1d6c44cb377fca2ae982b78790506e73.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Cognitive Radios for Open Access to Spectrum Narayan Mandayam Christopher Rose Predrag Spasojevic Roy Yates (in partnership with Lucent Technologies) Rutgers University www. winlab. rutgers. edu Email: narayan@winlab. rutgers. edu
Cognitive Radios for Open Access to Spectrum Narayan Mandayam Christopher Rose Predrag Spasojevic Roy Yates (in partnership with Lucent Technologies) Rutgers University www. winlab. rutgers. edu Email: narayan@winlab. rutgers. edu
 Project Motivation Triumph of Technology vs. Triumph of Economics • What everyone agrees on: – Spectrum use is inefficient – FCC licensing has yielded false scarcity • The Spectrum Debate: – Open Access (Commons) • [Noam, Benkler, Shepard, Reed …] • Agile wideband radios will dynamically share a commons – Spectrum Property Rights • [Coase, Hazlett, Faulhaber+Farber] • Owners can buy/sell/trade spectrum • Flexible use, flexible technology, flexible divisibility, transferability • A spectrum market will (by the force of economics) yield an efficient solution
Project Motivation Triumph of Technology vs. Triumph of Economics • What everyone agrees on: – Spectrum use is inefficient – FCC licensing has yielded false scarcity • The Spectrum Debate: – Open Access (Commons) • [Noam, Benkler, Shepard, Reed …] • Agile wideband radios will dynamically share a commons – Spectrum Property Rights • [Coase, Hazlett, Faulhaber+Farber] • Owners can buy/sell/trade spectrum • Flexible use, flexible technology, flexible divisibility, transferability • A spectrum market will (by the force of economics) yield an efficient solution
 The Open Access Conundrum • Systems of end-user devices • Technology Panacea – Spread spectrum, UWB, MIMO – Short range communications – Ad hoc multi-hop mesh networks • Evidence: success of 802. 11 vs. 3 G • Minor technical rules for transceivers – power, spreading • Technical arguments against Open Access – Partially developed theory • ad hoc network capacity, with/without mobility • IT relay and interference channel – Infant technology • UWB, antenna arrays • Transmitter agility – Technology not separable from user assumptions • Capabilities of technology vary with cooperation
The Open Access Conundrum • Systems of end-user devices • Technology Panacea – Spread spectrum, UWB, MIMO – Short range communications – Ad hoc multi-hop mesh networks • Evidence: success of 802. 11 vs. 3 G • Minor technical rules for transceivers – power, spreading • Technical arguments against Open Access – Partially developed theory • ad hoc network capacity, with/without mobility • IT relay and interference channel – Infant technology • UWB, antenna arrays • Transmitter agility – Technology not separable from user assumptions • Capabilities of technology vary with cooperation
 Technology for Enabling Open Access? Research themes that have emerged from adhoc/sensor networks research: • Hierarchical Architecture wins – Capacity scaling, energy efficiency, increases lifetimes, facilitates discovery • Cooperation wins – Fundamental performance limits via information theoretic relay and broadcast channels • “Global” awareness and coordination wins – Space, time and frequency awareness and coordination beyond local measurements
Technology for Enabling Open Access? Research themes that have emerged from adhoc/sensor networks research: • Hierarchical Architecture wins – Capacity scaling, energy efficiency, increases lifetimes, facilitates discovery • Cooperation wins – Fundamental performance limits via information theoretic relay and broadcast channels • “Global” awareness and coordination wins – Space, time and frequency awareness and coordination beyond local measurements
