36bfa3d2f12774f0f6e458f2790cc139.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Coding Technologies for Speech and Audio Signals ISPACS 2005. 12. 16 NTT Communication Science Labs. Takehiro Moriya 守谷 健弘 NTT Labs. 2005
Coding Technologies for Speech and Audio Signals ISPACS 2005. 12. 16 NTT Communication Science Labs. Takehiro Moriya 守谷 健弘 NTT Labs. 2005
 Self introduction • 1980 Joined NTT, Basic research – Transform domain interleave VQ – Conjugate VQ • • • 1989 guest researcher at AT&T Bell Labs 1990 Standardization for Japanese PDC (PSI-CELP) 1993 Standardization for ITU-T (CS-ACELP) 1995 Standardization for MPEG-4 (Twin. VQ) 2001 Standardization for MPEG lossless audio NTT Labs. 2005
Self introduction • 1980 Joined NTT, Basic research – Transform domain interleave VQ – Conjugate VQ • • • 1989 guest researcher at AT&T Bell Labs 1990 Standardization for Japanese PDC (PSI-CELP) 1993 Standardization for ITU-T (CS-ACELP) 1995 Standardization for MPEG-4 (Twin. VQ) 2001 Standardization for MPEG lossless audio NTT Labs. 2005
![Technologies of speech and audio coding bit rate [kbit/s] ubiquitous 1024 music 512 MPEG-4 Technologies of speech and audio coding bit rate [kbit/s] ubiquitous 1024 music 512 MPEG-4](https://present5.com/presentation/36bfa3d2f12774f0f6e458f2790cc139/image-3.jpg) Technologies of speech and audio coding bit rate [kbit/s] ubiquitous 1024 music 512 MPEG-4 MPEG-1 MPEG-2 CD, DAT (lossless) 256 MP 3 wideband 128 archive AAC telephone G. 722 MPEG-4 64 G. 711 32 APC-AB G. 726 G. 728 16 streaming mobile 8 vocoder Vo. IP/mobile VSELP G. 729 4 LSP PSI-CELP mobile phone PARCOR 2 year 1975 2000 2005 1980 1985 1990 1995 NTT Labs. 2005
Technologies of speech and audio coding bit rate [kbit/s] ubiquitous 1024 music 512 MPEG-4 MPEG-1 MPEG-2 CD, DAT (lossless) 256 MP 3 wideband 128 archive AAC telephone G. 722 MPEG-4 64 G. 711 32 APC-AB G. 726 G. 728 16 streaming mobile 8 vocoder Vo. IP/mobile VSELP G. 729 4 LSP PSI-CELP mobile phone PARCOR 2 year 1975 2000 2005 1980 1985 1990 1995 NTT Labs. 2005
 Outline • 1. Fundamentals – 1. 1 Time domain for speech – 1. 2 Frequency domain for audio • 2. Standardization – 2. 1 ITU-T speech coding – 2. 2 MPEG audio coding • 3. Hot topics – 3. 1 MPEG lossless (ALS, SLS, DTS) – 3. 2 MPEG SBR and SSC – 3. 3 MPEG surround NTT Labs. 2005
Outline • 1. Fundamentals – 1. 1 Time domain for speech – 1. 2 Frequency domain for audio • 2. Standardization – 2. 1 ITU-T speech coding – 2. 2 MPEG audio coding • 3. Hot topics – 3. 1 MPEG lossless (ALS, SLS, DTS) – 3. 2 MPEG SBR and SSC – 3. 3 MPEG surround NTT Labs. 2005
 Fundamentals NTT Labs. 2005
Fundamentals NTT Labs. 2005
 Category of coding lossless compression coding lossy presentation metadata speech language NTT Labs. 2005 text timedomain frequencydomain speech audio image video
Category of coding lossless compression coding lossy presentation metadata speech language NTT Labs. 2005 text timedomain frequencydomain speech audio image video
 Time-domain • linear prediction -> CELP • predictive coefficients – PARCOR (partial auto correlation) – LSP (line spectral pair) • vector quantization of excitation source – algebraic structure (ACELP) • Big market for cellular phone and Vo. IP NTT Labs. 2005
Time-domain • linear prediction -> CELP • predictive coefficients – PARCOR (partial auto correlation) – LSP (line spectral pair) • vector quantization of excitation source – algebraic structure (ACELP) • Big market for cellular phone and Vo. IP NTT Labs. 2005
