e27779f9a1fcb17d4ec893928876d01e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 CMR Metadata Curation GCMD Science Coordinators GCSync Technical Tag up Meeting 2016 -01 -28
CMR Metadata Curation GCMD Science Coordinators GCSync Technical Tag up Meeting 2016 -01 -28
 Outline • • Metadata Curation Goals Roles and Responsibilities Metadata Curation Process Metadata Curation Tools Communication with Providers (Current) Communication with Providers (Future) Discussion Points Additional Details 2
Outline • • Metadata Curation Goals Roles and Responsibilities Metadata Curation Process Metadata Curation Tools Communication with Providers (Current) Communication with Providers (Future) Discussion Points Additional Details 2
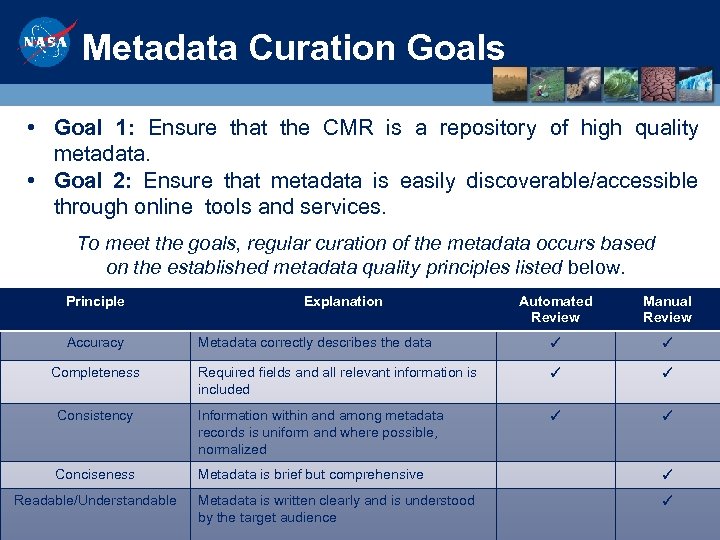 Metadata Curation Goals • Goal 1: Ensure that the CMR is a repository of high quality metadata. • Goal 2: Ensure that metadata is easily discoverable/accessible through online tools and services. To meet the goals, regular curation of the metadata occurs based on the established metadata quality principles listed below. Principle Automated Review Manual Review Metadata correctly describes the data ✓ ✓ Required fields and all relevant information is included ✓ ✓ Consistency Information within and among metadata records is uniform and where possible, normalized ✓ ✓ Conciseness Metadata is brief but comprehensive ✓ Metadata is written clearly and is understood by the target audience ✓ Accuracy Completeness Readable/Understandable Explanation 3
Metadata Curation Goals • Goal 1: Ensure that the CMR is a repository of high quality metadata. • Goal 2: Ensure that metadata is easily discoverable/accessible through online tools and services. To meet the goals, regular curation of the metadata occurs based on the established metadata quality principles listed below. Principle Automated Review Manual Review Metadata correctly describes the data ✓ ✓ Required fields and all relevant information is included ✓ ✓ Consistency Information within and among metadata records is uniform and where possible, normalized ✓ ✓ Conciseness Metadata is brief but comprehensive ✓ Metadata is written clearly and is understood by the target audience ✓ Accuracy Completeness Readable/Understandable Explanation 3
 Roles and Responsibilities • Metadata Providers: An individual or organization who submits metadata to the CMR that meets the standards as outlined in the Unified Metadata Model - Collections (UMM -C). Examples of providers: • EOSDIS Data Centers • CEOS IDN Partners • Individual PI’s • Science Coordinators (Sci. Ops Team): Responsible for the quality assessment and curation of collection level metadata in the CMR. 4
