367ef086fa40de243f2cd368a2691681.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 COASTAL DATA INFORMATION PROGRAM 1975 - present Quality Assurance of Real-Time Data February 2004
COASTAL DATA INFORMATION PROGRAM 1975 - present Quality Assurance of Real-Time Data February 2004
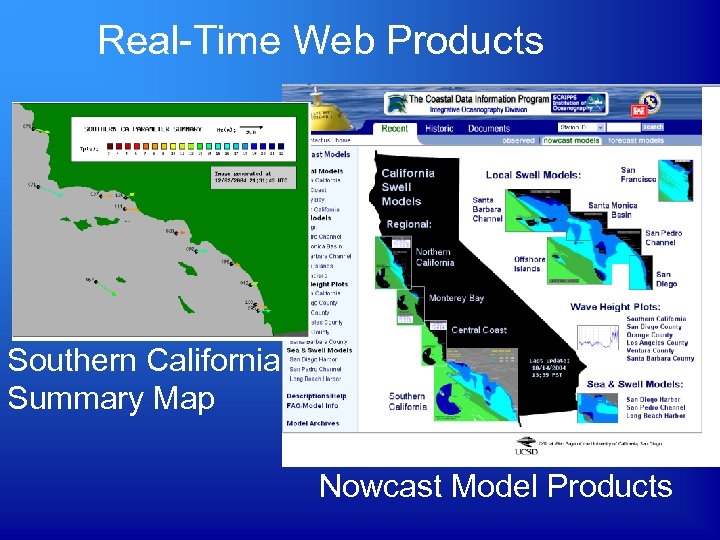 Real-Time Web Products Southern California Summary Map Nowcast Model Products
Real-Time Web Products Southern California Summary Map Nowcast Model Products
 1995: Wave Data Standards Analysis – US Army Corps of Engineers “… provide specifications on the analysis techniques that must be applied to wave data …. to ensure quality and uniformity of the final product. … The standard has evolved through a consensual approach involving the principal organizations which are responsible for the vast majority of wave measurements for this country. “ 2003: Handbook of Automated Data Quality Control Checks and Procedure of the National Data Buoy Center
1995: Wave Data Standards Analysis – US Army Corps of Engineers “… provide specifications on the analysis techniques that must be applied to wave data …. to ensure quality and uniformity of the final product. … The standard has evolved through a consensual approach involving the principal organizations which are responsible for the vast majority of wave measurements for this country. “ 2003: Handbook of Automated Data Quality Control Checks and Procedure of the National Data Buoy Center
 QUALITY ASSURANCE Pressure Sensor Calibration COLD BOX • Constant Temperature • Standard Paros • Battery of statistical test of dynamic pressure responses over several weeks to establish noise floor. DEEP TANK Soak complete package (sensors & cable) – Establish noise floor
QUALITY ASSURANCE Pressure Sensor Calibration COLD BOX • Constant Temperature • Standard Paros • Battery of statistical test of dynamic pressure responses over several weeks to establish noise floor. DEEP TANK Soak complete package (sensors & cable) – Establish noise floor
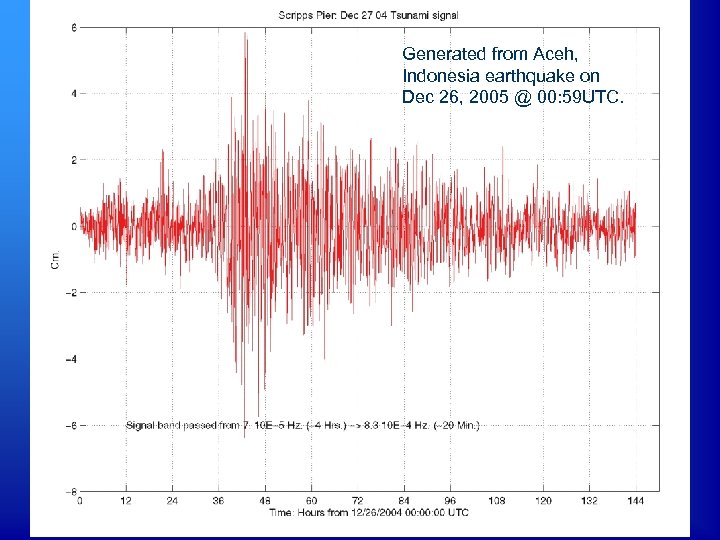 Generated from Aceh, Indonesia earthquake on Dec 26, 2005 @ 00: 59 UTC.
