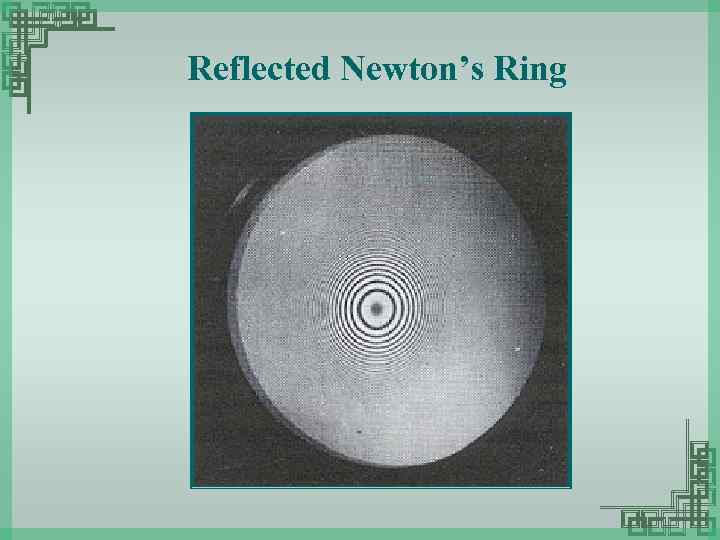 Reflected Newton’s Ring
Reflected Newton’s Ring
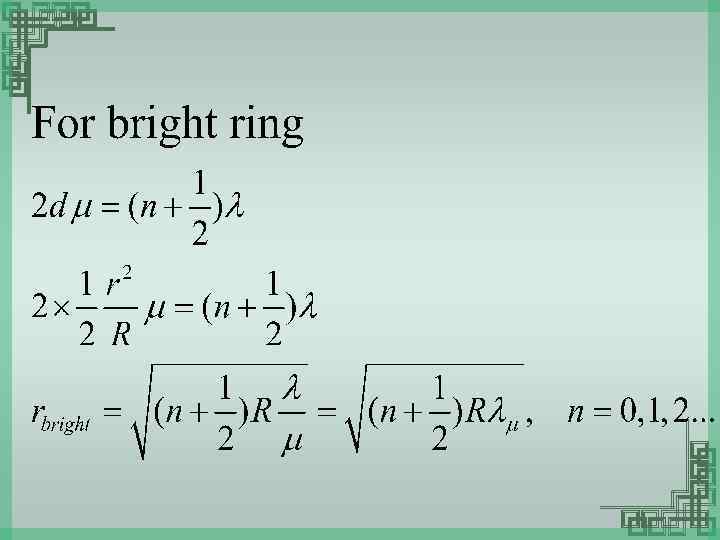
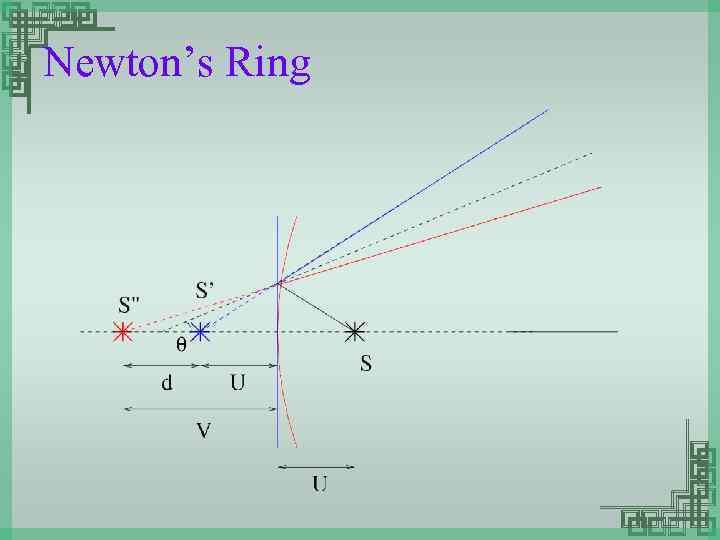 Newton’s Ring
Newton’s Ring
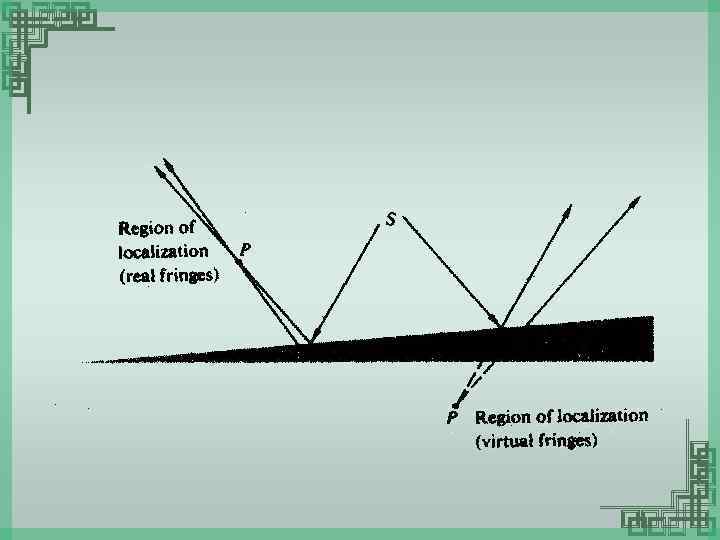
 Types of localization of fringes
Types of localization of fringes
 Interference fringes Real Virtual Localized Non-localized
Interference fringes Real Virtual Localized Non-localized
 Localized fringe ØObserved over particular surface ØResult of extended source
Localized fringe ØObserved over particular surface ØResult of extended source
 Non-localized fringe ØExists everywhere ØResult of point/line source
Non-localized fringe ØExists everywhere ØResult of point/line source
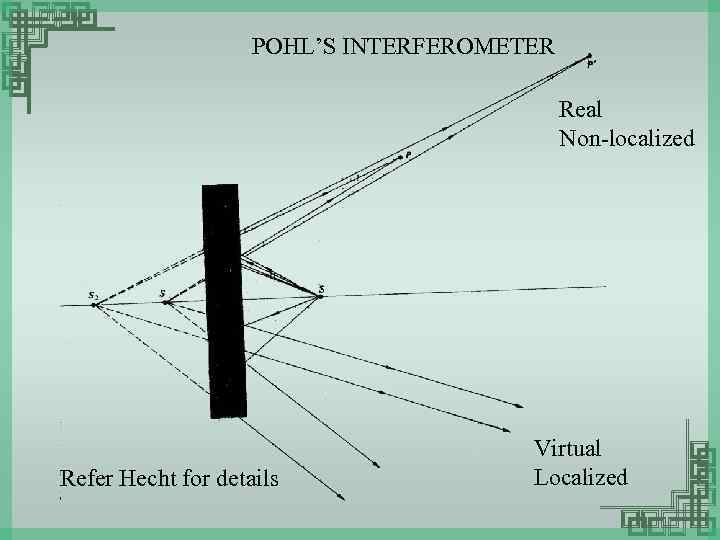 POHL’S INTERFEROMETER Real Non-localized Refer Hecht for details Virtual Localized
POHL’S INTERFEROMETER Real Non-localized Refer Hecht for details Virtual Localized
 Problem The width of a certain spectral line at 500 nm is 2× 10 -2 nm. Approximately what is the largest path difference for which the interference fringes produces by the light are clearly visible?
Problem The width of a certain spectral line at 500 nm is 2× 10 -2 nm. Approximately what is the largest path difference for which the interference fringes produces by the light are clearly visible?


