e06811c1e165fbac8d2f0432db58f224.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 90
 CMRP CERTIFICATION Overview Session
CMRP CERTIFICATION Overview Session
 A Mark of Distinction CMRP status allows you to: Have a premier credential based on a sound assessment to distinguish yourself in an increasingly competitive marketplace. Enjoy the pride of recognition and knowing you are among the elite in the field of healthcare materials management.
A Mark of Distinction CMRP status allows you to: Have a premier credential based on a sound assessment to distinguish yourself in an increasingly competitive marketplace. Enjoy the pride of recognition and knowing you are among the elite in the field of healthcare materials management.
 CMRP Overview Session Disclaimer Please be advised that this is only an overview of the Materials Management Review Guide. It should not be inferred that test items in the examination are selected from any single reference or set of references or that participation in this review session guarantees a passing score on the examination.
CMRP Overview Session Disclaimer Please be advised that this is only an overview of the Materials Management Review Guide. It should not be inferred that test items in the examination are selected from any single reference or set of references or that participation in this review session guarantees a passing score on the examination.
 American Hospital Association Certification Center • Governed by a Board of Directors • An independent body affiliated with the AHA • Certification Program Committee – Content experts – Test development – Scoring and analysis • Designed to test full scope competency of individuals involved in materials management
American Hospital Association Certification Center • Governed by a Board of Directors • An independent body affiliated with the AHA • Certification Program Committee – Content experts – Test development – Scoring and analysis • Designed to test full scope competency of individuals involved in materials management
 Eligibility - Concept In 2003, the CMRP eligibility requirements changed. The requirements continue to blend experience and education and are designed to include experienced healthcare resource and materials managers. (There is no membership requirement. )
Eligibility - Concept In 2003, the CMRP eligibility requirements changed. The requirements continue to blend experience and education and are designed to include experienced healthcare resource and materials managers. (There is no membership requirement. )
 CMRP Eligibility • Baccalaureate degree plus three (3) years of associated healthcare resource and materials management* experience; or • Associate degree or equivalent plus five (5) years of associated healthcare resource and materials management* experience; or • High school diploma or equivalent plus seven (7) years of associated healthcare resource and materials management* experience.
CMRP Eligibility • Baccalaureate degree plus three (3) years of associated healthcare resource and materials management* experience; or • Associate degree or equivalent plus five (5) years of associated healthcare resource and materials management* experience; or • High school diploma or equivalent plus seven (7) years of associated healthcare resource and materials management* experience.
 CMRP Eligibility * Associated healthcare resource and materials management includes persons who are involved in the materials functions of healthcare facilities; or are active in the healthcare materials supply chain, including manufacturers, vendors, distributors, consultants, and employees of group purchasing organizations.
CMRP Eligibility * Associated healthcare resource and materials management includes persons who are involved in the materials functions of healthcare facilities; or are active in the healthcare materials supply chain, including manufacturers, vendors, distributors, consultants, and employees of group purchasing organizations.
 Administration • • Application for examination processed Eligibility confirmation sent to candidate Confirmation notice received Fees – Members - $275 – Non-members - $345 • Schedule appointment; reschedule once within 4 business days at no charge • Rescheduled within 90 days - $100 rescheduling fee
Administration • • Application for examination processed Eligibility confirmation sent to candidate Confirmation notice received Fees – Members - $275 – Non-members - $345 • Schedule appointment; reschedule once within 4 business days at no charge • Rescheduled within 90 days - $100 rescheduling fee
 Administration • Reschedule after 90 days must resubmit application and pay a fee of $275/members or $345/nonmembers
Administration • Reschedule after 90 days must resubmit application and pay a fee of $275/members or $345/nonmembers
 Administration • Selected H&R Block computer centers • Photo ID (2 forms of ID) • Paper and pencil or computer-based – 2 hours – 110 questions (10 pretest) • Results upon completion of computer-based • Certification – – Letter Lapel pin Renewal Application Employer Notification Form
Administration • Selected H&R Block computer centers • Photo ID (2 forms of ID) • Paper and pencil or computer-based – 2 hours – 110 questions (10 pretest) • Results upon completion of computer-based • Certification – – Letter Lapel pin Renewal Application Employer Notification Form
 Exam Specifications The AHRMM role delineation study identified real-world tasks that were grouped into categories and weighted to produce exam specifications. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Purchasing/Product Value Analysis – 25% Inventory Distribution Management – 20% Support Services – 10% Information Systems – 13% Finance – 12% Strategic Planning/Leadership – 20%
Exam Specifications The AHRMM role delineation study identified real-world tasks that were grouped into categories and weighted to produce exam specifications. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Purchasing/Product Value Analysis – 25% Inventory Distribution Management – 20% Support Services – 10% Information Systems – 13% Finance – 12% Strategic Planning/Leadership – 20%
 Exam Categorized • Recall – The ability to recall or recognize specific information • Application – The ability to comprehend, relate or apply knowledge to new or changing situations • Analysis – The ability to analyze and synthesize information, determine solutions and/or to evaluate solutions
Exam Categorized • Recall – The ability to recall or recognize specific information • Application – The ability to comprehend, relate or apply knowledge to new or changing situations • Analysis – The ability to analyze and synthesize information, determine solutions and/or to evaluate solutions
 Test Items To ensure reliability and validity, test items are: ü Written by experienced healthcare resource and materials managers; ü Geared to test application of knowledge - not just recall of facts; and, ü Reviewed annually to ensure clarity.
Test Items To ensure reliability and validity, test items are: ü Written by experienced healthcare resource and materials managers; ü Geared to test application of knowledge - not just recall of facts; and, ü Reviewed annually to ensure clarity.
