a85fde7f1915ff54c44bcd04cb501772.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 6
 CMS 1. Goal of the experiment CMS is a general purpose apparatus for LHC designed to study the physics of p-p collisions at the center-ofmass energy of 14 Te. V. The main goal of the experiment is the search for the Higgs boson and for the supersymmetric partners of known particles. The scientific program includes also detailed studies of the top quark and precision measurements of CP violation parameters in the b-system. The physics of heavy ion collisions, and, in particular, the clear identification of a new state of matter as the quark-gluon plasma will also be addressed. 2. Physics achievements in 2002 The experiment is still in construction, therefore no physics result has been achieved in 2002. Important results have been obtained from the R&D activity carried on for all sub-detectors including computing. The main goal of this phase of the experiment is a successful commissioning of the main detector components. 3. INFN contribution to the experiment in terms of manpower and financial support INFN researchers are involved in the following sub-detectors: Solenoidal Magnet, Tracker, Electromagnetic Calorimeter, Muon System and Computing. The total number of physicists and engineers working in CMS in 2002 is 252. They come from 13 INFN Laboratories and account for about 16% of the total number of CMS collaborators. Technicians are not included in these figures. The INFN financial support to CMS deliverables amounts to about 63. 9 MCHF over an estimated total cost of the experiment around 500 MCHF. The overall INFN financial support to CMS for the year 2002 is 8141 KEuro, including travel expenses and consumables.
CMS 1. Goal of the experiment CMS is a general purpose apparatus for LHC designed to study the physics of p-p collisions at the center-ofmass energy of 14 Te. V. The main goal of the experiment is the search for the Higgs boson and for the supersymmetric partners of known particles. The scientific program includes also detailed studies of the top quark and precision measurements of CP violation parameters in the b-system. The physics of heavy ion collisions, and, in particular, the clear identification of a new state of matter as the quark-gluon plasma will also be addressed. 2. Physics achievements in 2002 The experiment is still in construction, therefore no physics result has been achieved in 2002. Important results have been obtained from the R&D activity carried on for all sub-detectors including computing. The main goal of this phase of the experiment is a successful commissioning of the main detector components. 3. INFN contribution to the experiment in terms of manpower and financial support INFN researchers are involved in the following sub-detectors: Solenoidal Magnet, Tracker, Electromagnetic Calorimeter, Muon System and Computing. The total number of physicists and engineers working in CMS in 2002 is 252. They come from 13 INFN Laboratories and account for about 16% of the total number of CMS collaborators. Technicians are not included in these figures. The INFN financial support to CMS deliverables amounts to about 63. 9 MCHF over an estimated total cost of the experiment around 500 MCHF. The overall INFN financial support to CMS for the year 2002 is 8141 KEuro, including travel expenses and consumables.
 4. Number of publications in refereed journals ~ 40 5. Number of talks at conferences (from INFN) ~ 20 6. Number of undergraduate and doctoral theses on the experiment 15 undergraduate and 8 doctoral theses 7. Leadership role in the experiment - Lorenzo Foa‘ : - Rino Castaldi: - Fabrizio Gasparini: - Cristiana Peroni: - Guido Tonelli: 8. Chairman of the Collaboration Board Deputy Project Leader (Tracker) Project Leader (Muon) Finance Board Management Board and Finance Board Innovative instruments 4 T magnet; large area RPC’s; radiation-hard silicon detectors and read-out electronics; analog optical links; new crystals and APDs; new approach on trigger, data handling and computing. 9. Competing experiments ATLAS for the entire physics program. CDF and LHC-B for part of the program; ALICE for Heavy Ions physics. 10. International committees which have reviewed the experiment The most important one is the LHC Committee at CERN that monitors continuosly the progress of activities.
4. Number of publications in refereed journals ~ 40 5. Number of talks at conferences (from INFN) ~ 20 6. Number of undergraduate and doctoral theses on the experiment 15 undergraduate and 8 doctoral theses 7. Leadership role in the experiment - Lorenzo Foa‘ : - Rino Castaldi: - Fabrizio Gasparini: - Cristiana Peroni: - Guido Tonelli: 8. Chairman of the Collaboration Board Deputy Project Leader (Tracker) Project Leader (Muon) Finance Board Management Board and Finance Board Innovative instruments 4 T magnet; large area RPC’s; radiation-hard silicon detectors and read-out electronics; analog optical links; new crystals and APDs; new approach on trigger, data handling and computing. 9. Competing experiments ATLAS for the entire physics program. CDF and LHC-B for part of the program; ALICE for Heavy Ions physics. 10. International committees which have reviewed the experiment The most important one is the LHC Committee at CERN that monitors continuosly the progress of activities.
