776d310e5a9df564df7568601491ad2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 CNS Infections 11 -23 -04 Chapter 235
CNS Infections 11 -23 -04 Chapter 235
 Bacterial Meningitis
Bacterial Meningitis
 Epidemiology 400 per 100, 000 in neonates n 1 -2 per 100, 000 in adults n S pneumoniae & N meningitidis m/c n n n HIB vaccine has been very effective Mortality 5% in children beyond infancy n 25% in neonates and in adults n
Epidemiology 400 per 100, 000 in neonates n 1 -2 per 100, 000 in adults n S pneumoniae & N meningitidis m/c n n n HIB vaccine has been very effective Mortality 5% in children beyond infancy n 25% in neonates and in adults n
 Pathophysiology S. pneumonia and N. meningitidis (and H. influenzae) are encapsulated which provides them with increased ability to invade BBB n Upper airway bloodstream subarachnoid space subcapsular constituents trigger inflammation fever, meningimus, change in MS brain/meningeal edema decreased CSF drainage hydrocephalus increased ICP>CPP n
Pathophysiology S. pneumonia and N. meningitidis (and H. influenzae) are encapsulated which provides them with increased ability to invade BBB n Upper airway bloodstream subarachnoid space subcapsular constituents trigger inflammation fever, meningimus, change in MS brain/meningeal edema decreased CSF drainage hydrocephalus increased ICP>CPP n
 Clinical Features n 25% of adult cases “classic” n Rapid development of n Fever n HA n Stiff neck n Photophobia n Change in MS Nonspecific signs/symptoms in very young/old n 25% will develop seizures n
Clinical Features n 25% of adult cases “classic” n Rapid development of n Fever n HA n Stiff neck n Photophobia n Change in MS Nonspecific signs/symptoms in very young/old n 25% will develop seizures n
 Clinical Features n History n Living conditions n College dorm/barracks N meningitidis n Trauma n Recent neurosurgery Staph/gram(-) rod Immunocompetence n Immunization hx n n None Hi. B n Antibiotic use
Clinical Features n History n Living conditions n College dorm/barracks N meningitidis n Trauma n Recent neurosurgery Staph/gram(-) rod Immunocompetence n Immunization hx n n None Hi. B n Antibiotic use
 Clinical Feratures n Physical Exam n Brudzinski n n Kernig n n Flex hip, ext knee hamstrings contract Skin n n Passive neck flex hips & knees flex Purpura Petechiae/splinter hem, pustular lesions microemboli Fundi Neuro Exam
Clinical Feratures n Physical Exam n Brudzinski n n Kernig n n Flex hip, ext knee hamstrings contract Skin n n Passive neck flex hips & knees flex Purpura Petechiae/splinter hem, pustular lesions microemboli Fundi Neuro Exam