 Measurement Expertise To ensure the highest standards in testing, the AHA Certification Center engaged Applied Measurement Professionals, Inc. (AMP) to assist with: ü Test development; ü Test administration; and ü Scoring, score reporting, and analysis.
Measurement Expertise To ensure the highest standards in testing, the AHA Certification Center engaged Applied Measurement Professionals, Inc. (AMP) to assist with: ü Test development; ü Test administration; and ü Scoring, score reporting, and analysis.
 Administration The CMRP Exam is offered on computer at over 110 secure test centers throughout the U. S. Scores are private. Only the test taker receives the scores.
Administration The CMRP Exam is offered on computer at over 110 secure test centers throughout the U. S. Scores are private. Only the test taker receives the scores.
 Administration Examination application is contained inside the CMRP Handbook and is available by downloading a copy from: • The AHA Certification Center, www. aha. org then click on “Certification”; or • AHRMM’s Web site, www. ahrmm. org; or
Administration Examination application is contained inside the CMRP Handbook and is available by downloading a copy from: • The AHA Certification Center, www. aha. org then click on “Certification”; or • AHRMM’s Web site, www. ahrmm. org; or
 Administration (cont. ) • Call Applied Measurement Professionals, Inc. (AMP) at 913/541 -0400
Administration (cont. ) • Call Applied Measurement Professionals, Inc. (AMP) at 913/541 -0400
 Exam Provisions The Examination fee is: $275 for any PMG or At-Large Member; or $345 for a nonmember. Certification is valid for three years.
Exam Provisions The Examination fee is: $275 for any PMG or At-Large Member; or $345 for a nonmember. Certification is valid for three years.
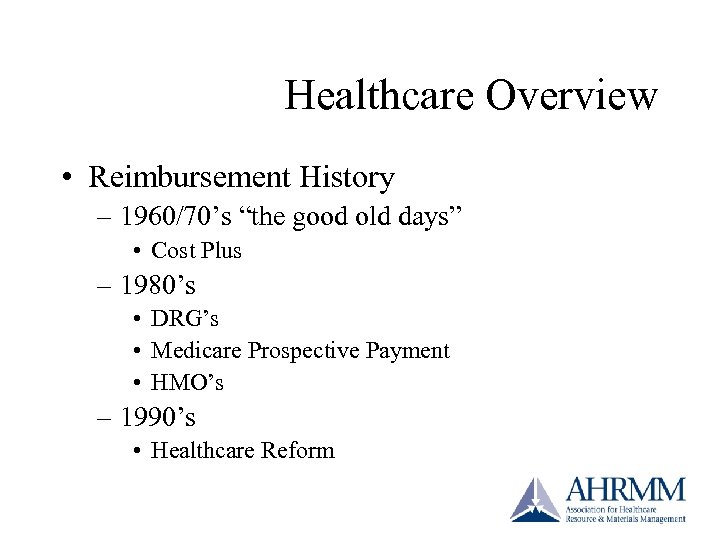 Healthcare Overview • Reimbursement History – 1960/70’s “the good old days” • Cost Plus – 1980’s • DRG’s • Medicare Prospective Payment • HMO’s – 1990’s • Healthcare Reform
Healthcare Overview • Reimbursement History – 1960/70’s “the good old days” • Cost Plus – 1980’s • DRG’s • Medicare Prospective Payment • HMO’s – 1990’s • Healthcare Reform
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis 25 items ( Recall-10, Application- 10, Analysis-5 ) Administer and direct the program to purchase materials, supplies, and capital equipment.
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis 25 items ( Recall-10, Application- 10, Analysis-5 ) Administer and direct the program to purchase materials, supplies, and capital equipment.
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis Act of Purchasing involves 4 steps: 1. Requisitioning 2. Sourcing 3. Negotiating 4. Ordering
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis Act of Purchasing involves 4 steps: 1. Requisitioning 2. Sourcing 3. Negotiating 4. Ordering
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Requisition/Purchase Order Types – Stock – Non-stock – Electronic – Traveling – Blanket – Standing – Open
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Requisition/Purchase Order Types – Stock – Non-stock – Electronic – Traveling – Blanket – Standing – Open
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Freight Terms and Title of Goods – – FOB Destination FOB Shipping Point FOB Destination, Prepay Freight, and Add FOB Shipping Point, Freight Allowed • Payment Terms and Conditions – 2% 10 days, net 30 – COD – Credit Card/Purchase Card
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Freight Terms and Title of Goods – – FOB Destination FOB Shipping Point FOB Destination, Prepay Freight, and Add FOB Shipping Point, Freight Allowed • Payment Terms and Conditions – 2% 10 days, net 30 – COD – Credit Card/Purchase Card
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Legal Aspects of Purchasing – Product liability – Wrongful rejection – Failure to deliver – Liabilities and warranties – Universal Commercial Code (UCC) – Robinson-Patman Act
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Legal Aspects of Purchasing – Product liability – Wrongful rejection – Failure to deliver – Liabilities and warranties – Universal Commercial Code (UCC) – Robinson-Patman Act
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Right of Possession – “absence of rightful rejection” • Noted by agreement, delivery, use or payment • Unconscionable Contracts – Unfair, one-sided but not illegal • Liabilities and Warranties – Implied – Expressed
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Right of Possession – “absence of rightful rejection” • Noted by agreement, delivery, use or payment • Unconscionable Contracts – Unfair, one-sided but not illegal • Liabilities and Warranties – Implied – Expressed
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Safe Harbor – Published in 1991 as an amendment to the 1972 Medicare Fraud regulation • Prohibits the following: » Knowing and willful solicitation, receipt, offer, payment of remuneration in return for referral of Medicare patients » Knowing, willful, payment, receipt renumeration to induce the purchase of goods/services which will be paid for by Medicare
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Safe Harbor – Published in 1991 as an amendment to the 1972 Medicare Fraud regulation • Prohibits the following: » Knowing and willful solicitation, receipt, offer, payment of remuneration in return for referral of Medicare patients » Knowing, willful, payment, receipt renumeration to induce the purchase of goods/services which will be paid for by Medicare
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Safe Harbor requires hospitals to: – Report all discounts, free goods, warranties in cost report, submitted to Medicare – Discounts are acceptable as rebates, credits. Must involve goods sold. – Cannot rebate one item based on purchase of another. – Cannot link incentive to furnish goods at no charge if another item is purchased.
