9bce33a888e0ac5b0701a9afd28fbcaf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
Cognitive Metrics for the Management of Model-based Software Development Reuven Gallant, Yehuda Badihi, Hagai Sugarman Jerusalem College of Technology-Machon Lev JCT
Why are managers afraid of model-based development? It sounds good notation method/process tool

Why are managers afraid of model-based development?
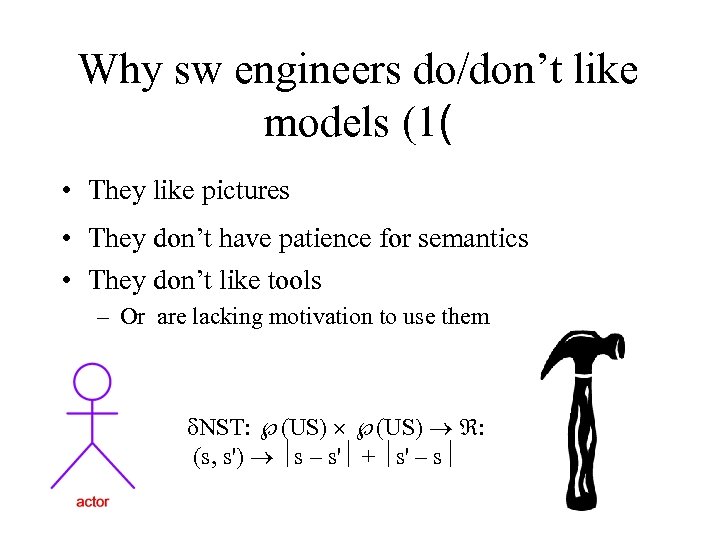
Why sw engineers do/don’t like models (1( • They like pictures • They don’t have patience for semantics • They don’t like tools – Or are lacking motivation to use them d. NST: Ã(US) ´ Ã(US) ® : (s, s') ® ½s – s'½ + ½s' – s½

Is a picture worth 1000 words? “To set the alarm , the key must be inserted into the lock , turned anti clockwise , and held for at least half a second. “To reset the alarm , the key must be inserted into the lock and turned clockwise. The alarm will be deactivated immediately. ”
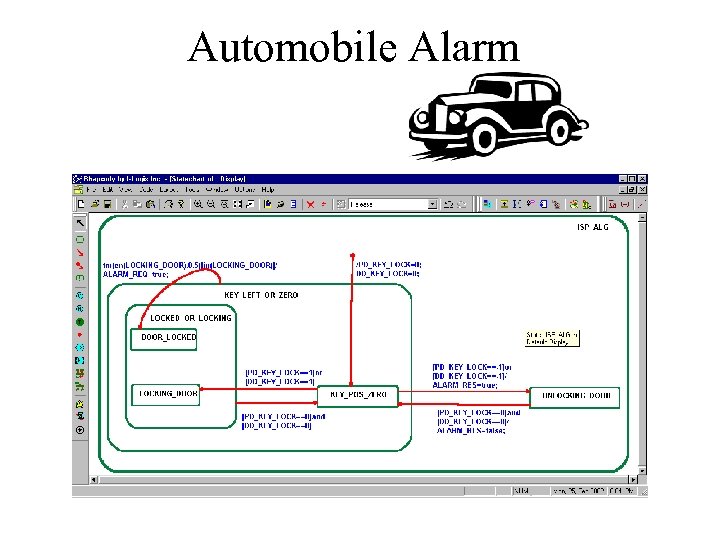
Automobile Alarm

Why sw engineers do/don’t like models (2)

Key Characteristics of Engineering Models • • • Abstraction Understandability Accuracy Predictiveness Inexpensive Brian Selic, “The Pragmatics of Model-Driven Development, ” IEEE Software, Sept. /Oct. 2003.