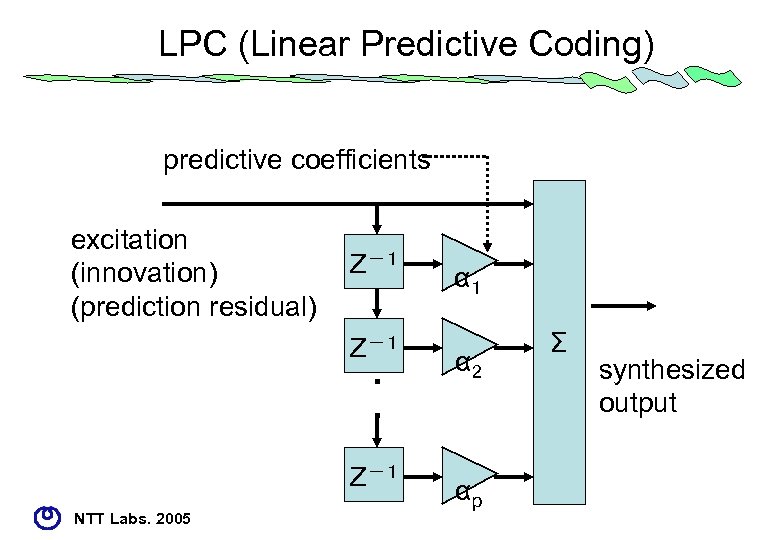 LPC (Linear Predictive Coding) predictive coefficients excitation (innovation) (prediction residual) Z-1 α1 Z-1 ・ ・ Z-1 NTT Labs. 2005 α 2 αp Σ synthesized output
LPC (Linear Predictive Coding) predictive coefficients excitation (innovation) (prediction residual) Z-1 α1 Z-1 ・ ・ Z-1 NTT Labs. 2005 α 2 αp Σ synthesized output
 Family of LPC parameters PARCOR coefficients k 1. . kp predictive coefficients α 1. . αp NTT Labs. 2005 LSP parameters ω1. . ωp ω1 ω2 merits of LSP • stability • interpolation • quantization • prediction ωp frequency
Family of LPC parameters PARCOR coefficients k 1. . kp predictive coefficients α 1. . αp NTT Labs. 2005 LSP parameters ω1. . ωp ω1 ω2 merits of LSP • stability • interpolation • quantization • prediction ωp frequency
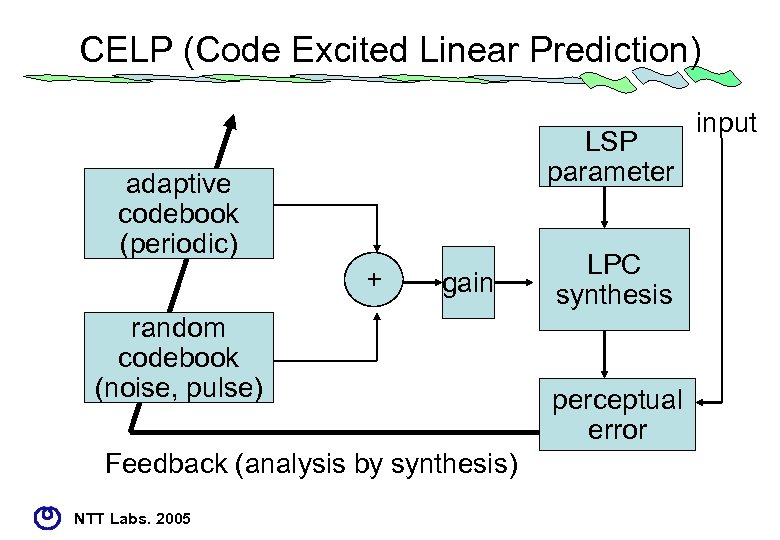 CELP (Code Excited Linear Prediction) LSP parameter adaptive codebook (periodic) + gain random codebook (noise, pulse) Feedback (analysis by synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005 LPC synthesis perceptual error input
CELP (Code Excited Linear Prediction) LSP parameter adaptive codebook (periodic) + gain random codebook (noise, pulse) Feedback (analysis by synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005 LPC synthesis perceptual error input
 Synthesis model for vocoder pitch interval gain (random) NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
Synthesis model for vocoder pitch interval gain (random) NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
 Synthesis model for multi-pulse pitch interval gain amplitude and position of pulse NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
Synthesis model for multi-pulse pitch interval gain amplitude and position of pulse NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
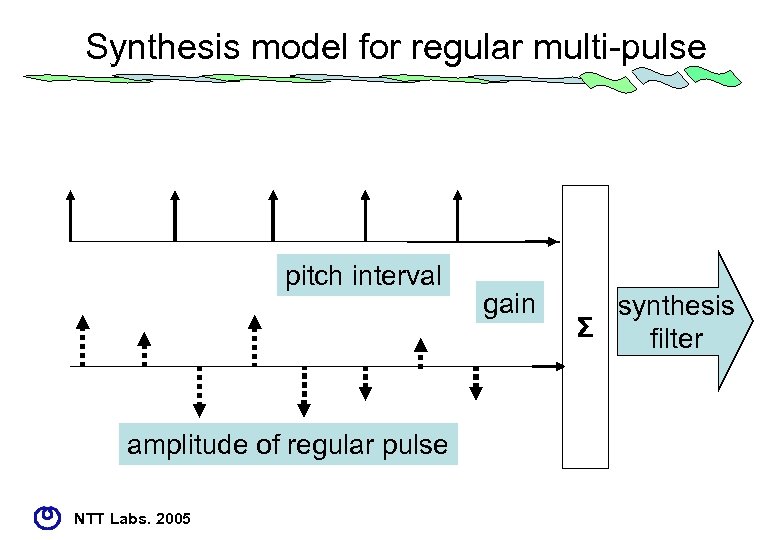 Synthesis model for regular multi-pulse pitch interval amplitude of regular pulse NTT Labs. 2005 gain synthesis Σ filter
Synthesis model for regular multi-pulse pitch interval amplitude of regular pulse NTT Labs. 2005 gain synthesis Σ filter
 Synthesis model for CELP pitch interval gain Σ ・・・・・・・ selection of code vector NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis filter
Synthesis model for CELP pitch interval gain Σ ・・・・・・・ selection of code vector NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis filter
 Synthesis model of VSELP pitch interval gain +/+/- ・・・・・・・ +/- polarity of base vector NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
Synthesis model of VSELP pitch interval gain +/+/- ・・・・・・・ +/- polarity of base vector NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
 Synthesis model for CS-CELP pitch interval gain +/+/- ・・・・・・・ +/- selection of vector pair NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
Synthesis model for CS-CELP pitch interval gain +/+/- ・・・・・・・ +/- selection of vector pair NTT Labs. 2005 synthesis Σ filter
 Synthesis model of ACELP pitch interval gain +/+/- Σ synthesis filter +/+/+/- selection of unit pulse position NTT Labs. 2005 Simplicity is the seal of truth
Synthesis model of ACELP pitch interval gain +/+/- Σ synthesis filter +/+/+/- selection of unit pulse position NTT Labs. 2005 Simplicity is the seal of truth