 Diagnosis n Parenchymal n CT is the imaging of choice n Brain abscess, encephalitis, toxoplasmosis n Meningeal n Lumbar puncture n Neoplasm, CNS vasculitis, SAH
Diagnosis n Parenchymal n CT is the imaging of choice n Brain abscess, encephalitis, toxoplasmosis n Meningeal n Lumbar puncture n Neoplasm, CNS vasculitis, SAH
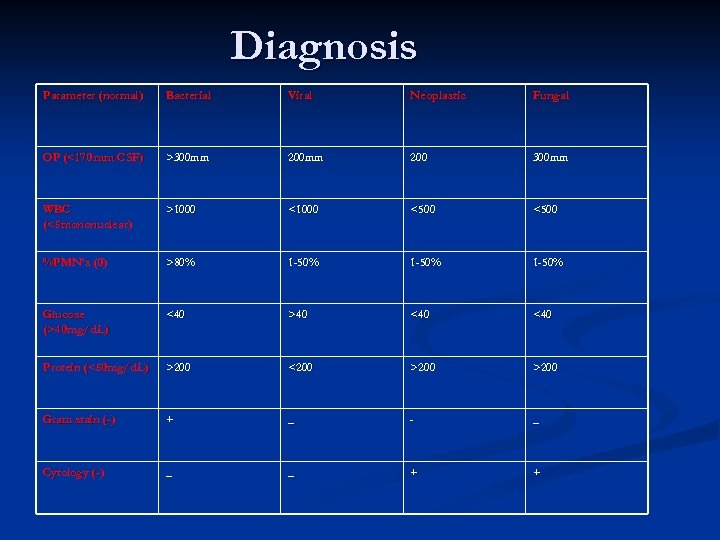 Diagnosis Parameter (normal) Bacterial Viral Neoplastic Fungal OP (<170 mm CSF) >300 mm 200 300 mm WBC (<5 mononuclear) >1000 <500 %PMN’s (0) >80% 1 -50% Glucose (>40 mg/d. L) <40 >40 <40 Protein (<50 mg/d. L) >200 <200 >200 Gram stain (-) + _ - _ Cytology (-) _ _ + +
Diagnosis Parameter (normal) Bacterial Viral Neoplastic Fungal OP (<170 mm CSF) >300 mm 200 300 mm WBC (<5 mononuclear) >1000 <500 %PMN’s (0) >80% 1 -50% Glucose (>40 mg/d. L) <40 >40 <40 Protein (<50 mg/d. L) >200 <200 >200 Gram stain (-) + _ - _ Cytology (-) _ _ + +
 Diagnosis n An aseptic profile n Must think about… n Partially treated bacterial infection n Bacterial infections adjacent to the subarachnoid space
Diagnosis n An aseptic profile n Must think about… n Partially treated bacterial infection n Bacterial infections adjacent to the subarachnoid space
 Diagnosis n Tests to order on the CSF n n Tube #1 cell count with diff Tube #2 protein, glucose Tube #4 cell count with diff, gram stain/culture Tube #3 n n n Viral cultures Borrelia (lyme disease) India ink/cryptococcal antigen (immunocomp) Acid fast stain/culture for mycobacteria (TB) Latex agglutination for bacterial Antigens PCR n Herpes, arbovirus
Diagnosis n Tests to order on the CSF n n Tube #1 cell count with diff Tube #2 protein, glucose Tube #4 cell count with diff, gram stain/culture Tube #3 n n n Viral cultures Borrelia (lyme disease) India ink/cryptococcal antigen (immunocomp) Acid fast stain/culture for mycobacteria (TB) Latex agglutination for bacterial Antigens PCR n Herpes, arbovirus
 Lumbar Puncture n Contraindications Infection in overlying skin n Relative n n Coagulopathy n Thrombocytopenia n If delay is anticipated obtain blood cultures and GIVE antibiotics n You have 2 hours after ATB given before sensitivity is effected
Lumbar Puncture n Contraindications Infection in overlying skin n Relative n n Coagulopathy n Thrombocytopenia n If delay is anticipated obtain blood cultures and GIVE antibiotics n You have 2 hours after ATB given before sensitivity is effected
 Lumbar Puncture n Considerations for not obtaining CT before performing LP Age <60 n Immunocompetent n No h/o CNS disease n No recent seizure (<1 week) n Normal sensorium & cognitition n No papilledema n No focal neuro deficits n