Where measurements can help us manage model-based development • • Tool Evaluation People Evaluation Training Evaluation Model Evaluation

Metrics must be simple and easy to automate Fenton N. and Neil M. (2000). Software Metrics: a Roadmap. Future of Software Engineering. Anthony Finkelstein Ed. , ACM, 359 -370.
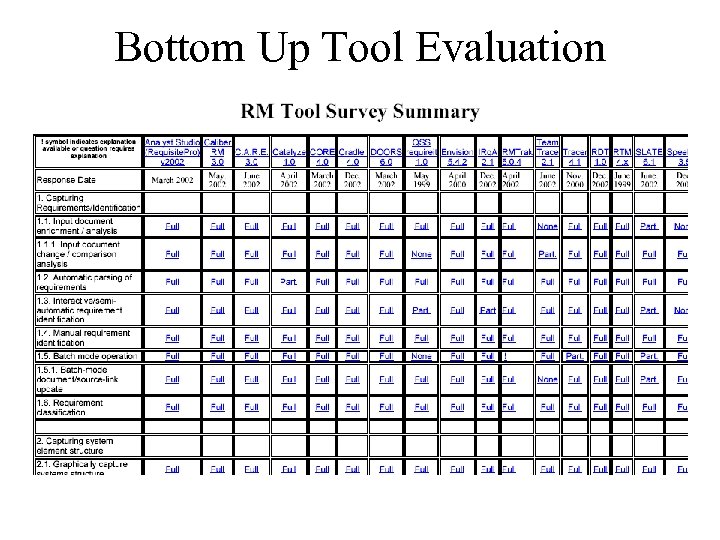
Bottom Up Tool Evaluation
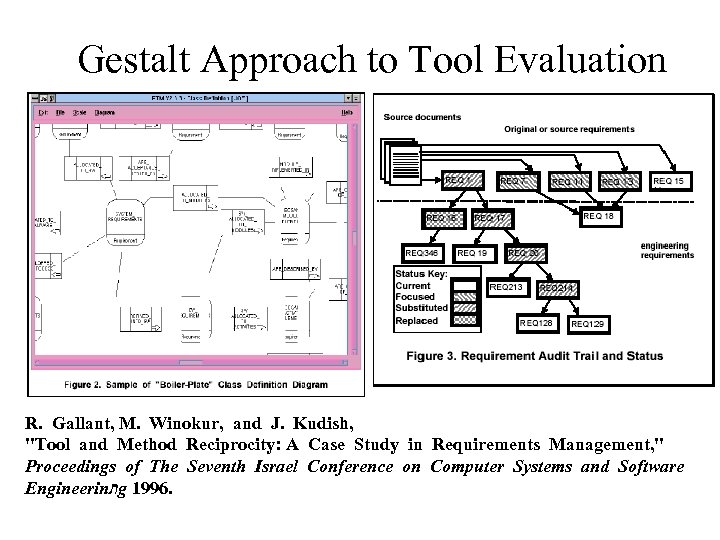
Gestalt Approach to Tool Evaluation R. Gallant, M. Winokur, and J. Kudish, "Tool and Method Reciprocity: A Case Study in Requirements Management, " Proceedings of The Seventh Israel Conference on Computer Systems and Software Engineerin ת g 1996.
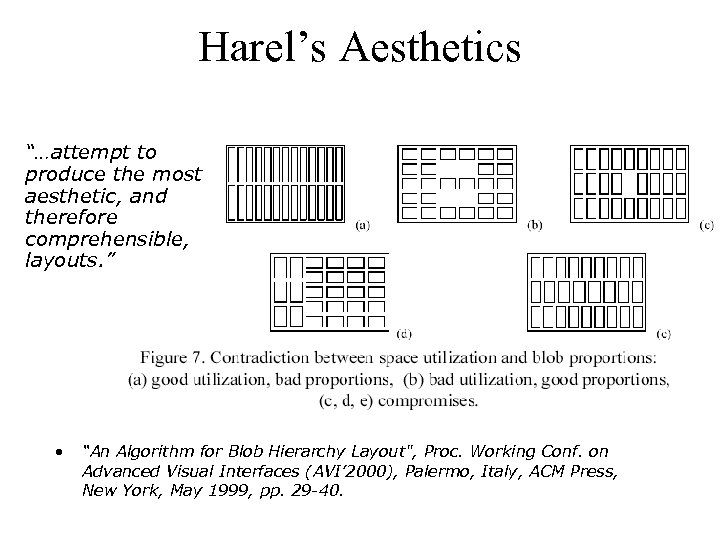
Harel’s Aesthetics “…attempt to produce the most aesthetic, and therefore comprehensible, layouts. ” • “An Algorithm for Blob Hierarchy Layout", Proc. Working Conf. on Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI’ 2000), Palermo, Italy, ACM Press, New York, May 1999, pp. 29 -40.
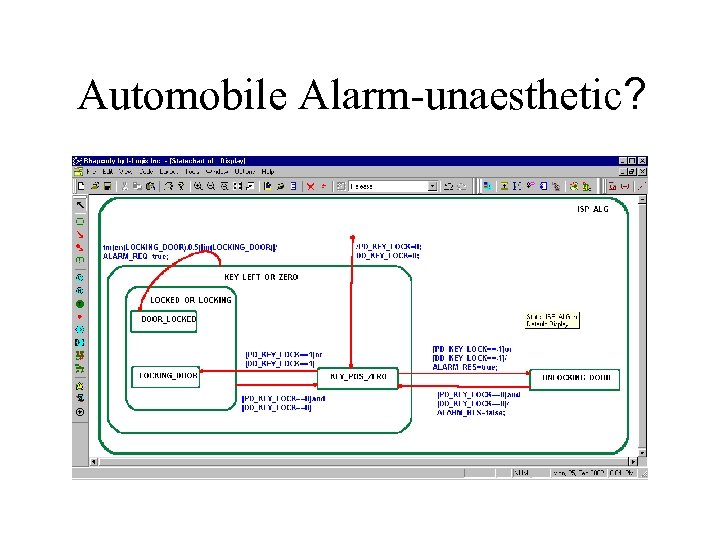
Automobile Alarm-unaesthetic?

