a7d34f3bd74402bb97e39682a53ee7c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 COACHING PLC Skill Up to Scale Up
COACHING PLC Skill Up to Scale Up
 Who? Why? What? How?
Who? Why? What? How?
 Who? Why? What? How?
Who? Why? What? How?
 Poll Question #1
Poll Question #1
 Who? Why? What? How? Focus on roles and functions, NOT titles.
Who? Why? What? How? Focus on roles and functions, NOT titles.
 Who? Why? What? How? • Part-time teachers/part-time coach (peer coaching) • Full-time coaches (FTE allocation) • Itinerant staff • Combination of the above
Who? Why? What? How? • Part-time teachers/part-time coach (peer coaching) • Full-time coaches (FTE allocation) • Itinerant staff • Combination of the above
 Who? Why? What? How? All can learn the SKILLS needed to provide feedback for improving classroom instruction.
Who? Why? What? How? All can learn the SKILLS needed to provide feedback for improving classroom instruction.
 Who? Why? What? How? credibility and experience with the target skills
Who? Why? What? How? credibility and experience with the target skills
 Who? Why? What? How?
Who? Why? What? How?
 Poll Question #2
Poll Question #2
 Who? Why? What? How? Working smarter not harder.
Who? Why? What? How? Working smarter not harder.

 State vs. Davis County
State vs. Davis County
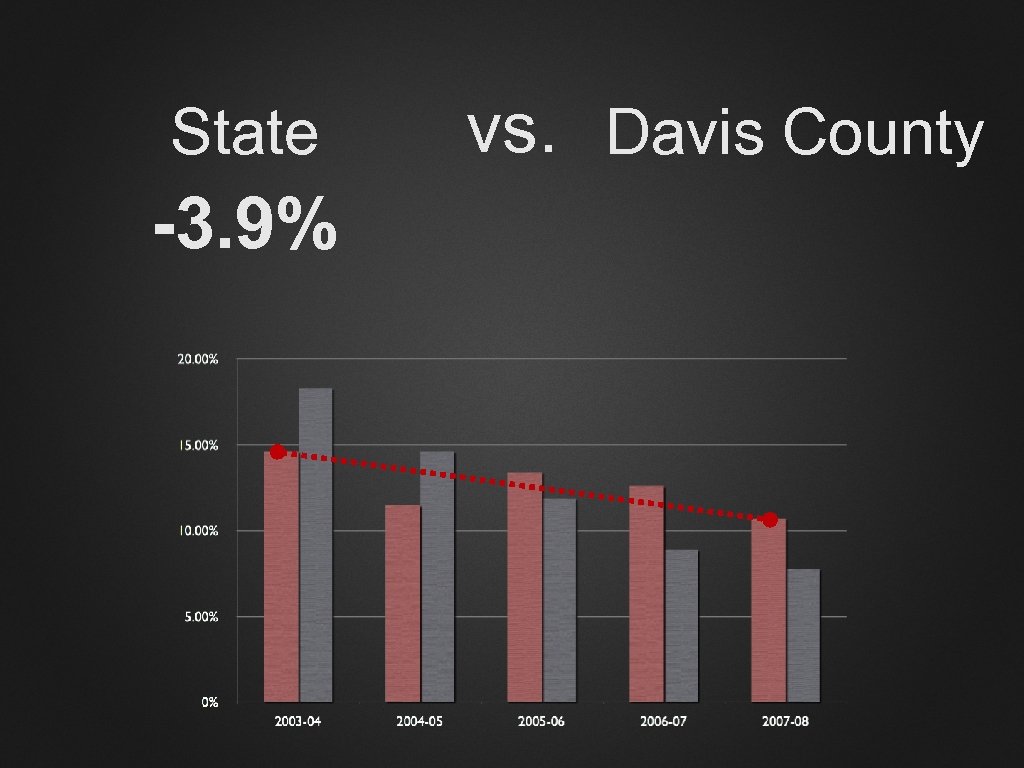 State -3. 9% vs. Davis County
State -3. 9% vs. Davis County
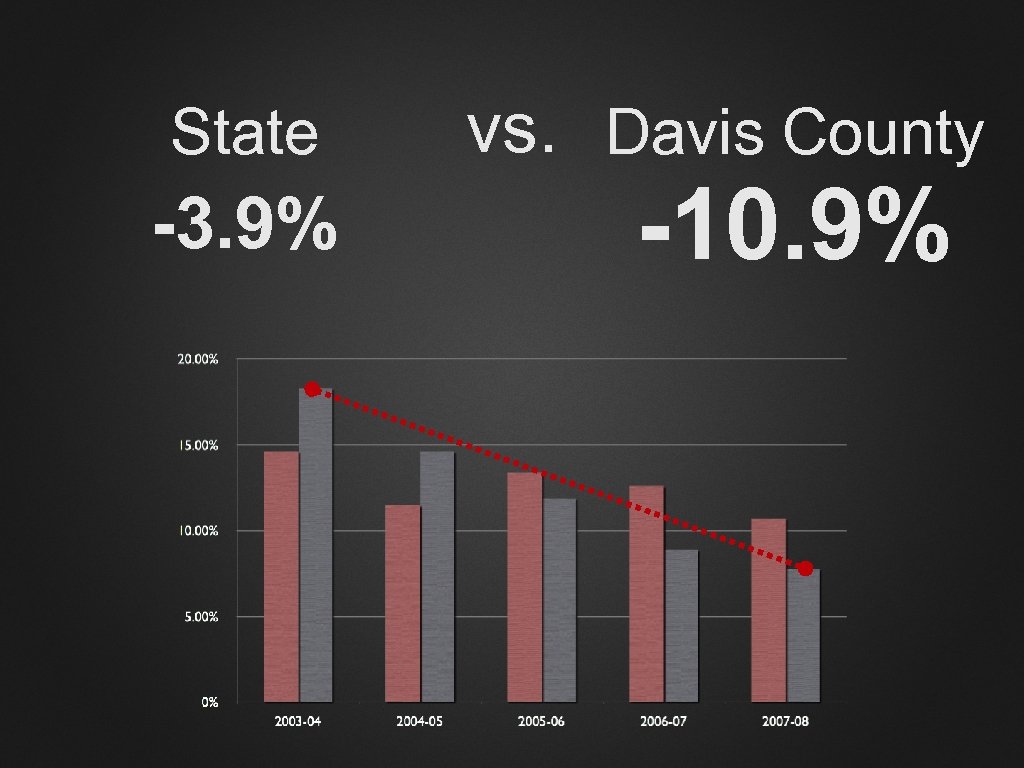 State -3. 9% vs. Davis County -10. 9%
State -3. 9% vs. Davis County -10. 9%
 What’s the Cost?
