d99188315714cab5a5c1652918bc6b5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Cognition and Perception: A Short Review
Cognition and Perception: A Short Review
 To add: non-tech error stuff Attention blindness demos Speech errors and disfluency Emotion and design (3 teapots) Just noticeable differences (JNDs) Add Strayer cell phone study
To add: non-tech error stuff Attention blindness demos Speech errors and disfluency Emotion and design (3 teapots) Just noticeable differences (JNDs) Add Strayer cell phone study
 Relevant topics Perception Motor abilities Attention Reading Sensory memory Working memory Long-term memory Reasoning Decision-making Speech perception and production Discourse
Relevant topics Perception Motor abilities Attention Reading Sensory memory Working memory Long-term memory Reasoning Decision-making Speech perception and production Discourse
 Perception Vision Rods and cones Visual acuity Color: hue, intensity, saturation Distance estimated by size (+intensity) Gestalt principles
Perception Vision Rods and cones Visual acuity Color: hue, intensity, saturation Distance estimated by size (+intensity) Gestalt principles
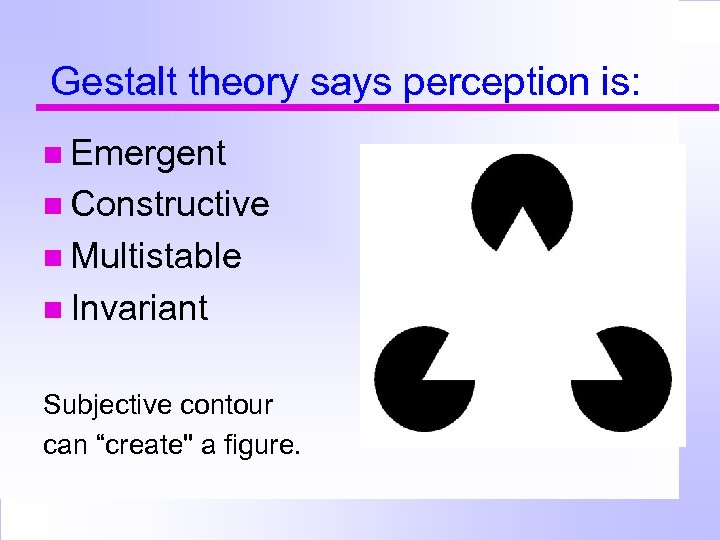 Gestalt theory says perception is: Emergent Constructive Multistable Invariant Subjective contour can “create" a figure.
Gestalt theory says perception is: Emergent Constructive Multistable Invariant Subjective contour can “create" a figure.
 What do you see?
What do you see?

 Some Gestalt Principles Proximity Similarity Good continuation Closure
Some Gestalt Principles Proximity Similarity Good continuation Closure