Statechart Complexity Metrics (1) “The aim of the experiment was to investigate the relationship between the complexity of UML statechart diagrams and their understandability (one maintainability subcharacteristic). Defining and Validating Metrics for UML Statechart Diagrams Marcela Genero, David Miranda and Mario Piattini, QAOOSE 2002
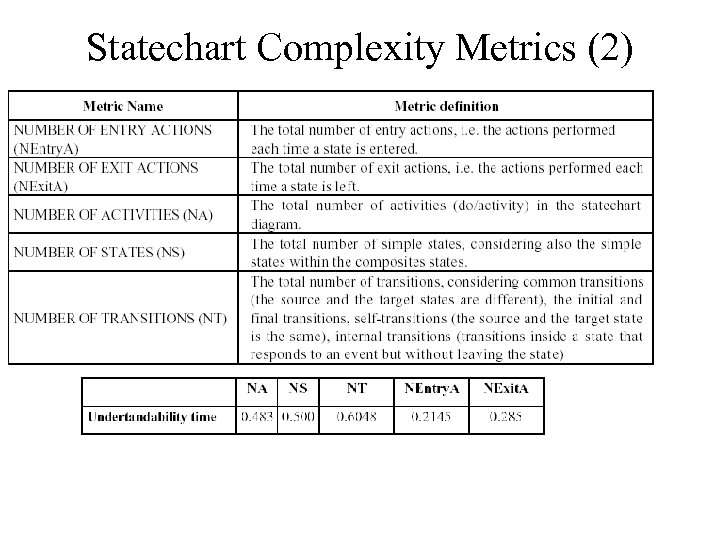
Statechart Complexity Metrics (2) •
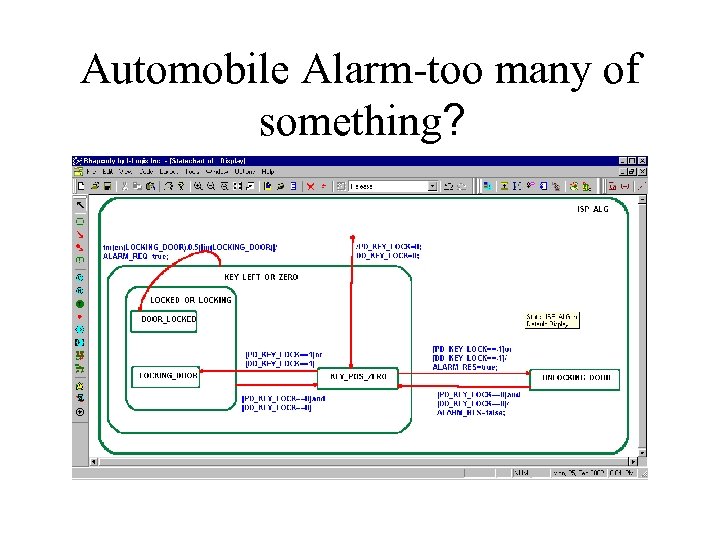
Automobile Alarm-too many of something?
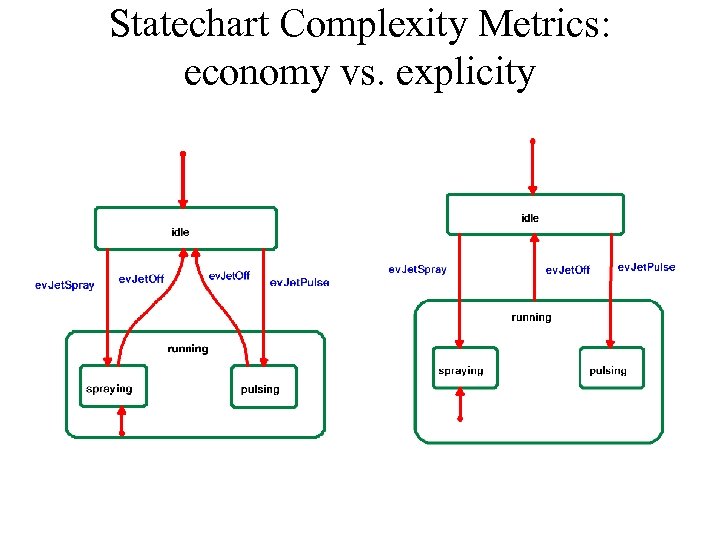
Statechart Complexity Metrics: economy vs. explicity