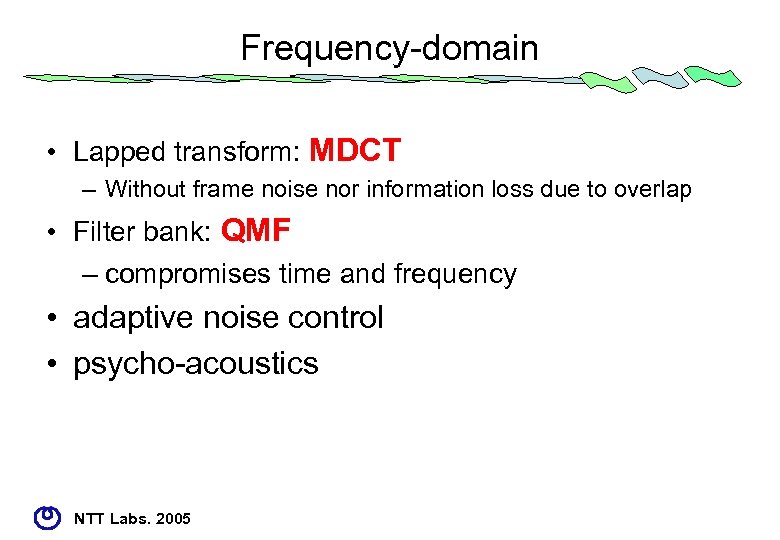 Frequency-domain • Lapped transform: MDCT – Without frame noise nor information loss due to overlap • Filter bank: QMF – compromises time and frequency • adaptive noise control • psycho-acoustics NTT Labs. 2005
Frequency-domain • Lapped transform: MDCT – Without frame noise nor information loss due to overlap • Filter bank: QMF – compromises time and frequency • adaptive noise control • psycho-acoustics NTT Labs. 2005
 Transform coding input output Transform time to frequency envelope estimation NTT Labs. 2005 quantization Adaptive bit allocation Transform frequency to time Side information
Transform coding input output Transform time to frequency envelope estimation NTT Labs. 2005 quantization Adaptive bit allocation Transform frequency to time Side information
 Base of DCT frequency time NTT Labs. 2005
Base of DCT frequency time NTT Labs. 2005
 Base of MDCT 0 verlap with previous frame anti-symmetry NTT Labs. 2005 symmetry 0 verlap with next frame
Base of MDCT 0 verlap with previous frame anti-symmetry NTT Labs. 2005 symmetry 0 verlap with next frame
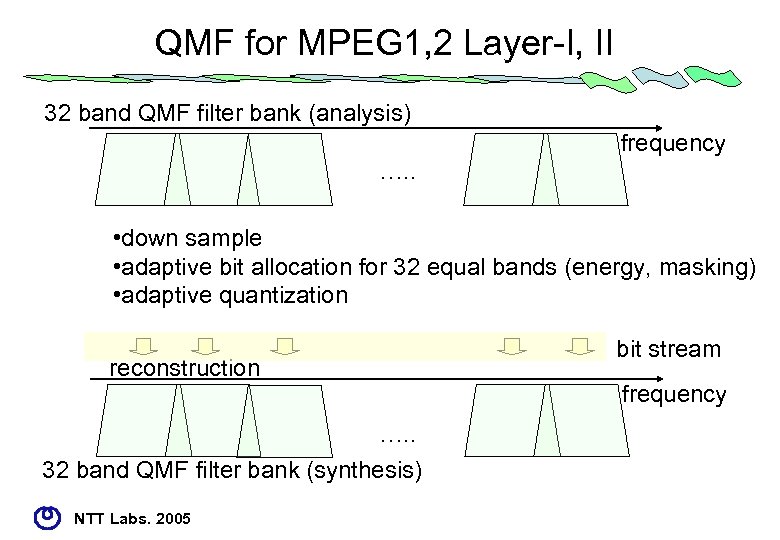 QMF for MPEG 1, 2 Layer-I, II 32 band QMF filter bank (analysis) frequency …. . • down sample • adaptive bit allocation for 32 equal bands (energy, masking) • adaptive quantization reconstruction …. . 32 band QMF filter bank (synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005 bit stream frequency
QMF for MPEG 1, 2 Layer-I, II 32 band QMF filter bank (analysis) frequency …. . • down sample • adaptive bit allocation for 32 equal bands (energy, masking) • adaptive quantization reconstruction …. . 32 band QMF filter bank (synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005 bit stream frequency
 QMF for MPEG 1, 2 Layer-III 32 band QMF filter bank (analysis) frequency …. . • down sample • long and short MDCT • adaptive bit allocation for Bark-scale (energy, masking) • adaptive quantization (Huffman coding), bit reservoir bit stream reconstruction frequency …. . 32 band QMF filter bank (synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005
QMF for MPEG 1, 2 Layer-III 32 band QMF filter bank (analysis) frequency …. . • down sample • long and short MDCT • adaptive bit allocation for Bark-scale (energy, masking) • adaptive quantization (Huffman coding), bit reservoir bit stream reconstruction frequency …. . 32 band QMF filter bank (synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005
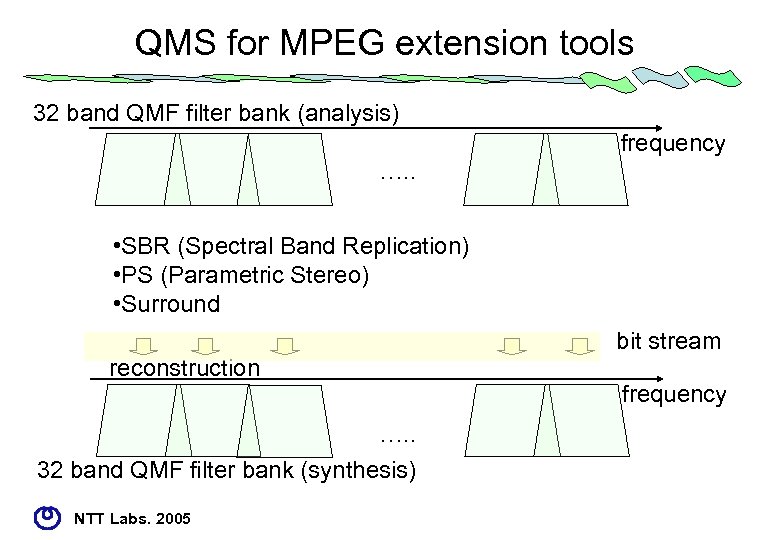 QMS for MPEG extension tools 32 band QMF filter bank (analysis) frequency …. . • SBR (Spectral Band Replication) • PS (Parametric Stereo) • Surround reconstruction …. . 32 band QMF filter bank (synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005 bit stream frequency
QMS for MPEG extension tools 32 band QMF filter bank (analysis) frequency …. . • SBR (Spectral Band Replication) • PS (Parametric Stereo) • Surround reconstruction …. . 32 band QMF filter bank (synthesis) NTT Labs. 2005 bit stream frequency
 Masking effect log spectrum original spectrum allowable noise level masked region audible level frequency NTT Labs. 2005
Masking effect log spectrum original spectrum allowable noise level masked region audible level frequency NTT Labs. 2005