Generated from Aceh, Indonesia earthquake on Dec 26, 2005 @ 00: 59 UTC.
 Quality Control Specifications Pressure Sensors: Time Domain • • • Max Wave Height Test Flat episodes Test Spike Test Max value Test: successive trough to crest Min Value Test: successive trough to crest Mean Shift Test Equal Peaks Test Acceleration Test Mean crossing Test Period Distribution Test
Quality Control Specifications Pressure Sensors: Time Domain • • • Max Wave Height Test Flat episodes Test Spike Test Max value Test: successive trough to crest Min Value Test: successive trough to crest Mean Shift Test Equal Peaks Test Acceleration Test Mean crossing Test Period Distribution Test
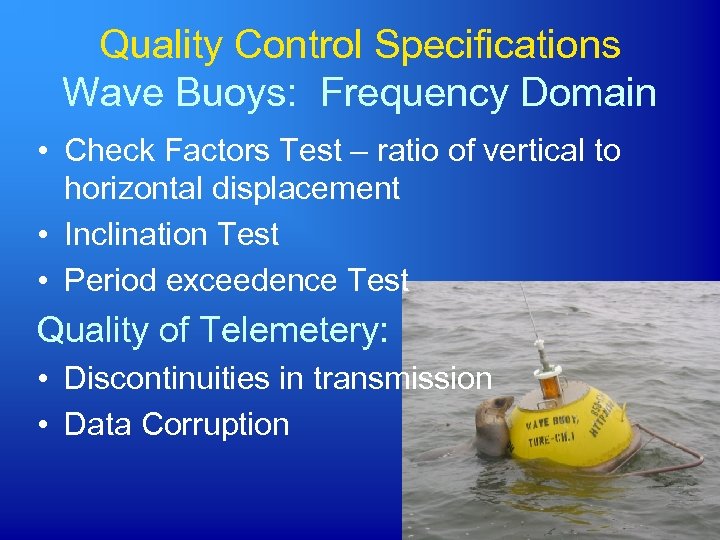 Quality Control Specifications Wave Buoys: Frequency Domain • Check Factors Test – ratio of vertical to horizontal displacement • Inclination Test • Period exceedence Test Quality of Telemetery: • Discontinuities in transmission • Data Corruption
Quality Control Specifications Wave Buoys: Frequency Domain • Check Factors Test – ratio of vertical to horizontal displacement • Inclination Test • Period exceedence Test Quality of Telemetery: • Discontinuities in transmission • Data Corruption
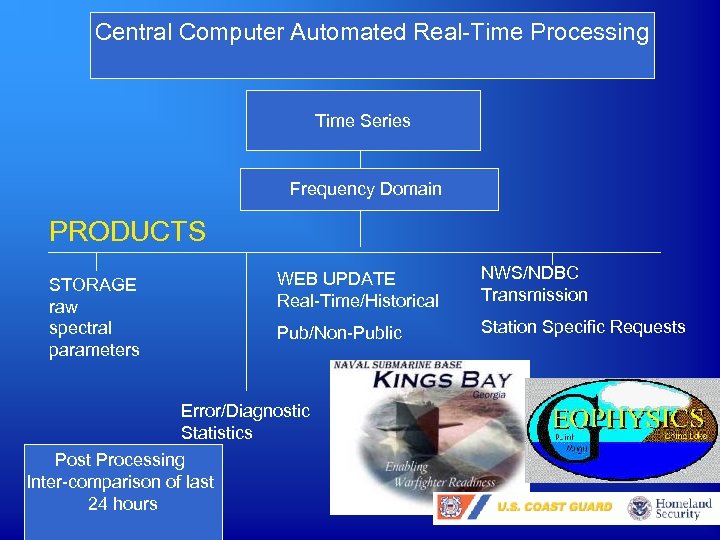 Central Computer Automated Real-Time Processing Time Domain Time Series Quality Control Frequency Domain PRODUCTS WEB UPDATE Real-Time/Historical NWS/NDBC Transmission Pub/Non-Public STORAGE raw spectral parameters Station Specific Requests Error/Diagnostic Statistics Post Processing Inter-comparison of last 24 hours