What’s the Cost?
 Recruit, Hire, Train National Commission on Teaching & America’s Future
Recruit, Hire, Train National Commission on Teaching & America’s Future
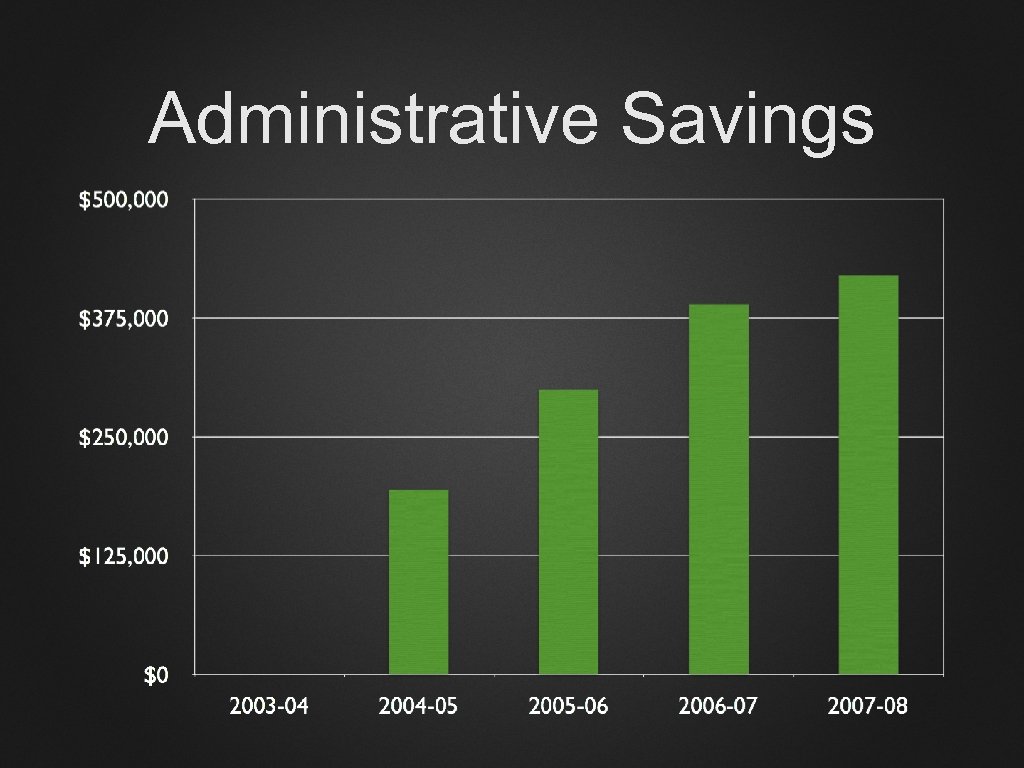 Administrative Savings
Administrative Savings
 What’s the Cost to the Child?
What’s the Cost to the Child?
 Evidenced-Based PD Coaching Impact Joyce & Showers, 2002
Evidenced-Based PD Coaching Impact Joyce & Showers, 2002
 Who? Why? What? How?
Who? Why? What? How?