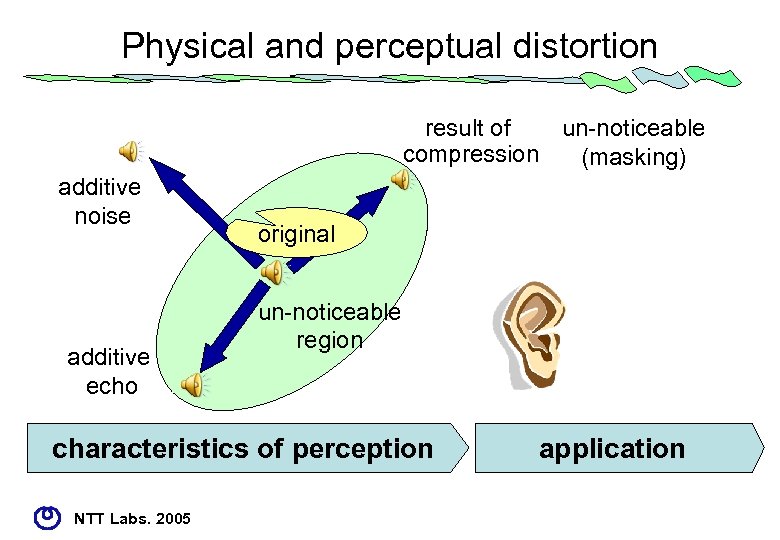 Physical and perceptual distortion un-noticeable result of compression (masking) additive noise additive echo original un-noticeable region characteristics of perception NTT Labs. 2005 application
Physical and perceptual distortion un-noticeable result of compression (masking) additive noise additive echo original un-noticeable region characteristics of perception NTT Labs. 2005 application
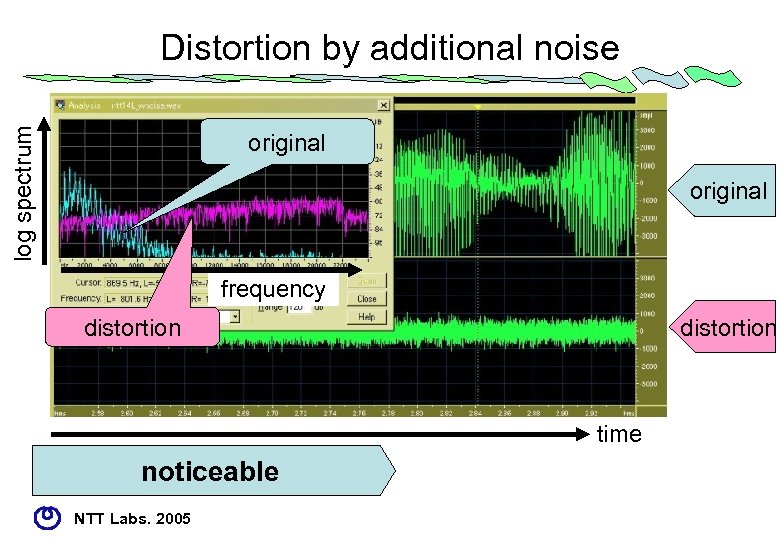 log spectrum Distortion by additional noise original frequency distortion time noticeable NTT Labs. 2005
log spectrum Distortion by additional noise original frequency distortion time noticeable NTT Labs. 2005
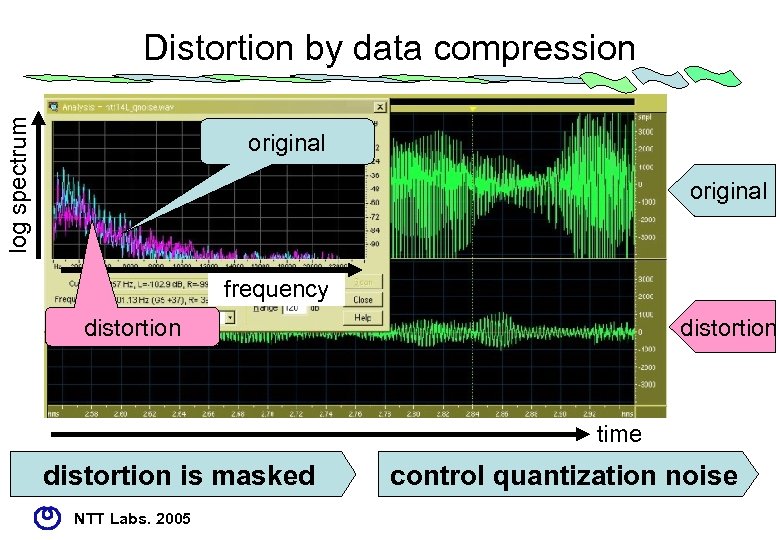 log spectrum Distortion by data compression original frequency distortion time distortion is masked NTT Labs. 2005 control quantization noise
log spectrum Distortion by data compression original frequency distortion time distortion is masked NTT Labs. 2005 control quantization noise
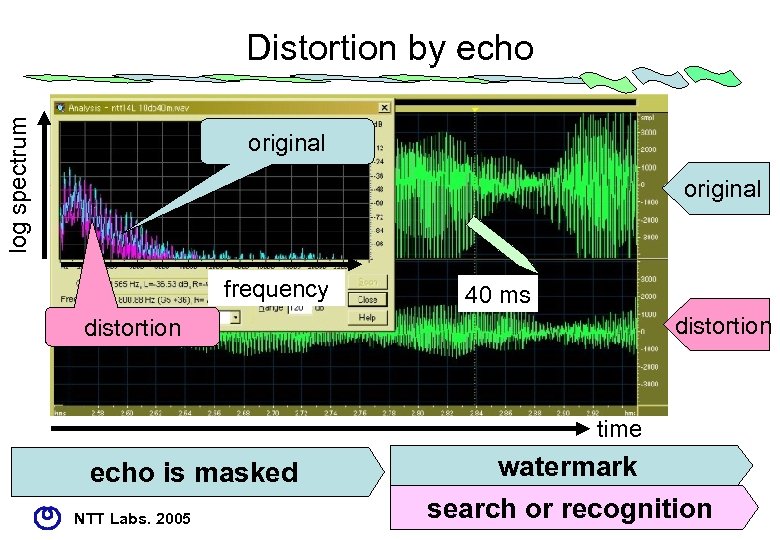 log spectrum Distortion by echo original frequency 40 ms distortion time echo is masked NTT Labs. 2005 watermark search or recognition
log spectrum Distortion by echo original frequency 40 ms distortion time echo is masked NTT Labs. 2005 watermark search or recognition
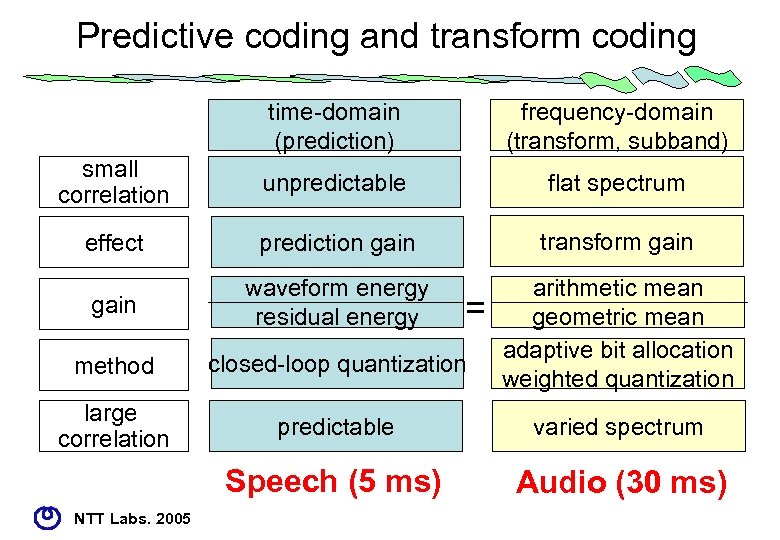 Predictive coding and transform coding time-domain (prediction) frequency-domain (transform, subband) small correlation unpredictable flat spectrum effect prediction gain transform gain waveform energy residual energy method closed-loop quantization arithmetic mean geometric mean adaptive bit allocation weighted quantization large correlation predictable varied spectrum Speech (5 ms) Audio (30 ms) NTT Labs. 2005 =
Predictive coding and transform coding time-domain (prediction) frequency-domain (transform, subband) small correlation unpredictable flat spectrum effect prediction gain transform gain waveform energy residual energy method closed-loop quantization arithmetic mean geometric mean adaptive bit allocation weighted quantization large correlation predictable varied spectrum Speech (5 ms) Audio (30 ms) NTT Labs. 2005 =
 Standards NTT Labs. 2005
Standards NTT Labs. 2005
 Example of standard • ITU-T – cellular phone – Vo. IP – TV-phone – FAX • ISO/IEC JPEG, MPEG – digital camera, video – digital broadcasting – portable music player, DVD NTT Labs. 2005
Example of standard • ITU-T – cellular phone – Vo. IP – TV-phone – FAX • ISO/IEC JPEG, MPEG – digital camera, video – digital broadcasting – portable music player, DVD NTT Labs. 2005
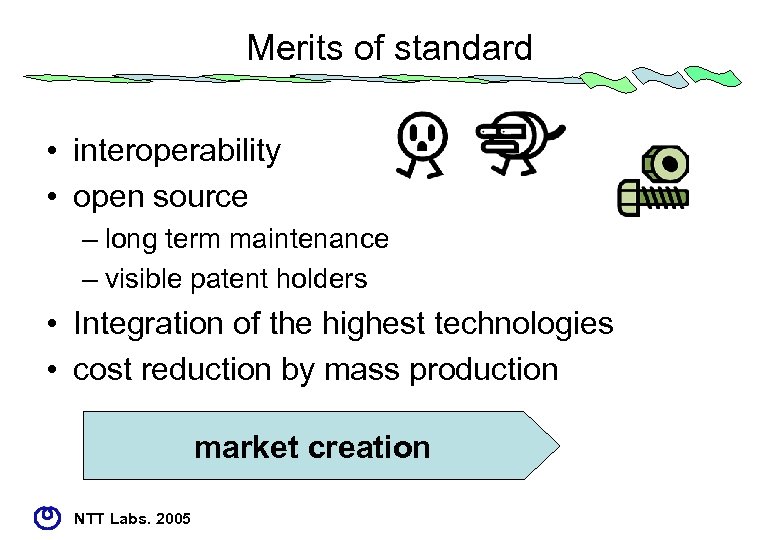 Merits of standard • interoperability • open source – long term maintenance – visible patent holders • Integration of the highest technologies • cost reduction by mass production market creation NTT Labs. 2005
Merits of standard • interoperability • open source – long term maintenance – visible patent holders • Integration of the highest technologies • cost reduction by mass production market creation NTT Labs. 2005
 Circulatory evolution of market cost reduction disclosure of technology patent standard R&D basic research NTT Labs. 2005 service product market research service and products users convenient competition royalty patent pool
Circulatory evolution of market cost reduction disclosure of technology patent standard R&D basic research NTT Labs. 2005 service product market research service and products users convenient competition royalty patent pool
