caeb4c5f9972c07ad5e5e22a619a0f0a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 CMS HCAL Report US CMS HADRON CALORIMETER REPORT Andris Skuja University of Maryland US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review Brookhaven National Laboratory May 19, 2003 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 1
CMS HCAL Report US CMS HADRON CALORIMETER REPORT Andris Skuja University of Maryland US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review Brookhaven National Laboratory May 19, 2003 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 1
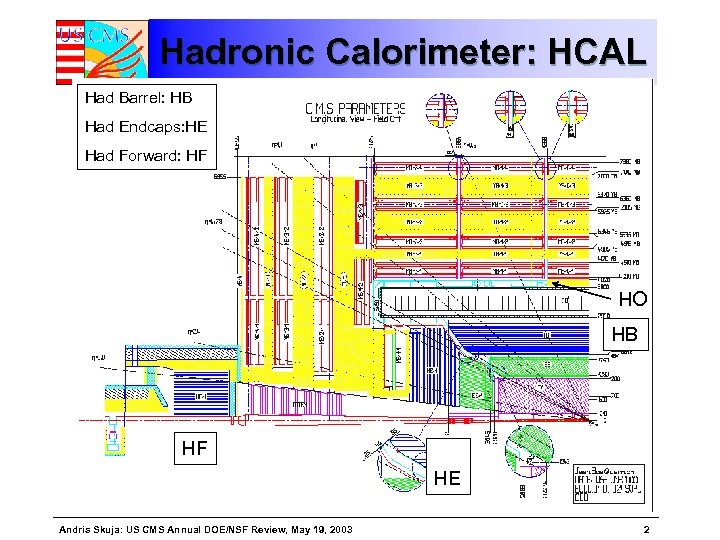 Hadronic Calorimeter: HCAL Had Barrel: HB Had Endcaps: HE Had Forward: HF HO HB HF HE Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 2
Hadronic Calorimeter: HCAL Had Barrel: HB Had Endcaps: HE Had Forward: HF HO HB HF HE Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 2
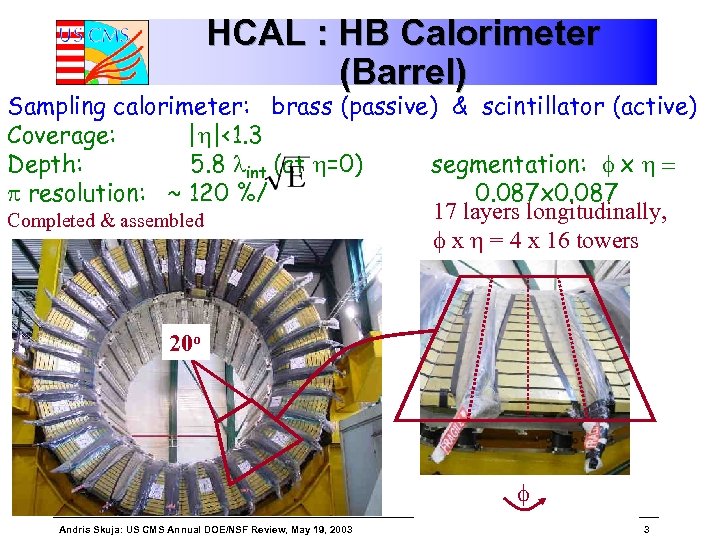 HCAL : HB Calorimeter (Barrel) Sampling calorimeter: brass (passive) & scintillator (active) Coverage: |h|<1. 3 Depth: 5. 8 lint (at h=0) segmentation: f x h = p resolution: ~ 120 %/ 0. 087 x 0. 087 17 layers longitudinally, Completed & assembled f x h = 4 x 16 towers 20 o f Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 3
HCAL : HB Calorimeter (Barrel) Sampling calorimeter: brass (passive) & scintillator (active) Coverage: |h|<1. 3 Depth: 5. 8 lint (at h=0) segmentation: f x h = p resolution: ~ 120 %/ 0. 087 x 0. 087 17 layers longitudinally, Completed & assembled f x h = 4 x 16 towers 20 o f Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 3
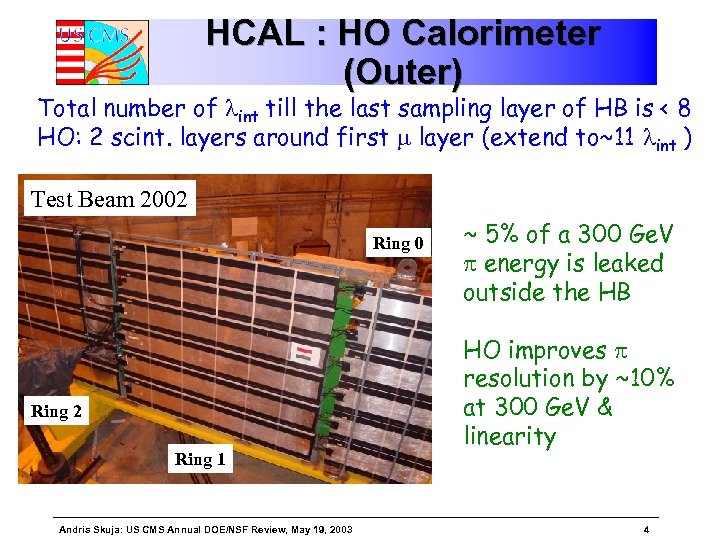 HCAL : HO Calorimeter (Outer) Total number of lint till the last sampling layer of HB is < 8 HO: 2 scint. layers around first m layer (extend to~11 lint ) Test Beam 2002 Ring 0 Ring 2 Ring 1 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 ~ 5% of a 300 Ge. V p energy is leaked outside the HB HO improves p resolution by ~10% at 300 Ge. V & linearity 4
HCAL : HO Calorimeter (Outer) Total number of lint till the last sampling layer of HB is < 8 HO: 2 scint. layers around first m layer (extend to~11 lint ) Test Beam 2002 Ring 0 Ring 2 Ring 1 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 ~ 5% of a 300 Ge. V p energy is leaked outside the HB HO improves p resolution by ~10% at 300 Ge. V & linearity 4
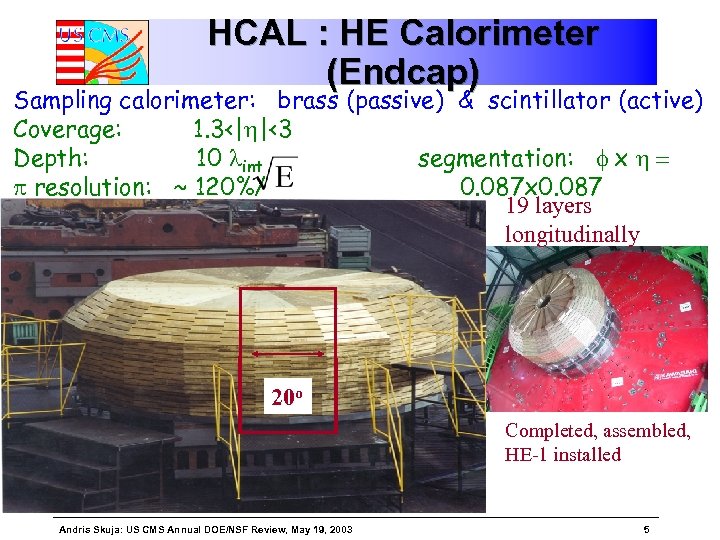 HCAL : HE Calorimeter (Endcap) Sampling calorimeter: brass (passive) & scintillator (active) Coverage: 1. 3<|h|<3 Depth: 10 lint segmentation: f x h = p resolution: ~ 120%/ 0. 087 x 0. 087 19 layers longitudinally 20 o Completed, assembled, HE-1 installed Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 5