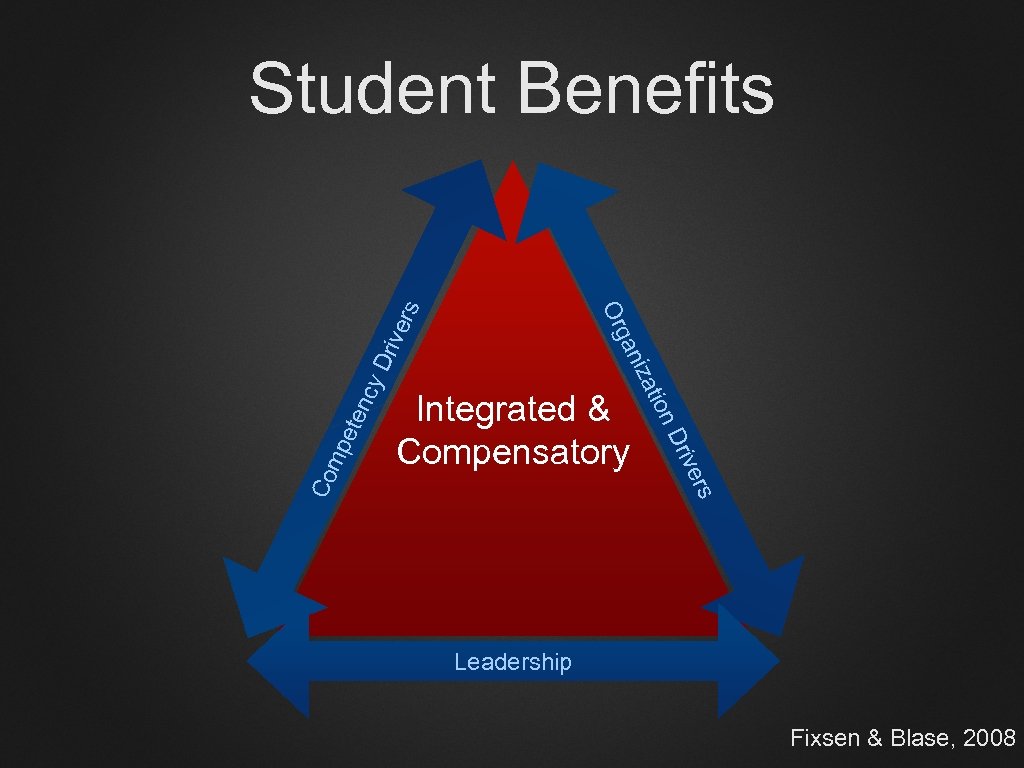 rs enc y pet rive n D Integrated & Compensatory atio Co m niz Dr ive r ga Or s Student Benefits Leadership Fixsen & Blase, 2008
rs enc y pet rive n D Integrated & Compensatory atio Co m niz Dr ive r ga Or s Student Benefits Leadership Fixsen & Blase, 2008
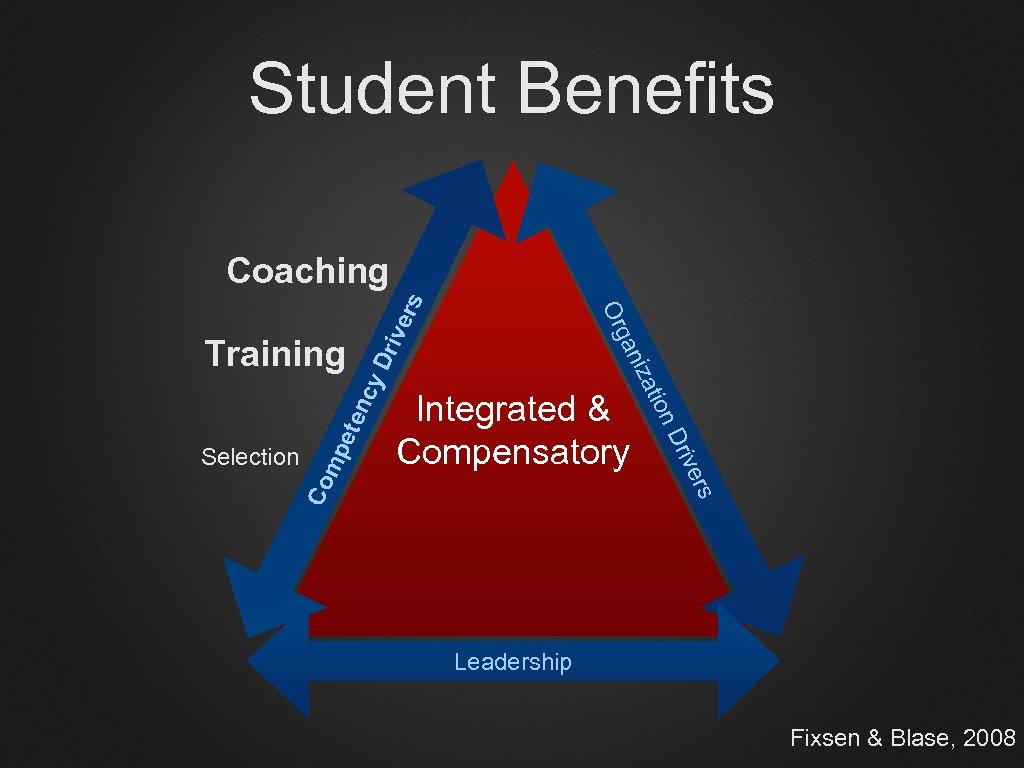 Student Benefits Dri v Co mp ete nc y rs rive n D Integrated & Compensatory atio Selection niz Training ga Or ers Coaching Leadership Fixsen & Blase, 2008
Student Benefits Dri v Co mp ete nc y rs rive n D Integrated & Compensatory atio Selection niz Training ga Or ers Coaching Leadership Fixsen & Blase, 2008
 Evidence-Based PD • Any skill development effort should be supplemented with active coaching: • to facilitate fidelity of implementation. • to facilitate sustained implementation. Rob Horner, 2010
Evidence-Based PD • Any skill development effort should be supplemented with active coaching: • to facilitate fidelity of implementation. • to facilitate sustained implementation. Rob Horner, 2010
 Active & iterative delivery of: prompts corrections successful behavior unsuccessful behavior Rob Horner, 2010
Active & iterative delivery of: prompts corrections successful behavior unsuccessful behavior Rob Horner, 2010
 Coaching is done: • by someone with credibility and experience with the target skill(s) • on-site, in real time • after initial training • repeatedly (e. g. , monthly) • with intensity adjusted to need Rob Horner, 2010
Coaching is done: • by someone with credibility and experience with the target skill(s) • on-site, in real time • after initial training • repeatedly (e. g. , monthly) • with intensity adjusted to need Rob Horner, 2010
 Who? Why? What? How?