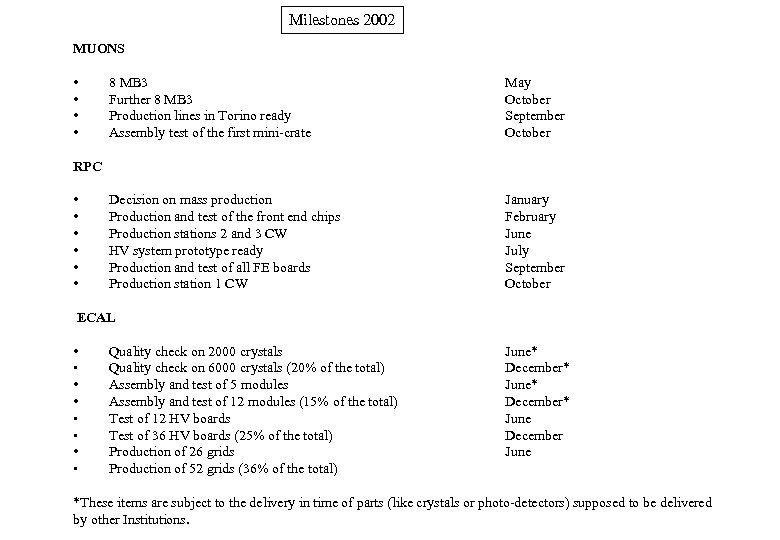 Milestones 2002 MUONS • • 8 MB 3 Further 8 MB 3 Production lines in Torino ready Assembly test of the first mini-crate May October September October Decision on mass production Production and test of the front end chips Production stations 2 and 3 CW HV system prototype ready Production and test of all FE boards Production station 1 CW January February June July September October RPC • • • ECAL • • Quality check on 2000 crystals Quality check on 6000 crystals (20% of the total) Assembly and test of 5 modules Assembly and test of 12 modules (15% of the total) Test of 12 HV boards Test of 36 HV boards (25% of the total) Production of 26 grids Production of 52 grids (36% of the total) June* December* June December June *These items are subject to the delivery in time of parts (like crystals or photo-detectors) supposed to be delivered by other Institutions.
Milestones 2002 MUONS • • 8 MB 3 Further 8 MB 3 Production lines in Torino ready Assembly test of the first mini-crate May October September October Decision on mass production Production and test of the front end chips Production stations 2 and 3 CW HV system prototype ready Production and test of all FE boards Production station 1 CW January February June July September October RPC • • • ECAL • • Quality check on 2000 crystals Quality check on 6000 crystals (20% of the total) Assembly and test of 5 modules Assembly and test of 12 modules (15% of the total) Test of 12 HV boards Test of 36 HV boards (25% of the total) Production of 26 grids Production of 52 grids (36% of the total) June* December* June December June *These items are subject to the delivery in time of parts (like crystals or photo-detectors) supposed to be delivered by other Institutions.
