4d7fe07aad801dfca7daa7dbf0b658e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 126
 Coding 2015 Challenges and Opportunities Richard H. Tuck, MD, FAAP © 10/1/14
Coding 2015 Challenges and Opportunities Richard H. Tuck, MD, FAAP © 10/1/14
 IMPORTANCE OF ACCURATE APPROPRIATE CODING n INCREASED PAYMENT n DECREASED LIABILITY n IMPROVED INFORMATION FLOW
IMPORTANCE OF ACCURATE APPROPRIATE CODING n INCREASED PAYMENT n DECREASED LIABILITY n IMPROVED INFORMATION FLOW
 ICD-10 -CM READY OR NOT ? ! October 1, 2015
ICD-10 -CM READY OR NOT ? ! October 1, 2015
 ICD-10 -CM n Will become effective October 1, 2015 – NO EXCEPTIONS if you are a covered entity under HIPAA. – Currently there is a freeze on new ICD-9 -CM and ICD -10 -CM codes to prepare for the changeover.
ICD-10 -CM n Will become effective October 1, 2015 – NO EXCEPTIONS if you are a covered entity under HIPAA. – Currently there is a freeze on new ICD-9 -CM and ICD -10 -CM codes to prepare for the changeover.
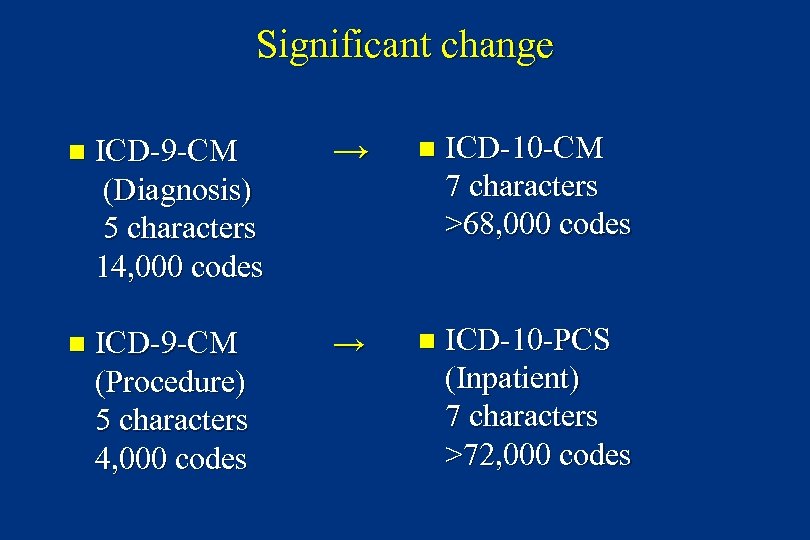 Significant change n ICD-9 -CM (Diagnosis) 5 characters 14, 000 codes → n ICD-10 -CM 7 characters >68, 000 codes n ICD-9 -CM (Procedure) 5 characters 4, 000 codes → n ICD-10 -PCS (Inpatient) 7 characters >72, 000 codes
Significant change n ICD-9 -CM (Diagnosis) 5 characters 14, 000 codes → n ICD-10 -CM 7 characters >68, 000 codes n ICD-9 -CM (Procedure) 5 characters 4, 000 codes → n ICD-10 -PCS (Inpatient) 7 characters >72, 000 codes
 Value to Providers More accurately reflects the acuity of the patient population n More accurately reflects application of advances in medical knowledge n Improved visibility into population health/risks n Better defined and automated referrals and approvals n More detail for preauthorization medical review n
Value to Providers More accurately reflects the acuity of the patient population n More accurately reflects application of advances in medical knowledge n Improved visibility into population health/risks n Better defined and automated referrals and approvals n More detail for preauthorization medical review n
 Enhanced Care Management + ? Payment More detail to support effective engagement and interventions n Enhanced knowledge sharing, communication, and coordination n Improved analytics and compliance n Better identification of gaps in care n
Enhanced Care Management + ? Payment More detail to support effective engagement and interventions n Enhanced knowledge sharing, communication, and coordination n Improved analytics and compliance n Better identification of gaps in care n
 Innovation Supports: n Patient Centered Primary Care n Clinical Integration Strategies n Accountable Care Organizations n Value Based Reimbursement
Innovation Supports: n Patient Centered Primary Care n Clinical Integration Strategies n Accountable Care Organizations n Value Based Reimbursement
 Using and Reporting ICD-9 (10)-CM Codes Code to the highest degree of specificity Code to the highest degree of certainty for the encounter such as symptoms, signs, abnormal test results, Probable, suspected , questionable, or rule out should not be coded List the ICD code that is identified as the main reason for the service first. Next list any current coexisting conditions. Chronic disease treated on an ongoing basis may be coded Do not code for conditions that were previously treated and no longer exist
Using and Reporting ICD-9 (10)-CM Codes Code to the highest degree of specificity Code to the highest degree of certainty for the encounter such as symptoms, signs, abnormal test results, Probable, suspected , questionable, or rule out should not be coded List the ICD code that is identified as the main reason for the service first. Next list any current coexisting conditions. Chronic disease treated on an ongoing basis may be coded Do not code for conditions that were previously treated and no longer exist
 ICD-10 -CM Code Format and Structure S 60 Superficial injury of wrist, hand fingers* n S 60. 4 Other superficial injuries of other fingers n S 60. 45 Superficial foreign body [splinter] of fingers** n S 60. 451 Superficial foreign body [splinter] of left index finger n S 60. 451 A Superficial foreign body [splinter] of left index finger, initial encounter*** n Required to use the 7 digit code for this condition » *category, **subcategory, ***code n
ICD-10 -CM Code Format and Structure S 60 Superficial injury of wrist, hand fingers* n S 60. 4 Other superficial injuries of other fingers n S 60. 45 Superficial foreign body [splinter] of fingers** n S 60. 451 Superficial foreign body [splinter] of left index finger n S 60. 451 A Superficial foreign body [splinter] of left index finger, initial encounter*** n Required to use the 7 digit code for this condition » *category, **subcategory, ***code n
 How Do Codes Translate ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM?
How Do Codes Translate ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM?
 ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n Some codes will have the same wording between the 2 codes sets and basically “crosswalk” over ICD-9 -CM 003. 21 Salmonella meningitis to = ICD-10 -CM A 02. 21 Salmonella meningitis 745. 2 Tetralogy of Fallot = Q 21. 3 Tetralogy of Fallot
ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n Some codes will have the same wording between the 2 codes sets and basically “crosswalk” over ICD-9 -CM 003. 21 Salmonella meningitis to = ICD-10 -CM A 02. 21 Salmonella meningitis 745. 2 Tetralogy of Fallot = Q 21. 3 Tetralogy of Fallot
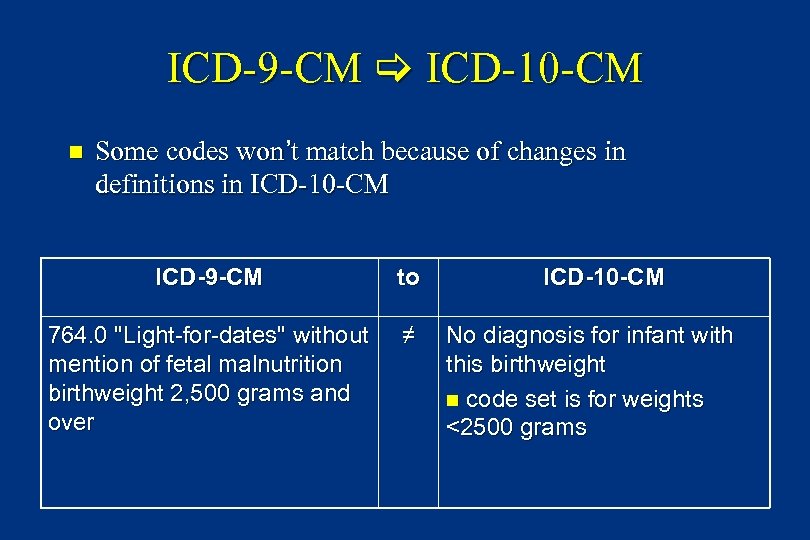 ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n Some codes won’t match because of changes in definitions in ICD-10 -CM ICD-9 -CM to 764. 0 "Light-for-dates" without mention of fetal malnutrition birthweight 2, 500 grams and over ≠ ICD-10 -CM No diagnosis for infant with this birthweight n code set is for weights <2500 grams
ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n Some codes won’t match because of changes in definitions in ICD-10 -CM ICD-9 -CM to 764. 0 "Light-for-dates" without mention of fetal malnutrition birthweight 2, 500 grams and over ≠ ICD-10 -CM No diagnosis for infant with this birthweight n code set is for weights <2500 grams
 ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n When there is more specificity in I-10, there may be multiple codes to describe the condition or disease. Increased physician documentation will be vital ICD-9 -CM Source to ICD-10 -CM Target 599. 72 Microscopic hematuria ≈ R 31. 1 Benign essential microscopic hematuria 599. 72 Microscopic hematuria ≈ R 31. 2 Other microscopic hematuria
ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n When there is more specificity in I-10, there may be multiple codes to describe the condition or disease. Increased physician documentation will be vital ICD-9 -CM Source to ICD-10 -CM Target 599. 72 Microscopic hematuria ≈ R 31. 1 Benign essential microscopic hematuria 599. 72 Microscopic hematuria ≈ R 31. 2 Other microscopic hematuria
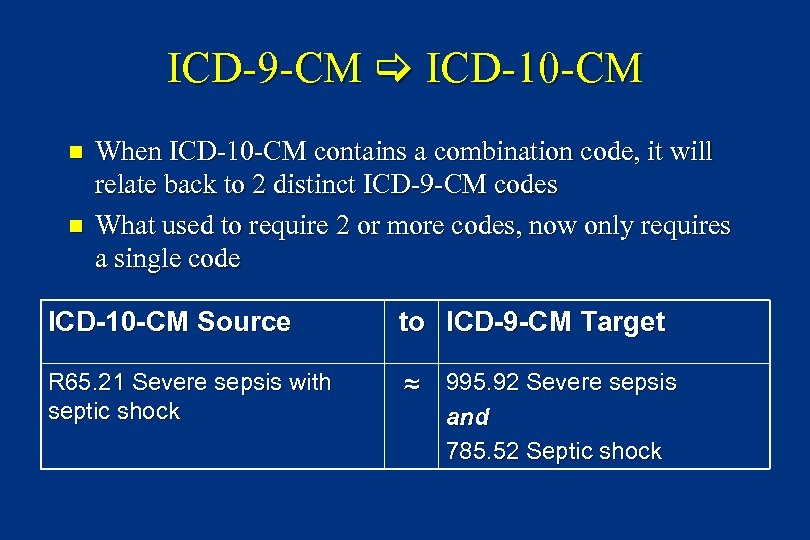 ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n n When ICD-10 -CM contains a combination code, it will relate back to 2 distinct ICD-9 -CM codes What used to require 2 or more codes, now only requires a single code ICD-10 -CM Source to ICD-9 -CM Target R 65. 21 Severe sepsis with septic shock ≈ 995. 92 Severe sepsis and 785. 52 Septic shock
ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM n n When ICD-10 -CM contains a combination code, it will relate back to 2 distinct ICD-9 -CM codes What used to require 2 or more codes, now only requires a single code ICD-10 -CM Source to ICD-9 -CM Target R 65. 21 Severe sepsis with septic shock ≈ 995. 92 Severe sepsis and 785. 52 Septic shock
 Otitis Media ICD-10 n Specific Variables – Acuity » Acute/subacute vs. chronic – Specific Type » Serous, mucoid, suppurative, sanguineous – Rupture of eardrum – Laterality » Right, Left, Bilateral – Recurrence
Otitis Media ICD-10 n Specific Variables – Acuity » Acute/subacute vs. chronic – Specific Type » Serous, mucoid, suppurative, sanguineous – Rupture of eardrum – Laterality » Right, Left, Bilateral – Recurrence
 Terminology matters n Acute suppurative otitis media without spontaneous rupture of ear drum – H 66. 001, right ear – H 66. 002, left ear – H 66. 003, bilateral – H 66. 004, recurrent, right ear – H 66. 005, recurrent, left ear – H 66. 006, recurrent, bilateral – H 66. 007, recurrent, unspecified ear – H 66. 009, unspecified ear
Terminology matters n Acute suppurative otitis media without spontaneous rupture of ear drum – H 66. 001, right ear – H 66. 002, left ear – H 66. 003, bilateral – H 66. 004, recurrent, right ear – H 66. 005, recurrent, left ear – H 66. 006, recurrent, bilateral – H 66. 007, recurrent, unspecified ear – H 66. 009, unspecified ear
 Asthma Documentation Improved State of the asthma Uncomplicate, acute exacerbation, status n Frequency Mild intermittent Mild, moderate, severe persistent n Triggers Ex tobacco smoke n
Asthma Documentation Improved State of the asthma Uncomplicate, acute exacerbation, status n Frequency Mild intermittent Mild, moderate, severe persistent n Triggers Ex tobacco smoke n
 Asthma ICD-10 n n n J 45. 2 x J 45. 3 x J 45. 4 x J 45. 5 x X= – 0 – 1 – 2 Mild intermitent Mild persistent Mod persistent Severe persistent Uncomplicated With acute exacerbation With status asthmaticus Z 77. 22 Exposure to tobacco smoke
Asthma ICD-10 n n n J 45. 2 x J 45. 3 x J 45. 4 x J 45. 5 x X= – 0 – 1 – 2 Mild intermitent Mild persistent Mod persistent Severe persistent Uncomplicated With acute exacerbation With status asthmaticus Z 77. 22 Exposure to tobacco smoke
 Case Scenario n n You see an est pt, 4 year old boy, with a hx of asthma. Exp Prob Focused Hx: Intermittent night time cough, with occasional episodes of wheezing, relieved using an albuterol MDI; No restrictions of activity noted FHx: No others ill; SHx Parents smoke “outside” Vitals wnl, pulse ox 98%; No respiratory distress; Detailed exam: rare expiratory wheezes. You make a diagnosis of asthma using current asthma dx guidelines. You discuss the diagnosis in detail, including management of asthma using rescue (albuterol) and controller (inhaled steroid) MDIs. The use of MDI’s with a spacer is discussed, demonstrated, and documented. Followup visit is scheduled in two weeks.
