cc84a309a258c75fdb71da9c23525869.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Co. WTe. St: A Cost Weighted Test Strategy
Co. WTe. St: A Cost Weighted Test Strategy
 Test Planning Strategy Objectives: § Decide which and how many test cases should be executed. § Give a practical help to managers to support test planning and evaluate the impact of testing the phase on the cost of the final product.
Test Planning Strategy Objectives: § Decide which and how many test cases should be executed. § Give a practical help to managers to support test planning and evaluate the impact of testing the phase on the cost of the final product.
 § § § Features (Exclusively) UML based: It uses the Use Cases and Interaction diagrams developed during analysis and design phases Cowtest strategy: development of a systematic method for UML design-based integration test of complex system. Based exclusively on the use of UML diagrams: • • § immediately usable from industries already using UML (no additional modeling or design costs); analysis can be started soon, and done contemporarily with project development; Different strategies for test cases selection
§ § § Features (Exclusively) UML based: It uses the Use Cases and Interaction diagrams developed during analysis and design phases Cowtest strategy: development of a systematic method for UML design-based integration test of complex system. Based exclusively on the use of UML diagrams: • • § immediately usable from industries already using UML (no additional modeling or design costs); analysis can be started soon, and done contemporarily with project development; Different strategies for test cases selection
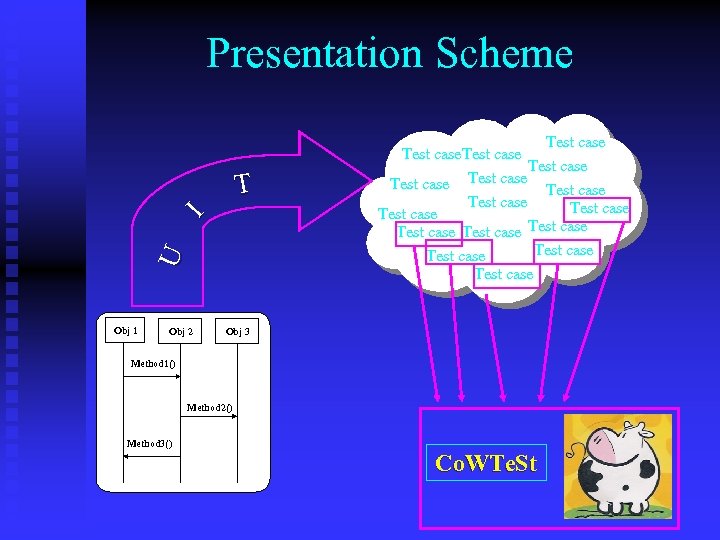 Presentation Scheme U I T Obj 1 Obj 2 Test case Test case Test case Test case Obj 3 Method 1() Method 2() Method 3() Co. WTe. St
Presentation Scheme U I T Obj 1 Obj 2 Test case Test case Test case Test case Obj 3 Method 1() Method 2() Method 3() Co. WTe. St
 Co. WTe. St: A Cost Weighted Test Strategy Weighted Tree Derivation: 1. Starting from the main UCD the UCs and SDs are organized in a sort of hierarchical tree 2. Deduce the Critical Profile: annotate every arch with a value representing “the importance” of the associate node (be it a UC or a SD scenario) 3. Test Case Derivation: apply UIT for test derivation
Co. WTe. St: A Cost Weighted Test Strategy Weighted Tree Derivation: 1. Starting from the main UCD the UCs and SDs are organized in a sort of hierarchical tree 2. Deduce the Critical Profile: annotate every arch with a value representing “the importance” of the associate node (be it a UC or a SD scenario) 3. Test Case Derivation: apply UIT for test derivation


 Integration Stage n. The first integration stage is represented by the main UC and the SDs (if any), which are children of this node (hence they are at level 2 of the tree). n. The i-th integration stage is represented by the UCs positioned in at i-th level of the tree and every SDs, children of these nodes, situated at i+1 -th level. NOTE: In the i-th integration stage the SDs at level i+1 are considered, because they represent the interaction between the different components that realize the functionalities described in the UCs at i-th level of the tree.
Integration Stage n. The first integration stage is represented by the main UC and the SDs (if any), which are children of this node (hence they are at level 2 of the tree). n. The i-th integration stage is represented by the UCs positioned in at i-th level of the tree and every SDs, children of these nodes, situated at i+1 -th level. NOTE: In the i-th integration stage the SDs at level i+1 are considered, because they represent the interaction between the different components that realize the functionalities described in the UCs at i-th level of the tree.