How Do We Measure Understandability? (2) Cognitive Dimensions (CDs) • Viscosity • Visibility • Premature commitment • Hidden dependencies • Role expressiveness • Error-proneness • Abstraction • • • Secondary notation Closeness of mapping Consistency Diffuseness Hard mental operations • Provisionality • Progressive evaluation Proposed by Greene in 1989, who has developed it since then with Petre, Blackwell, et al.
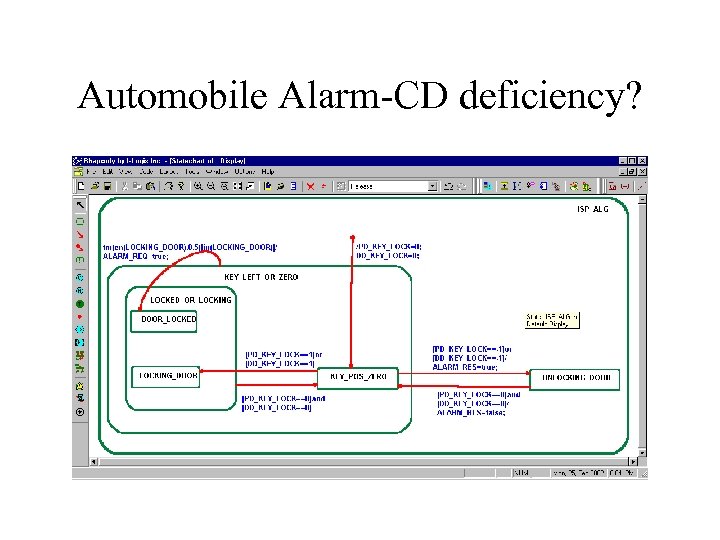
Automobile Alarm-CD deficiency?
![Patterns to the rescue! tm(set. Time)[IS_IN(setting)]/set. Action /setup() set. Or. Neutral set. Or. Setting Patterns to the rescue! tm(set. Time)[IS_IN(setting)]/set. Action /setup() set. Or. Neutral set. Or. Setting](https://present5.com/presentation/9bce33a888e0ac5b0701a9afd28fbcaf/image-21.jpg)
Patterns to the rescue! tm(set. Time)[IS_IN(setting)]/set. Action /setup() set. Or. Neutral set. Or. Setting set [setting. Condition] setting neutral [neutral. Condition] [resetting. Condition]/reset. Action resetting [neutral. Condition]/neutral. Action