Central Computer Automated Real-Time Processing Time Domain Time Series Quality Control Frequency Domain PRODUCTS WEB UPDATE Real-Time/Historical NWS/NDBC Transmission Pub/Non-Public STORAGE raw spectral parameters Station Specific Requests Error/Diagnostic Statistics Post Processing Inter-comparison of last 24 hours
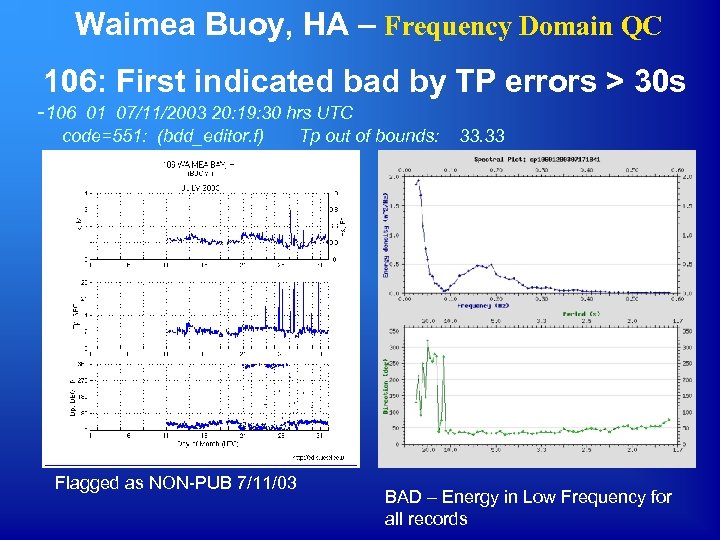 Waimea Buoy, HA – Frequency Domain QC 106: First indicated bad by TP errors > 30 s -106 01 07/11/2003 20: 19: 30 hrs UTC code=551: (bdd_editor. f) Tp out of bounds: Flagged as NON-PUB 7/11/03 33. 33 BAD – Energy in Low Frequency for all records
Waimea Buoy, HA – Frequency Domain QC 106: First indicated bad by TP errors > 30 s -106 01 07/11/2003 20: 19: 30 hrs UTC code=551: (bdd_editor. f) Tp out of bounds: Flagged as NON-PUB 7/11/03 33. 33 BAD – Energy in Low Frequency for all records
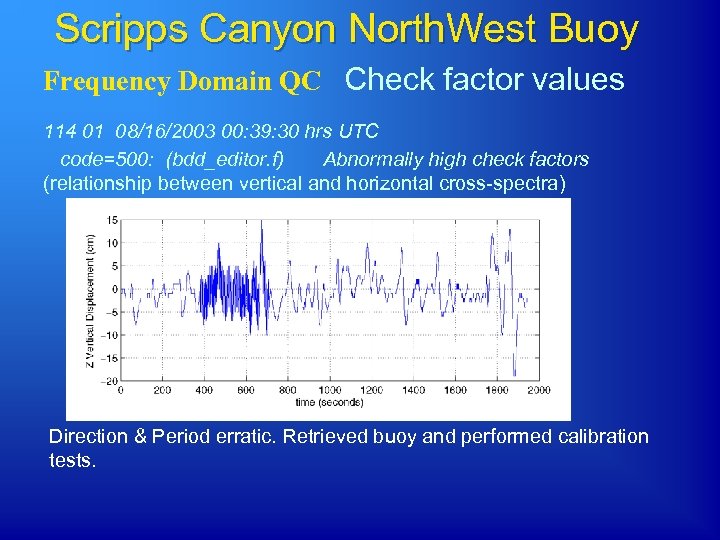 Scripps Canyon North. West Buoy Frequency Domain QC Check factor values 114 01 08/16/2003 00: 39: 30 hrs UTC code=500: (bdd_editor. f) Abnormally high check factors (relationship between vertical and horizontal cross-spectra) Calibration Test – Bad displacement Direction & Period erratic. Retrieved buoy and performed calibration tests.