 3 rd Integration Stage
3 rd Integration Stage
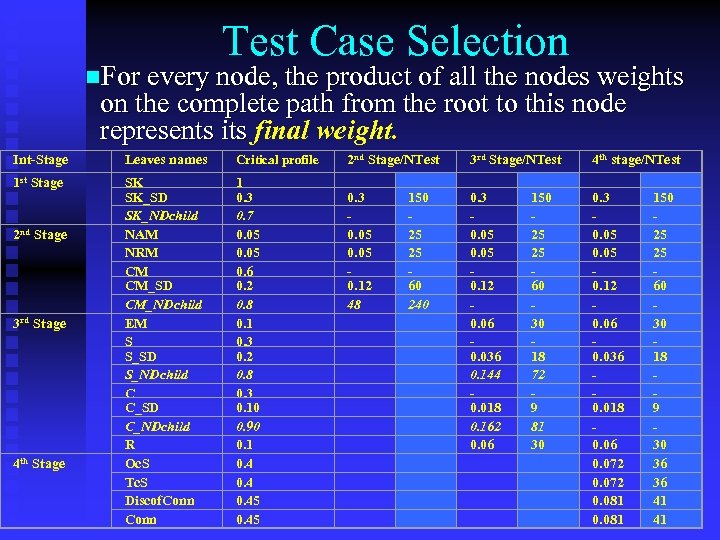 Test Case Selection n. For every node, the product of all the nodes weights on the complete path from the root to this node represents its final weight. represents its Int-Stage Leaves names Critical profile 2 nd Stage/NTest 3 rd Stage/NTest 4 th stage/NTest 1 st Stage SK SK_SD SK_NDchild NAM NRM CM CM_SD CM_NDchild EM S S_SD S_NDchild C C_SD C_NDchild R Oc. S Tc. S Discof. Conn 1 0. 3 0. 7 0. 05 0. 6 0. 2 0. 8 0. 1 0. 3 0. 2 0. 8 0. 3 0. 10 0. 90 0. 1 0. 45 0. 3 0. 05 0. 12 48 0. 3 0. 05 0. 12 0. 06 0. 036 0. 144 0. 018 0. 162 0. 06 0. 3 0. 05 0. 12 0. 06 0. 036 0. 018 0. 06 0. 072 0. 081 2 nd Stage 3 rd Stage 4 th Stage 150 25 25 60 240 150 25 25 60 30 18 72 9 81 30 150 25 25 60 30 18 9 30 36 36 41 41
Test Case Selection n. For every node, the product of all the nodes weights on the complete path from the root to this node represents its final weight. represents its Int-Stage Leaves names Critical profile 2 nd Stage/NTest 3 rd Stage/NTest 4 th stage/NTest 1 st Stage SK SK_SD SK_NDchild NAM NRM CM CM_SD CM_NDchild EM S S_SD S_NDchild C C_SD C_NDchild R Oc. S Tc. S Discof. Conn 1 0. 3 0. 7 0. 05 0. 6 0. 2 0. 8 0. 1 0. 3 0. 2 0. 8 0. 3 0. 10 0. 90 0. 1 0. 45 0. 3 0. 05 0. 12 48 0. 3 0. 05 0. 12 0. 06 0. 036 0. 144 0. 018 0. 162 0. 06 0. 3 0. 05 0. 12 0. 06 0. 036 0. 018 0. 06 0. 072 0. 081 2 nd Stage 3 rd Stage 4 th Stage 150 25 25 60 240 150 25 25 60 30 18 72 9 81 30 150 25 25 60 30 18 9 30 36 36 41 41
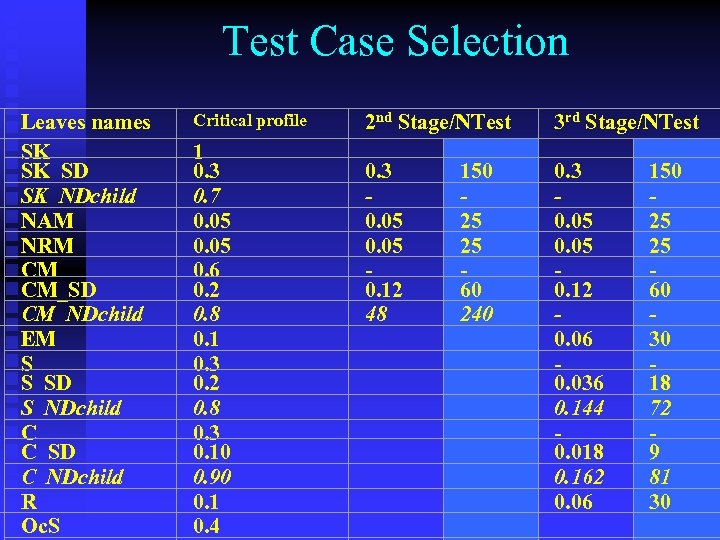 Test Case Selection Leaves names SK SK_SD SK_NDchild NAM NRM CM CM_SD CM_NDchild EM S S_SD S_NDchild C C_SD C_NDchild R Oc. S Critical profile 1 0. 3 0. 7 0. 05 0. 6 0. 2 0. 8 0. 1 0. 3 0. 2 0. 8 0. 3 0. 10 0. 90 0. 1 0. 4 2 nd Stage/NTest 0. 3 150 0. 05 25 0. 12 60 48 240 3 rd Stage/NTest 0. 3 150 0. 05 25 0. 12 60 0. 06 30 0. 036 18 72 0. 144 0. 018 9 81 0. 162 0. 06 30