 Gestalt Principles Proximity
Gestalt Principles Proximity
 Gestalt Principles Similarity
Gestalt Principles Similarity
 Gestalt Principles Good continuation
Gestalt Principles Good continuation
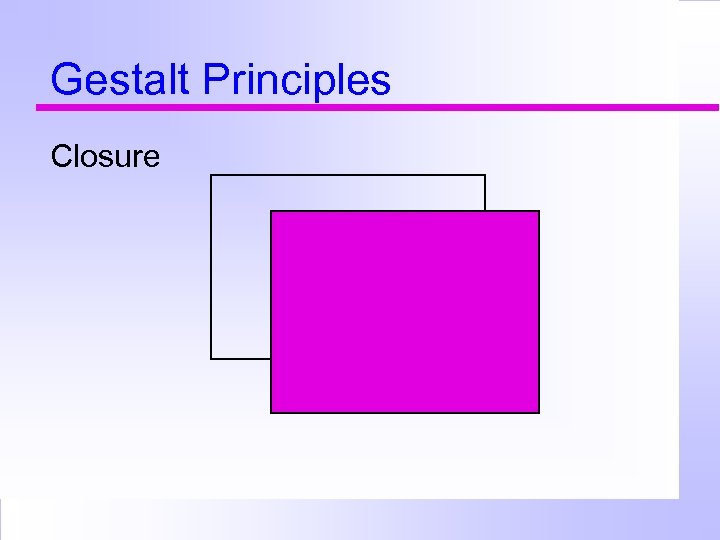 Gestalt Principles Closure
Gestalt Principles Closure
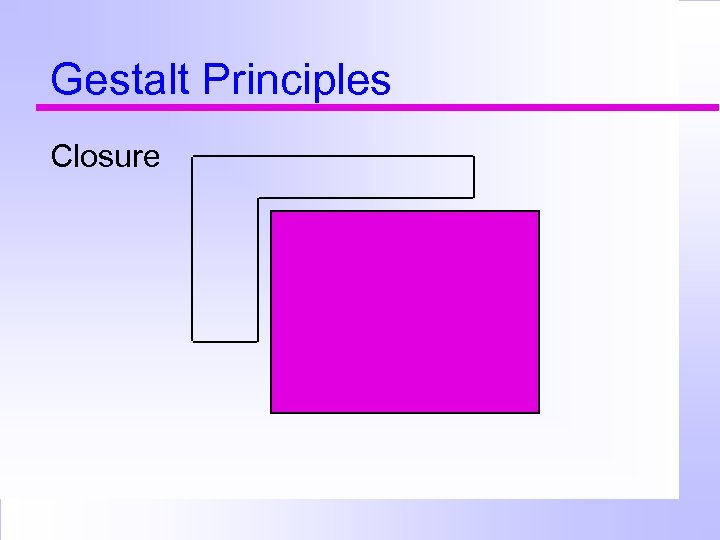 Gestalt Principles Closure
Gestalt Principles Closure
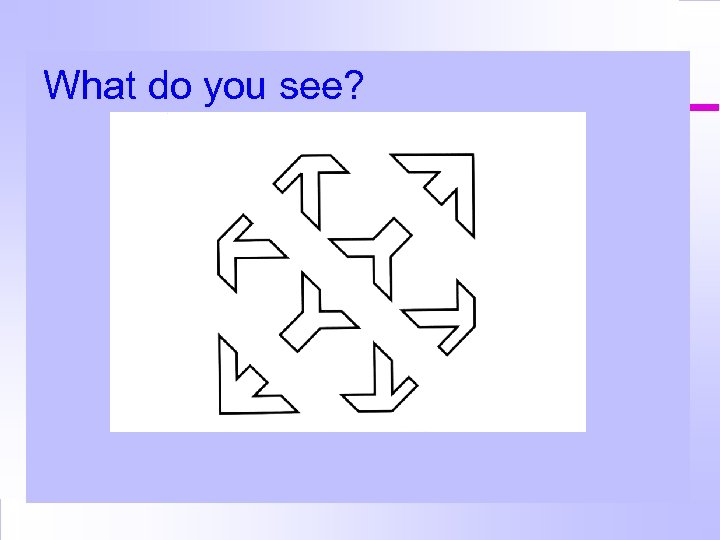 What do you see?
What do you see?
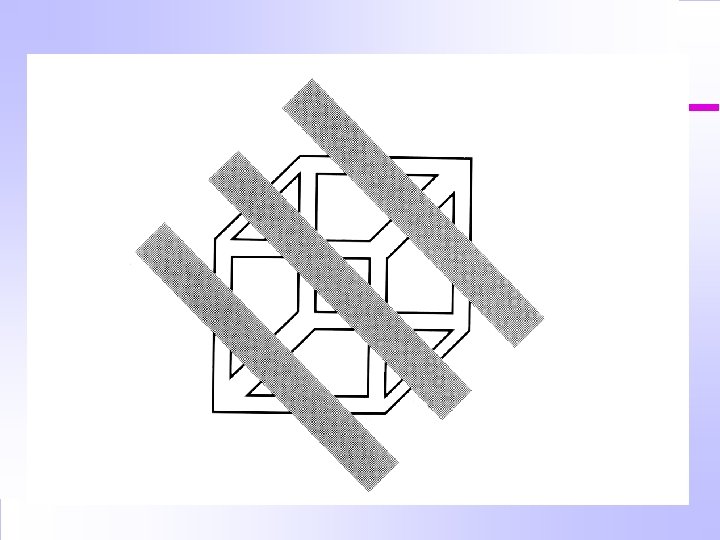
 Figure-ground segregation (stable) Figure more thing-like, more memorable, smaller seen as being in front of the ground Ground seen as unformed material extends behind the figure
Figure-ground segregation (stable) Figure more thing-like, more memorable, smaller seen as being in front of the ground Ground seen as unformed material extends behind the figure
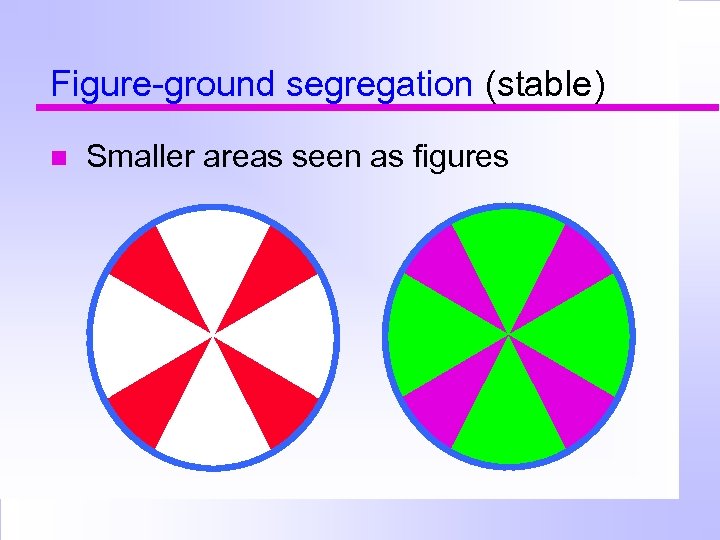 Figure-ground segregation (stable) Smaller areas seen as figures
Figure-ground segregation (stable) Smaller areas seen as figures
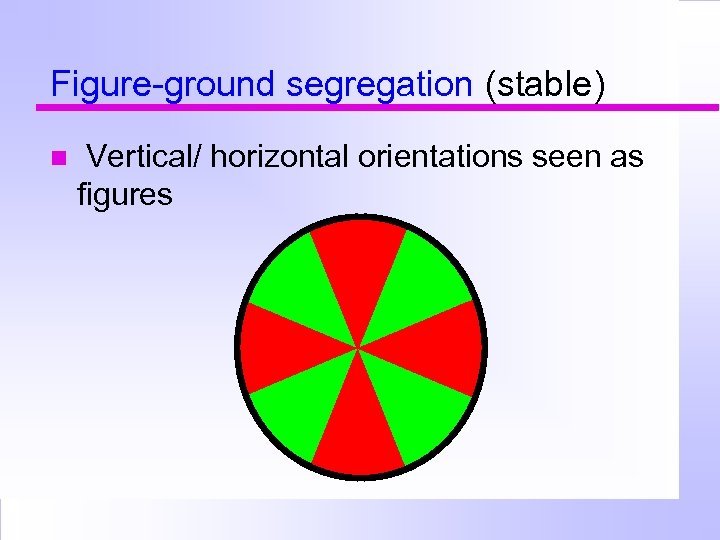 Figure-ground segregation (stable) Vertical/ horizontal orientations seen as figures
Figure-ground segregation (stable) Vertical/ horizontal orientations seen as figures
 Perception Vision Hearing Pitch, loudness, and timbre Pitch range: 20 Hertz - 15, 000 Hertz Resolution Speech vs. other sounds
Perception Vision Hearing Pitch, loudness, and timbre Pitch range: 20 Hertz - 15, 000 Hertz Resolution Speech vs. other sounds
 Perception Vision Hearing Touch Mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, nociceptors (pain) Different resolution at different points Feedback is important
