408f586606e17bd1520ccaa9c41c160c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 COE 308 Computer Architecture Term - 062 Dr Abdelhafid Bouhraoua
COE 308 Computer Architecture Term - 062 Dr Abdelhafid Bouhraoua
 Instructor Dr Abdelhafid Bouhraoua Office Hours: Sun. Tue. 10: 00 - 12: 00 PM Office Location: Bldg 22 Office 137 -1 Phone: 2178 Email: abouh@kfupm. edu. sa Web page: www. ccse. kfupm. edu. sa/~abouh
Instructor Dr Abdelhafid Bouhraoua Office Hours: Sun. Tue. 10: 00 - 12: 00 PM Office Location: Bldg 22 Office 137 -1 Phone: 2178 Email: abouh@kfupm. edu. sa Web page: www. ccse. kfupm. edu. sa/~abouh
 Syllabus
Syllabus
 Course Objectives • • To introduce students to the techniques used to enhance the performance of computer architecture including memory hierarchy, pipelining, and parallelism, To introduce students to the trade-off analysis in the design of various aspects of Computer Architecture including Instruction Set Design, Memory Hierarchy, Instruction Level Pipeline, and Multiprocessing
Course Objectives • • To introduce students to the techniques used to enhance the performance of computer architecture including memory hierarchy, pipelining, and parallelism, To introduce students to the trade-off analysis in the design of various aspects of Computer Architecture including Instruction Set Design, Memory Hierarchy, Instruction Level Pipeline, and Multiprocessing
 Course Outcome (1) • • • Discuss how various architectural enhancements and instructions sets have evolved and their effects on system performance. Understand the design of arithmetic units and their impact on overall performance. Explain the effect of memory latency and bandwidth on performance. Explain the use of memory hierarchy to reduce the effective memory latency, and understand the design tradeoffs in hierarchical memories and its impact on performance. Describe the principles of memory management.
Course Outcome (1) • • • Discuss how various architectural enhancements and instructions sets have evolved and their effects on system performance. Understand the design of arithmetic units and their impact on overall performance. Explain the effect of memory latency and bandwidth on performance. Explain the use of memory hierarchy to reduce the effective memory latency, and understand the design tradeoffs in hierarchical memories and its impact on performance. Describe the principles of memory management.
 Course Outcome (2) • • Discuss how pipelining and parallelism can be applied to the design of scalar and superscalar processors, and can perform speed-up analysis. Be able to identify the problems and hazards that arise in pipelined processors and identify their corresponding solutions. Appreciate the problems caused by cache coherency in shared and distributed memories and understand the ways in which the problem can be overcome Describe the limitations imposed by interconnections and memory on multiprocessing systems, and understand
Course Outcome (2) • • Discuss how pipelining and parallelism can be applied to the design of scalar and superscalar processors, and can perform speed-up analysis. Be able to identify the problems and hazards that arise in pipelined processors and identify their corresponding solutions. Appreciate the problems caused by cache coherency in shared and distributed memories and understand the ways in which the problem can be overcome Describe the limitations imposed by interconnections and memory on multiprocessing systems, and understand