Who? Why? What? How?
 Establishing Coaching Infrastructures Focus on roles and functions of coaches, not titles. Related servers, teachers, and administrators can all learn the skills needed to provide feedback for improving classroom instruction. Share data about how instructional coaching can help reduce turnover and save $$.
Establishing Coaching Infrastructures Focus on roles and functions of coaches, not titles. Related servers, teachers, and administrators can all learn the skills needed to provide feedback for improving classroom instruction. Share data about how instructional coaching can help reduce turnover and save $$.
 Model Instructional Coaching Support Systems
Model Instructional Coaching Support Systems
 Running Start New Teacher Training
Running Start New Teacher Training
 Who? Why? What? How? Induction Specialist Coaches
Who? Why? What? How? Induction Specialist Coaches
 Who? Why? What? How? Infrastructure to address teacher shortage (SPDG Performance Measure)
Who? Why? What? How? Infrastructure to address teacher shortage (SPDG Performance Measure)

 Who? Why? What? How? Vital Teaching & Coaching Behaviors
Who? Why? What? How? Vital Teaching & Coaching Behaviors
 T each routines & procedures E xpectations A ttention C ycle of instruction H igh rate of reinforcement E rror correction R esponse opportunities
T each routines & procedures E xpectations A ttention C ycle of instruction H igh rate of reinforcement E rror correction R esponse opportunities
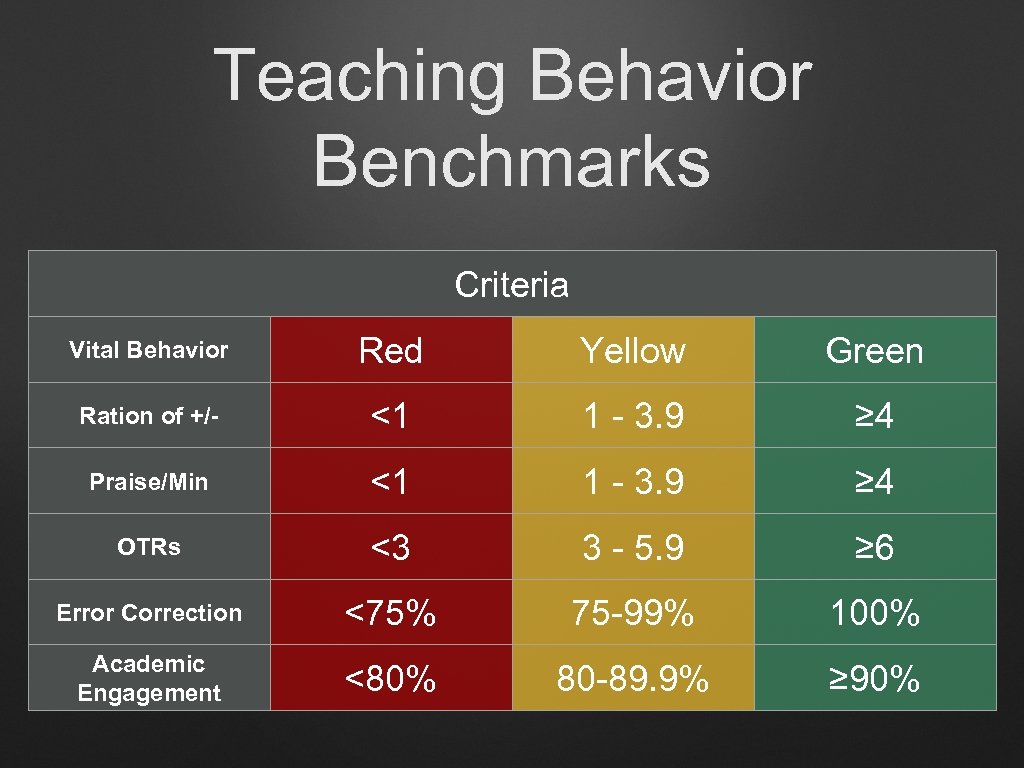 Teaching Behavior Benchmarks Criteria Vital Behavior Red Yellow Green Ration of +/- <1 1 - 3. 9 ≥ 4 Praise/Min <1 1 - 3. 9 ≥ 4 OTRs <3 3 - 5. 9 ≥ 6 Error Correction <75% 75 -99% 100% Academic Engagement <80% 80 -89. 9% ≥ 90%
Teaching Behavior Benchmarks Criteria Vital Behavior Red Yellow Green Ration of +/- <1 1 - 3. 9 ≥ 4 Praise/Min <1 1 - 3. 9 ≥ 4 OTRs <3 3 - 5. 9 ≥ 6 Error Correction <75% 75 -99% 100% Academic Engagement <80% 80 -89. 9% ≥ 90%
 C ommunication skills O bserve & collect data A ssist with materials, curriculum & lesson plans C oaching cycle H elp in making data-based decisions E motional support & encouragement M odeling
C ommunication skills O bserve & collect data A ssist with materials, curriculum & lesson plans C oaching cycle H elp in making data-based decisions E motional support & encouragement M odeling
 Who? Why? What? How? Training Ongoing Coaching Data Feedback Loop
Who? Why? What? How? Training Ongoing Coaching Data Feedback Loop
 4 Phases of running start
4 Phases of running start
 What Difference Does it Make?