Perception Vision Hearing Touch Mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, nociceptors (pain) Different resolution at different points Feedback is important
 Perception Vision Hearing Touch Smell Taste
Perception Vision Hearing Touch Smell Taste
 Modalities; speed/accuracy; practice effects Reaction times differ by modality Integrating 2 modalities into 1 percept Speed trades off with accuracy Skill increases with practice (Power Law of Practice)
Modalities; speed/accuracy; practice effects Reaction times differ by modality Integrating 2 modalities into 1 percept Speed trades off with accuracy Skill increases with practice (Power Law of Practice)
 Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search
Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search
 Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search 0000000000 V 0000000000
Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search 0000000000 V 0000000000
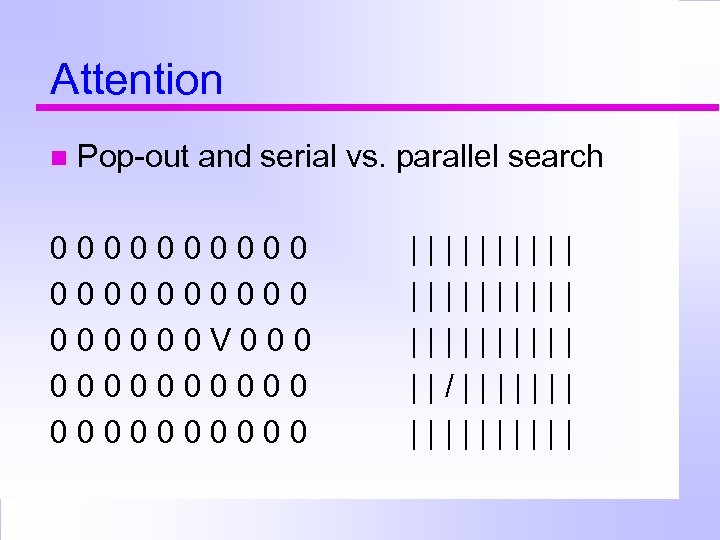 Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search 0000000000 V 0000000000 |||||||||| ||/|||||||
Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search 0000000000 V 0000000000 |||||||||| ||/|||||||
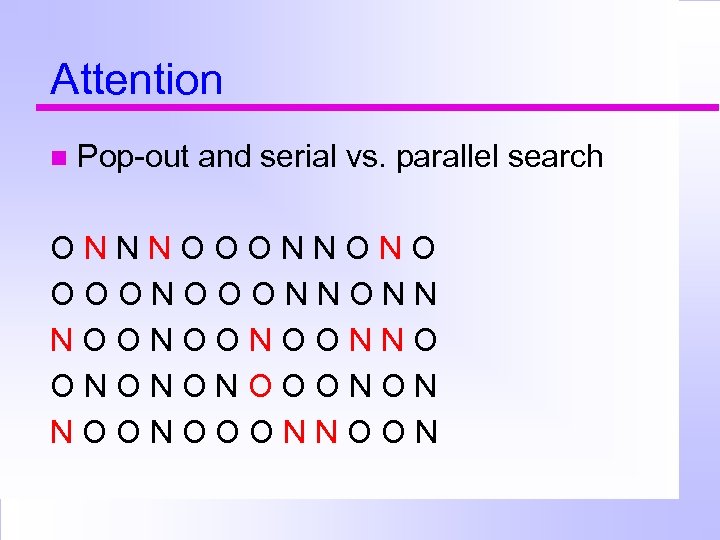 Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search ONNNOOONNONO OOONNONN NOONOONOONNO ONONONOOONON NOONOOONNOON
Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search ONNNOOONNONO OOONNONN NOONOONOONNO ONONONOOONON NOONOOONNOON
 Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search Highlighting Motion, flicker Sounds