Test Case Selection Leaves names SK SK_SD SK_NDchild NAM NRM CM CM_SD CM_NDchild EM S S_SD S_NDchild C C_SD C_NDchild R Oc. S Critical profile 1 0. 3 0. 7 0. 05 0. 6 0. 2 0. 8 0. 1 0. 3 0. 2 0. 8 0. 3 0. 10 0. 90 0. 1 0. 4 2 nd Stage/NTest 0. 3 150 0. 05 25 0. 12 60 48 240 3 rd Stage/NTest 0. 3 150 0. 05 25 0. 12 60 0. 06 30 0. 036 18 72 0. 144 0. 018 9 81 0. 162 0. 06 30
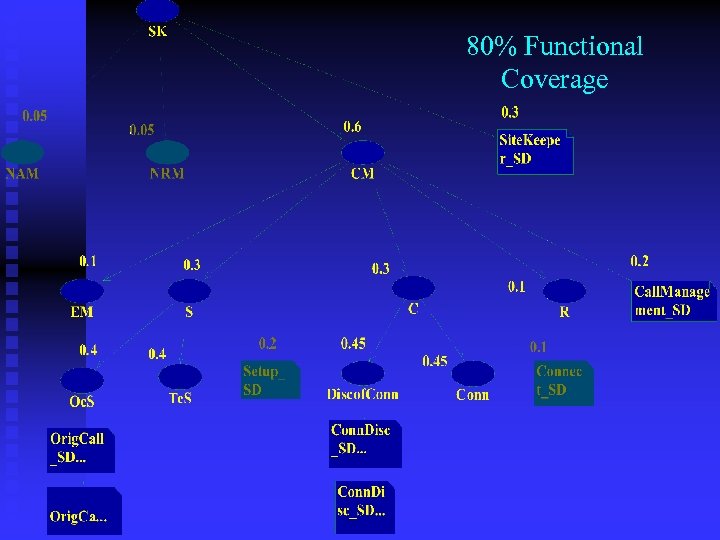 80% Functional Coverage
80% Functional Coverage
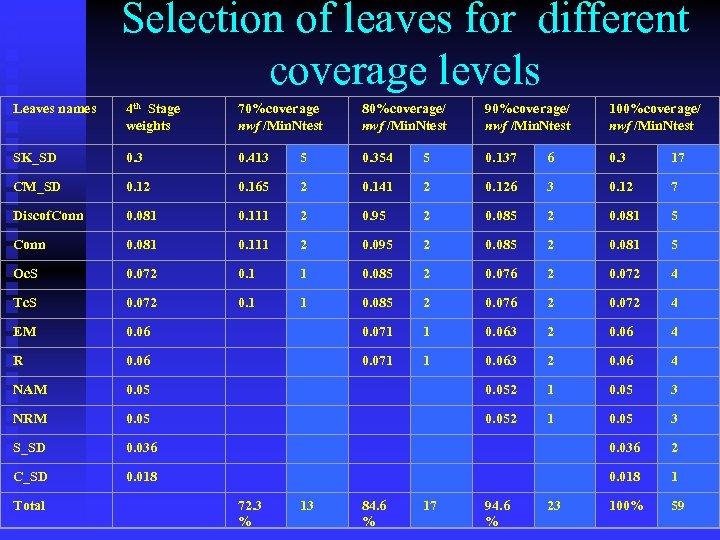 Selection of leaves for different coverage levels Leaves names 4 th Stage weights 70%coverage nwf /Min. Ntest 80%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest 90%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest 100%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest SK_SD 0. 3 0. 413 5 0. 354 5 0. 137 6 0. 3 17 CM_SD 0. 12 0. 165 2 0. 141 2 0. 126 3 0. 12 7 Discof. Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 95 2 0. 081 5 Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 095 2 0. 081 5 Oc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 0. 076 2 0. 072 4 Tc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 0. 076 2 0. 072 4 EM 0. 06 0. 071 1 0. 063 2 0. 06 4 R 0. 06 0. 071 1 0. 063 2 0. 06 4 NAM 0. 05 0. 052 1 0. 05 3 NRM 0. 05 0. 052 1 0. 05 3 S_SD 0. 036 0. 036 2 C_SD 0. 018 0. 018 1 Total 72. 3 % 13 84. 6 % 17 94. 6 % 23 100% 59
Selection of leaves for different coverage levels Leaves names 4 th Stage weights 70%coverage nwf /Min. Ntest 80%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest 90%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest 100%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest SK_SD 0. 3 0. 413 5 0. 354 5 0. 137 6 0. 3 17 CM_SD 0. 12 0. 165 2 0. 141 2 0. 126 3 0. 12 7 Discof. Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 95 2 0. 081 5 Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 095 2 0. 