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Safe Harbor requires hospitals to: – Report all discounts, free goods, warranties in cost report, submitted to Medicare – Discounts are acceptable as rebates, credits. Must involve goods sold. – Cannot rebate one item based on purchase of another. – Cannot link incentive to furnish goods at no charge if another item is purchased.
 Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Universal Commercial Code (UCC) – Established in 1952 – Governs purchases in 49 states – Excludes services associated with products – Purchase of goods > $500 must be confirmed in writing to be enforceable under the law – Statute of limitations is 4 years
Purchasing/Product Value Analysis • Universal Commercial Code (UCC) – Established in 1952 – Governs purchases in 49 states – Excludes services associated with products – Purchase of goods > $500 must be confirmed in writing to be enforceable under the law – Statute of limitations is 4 years
 Materials & Resource Manager’s “Tool Bag” • Activity Based Costing (ABC) – A cost management tool to identify and allocate overhead costs • Activity Based Management (ABM) – Minimize costs, eliminate duplication – Continually evaluate new supply chain process Using ABC/ABM procedures will help ensure maximum returns for efforts expended and costs that have been incurred.
Materials & Resource Manager’s “Tool Bag” • Activity Based Costing (ABC) – A cost management tool to identify and allocate overhead costs • Activity Based Management (ABM) – Minimize costs, eliminate duplication – Continually evaluate new supply chain process Using ABC/ABM procedures will help ensure maximum returns for efforts expended and costs that have been incurred.
 Materials & Resource Manager’s “Tool Bag” • Value Added Opportunities – Additional services offered as incentives • Value Analysis – Functionally oriented process – Best and most economical procedures, products, equipment, or services – Meet the needs of the user while reducing the overall cost involved
Materials & Resource Manager’s “Tool Bag” • Value Added Opportunities – Additional services offered as incentives • Value Analysis – Functionally oriented process – Best and most economical procedures, products, equipment, or services – Meet the needs of the user while reducing the overall cost involved
 Materials & Resource Manager’s “Tool Bag” • Total Delivered Costs – All aspects of the product cycle • Purchase price, receiving, warehousing, delivery • Holding, value of money, pilferage, obsolescence • Outsourcing – Reduce the overall cost – Increase the quality
Materials & Resource Manager’s “Tool Bag” • Total Delivered Costs – All aspects of the product cycle • Purchase price, receiving, warehousing, delivery • Holding, value of money, pilferage, obsolescence • Outsourcing – Reduce the overall cost – Increase the quality
 Inventory Distribution Management 20 items (Recall – 10, Application – 6, Analysis – 4) Assure that the organization’s acquisition and distribution strategies and practices improve the overall healthcare supply chain system.
Inventory Distribution Management 20 items (Recall – 10, Application – 6, Analysis – 4) Assure that the organization’s acquisition and distribution strategies and practices improve the overall healthcare supply chain system.
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory control should: ØProvide monetary savings ØImprove service levels ØImprove internal operations ØReview supply utilization ØReduce waste ØFully utilize MMIS
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory control should: ØProvide monetary savings ØImprove service levels ØImprove internal operations ØReview supply utilization ØReduce waste ØFully utilize MMIS
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory – product on-hand ØTurns – current asset that has been acquired by cash and is yet to be consumed ØStock – may also be used to describe inventory ØDetermined by dividing the total annual inventory purchases by the end inventory value ØPhysical inventory is the actual counting of supplies and comparing the amount on hand with the amount on the financial statement
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory – product on-hand ØTurns – current asset that has been acquired by cash and is yet to be consumed ØStock – may also be used to describe inventory ØDetermined by dividing the total annual inventory purchases by the end inventory value ØPhysical inventory is the actual counting of supplies and comparing the amount on hand with the amount on the financial statement
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory can be counted two ways: ØPeriodic counting ØDone at regular intervals (usually 6 or 12 months) ØCycle counting ØContinuously selecting subgroups to count ØTypically 10% of stock per month