 Standardization for speech • • • ITU-T G. IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunication) GSM (European, Asia) TIA (North America) US FS-1015 (LPC-10), 1016 (CELP), 1017 (MELP) Japanese Cellular - PDC full/half rate - PHS - cdma. One - PDC enhanced full rate NTT Labs. 2005
Standardization for speech • • • ITU-T G. IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunication) GSM (European, Asia) TIA (North America) US FS-1015 (LPC-10), 1016 (CELP), 1017 (MELP) Japanese Cellular - PDC full/half rate - PHS - cdma. One - PDC enhanced full rate NTT Labs. 2005
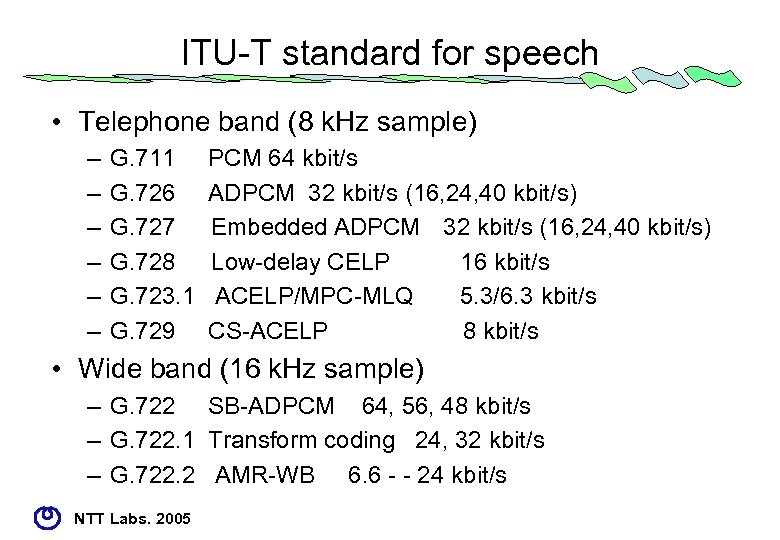 ITU-T standard for speech • Telephone band (8 k. Hz sample) – – – G. 711 G. 726 G. 727 G. 728 G. 723. 1 G. 729 PCM 64 kbit/s ADPCM 32 kbit/s (16, 24, 40 kbit/s) Embedded ADPCM 32 kbit/s (16, 24, 40 kbit/s) Low-delay CELP 16 kbit/s ACELP/MPC-MLQ 5. 3/6. 3 kbit/s CS-ACELP 8 kbit/s • Wide band (16 k. Hz sample) – G. 722 SB-ADPCM 64, 56, 48 kbit/s – G. 722. 1 Transform coding 24, 32 kbit/s – G. 722. 2 AMR-WB 6. 6 - - 24 kbit/s NTT Labs. 2005
ITU-T standard for speech • Telephone band (8 k. Hz sample) – – – G. 711 G. 726 G. 727 G. 728 G. 723. 1 G. 729 PCM 64 kbit/s ADPCM 32 kbit/s (16, 24, 40 kbit/s) Embedded ADPCM 32 kbit/s (16, 24, 40 kbit/s) Low-delay CELP 16 kbit/s ACELP/MPC-MLQ 5. 3/6. 3 kbit/s CS-ACELP 8 kbit/s • Wide band (16 k. Hz sample) – G. 722 SB-ADPCM 64, 56, 48 kbit/s – G. 722. 1 Transform coding 24, 32 kbit/s – G. 722. 2 AMR-WB 6. 6 - - 24 kbit/s NTT Labs. 2005
 Standard for IMT-2000 • 3 GPP (3 rd Generation Partnership Project) (ARIB, TTC, T 1, ETSI, TTA ) • 3 GPP 2 • bi-directional CODEC AMR (Advanced Multi Rate) AMR-WB (wide band) • video phone (H. 263) • Audio/Low rate speech • packet transmission (MPEG-4) NTT Labs. 2005
Standard for IMT-2000 • 3 GPP (3 rd Generation Partnership Project) (ARIB, TTC, T 1, ETSI, TTA ) • 3 GPP 2 • bi-directional CODEC AMR (Advanced Multi Rate) AMR-WB (wide band) • video phone (H. 263) • Audio/Low rate speech • packet transmission (MPEG-4) NTT Labs. 2005
![Bandwidth and bitrate for audio coding bandwidth [k. Hz] 24 18 MPEG-4 DAT CD Bandwidth and bitrate for audio coding bandwidth [k. Hz] 24 18 MPEG-4 DAT CD](https://present5.com/presentation/36bfa3d2f12774f0f6e458f2790cc139/image-38.jpg) Bandwidth and bitrate for audio coding bandwidth [k. Hz] 24 18 MPEG-4 DAT CD MPEG-2 MD multi-channel MPEG-1 AC-3, AAC 12 MPEG-2, 1/2 sample 6 0 24 48 96 Rate[kbit/s] NTT Labs. 2005 192 384 768
Bandwidth and bitrate for audio coding bandwidth [k. Hz] 24 18 MPEG-4 DAT CD MPEG-2 MD multi-channel MPEG-1 AC-3, AAC 12 MPEG-2, 1/2 sample 6 0 24 48 96 Rate[kbit/s] NTT Labs. 2005 192 384 768
 Basic technology for audio coding Transform Quantization MPEG-1 L 1, 2 subband adaptive bit MPEG-1 L 3 subband+MDCT adaptive+Huffman ATRAC subband+MDCT adaptive bit AC-3 MDCT adaptive+Huffman AAC MDCT adaptive+Huffman Twin. VQ MDCT adaptive VQ NTT Labs. 2005
Basic technology for audio coding Transform Quantization MPEG-1 L 1, 2 subband adaptive bit MPEG-1 L 3 subband+MDCT adaptive+Huffman ATRAC subband+MDCT adaptive bit AC-3 MDCT adaptive+Huffman AAC MDCT adaptive+Huffman Twin. VQ MDCT adaptive VQ NTT Labs. 2005
