cb5166a530fd8ad502719069a3d3eff7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Code for sustainable homes Water efficiency and surface water runoff Jonathan Reed Atkins Water & Environment

Introduction n Atkins n Water – why important? n The Code objectives n Water efficiency n Surface n water runoff Conclusions

Atkins at a glance With a turnover of c. £ 1. 2 bn, Atkins is: n One of the top 10 Best Big Companies to work for n The largest engineering consultancy in the UK n The largest multi-discipline consultancy in Europe n The 4 th largest design firm in the world n Voted no. 1 with ‘Best Reputation’ in Environment
![Water “[water efficiency has] minimum standards that must be achieved at every level of Water “[water efficiency has] minimum standards that must be achieved at every level of](https://present5.com/presentation/cb5166a530fd8ad502719069a3d3eff7/image-4.jpg)
Water “[water efficiency has] minimum standards that must be achieved at every level of the code, recognising [it’s] importance to the sustainability of any home. ” Why? n Water efficiency can be implemented now; n Range of sustainability benefits – energy, environmental impacts, etc. n Improved adaptation to climate change. Two areas covered by Code: n Water efficiency n Surface water run-off

Water Efficiency n Weir Wood Reservoir in August 2005 n Lowest recorded levels n Increase in demand for water should be minimised n Demand for water measured as a ‘Per Capita Consumption’, i. e. litres per head per day

Surface water run-off and flooding n Impact of hard surfacing on run-off, infiltration and drainage
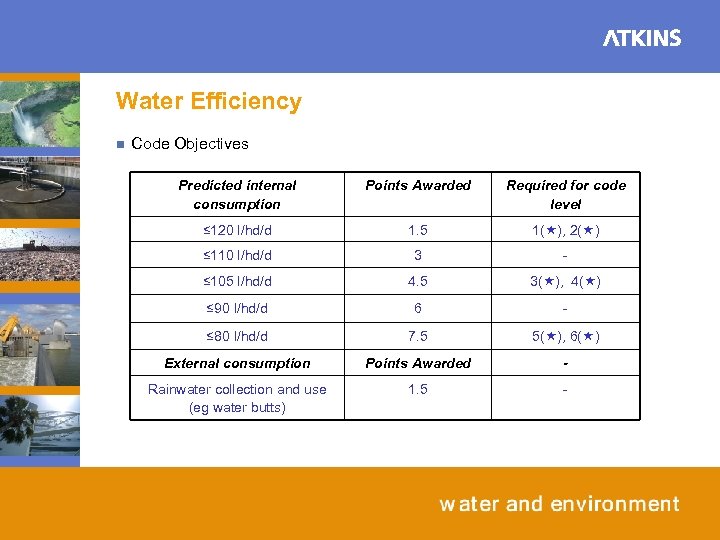
Water Efficiency n Code Objectives Predicted internal consumption Points Awarded Required for code level ≤ 120 l/hd/d 1. 5 1( ), 2( ) ≤ 110 l/hd/d 3 - ≤ 105 l/hd/d 4. 5 3( ), 4( ) ≤ 90 l/hd/d 6 - ≤ 80 l/hd/d 7. 5 5( ), 6( ) External consumption Points Awarded - Rainwater collection and use (eg water butts) 1. 5 -
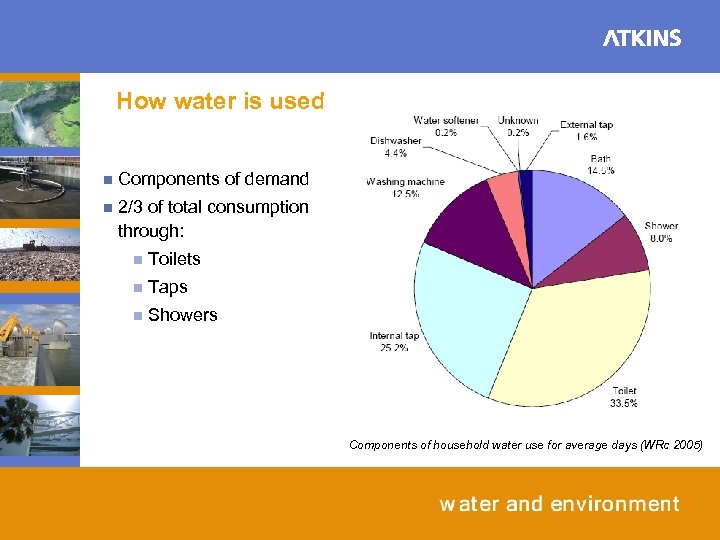
How water is used n Components of demand n 2/3 of total consumption through: n Toilets n Taps n Showers Components of household water use for average days (WRc 2005)