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory can be counted two ways: ØPeriodic counting ØDone at regular intervals (usually 6 or 12 months) ØCycle counting ØContinuously selecting subgroups to count ØTypically 10% of stock per month
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Successful Inventory Control is to achieve balance between stock on-hand need Ø Basic components to assist this are: ØOrder quantity ØLead time ØSafety stock
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Successful Inventory Control is to achieve balance between stock on-hand need Ø Basic components to assist this are: ØOrder quantity ØLead time ØSafety stock
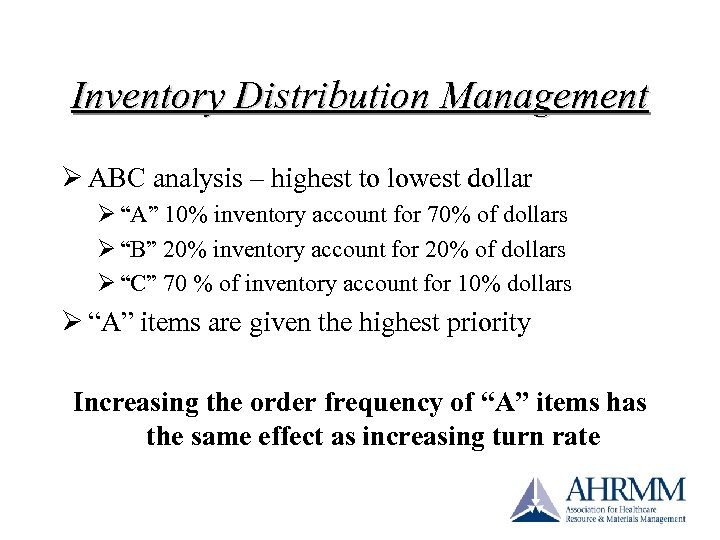 Inventory Distribution Management Ø ABC analysis – highest to lowest dollar Ø “A” 10% inventory account for 70% of dollars Ø “B” 20% inventory account for 20% of dollars Ø “C” 70 % of inventory account for 10% dollars Ø “A” items are given the highest priority Increasing the order frequency of “A” items has the same effect as increasing turn rate
Inventory Distribution Management Ø ABC analysis – highest to lowest dollar Ø “A” 10% inventory account for 70% of dollars Ø “B” 20% inventory account for 20% of dollars Ø “C” 70 % of inventory account for 10% dollars Ø “A” items are given the highest priority Increasing the order frequency of “A” items has the same effect as increasing turn rate
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Lead time = require/order/receive/distribute Ø Safety stock- protection against stock-out Ø Supply level calculations Ø Maximum/minimum Ø Economic order quantity ü The greater the order quantity, larger the inventory. ü The longer the lead time, the greater the inventory. ü The higher the safety stock, the greater the inventory.
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Lead time = require/order/receive/distribute Ø Safety stock- protection against stock-out Ø Supply level calculations Ø Maximum/minimum Ø Economic order quantity ü The greater the order quantity, larger the inventory. ü The longer the lead time, the greater the inventory. ü The higher the safety stock, the greater the inventory.
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory Valuation ØLast in, First out (LIFO) ØNewest define cost ØFirst in, First out (FIFO) ØOldest define cost ØAverage costing inventory ØWeighed average cost
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory Valuation ØLast in, First out (LIFO) ØNewest define cost ØFirst in, First out (FIFO) ØOldest define cost ØAverage costing inventory ØWeighed average cost
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Carrying Costs includes such areas as: üInvested capital üHandling charges üStorage üInsurance üCost of money üSpoilage üData processing
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Carrying Costs includes such areas as: üInvested capital üHandling charges üStorage üInsurance üCost of money üSpoilage üData processing
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø 3 Different Types of Inventory ØOfficial ØMaintained as assets on balance sheets ØUnofficial ØExpenses upon receipt ØConsignment ØHoused by the facility, purchased when used
Inventory Distribution Management Ø 3 Different Types of Inventory ØOfficial ØMaintained as assets on balance sheets ØUnofficial ØExpenses upon receipt ØConsignment ØHoused by the facility, purchased when used
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory Strategies ØConsolidation ØReduction ØStorage space Ø Inventory Ratios ØNot-In –Stock ØFill-Rate Ø% of Back-Orders
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory Strategies ØConsolidation ØReduction ØStorage space Ø Inventory Ratios ØNot-In –Stock ØFill-Rate Ø% of Back-Orders
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Distribution Methods ØRandom request ØEmergency ØPAR ØExchange carts ØCase carts ØJIT ØStockless
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Distribution Methods ØRandom request ØEmergency ØPAR ØExchange carts ØCase carts ØJIT ØStockless
 Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory management in the OR ØIntense need ØDiverse users ØLargest dollar volume Ø“Unofficial” ØPreference items ØLow turn rate Ø(out of control)
Inventory Distribution Management Ø Inventory management in the OR ØIntense need ØDiverse users ØLargest dollar volume Ø“Unofficial” ØPreference items ØLow turn rate Ø(out of control)
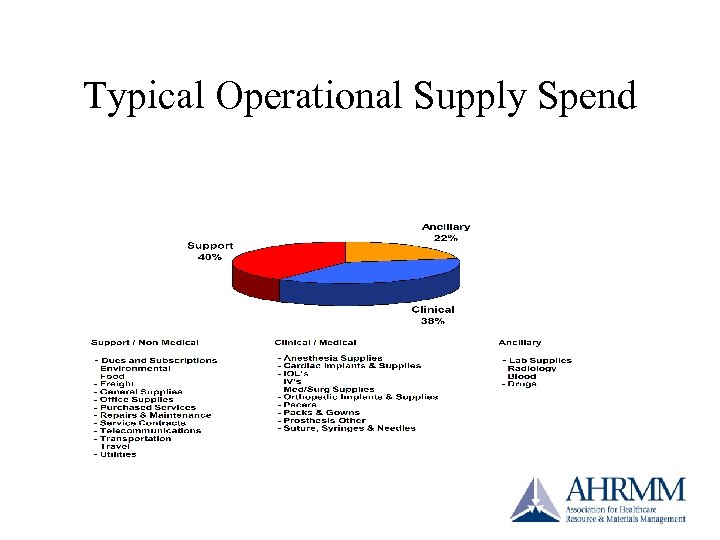 Typical Operational Supply Spend
Typical Operational Supply Spend
 Time for a Break • Take 5…………. .
Time for a Break • Take 5…………. .