Lumbar Puncture n Considerations for not obtaining CT before performing LP Age <60 n Immunocompetent n No h/o CNS disease n No recent seizure (<1 week) n Normal sensorium & cognitition n No papilledema n No focal neuro deficits n
 Treatment n First priority n n Second priority in some cases n n Antibiotics Anti-inflammatories Third priority n Counter the adverse effects of increased ICP & vasculopathy
Treatment n First priority n n Second priority in some cases n n Antibiotics Anti-inflammatories Third priority n Counter the adverse effects of increased ICP & vasculopathy
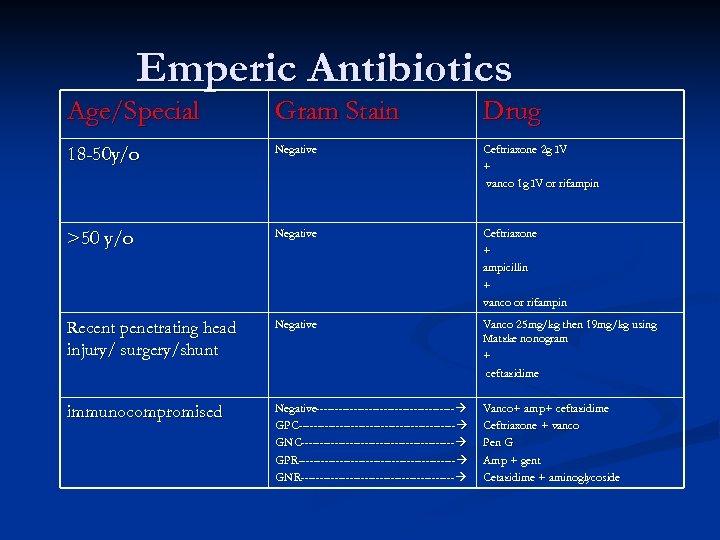 Emperic Antibiotics Age/Special Gram Stain Drug 18 -50 y/o Negative Ceftriaxone 2 g IV + vanco 1 g IV or rifampin >50 y/o Negative Ceftriaxone + ampicillin + vanco or rifampin Recent penetrating head injury/ surgery/shunt Negative Vanco 25 mg/kg then 19 mg/kg using Matzke nonogram + ceftazidime immunocompromised Negative------------------------------------- GPC------------------------------------------ GNC----------------------------------------- GPR------------------------------------------ GNR----------------------------------------- Vanco+ amp+ ceftazidime Vanco+ Ceftriaxone + vanco Pen G Amp + gent Cetazidime + aminoglycoside
Emperic Antibiotics Age/Special Gram Stain Drug 18 -50 y/o Negative Ceftriaxone 2 g IV + vanco 1 g IV or rifampin >50 y/o Negative Ceftriaxone + ampicillin + vanco or rifampin Recent penetrating head injury/ surgery/shunt Negative Vanco 25 mg/kg then 19 mg/kg using Matzke nonogram + ceftazidime immunocompromised Negative------------------------------------- GPC------------------------------------------ GNC----------------------------------------- GPR------------------------------------------ GNR----------------------------------------- Vanco+ amp+ ceftazidime Vanco+ Ceftriaxone + vanco Pen G Amp + gent Cetazidime + aminoglycoside
 Emperic Antivirals n Concern of herpes n Acyclovir 10 mg/kg IV Q 8 hours
Emperic Antivirals n Concern of herpes n Acyclovir 10 mg/kg IV Q 8 hours
 Steroids n Dexamethasone 10 mg IV 15 minutes prior to antibiotics n Shown to decrease M&M in S. pneumoniae but NOT N. meningitidis n n N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 1549 -1556, Nov 14, 2002.
Steroids n Dexamethasone 10 mg IV 15 minutes prior to antibiotics n Shown to decrease M&M in S. pneumoniae but NOT N. meningitidis n n N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 1549 -1556, Nov 14, 2002.