 MPEG-1, 2/audio • MPEG-1 – sampling rate: 32, 44. 1, 48 k. Hz stereo – algorithm: Layer-I 32 band split Layer-II + improved quantizer Layer-III + MDCT + Variable length + bit reservoir ++ • MPEG-2 – low sampling rate 16, 22. 05, 24 k. Hz – multi channel 5. 1 ch – backward compatibility NTT Labs. 2005
MPEG-1, 2/audio • MPEG-1 – sampling rate: 32, 44. 1, 48 k. Hz stereo – algorithm: Layer-I 32 band split Layer-II + improved quantizer Layer-III + MDCT + Variable length + bit reservoir ++ • MPEG-2 – low sampling rate 16, 22. 05, 24 k. Hz – multi channel 5. 1 ch – backward compatibility NTT Labs. 2005
 MPEG-2/AAC • 3 profiles -main, -LC (Low Complexity), -SSR (Scalable Sampling Rate) • • • sampling rate: 32, 44. 1, 48 k. Hz, +X 2, X 1/4 channel: 1 -48 bit rate: 8 -576 kbit/s/ch MDCT 1024 or 128 TNS (Time domain Noise Shaping) MS (Middle-Side) stereo/intensity stereo • non-linear scale quantizer + variable length code (2 and 4 dimension Huffman code) NTT Labs. 2005
MPEG-2/AAC • 3 profiles -main, -LC (Low Complexity), -SSR (Scalable Sampling Rate) • • • sampling rate: 32, 44. 1, 48 k. Hz, +X 2, X 1/4 channel: 1 -48 bit rate: 8 -576 kbit/s/ch MDCT 1024 or 128 TNS (Time domain Noise Shaping) MS (Middle-Side) stereo/intensity stereo • non-linear scale quantizer + variable length code (2 and 4 dimension Huffman code) NTT Labs. 2005
 Tools in MPEG-4 audio l. Low rate speech HVXC (Harmonic Vector e. Xcitation Coder) l. Speech (narrow/wide) CELP l. Low rate audio Twin. VQ (Transform domain Weighted Interleave VQ) l. Audio MPEG-2 AAC (Advanced Audio Coder) l. Error resilient framework l. Parametric audio coding HILN l. Fine granular scalable audio coding BSAC l. Low delay audio coding LD-AAC l. Low overhead Audio Transport LATM NTT Labs. 2005
Tools in MPEG-4 audio l. Low rate speech HVXC (Harmonic Vector e. Xcitation Coder) l. Speech (narrow/wide) CELP l. Low rate audio Twin. VQ (Transform domain Weighted Interleave VQ) l. Audio MPEG-2 AAC (Advanced Audio Coder) l. Error resilient framework l. Parametric audio coding HILN l. Fine granular scalable audio coding BSAC l. Low delay audio coding LD-AAC l. Low overhead Audio Transport LATM NTT Labs. 2005
 MPEG-4 General audio Twin. VQ interleave VQ for MDCT AAC scale factor Huffman coding BSAC scale factor Bit-slice arithmetic NTT Labs. 2005 common tools LTP TNS stereo coding scalability IMDCT output
MPEG-4 General audio Twin. VQ interleave VQ for MDCT AAC scale factor Huffman coding BSAC scale factor Bit-slice arithmetic NTT Labs. 2005 common tools LTP TNS stereo coding scalability IMDCT output
 Audio Demo (low rate) • ITU-T G. 711 64 kbit/s • ITU-T G. 726 32 kbit/s • ITU-T G. 728 16 kbit/s • ITU-T G. 729 8 kbit/s • PDC Full 6. 7 kbit/s • PDC Half 3. 45 kbit/s • MPEG 4 HVXC 2 kbit/s • MPEG 4 Twin. VQ 8 kbit/s NTT Labs. 2005
Audio Demo (low rate) • ITU-T G. 711 64 kbit/s • ITU-T G. 726 32 kbit/s • ITU-T G. 728 16 kbit/s • ITU-T G. 729 8 kbit/s • PDC Full 6. 7 kbit/s • PDC Half 3. 45 kbit/s • MPEG 4 HVXC 2 kbit/s • MPEG 4 Twin. VQ 8 kbit/s NTT Labs. 2005
 Hot Topics NTT Labs. 2005
Hot Topics NTT Labs. 2005
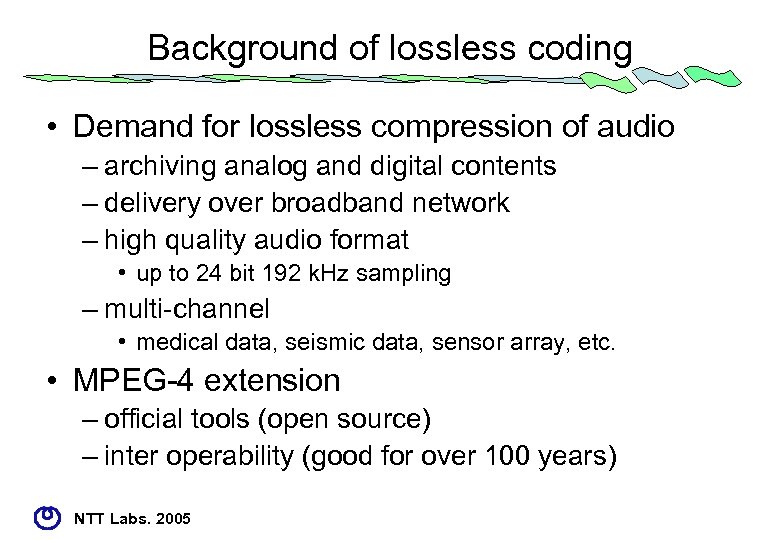 Background of lossless coding • Demand for lossless compression of audio – archiving analog and digital contents – delivery over broadband network – high quality audio format • up to 24 bit 192 k. Hz sampling – multi-channel • medical data, seismic data, sensor array, etc. • MPEG-4 extension – official tools (open source) – inter operability (good for over 100 years) NTT Labs. 2005