Scripps Canyon North. West Buoy Frequency Domain QC Check factor values 114 01 08/16/2003 00: 39: 30 hrs UTC code=500: (bdd_editor. f) Abnormally high check factors (relationship between vertical and horizontal cross-spectra) Calibration Test – Bad displacement Direction & Period erratic. Retrieved buoy and performed calibration tests.
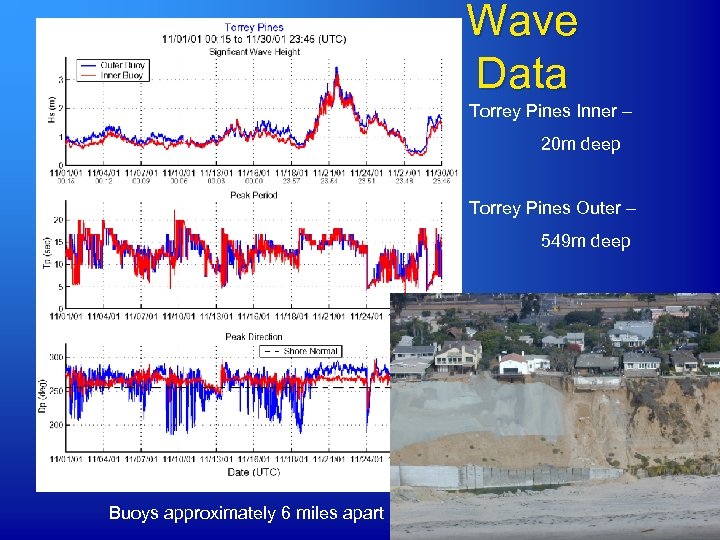 Wave Data Torrey Pines Inner – 20 m deep Torrey Pines Outer – 549 m deep Buoys approximately 6 miles apart
Wave Data Torrey Pines Inner – 20 m deep Torrey Pines Outer – 549 m deep Buoys approximately 6 miles apart
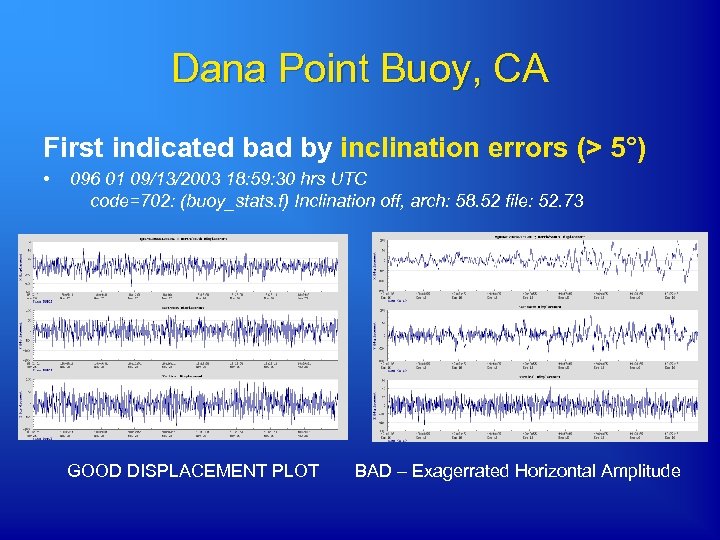 Dana Point Buoy, CA First indicated bad by inclination errors (> 5°) • 096 01 09/13/2003 18: 59: 30 hrs UTC code=702: (buoy_stats. f) Inclination off, arch: 58. 52 file: 52. 73 GOOD DISPLACEMENT PLOT BAD – Exagerrated Horizontal Amplitude
Dana Point Buoy, CA First indicated bad by inclination errors (> 5°) • 096 01 09/13/2003 18: 59: 30 hrs UTC code=702: (buoy_stats. f) Inclination off, arch: 58. 52 file: 52. 73 GOOD DISPLACEMENT PLOT BAD – Exagerrated Horizontal Amplitude
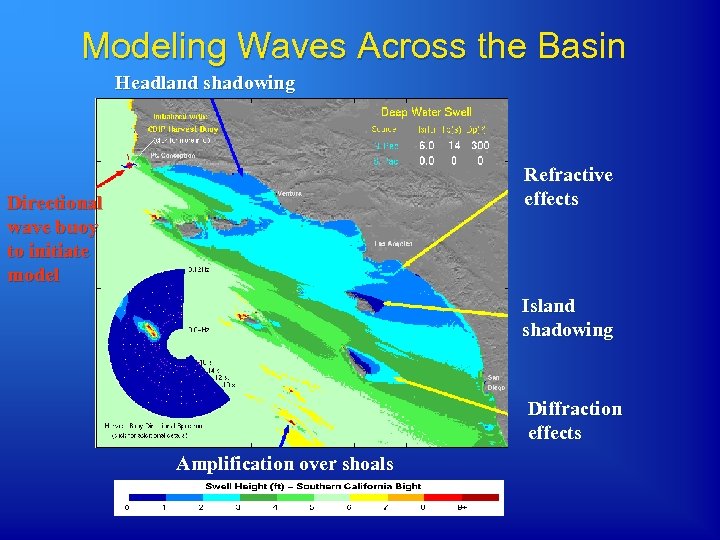 Modeling Waves Across the Basin Headland shadowing Refractive effects Directional wave buoy to initiate model Island shadowing Diffraction effects Amplification over shoals