Cognitive “Measures” • Automatization – Automatized vs. controlled tasks • Types of knowledge – Declarative, Conceptual, Procedural • Expertise – From novice to expert • Learning hierarchy – Associations and chains; Discriminations Concepts; Rules ; Higher order rules • Knowledge structuring – Surface features task specific features abstract/hierarchical features • Mental workload – single resource pool, multiple-resource
![Automatization(1( Please enter OMTracer Command>> go idle OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Sent to Automatization(1( Please enter OMTracer Command>> go idle OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Sent to](https://present5.com/presentation/9bce33a888e0ac5b0701a9afd28fbcaf/image-23.jpg)
Automatization(1( Please enter OMTracer Command>> go idle OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Sent to itself Event tm(200) at ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Received from itself Event tm(200) at ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) main() Invoked Display[0]->Take Event Timeout OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Invoked is. Done() OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0]->is. Done() Returned OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Exited State ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Invoked print(n = 1) OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0]->print(n = 1) Returned OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Entered State ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] set tm(200) at ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0]->Take Event Timeout Returned
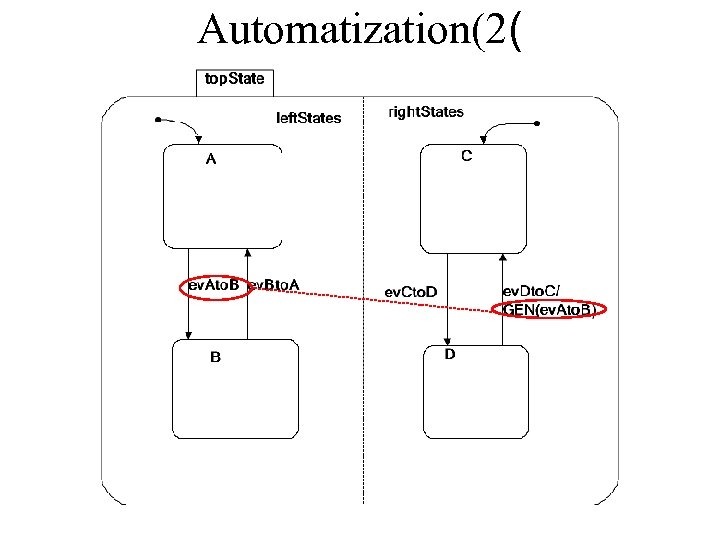
Automatization(2(
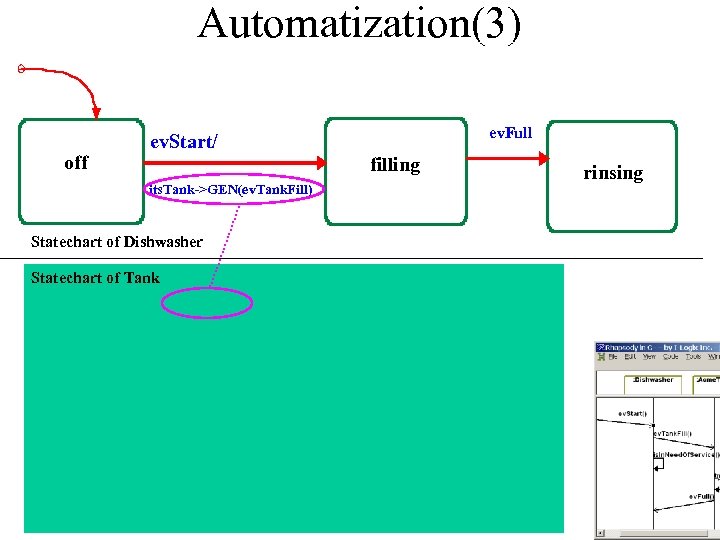
Automatization(3) off ev. Full ev. Start/ filling its. Tank->GEN(ev. Tank. Fill) Statechart of Dishwasher Statechart of Tank rinsing

Any questions?