Attention Pop-out and serial vs. parallel search Highlighting Motion, flicker Sounds
 Change blindness Some fun demos: http: //viscog. beckman. uiuc. edu/djs_lab/demos. html
Change blindness Some fun demos: http: //viscog. beckman. uiuc. edu/djs_lab/demos. html
 What’s changing?
What’s changing?
 What’s changing? What makes seeing the change so hard?
What’s changing? What makes seeing the change so hard?
 Change blindness Inability to detect what should be obvious changes in a scene Original Image | 400 ms Blank | 40 -80 ms | Modified Image 400 ms |
Change blindness Inability to detect what should be obvious changes in a scene Original Image | 400 ms Blank | 40 -80 ms | Modified Image 400 ms |
 Mud Splashes
Mud Splashes
 No Mud Splashes
No Mud Splashes
 Change blindness Inability to detect what should be obvious changes in a scene. This is affected by Interrupting with a blank screen Distraction such as the “mud” (captures attention) Original Image | Blank/Mud Modified Image 400 ms | 40 -80 ms | 400 ms |
Change blindness Inability to detect what should be obvious changes in a scene. This is affected by Interrupting with a blank screen Distraction such as the “mud” (captures attention) Original Image | Blank/Mud Modified Image 400 ms | 40 -80 ms | 400 ms |
 Flicker
Flicker
 No Flicker
No Flicker
 More examples: http: //www. usd. edu/psyc 301/Rensink. htm
More examples: http: //www. usd. edu/psyc 301/Rensink. htm
 Conversations and cell phones Auto accidents increase during cell phone use Yet people safely talk to their passengers all the time So it follows that the problem must be due to dialing, handling the phone, etc. Or does it?