HCAL : HE Calorimeter (Endcap) Sampling calorimeter: brass (passive) & scintillator (active) Coverage: 1. 3<|h|<3 Depth: 10 lint segmentation: f x h = p resolution: ~ 120%/ 0. 087 x 0. 087 19 layers longitudinally 20 o Completed, assembled, HE-1 installed Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 5
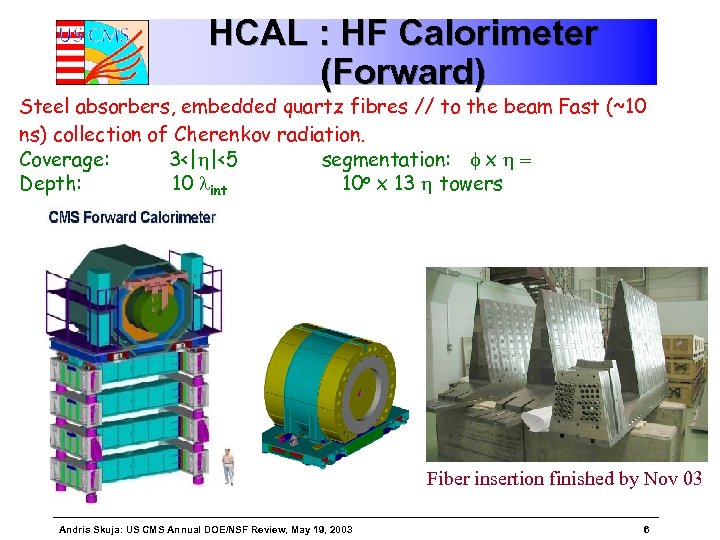 HCAL : HF Calorimeter (Forward) Steel absorbers, embedded quartz fibres // to the beam Fast (~10 ns) collection of Cherenkov radiation. Coverage: 3<|h|<5 segmentation: f x h = Depth: 10 lint 10 o x 13 h towers Fiber insertion finished by Nov 03 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 6
HCAL : HF Calorimeter (Forward) Steel absorbers, embedded quartz fibres // to the beam Fast (~10 ns) collection of Cherenkov radiation. Coverage: 3<|h|<5 segmentation: f x h = Depth: 10 lint 10 o x 13 h towers Fiber insertion finished by Nov 03 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 6
 HCAL : HE and HB HB complete, install onboard electronics by Q 2 -04 Back-flange 18 Brackets 3 Layers of absorber HE-1 re-installed on YE-1 in Jan/Feb 2003. Only 3 mm droop. Mount HE+1 by end of 2003, Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 7
HCAL : HE and HB HB complete, install onboard electronics by Q 2 -04 Back-flange 18 Brackets 3 Layers of absorber HE-1 re-installed on YE-1 in Jan/Feb 2003. Only 3 mm droop. Mount HE+1 by end of 2003, Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 7
 HB Both HCAL half-barrels are complete and in their alcove positions at the CMS hall. Starting in Autumn 03, electronics will be installed. After a burn-in period, vertical slice operations will begin and continue until the CMS magnet test in late 2005. Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 8
HB Both HCAL half-barrels are complete and in their alcove positions at the CMS hall. Starting in Autumn 03, electronics will be installed. After a burn-in period, vertical slice operations will begin and continue until the CMS magnet test in late 2005. Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 8
 Permanent H 2 Testbeam Facility Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 9
Permanent H 2 Testbeam Facility Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 9
 HCAL Completion and M&O • HCAL Deliverables are stand-alone working calorimeter modules (HB+, HB-, HE+, HE-, HF+, HF-, 5 units of HO) that are installed and cabled up, but not operating in an integrated manner. This will be done by early ’ 04. • Delivery includes HPD’s, Electronics (FE/TRIDAS) and Optical Links from Detectors to Underground Counting Room • Test beam calibration (’ 02, ‘ 03) is NOT M&O • Spares and components needed to keep HCAL operational are NOT M&O. • There is a vertical slice operations period before installation underground. This is a period of M&O • Test beam studies called for by operational experience IS M&O (’ 04 onward) • Technicians and engineers required to keep an operating sub-component of HCAL operating (independent of when) ARE M&O • Physics and simulation software development, calibration data base maintenance IS M&O Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 10