Case Scenario n n You see an est pt, 4 year old boy, with a hx of asthma. Exp Prob Focused Hx: Intermittent night time cough, with occasional episodes of wheezing, relieved using an albuterol MDI; No restrictions of activity noted FHx: No others ill; SHx Parents smoke “outside” Vitals wnl, pulse ox 98%; No respiratory distress; Detailed exam: rare expiratory wheezes. You make a diagnosis of asthma using current asthma dx guidelines. You discuss the diagnosis in detail, including management of asthma using rescue (albuterol) and controller (inhaled steroid) MDIs. The use of MDI’s with a spacer is discussed, demonstrated, and documented. Followup visit is scheduled in two weeks.
 Asthma Scenario Coding n n n CPT – E/M 99214 – Pulse Ox 94760 – MDI Teaching 94664 -59 ICD-9 – 493. 00 Asthma, Childhood w/o status ICD-10 – J 45. 21 Asthma, Mild Intermittent, Exacerbation – Z 77. 22 Exposure to tobacco smoke
Asthma Scenario Coding n n n CPT – E/M 99214 – Pulse Ox 94760 – MDI Teaching 94664 -59 ICD-9 – 493. 00 Asthma, Childhood w/o status ICD-10 – J 45. 21 Asthma, Mild Intermittent, Exacerbation – Z 77. 22 Exposure to tobacco smoke
 Dermatitis n Atopic/eczematous – Flexural – Infantile – Ear – Eyelid n L 20. 82 L 20. 83 H 60. 541 - H 60. 543 (laterality) H 01. 131 - H 01. 135 (laterality) Due to substances taken internally – Generalized skin eruption L 27. 0 – Localized skin eruption L 27. 1
Dermatitis n Atopic/eczematous – Flexural – Infantile – Ear – Eyelid n L 20. 82 L 20. 83 H 60. 541 - H 60. 543 (laterality) H 01. 131 - H 01. 135 (laterality) Due to substances taken internally – Generalized skin eruption L 27. 0 – Localized skin eruption L 27. 1
 Dermatitis n. Diaper – Erythema to dermatitis n. Dry skin n. Seborrheic – Cradle cap – Seborrheic infantile L 22 L 85. 3 L 21. 0 L 21. 1
Dermatitis n. Diaper – Erythema to dermatitis n. Dry skin n. Seborrheic – Cradle cap – Seborrheic infantile L 22 L 85. 3 L 21. 0 L 21. 1
 Dermatitis n Contact dermatitis – Allergic L 23. 1 – L 23. 9 » Adhesive, cosmetics, drugs, food, metals, plants (poison ivy, etc. ) » Ear H 60. 531 -3 Eyelid H 01. 111 -5 – Irritant L 25. 3 – L 24. 9 » Cement, cosmetics, drugs, etc. – Not specified as Allergic or Irritant L 25. 3 – L 25. 9 » Cement, dyes, food
Dermatitis n Contact dermatitis – Allergic L 23. 1 – L 23. 9 » Adhesive, cosmetics, drugs, food, metals, plants (poison ivy, etc. ) » Ear H 60. 531 -3 Eyelid H 01. 111 -5 – Irritant L 25. 3 – L 24. 9 » Cement, cosmetics, drugs, etc. – Not specified as Allergic or Irritant L 25. 3 – L 25. 9 » Cement, dyes, food
 Symptom/Compliant Based Coding A 3 yo child presents with a cough, fever and vomiting. It appears the symtoms are due to a viral process, but this is not a firm diagnosis. n Code for the symptoms and complaints: ICD-9 ICD-10 n – Fever – Cough – Vomiting 780. 60 R 50. 9 786. 2 R 05 787. 03 R 11. 11 (w/o nausea) R 11. 10 (unspecified)
Symptom/Compliant Based Coding A 3 yo child presents with a cough, fever and vomiting. It appears the symtoms are due to a viral process, but this is not a firm diagnosis. n Code for the symptoms and complaints: ICD-9 ICD-10 n – Fever – Cough – Vomiting 780. 60 R 50. 9 786. 2 R 05 787. 03 R 11. 11 (w/o nausea) R 11. 10 (unspecified)
 “Inherent” conditions n Do not separately code for presenting problems or findings inherent to a condition – Vomiting and diarrhea are inherent in acute gastroenteritis, Do not code separately – Ear pain (otalgia) is inherent in otitis media n Do code for conditions not inherent in a diagnosis – Hypoxia is not inherent in pneumonia
“Inherent” conditions n Do not separately code for presenting problems or findings inherent to a condition – Vomiting and diarrhea are inherent in acute gastroenteritis, Do not code separately – Ear pain (otalgia) is inherent in otitis media n Do code for conditions not inherent in a diagnosis – Hypoxia is not inherent in pneumonia
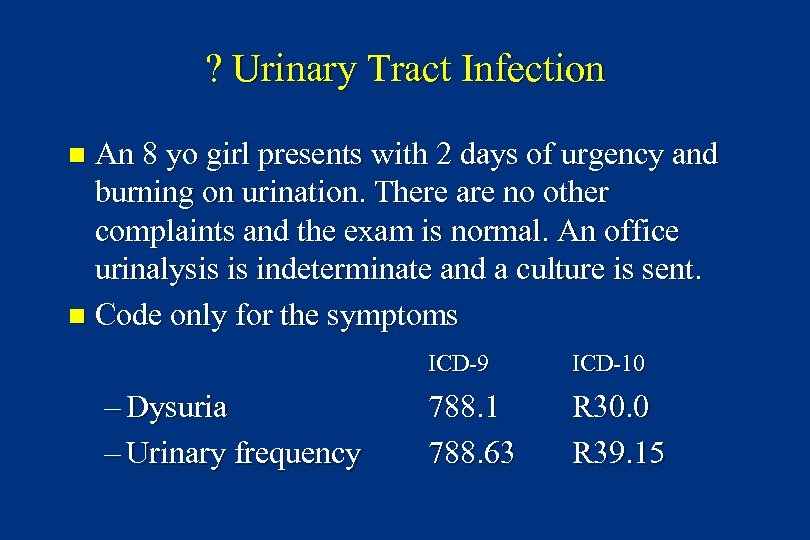 ? Urinary Tract Infection An 8 yo girl presents with 2 days of urgency and burning on urination. There are no other complaints and the exam is normal. An office urinalysis is indeterminate and a culture is sent. n Code only for the symptoms n ICD-9 – Dysuria – Urinary frequency ICD-10 788. 1 788. 63 R 30. 0 R 39. 15
? Urinary Tract Infection An 8 yo girl presents with 2 days of urgency and burning on urination. There are no other complaints and the exam is normal. An office urinalysis is indeterminate and a culture is sent. n Code only for the symptoms n ICD-9 – Dysuria – Urinary frequency ICD-10 788. 1 788. 63 R 30. 0 R 39. 15
 Neonate Neonatal period is the first 28 days of life n Neonatal codes should be used for conditions in this age group – Newborn vomiting P 92. 01 -P 92. 09 – Newborn seizure P 90 n May be used after the neonatal period if the condition affects the visit – Infant of substance abusing mother P 04. 3 -P 04. 49 – Bronchopulmonary dysplasia P 27. 1 n
Neonate Neonatal period is the first 28 days of life n Neonatal codes should be used for conditions in this age group – Newborn vomiting P 92. 01 -P 92. 09 – Newborn seizure P 90 n May be used after the neonatal period if the condition affects the visit – Infant of substance abusing mother P 04. 3 -P 04. 49 – Bronchopulmonary dysplasia P 27. 1 n
 Z-codes (The New “V” Codes) Encounter for healthcare exams n Must be recognized by third party payors n May be used as primary diagnosis n
Z-codes (The New “V” Codes) Encounter for healthcare exams n Must be recognized by third party payors n May be used as primary diagnosis n
 Preventive Medicine/Vaccine ICD-10 Coding ICD-10 effective October 1, 2015 n Preventive Care V 20. 2 crosswalks: Z 00. 129 w/o abnl findings Z 00. 121 with abnl findings n Vaccine product V codes all crosswalk to one ICD-10 code: Z 23, encounter for immunization n Vaccination not carried out (V 64. 00 - V 64. 09) crosswalk with Z 28. 20 -Z 28. 9 codes n
Preventive Medicine/Vaccine ICD-10 Coding ICD-10 effective October 1, 2015 n Preventive Care V 20. 2 crosswalks: Z 00. 129 w/o abnl findings Z 00. 121 with abnl findings n Vaccine product V codes all crosswalk to one ICD-10 code: Z 23, encounter for immunization n Vaccination not carried out (V 64. 00 - V 64. 09) crosswalk with Z 28. 20 -Z 28. 9 codes n
 Vaccines not given n n n Z 28. 20 Z 28. 21 Z 28. 29 Z 28. 81 Z 28. 82 Z 28. 89 Z 28. 9 Due to patient decision for unspecified reason Due to patient refusal Due to patient decision for other reason Due to patient having had the disease Due to caregiver refusal For other reason For unspecified reason
Vaccines not given n n n Z 28. 20 Z 28. 21 Z 28. 29 Z 28. 81 Z 28. 82 Z 28. 89 Z 28. 9 Due to patient decision for unspecified reason Due to patient refusal Due to patient decision for other reason Due to patient having had the disease Due to caregiver refusal For other reason For unspecified reason
 Other Routine Health Visits Z 01. 818 Pre-operative examination n Z 02. 0 School physicals n Z 02. 5 Sport physicals n Z 02. 82 Pre-adoption exam n
Other Routine Health Visits Z 01. 818 Pre-operative examination n Z 02. 0 School physicals n Z 02. 5 Sport physicals n Z 02. 82 Pre-adoption exam n
 Overweight/obesity n Add BMI code if concern about: ICD-9 – Underweight – Overweight – Obesity 783. 22 278. 00 ICD-10 R 63. 6 E 66. 3 E 66. 01 (excessive calories) E 66. 09 (other obesity) E 66. 8 (unspecified) Diet surveillance and counseling V 65. 3 Z 71. 3
Overweight/obesity n Add BMI code if concern about: ICD-9 – Underweight – Overweight – Obesity 783. 22 278. 00 ICD-10 R 63. 6 E 66. 3 E 66. 01 (excessive calories) E 66. 09 (other obesity) E 66. 8 (unspecified) Diet surveillance and counseling V 65. 3 Z 71. 3
 Overweight/obesity – Z 68. 51 pediatric BMI – Z 68. 52 pediatric BMI – Z 68. 53 pediatric BMI – Z 68. 54 pediatric BMI <5 th% for age 5 th<85 th% for age 85 th–<95 th% for age ≥ 95 th% for age
Overweight/obesity – Z 68. 51 pediatric BMI – Z 68. 52 pediatric BMI – Z 68. 53 pediatric BMI – Z 68. 54 pediatric BMI <5 th% for age 5 th<85 th% for age 85 th–<95 th% for age ≥ 95 th% for age
 Healthcare Services n n n Z 09 Follow-up exam, after treatment – Use additional code to identify any applicable history of disease code (Z 86. -. Z 87. -) Z 48. 02 Suture removal Z 48. 817 Post I&D aftercare Z 71. 0 Parent (family) conference Z 71. 3 Diet management (for obesity) Z 76. 81 Parents pre-birth or pre-adoption visit