Step 1 – minimise water use n Toilets n Dual n Can n flush 6/4 litre be reduced further Showers n Flow rates of 6 -9 l/min n Aerating n Flow n shower heads restrictors Baths n Shaped baths

Step 1 – minimise water use n Taps n Aerated n Flow n taps (downstairs sinks) restrictors Appliances n Dishwashers n Washing n machines External n Fit a water butt
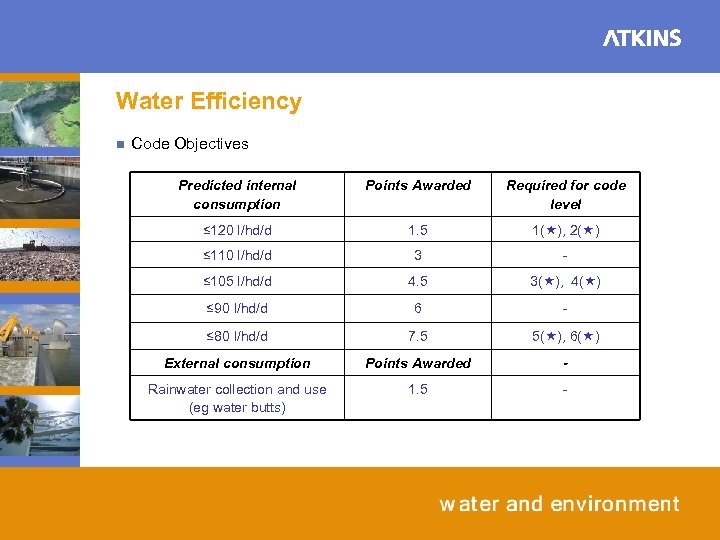
Water Efficiency n Code Objectives Predicted internal consumption Points Awarded Required for code level ≤ 120 l/hd/d 1. 5 1( ), 2( ) ≤ 110 l/hd/d 3 - ≤ 105 l/hd/d 4. 5 3( ), 4( ) ≤ 90 l/hd/d 6 - ≤ 80 l/hd/d 7. 5 5( ), 6( ) External consumption Points Awarded - Rainwater collection and use (eg water butts) 1. 5 -
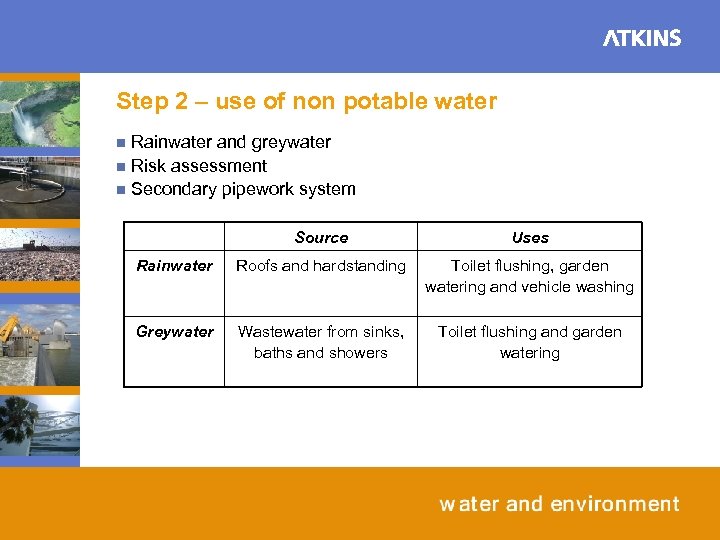
Step 2 – use of non potable water Rainwater and greywater n Risk assessment n Secondary pipework system n Source Uses Rainwater Roofs and hardstanding Toilet flushing, garden watering and vehicle washing Greywater Wastewater from sinks, baths and showers Toilet flushing and garden watering