Conversations and cell phones Auto accidents increase during cell phone use Yet people safely talk to their passengers all the time So it follows that the problem must be due to dialing, handling the phone, etc. Or does it?
 Strayer & Johnston’s expts (in press) Visual tracking task with joystick Conditions: hands free or handheld Converse with someone in another room Listen to the radio or books on tape Shadowing Prompted word generation task
Strayer & Johnston’s expts (in press) Visual tracking task with joystick Conditions: hands free or handheld Converse with someone in another room Listen to the radio or books on tape Shadowing Prompted word generation task
 Results: Performance was worse for subjects on cell phones than for subjects listening to radio, books on tape, or shadowing. Twice as many red lights were missed, and RTs increased!! Whether the phone was hand-held didn’t matter at all! What do you think causes the poor performance of people on cell phones?
Results: Performance was worse for subjects on cell phones than for subjects listening to radio, books on tape, or shadowing. Twice as many red lights were missed, and RTs increased!! Whether the phone was hand-held didn’t matter at all! What do you think causes the poor performance of people on cell phones?
 Inattention Blindness (IB) When observers fail to notice an unexpected object or event Occurs when attentional resources are directed toward another task
Inattention Blindness (IB) When observers fail to notice an unexpected object or event Occurs when attentional resources are directed toward another task
 Attention Influences Perception Inattentional Blindness: involves missing a (remarkable!) change because you’re not expecting it and not attending to it. Example: Man/office/phone movie http: //viscog. beckman. uiuc. edu/grafs/demos/23. html Notice anything strange? Simons & Chabris (1999)
Attention Influences Perception Inattentional Blindness: involves missing a (remarkable!) change because you’re not expecting it and not attending to it. Example: Man/office/phone movie http: //viscog. beckman. uiuc. edu/grafs/demos/23. html Notice anything strange? Simons & Chabris (1999)
 Attention Influences Perception Inattentional Blindness: involves missing a (remarkable!) change because you’re not expecting it and not attending to it. Example: http: //viscog. beckman. uiuc. edu/grafs/demos/15. html Count passes made by the white team or the black team (easy task) Count bounce passes and also count aerial passes (hard task) Simons & Chabris (1999)
