89b913fa09db90e2e312ba5f563f1276.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Co-ordinating careers work across a school or college Sue Barr Education for Employability Skills Show Seminar 20 th November 2015
Co-ordinating careers work across a school or college Sue Barr Education for Employability Skills Show Seminar 20 th November 2015
 Why is careers important for young people? • 30. 5 million 16 -64 year olds in work (May 2015) • young people’s unemployment is falling (currently 943, 000 which is 45, 000 less than same time last year) • BUT young people still three times as likely to be unemployed as adults • perception by employers that they are not such a ‘good bet’? (Office of National Statistics, May 2015) 2
Why is careers important for young people? • 30. 5 million 16 -64 year olds in work (May 2015) • young people’s unemployment is falling (currently 943, 000 which is 45, 000 less than same time last year) • BUT young people still three times as likely to be unemployed as adults • perception by employers that they are not such a ‘good bet’? (Office of National Statistics, May 2015) 2
 Why are employability skills important for young people? ‘As the world of work becomes more flexible, employees are expected to shoulder more of the responsibility for skills development. Selfmanagement alongside core business skills such as project management expertise and the ability to promote your personal brand will become increasingly vital. Personal agility and resilience, such as the ability to adapt to or embrace change is important, particularly for young people who will be competing for jobs with those who have been in work for longer. ’ 3
Why are employability skills important for young people? ‘As the world of work becomes more flexible, employees are expected to shoulder more of the responsibility for skills development. Selfmanagement alongside core business skills such as project management expertise and the ability to promote your personal brand will become increasingly vital. Personal agility and resilience, such as the ability to adapt to or embrace change is important, particularly for young people who will be competing for jobs with those who have been in work for longer. ’ 3
 4 CBI views ‘Our education system needs to deliver rigorous, rounded and grounded young people with some work experience under their belt who have a good idea about the career path they want to follow. ’ Future Possible: the business vision for giving young people the chance they deserve. CBI (2014)
4 CBI views ‘Our education system needs to deliver rigorous, rounded and grounded young people with some work experience under their belt who have a good idea about the career path they want to follow. ’ Future Possible: the business vision for giving young people the chance they deserve. CBI (2014)
 5 What’s hot and what’s not? Admin Assistant Digital Forensic Analyst Engineer Factory Assembler Fighter Pilot Home Healthcare Nurse Legal Professional Personal Trainer Physics Teacher Printer Recycling Officer Social Media Executive Social Worker Supermarket Checkout Operator Travel Information Adviser
5 What’s hot and what’s not? Admin Assistant Digital Forensic Analyst Engineer Factory Assembler Fighter Pilot Home Healthcare Nurse Legal Professional Personal Trainer Physics Teacher Printer Recycling Officer Social Media Executive Social Worker Supermarket Checkout Operator Travel Information Adviser
 6 Curriculum development • What are you trying to achieve? • How will you organise learning? • How will you know you are achieving your aims? Disciplined curriculum innovation: Qualifications and Curriculum Authority (QCA), 2008
6 Curriculum development • What are you trying to achieve? • How will you organise learning? • How will you know you are achieving your aims? Disciplined curriculum innovation: Qualifications and Curriculum Authority (QCA), 2008
 CDI Framework for careers, employability and enterprise 7 – 19 • Based on ACEG Framework, 2013 • 17 areas of learning for careers, employability and enterprise education • Revised November 2015 by CDI Co. ICE • Coherent with – Gatsby benchmarks for Good Careers Guidance – Careers and Enterprise Company – Quality in Careers Standard – Ofsted 7
CDI Framework for careers, employability and enterprise 7 – 19 • Based on ACEG Framework, 2013 • 17 areas of learning for careers, employability and enterprise education • Revised November 2015 by CDI Co. ICE • Coherent with – Gatsby benchmarks for Good Careers Guidance – Careers and Enterprise Company – Quality in Careers Standard – Ofsted 7
 8 Critical factors to develop careers programmes • leadership and management • curriculum and assessment • working with partners • monitoring and evaluation
8 Critical factors to develop careers programmes • leadership and management • curriculum and assessment • working with partners • monitoring and evaluation
 Your aims for students’ careers, employability and enterprise learning Skills Attitudes Knowle K dge Experiences 9
Your aims for students’ careers, employability and enterprise learning Skills Attitudes Knowle K dge Experiences 9
 10 Strategy – setting out your aims for students • work in groups of 2 -3 • use the Strategic Planning sheet • agree as a pair the attitudes, skills, knowledge and experiences students should have in relation to their careers, employability and enterprise learning • whole group feedback
10 Strategy – setting out your aims for students • work in groups of 2 -3 • use the Strategic Planning sheet • agree as a pair the attitudes, skills, knowledge and experiences students should have in relation to their careers, employability and enterprise learning • whole group feedback
 11 How will you organise learning? Once you are clear about your aims, how will you ensure you can achieve them? • where in the curriculum do students develop employability skills? • what approaches to learning will you need? • how will you build in assessment?