081 5 Oc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 0. 076 2 0. 072 4 Tc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 0. 076 2 0. 072 4 EM 0. 06 0. 071 1 0. 063 2 0. 06 4 R 0. 06 0. 071 1 0. 063 2 0. 06 4 NAM 0. 05 0. 052 1 0. 05 3 NRM 0. 05 0. 052 1 0. 05 3 S_SD 0. 036 0. 036 2 C_SD 0. 018 0. 018 1 Total 72. 3 % 13 84. 6 % 17 94. 6 % 23 100% 59
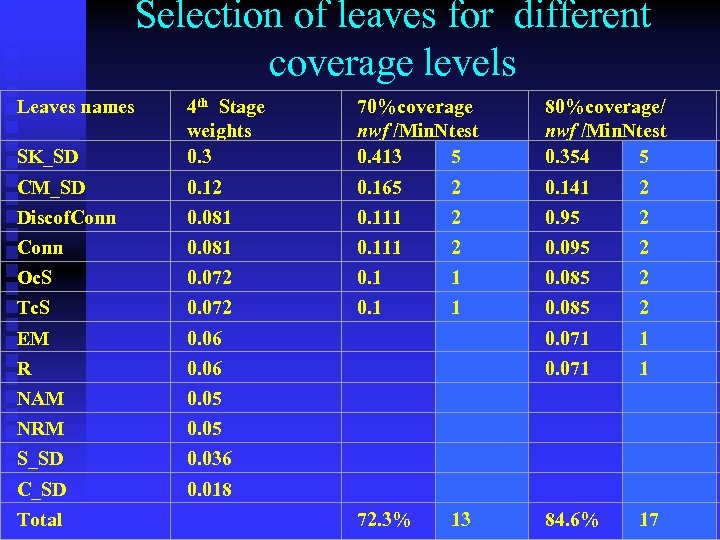 Selection of leaves for different coverage levels Leaves names SK_SD 4 th Stage weights 0. 3 70%coverage nwf /Min. Ntest 0. 413 5 80%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest 0. 354 5 CM_SD 0. 12 0. 165 2 0. 141 2 Discof. Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 95 2 Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 095 2 Oc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 Tc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 EM 0. 06 0. 071 1 R 0. 06 0. 071 1 NAM 0. 05 NRM 0. 05 S_SD 0. 036 C_SD 0. 018 Total 72. 3% 13 84. 6% 17
Selection of leaves for different coverage levels Leaves names SK_SD 4 th Stage weights 0. 3 70%coverage nwf /Min. Ntest 0. 413 5 80%coverage/ nwf /Min. Ntest 0. 354 5 CM_SD 0. 12 0. 165 2 0. 141 2 Discof. Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 95 2 Conn 0. 081 0. 111 2 0. 095 2 Oc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 Tc. S 0. 072 0. 1 1 0. 085 2 EM 0. 06 0. 071 1 R 0. 06 0. 071 1 NAM 0. 05 NRM 0. 05 S_SD 0. 036 C_SD 0. 018 Total 72. 3% 13 84. 6% 17
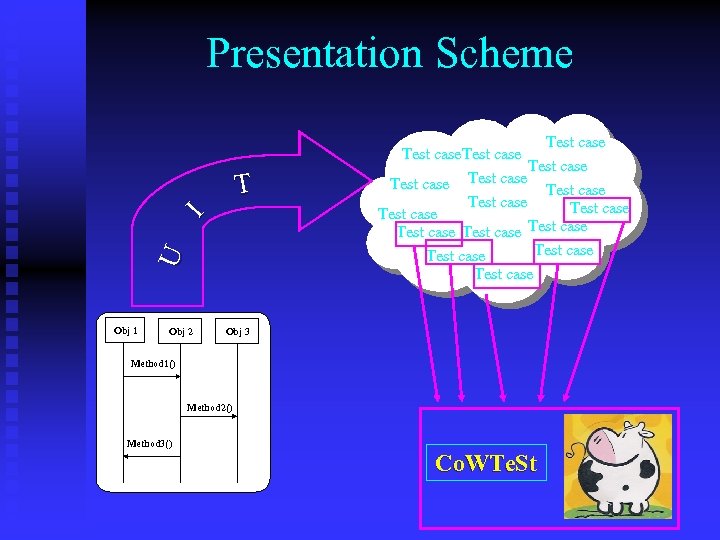 Presentation Scheme U I T Obj 1 Obj 2 Test case Test case Test case Test case Obj 3 Method 1() Method 2() Method 3() Co. WTe. St
Presentation Scheme U I T Obj 1 Obj 2 Test case Test case Test case Test case Obj 3 Method 1() Method 2() Method 3() Co. WTe. St