Attention Influences Perception Inattentional Blindness: involves missing a (remarkable!) change because you’re not expecting it and not attending to it. Example: http: //viscog. beckman. uiuc. edu/grafs/demos/15. html Count passes made by the white team or the black team (easy task) Count bounce passes and also count aerial passes (hard task) Simons & Chabris (1999)
 Attention Influences Perception Inattentional Blindness: involves missing a (remarkable!) change because you’re not expecting it and not attending to it. Example: More people see gorilla with easy task More people see gorilla when attending to black team (83%) than white team (42%) Similarity matters! Simons & Chabris (1999)
Attention Influences Perception Inattentional Blindness: involves missing a (remarkable!) change because you’re not expecting it and not attending to it. Example: More people see gorilla with easy task More people see gorilla when attending to black team (83%) than white team (42%) Similarity matters! Simons & Chabris (1999)
 Inattentional Blindness - another ex. Pilots landing an aircraft simulator Experimenters were interested in a new heads-up display Pilots didn’t notice a large plane placed on the runway at the last minute Haines (1991)
Inattentional Blindness - another ex. Pilots landing an aircraft simulator Experimenters were interested in a new heads-up display Pilots didn’t notice a large plane placed on the runway at the last minute Haines (1991)
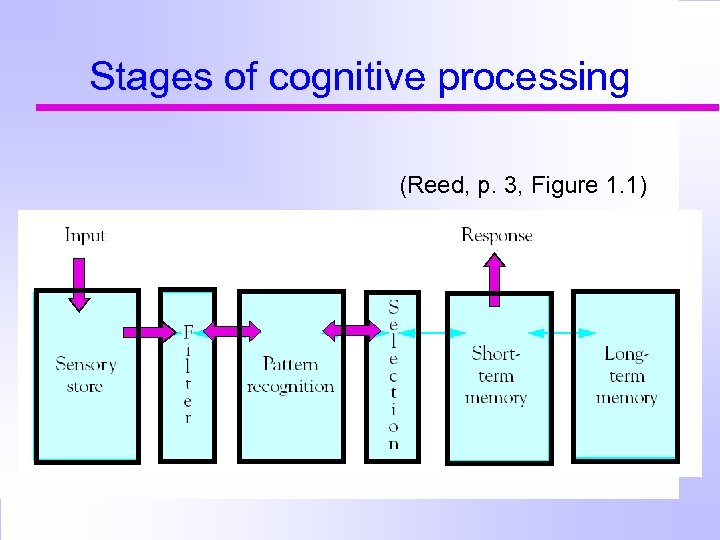 Stages of cognitive processing (Reed, p. 3, Figure 1. 1)
Stages of cognitive processing (Reed, p. 3, Figure 1. 1)
 Sensory memory Iconic memory - fleeting, hi-res buffer Must be attended to to be remembered Echoic memory Haptic memory (Characteristics vary with context)
Sensory memory Iconic memory - fleeting, hi-res buffer Must be attended to to be remembered Echoic memory Haptic memory (Characteristics vary with context)
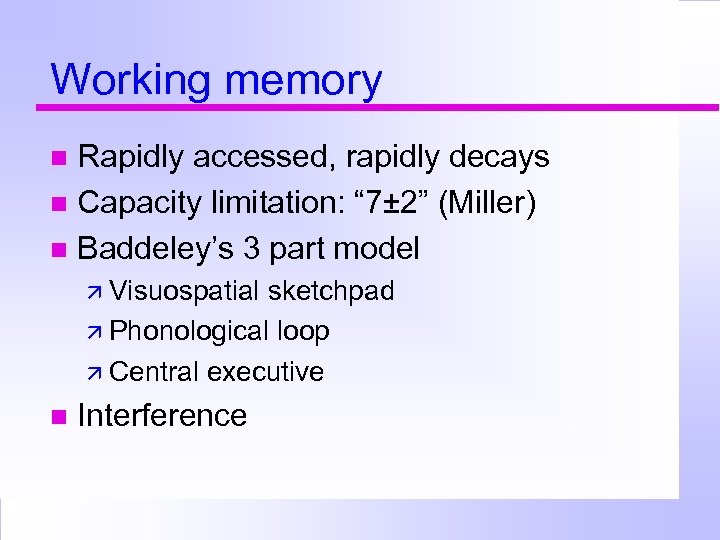 Working memory Rapidly accessed, rapidly decays Capacity limitation: “ 7± 2” (Miller) Baddeley’s 3 part model Visuospatial sketchpad Phonological loop Central executive Interference
Working memory Rapidly accessed, rapidly decays Capacity limitation: “ 7± 2” (Miller) Baddeley’s 3 part model Visuospatial sketchpad Phonological loop Central executive Interference
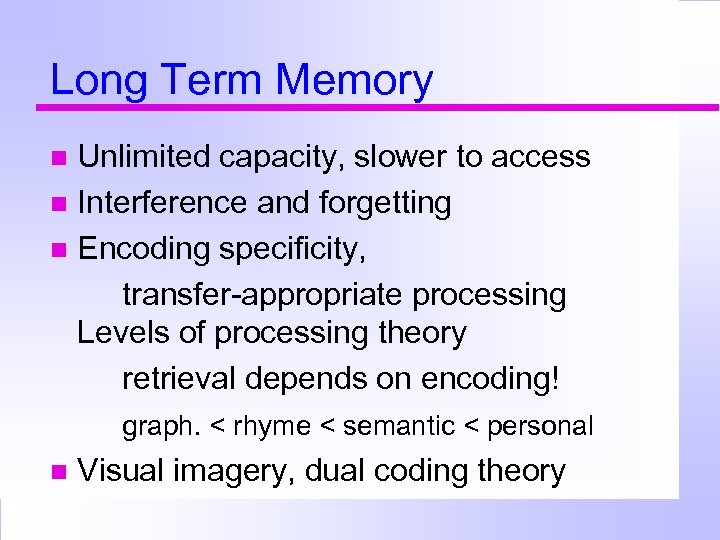 Long Term Memory Unlimited capacity, slower to access Interference and forgetting Encoding specificity, transfer-appropriate processing Levels of processing theory retrieval depends on encoding! graph. < rhyme < semantic < personal Visual imagery, dual coding theory
Long Term Memory Unlimited capacity, slower to access Interference and forgetting Encoding specificity, transfer-appropriate processing Levels of processing theory retrieval depends on encoding! graph. < rhyme < semantic < personal Visual imagery, dual coding theory