Healthcare Services n n n Z 09 Follow-up exam, after treatment – Use additional code to identify any applicable history of disease code (Z 86. -. Z 87. -) Z 48. 02 Suture removal Z 48. 817 Post I&D aftercare Z 71. 0 Parent (family) conference Z 71. 3 Diet management (for obesity) Z 76. 81 Parents pre-birth or pre-adoption visit
 Follow-up Visit n A 2 yo is seen for a f/u visit after completing a course of antibiotics for otitis media. The ears are normal to examination and the child is eating and acting well. ICD-9 ICD-10 Follow-up after Rx V 67. 59 Z 09 n PMHx respiratory disease Z 86. 09 n Code condition if still present or other n
Follow-up Visit n A 2 yo is seen for a f/u visit after completing a course of antibiotics for otitis media. The ears are normal to examination and the child is eating and acting well. ICD-9 ICD-10 Follow-up after Rx V 67. 59 Z 09 n PMHx respiratory disease Z 86. 09 n Code condition if still present or other n
 What if nothing’s wrong? n When unable to find specific conditions then code for “ Observation (exam) for: ” – following transport accident (Z 04. 1) – for work (school) related incident (Z 04. 2) – for alleged child rape or sexual assault (Z 04. 42) – for suspected child abuse or neglect (Z 04. 72) – for alleged assault (Z 04. 72) – for other suspected disease or condition ruled out (Z 03. 89) – for suspected neonatal condition (P 00. -)
What if nothing’s wrong? n When unable to find specific conditions then code for “ Observation (exam) for: ” – following transport accident (Z 04. 1) – for work (school) related incident (Z 04. 2) – for alleged child rape or sexual assault (Z 04. 42) – for suspected child abuse or neglect (Z 04. 72) – for alleged assault (Z 04. 72) – for other suspected disease or condition ruled out (Z 03. 89) – for suspected neonatal condition (P 00. -)
 Transition n Encounters that take place on or after October 1, 2015 are reported with ICD-10 -CM codes Encounters that take place before October 1, 2015 are reported with ICD-9 -CM codes You will have to run simultaneous systems of ICD-9 and ICD-10 until all your claims from before October 1, 2015 have cleared
Transition n Encounters that take place on or after October 1, 2015 are reported with ICD-10 -CM codes Encounters that take place before October 1, 2015 are reported with ICD-9 -CM codes You will have to run simultaneous systems of ICD-9 and ICD-10 until all your claims from before October 1, 2015 have cleared
 ICD-10 Implementation Business and Practice Considerations Touches every area of the Practice n Everyone needs some basic training n Coder and billing staff education to include handson use of ICD-10 -CM and PCS code sets n
ICD-10 Implementation Business and Practice Considerations Touches every area of the Practice n Everyone needs some basic training n Coder and billing staff education to include handson use of ICD-10 -CM and PCS code sets n
 How Do Codes Translate ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM?
How Do Codes Translate ICD-9 -CM ICD-10 -CM?
 ICD-10 GEMs General Equivalence Mappings n Tool for converting ICD-9 -CM databases to ICD 10 -CM or ICD-10 -PCS n Backward and forward mapping n Move to coding books and encoder systems October 1, 2015 n Free GEMS download: www. cdc. gov/nchs/icd 10 cm. htm#icd 2014 n
ICD-10 GEMs General Equivalence Mappings n Tool for converting ICD-9 -CM databases to ICD 10 -CM or ICD-10 -PCS n Backward and forward mapping n Move to coding books and encoder systems October 1, 2015 n Free GEMS download: www. cdc. gov/nchs/icd 10 cm. htm#icd 2014 n
 Analyze Your Top Dxs By frequency n By revenue n Know replacement codes Include additional details on Superbill EMR Train staff n
Analyze Your Top Dxs By frequency n By revenue n Know replacement codes Include additional details on Superbill EMR Train staff n
 ICD-10 Implementation Business and Practice Considerations Download GEMS free n Convert your top diagnosis codes – Start with the top ten – Complete the top twenty to thirty n Conduct chart audits n End to End testing is the ultimate test – Send claims – Receive payment n
ICD-10 Implementation Business and Practice Considerations Download GEMS free n Convert your top diagnosis codes – Start with the top ten – Complete the top twenty to thirty n Conduct chart audits n End to End testing is the ultimate test – Send claims – Receive payment n
 Determine Impact on Your Systems Update superbills, charge sheets 2 -4 hours n Add additional details in HER n Train staff on added detail requirements 2 -8 hours Outpatient Coders 16 hours n Certified coders must pass test to maintain certification n Train physicians 8 -12 hours n
Determine Impact on Your Systems Update superbills, charge sheets 2 -4 hours n Add additional details in HER n Train staff on added detail requirements 2 -8 hours Outpatient Coders 16 hours n Certified coders must pass test to maintain certification n Train physicians 8 -12 hours n
 ICD-10 Implementation Business and Practice Considerations Y 2 K ? ? n Initial Loss of Productivity – Up to 40% ! n Line of Credit to support the Transition – CMS recommends 6 mos line of credit Minimum 30 – 60 days cash reserve – AMA estimates cost of $10, 000 per physician – May need to hire an additional coder n Hardware and software impact n
ICD-10 Implementation Business and Practice Considerations Y 2 K ? ? n Initial Loss of Productivity – Up to 40% ! n Line of Credit to support the Transition – CMS recommends 6 mos line of credit Minimum 30 – 60 days cash reserve – AMA estimates cost of $10, 000 per physician – May need to hire an additional coder n Hardware and software impact n
 7 Step Planning and Implementation PLAN – Complete by Winter 2014 Establish structure and leadership Physician champion Project manager / Team n COMMUNICATE – Ongoing with all “stakeholders” Education and Planning with confidence n IMPACT ASSESSMENT -Now Business and policy impacts Technology impacts n
7 Step Planning and Implementation PLAN – Complete by Winter 2014 Establish structure and leadership Physician champion Project manager / Team n COMMUNICATE – Ongoing with all “stakeholders” Education and Planning with confidence n IMPACT ASSESSMENT -Now Business and policy impacts Technology impacts n
 7 Step Planning and Implementation IMPLEMENTATION – To follow Identification of systems issues Preparation for training n TESTING – Early 2015 Vendors, payers, billing companies n BUDGETING – Early 2015 Financial Impact / Line of Credit n TRANSITION – Summer 2015 Go live environment for October 1, 2015 n
7 Step Planning and Implementation IMPLEMENTATION – To follow Identification of systems issues Preparation for training n TESTING – Early 2015 Vendors, payers, billing companies n BUDGETING – Early 2015 Financial Impact / Line of Credit n TRANSITION – Summer 2015 Go live environment for October 1, 2015 n
 PHYSICIANS: DO IT FOR ME ! Detailed Documentation Is Critical Tell the Story with Documentation Coder/Biller cannot make a Diagnosis Do Your Part ! How Your Performance is Measured How You Get Paid You are Ultimately Responsible !
PHYSICIANS: DO IT FOR ME ! Detailed Documentation Is Critical Tell the Story with Documentation Coder/Biller cannot make a Diagnosis Do Your Part ! How Your Performance is Measured How You Get Paid You are Ultimately Responsible !
 Transition: What you can do NOW ? n n n Encourage physicians to document and use more specific codes – Especially those who tend to use unspecified codes or whose documentation leads to an “unspecified” code Work with those physicians on their documentation and in areas where you know more documentation is needed (e. g. Otitis Media) Remember that all HIPAA covered entities are required to adhere to the transition to ICD-10 -CM – So do you!
Transition: What you can do NOW ? n n n Encourage physicians to document and use more specific codes – Especially those who tend to use unspecified codes or whose documentation leads to an “unspecified” code Work with those physicians on their documentation and in areas where you know more documentation is needed (e. g. Otitis Media) Remember that all HIPAA covered entities are required to adhere to the transition to ICD-10 -CM – So do you!