 Complications Seizures n Hyponatremia n SIADH n CVA n Coagulopathies n Cognitive deficits, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, hearing loss affect 25% of survivors n
Complications Seizures n Hyponatremia n SIADH n CVA n Coagulopathies n Cognitive deficits, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, hearing loss affect 25% of survivors n
 Chemoprophylaxis Household/school/daycare contacts last 7 days n Direct exposure to secretions n n Kissing, sharing utensils/toothbrushes, mouth to mouth, intubation without a mask First line: rifampin 10 mg/kg (max dose 600 mg) Q 12 h x 4 doses n Alternative: ceftriaxone, cipro, sulfisoxazole n
Chemoprophylaxis Household/school/daycare contacts last 7 days n Direct exposure to secretions n n Kissing, sharing utensils/toothbrushes, mouth to mouth, intubation without a mask First line: rifampin 10 mg/kg (max dose 600 mg) Q 12 h x 4 doses n Alternative: ceftriaxone, cipro, sulfisoxazole n
 Viral Meningitis
Viral Meningitis
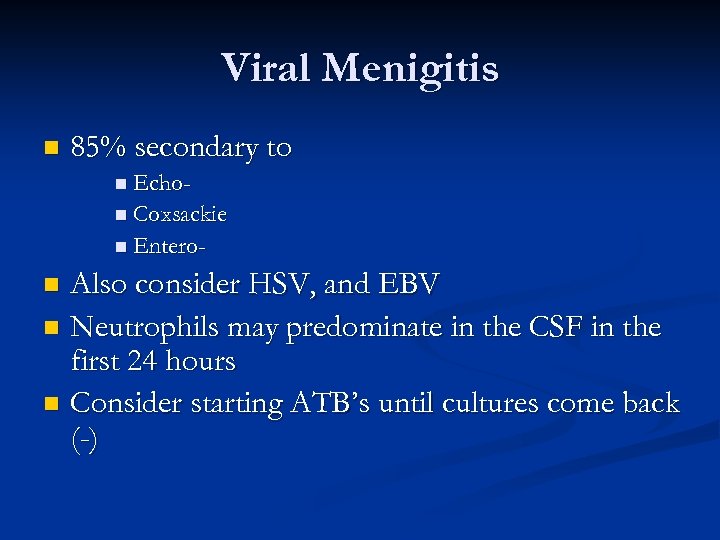 Viral Menigitis n 85% secondary to n Echon Coxsackie n Entero- Also consider HSV, and EBV n Neutrophils may predominate in the CSF in the first 24 hours n Consider starting ATB’s until cultures come back (-) n
Viral Menigitis n 85% secondary to n Echon Coxsackie n Entero- Also consider HSV, and EBV n Neutrophils may predominate in the CSF in the first 24 hours n Consider starting ATB’s until cultures come back (-) n
 Viral Encephalitis
Viral Encephalitis
 Viral Encephalitis Infection of brain parenchyma n Presents of neurological abnormalities distinguish it from meningitis n
Viral Encephalitis Infection of brain parenchyma n Presents of neurological abnormalities distinguish it from meningitis n
 Epidemiology Incidence is 1/10 of bacterial meningitis n HSV-1, zoster, EBV, CMV, rabies, arbo n n Arbo n LAC (La Crosse)-diagnosed most frequently n SEE(St Louis)-20% mortality in elderly n WEE(Western)- causes seizures in 90% of infected infants, permanent neuro deficits in 50% n EEE(Eastern)- most devastating, mortality 70% n WNV(West Nile)
Epidemiology Incidence is 1/10 of bacterial meningitis n HSV-1, zoster, EBV, CMV, rabies, arbo n n Arbo n LAC (La Crosse)-diagnosed most frequently n SEE(St Louis)-20% mortality in elderly n WEE(Western)- causes seizures in 90% of infected infants, permanent neuro deficits in 50% n EEE(Eastern)- most devastating, mortality 70% n WNV(West Nile)
 Pathophysiology n Portals of entry Arbo-transmitted by mosquitoes, ticks n Rabies-bite by infected animal n Hematogenous dissemination v. travel backwards on axons (HSV, HZV, rabies) n Dysfunction & damage caused by disruption of neural cell function & inflammation n
Pathophysiology n Portals of entry Arbo-transmitted by mosquitoes, ticks n Rabies-bite by infected animal n Hematogenous dissemination v. travel backwards on axons (HSV, HZV, rabies) n Dysfunction & damage caused by disruption of neural cell function & inflammation n
 Pathophysiology cont. n Gray matter predominately affected n n Cognitive/psychiatric signs, lethargy, seizures White matter affected in post-infectious encephalomyelitis