 Long Term Memory (cont. ) Semantic organization Tip-of-the-tongue effect (interference) Schemas Distortions in memory
Long Term Memory (cont. ) Semantic organization Tip-of-the-tongue effect (interference) Schemas Distortions in memory
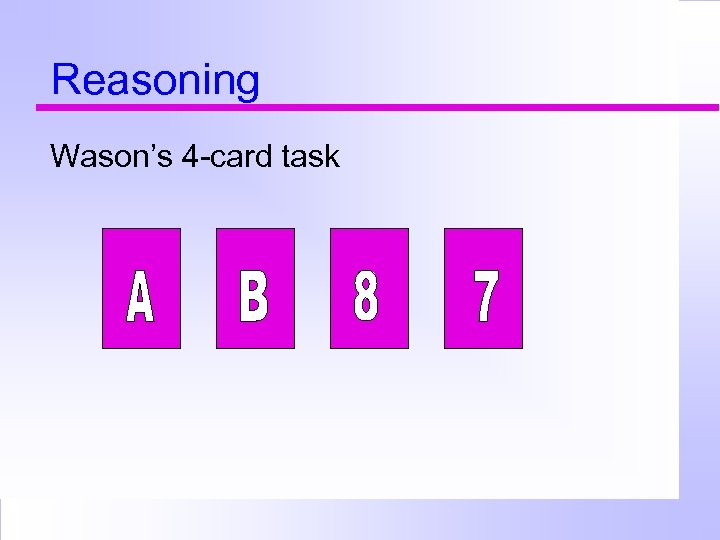 Reasoning Wason’s 4 -card task
Reasoning Wason’s 4 -card task
 Reasoning Wason’s 4 -card task
Reasoning Wason’s 4 -card task
 Decision making Framing effects Program A: save 200 people Program B: 1/3 probability of saving all 600 2/3 probability of saving no one
Decision making Framing effects Program A: save 200 people Program B: 1/3 probability of saving all 600 2/3 probability of saving no one
 Decision making Framing effects Program A: save 200 people Program B: 1/3 probability of saving all 600 2/3 probability of saving no one 72% choose A; 28% choose B!!
Decision making Framing effects Program A: save 200 people Program B: 1/3 probability of saving all 600 2/3 probability of saving no one 72% choose A; 28% choose B!!
 Decision making Framing effects Lose a $50 ticket Lose a $50 bill Would you buy another ticket?
Decision making Framing effects Lose a $50 ticket Lose a $50 bill Would you buy another ticket?
 Decision making Framing effects Lose a $50 ticket Lose a $50 bill 46% YES, 54% NO 88% YES, 12% NO Would you buy another ticket?
Decision making Framing effects Lose a $50 ticket Lose a $50 bill 46% YES, 54% NO 88% YES, 12% NO Would you buy another ticket?
 Decision making Framing effects Anchoring effects Do you think Dr. Brennan is older or younger than 20/60? Please give your best estimate of her age.
Decision making Framing effects Anchoring effects Do you think Dr. Brennan is older or younger than 20/60? Please give your best estimate of her age.
 Decision making Framing effects Anchoring effects Do you think Dr. Brennan is older or younger than 20/60? Please give your best estimate of her age. Anchored at 20: 37. 7 years old Anchored at 60: 39. 3 years old (p <. 05)
Decision making Framing effects Anchoring effects Do you think Dr. Brennan is older or younger than 20/60? Please give your best estimate of her age. Anchored at 20: 37. 7 years old Anchored at 60: 39. 3 years old (p <. 05)
 Conclusion: Review your knowledge of cognitive and perceptual psychology! You can distill principles of humancomputer interaction and explain people’s performance and errors from what you know about human cognition and perception!
Conclusion: Review your knowledge of cognitive and perceptual psychology! You can distill principles of humancomputer interaction and explain people’s performance and errors from what you know about human cognition and perception!