 Transition: What can you do THEN? n n n n n Communicate with everyone! Internal system design and development Work with system vendors Policy change development Develop education and training plan Work with physicians and clinical staff on documentation Plan for a coding process slow down Check commercial payors status GO LIVE – implementation compliance
Transition: What can you do THEN? n n n n n Communicate with everyone! Internal system design and development Work with system vendors Policy change development Develop education and training plan Work with physicians and clinical staff on documentation Plan for a coding process slow down Check commercial payors status GO LIVE – implementation compliance
 ICD-10 -CM + n Leverage your investment n Move beyond mere compliance to achieve strategic advantage
ICD-10 -CM + n Leverage your investment n Move beyond mere compliance to achieve strategic advantage
 Thanksgiving ICD-10 ! Y 93. 63 Activity Cooking and Baking n W 26. 0 Contact with knife n W 61. 42 Struck by Turkey n W 71. 43 Pecked by Turkey n W 61. 49 Other contact with Turkey n W 21. 01 Struck by Football n
Thanksgiving ICD-10 ! Y 93. 63 Activity Cooking and Baking n W 26. 0 Contact with knife n W 61. 42 Struck by Turkey n W 71. 43 Pecked by Turkey n W 61. 49 Other contact with Turkey n W 21. 01 Struck by Football n
 AAP Coding Resources ICD-10 n n n Principles of Pediatric ICD-10 -CM Coding Pediatric Code Crosswalk: ICD-9 -CM to ICD-10 -CM Implementation Set for October 1, 2015 – Small and Medium Practices Large Practices » Checklists for Planning » Timeline » Implementation Guides – Communication Plan for External Resources
AAP Coding Resources ICD-10 n n n Principles of Pediatric ICD-10 -CM Coding Pediatric Code Crosswalk: ICD-9 -CM to ICD-10 -CM Implementation Set for October 1, 2015 – Small and Medium Practices Large Practices » Checklists for Planning » Timeline » Implementation Guides – Communication Plan for External Resources
 AAP Coding Resources ICD-10 Webinars ICD-10 -CM, June 25, 2013: Postponed, Not canceled! Jeff Linzer, MD, FAAP n Preparing for ICD-10 Implementation: Business and Practice Considerations, January 13, 2014 n ICD-10 -CM Coding: Part I, February 11, 2014 Jeff Linzer, MD, FAAP n ICD-10 -CM Coding: Part II, March 25, 2014 Jeff Linzer, MD, FAAP n
AAP Coding Resources ICD-10 Webinars ICD-10 -CM, June 25, 2013: Postponed, Not canceled! Jeff Linzer, MD, FAAP n Preparing for ICD-10 Implementation: Business and Practice Considerations, January 13, 2014 n ICD-10 -CM Coding: Part I, February 11, 2014 Jeff Linzer, MD, FAAP n ICD-10 -CM Coding: Part II, March 25, 2014 Jeff Linzer, MD, FAAP n
 CPT Coding Three Basic Principles of Use 1. Physician should select diagnosis and procedure codes Coding confirmed by the “coding team” 2. Document patient services to support codes Good Care and Compliance 3. Use separate codes for different encounters
CPT Coding Three Basic Principles of Use 1. Physician should select diagnosis and procedure codes Coding confirmed by the “coding team” 2. Document patient services to support codes Good Care and Compliance 3. Use separate codes for different encounters
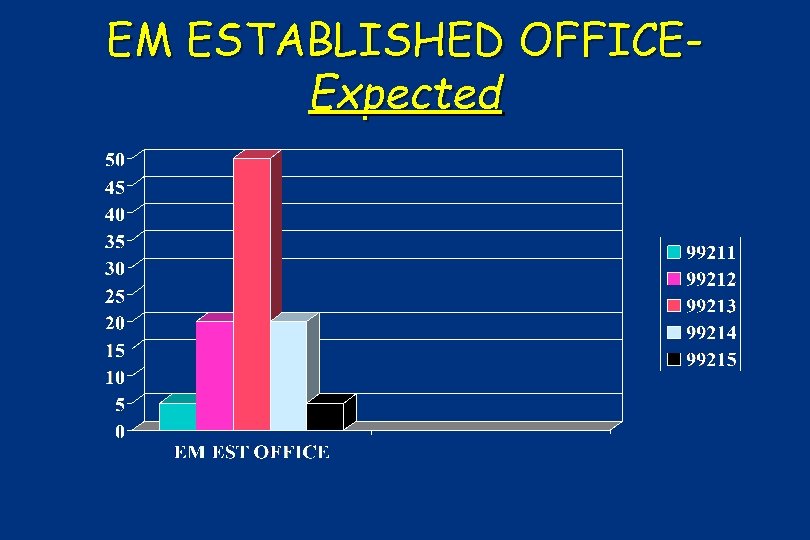 EM ESTABLISHED OFFICEExpected
EM ESTABLISHED OFFICEExpected
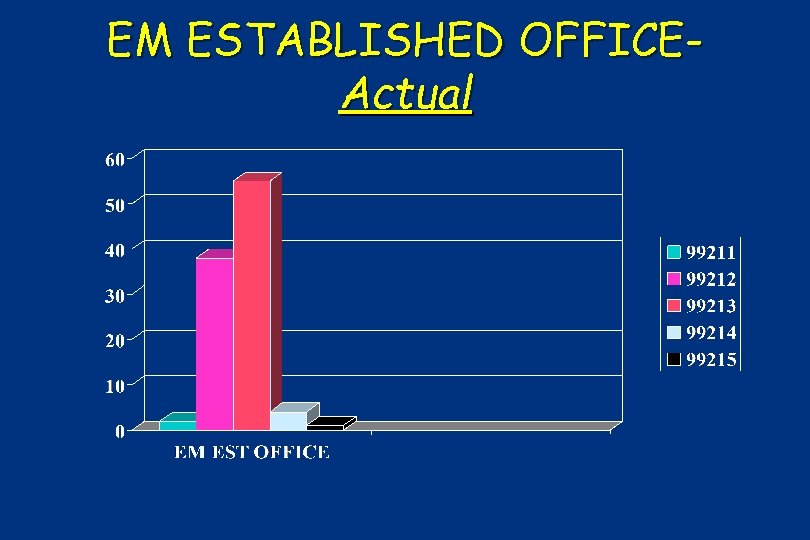 EM ESTABLISHED OFFICEActual
EM ESTABLISHED OFFICEActual
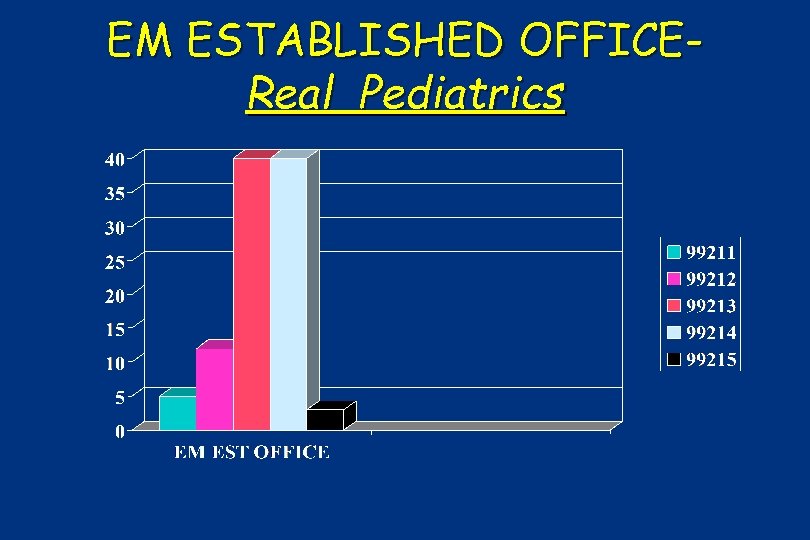 EM ESTABLISHED OFFICEReal Pediatrics
EM ESTABLISHED OFFICEReal Pediatrics
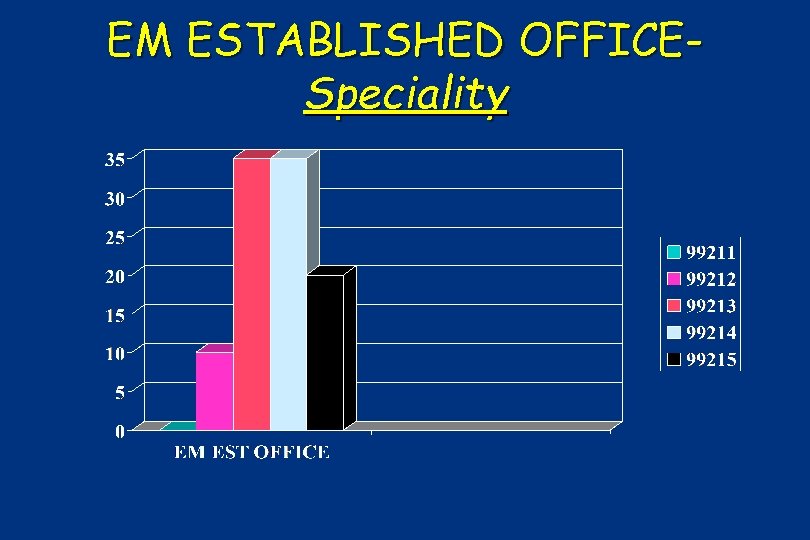 EM ESTABLISHED OFFICESpeciality
EM ESTABLISHED OFFICESpeciality
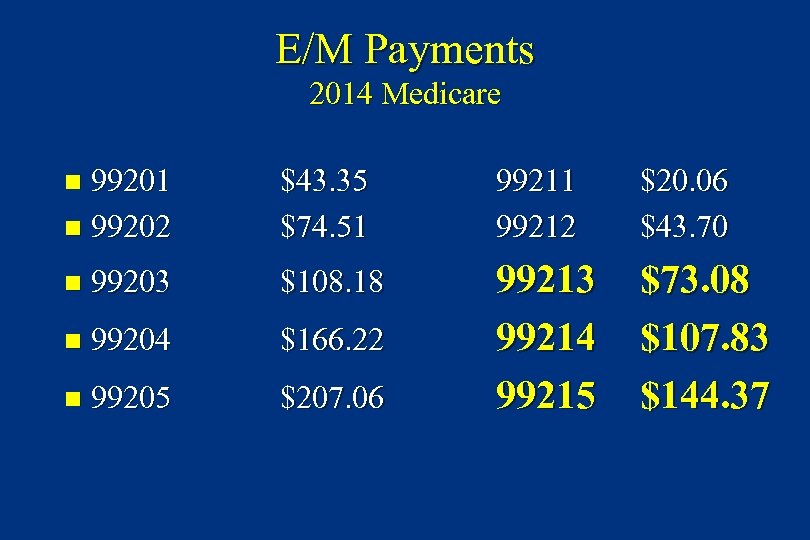 E/M Payments 2014 Medicare 99201 n 99202 n $43. 35 $74. 51 99212 $20. 06 $43. 70 99213 99214 99215 $73. 08 $107. 83 $144. 37 n 99203 $108. 18 n 99204 $166. 22 n 99205 $207. 06
E/M Payments 2014 Medicare 99201 n 99202 n $43. 35 $74. 51 99212 $20. 06 $43. 70 99213 99214 99215 $73. 08 $107. 83 $144. 37 n 99203 $108. 18 n 99204 $166. 22 n 99205 $207. 06
 Auditing / Documentation n n n 95, 97 Guidelines Code to meet your documentation If it’s not in the chart, it wasn’t done Templates/ Clinical forms Computer Assists medical records Beware of “Documentation Upcoding” be medically necessary ! Electronic Must
Auditing / Documentation n n n 95, 97 Guidelines Code to meet your documentation If it’s not in the chart, it wasn’t done Templates/ Clinical forms Computer Assists medical records Beware of “Documentation Upcoding” be medically necessary ! Electronic Must
 Audit Friendly Documentation n n n Vital Signs (3 of Ht Wt BP RR HR Temp) SOAP format CC: chief complaint HPI: History of present illness PFSH: Past, Family, Social History ROS: Review of Systems Impression/Plan (Medical Decision Making) – DDx , Tests, Treatment, Prescriptions – Counseling/coordination of care Time - Note time of encounter Total Time/ Time Counseling-Coordinating care
Audit Friendly Documentation n n n Vital Signs (3 of Ht Wt BP RR HR Temp) SOAP format CC: chief complaint HPI: History of present illness PFSH: Past, Family, Social History ROS: Review of Systems Impression/Plan (Medical Decision Making) – DDx , Tests, Treatment, Prescriptions – Counseling/coordination of care Time - Note time of encounter Total Time/ Time Counseling-Coordinating care
 Evaluation and Management Codes 7 Components The “SCIENCE” of Coding n n n Key – History – Examination – Medical Decision Making Contributory – Counseling – Coordination of Care – Nature of Presenting Problem Explicit – Time – Only to assist physician in selection
Evaluation and Management Codes 7 Components The “SCIENCE” of Coding n n n Key – History – Examination – Medical Decision Making Contributory – Counseling – Coordination of Care – Nature of Presenting Problem Explicit – Time – Only to assist physician in selection
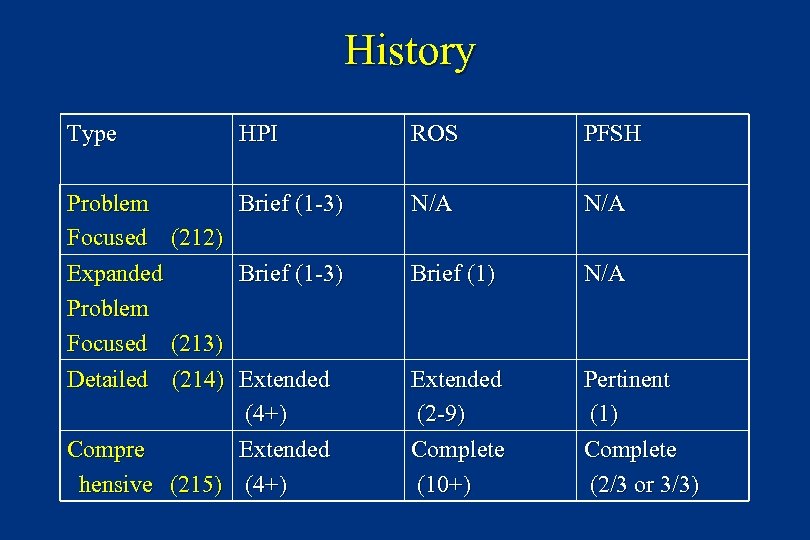 History Type HPI Problem Brief (1 -3) Focused (212) Expanded Brief (1 -3) Problem Focused (213) Detailed (214) Extended (4+) Compre Extended hensive (215) (4+) ROS PFSH N/A Brief (1) N/A Extended (2 -9) Complete (10+) Pertinent (1) Complete (2/3 or 3/3)
History Type HPI Problem Brief (1 -3) Focused (212) Expanded Brief (1 -3) Problem Focused (213) Detailed (214) Extended (4+) Compre Extended hensive (215) (4+) ROS PFSH N/A Brief (1) N/A Extended (2 -9) Complete (10+) Pertinent (1) Complete (2/3 or 3/3)
 n Problem Focused Examination (212) – Limited to affected body area or organ system – 1 body area / organ system n Expanded Problem Focused (213) – Affected body area or organ system and other symptomatic or related organ systems – 2 – 7 body areas / organ systems n Detailed (214) – Extended exam of affected body area(s) and other symptomatic or related organ systems - 2 – 7 body areas / organ systems n Comprehensive (215) – Complete single system specialty exam or – Complete multi-system exam – 8 organ systems