 Technology for Enabling Open Access? Require radios that can : – – Discover Cooperate Collaborate Self-Organize into hierarchical networks • Agility is necessary at every layer of the “protocol stack” • But cannot yet predict environments The Answer? “Cognitive Radios”
Technology for Enabling Open Access? Require radios that can : – – Discover Cooperate Collaborate Self-Organize into hierarchical networks • Agility is necessary at every layer of the “protocol stack” • But cannot yet predict environments The Answer? “Cognitive Radios”
 Cognitive Radios for Enabling Open Access POOF! Let there be cognitive radios! (let Bryan worry about details) Then What? ? ? • Discovery strategies for available spectrum – Algorithms and protocols for frequency selection, coordination and cooperation • Coding strategies for efficient sharing – Cooperative diversity and coding for increased spectrum utilization • Information strategies for efficient cooperation – “Spectrum Servers” to advise/mediate sharing • Negotiation strategies for situations of conflict – Pricing and game theoretic strategies to promote cooperation • Domination strategies for situations of conflict – Spectrum warfare with agile waveforms
Cognitive Radios for Enabling Open Access POOF! Let there be cognitive radios! (let Bryan worry about details) Then What? ? ? • Discovery strategies for available spectrum – Algorithms and protocols for frequency selection, coordination and cooperation • Coding strategies for efficient sharing – Cooperative diversity and coding for increased spectrum utilization • Information strategies for efficient cooperation – “Spectrum Servers” to advise/mediate sharing • Negotiation strategies for situations of conflict – Pricing and game theoretic strategies to promote cooperation • Domination strategies for situations of conflict – Spectrum warfare with agile waveforms
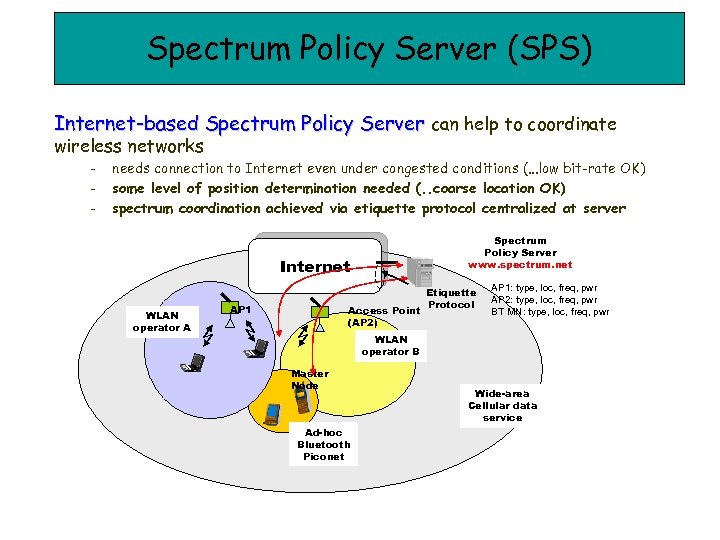 Spectrum Policy Server (SPS) Internet-based Spectrum Policy Server can help to coordinate wireless networks - needs connection to Internet even under congested conditions (. . . low bit-rate OK) some level of position determination needed (. . coarse location OK) spectrum coordination achieved via etiquette protocol centralized at server Spectrum Policy Server www. spectrum. net Internet WLAN operator A AP 1 Access Point (AP 2) Etiquette Protocol AP 1: type, loc, freq, pwr AP 2: type, loc, freq, pwr BT MN: type, loc, freq, pwr WLAN operator B Master Node Ad-hoc Bluetooth Piconet Wide-area Cellular data service
Spectrum Policy Server (SPS) Internet-based Spectrum Policy Server can help to coordinate wireless networks - needs connection to Internet even under congested conditions (. . . low bit-rate OK) some level of position determination needed (. . coarse location OK) spectrum coordination achieved via etiquette protocol centralized at server Spectrum Policy Server www. spectrum. net Internet WLAN operator A AP 1 Access Point (AP 2) Etiquette Protocol AP 1: type, loc, freq, pwr AP 2: type, loc, freq, pwr BT MN: type, loc, freq, pwr WLAN operator B Master Node Ad-hoc Bluetooth Piconet Wide-area Cellular data service
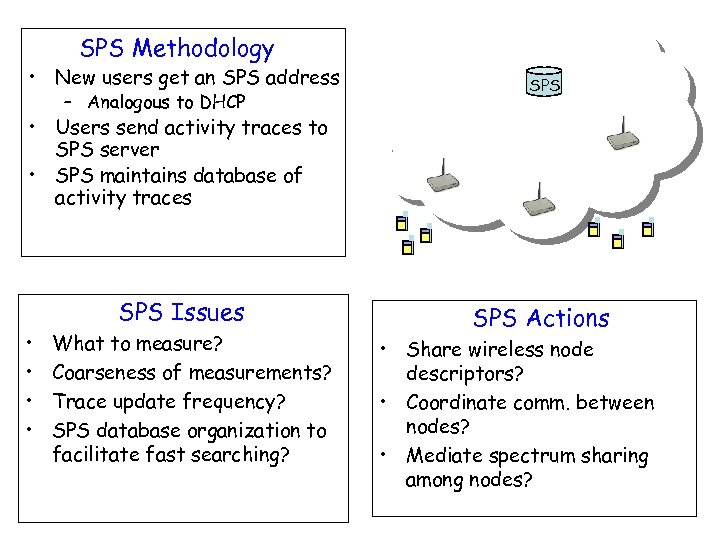 SPS Methodology • New users get an SPS address – Analogous to DHCP SPS • Users send activity traces to SPS server • SPS maintains database of activity traces SPS Issues • • What to measure? Coarseness of measurements? Trace update frequency? SPS database organization to facilitate fast searching? SPS Actions • Share wireless node descriptors? • Coordinate comm. between nodes? • Mediate spectrum sharing among nodes?