What Difference Does it Make?






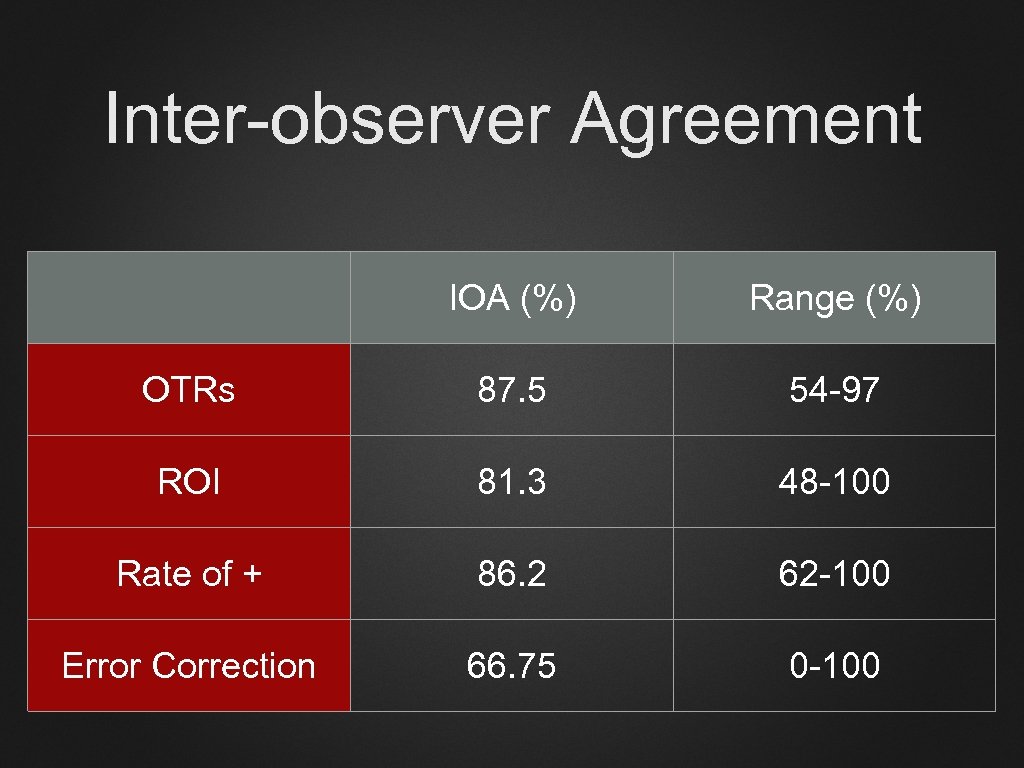 Inter-observer Agreement IOA (%) Range (%) OTRs 87. 5 54 -97 ROI 81. 3 48 -100 Rate of + 86. 2 62 -100 Error Correction 66. 75 0 -100
Inter-observer Agreement IOA (%) Range (%) OTRs 87. 5 54 -97 ROI 81. 3 48 -100 Rate of + 86. 2 62 -100 Error Correction 66. 75 0 -100
 MOVING FORWARD Coaching Matters! • Transfer all observational data to LEA instructional coaches • Collect Observer agreement data on 20% of observations • Train instructional coaches on online data entry Scale up State-wide
MOVING FORWARD Coaching Matters! • Transfer all observational data to LEA instructional coaches • Collect Observer agreement data on 20% of observations • Train instructional coaches on online data entry Scale up State-wide
 Utah Coaching Network
Utah Coaching Network
 Who? Why? What? How? LEA Instructional Coaches
Who? Why? What? How? LEA Instructional Coaches
 Who? Why? What? How? Increase LEA Capacity
Who? Why? What? How? Increase LEA Capacity


 Ogden City Schools Director Executive Director Coordinator Induction Coordinator School Support Team Teacher Specialists Lead Coach Instructional Coaches Special Education Coaches All Teachers Special Education Teachers Human Resources K-6 Instructional Coaches Provisional Teachers Special Education
Ogden City Schools Director Executive Director Coordinator Induction Coordinator School Support Team Teacher Specialists Lead Coach Instructional Coaches Special Education Coaches All Teachers Special Education Teachers Human Resources K-6 Instructional Coaches Provisional Teachers Special Education
 Who? Why? What? How? Vital Teaching & Coaching Behaviors
Who? Why? What? How? Vital Teaching & Coaching Behaviors


 Resources
Resources

 Who? Why? What? How? Ongoing Training - microteaching Ongoing Coaching Data Feedback Loop
Who? Why? What? How? Ongoing Training - microteaching Ongoing Coaching Data Feedback Loop
 What Difference Does it Make?
What Difference Does it Make?