HCAL Completion and M&O • HCAL Deliverables are stand-alone working calorimeter modules (HB+, HB-, HE+, HE-, HF+, HF-, 5 units of HO) that are installed and cabled up, but not operating in an integrated manner. This will be done by early ’ 04. • Delivery includes HPD’s, Electronics (FE/TRIDAS) and Optical Links from Detectors to Underground Counting Room • Test beam calibration (’ 02, ‘ 03) is NOT M&O • Spares and components needed to keep HCAL operational are NOT M&O. • There is a vertical slice operations period before installation underground. This is a period of M&O • Test beam studies called for by operational experience IS M&O (’ 04 onward) • Technicians and engineers required to keep an operating sub-component of HCAL operating (independent of when) ARE M&O • Physics and simulation software development, calibration data base maintenance IS M&O Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 10
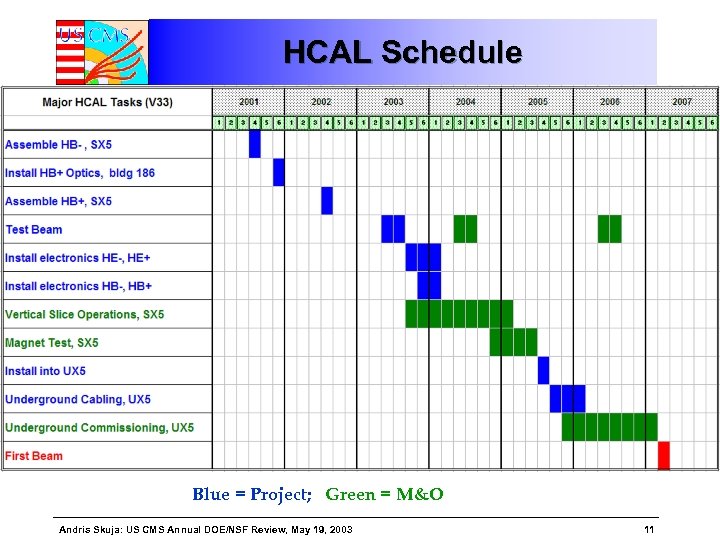 HCAL Schedule Blue = Project; Green = M&O Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 11
HCAL Schedule Blue = Project; Green = M&O Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 11
 RBX Status • Efforts in the previous calendar year have been dominated by preparations for test beam. • The RBX’s house RMs which contain photodetectors (HPD’s for HB and HE), the Front End electronics and Optical Links all in a single Unit. They also house LV/HV Units, Calibration Units and Control Modules. • The HB RBX’s are complete, except for • Need to complete cooling channels for full RM production (for 160 units) • Need CCM (40 units) • Need Calibration modules (40 units) • Need LV modules (40 units) • Services/integration items • The HE RBX’s are complete except for the items above • The HO RBX design is being finalized (including RM’s) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 12
RBX Status • Efforts in the previous calendar year have been dominated by preparations for test beam. • The RBX’s house RMs which contain photodetectors (HPD’s for HB and HE), the Front End electronics and Optical Links all in a single Unit. They also house LV/HV Units, Calibration Units and Control Modules. • The HB RBX’s are complete, except for • Need to complete cooling channels for full RM production (for 160 units) • Need CCM (40 units) • Need Calibration modules (40 units) • Need LV modules (40 units) • Services/integration items • The HE RBX’s are complete except for the items above • The HO RBX design is being finalized (including RM’s) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 12
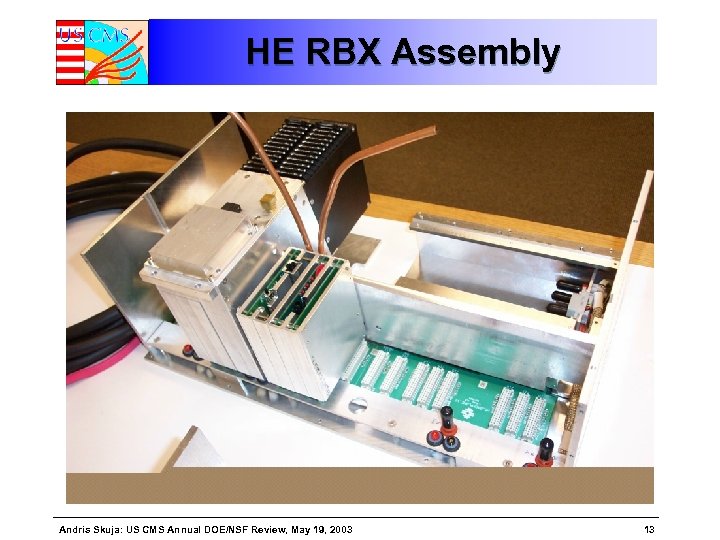 HE RBX Assembly Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 13