SPS Methodology • New users get an SPS address – Analogous to DHCP SPS • Users send activity traces to SPS server • SPS maintains database of activity traces SPS Issues • • What to measure? Coarseness of measurements? Trace update frequency? SPS database organization to facilitate fast searching? SPS Actions • Share wireless node descriptors? • Coordinate comm. between nodes? • Mediate spectrum sharing among nodes?
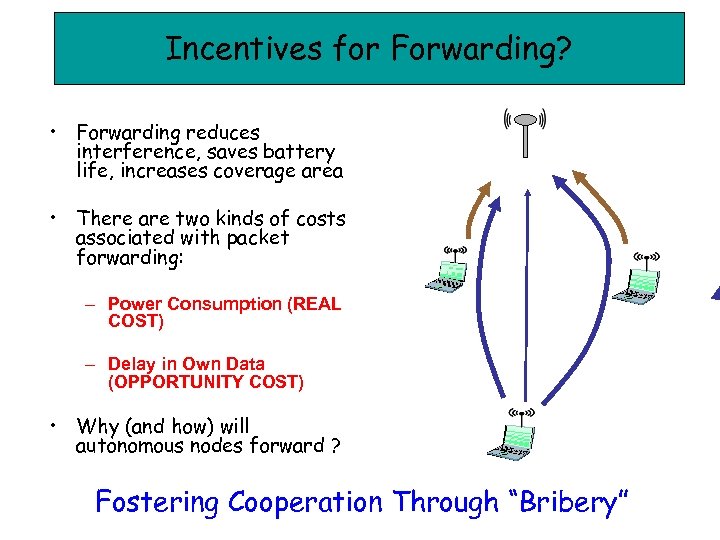 Incentives for Forwarding? • Forwarding reduces interference, saves battery life, increases coverage area • There are two kinds of costs associated with packet forwarding: – Power Consumption (REAL COST) – Delay in Own Data (OPPORTUNITY COST) • Why (and how) will autonomous nodes forward ? Fostering Cooperation Through “Bribery”
Incentives for Forwarding? • Forwarding reduces interference, saves battery life, increases coverage area • There are two kinds of costs associated with packet forwarding: – Power Consumption (REAL COST) – Delay in Own Data (OPPORTUNITY COST) • Why (and how) will autonomous nodes forward ? Fostering Cooperation Through “Bribery”
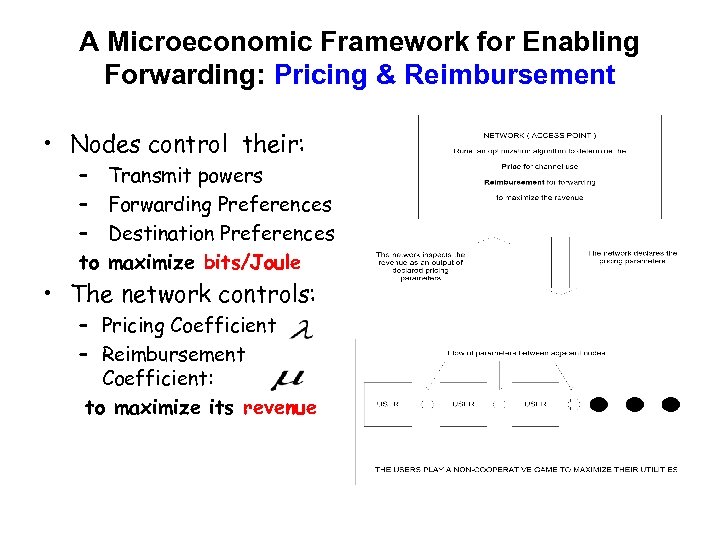 A Microeconomic Framework for Enabling Forwarding: Pricing & Reimbursement • Nodes control their: – – – to Transmit powers Forwarding Preferences Destination Preferences maximize bits/Joule • The network controls: – Pricing Coefficient – Reimbursement Coefficient: to maximize its revenue
A Microeconomic Framework for Enabling Forwarding: Pricing & Reimbursement • Nodes control their: – – – to Transmit powers Forwarding Preferences Destination Preferences maximize bits/Joule • The network controls: – Pricing Coefficient – Reimbursement Coefficient: to maximize its revenue