 Textbook Computer Organization & Design – The Hardware/Software Interface
Textbook Computer Organization & Design – The Hardware/Software Interface
 Exams and Assignments 5 -6 4 -5 2 1 Written Assignments Quizzes Major Exams Final Exam
Exams and Assignments 5 -6 4 -5 2 1 Written Assignments Quizzes Major Exams Final Exam
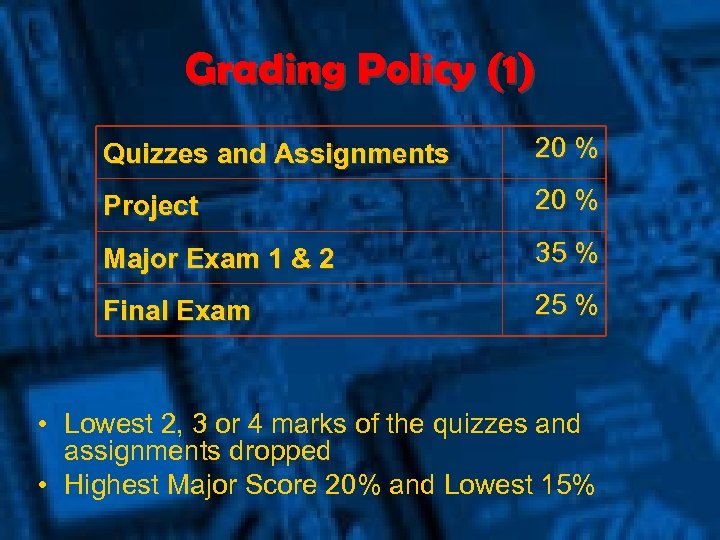 Grading Policy (1) Quizzes and Assignments 20 % Project 20 % Major Exam 1 & 2 35 % Final Exam 25 % • Lowest 2, 3 or 4 marks of the quizzes and assignments dropped • Highest Major Score 20% and Lowest 15%
Grading Policy (1) Quizzes and Assignments 20 % Project 20 % Major Exam 1 & 2 35 % Final Exam 25 % • Lowest 2, 3 or 4 marks of the quizzes and assignments dropped • Highest Major Score 20% and Lowest 15%
 Grading Policy (2) • Assignments are to be submitted in class or by email in the specified due date. • Late assignments will be accepted for five days after the due date and be penalized 10% per each late day
Grading Policy (2) • Assignments are to be submitted in class or by email in the specified due date. • Late assignments will be accepted for five days after the due date and be penalized 10% per each late day
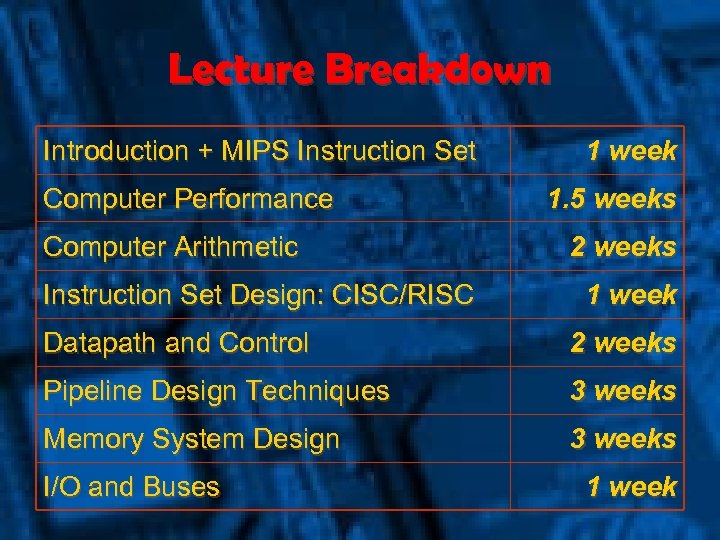 Lecture Breakdown Introduction + MIPS Instruction Set Computer Performance Computer Arithmetic Instruction Set Design: CISC/RISC 1 week 1. 5 weeks 2 weeks 1 week Datapath and Control 2 weeks Pipeline Design Techniques 3 weeks Memory System Design 3 weeks I/O and Buses 1 week
Lecture Breakdown Introduction + MIPS Instruction Set Computer Performance Computer Arithmetic Instruction Set Design: CISC/RISC 1 week 1. 5 weeks 2 weeks 1 week Datapath and Control 2 weeks Pipeline Design Techniques 3 weeks Memory System Design 3 weeks I/O and Buses 1 week
 Ethics (1) • All assignments are individual and ONLY individual work will be accepted. • Detected copies of assignments (written or programming assignments) will result in ZEROS for the whole group (including the student who actually solved the problem)
Ethics (1) • All assignments are individual and ONLY individual work will be accepted. • Detected copies of assignments (written or programming assignments) will result in ZEROS for the whole group (including the student who actually solved the problem)
 Ethics (2) • Using unauthorized information or notes on an examination, peeking at others work, or altering a graded exam to claim more grades are severe violations of academic honesty. • Remember that if you CHEAT, you are cheating no one but yourself. • Detected situations will result in failing grades in the course, and depending on the severity of the situation, some cases may possibly end up in SUSPENSION from the university.
Ethics (2) • Using unauthorized information or notes on an examination, peeking at others work, or altering a graded exam to claim more grades are severe violations of academic honesty. • Remember that if you CHEAT, you are cheating no one but yourself. • Detected situations will result in failing grades in the course, and depending on the severity of the situation, some cases may possibly end up in SUSPENSION from the university.