HE RBX Assembly Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 13
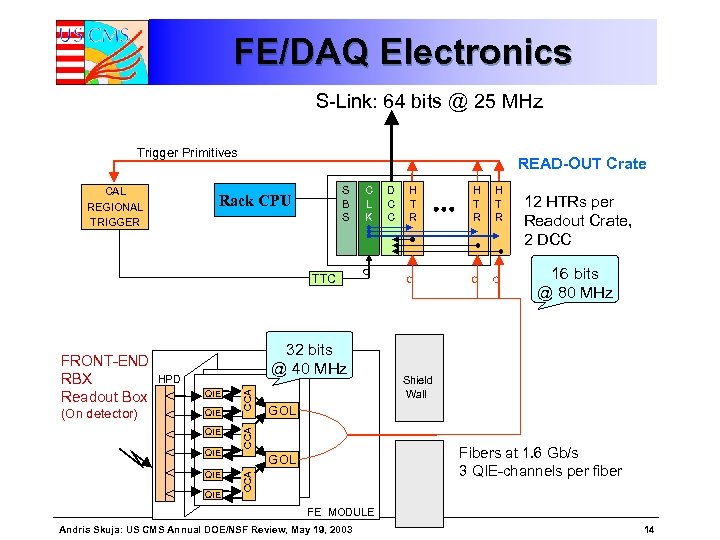 FE/DAQ Electronics S-Link: 64 bits @ 25 MHz Trigger Primitives CAL REGIONAL TRIGGER READ-OUT Crate S B S Rack CPU C L K D C C H T R QIE QIE QIE 12 HTRs per Readout Crate, 2 DCC Shield Wall GOL CCA QIE CCA HPD Fibers at 1. 6 Gb/s 3 QIE-channels per fiber GOL CCA (On detector) 32 bits @ 40 MHz H T R 16 bits @ 80 MHz TTC FRONT-END RBX Readout Box H T R FE MODULE Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 14
FE/DAQ Electronics S-Link: 64 bits @ 25 MHz Trigger Primitives CAL REGIONAL TRIGGER READ-OUT Crate S B S Rack CPU C L K D C C H T R QIE QIE QIE 12 HTRs per Readout Crate, 2 DCC Shield Wall GOL CCA QIE CCA HPD Fibers at 1. 6 Gb/s 3 QIE-channels per fiber GOL CCA (On detector) 32 bits @ 40 MHz H T R 16 bits @ 80 MHz TTC FRONT-END RBX Readout Box H T R FE MODULE Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 14
 HPD Acquisition & Testing R&D phase over except for Understanding a few odd-acting tubes: Continuing lifetime tests under several different HV conditions Understanding the test beam data from last summer Irradiation of selected tubes Status: • Of the 88 still in house, 32 are fully tested, but not yet graded • The 56 left are mostly tested. • We have accepted 92 and rejected 22 (which have been returned) • We have 22 in standby (small discrepancies or odd behavior) The best guess for yield is therefore 114/136 = 84%, since the standby category would have technically met our contractual specifications. • Out of 224 production tubes at UMN, 136 have been fully tested/graded Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 15
HPD Acquisition & Testing R&D phase over except for Understanding a few odd-acting tubes: Continuing lifetime tests under several different HV conditions Understanding the test beam data from last summer Irradiation of selected tubes Status: • Of the 88 still in house, 32 are fully tested, but not yet graded • The 56 left are mostly tested. • We have accepted 92 and rejected 22 (which have been returned) • We have 22 in standby (small discrepancies or odd behavior) The best guess for yield is therefore 114/136 = 84%, since the standby category would have technically met our contractual specifications. • Out of 224 production tubes at UMN, 136 have been fully tested/graded Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 15
 Front End Electronics Principal components: 1. QIE (charge integrator and encoder) Fermilab ASIC • Production wafers are in hand (QIEs meet specs) • Noise levels 3000 -4000 electrons rms 2. CCA (channel control ASIC) Fermilab ASIC. Packaged & tested Production chips are in hand 3. GOL (gigabit optical link) CERN ASIC • Proto GOL ASIC tested - ok • Gigabit Ethernet protocol at 1. 6 Gbits/s • 2 Engineering wafers back from Fab. – have been packaged and are being tested • Design work under way for GOL tester 4. L 4913 (rad hard voltage regulator) STC ASIC from CERN specifications 5. HFE 419 X-521 (connectorized VCSEL diode) Honeywell standard 2. 5 Gbit/sec device Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 16