 Support Services 10 items (Recall - 6, Application – 2, Analysis – 2) Sterile Processing Linen Management Food Services Patient Transport Universal Precautions
Support Services 10 items (Recall - 6, Application – 2, Analysis – 2) Sterile Processing Linen Management Food Services Patient Transport Universal Precautions
 Support Services v Overview of Hazardous Materials & Waste v. Government guidelines that control the handling and transportation include: v. OSHA v Occupational Safety & Health Administration v. EPA v Environmental Protection Agency v. JCAHO v Joint Commission & Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations v. DOT v Department of Transportation
Support Services v Overview of Hazardous Materials & Waste v. Government guidelines that control the handling and transportation include: v. OSHA v Occupational Safety & Health Administration v. EPA v Environmental Protection Agency v. JCAHO v Joint Commission & Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations v. DOT v Department of Transportation
 Support Services v. Chemical Hazards Communication Standard (CHCS) spells out employee “right to know” regulations v. Education and training v. Material Safety and Data Sheets (MSDS) v. Use and location of safety equipment v. Policies and procedures v. Documentation and labeling
Support Services v. Chemical Hazards Communication Standard (CHCS) spells out employee “right to know” regulations v. Education and training v. Material Safety and Data Sheets (MSDS) v. Use and location of safety equipment v. Policies and procedures v. Documentation and labeling
 Support Services v Classification of Hazardous Materials/Waste v. Six specific classifications of waste v. Non-hazardous, general solid v. Hazardous v Corrosives, Flammables, Reactive/toxic chemicals v. Cytoxic v. Medical v. Physical hazardous v Sharps, Needles, Glass v. Radioactive
Support Services v Classification of Hazardous Materials/Waste v. Six specific classifications of waste v. Non-hazardous, general solid v. Hazardous v Corrosives, Flammables, Reactive/toxic chemicals v. Cytoxic v. Medical v. Physical hazardous v Sharps, Needles, Glass v. Radioactive
 Support Services v v v v Medical Waste Disposal Steam sterilization Dry Heat Sterilization Et. O sterilization Incineration Off-site disposal (landfill) Microwave techniques
Support Services v v v v Medical Waste Disposal Steam sterilization Dry Heat Sterilization Et. O sterilization Incineration Off-site disposal (landfill) Microwave techniques
 Support Services v. Linen Selection v. Size (cut/finish) v. Fiber content (cotton, blend) v. Thread count (density of fiber) v. Weight of fabric v. Color (steadfastness) v. Quality/cost recovery (washing cycle)
Support Services v. Linen Selection v. Size (cut/finish) v. Fiber content (cotton, blend) v. Thread count (density of fiber) v. Weight of fabric v. Color (steadfastness) v. Quality/cost recovery (washing cycle)
 Support Services v. Surgical Linen Standards (AORN) v. Blood and aqueous fluid resistant v. Abrasive resistant v. Lint free v. Meet NFPA requirements v. Eliminate heat build up v. Be easily draped
Support Services v. Surgical Linen Standards (AORN) v. Blood and aqueous fluid resistant v. Abrasive resistant v. Lint free v. Meet NFPA requirements v. Eliminate heat build up v. Be easily draped
 Support Services v. Linen general v. Flame retardant fabrics v. Security and identification v. Transportation and storage v. Chemicals and laundering v. Inventory and tracking v. Pounds per patient day/charge back v. Ordering and cycling
Support Services v. Linen general v. Flame retardant fabrics v. Security and identification v. Transportation and storage v. Chemicals and laundering v. Inventory and tracking v. Pounds per patient day/charge back v. Ordering and cycling
 Support Services v Overview of Sterile Processing v. Decontamination process: v. Thorough cleaning procedure v Sorting v Pre-cleaning v Transportation v Disassembly v Cleaning v Decontamination v. Disinfection v Chemicals v Ultrasonic
Support Services v Overview of Sterile Processing v. Decontamination process: v. Thorough cleaning procedure v Sorting v Pre-cleaning v Transportation v Disassembly v Cleaning v Decontamination v. Disinfection v Chemicals v Ultrasonic
 Support Services v. Sterilization v. Thermal is steam or dry heat v. Steam safest, most practical v. Dry heat slower less even v. Ethylene Oxide (Et. O) Gas v. Require proper aeration v. Maintenance of equipment by a professional v. Packaging should allow max penetration
Support Services v. Sterilization v. Thermal is steam or dry heat v. Steam safest, most practical v. Dry heat slower less even v. Ethylene Oxide (Et. O) Gas v. Require proper aeration v. Maintenance of equipment by a professional v. Packaging should allow max penetration
 Support Services v Sterilization cont. v. Monitoring v. Mechanical v. Chemical v. Biological v. Documentation (JCAHO) v. Maintenance records v. Monitoring v. Staff education v. Policies and procedures
Support Services v Sterilization cont. v. Monitoring v. Mechanical v. Chemical v. Biological v. Documentation (JCAHO) v. Maintenance records v. Monitoring v. Staff education v. Policies and procedures
 Information Systems 13 items (Recall – 5, Application – 4, Analysis – 4) Direct acquisition and implementation of an automated, system-wide materials management information system.
Information Systems 13 items (Recall – 5, Application – 4, Analysis – 4) Direct acquisition and implementation of an automated, system-wide materials management information system.