Pathophysiology cont. n Gray matter predominately affected n n Cognitive/psychiatric signs, lethargy, seizures White matter affected in post-infectious encephalomyelitis
 Clinical features New psych symptoms n Cognitive deficit (aphasia, amnesia, confusion) n Seizure n Movement d/o n
Clinical features New psych symptoms n Cognitive deficit (aphasia, amnesia, confusion) n Seizure n Movement d/o n
 Diagnosis MRI-more sensitive than CT n EEG n LP-findings consistent with aseptic meningitis n
Diagnosis MRI-more sensitive than CT n EEG n LP-findings consistent with aseptic meningitis n
 Differential n Exclude the killers n n More meningeal symptoms n n Bacterial meningitis & SAH Lyme, TB, fungal, bacterial, viral, neoplastic More parenchymal symptoms n Abscess, bacterial endocarditis, post-infectious encephalomyelitis, toxic or metabolic encephalopathy
Differential n Exclude the killers n n More meningeal symptoms n n Bacterial meningitis & SAH Lyme, TB, fungal, bacterial, viral, neoplastic More parenchymal symptoms n Abscess, bacterial endocarditis, post-infectious encephalomyelitis, toxic or metabolic encephalopathy
 Treatment HSV: acyclovir 10 mg/kg IV n CMV: ganciclovir n Rabies/EEE/HSV devastating & usually fatal or residual deficits n
Treatment HSV: acyclovir 10 mg/kg IV n CMV: ganciclovir n Rabies/EEE/HSV devastating & usually fatal or residual deficits n
 Brain Abscess
Brain Abscess
 Brain Abscess Focal pyogenic infection n Pus-filled cavity ringed by granulation tissue & outer fibrous capsule surrounded by edematous brain tissue n
Brain Abscess Focal pyogenic infection n Pus-filled cavity ringed by granulation tissue & outer fibrous capsule surrounded by edematous brain tissue n
 Epidemiology n Paranasal sinus focus n n 10 -30 y/o Otic n Bimodal: <20 y/o & >40 y/o
Epidemiology n Paranasal sinus focus n n 10 -30 y/o Otic n Bimodal: <20 y/o & >40 y/o
 Pathophysiology n Hematogenous spread n n 1/3 of cases Contiguous (middle ear, sinus, teeth) 1/3 of cases n Otogenic (Bacteroides) temporal lobe/cerebellum n Sinogenic & odontogenic(anaerobic & microaerophilic streptococci) frontal lobe n
Pathophysiology n Hematogenous spread n n 1/3 of cases Contiguous (middle ear, sinus, teeth) 1/3 of cases n Otogenic (Bacteroides) temporal lobe/cerebellum n Sinogenic & odontogenic(anaerobic & microaerophilic streptococci) frontal lobe n
 Clinical Features n Classic triad n HA, fever, focal deficit n <1/3 of cases Toxic appearance is rare n Seizures, vomiting, confusion, obtundation possible n Frontal lobe-hemiparesis n Temporal lobe- homonymous superior quadrant visual field deficit or aphasia n Cerebellum-limb incoordination or nystagmus n
Clinical Features n Classic triad n HA, fever, focal deficit n <1/3 of cases Toxic appearance is rare n Seizures, vomiting, confusion, obtundation possible n Frontal lobe-hemiparesis n Temporal lobe- homonymous superior quadrant visual field deficit or aphasia n Cerebellum-limb incoordination or nystagmus n
 Diagnosis CT with contrast n LP contraindicated n Biopsy or aspiration for confirmation n