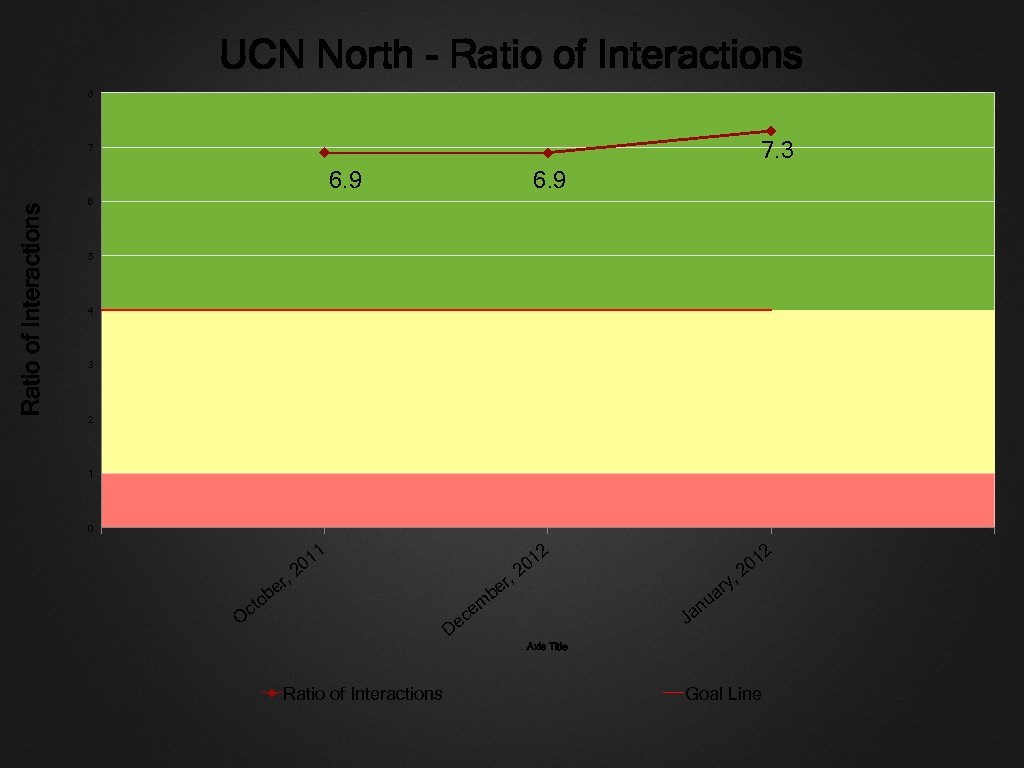 UCN North - Ratio of Interactions 8 7. 3 7 Ratio of Interactions 6. 9 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 , er ob ct O 2 2 1 1 20 , m ce er b 1 20 , u n Ja De y ar 1 20 Axis Title Ratio of Interactions Goal Line
UCN North - Ratio of Interactions 8 7. 3 7 Ratio of Interactions 6. 9 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 , er ob ct O 2 2 1 1 20 , m ce er b 1 20 , u n Ja De y ar 1 20 Axis Title Ratio of Interactions Goal Line
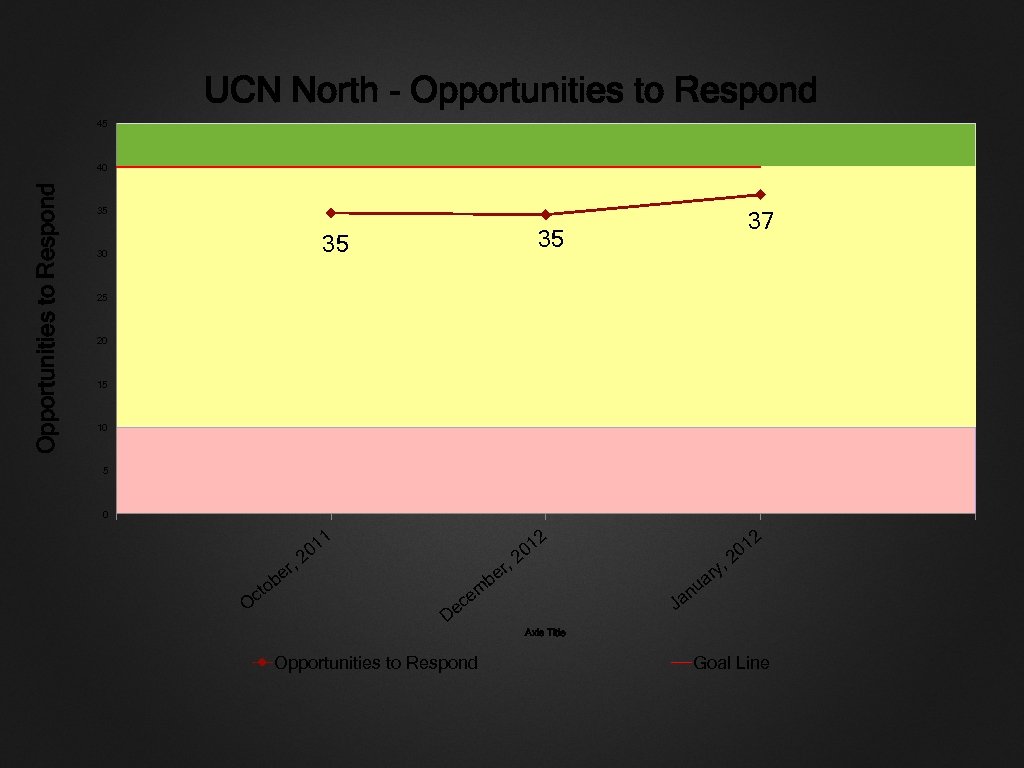 UCN North - Opportunities to Respond 45 Opportunities to Respond 40 35 35 35 30 37 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 r be cto O 1 20 , , r be 1 20 2 2 , u m ce n Ja De y ar 1 20 Axis Title Opportunities to Respond Goal Line
UCN North - Opportunities to Respond 45 Opportunities to Respond 40 35 35 35 30 37 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 r be cto O 1 20 , , r be 1 20 2 2 , u m ce n Ja De y ar 1 20 Axis Title Opportunities to Respond Goal Line
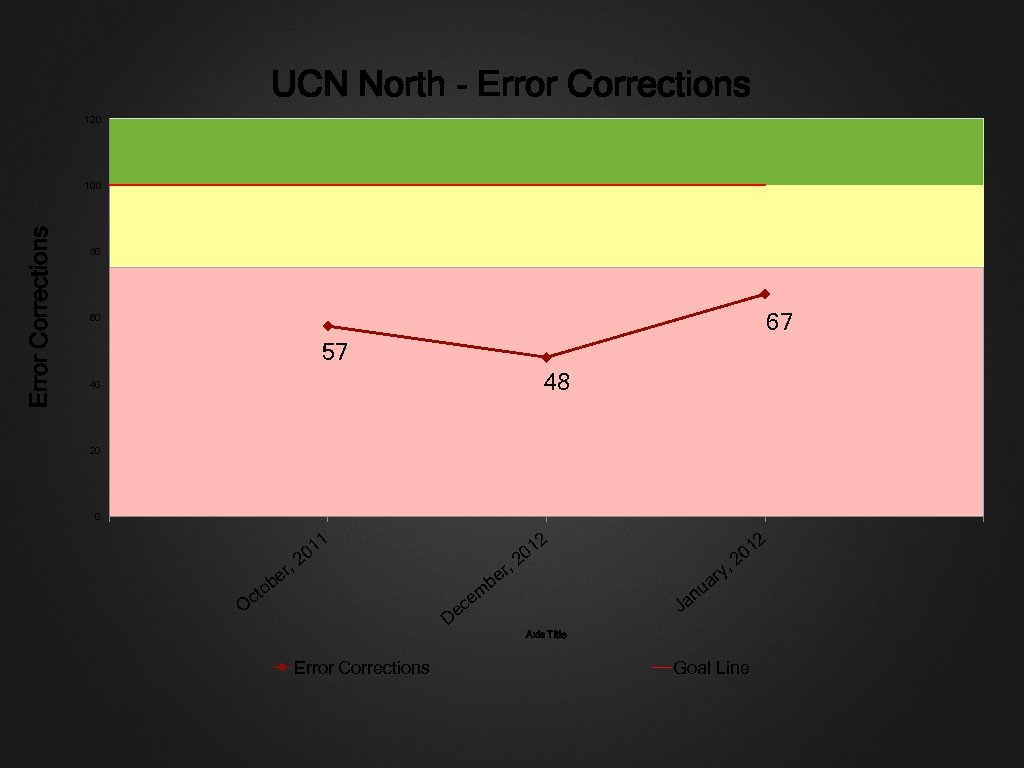 UCN North - Error Corrections 120 Error Corrections 100 80 67 60 57 48 40 20 0 , r be cto O 2 2 1 01 2 , r be 1 20 , u m ce n Ja De y ar 1 20 Axis Title Error Corrections Goal Line