11 How will you organise learning? Once you are clear about your aims, how will you ensure you can achieve them? • where in the curriculum do students develop employability skills? • what approaches to learning will you need? • how will you build in assessment?
 12 Delivery models – key lessons • a mixed model is most effective – – integrated into all lessons some discrete lessons (eg. PSHEe) reflection in tutorial time enrichment activities for impact • structure and plan the programme against learning outcomes • incorporate ‘compelling’ learning approaches • make use of experts including external partners • plan assessment from beginning and monitor outcomes and impact
12 Delivery models – key lessons • a mixed model is most effective – – integrated into all lessons some discrete lessons (eg. PSHEe) reflection in tutorial time enrichment activities for impact • structure and plan the programme against learning outcomes • incorporate ‘compelling’ learning approaches • make use of experts including external partners • plan assessment from beginning and monitor outcomes and impact
 13 Who will you work with? • careers advisers • universities • FE colleges • employers • training providers
13 Who will you work with? • careers advisers • universities • FE colleges • employers • training providers
 14 Some currently funded programmes
14 Some currently funded programmes
 15 How will you know you’ve got there? • attitude questionnaires (young people, staff, parents, other partners) • young people’s focus group/discussion • destination data • attainment data • employers’ views of young people’s employability • observation during activities/lessons • assessing students’ work • previous Ofsted judgements
15 How will you know you’ve got there? • attitude questionnaires (young people, staff, parents, other partners) • young people’s focus group/discussion • destination data • attainment data • employers’ views of young people’s employability • observation during activities/lessons • assessing students’ work • previous Ofsted judgements
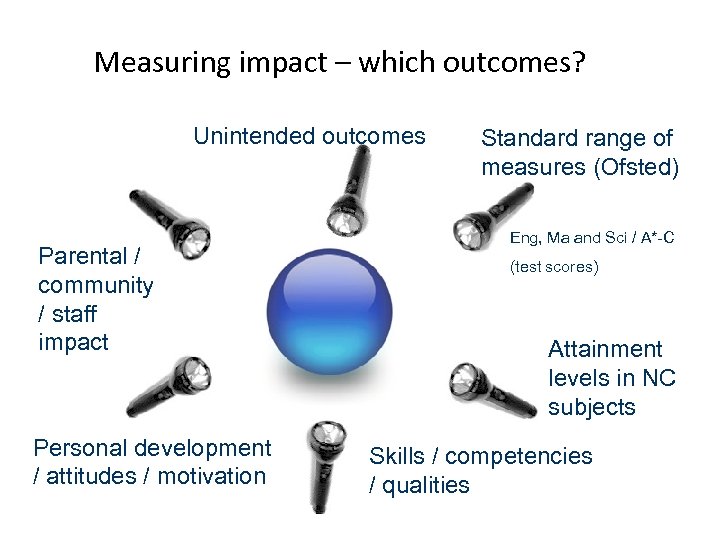 Measuring impact – which outcomes? Unintended outcomes Parental / community / staff impact Personal development / attitudes / motivation Standard range of measures (Ofsted) Eng, Ma and Sci / A*-C (test scores) Attainment levels in NC subjects Skills / competencies / qualities
Measuring impact – which outcomes? Unintended outcomes Parental / community / staff impact Personal development / attitudes / motivation Standard range of measures (Ofsted) Eng, Ma and Sci / A*-C (test scores) Attainment levels in NC subjects Skills / competencies / qualities
 17 For further details please contact Sue Barr sue@suebarr. co. uk www. educationforemployability. co. uk
17 For further details please contact Sue Barr sue@suebarr. co. uk www. educationforemployability. co. uk