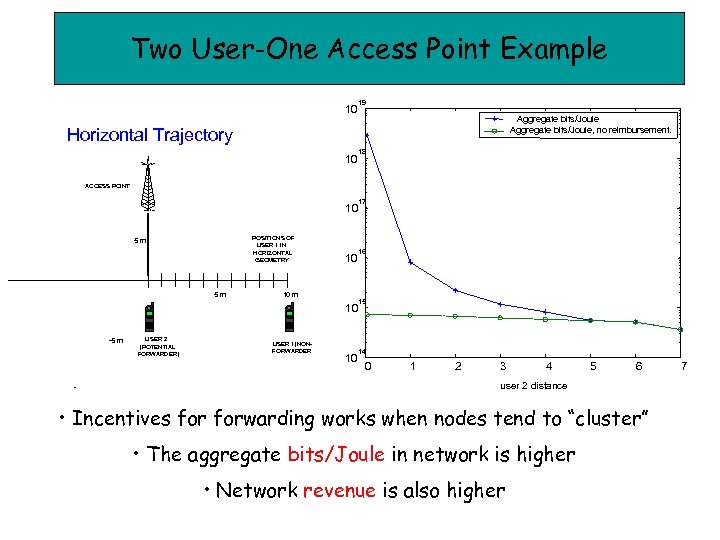 Two User-One Access Point Example 10 19 Aggregate bits/Joule, no reimbursement. Horizontal Trajectory 10 18 ACCESS POINT 10 Radio tower POSITIONS OF USER 1 IN HORIZONTAL GEOMETRY 5 m 5 m 10 10 m 10 -5 m - USER 2 (POTENTIAL FORWARDER) USER 1(NONFORWARDER) 10 17 16 15 14 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 user 2 distance • Incentives forwarding works when nodes tend to “cluster” • The aggregate bits/Joule in network is higher • Network revenue is also higher 7
Two User-One Access Point Example 10 19 Aggregate bits/Joule, no reimbursement. Horizontal Trajectory 10 18 ACCESS POINT 10 Radio tower POSITIONS OF USER 1 IN HORIZONTAL GEOMETRY 5 m 5 m 10 10 m 10 -5 m - USER 2 (POTENTIAL FORWARDER) USER 1(NONFORWARDER) 10 17 16 15 14 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 user 2 distance • Incentives forwarding works when nodes tend to “cluster” • The aggregate bits/Joule in network is higher • Network revenue is also higher 7
 What You Learned in Kindergarten The World Is A Rough Place • Everybody wants what they want – Greed is the norm • The Golden Rule – Be Polite – Play Nice • The REAL Golden Rule – – Be aware of your surroundings Develop a good left hook Bruises are bad Forgiveness is divine (when you have a good left hook)
What You Learned in Kindergarten The World Is A Rough Place • Everybody wants what they want – Greed is the norm • The Golden Rule – Be Polite – Play Nice • The REAL Golden Rule – – Be aware of your surroundings Develop a good left hook Bruises are bad Forgiveness is divine (when you have a good left hook)
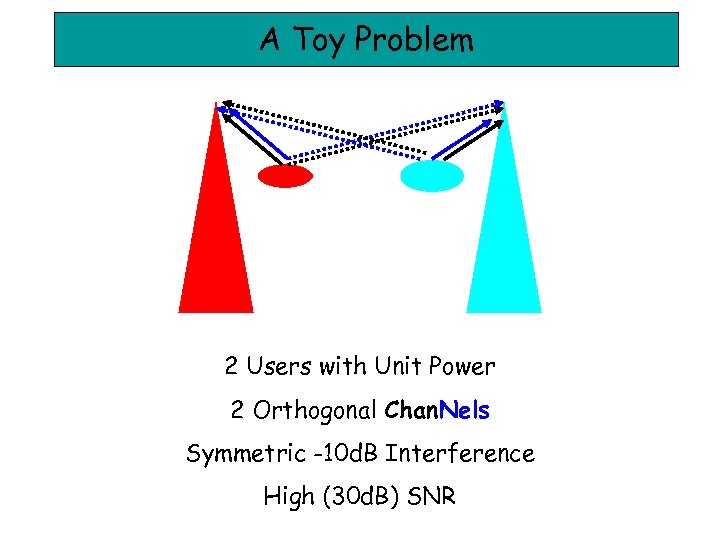 A Toy Problem 2 Users with Unit Power 2 Orthogonal Chan. Nels Symmetric -10 d. B Interference High (30 d. B) SNR