Front End Electronics Principal components: 1. QIE (charge integrator and encoder) Fermilab ASIC • Production wafers are in hand (QIEs meet specs) • Noise levels 3000 -4000 electrons rms 2. CCA (channel control ASIC) Fermilab ASIC. Packaged & tested Production chips are in hand 3. GOL (gigabit optical link) CERN ASIC • Proto GOL ASIC tested - ok • Gigabit Ethernet protocol at 1. 6 Gbits/s • 2 Engineering wafers back from Fab. – have been packaged and are being tested • Design work under way for GOL tester 4. L 4913 (rad hard voltage regulator) STC ASIC from CERN specifications 5. HFE 419 X-521 (connectorized VCSEL diode) Honeywell standard 2. 5 Gbit/sec device Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 16
 (Pre-) Production FE Card Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 17
(Pre-) Production FE Card Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 17
 FE Status Summary 1. Steady Progress QIE development/bench studies – began 1999 2. Front-end electronics are on schedule Very little schedule float for GOL Infrastructure at SX 5 for burn-in and slice tests must be provided 200 Pre-prod cards have been built Feb/Mar’ 03 3. Ramping up the nested production, test and assembly lines for readout modules 4. Complete analysis of board level radiation testing 5. Full Production to start July/Aug. ‘ 03 6. Development of a low-noise cable and connector configuration for the HF photomultipliers Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 18
FE Status Summary 1. Steady Progress QIE development/bench studies – began 1999 2. Front-end electronics are on schedule Very little schedule float for GOL Infrastructure at SX 5 for burn-in and slice tests must be provided 200 Pre-prod cards have been built Feb/Mar’ 03 3. Ramping up the nested production, test and assembly lines for readout modules 4. Complete analysis of board level radiation testing 5. Full Production to start July/Aug. ‘ 03 6. Development of a low-noise cable and connector configuration for the HF photomultipliers Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 18
 HCAL TRIDAS/DAQ STATUS Collaboration of BU, Fermilab, Maryland Princeton • Consists of HTRs, DCCs, Clock, PC Interface Status of Principal Components • DCC: final boards are produced, firmware in progress • HTR: Test Beam prototypes are finished, Firmware in progress, checkout for production boards this summer. Final production anytime after that. • Clocking scheme is defined and prototypes done • PC interface is specified and well understood Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 19