 Information Systems § Materials Management Information System (MMIS) includes: § Purchasing, receiving, inventory § Interfaces to: § § § Accounts payable General ledger Patient accounts Surgery Other clinical departments as determined
Information Systems § Materials Management Information System (MMIS) includes: § Purchasing, receiving, inventory § Interfaces to: § § § Accounts payable General ledger Patient accounts Surgery Other clinical departments as determined
 Information Systems § Selection Process § § § § Multi-disciplinary taskforce Identified processes Research marketplace Determine functionality requirements Develop RRP Demonstrations Develop project plan
Information Systems § Selection Process § § § § Multi-disciplinary taskforce Identified processes Research marketplace Determine functionality requirements Develop RRP Demonstrations Develop project plan
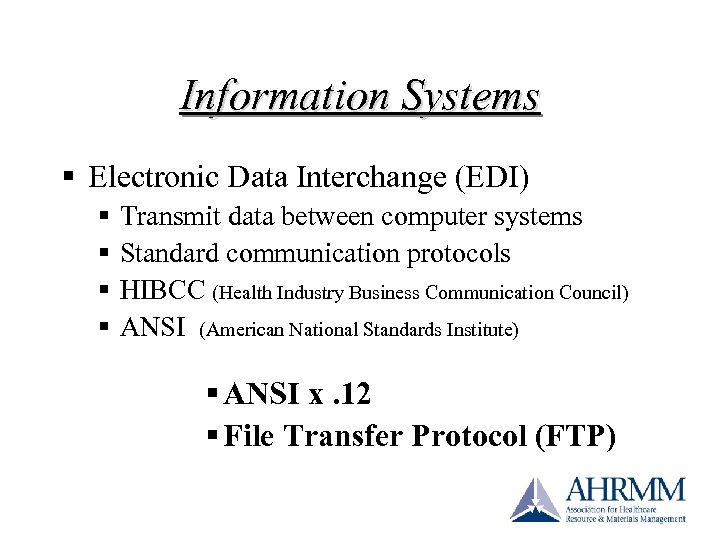 Information Systems § Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) § § Transmit data between computer systems Standard communication protocols HIBCC (Health Industry Business Communication Council) ANSI (American National Standards Institute) § ANSI x. 12 § File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Information Systems § Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) § § Transmit data between computer systems Standard communication protocols HIBCC (Health Industry Business Communication Council) ANSI (American National Standards Institute) § ANSI x. 12 § File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
 Information Systems § Bar-Coding standards adopted by HIBCC § “Code 39” or “Code 3 of 9” § EDI Data Sets most commonly used: § § § 832 -price catalog 850 -purchase order 855 -PO confirmation 856 -advance ship notice/auto receipt 810 -invoice
Information Systems § Bar-Coding standards adopted by HIBCC § “Code 39” or “Code 3 of 9” § EDI Data Sets most commonly used: § § § 832 -price catalog 850 -purchase order 855 -PO confirmation 856 -advance ship notice/auto receipt 810 -invoice
 Information Systems § The Internet and Business § § § § WWW – world wide web XML – standard for internet communication HTTP – hypertext transfer protocol UML – unified modeling language URL – uniform resource locator LAN – local area network ERP – enterprise recourse planning
Information Systems § The Internet and Business § § § § WWW – world wide web XML – standard for internet communication HTTP – hypertext transfer protocol UML – unified modeling language URL – uniform resource locator LAN – local area network ERP – enterprise recourse planning
 Time for a Break • Take 5…………. .
Time for a Break • Take 5…………. .
 Finance 12 items (Recall – 5, Application – 4, Analysis – 3) Finance and Accounting Principles used to better understand an organization’s financial culture.
Finance 12 items (Recall – 5, Application – 4, Analysis – 3) Finance and Accounting Principles used to better understand an organization’s financial culture.
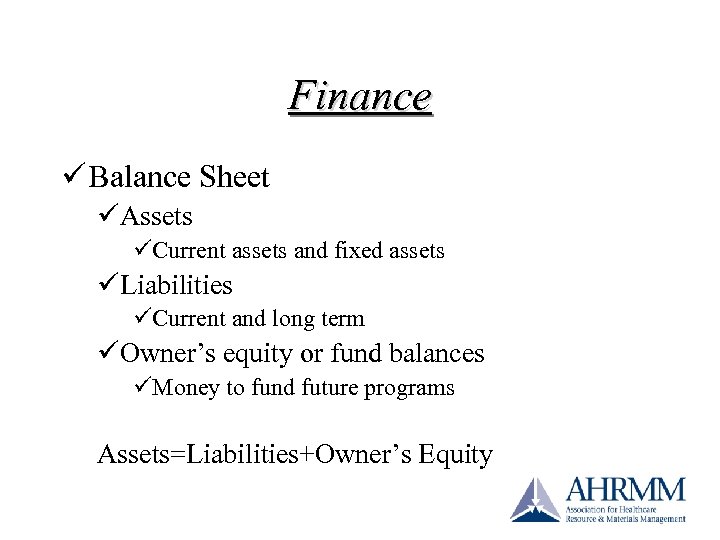 Finance ü Balance Sheet üAssets üCurrent assets and fixed assets üLiabilities üCurrent and long term üOwner’s equity or fund balances üMoney to fund future programs Assets=Liabilities+Owner’s Equity
Finance ü Balance Sheet üAssets üCurrent assets and fixed assets üLiabilities üCurrent and long term üOwner’s equity or fund balances üMoney to fund future programs Assets=Liabilities+Owner’s Equity
 Finance ü Ratios üLiquidity ratio üThe ability to pay bills üLeverage ratios üMeasure ability to meet long-term needs üEfficiency ratios üHow well assets are managed to produce a profit
Finance ü Ratios üLiquidity ratio üThe ability to pay bills üLeverage ratios üMeasure ability to meet long-term needs üEfficiency ratios üHow well assets are managed to produce a profit