A Toy Problem 2 Users with Unit Power 2 Orthogonal Chan. Nels Symmetric -10 d. B Interference High (30 d. B) SNR
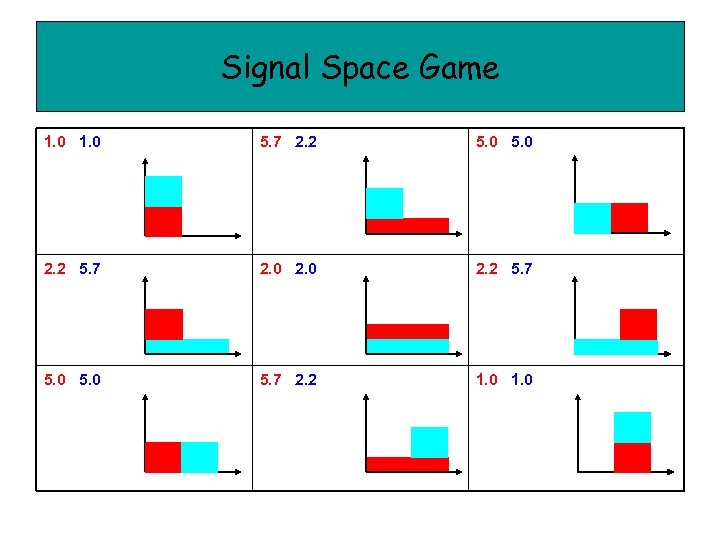 Signal Space Game 1. 0 5. 7 2. 2 5. 0 2. 2 5. 7 2. 0 2. 2 5. 7 5. 0 5. 7 2. 2 1. 0
Signal Space Game 1. 0 5. 7 2. 2 5. 0 2. 2 5. 7 2. 0 2. 2 5. 7 5. 0 5. 7 2. 2 1. 0
 Preliminary Results If Better Performers Survive in Marketplace… • Adaptive Policy – tit for tat • Even Better – tit for tat with random start – forgiveness is divine • Use Genetic Algorithms – evolve against chosen policies – evolve against evolving policies
Preliminary Results If Better Performers Survive in Marketplace… • Adaptive Policy – tit for tat • Even Better – tit for tat with random start – forgiveness is divine • Use Genetic Algorithms – evolve against chosen policies – evolve against evolving policies
 Evaluation of Cognitive Approaches • Capacity performance – Information rates, spectral efficiency, BER, FER, outage Efficiency • Cost performance – Hardware complexity – Software complexity • Emulation of large-scale networks of cognitive radios – ORBIT Testbed – Emergent behavior Hardware Complexity Agile radio Spectrum server Protocol Complexity Pricing collaboration Cognitive protocols Coded cooperation
Evaluation of Cognitive Approaches • Capacity performance – Information rates, spectral efficiency, BER, FER, outage Efficiency • Cost performance – Hardware complexity – Software complexity • Emulation of large-scale networks of cognitive radios – ORBIT Testbed – Emergent behavior Hardware Complexity Agile radio Spectrum server Protocol Complexity Pricing collaboration Cognitive protocols Coded cooperation