HCAL TRIDAS/DAQ STATUS Collaboration of BU, Fermilab, Maryland Princeton • Consists of HTRs, DCCs, Clock, PC Interface Status of Principal Components • DCC: final boards are produced, firmware in progress • HTR: Test Beam prototypes are finished, Firmware in progress, checkout for production boards this summer. Final production anytime after that. • Clocking scheme is defined and prototypes done • PC interface is specified and well understood Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 19
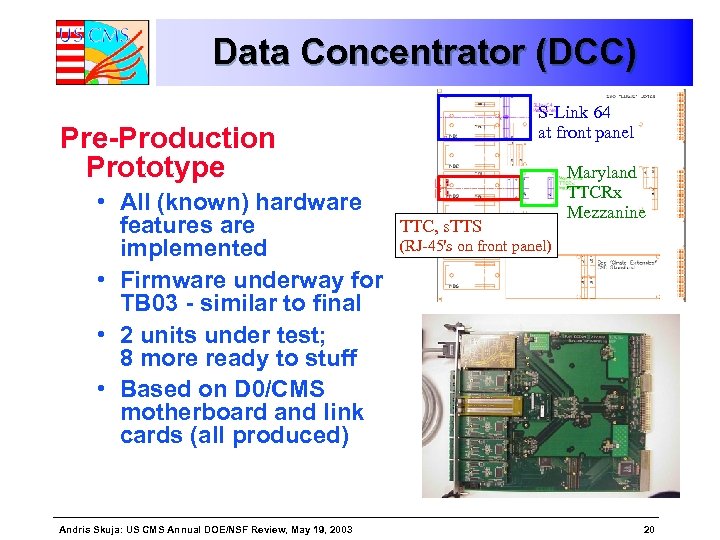 Data Concentrator (DCC) S-Link 64 at front panel Pre-Production Prototype • All (known) hardware features are implemented • Firmware underway for TB 03 - similar to final • 2 units under test; 8 more ready to stuff • Based on D 0/CMS motherboard and link cards (all produced) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 TTC, s. TTS Maryland TTCRx Mezzanine (RJ-45's on front panel) 20
Data Concentrator (DCC) S-Link 64 at front panel Pre-Production Prototype • All (known) hardware features are implemented • Firmware underway for TB 03 - similar to final • 2 units under test; 8 more ready to stuff • Based on D 0/CMS motherboard and link cards (all produced) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 TTC, s. TTS Maryland TTCRx Mezzanine (RJ-45's on front panel) 20
 HTR Rev 3 will be used in the 2003 testbeam 30 built, tested & shipped to CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 21
HTR Rev 3 will be used in the 2003 testbeam 30 built, tested & shipped to CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 21
 HCAL Calibration Goal: Calibrate from test beam to 3 Te. V. Time HCAL electronics. Monitor performance, including radiation damage. Tools: 1. Nitrogen laser distributed to each sub-detector. Excites scintillator 2. Laser injects light to photo-detectors. 3. LEDs (fast) inject light to photodetector. Programmable pulser. 4. Moving wire radioactive source for long term calibration. 5. Charge injection to ADC’s (QIE). Specialized calibration modules designed and built to achieve goals. Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 22
HCAL Calibration Goal: Calibrate from test beam to 3 Te. V. Time HCAL electronics. Monitor performance, including radiation damage. Tools: 1. Nitrogen laser distributed to each sub-detector. Excites scintillator 2. Laser injects light to photo-detectors. 3. LEDs (fast) inject light to photodetector. Programmable pulser. 4. Moving wire radioactive source for long term calibration. 5. Charge injection to ADC’s (QIE). Specialized calibration modules designed and built to achieve goals. Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 22
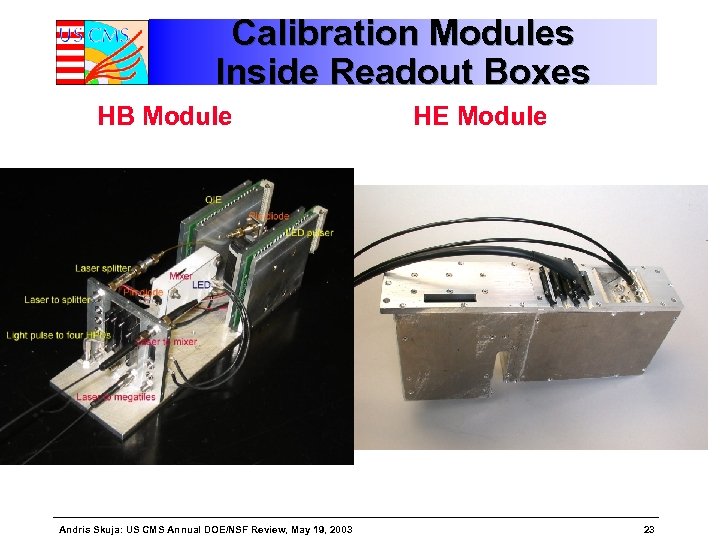 Calibration Modules Inside Readout Boxes HB Module Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 HE Module 23