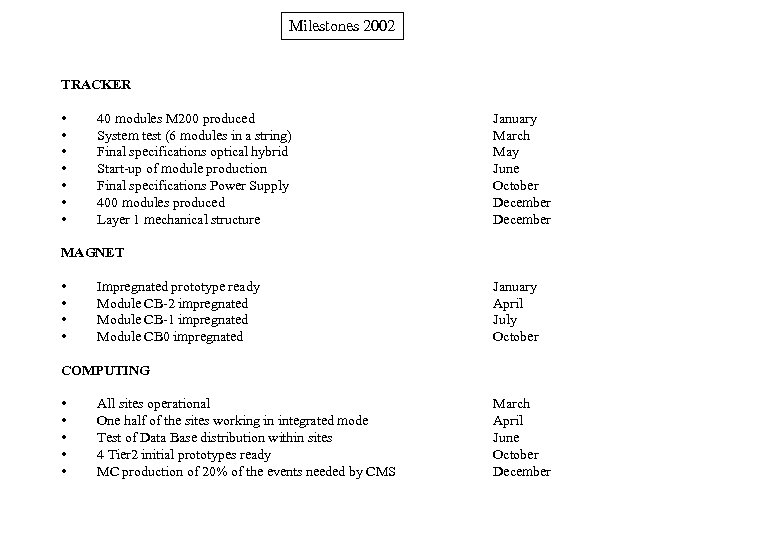 Milestones 2002 TRACKER • • 40 modules M 200 produced System test (6 modules in a string) Final specifications optical hybrid Start-up of module production Final specifications Power Supply 400 modules produced Layer 1 mechanical structure January March May June October December MAGNET • • Impregnated prototype ready Module CB-2 impregnated Module CB-1 impregnated Module CB 0 impregnated January April July October COMPUTING • • • All sites operational One half of the sites working in integrated mode Test of Data Base distribution within sites 4 Tier 2 initial prototypes ready MC production of 20% of the events needed by CMS March April June October December
Milestones 2002 TRACKER • • 40 modules M 200 produced System test (6 modules in a string) Final specifications optical hybrid Start-up of module production Final specifications Power Supply 400 modules produced Layer 1 mechanical structure January March May June October December MAGNET • • Impregnated prototype ready Module CB-2 impregnated Module CB-1 impregnated Module CB 0 impregnated January April July October COMPUTING • • • All sites operational One half of the sites working in integrated mode Test of Data Base distribution within sites 4 Tier 2 initial prototypes ready MC production of 20% of the events needed by CMS March April June October December
 Milestones 2003 DT • • • First MB 4 chamber assembled in Torino Start mass assembly of minicrates Test of chambers and of the trigger system on 25 ns beam Assembly line in Torino working at planned production rate Installation of the central wheel 18 MB 3 chambers ready (35 since the beginning) March June July October December Protocol and test system with cosmic rays frozen All assembly and test sites in operation Production and test of 100 W-O stations Production and test of 100 W-1 stations Pre-production of the HV/LV system January March April December RPC • • • ECAL • • Cooling system for SM 1 designed QC of 9600 crystals (15600 since the beginning) Assembly and test of 24 modules (36 since the beginning) Test of 36 HV boards Production of 52 grids (104 since the beginning) Production of 16 superbaskets Test of SM 1 June December December
Milestones 2003 DT • • • First MB 4 chamber assembled in Torino Start mass assembly of minicrates Test of chambers and of the trigger system on 25 ns beam Assembly line in Torino working at planned production rate Installation of the central wheel 18 MB 3 chambers ready (35 since the beginning) March June July October December Protocol and test system with cosmic rays frozen All assembly and test sites in operation Production and test of 100 W-O stations Production and test of 100 W-1 stations Pre-production of the HV/LV system January March April December RPC • • • ECAL • • Cooling system for SM 1 designed QC of 9600 crystals (15600 since the beginning) Assembly and test of 24 modules (36 since the beginning) Test of 36 HV boards Production of 52 grids (104 since the beginning) Production of 16 superbaskets Test of SM 1 June December December
 Milestones 2003 TRACKER • • • 200 TIB modules assembled and tested System test of the TIB DS layers First TID disk manufactured Tender for the Power Supply System 1400 TIB-TID modules assembled TIB/TID structural parts ready February April June July December MAGNET • • CB-1 module impregnated CB-0 module impregnated CB+1 module impregnated CB+2 module impregnated April July September December COMPUTING • • • 50% GRID sites enabled Production prototypes for LCG (Tier 1+Tier 2) ready New analysis environment for CMS installed and working 50% Sites operational with the new software Participation of Tier 1 and of 50% of Tier 2 to the 5% Data Challenge April June October December
Milestones 2003 TRACKER • • • 200 TIB modules assembled and tested System test of the TIB DS layers First TID disk manufactured Tender for the Power Supply System 1400 TIB-TID modules assembled TIB/TID structural parts ready February April June July December MAGNET • • CB-1 module impregnated CB-0 module impregnated CB+1 module impregnated CB+2 module impregnated April July September December COMPUTING • • • 50% GRID sites enabled Production prototypes for LCG (Tier 1+Tier 2) ready New analysis environment for CMS installed and working 50% Sites operational with the new software Participation of Tier 1 and of 50% of Tier 2 to the 5% Data Challenge April June October December