Why engineers won’t use tools
Enter Professor Harel
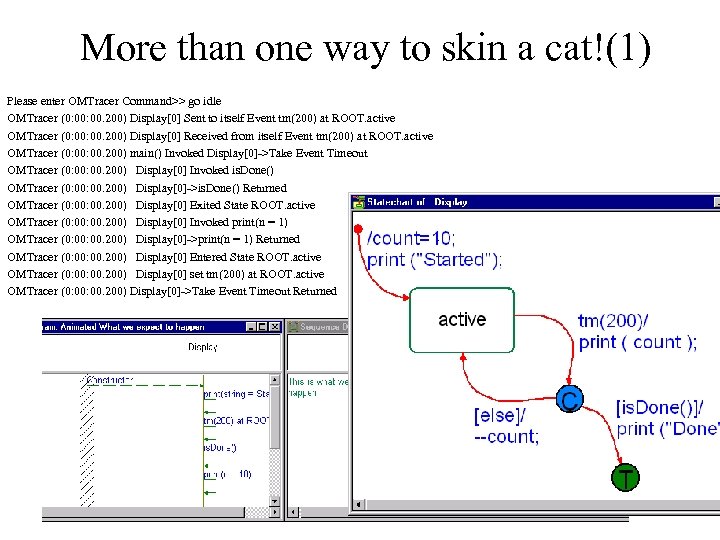
More than one way to skin a cat!(1) Please enter OMTracer Command>> go idle OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Sent to itself Event tm(200) at ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Received from itself Event tm(200) at ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) main() Invoked Display[0]->Take Event Timeout OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Invoked is. Done() OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0]->is. Done() Returned OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Exited State ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Invoked print(n = 1) OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0]->print(n = 1) Returned OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] Entered State ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0] set tm(200) at ROOT. active OMTracer (0: 00. 200) Display[0]->Take Event Timeout Returned
![Automatization • Shiffrin et al. [9] [10] distinguish between controlled and automatic processes. Whereas Automatization • Shiffrin et al. [9] [10] distinguish between controlled and automatic processes. Whereas](https://present5.com/presentation/9bce33a888e0ac5b0701a9afd28fbcaf/image-31.jpg)
Automatization • Shiffrin et al. [9] [10] distinguish between controlled and automatic processes. Whereas “automatized” processes require little or no cognitive resources, “controlled” processes are resource intensive. Abilities are important for mastering repetitive tasks, but not for performing them once mastered. In contrast, abilities continue to be important in the performance of controlled processes.
Application Type Diagram Type Level of Detail

How did the SHADOW get its name? ? ? • 2 Theories

Theory I • Sikorsky Helicopter Advanced Demonstrator of Operator Workload

Theory II • Jimmy Durante’s radio program and nose!

The SHADOW was top secret!!!! • Not members of the U. S. House of Representatives… • Not even Senators… – Got to see the SHADOW

The SHADOW was top secret!!!! • But the King got to fly in it!

4 Helicopters were sent to fetch the King from Boston

It was raining, and the King decided that discretion was the better part of valour

How Do We Measure Understandability? (2) Cognitive Dimensions (CDs) • • Viscosity: resistance to change Visibility Greene, T. R. G. (1989). Cognitive Dimensions of Notations. In People and Computers V. A. Sutcliffe and L. Macaulay, (Ed. ). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 443 -460. For non-specialists (no expertise in cognitive science or HFE required) Broad-brush Quick to apply, no lengthy analysis Check list approach: – abstraction, hidden dependencies, premature commitment, secondary notation, viscosity, visibility, closeness of mapping, diffuseness, error-proneness, hard mental operations, progressive evaluation, provisionality, role-expressiveness
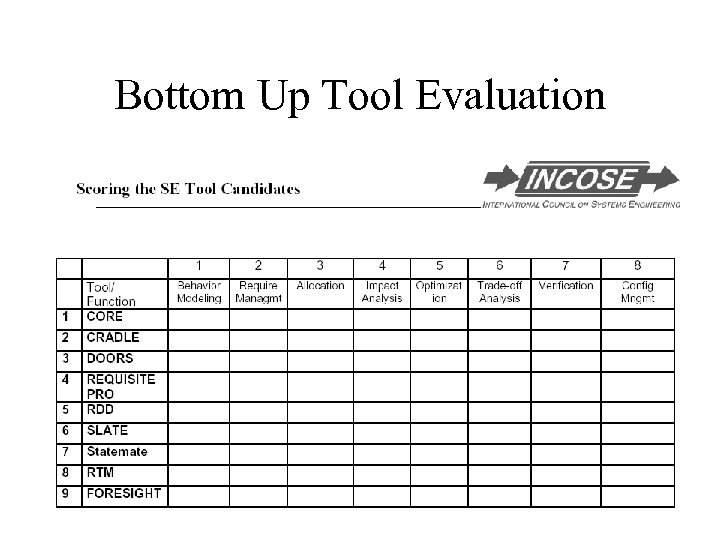
Bottom Up Tool Evaluation
9bce33a888e0ac5b0701a9afd28fbcaf.ppt