Calibration Modules Inside Readout Boxes HB Module Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 HE Module 23
 HCAL DCS Status DCS is the Detector Control System. It monitors the Detector and performs what used to be called “Slow controls” The low level servers of HCAL control subsystems are almost ready. All defined server prototypes tested during beam-test in June-September of 2002. Bugs found and fixed. HCAL is in the vanguard of DCS on CMS Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 24
HCAL DCS Status DCS is the Detector Control System. It monitors the Detector and performs what used to be called “Slow controls” The low level servers of HCAL control subsystems are almost ready. All defined server prototypes tested during beam-test in June-September of 2002. Bugs found and fixed. HCAL is in the vanguard of DCS on CMS Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 24
 HF status The HF is a diversified project consisting of contributions from many nations as well as CERN. All detector mechanical components (wedges, strongbacks, backplanes) have been delivered ahead of schedule and are at CERN. Production of HF tables is well advanced: for the first one, the welding and thermal treatment is done and is being machined now, for the second, the welding is complete. Production of the support outer shield has started for the first HF. Contracts for machining placed. Expect delivery of first table+shields at end of September 03. Second set by spring 2004. All PMTs have been delivered to IOWA and testing is >90% complete 85% of quartz fibers have been delivered to CERN and are being cleaved and bundled in Hungary 21/36 wedges will be completed in May ‘ 03 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 25
HF status The HF is a diversified project consisting of contributions from many nations as well as CERN. All detector mechanical components (wedges, strongbacks, backplanes) have been delivered ahead of schedule and are at CERN. Production of HF tables is well advanced: for the first one, the welding and thermal treatment is done and is being machined now, for the second, the welding is complete. Production of the support outer shield has started for the first HF. Contracts for machining placed. Expect delivery of first table+shields at end of September 03. Second set by spring 2004. All PMTs have been delivered to IOWA and testing is >90% complete 85% of quartz fibers have been delivered to CERN and are being cleaved and bundled in Hungary 21/36 wedges will be completed in May ‘ 03 Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 25
 Fiber stuffing at CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 26
Fiber stuffing at CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 26