 Use Interaction Test methodology § § A method to systematically derive Integration Test suites from UML diagrams: • Use case diagrams • Sequence (Interaction) diagrams • Class diagrams Incremental test strategy (over the Use Case organizational structure) Seven steps involved
Use Interaction Test methodology § § A method to systematically derive Integration Test suites from UML diagrams: • Use case diagrams • Sequence (Interaction) diagrams • Class diagrams Incremental test strategy (over the Use Case organizational structure) Seven steps involved
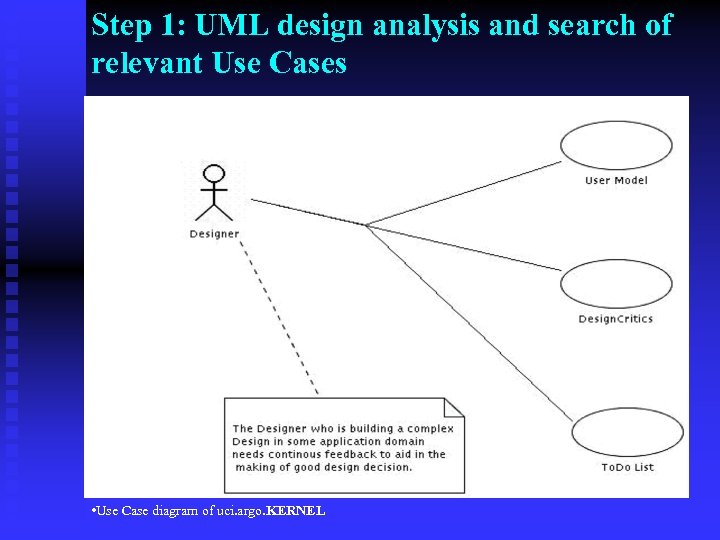 Step 1: UML design analysis and search of relevant Use Cases • Use Case diagram of uci. argo. KERNEL
Step 1: UML design analysis and search of relevant Use Cases • Use Case diagram of uci. argo. KERNEL
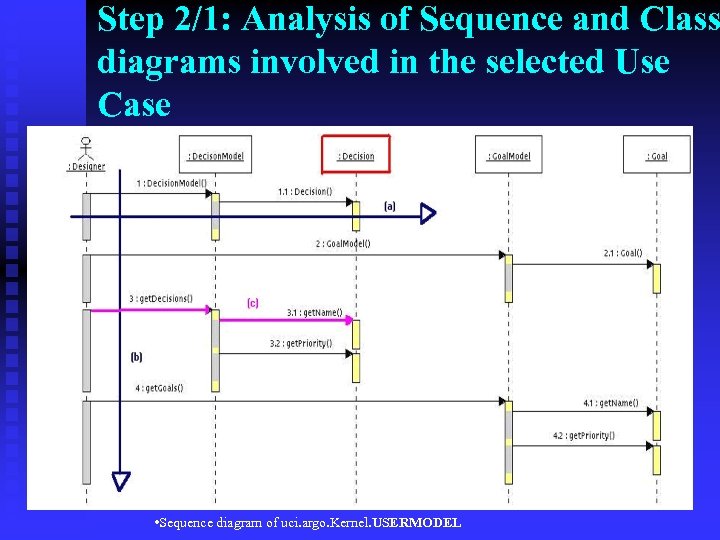 Step 2/1: Analysis of Sequence and Class diagrams involved in the selected Use Case • Sequence diagram of uci. argo. Kernel. USERMODEL
Step 2/1: Analysis of Sequence and Class diagrams involved in the selected Use Case • Sequence diagram of uci. argo. Kernel. USERMODEL
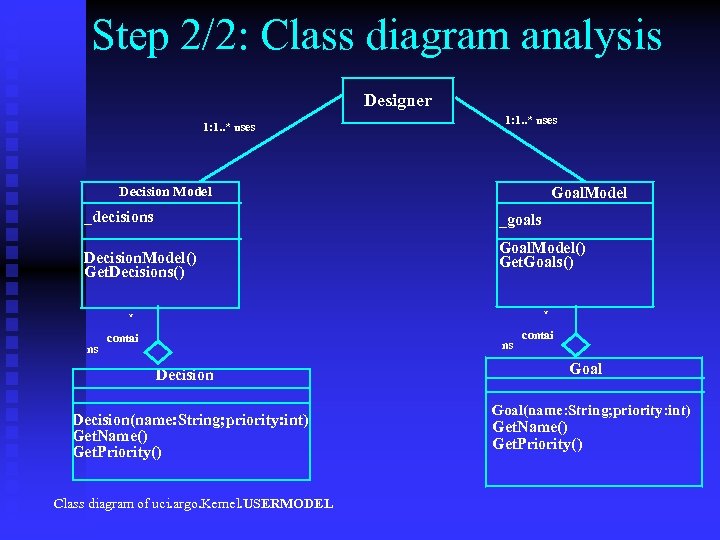 Step 2/2: Class diagram analysis Designer 1: 1. . * uses Goal. Model Decision Model _decisions _goals Decision. Model() Get. Decisions() Goal. Model() Get. Goals() * * ns contai ns Decision(name: String; priority: int) Get. Name() Get. Priority() Class diagram of uci. argo. Kernel. USERMODEL contai Goal(name: String; priority: int) Get. Name() Get. Priority()
Step 2/2: Class diagram analysis Designer 1: 1. . * uses Goal. Model Decision Model _decisions _goals Decision. Model() Get. Decisions() Goal. Model() Get. Goals() * * ns contai ns Decision(name: String; priority: int) Get. Name() Get. Priority() Class diagram of uci. argo. Kernel. USERMODEL contai Goal(name: String; priority: int) Get. Name() Get. Priority()
 Step 3 Test Units definition Test Units: those system units separately testable for exercising a possible use of system: Test Units: Decision. Model, Decision, Goal. Model, Goal.