 What is Computer Architecture ? • The Way The Computer Is Built • Architecture Suggests Two Things: – Learning about the Computer Components and their Interaction – Learning the “Art” of Making (Designing) New High Performance Computer Plans • Becoming The ARCHITECT of the Computer The “Art” of Making Computers
What is Computer Architecture ? • The Way The Computer Is Built • Architecture Suggests Two Things: – Learning about the Computer Components and their Interaction – Learning the “Art” of Making (Designing) New High Performance Computer Plans • Becoming The ARCHITECT of the Computer The “Art” of Making Computers
 Computer Organization • CPU: Central Processing Unit (Where Data is Processed) • Memory: Data Storage Unit (Temporary Storage) • Input Output: Interface the outside world to the CPU – Input Devices: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, etc… – Output Devices: Display, Printer – Bi-Directional Devices: Hard Drives, CD-ROM,
Computer Organization • CPU: Central Processing Unit (Where Data is Processed) • Memory: Data Storage Unit (Temporary Storage) • Input Output: Interface the outside world to the CPU – Input Devices: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, etc… – Output Devices: Display, Printer – Bi-Directional Devices: Hard Drives, CD-ROM,
 Computer Usage Evolution • First Developed Primarily as a: Business Data Processing Machine – Main Customers: Banks, Government, Businesses – Applications: Financial, Scientific • 1972: Intel’s 4004 First Microprocessor – Evolved into Microcomputer • 1981: IBM launches the IBM PC – The Personal Computer is born • Most of Today’s Computers are Based on the PC – Concept of Individual Workstation and Networked Server Base
Computer Usage Evolution • First Developed Primarily as a: Business Data Processing Machine – Main Customers: Banks, Government, Businesses – Applications: Financial, Scientific • 1972: Intel’s 4004 First Microprocessor – Evolved into Microcomputer • 1981: IBM launches the IBM PC – The Personal Computer is born • Most of Today’s Computers are Based on the PC – Concept of Individual Workstation and Networked Server Base
 Computer Performance • High Demand for Performance because: – Explosion of Applications and Usages • Personal Usage, Industrial, Domestic, Games, etc … • Communication • Huge Market: – Architecture War: • Buses War: ISA, E-ISA, IBM MCA, Killed by PCI (Intel) – Processor War: • Intel, AMD, IBM, Cyrix, DEC • Only Intel and AMD survived
Computer Performance • High Demand for Performance because: – Explosion of Applications and Usages • Personal Usage, Industrial, Domestic, Games, etc … • Communication • Huge Market: – Architecture War: • Buses War: ISA, E-ISA, IBM MCA, Killed by PCI (Intel) – Processor War: • Intel, AMD, IBM, Cyrix, DEC • Only Intel and AMD survived
 Computer Components • Commodity Components – Memory, Drives (CD and HD), IO Devices • Technological Components – Processors ONLY • Computer Architecture’s Goal: – Increase Processor Performance by the ART of Design – Based on two things: • Intrinsic ART of Pure Computer Architecture Skills • Manufacturing Technology Provides a Tool that makes the “Craziest” Design of Yesterday possible Today