n Problem Focused Examination (212) – Limited to affected body area or organ system – 1 body area / organ system n Expanded Problem Focused (213) – Affected body area or organ system and other symptomatic or related organ systems – 2 – 7 body areas / organ systems n Detailed (214) – Extended exam of affected body area(s) and other symptomatic or related organ systems - 2 – 7 body areas / organ systems n Comprehensive (215) – Complete single system specialty exam or – Complete multi-system exam – 8 organ systems
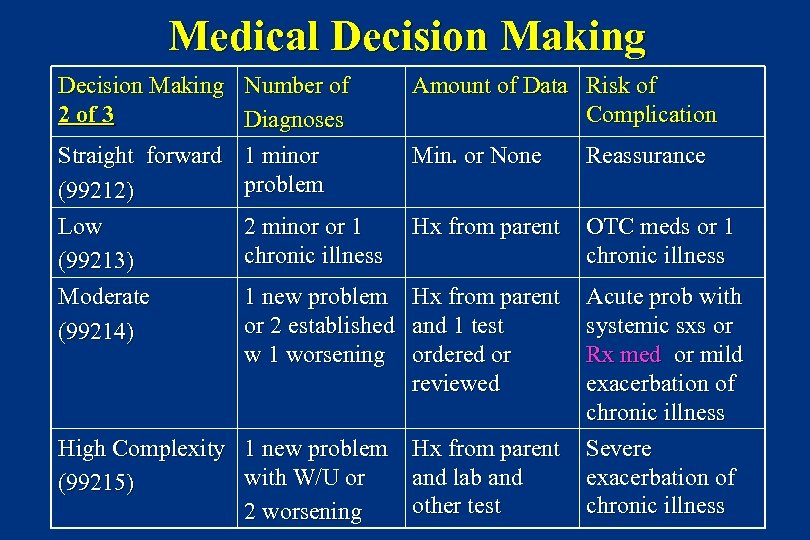 Medical Decision Making Number of 2 of 3 Diagnoses Straight forward 1 minor problem (99212) Low 2 minor or 1 chronic illness (99213) Moderate 1 new problem or 2 established (99214) w 1 worsening Amount of Data Risk of Complication Min. or None Reassurance Hx from parent OTC meds or 1 chronic illness Hx from parent and 1 test ordered or reviewed Acute prob with systemic sxs or Rx med or mild exacerbation of chronic illness Severe exacerbation of chronic illness High Complexity 1 new problem Hx from parent with W/U or and lab and (99215) other test 2 worsening
Medical Decision Making Number of 2 of 3 Diagnoses Straight forward 1 minor problem (99212) Low 2 minor or 1 chronic illness (99213) Moderate 1 new problem or 2 established (99214) w 1 worsening Amount of Data Risk of Complication Min. or None Reassurance Hx from parent OTC meds or 1 chronic illness Hx from parent and 1 test ordered or reviewed Acute prob with systemic sxs or Rx med or mild exacerbation of chronic illness Severe exacerbation of chronic illness High Complexity 1 new problem Hx from parent with W/U or and lab and (99215) other test 2 worsening
 Medical Decision Making Best 2 of 3 elements: Data, Diagnoses, Risk 1. Amount and/or complexity of data reviewed/ordered – Note if you reviewed the chart or obtained history from someone other than the patient, or discussed the case with another healthcare provider – Note if you intend to order old records – Note if you personally reviewed a specimen, image or tracing – Note any other diagnostic test results or orders 2. Number of diagnoses and/or management options – Note any workup planned – Note any comorbidities effecting decision making and status of problems 3. Risk of complications, morbidity, mortality
Medical Decision Making Best 2 of 3 elements: Data, Diagnoses, Risk 1. Amount and/or complexity of data reviewed/ordered – Note if you reviewed the chart or obtained history from someone other than the patient, or discussed the case with another healthcare provider – Note if you intend to order old records – Note if you personally reviewed a specimen, image or tracing – Note any other diagnostic test results or orders 2. Number of diagnoses and/or management options – Note any workup planned – Note any comorbidities effecting decision making and status of problems 3. Risk of complications, morbidity, mortality
 Key Concepts – Outpatient E/M Coding n n Time spent is “face to face” One E/M code per day – Few exceptions: » -25 modifier » Prolonged services codes Attending physician must see the patient and fulfill / document criteria supporting code used Procedures and other services should be coded separately – May require modifiers (-25 on the E/M code)
Key Concepts – Outpatient E/M Coding n n Time spent is “face to face” One E/M code per day – Few exceptions: » -25 modifier » Prolonged services codes Attending physician must see the patient and fulfill / document criteria supporting code used Procedures and other services should be coded separately – May require modifiers (-25 on the E/M code)
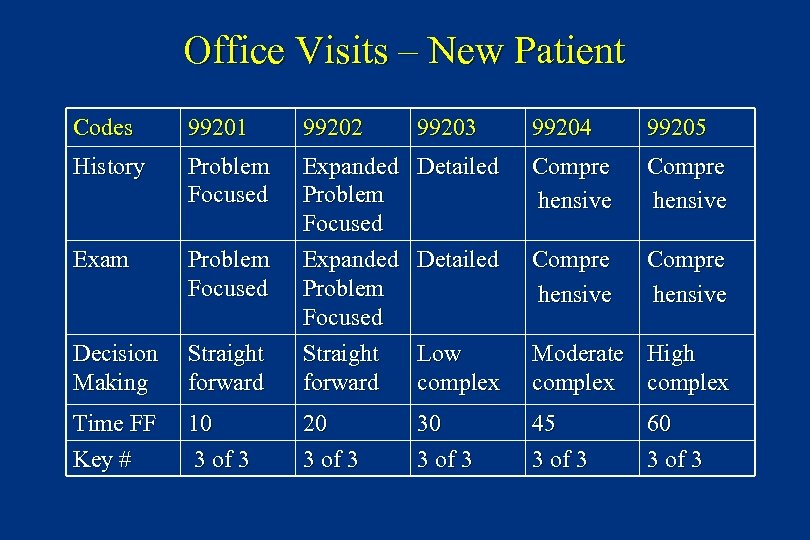 Office Visits – New Patient Codes 99201 99202 99203 99204 99205 History Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Exam Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Decision Making Straight forward Expanded Problem Focused Straight forward Low complex Moderate High complex Time FF Key # 10 3 of 3 20 3 of 3 30 3 of 3 45 3 of 3 60 3 of 3
Office Visits – New Patient Codes 99201 99202 99203 99204 99205 History Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Exam Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Decision Making Straight forward Expanded Problem Focused Straight forward Low complex Moderate High complex Time FF Key # 10 3 of 3 20 3 of 3 30 3 of 3 45 3 of 3 60 3 of 3
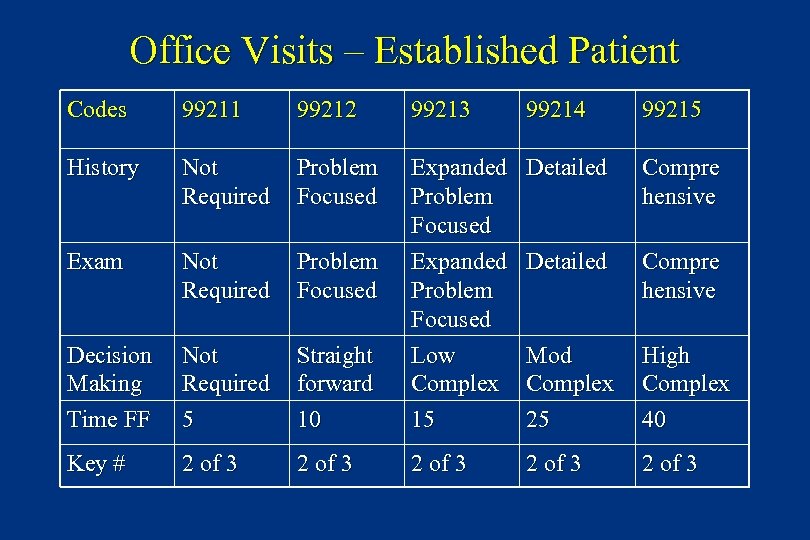 Office Visits – Established Patient Codes 99211 99212 99213 99214 99215 History Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Exam Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Decision Making Time FF Not Required 5 Straight forward 10 Expanded Problem Focused Low Complex 15 Mod Complex 25 High Complex 40 Key # 2 of 3 2 of 3
Office Visits – Established Patient Codes 99211 99212 99213 99214 99215 History Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Exam Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Decision Making Time FF Not Required 5 Straight forward 10 Expanded Problem Focused Low Complex 15 Mod Complex 25 High Complex 40 Key # 2 of 3 2 of 3
 Time An explicit factor to assist in selecting the most appropriate level of E/M services n When counseling and/or coordination of care more than 50% of the face to face encounter, then time is the key controlling factor. n Utilize prolonged services codes (time based) *Documentation in the medical record is a must n
Time An explicit factor to assist in selecting the most appropriate level of E/M services n When counseling and/or coordination of care more than 50% of the face to face encounter, then time is the key controlling factor. n Utilize prolonged services codes (time based) *Documentation in the medical record is a must n
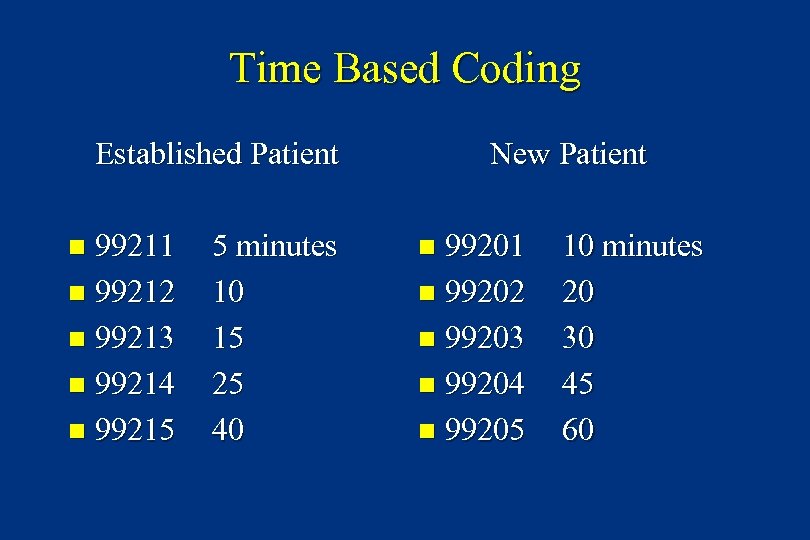 Time Based Coding Established Patient 99211 n 99212 n 99213 n 99214 n 99215 n 5 minutes 10 15 25 40 New Patient 99201 n 99202 n 99203 n 99204 n 99205 n 10 minutes 20 30 45 60
Time Based Coding Established Patient 99211 n 99212 n 99213 n 99214 n 99215 n 5 minutes 10 15 25 40 New Patient 99201 n 99202 n 99203 n 99204 n 99205 n 10 minutes 20 30 45 60
 The ART of Coding n The “FEEL” – Established Patient – 99211 - Nurse Visit – 99212 - Easy, Brief Problems – 99213 - Average, Usual Problems – 99214 - “ OH NO !” – 99215 - “ Just Ran a Marathon”
The ART of Coding n The “FEEL” – Established Patient – 99211 - Nurse Visit – 99212 - Easy, Brief Problems – 99213 - Average, Usual Problems – 99214 - “ OH NO !” – 99215 - “ Just Ran a Marathon”
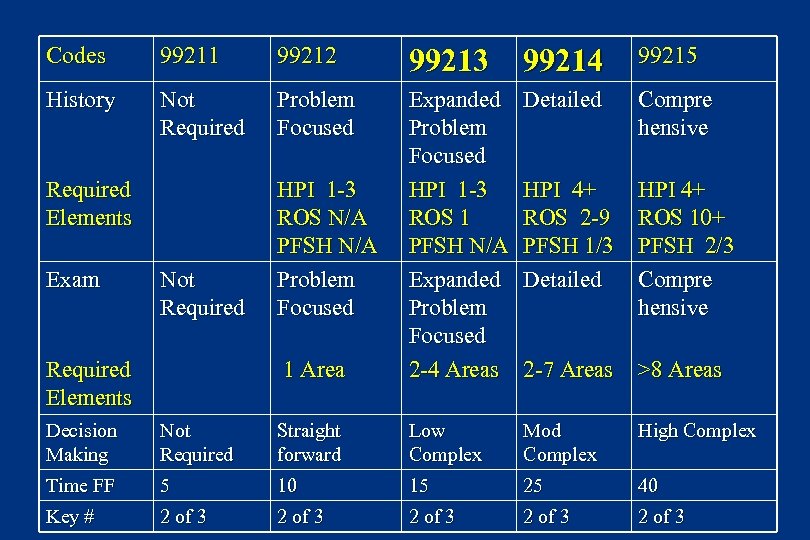 Codes 99211 99212 99213 99214 99215 History Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Not Required HPI 1 -3 ROS N/A PFSH N/A Problem Focused HPI 4+ ROS 2 -9 PFSH 1/3 Detailed HPI 4+ ROS 10+ PFSH 2/3 Compre hensive 1 Area Expanded Problem Focused HPI 1 -3 ROS 1 PFSH N/A Expanded Problem Focused 2 -4 Areas 2 -7 Areas >8 Areas Required Elements Exam Required Elements Decision Making Not Required Straight forward Low Complex Mod Complex High Complex Time FF 5 10 15 25 40 Key # 2 of 3 2 of 3