UCN North - Error Corrections 120 Error Corrections 100 80 67 60 57 48 40 20 0 , r be cto O 2 2 1 01 2 , r be 1 20 , u m ce n Ja De y ar 1 20 Axis Title Error Corrections Goal Line
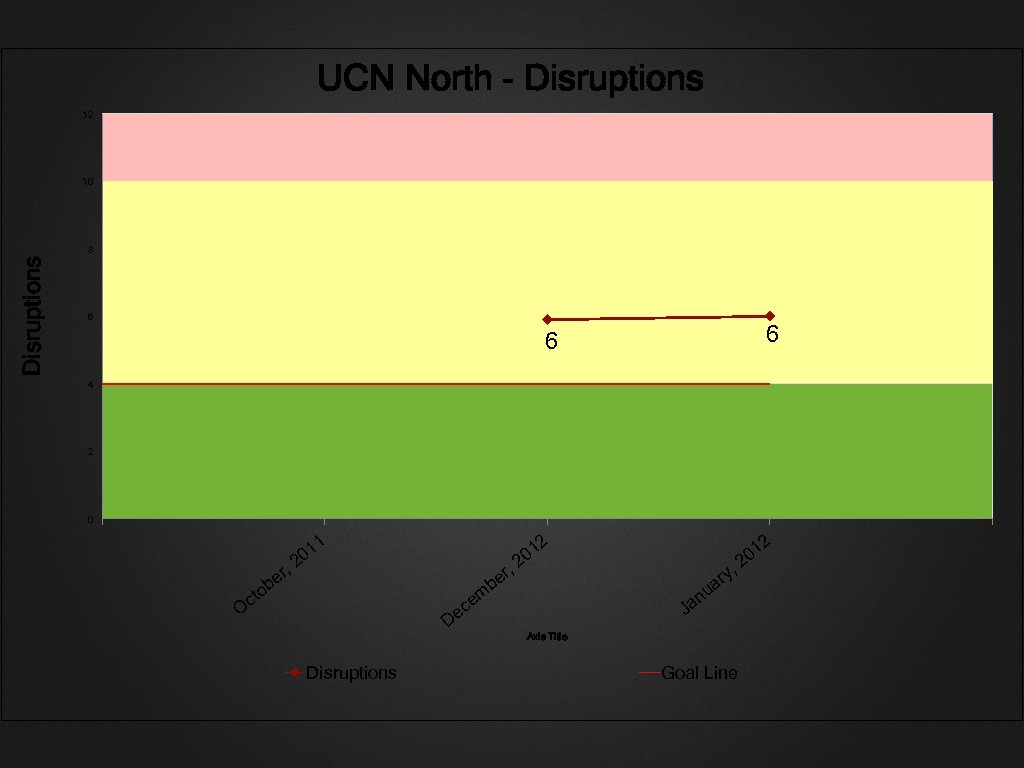 UCN North - Disruptions 12 10 Disruptions 8 6 6 6 4 2 0 , r be cto O 2 2 1 01 2 , m ce r be 01 2 , u n Ja De y ar Axis Title Disruptions Goal Line 01 2
UCN North - Disruptions 12 10 Disruptions 8 6 6 6 4 2 0 , r be cto O 2 2 1 01 2 , m ce r be 01 2 , u n Ja De y ar Axis Title Disruptions Goal Line 01 2
 UCN North - Time on Task 100 90 87 82 80 Time on Task 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 , r be cto O 2 2 1 01 2 , m ce r be 01 2 , u n Ja De y ar 01 2 Axis Title Time on Task Goal Line
UCN North - Time on Task 100 90 87 82 80 Time on Task 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 , r be cto O 2 2 1 01 2 , m ce r be 01 2 , u n Ja De y ar 01 2 Axis Title Time on Task Goal Line
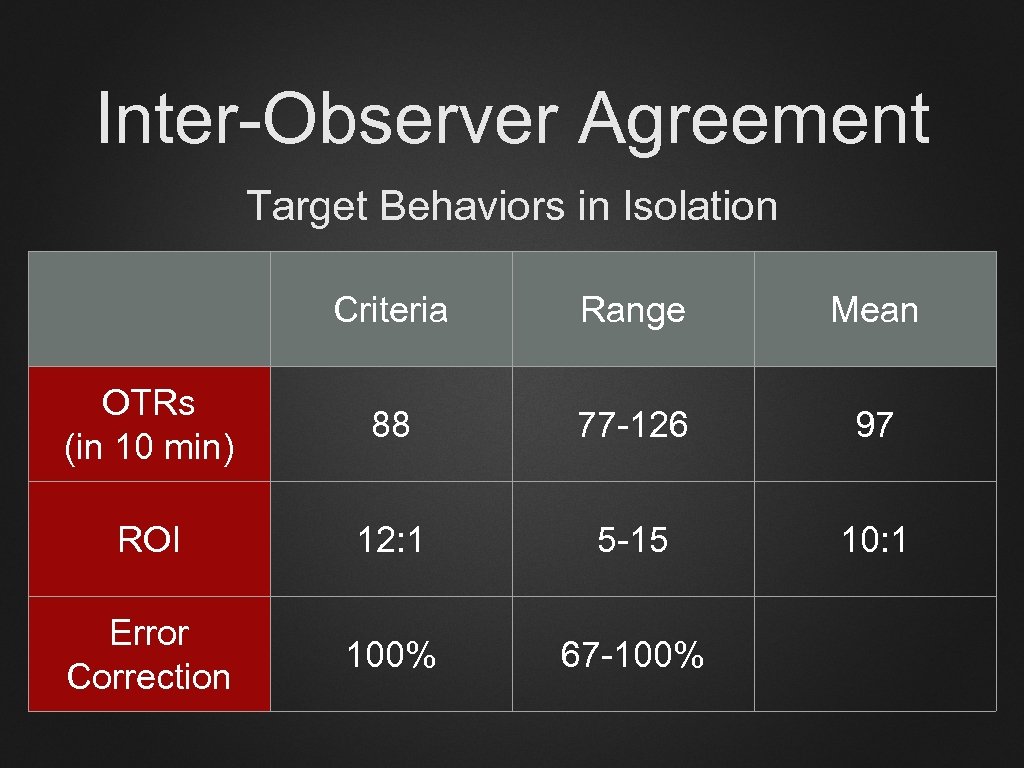 Inter-Observer Agreement Target Behaviors in Isolation Criteria Range Mean OTRs (in 10 min) 88 77 -126 97 ROI 12: 1 5 -15 10: 1 Error Correction 100% 67 -100%