Surface water runoff New development has two main impacts: 1 Increases runoff rates – making flooding worse elsewhere 2 Reduces volume available for floodwater in the floodplain
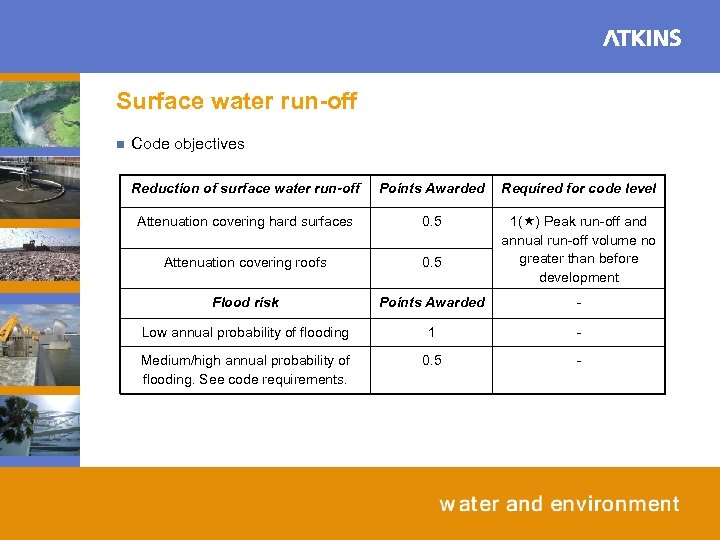
Surface water run-off n Code objectives Reduction of surface water run-off Points Awarded Required for code level Attenuation covering hard surfaces 0. 5 Attenuation covering roofs 0. 5 1( ) Peak run-off and annual run-off volume no greater than before development Flood risk Points Awarded - Low annual probability of flooding 1 - Medium/high annual probability of flooding. See code requirements. 0. 5 -

PPS 25 – Development and flood risk n n n Environment Agency are statutory consultees Aims to minimise the risks of development in flood risk areas Areas designated by the risk of flooding
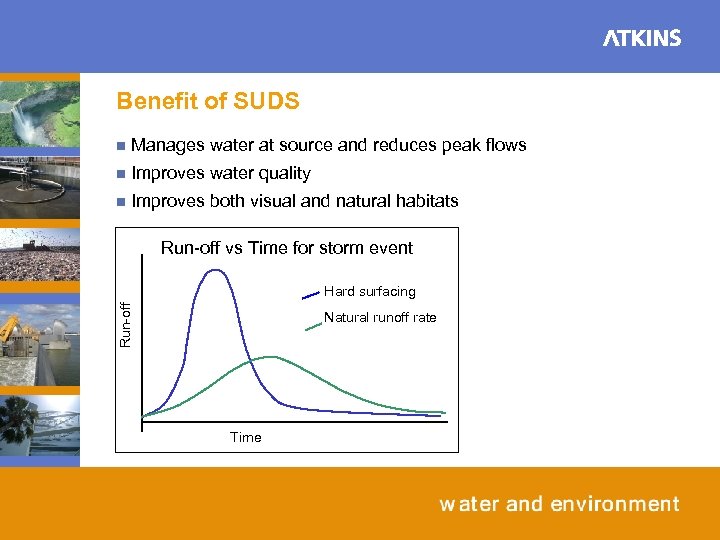
Benefit of SUDS n Manages water at source and reduces peak flows n Improves water quality n Improves both visual and natural habitats Run-off vs Time for storm event Run-off Hard surfacing Natural runoff rate Time
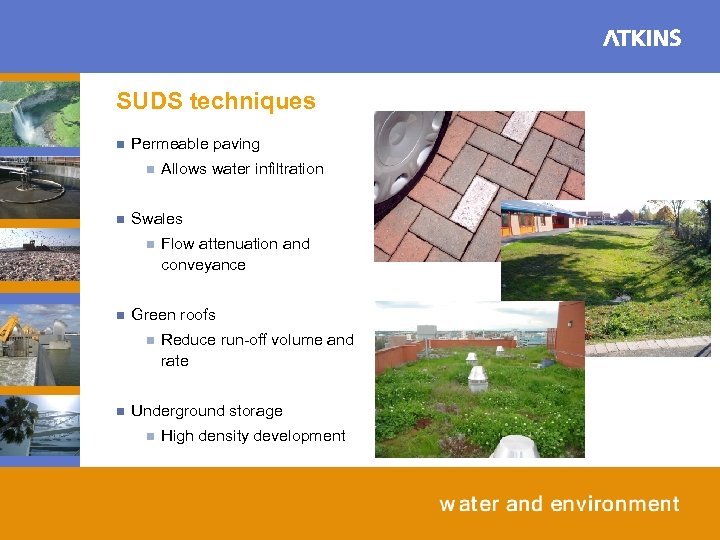
SUDS techniques n Permeable paving n n Swales n n Flow attenuation and conveyance Green roofs n n Allows water infiltration Reduce run-off volume and rate Underground storage n High density development
Long term maintenance of SUDS n Maintenance n Long term maintenance of SUDS needed n Who by? n Sewerage n Local Authority n Highways n undertaker Authority How? n Early consultation needed n Sewers n Model SUDS for Adoption agreements for

Conclusions n Water efficiency n Water n Toilets and showers n Non n potable use of water Rainwater or greywater for toilet flushing n Water n efficient appliances butts Surface water runoff n SUDS n Flood to reduce and improve surface water runoff risk controlled through links with PPS 25
Thank you
cb5166a530fd8ad502719069a3d3eff7.ppt