Step 3 Test Units definition Test Units: those system units separately testable for exercising a possible use of system: Test Units: Decision. Model, Decision, Goal. Model, Goal.
 Step 4: Research of Settings and Interactions Categories - Settings. Categories: parameters and inputs relevant in the Test Unit. - Interactions. Categories: objects interactions, exchanged messages. Categories: Decision. Model Settings: _decisions Interactions: Decision. Model() get. Decisions() Decision Interactions: Decision(name: String, priority: int) Get. Name()
Step 4: Research of Settings and Interactions Categories - Settings. Categories: parameters and inputs relevant in the Test Unit. - Interactions. Categories: objects interactions, exchanged messages. Categories: Decision. Model Settings: _decisions Interactions: Decision. Model() get. Decisions() Decision Interactions: Decision(name: String, priority: int) Get. Name()
 Step 5: Test Specification construction n For each identified category, we consider all its possible values and constraints. Test Specification: Decision. Model: Settings: Interactions: _decisions get. Decisions() Naming Opening a new file Storage Opening a saved file Modularity After a modification and before saving Inheritance After a modification and after saving Stereotypes Decision. Model() Relationship. . Class constructor
Step 5: Test Specification construction n For each identified category, we consider all its possible values and constraints. Test Specification: Decision. Model: Settings: Interactions: _decisions get. Decisions() Naming Opening a new file Storage Opening a saved file Modularity After a modification and before saving Inheritance After a modification and after saving Stereotypes Decision. Model() Relationship. . Class constructor
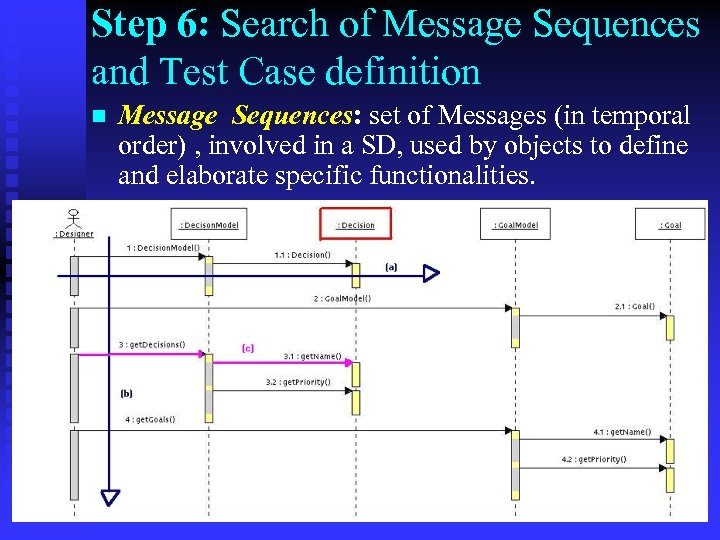 Step 6: Search of Message Sequences and Test Case definition n Message Sequences: set of Messages (in temporal order) , involved in a SD, used by objects to define and elaborate specific functionalities.
Step 6: Search of Message Sequences and Test Case definition n Message Sequences: set of Messages (in temporal order) , involved in a SD, used by objects to define and elaborate specific functionalities.
 Step 6: Search of Message Sequences and Test Case definition n Test Case: is constructed, from a Test Specification, for each possible combination of choices of every category involved in a Message Sequence Test Case get. Decisions() get. Name()/get. Priority() Opening a saved file _decisions Naming Note: Such a Test Case must be repeated for all possible values of _decisions