 HCAL M&O There was a Lehman review at FNAL on April 8, 9 & 10. The M&O proposal for CMS was baselined (budget approved). • Engineering personnel and techs at CERN for detector maintenance (shared with EMU) • “Slice Test” as pre-ops during 2004 -2006 • Test Beam work beginning in 2004 • Physics monitoring at CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 27
HCAL M&O There was a Lehman review at FNAL on April 8, 9 & 10. The M&O proposal for CMS was baselined (budget approved). • Engineering personnel and techs at CERN for detector maintenance (shared with EMU) • “Slice Test” as pre-ops during 2004 -2006 • Test Beam work beginning in 2004 • Physics monitoring at CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 27
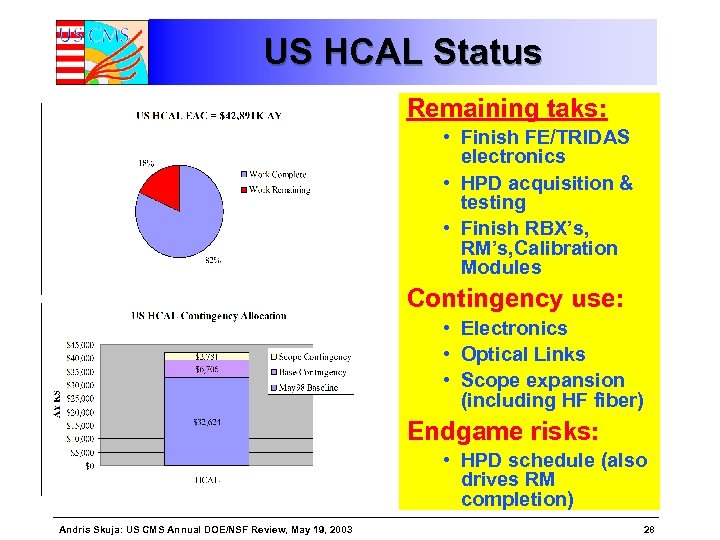 US HCAL Status Remaining taks: • Finish FE/TRIDAS electronics • HPD acquisition & testing • Finish RBX’s, RM’s, Calibration Modules Contingency use: • Electronics • Optical Links • Scope expansion (including HF fiber) Endgame risks: • HPD schedule (also drives RM completion) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 28
US HCAL Status Remaining taks: • Finish FE/TRIDAS electronics • HPD acquisition & testing • Finish RBX’s, RM’s, Calibration Modules Contingency use: • Electronics • Optical Links • Scope expansion (including HF fiber) Endgame risks: • HPD schedule (also drives RM completion) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 28
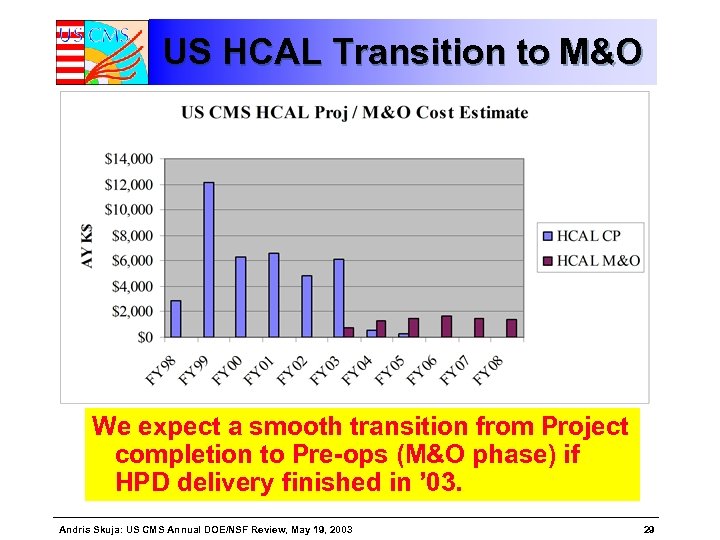 US HCAL Transition to M&O We expect a smooth transition from Project completion to Pre-ops (M&O phase) if HPD delivery finished in ’ 03. Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 29
US HCAL Transition to M&O We expect a smooth transition from Project completion to Pre-ops (M&O phase) if HPD delivery finished in ’ 03. Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 29
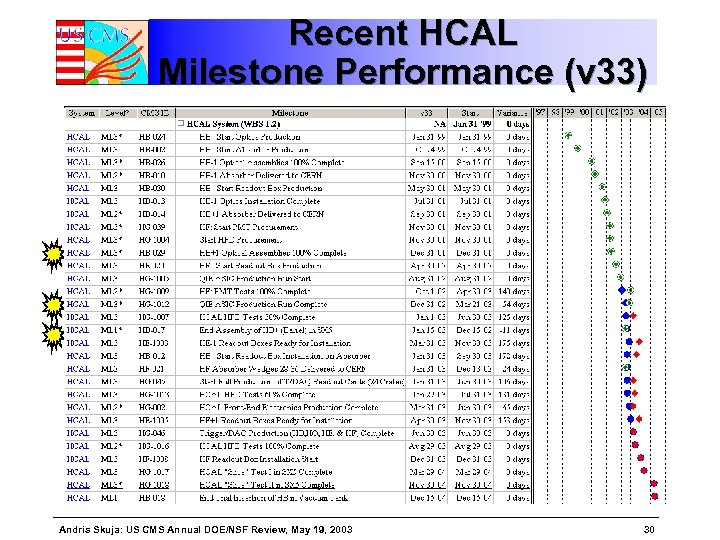 Recent HCAL Milestone Performance (v 33) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 30
Recent HCAL Milestone Performance (v 33) Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 30
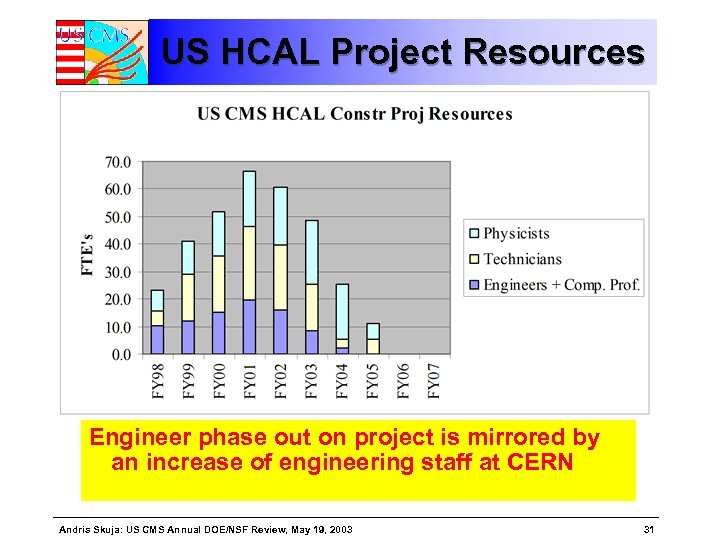 US HCAL Project Resources Engineer phase out on project is mirrored by an increase of engineering staff at CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 31
US HCAL Project Resources Engineer phase out on project is mirrored by an increase of engineering staff at CERN Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 31
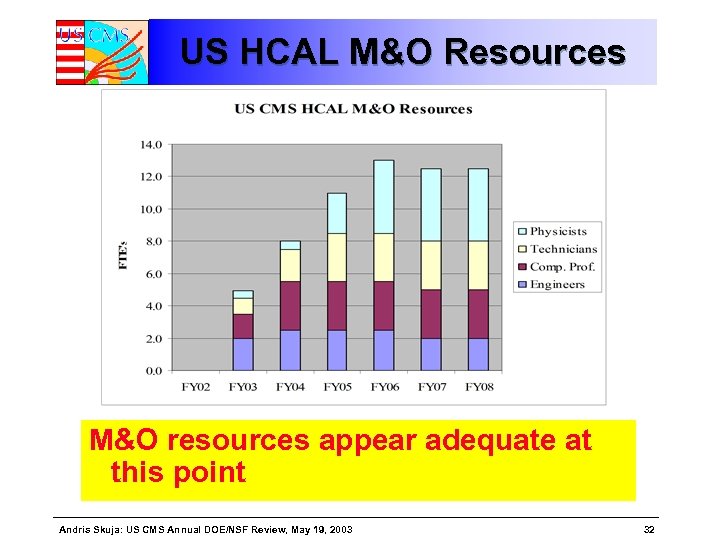 US HCAL M&O Resources M&O resources appear adequate at this point Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 32
US HCAL M&O Resources M&O resources appear adequate at this point Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 32
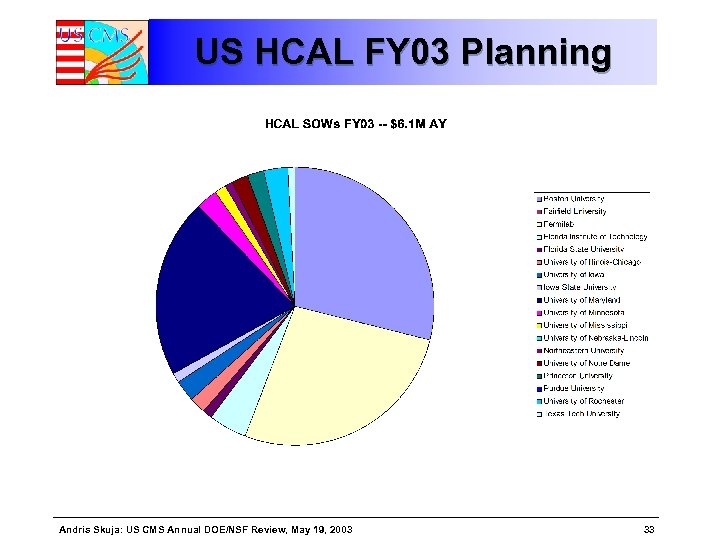 US HCAL FY 03 Planning Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 33
US HCAL FY 03 Planning Andris Skuja: US CMS Annual DOE/NSF Review, May 19, 2003 33