 Finance ü Break-Even Analysis ü Revenue ü Fixed costs ü Variable costs ü Volume ü ( V x R = FC + VC x V ) ü Return on Investment (ROI) ü Revenue from investment resulting in profit
Finance ü Break-Even Analysis ü Revenue ü Fixed costs ü Variable costs ü Volume ü ( V x R = FC + VC x V ) ü Return on Investment (ROI) ü Revenue from investment resulting in profit
 Finance ü Value Analysis ü Looks at the reduction of non-salaried expenses from a multidisciplinary or team approach ü Some quantitative techniques used are: ü Cost benefit analysis ü Life cycle ü Forecasting ü Unit cost ü In-use cost ü Environmental cost ü Impact of staff productivity
Finance ü Value Analysis ü Looks at the reduction of non-salaried expenses from a multidisciplinary or team approach ü Some quantitative techniques used are: ü Cost benefit analysis ü Life cycle ü Forecasting ü Unit cost ü In-use cost ü Environmental cost ü Impact of staff productivity
 Finance ü Value Analysis Application includes: üMultidisciplinary approach üUtilize brainstorming to problem solve üBreaks down functions üIdentifies potential alternatives üReviews the total delivered cost üPatient focused high quality approach
Finance ü Value Analysis Application includes: üMultidisciplinary approach üUtilize brainstorming to problem solve üBreaks down functions üIdentifies potential alternatives üReviews the total delivered cost üPatient focused high quality approach
 Finance ü Retention of Health Information / Records üLegal regulatory include: üHCFA üMedicare üOSHA üJCAHO üSpecific state regulation
Finance ü Retention of Health Information / Records üLegal regulatory include: üHCFA üMedicare üOSHA üJCAHO üSpecific state regulation
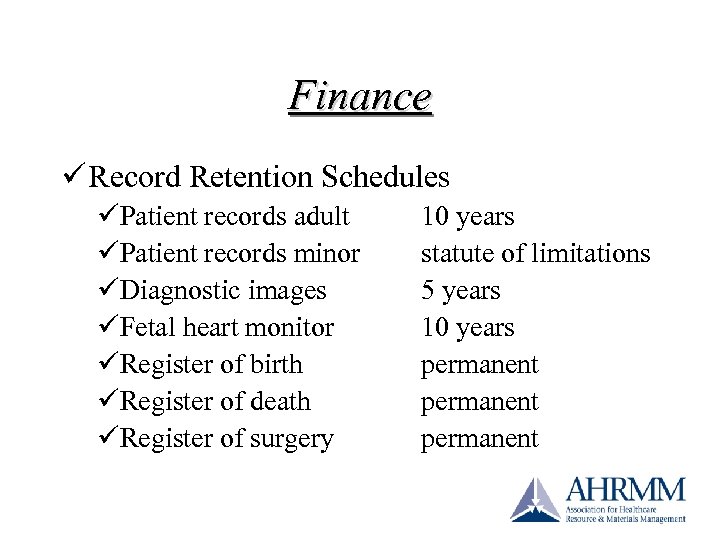 Finance ü Record Retention Schedules üPatient records adult üPatient records minor üDiagnostic images üFetal heart monitor üRegister of birth üRegister of death üRegister of surgery 10 years statute of limitations 5 years 10 years permanent
Finance ü Record Retention Schedules üPatient records adult üPatient records minor üDiagnostic images üFetal heart monitor üRegister of birth üRegister of death üRegister of surgery 10 years statute of limitations 5 years 10 years permanent
 Finance ü Records for Materials Management: üCapital budget purchasing üConsultant contracts üLeases and rentals üMaintenance and service üWarranty contracts üPurchase orders üRequisitions 10 years permanent 5 years permanent 2 years 1 year
Finance ü Records for Materials Management: üCapital budget purchasing üConsultant contracts üLeases and rentals üMaintenance and service üWarranty contracts üPurchase orders üRequisitions 10 years permanent 5 years permanent 2 years 1 year
 Finance ü Corporate Compliance Programs üConflict of interest policy üBackground check on employees üGuidelines for ethical behavior üState and federal statute associated with Medicare and Medicaid
Finance ü Corporate Compliance Programs üConflict of interest policy üBackground check on employees üGuidelines for ethical behavior üState and federal statute associated with Medicare and Medicaid
 Finance ü Asset Management Program ü Financial analysis ü Acquisition vs. Rent ü Receipt ü Distribution and tracking ü Charging ü Maintenance ü Replacement ü Disposal
Finance ü Asset Management Program ü Financial analysis ü Acquisition vs. Rent ü Receipt ü Distribution and tracking ü Charging ü Maintenance ü Replacement ü Disposal
 Strategic Planning/Leadership 20 items (Recall – 8, Application – 8, Analysis – 4) Overview of using the principles of strategic planning and quality management to manage customer services.
Strategic Planning/Leadership 20 items (Recall – 8, Application – 8, Analysis – 4) Overview of using the principles of strategic planning and quality management to manage customer services.