Modeling Waves Across the Basin Headland shadowing Refractive effects Directional wave buoy to initiate model Island shadowing Diffraction effects Amplification over shoals
 Pacific Gas & Electric Company Diablo Canyon Nuclear Power Plant 2004
Pacific Gas & Electric Company Diablo Canyon Nuclear Power Plant 2004
 CDIP In-House Diagnostics • Paged: – off site (GPS & ARGOS) – data is > 1 hr old, – computer system is down, – computer partitions are > 90% full. • Programmers emailed : – Offsite – Data > 1 hr old, power outages, data transfer failed. System messages
CDIP In-House Diagnostics • Paged: – off site (GPS & ARGOS) – data is > 1 hr old, – computer system is down, – computer partitions are > 90% full. • Programmers emailed : – Offsite – Data > 1 hr old, power outages, data transfer failed. System messages
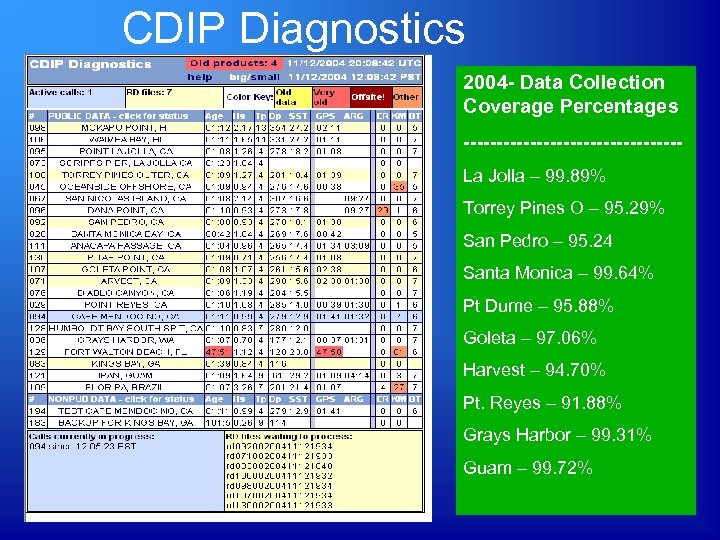 CDIP Diagnostics 2004 - Data Collection Coverage Percentages ----------------La Jolla – 99. 89% Torrey Pines O – 95. 29% San Pedro – 95. 24 Santa Monica – 99. 64% Pt Dume – 95. 88% Goleta – 97. 06% Harvest – 94. 70% Pt. Reyes – 91. 88% Grays Harbor – 99. 31% Guam – 99. 72%
CDIP Diagnostics 2004 - Data Collection Coverage Percentages ----------------La Jolla – 99. 89% Torrey Pines O – 95. 29% San Pedro – 95. 24 Santa Monica – 99. 64% Pt Dume – 95. 88% Goleta – 97. 06% Harvest – 94. 70% Pt. Reyes – 91. 88% Grays Harbor – 99. 31% Guam – 99. 72%
 http: //cdip. ucsd. edu
http: //cdip. ucsd. edu