Background of lossless coding • Demand for lossless compression of audio – archiving analog and digital contents – delivery over broadband network – high quality audio format • up to 24 bit 192 k. Hz sampling – multi-channel • medical data, seismic data, sensor array, etc. • MPEG-4 extension – official tools (open source) – inter operability (good for over 100 years) NTT Labs. 2005
 Family of MPEG lossless • ALS – one-step compression in time domain • SLS – scalable to lossless from MPEG lossy core – fine grain scalability in frequency domain – Integer MDCT • DTS – 1 -bit oversample format – compatible with Sony-Philips SACD format NTT Labs. 2005
Family of MPEG lossless • ALS – one-step compression in time domain • SLS – scalable to lossless from MPEG lossy core – fine grain scalability in frequency domain – Integer MDCT • DTS – 1 -bit oversample format – compatible with Sony-Philips SACD format NTT Labs. 2005
 Property of ALS • Time domain adaptive prediction – – – simple to high-performance backward prediction BGMC for prediction residual Golomb-Rice Code for PARCOR Progressive order prediction Long-term prediction Hierarchical block switching • extension – Floating-point support – Multi-channel predictive coding NTT Labs. 2005
Property of ALS • Time domain adaptive prediction – – – simple to high-performance backward prediction BGMC for prediction residual Golomb-Rice Code for PARCOR Progressive order prediction Long-term prediction Hierarchical block switching • extension – Floating-point support – Multi-channel predictive coding NTT Labs. 2005
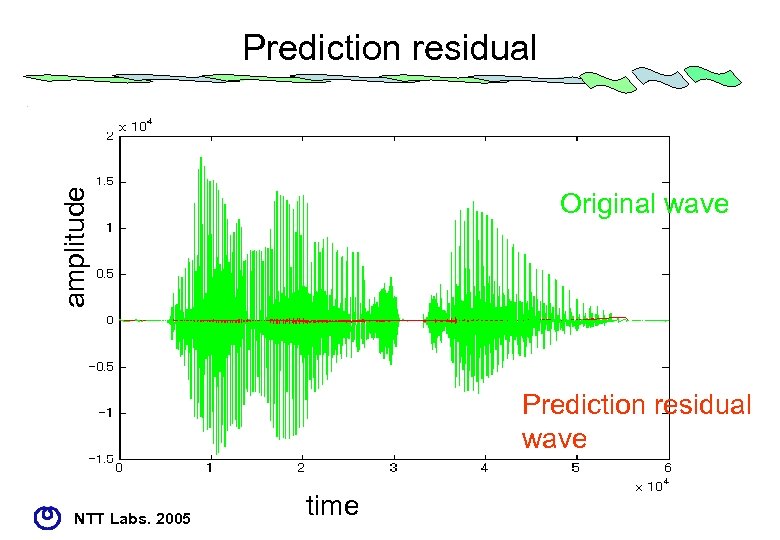 amplitude Prediction residual Original wave Prediction residual wave NTT Labs. 2005 time
amplitude Prediction residual Original wave Prediction residual wave NTT Labs. 2005 time
 Predictive coding input residual prediction magnify 30 times vocoder compression ratio pulse interval 1/30 waveform coding codebook for residual synthesis parameters different framework NTT Labs. 2005 lossless coding all residual ratio 1/10 ratio 1/2 rich commonality
Predictive coding input residual prediction magnify 30 times vocoder compression ratio pulse interval 1/30 waveform coding codebook for residual synthesis parameters different framework NTT Labs. 2005 lossless coding all residual ratio 1/10 ratio 1/2 rich commonality
![Compression and decoding time compression ratio [%] ALS (reference decoder) Monkey’s Audio (free Software) Compression and decoding time compression ratio [%] ALS (reference decoder) Monkey’s Audio (free Software)](https://present5.com/presentation/36bfa3d2f12774f0f6e458f2790cc139/image-51.jpg) Compression and decoding time compression ratio [%] ALS (reference decoder) Monkey’s Audio (free Software) 50 [%] 49 49 50 48 48 MPEG-4 SLS 47 Optim. Frog (free Software) 46 45 5 10 15 averaged decoding time for 30 NTT Labs. 2005 47 46 ALS (enhanced decoder) 0 ALS (high-compression) 45 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 sec files (48, 96, 192 k. Hz) [sec]
Compression and decoding time compression ratio [%] ALS (reference decoder) Monkey’s Audio (free Software) 50 [%] 49 49 50 48 48 MPEG-4 SLS 47 Optim. Frog (free Software) 46 45 5 10 15 averaged decoding time for 30 NTT Labs. 2005 47 46 ALS (enhanced decoder) 0 ALS (high-compression) 45 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 sec files (48, 96, 192 k. Hz) [sec]