Codes 99211 99212 99213 99214 99215 History Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Not Required HPI 1 -3 ROS N/A PFSH N/A Problem Focused HPI 4+ ROS 2 -9 PFSH 1/3 Detailed HPI 4+ ROS 10+ PFSH 2/3 Compre hensive 1 Area Expanded Problem Focused HPI 1 -3 ROS 1 PFSH N/A Expanded Problem Focused 2 -4 Areas 2 -7 Areas >8 Areas Required Elements Exam Required Elements Decision Making Not Required Straight forward Low Complex Mod Complex High Complex Time FF 5 10 15 25 40 Key # 2 of 3 2 of 3
 ? 99213 99214 99215 ? CSHCN n New Diagnosis n Multiple Diagnoses n Repeat visit – patient worse n Comorbidities n Lab or Xray ordered n Consultation indicated n Prescription written n Office procedures required (aerosol, pulse ox) n Chronic problem – exacerbation, changes in Rx n Time based problem/ “consultation” n
? 99213 99214 99215 ? CSHCN n New Diagnosis n Multiple Diagnoses n Repeat visit – patient worse n Comorbidities n Lab or Xray ordered n Consultation indicated n Prescription written n Office procedures required (aerosol, pulse ox) n Chronic problem – exacerbation, changes in Rx n Time based problem/ “consultation” n
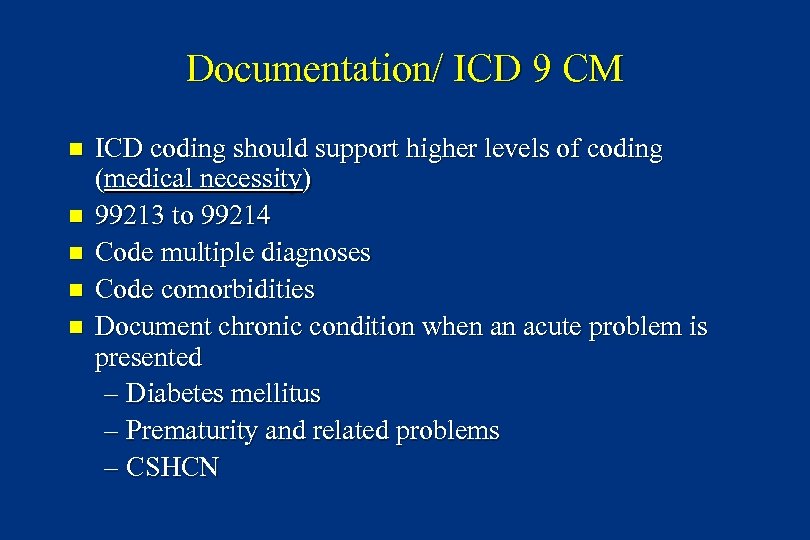 Documentation/ ICD 9 CM n n n ICD coding should support higher levels of coding (medical necessity) 99213 to 99214 Code multiple diagnoses Code comorbidities Document chronic condition when an acute problem is presented – Diabetes mellitus – Prematurity and related problems – CSHCN
Documentation/ ICD 9 CM n n n ICD coding should support higher levels of coding (medical necessity) 99213 to 99214 Code multiple diagnoses Code comorbidities Document chronic condition when an acute problem is presented – Diabetes mellitus – Prematurity and related problems – CSHCN
 ? 99213 – 99214 - 99215 You select the level !
? 99213 – 99214 - 99215 You select the level !
 MAKE ME BETTER n A 12 yo teenager est patient presents with a sore throat for 2 days, associated with swollen glands. An expanded problem focused Hx and PE are done. A strep FA is obtained and treatment with acetaminophen/ibuprofen reviewed. n How would you code for this patient ?
MAKE ME BETTER n A 12 yo teenager est patient presents with a sore throat for 2 days, associated with swollen glands. An expanded problem focused Hx and PE are done. A strep FA is obtained and treatment with acetaminophen/ibuprofen reviewed. n How would you code for this patient ?
 MAKE ME BETTER n A. 99212 87880 (strep FA) n C. 99214 87880 (strep FA) n B. 99213 87880 (strep FA) n D. 99215 87880 (strep FA)
MAKE ME BETTER n A. 99212 87880 (strep FA) n C. 99214 87880 (strep FA) n B. 99213 87880 (strep FA) n D. 99215 87880 (strep FA)
 MAKE ME BETTER n A. 99212 87880 (strep FA) n C. 99214 87880 (strep FA) n B. 99213 87880 (strep FA) n D. 99215 87880 (strep FA)
MAKE ME BETTER n A. 99212 87880 (strep FA) n C. 99214 87880 (strep FA) n B. 99213 87880 (strep FA) n D. 99215 87880 (strep FA)
 I’M STILL SICK ! n Our patient returns 5 days later. She is miserable, cannot swallow, and looks dry. She is congested and has been sleeping all the time. A detailed Hx and PE is completed. Lab work including a Mono spot, chem-8, and urinalysis are ordered. Extensive discussion re the DDx, Rx and F/U is completed. The patient is treated with a short course of steroids when the Mono spot is positive. n How would you code for these services ?
I’M STILL SICK ! n Our patient returns 5 days later. She is miserable, cannot swallow, and looks dry. She is congested and has been sleeping all the time. A detailed Hx and PE is completed. Lab work including a Mono spot, chem-8, and urinalysis are ordered. Extensive discussion re the DDx, Rx and F/U is completed. The patient is treated with a short course of steroids when the Mono spot is positive. n How would you code for these services ?
 I’M STILL SICK ! n A. 99212 (venipuncture) (specimen transfer) 36415 99000 n B. 99213 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n C. 99214 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n D. 99215 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer)
I’M STILL SICK ! n A. 99212 (venipuncture) (specimen transfer) 36415 99000 n B. 99213 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n C. 99214 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n D. 99215 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer)
 I’M STILL SICK ! n A. 99212 (venipuncture) (specimen transfer) 36415 99000 n B. 99213 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n C. 99214 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n D. 99215 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer)
I’M STILL SICK ! n A. 99212 (venipuncture) (specimen transfer) 36415 99000 n B. 99213 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n C. 99214 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer) n D. 99215 36415 (venipuncture) 99000 (specimen transfer)
 QUICK SICKIE n A 13 yo boy comes in announcing he has poison ivy. A brief Hx and PE support his diagnosis. It is in several small patches on his extremities. You treat with a topical steroid prescription. n How would you code for this quickie ?
QUICK SICKIE n A 13 yo boy comes in announcing he has poison ivy. A brief Hx and PE support his diagnosis. It is in several small patches on his extremities. You treat with a topical steroid prescription. n How would you code for this quickie ?
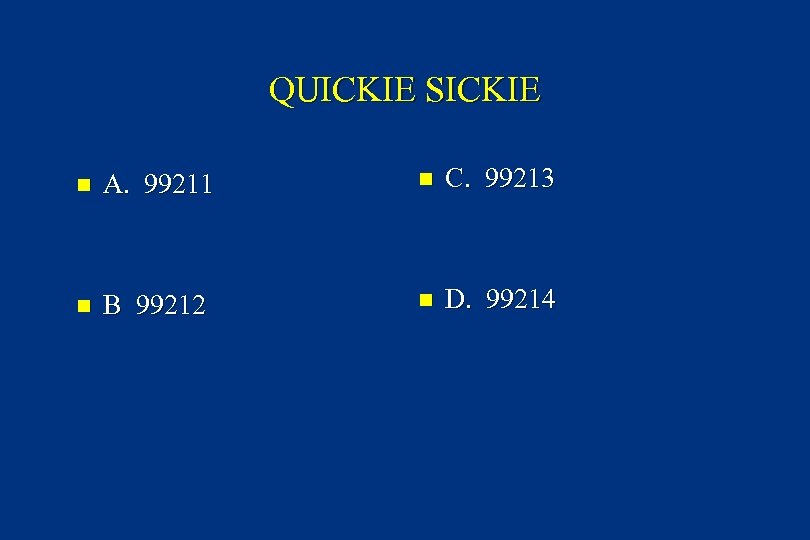 QUICKIE SICKIE n A. 99211 n C. 99213 n B 99212 n D. 99214
QUICKIE SICKIE n A. 99211 n C. 99213 n B 99212 n D. 99214
 QUICKIE SICKIE n A. 99211 n C. 99213 n B 99212 n D. 99214
QUICKIE SICKIE n A. 99211 n C. 99213 n B 99212 n D. 99214
 DISASTER TIME n A 15 yo patient of your partner is scheduled with a cc of “anxiety attacks”. She is inappropriately scheduled in a 10 minute ill appointment time. You complete a comprehensive Hx, extended PE, and provide extensive counseling for this adolescent who is depressed and suicidal. Total face to face time for this encounter is 50 minutes, with 30 minutes spent counseling and coordinating care for this crisis. n How would you code for this total loss of your lunch time ?
DISASTER TIME n A 15 yo patient of your partner is scheduled with a cc of “anxiety attacks”. She is inappropriately scheduled in a 10 minute ill appointment time. You complete a comprehensive Hx, extended PE, and provide extensive counseling for this adolescent who is depressed and suicidal. Total face to face time for this encounter is 50 minutes, with 30 minutes spent counseling and coordinating care for this crisis. n How would you code for this total loss of your lunch time ?
 DISASTER TIME n A. 99213 n C. 99215 n B. 99214 n D. 99216 !
DISASTER TIME n A. 99213 n C. 99215 n B. 99214 n D. 99216 !