Diagnosis CT with contrast n LP contraindicated n Biopsy or aspiration for confirmation n
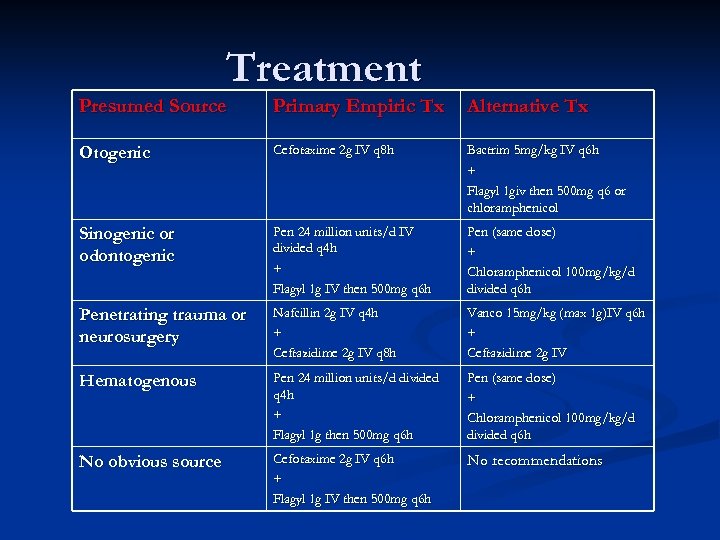 Treatment Presumed Source Primary Empiric Tx Alternative Tx Otogenic Cefotaxime 2 g IV q 8 h Bactrim 5 mg/kg IV q 6 h + Flagyl 1 giv then 500 mg q 6 or chloramphenicol Sinogenic or odontogenic Pen 24 million units/d IV divided q 4 h + Flagyl 1 g IV then 500 mg q 6 h Pen (same dose) + Chloramphenicol 100 mg/kg/d divided q 6 h Penetrating trauma or neurosurgery Nafcillin 2 g IV q 4 h + Ceftazidime 2 g IV q 8 h Vanco 15 mg/kg (max 1 g)IV q 6 h + Ceftazidime 2 g IV Hematogenous Pen 24 million units/d divided q 4 h + Flagyl 1 g then 500 mg q 6 h Pen (same dose) + Chloramphenicol 100 mg/kg/d divided q 6 h No obvious source Cefotaxime 2 g IV q 6 h + Flagyl 1 g IV then 500 mg q 6 h No recommendations
Treatment Presumed Source Primary Empiric Tx Alternative Tx Otogenic Cefotaxime 2 g IV q 8 h Bactrim 5 mg/kg IV q 6 h + Flagyl 1 giv then 500 mg q 6 or chloramphenicol Sinogenic or odontogenic Pen 24 million units/d IV divided q 4 h + Flagyl 1 g IV then 500 mg q 6 h Pen (same dose) + Chloramphenicol 100 mg/kg/d divided q 6 h Penetrating trauma or neurosurgery Nafcillin 2 g IV q 4 h + Ceftazidime 2 g IV q 8 h Vanco 15 mg/kg (max 1 g)IV q 6 h + Ceftazidime 2 g IV Hematogenous Pen 24 million units/d divided q 4 h + Flagyl 1 g then 500 mg q 6 h Pen (same dose) + Chloramphenicol 100 mg/kg/d divided q 6 h No obvious source Cefotaxime 2 g IV q 6 h + Flagyl 1 g IV then 500 mg q 6 h No recommendations
 Questions n 1. CSF analysis returns with the following values: glucose 20 WBC 1200 Protein 300. This profile is consistent with n n A. Bacterial meningitis B. viral meningitis C. Fungal meningitis 2. Which of the following is an absolute contraindication to performing an LP n n n A. B. C. Coagulopathy Infection of the overlying skin thrombocytopenia
Questions n 1. CSF analysis returns with the following values: glucose 20 WBC 1200 Protein 300. This profile is consistent with n n A. Bacterial meningitis B. viral meningitis C. Fungal meningitis 2. Which of the following is an absolute contraindication to performing an LP n n n A. B. C. Coagulopathy Infection of the overlying skin thrombocytopenia
 Questions n n n 3. T/F Steroids have been shown to decrease morbidity & mortality in meningitis caused by Strep pneumo 4. T/F Brain abscesses are confirmed by LP. 5. Which antibiotic regimen should be initiated in an immunocompromised patient suspected of having bacterial meningitis without any allergies n n A. B. C. Pen G Ceftriaxone & vanco Vanco, gent, & ceftazidime Answers: 1. A 2. B 3. T 4. F 5. C
Questions n n n 3. T/F Steroids have been shown to decrease morbidity & mortality in meningitis caused by Strep pneumo 4. T/F Brain abscesses are confirmed by LP. 5. Which antibiotic regimen should be initiated in an immunocompromised patient suspected of having bacterial meningitis without any allergies n n A. B. C. Pen G Ceftriaxone & vanco Vanco, gent, & ceftazidime Answers: 1. A 2. B 3. T 4. F 5. C