Step 6: Search of Message Sequences and Test Case definition n Test Case: is constructed, from a Test Specification, for each possible combination of choices of every category involved in a Message Sequence Test Case get. Decisions() get. Name()/get. Priority() Opening a saved file _decisions Naming Note: Such a Test Case must be repeated for all possible values of _decisions
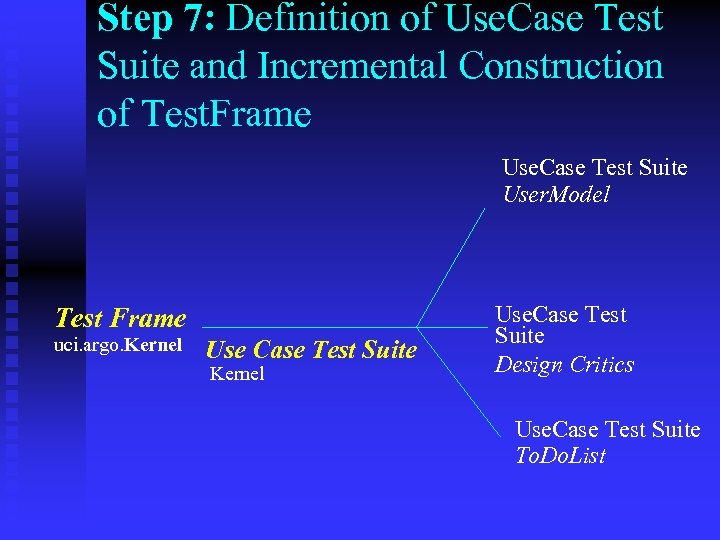 Step 7: Definition of Use. Case Test Suite and Incremental Construction of Test. Frame Use. Case Test Suite User. Model Test Frame uci. argo. Kernel Use Case Test Suite Kernel Use. Case Test Suite Design Critics Use. Case Test Suite To. Do. List
Step 7: Definition of Use. Case Test Suite and Incremental Construction of Test. Frame Use. Case Test Suite User. Model Test Frame uci. argo. Kernel Use Case Test Suite Kernel Use. Case Test Suite Design Critics Use. Case Test Suite To. Do. List
 Cow_Suite: Cow plu. S UIT Environment Tool for automating t Test cases derivation, from UIT t Test management strategy, from COWTe. ST n Uses UML diagrams already developed for the analysis and design phase no additional effort or information. n Rational Rose environment n
Cow_Suite: Cow plu. S UIT Environment Tool for automating t Test cases derivation, from UIT t Test management strategy, from COWTe. ST n Uses UML diagrams already developed for the analysis and design phase no additional effort or information. n Rational Rose environment n
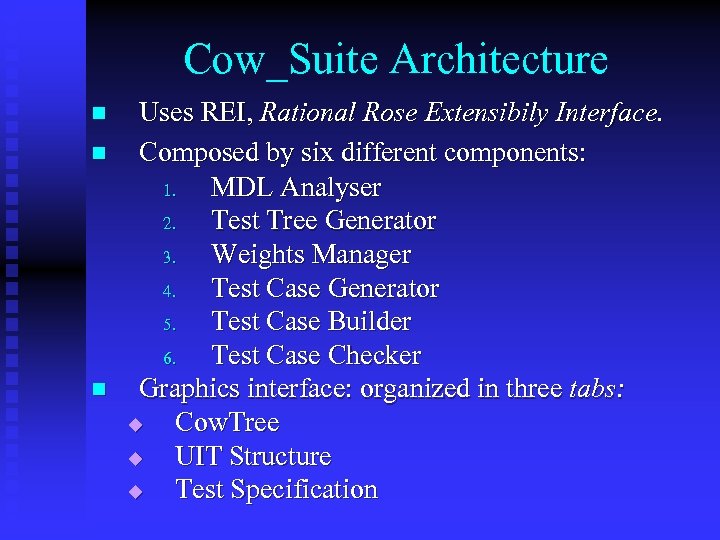 Cow_Suite Architecture n n n Uses REI, Rational Rose Extensibily Interface. Composed by six different components: 1. MDL Analyser 2. Test Tree Generator 3. Weights Manager 4. Test Case Generator 5. Test Case Builder 6. Test Case Checker Graphics interface: organized in three tabs: u Cow. Tree u UIT Structure u Test Specification
Cow_Suite Architecture n n n Uses REI, Rational Rose Extensibily Interface. Composed by six different components: 1. MDL Analyser 2. Test Tree Generator 3. Weights Manager 4. Test Case Generator 5. Test Case Builder 6. Test Case Checker Graphics interface: organized in three tabs: u Cow. Tree u UIT Structure u Test Specification
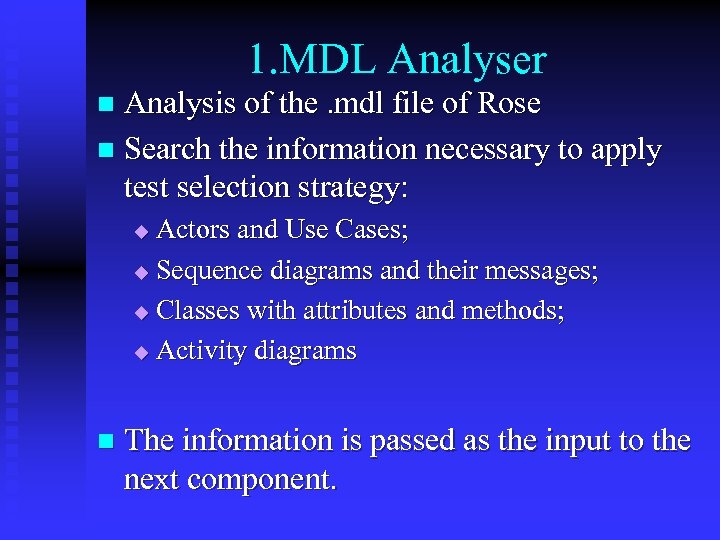 1. MDL Analyser Analysis of the. mdl file of Rose n Search the information necessary to apply test selection strategy: n Actors and Use Cases; u Sequence diagrams and their messages; u Classes with attributes and methods; u Activity diagrams u n The information is passed as the input to the next component.
1. MDL Analyser Analysis of the. mdl file of Rose n Search the information necessary to apply test selection strategy: n Actors and Use Cases; u Sequence diagrams and their messages; u Classes with attributes and methods; u Activity diagrams u n The information is passed as the input to the next component.