 relative quality Quality improvements by SBR and PS Japanese mobile digital broadcasting (2006) AAC MP 3 HE-AAC V 2 HE-AAC Japanese digital broadcasting (2003) AAC SBR PS AAC profile HE-AAC V 2 profile 24 NTT Labs. 2005 48 72 96 120 144 stereo bit rate [kbit/s]
relative quality Quality improvements by SBR and PS Japanese mobile digital broadcasting (2006) AAC MP 3 HE-AAC V 2 HE-AAC Japanese digital broadcasting (2003) AAC SBR PS AAC profile HE-AAC V 2 profile 24 NTT Labs. 2005 48 72 96 120 144 stereo bit rate [kbit/s]
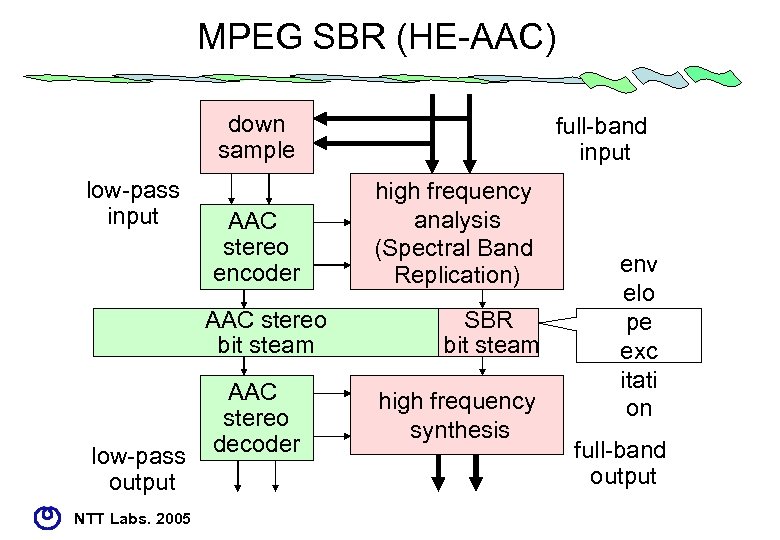 MPEG SBR (HE-AAC) down sample low-pass input AAC stereo encoder AAC stereo bit steam low-pass output NTT Labs. 2005 AAC stereo decoder full-band input high frequency analysis (Spectral Band Replication) SBR bit steam high frequency synthesis env elo pe exc itati on full-band output
MPEG SBR (HE-AAC) down sample low-pass input AAC stereo encoder AAC stereo bit steam low-pass output NTT Labs. 2005 AAC stereo decoder full-band input high frequency analysis (Spectral Band Replication) SBR bit steam high frequency synthesis env elo pe exc itati on full-band output
 MPEG SBR+PS (HE-AAC v 2) monaural input mix down AAC monaural encoder AAC monaural bit steam monaural output AAC monaural decoder NTT Labs. 2005 stereo input PS (parametric stereo) analysis PS bit stream Channel level differences Inter channel correlation PS (parametric stereo) synthesis stereo output
MPEG SBR+PS (HE-AAC v 2) monaural input mix down AAC monaural encoder AAC monaural bit steam monaural output AAC monaural decoder NTT Labs. 2005 stereo input PS (parametric stereo) analysis PS bit stream Channel level differences Inter channel correlation PS (parametric stereo) synthesis stereo output
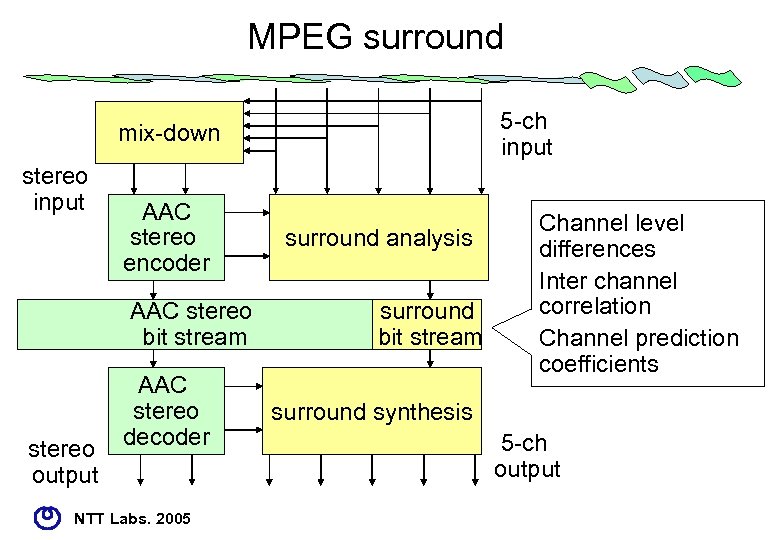 MPEG surround 5 -ch input mix-down stereo input AAC stereo encoder AAC stereo bit stream stereo output AAC stereo decoder NTT Labs. 2005 surround analysis surround bit stream Channel level differences Inter channel correlation Channel prediction coefficients surround synthesis 5 -ch output
MPEG surround 5 -ch input mix-down stereo input AAC stereo encoder AAC stereo bit stream stereo output AAC stereo decoder NTT Labs. 2005 surround analysis surround bit stream Channel level differences Inter channel correlation Channel prediction coefficients surround synthesis 5 -ch output
 History of MPEG Audio surround forward and backward compatibility MPEG-2 MC/LSF SLS SBR SSC MPEG-4 V 1 V 2 2001 ALS MP 3 on 4 MPEG-2 AAC DST 2005 lossless MPEG-1 *Multi-channel and Low Sampling Frequency 1992 1994 NTT Labs. 2005 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006
History of MPEG Audio surround forward and backward compatibility MPEG-2 MC/LSF SLS SBR SSC MPEG-4 V 1 V 2 2001 ALS MP 3 on 4 MPEG-2 AAC DST 2005 lossless MPEG-1 *Multi-channel and Low Sampling Frequency 1992 1994 NTT Labs. 2005 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006
 Future challenge • Open problems – all-mighty coder for both speech and audio at less than 16 kbit/s – Wave field synthesis (multi-channel) • Integrated service – video – copyright management NTT Labs. 2005
Future challenge • Open problems – all-mighty coder for both speech and audio at less than 16 kbit/s – Wave field synthesis (multi-channel) • Integrated service – video – copyright management NTT Labs. 2005