Computer Components • Commodity Components – Memory, Drives (CD and HD), IO Devices • Technological Components – Processors ONLY • Computer Architecture’s Goal: – Increase Processor Performance by the ART of Design – Based on two things: • Intrinsic ART of Pure Computer Architecture Skills • Manufacturing Technology Provides a Tool that makes the “Craziest” Design of Yesterday possible Today
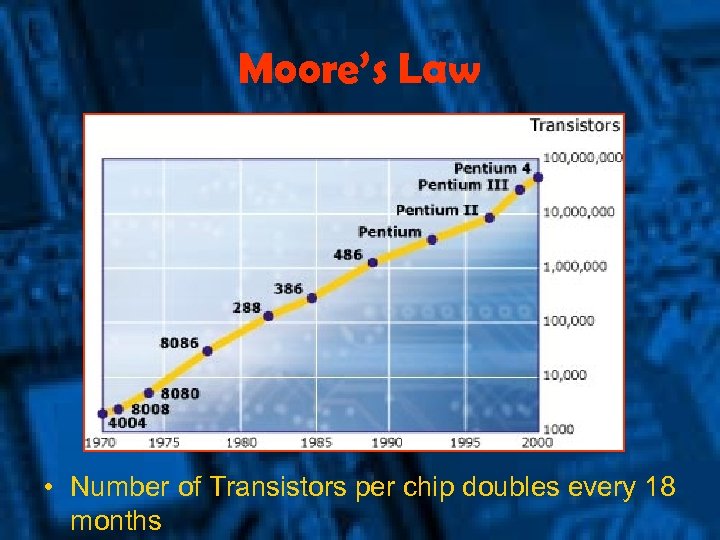 Moore’s Law • Number of Transistors per chip doubles every 18 months
Moore’s Law • Number of Transistors per chip doubles every 18 months
 Intel. vs. AMD IC Technolo Advanced gy Computer Architectu re Techniqu IC es Technolo gy Intel’s Clock Frequency Higher But AMD’s Performance (Scaled to Clock Frequency) Higher
Intel. vs. AMD IC Technolo Advanced gy Computer Architectu re Techniqu IC es Technolo gy Intel’s Clock Frequency Higher But AMD’s Performance (Scaled to Clock Frequency) Higher
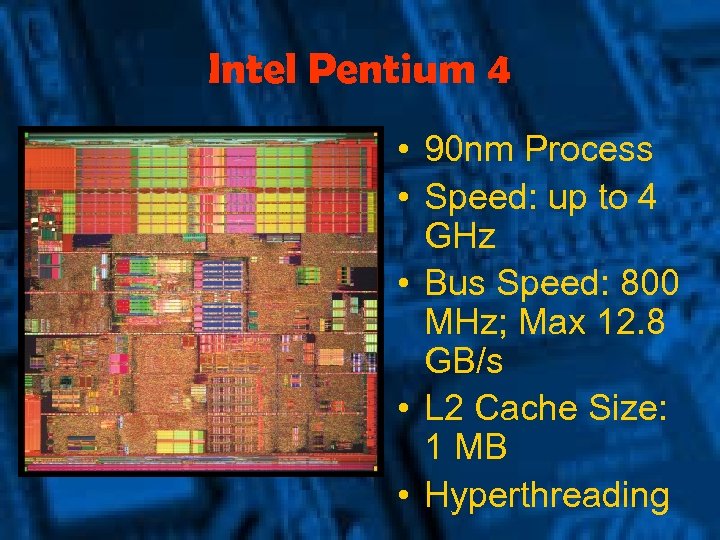 Intel Pentium 4 • 90 nm Process • Speed: up to 4 GHz • Bus Speed: 800 MHz; Max 12. 8 GB/s • L 2 Cache Size: 1 MB • Hyperthreading
Intel Pentium 4 • 90 nm Process • Speed: up to 4 GHz • Bus Speed: 800 MHz; Max 12. 8 GB/s • L 2 Cache Size: 1 MB • Hyperthreading
 AMD Athlon 64 • 90 nm Process • Speed: up to 2. 8 GHz • Bus Speed: On -Chip DDR 2 and HT Max 18. 6 GB/s • L 2 Cache Size: 1 MB
AMD Athlon 64 • 90 nm Process • Speed: up to 2. 8 GHz • Bus Speed: On -Chip DDR 2 and HT Max 18. 6 GB/s • L 2 Cache Size: 1 MB
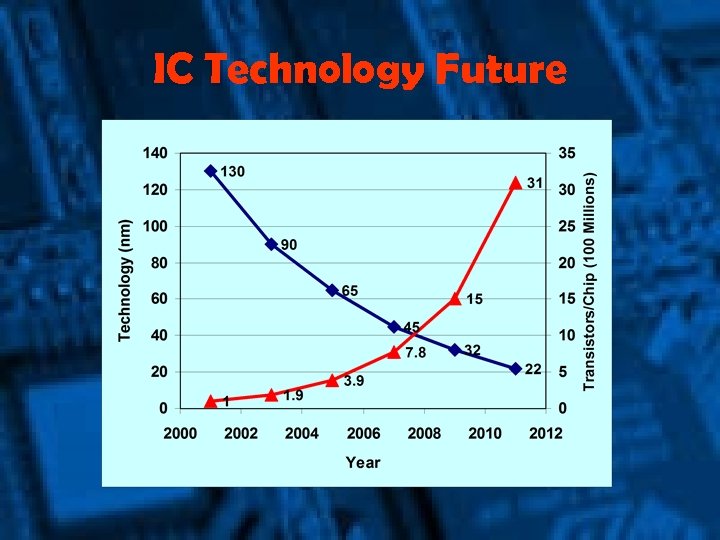 IC Technology Future
IC Technology Future
 IC Technology Limits • Reaching Limits of: – Speed but NOT Integration • Intel (and AMD) turning to improving Space Rather than Time. – Multiple Core Processor (Dual Core) – In reality the Old New Parallel Processing – Technology Enabling New Ways of Making the Old
IC Technology Limits • Reaching Limits of: – Speed but NOT Integration • Intel (and AMD) turning to improving Space Rather than Time. – Multiple Core Processor (Dual Core) – In reality the Old New Parallel Processing – Technology Enabling New Ways of Making the Old
 Conclusion • IC Technology has been Thought as a Killer for Computer Architecture as Performance has consistently been improved by increasing the Clock Frequency • Computer Architecture is making a Great Come-Back to help solve the new issues of multiple core processors. – Clock Frequency is now seen as a burden over core integration because of: • Clock Distribution • Power Consumption
Conclusion • IC Technology has been Thought as a Killer for Computer Architecture as Performance has consistently been improved by increasing the Clock Frequency • Computer Architecture is making a Great Come-Back to help solve the new issues of multiple core processors. – Clock Frequency is now seen as a burden over core integration because of: • Clock Distribution • Power Consumption