 Strategic Planning/Leadership Ø Plan – Control – Improve Ø Set goals Ø Provide infrastructure Ø Provide resources Ø Quality leadership and support NEW JCAHO REQUIREMENT FOR FACILITIES KEY TO YOUR FUTURE SUCCESS
Strategic Planning/Leadership Ø Plan – Control – Improve Ø Set goals Ø Provide infrastructure Ø Provide resources Ø Quality leadership and support NEW JCAHO REQUIREMENT FOR FACILITIES KEY TO YOUR FUTURE SUCCESS
 Strategic Planning/Leadership 12 STEPS Ø Identify customers Ø Determine customers needs Ø Respond to customer needs Ø Quality goals to meet customer needs Ø Produce product/process Ø Prove process Ø Ø Ø Measure and control Establish standards Identify problems Solve problems Measure success On-going process plan
Strategic Planning/Leadership 12 STEPS Ø Identify customers Ø Determine customers needs Ø Respond to customer needs Ø Quality goals to meet customer needs Ø Produce product/process Ø Prove process Ø Ø Ø Measure and control Establish standards Identify problems Solve problems Measure success On-going process plan
 Strategic Planning/Leadership Ø Framework ØVision – Mission – Principles Ø Implementation ØGoals – Objectives - Strategies Ø Process ØAnnual Plan – Evaluation – Performance Reports
Strategic Planning/Leadership Ø Framework ØVision – Mission – Principles Ø Implementation ØGoals – Objectives - Strategies Ø Process ØAnnual Plan – Evaluation – Performance Reports
 Frequently Asked Questions Why is a true certification program important? – Certification is important as it recognizes a level of competency. It is a way to express value to your employer. – It encourages continued personal and professional growth in the practice of healthcare materials and resource management.
Frequently Asked Questions Why is a true certification program important? – Certification is important as it recognizes a level of competency. It is a way to express value to your employer. – It encourages continued personal and professional growth in the practice of healthcare materials and resource management.
 Frequently Asked Questions What makes this certification different from AHRMM’s Fellow of the Association for Healthcare Resource & Materials Management (FAHRMM)? – The American Hospital Association’s Certification Center is independent of AHRMM and administers the certification. – The CMRP is the recognized credential for the profession. Passing the CMRP demonstrates a mastery of a well-defined body of knowledge and is based on national standards.
Frequently Asked Questions What makes this certification different from AHRMM’s Fellow of the Association for Healthcare Resource & Materials Management (FAHRMM)? – The American Hospital Association’s Certification Center is independent of AHRMM and administers the certification. – The CMRP is the recognized credential for the profession. Passing the CMRP demonstrates a mastery of a well-defined body of knowledge and is based on national standards.
 Frequently Asked Questions – Fellow status is presented to Certified Senior or Certified Materials and Resource Professional (CMRP) members in good standing, who have met specified achievement criteria, and have submitted an acceptable, original unpublished paper on a current aspect of materials management. – The requirements for Fellow are designed so that those who apply and attain this level must be persons of exceptional achievement as judged by their peers.
Frequently Asked Questions – Fellow status is presented to Certified Senior or Certified Materials and Resource Professional (CMRP) members in good standing, who have met specified achievement criteria, and have submitted an acceptable, original unpublished paper on a current aspect of materials management. – The requirements for Fellow are designed so that those who apply and attain this level must be persons of exceptional achievement as judged by their peers.
 Frequently Asked Questions Certification is valid for three years. What happens after that? – Renewal is obtained through 45 contact hours of continuing professional education or successful re-examination, at the option of the certificant.
Frequently Asked Questions Certification is valid for three years. What happens after that? – Renewal is obtained through 45 contact hours of continuing professional education or successful re-examination, at the option of the certificant.
 For Information Obtain a Candidate Handbook by: Visiting the AHA Certification Center at www. aha. org/certification; or Calling AMP (913 -541 -0400); or Visiting www. ahrmm. org.
For Information Obtain a Candidate Handbook by: Visiting the AHA Certification Center at www. aha. org/certification; or Calling AMP (913 -541 -0400); or Visiting www. ahrmm. org.
 Distinguish Yourself CMRP 300+ individuals have the CMRP designation and the number continues to rise monthly.
Distinguish Yourself CMRP 300+ individuals have the CMRP designation and the number continues to rise monthly.
 AHRMM 2006 Test • July 7 th Deadline to Register • August 16 th at 1: 30 pm @ ARHMM in Orlando • Laptop with Instant Feedback
AHRMM 2006 Test • July 7 th Deadline to Register • August 16 th at 1: 30 pm @ ARHMM in Orlando • Laptop with Instant Feedback
 Distinguish Yourself SUCCESSFUL CANDIDATES will be recognized at AHRMM’s Annual Conference, and a letter will be sent to candidate’s employer by the AHA-CC, if requested.
Distinguish Yourself SUCCESSFUL CANDIDATES will be recognized at AHRMM’s Annual Conference, and a letter will be sent to candidate’s employer by the AHA-CC, if requested.
 Purpose of CMRP Certification • Recognize individuals demonstrating a level of competency; proven value for employers • Encourage continued personal and professional growth in the practice. • Provide a national standard of requisite knowledge required for certification. Our Standard of Excellence – Be Proud of It
Purpose of CMRP Certification • Recognize individuals demonstrating a level of competency; proven value for employers • Encourage continued personal and professional growth in the practice. • Provide a national standard of requisite knowledge required for certification. Our Standard of Excellence – Be Proud of It
 Recognizing WSHMMA’s Own WASHINGTON • • • Jack Gallagher Kathi Pressley John Frasso Nancy Chester Tony Carrillo Adrian Cushman
Recognizing WSHMMA’s Own WASHINGTON • • • Jack Gallagher Kathi Pressley John Frasso Nancy Chester Tony Carrillo Adrian Cushman
 Recognizing WSHMMA’s Own OREGON • • • Valerie A. Bailey – Eugene Shanna Wray Oberbeck -- Eugene Tammie A. Shultz -- Eugene Brett E. Still -- Portland Kevin A. Swartout -- Portland
Recognizing WSHMMA’s Own OREGON • • • Valerie A. Bailey – Eugene Shanna Wray Oberbeck -- Eugene Tammie A. Shultz -- Eugene Brett E. Still -- Portland Kevin A. Swartout -- Portland