 2. Test Tree Generator n All the UCDs and SDs from. mdl file are organized in a hierarchical tree using the explicit diagrams links or using the UC associations and classes relations n To each node we associate: u Level identification number; u Default weight such that the sum of this weight plus the weights associated to all its brothers is equal to 1.
2. Test Tree Generator n All the UCDs and SDs from. mdl file are organized in a hierarchical tree using the explicit diagrams links or using the UC associations and classes relations n To each node we associate: u Level identification number; u Default weight such that the sum of this weight plus the weights associated to all its brothers is equal to 1.
 3. Weights Manager n Interacts with the user for: a) Assigning the real weight to each node: – – ü b) Selecting directly a node Selecting a level number Check that the sum of the user assigned weights of a level nodes is equal to 1. Choosing the criterion for test case selection: – – Fixing the maximum number of test cases to be executed Fixing the percentage of functionalities to be covered.
3. Weights Manager n Interacts with the user for: a) Assigning the real weight to each node: – – ü b) Selecting directly a node Selecting a level number Check that the sum of the user assigned weights of a level nodes is equal to 1. Choosing the criterion for test case selection: – – Fixing the maximum number of test cases to be executed Fixing the percentage of functionalities to be covered.
 4. Test Case Generator n n n queries the user for the deepest integration level he/she is interested in and calculate the final weight of every leaf. implements the UIT method for test generation associates to each SD its test cases organized in a hierarchical manner. calculates and visualizes the number of test cases for each SD depending on the chosen selection criterion. associates to each SD the frames of the test cases that should be instantiated.
4. Test Case Generator n n n queries the user for the deepest integration level he/she is interested in and calculate the final weight of every leaf. implements the UIT method for test generation associates to each SD its test cases organized in a hierarchical manner. calculates and visualizes the number of test cases for each SD depending on the chosen selection criterion. associates to each SD the frames of the test cases that should be instantiated.
 Test Case Frame TEST CASE 8. 2 Description: Pre. Condition: Test Case 7 Flow of event: get. Enterprise. For. Source. Address(caller) [else] routing. Result =do. LRQ(caller, callee, Enterprise, callcase, Access. Agent, BGAResult) Categories: Settings. Categories: PEnterprise = Callee = BGAResult …… Interactions. Categories: get. Enterprise. For. Source. Address = do. LRQ = Post. Condition: Comment:
Test Case Frame TEST CASE 8. 2 Description: Pre. Condition: Test Case 7 Flow of event: get. Enterprise. For. Source. Address(caller) [else] routing. Result =do. LRQ(caller, callee, Enterprise, callcase, Access. Agent, BGAResult) Categories: Settings. Categories: PEnterprise = Callee = BGAResult …… Interactions. Categories: get. Enterprise. For. Source. Address = do. LRQ = Post. Condition: Comment:
 5. Test Case Builder Interaction with the user for test case implementation: t For the necessary parameters; t Adding and removing categories; t Changing operations value or even test cases structure. n The changes involving the UML design are finally saved in a new file. n
5. Test Case Builder Interaction with the user for test case implementation: t For the necessary parameters; t Adding and removing categories; t Changing operations value or even test cases structure. n The changes involving the UML design are finally saved in a new file. n
 6. Test Case Checker n n The tool maintains information about the test cases generation. This module will realize the comparison of different versions of the same. mdl file. The discovered differences, like, for example, the existence of new test cases or changes in those already generated, are saved into a separate file. n The evaluation of the cost and impact required for the updates to the test plan with respect to the “official version” is derived analyzing this file.
6. Test Case Checker n n The tool maintains information about the test cases generation. This module will realize the comparison of different versions of the same. mdl file. The discovered differences, like, for example, the existence of new test cases or changes in those already generated, are saved into a separate file. n The evaluation of the cost and impact required for the updates to the test plan with respect to the “official version” is derived analyzing this file.
 References: F. Basanieri, A. Bertolino, “A Practical Approach to UML-based Derivation of Integration Tests”, QWE 2000, Bruxelles, 20 -24 November, 3 T. Basanieri, F. , Bertolino, A. , Marchetti, E. , “Co. WTe. St: A Cost Weighed Test Strategy”, accepted for: ESCOM-SCOPE 2001, London, England, 2 -4 April 2001. Basanieri, F. , Bertolino, A. , Marchetti, E. , Ribolini, A. , “An Automated Test Strategy Based on UML Diagrams” submitted to: ICSE 2001 WAPATV workshop.
References: F. Basanieri, A. Bertolino, “A Practical Approach to UML-based Derivation of Integration Tests”, QWE 2000, Bruxelles, 20 -24 November, 3 T. Basanieri, F. , Bertolino, A. , Marchetti, E. , “Co. WTe. St: A Cost Weighed Test Strategy”, accepted for: ESCOM-SCOPE 2001, London, England, 2 -4 April 2001. Basanieri, F. , Bertolino, A. , Marchetti, E. , Ribolini, A. , “An Automated Test Strategy Based on UML Diagrams” submitted to: ICSE 2001 WAPATV workshop.