Inter-Observer Agreement Target Behaviors in Isolation Criteria Range Mean OTRs (in 10 min) 88 77 -126 97 ROI 12: 1 5 -15 10: 1 Error Correction 100% 67 -100%
 Inter-Observer Agreement Target Behaviors Simultaneously Criteria Range Mean OTRs (in 10 min) 105 90 -125 105 ROI 8: 1 4 -10 7: 1 Error Correction 67% 67 -100%
Inter-Observer Agreement Target Behaviors Simultaneously Criteria Range Mean OTRs (in 10 min) 105 90 -125 105 ROI 8: 1 4 -10 7: 1 Error Correction 67% 67 -100%
 SCALING UP Ongoing PD = Highly Skilled Coaches + LEA Infrastructure = Scaling Up
SCALING UP Ongoing PD = Highly Skilled Coaches + LEA Infrastructure = Scaling Up
 STUDENT BENEFITS Systems Intervention y. D ete nc Facilitative Administration ers riv n. D Integrated & Compensatory o ati Co mp niz ga Or Training riv ers Coaching Leadership Decision Support Data System
STUDENT BENEFITS Systems Intervention y. D ete nc Facilitative Administration ers riv n. D Integrated & Compensatory o ati Co mp niz ga Or Training riv ers Coaching Leadership Decision Support Data System
 http: //v. gd/better. UCN
http: //v. gd/better. UCN