 DISASTER TIME n A. 99213 n C. 99215 n B. 99214 n D. 99216 !
DISASTER TIME n A. 99213 n C. 99215 n B. 99214 n D. 99216 !
 FUSSY BABY n A 2 mos infant has been fussy since birth. He is difficult to console and has been very spitting, with vomiting once/ day. There have been no other symptoms of illness. A detailed history and detailed examination are completed. 15 minutes of face to face time are recorded for the visit. n How would you code for this fussy baby and fussy parent?
FUSSY BABY n A 2 mos infant has been fussy since birth. He is difficult to console and has been very spitting, with vomiting once/ day. There have been no other symptoms of illness. A detailed history and detailed examination are completed. 15 minutes of face to face time are recorded for the visit. n How would you code for this fussy baby and fussy parent?
 FUSSY BABY n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
FUSSY BABY n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
 FUSSY BABY n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
FUSSY BABY n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
 TEEN TROUBLE n n A 13 yo boy has been failing in school and was suspended today for threatening another student. Your assessment includes a plan to evaluate for ADHD/ learning disabilities, as well as, obtain counseling for his significant home and school adjustment problems. Total face to face time for the visit is 45 minutes, with 30 minutes spent counseling and coordinating care related to the issues, Dx, and Rx options. How would you code for this troubled teen visit?
TEEN TROUBLE n n A 13 yo boy has been failing in school and was suspended today for threatening another student. Your assessment includes a plan to evaluate for ADHD/ learning disabilities, as well as, obtain counseling for his significant home and school adjustment problems. Total face to face time for the visit is 45 minutes, with 30 minutes spent counseling and coordinating care related to the issues, Dx, and Rx options. How would you code for this troubled teen visit?
 TROUBLED TEEN n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
TROUBLED TEEN n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
 TROUBLED TEEN n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
TROUBLED TEEN n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
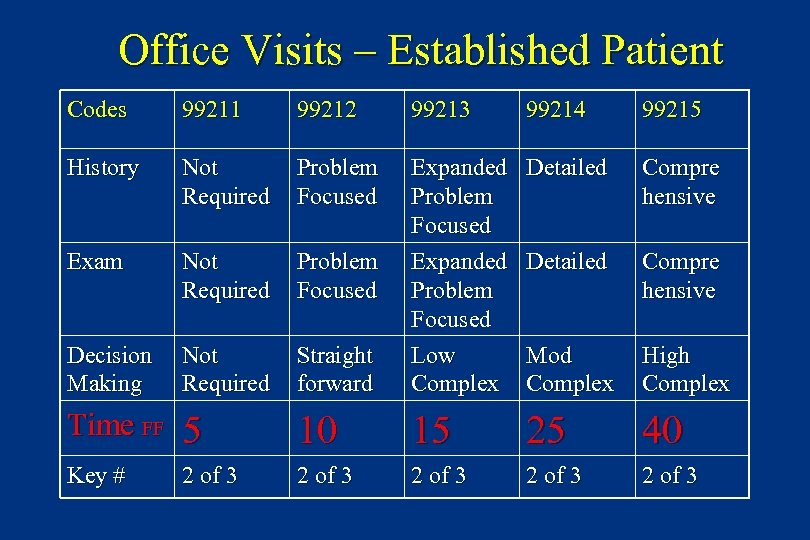 Office Visits – Established Patient Codes 99211 99212 99213 99214 99215 History Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Exam Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Decision Making Not Required Straight forward Expanded Problem Focused Low Complex Mod Complex High Complex Time FF 5 10 15 25 40 Key # 2 of 3 2 of 3
Office Visits – Established Patient Codes 99211 99212 99213 99214 99215 History Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Exam Not Required Problem Focused Detailed Compre hensive Decision Making Not Required Straight forward Expanded Problem Focused Low Complex Mod Complex High Complex Time FF 5 10 15 25 40 Key # 2 of 3 2 of 3
 THE STANDARD ILL VISIT n A new patient 4 yo girl presents with several days of burning pain with urination. An expanded problem focused history and expanded problem focused examination are completed. A urinalysis with microscopic analysis is done. The diagnosis is vulvitis and sitz baths are recommended. n What would you code for this bread and butter pediatric visit?
THE STANDARD ILL VISIT n A new patient 4 yo girl presents with several days of burning pain with urination. An expanded problem focused history and expanded problem focused examination are completed. A urinalysis with microscopic analysis is done. The diagnosis is vulvitis and sitz baths are recommended. n What would you code for this bread and butter pediatric visit?
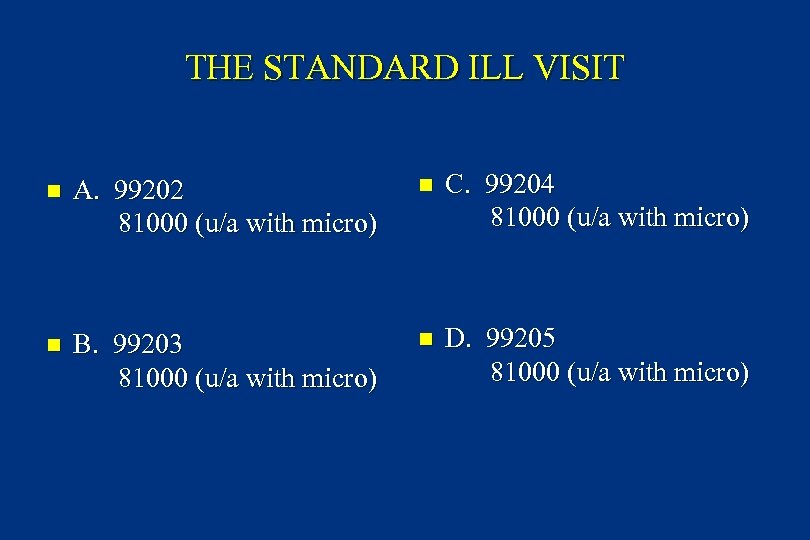 THE STANDARD ILL VISIT n A. 99202 81000 (u/a with micro) n C. 99204 81000 (u/a with micro) n B. 99203 81000 (u/a with micro) n D. 99205 81000 (u/a with micro)
THE STANDARD ILL VISIT n A. 99202 81000 (u/a with micro) n C. 99204 81000 (u/a with micro) n B. 99203 81000 (u/a with micro) n D. 99205 81000 (u/a with micro)
 THE STANDARD ILL VISIT n A. 99202 81000 (u/a with micro) n C. 99204 81000 (u/a with micro) n B. 99203 81000 (u/a with micro) n D. 99205 81000 (u/a with micro)
THE STANDARD ILL VISIT n A. 99202 81000 (u/a with micro) n C. 99204 81000 (u/a with micro) n B. 99203 81000 (u/a with micro) n D. 99205 81000 (u/a with micro)
 ANOTHER ONE! n A 3 yo female presents with twelve hours of fussiness and vomiting. She does not have fever and is urinating well. An expanded problem focused history and examination are completed. Slowly advancing clear fluids is reviewed, as well as, when to call if her condition worsens. n How would you code for this everyday patient?
ANOTHER ONE! n A 3 yo female presents with twelve hours of fussiness and vomiting. She does not have fever and is urinating well. An expanded problem focused history and examination are completed. Slowly advancing clear fluids is reviewed, as well as, when to call if her condition worsens. n How would you code for this everyday patient?
 ANOTHER ONE! n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
ANOTHER ONE! n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
 ANOTHER ONE! n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
ANOTHER ONE! n A. 99212 n C. 99214 n B. 99213 n D. 99215
 ANOTHER SICKER ONE! n A 5 yo female presents with one day of vomiting. She has a temp of 101, diarrhea, and lethargy. She is urinating less and not tolerating “anything”. A detailed history and examination are completed. A negative urinalysis is obtained with a specific gravity of 1. 020. Management is reviewed: slowly advancing clear fluids, treatment of fever, and when to call. n How would you code for this everyday patient?
ANOTHER SICKER ONE! n A 5 yo female presents with one day of vomiting. She has a temp of 101, diarrhea, and lethargy. She is urinating less and not tolerating “anything”. A detailed history and examination are completed. A negative urinalysis is obtained with a specific gravity of 1. 020. Management is reviewed: slowly advancing clear fluids, treatment of fever, and when to call. n How would you code for this everyday patient?
 ANOTHER SICKER ONE! n A. 99212 81002 (dip urinalysis) n C. 99214 81002 n B. 99213 81002 n D. 99215 81002
ANOTHER SICKER ONE! n A. 99212 81002 (dip urinalysis) n C. 99214 81002 n B. 99213 81002 n D. 99215 81002
 ANOTHER SICKER ONE! n A. 99212 81002 (dip urinalysis) n C. 99214 81002 n B. 99213 81002 n D. 99215 81002
ANOTHER SICKER ONE! n A. 99212 81002 (dip urinalysis) n C. 99214 81002 n B. 99213 81002 n D. 99215 81002
 Preventive Medicine Services New Patient Initial E/M of a new patient including an age and gender appropriate history, examination identification of risk factors, ordering of appropriate tests, and counseling $ 2014 Medicare 99381 Age < 1 year $111. 05 99382 Ages 1 – 4 years $115. 71 99383 Ages 5 – 11 years $115. 67 99384 Ages 12 – 17 years $131. 25 99385 Ages 18 – 39 years $127. 26
Preventive Medicine Services New Patient Initial E/M of a new patient including an age and gender appropriate history, examination identification of risk factors, ordering of appropriate tests, and counseling $ 2014 Medicare 99381 Age < 1 year $111. 05 99382 Ages 1 – 4 years $115. 71 99383 Ages 5 – 11 years $115. 67 99384 Ages 12 – 17 years $131. 25 99385 Ages 18 – 39 years $127. 26
 Preventive Medicine Services Established Patient Periodic reevaluation and management requiring an age and gender appropriate history, examination identification of risk factors, ordering of studies, and counseling 2014 Medicare 99391 Age < 1 $99. 95 99392 Ages 1 – 4 years $106. 75 99393 Ages 5 – 11 years $106. 39 99394 Ages 12 – 17 years $116. 42 99395 Ages 18 – 39 years $118. 93
Preventive Medicine Services Established Patient Periodic reevaluation and management requiring an age and gender appropriate history, examination identification of risk factors, ordering of studies, and counseling 2014 Medicare 99391 Age < 1 $99. 95 99392 Ages 1 – 4 years $106. 75 99393 Ages 5 – 11 years $106. 39 99394 Ages 12 – 17 years $116. 42 99395 Ages 18 – 39 years $118. 93
 Preventive Medicine vs E/M Office Visit ? What do you do if a significant illness or problem is found at a preventive medicine visit?
Preventive Medicine vs E/M Office Visit ? What do you do if a significant illness or problem is found at a preventive medicine visit?
 25 Modifier n If a significant problem/abnormality is found at a preventive medicine visit: – Code the appropriate E/M visit in addition to 99381 – 99395 - Add modifier – 25 to the E/M code - If not significant code only 99381 – 99395 - Option: Have patient return for a separate E/M visit for problem/abnormality found
25 Modifier n If a significant problem/abnormality is found at a preventive medicine visit: – Code the appropriate E/M visit in addition to 99381 – 99395 - Add modifier – 25 to the E/M code - If not significant code only 99381 – 99395 - Option: Have patient return for a separate E/M visit for problem/abnormality found
 PM + E/M-25 Modifier Significant Problem: – Separate Documentation – Separate Supporting Diagnosis – Prescription or Lab/ Xray Testing ordered – Consultation Required – Time intensive Problem n Acute n Chronic requiring discussion and/or intervention n
PM + E/M-25 Modifier Significant Problem: – Separate Documentation – Separate Supporting Diagnosis – Prescription or Lab/ Xray Testing ordered – Consultation Required – Time intensive Problem n Acute n Chronic requiring discussion and/or intervention n
 PM + E/M-25 Modifier Preventive Medicine – No copay – Not applied to deductible n + EM – 25 – Copay – Subject to deductible n Educate your patients and families n
PM + E/M-25 Modifier Preventive Medicine – No copay – Not applied to deductible n + EM – 25 – Copay – Subject to deductible n Educate your patients and families n
 ? WELL BABY TIME n n A 6 month infant boy presents for an est preventive visit. His mother is worried about the cold and fever he has had for several days. An age and gender appropriate Hx and PE are completed, in addition to an extended Hx addressing the ongoing illness. A Dx of otitis media is made and the infant is treated with po amoxicillin. His mother is not comfortable with proceeding with immunizations. It is agreed that she will return in several weeks for a nurse only visit to obtain these important vaccines. How would you code for this office visit ?
? WELL BABY TIME n n A 6 month infant boy presents for an est preventive visit. His mother is worried about the cold and fever he has had for several days. An age and gender appropriate Hx and PE are completed, in addition to an extended Hx addressing the ongoing illness. A Dx of otitis media is made and the infant is treated with po amoxicillin. His mother is not comfortable with proceeding with immunizations. It is agreed that she will return in several weeks for a nurse only visit to obtain these important vaccines. How would you code for this office visit ?
 ? WELL BABY TIME n A. 99391 n C. 99391 99212 -25 n B. 99214 n D. 99391 99213 -25
? WELL BABY TIME n A. 99391 n C. 99391 99212 -25 n B. 99214 n D. 99391 99213 -25
 ? WELL BABY TIME n A. 99391 n C. 99391 99212 -25 n B. 99214 n D. 99391 99213 -25
? WELL BABY TIME n A. 99391 n C. 99391 99212 -25 n B. 99214 n D. 99391 99213 -25
 Office procedures n n n Immunizations Screening procedures Minor procedures Lab and x-ray services Medical services Special services
Office procedures n n n Immunizations Screening procedures Minor procedures Lab and x-ray services Medical services Special services
 Immunizations 2014 How are you doing ? What are your challenges?
Immunizations 2014 How are you doing ? What are your challenges?
 Immunizations n n Bill and Document ALL: – E/M Visit - 25 » Office Visit, Preventive Medicine – Immunization Administration » 90471 – 90474 (individual vaccine based) » 90460 – 90461 (component based) – Vaccine/Toxoid » 90476 – 90749 Link to ICD Diagnoses – V 20. 2 Well Child – CSHCN Diagnosis – + Specific Vaccine V Codes (Z 23 ICD-10)
Immunizations n n Bill and Document ALL: – E/M Visit - 25 » Office Visit, Preventive Medicine – Immunization Administration » 90471 – 90474 (individual vaccine based) » 90460 – 90461 (component based) – Vaccine/Toxoid » 90476 – 90749 Link to ICD Diagnoses – V 20. 2 Well Child – CSHCN Diagnosis – + Specific Vaccine V Codes (Z 23 ICD-10)
 Office procedures n Immunizations n Screening procedures Minor procedures Lab and x-ray services Medical services Special services n n
Office procedures n Immunizations n Screening procedures Minor procedures Lab and x-ray services Medical services Special services n n
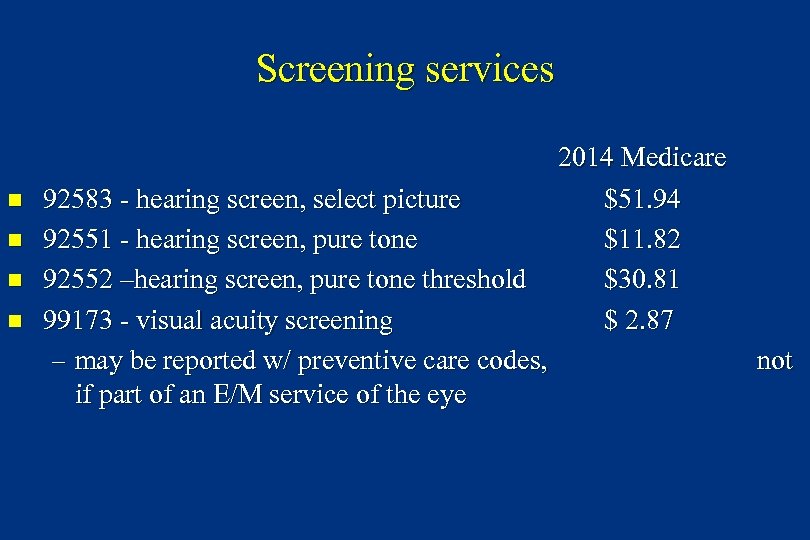 Screening services n n 92583 - hearing screen, select picture 92551 - hearing screen, pure tone 92552 –hearing screen, pure tone threshold 99173 - visual acuity screening – may be reported w/ preventive care codes, if part of an E/M service of the eye 2014 Medicare $51. 94 $11. 82 $30. 81 $ 2. 87 not
Screening services n n 92583 - hearing screen, select picture 92551 - hearing screen, pure tone 92552 –hearing screen, pure tone threshold 99173 - visual acuity screening – may be reported w/ preventive care codes, if part of an E/M service of the eye 2014 Medicare $51. 94 $11. 82 $30. 81 $ 2. 87 not
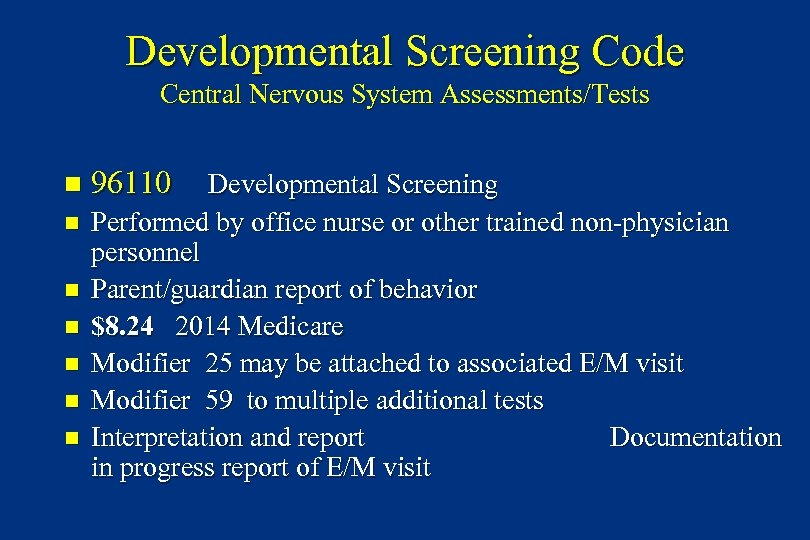 Developmental Screening Code Central Nervous System Assessments/Tests n n n n 96110 Developmental Screening Performed by office nurse or other trained non-physician personnel Parent/guardian report of behavior $8. 24 2014 Medicare Modifier 25 may be attached to associated E/M visit Modifier 59 to multiple additional tests Interpretation and report Documentation in progress report of E/M visit
Developmental Screening Code Central Nervous System Assessments/Tests n n n n 96110 Developmental Screening Performed by office nurse or other trained non-physician personnel Parent/guardian report of behavior $8. 24 2014 Medicare Modifier 25 may be attached to associated E/M visit Modifier 59 to multiple additional tests Interpretation and report Documentation in progress report of E/M visit
 96110 Examples n n n n n Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ) Brigance Early Preschool Developmental Profile II Early Language Milestone Scales PEDS PDQ Vanderbilt MCHAT NOT direct physician observation or general developmental assessment with checklist of milestones appropriate for age
96110 Examples n n n n n Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ) Brigance Early Preschool Developmental Profile II Early Language Milestone Scales PEDS PDQ Vanderbilt MCHAT NOT direct physician observation or general developmental assessment with checklist of milestones appropriate for age
 Depression Screening n 96110 Adolescent depression screening ($8. 24 - 2014 Medicare) n 99420 Maternal depression screening ($10. 75 - 2014 Medicare)
Depression Screening n 96110 Adolescent depression screening ($8. 24 - 2014 Medicare) n 99420 Maternal depression screening ($10. 75 - 2014 Medicare)
 2015 CNS Assessments / Tests 96110 – Developmental screening with scoring and documentation, per standardized form n 96127 – Brief emotional/behavioral assessment (depression inventory, ADHD scale, with scoring and documentation, per standardized instrument n
2015 CNS Assessments / Tests 96110 – Developmental screening with scoring and documentation, per standardized form n 96127 – Brief emotional/behavioral assessment (depression inventory, ADHD scale, with scoring and documentation, per standardized instrument n
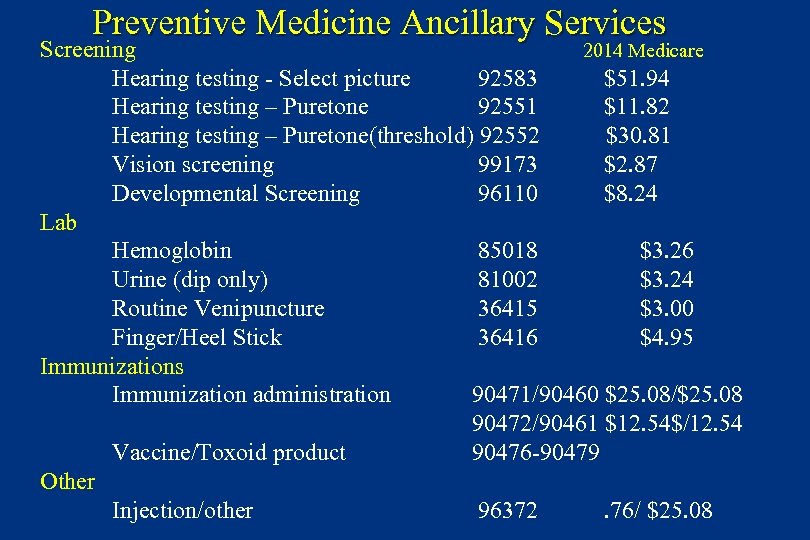 Preventive Medicine Ancillary Services Screening 2014 Medicare Hearing testing - Select picture 92583 $51. 94 Hearing testing – Puretone 92551 $11. 82 Hearing testing – Puretone(threshold) 92552 $30. 81 Vision screening 99173 $2. 87 Developmental Screening 96110 $8. 24 Lab Hemoglobin 85018 $3. 26 Urine (dip only) 81002 $3. 24 Routine Venipuncture 36415 $3. 00 Finger/Heel Stick 36416 $4. 95 Immunizations Immunization administration 90471/90460 $25. 08/$25. 08 90472/90461 $12. 54$/12. 54 Vaccine/Toxoid product 90476 -90479 Other Injection/other 96372. 76/ $25. 08
Preventive Medicine Ancillary Services Screening 2014 Medicare Hearing testing - Select picture 92583 $51. 94 Hearing testing – Puretone 92551 $11. 82 Hearing testing – Puretone(threshold) 92552 $30. 81 Vision screening 99173 $2. 87 Developmental Screening 96110 $8. 24 Lab Hemoglobin 85018 $3. 26 Urine (dip only) 81002 $3. 24 Routine Venipuncture 36415 $3. 00 Finger/Heel Stick 36416 $4. 95 Immunizations Immunization administration 90471/90460 $25. 08/$25. 08 90472/90461 $12. 54$/12. 54 Vaccine/Toxoid product 90476 -90479 Other Injection/other 96372. 76/ $25. 08
 DOCUMENT !
DOCUMENT !
 AAP Your CODING CONNECTION Coding & Reimbursement Resources n National AAP Coding Hotline: aapcodinghotline@aap. org or 800/433 -9016 ext 4022; free service to members and their office staff n Coding publications: Coding for Pediatrics, Pediatric Coding Companion, Quick Reference Guides, ICD-10 -CM Resources, RBRVS Brochure, AAP News Coding Corner
AAP Your CODING CONNECTION Coding & Reimbursement Resources n National AAP Coding Hotline: aapcodinghotline@aap. org or 800/433 -9016 ext 4022; free service to members and their office staff n Coding publications: Coding for Pediatrics, Pediatric Coding Companion, Quick Reference Guides, ICD-10 -CM Resources, RBRVS Brochure, AAP News Coding Corner