Roles and Responsibilities • Metadata Providers: An individual or organization who submits metadata to the CMR that meets the standards as outlined in the Unified Metadata Model - Collections (UMM -C). Examples of providers: • EOSDIS Data Centers • CEOS IDN Partners • Individual PI’s • Science Coordinators (Sci. Ops Team): Responsible for the quality assessment and curation of collection level metadata in the CMR. 4
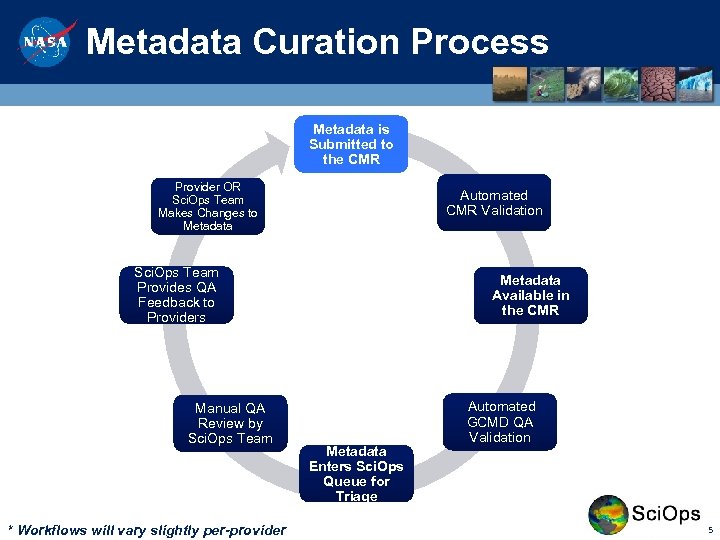 Metadata Curation Process Metadata is Submitted to the CMR Provider OR Sci. Ops Team Makes Changes to Metadata Automated CMR Validation Sci. Ops Team Provides QA Feedback to Providers Manual QA Review by Sci. Ops Team * Workflows will vary slightly per-provider Metadata Available in the CMR Metadata Enters Sci. Ops Queue for Triage Automated GCMD QA Validation 5
Metadata Curation Process Metadata is Submitted to the CMR Provider OR Sci. Ops Team Makes Changes to Metadata Automated CMR Validation Sci. Ops Team Provides QA Feedback to Providers Manual QA Review by Sci. Ops Team * Workflows will vary slightly per-provider Metadata Available in the CMR Metadata Enters Sci. Ops Queue for Triage Automated GCMD QA Validation 5
 Metadata Curation Process: Automated GCMD QA Validation • XML Validation (Similar to CMR validation): • Verifies syntax and enumerations • Inspects for required fields • Bulk QA Tool: • Checks QA rule compliance o Broken links, duplicate and invalid controlled vocabulary, field length constraints, numbers, dates, etc. • Generates QA score (used for triage) 6
Metadata Curation Process: Automated GCMD QA Validation • XML Validation (Similar to CMR validation): • Verifies syntax and enumerations • Inspects for required fields • Bulk QA Tool: • Checks QA rule compliance o Broken links, duplicate and invalid controlled vocabulary, field length constraints, numbers, dates, etc. • Generates QA score (used for triage) 6
 Metadata Curation Process: Manual QA Review Sci. Ops Team: • Examines the bulk QA tool report • Reviews field content for accuracy and any potential errors/discrepancies/omissions • Reviews controlled field values, including GCMD controlled vocabulary, to ensure content is consistent, accurate and suitable for the field • Review all content for completeness, conciseness, and readability • Confirm that URLs link to pertinent web pages and available data when applicable 7
Metadata Curation Process: Manual QA Review Sci. Ops Team: • Examines the bulk QA tool report • Reviews field content for accuracy and any potential errors/discrepancies/omissions • Reviews controlled field values, including GCMD controlled vocabulary, to ensure content is consistent, accurate and suitable for the field • Review all content for completeness, conciseness, and readability • Confirm that URLs link to pertinent web pages and available data when applicable 7
 Metadata Curation Process: Metadata Changes Scenario 1: Sci. Ops Team Provides Feedback to Metadata Provider • Metadata provider makes necessary changes and resubmits updated record to CMR. OR • Metadata provider sends Sci. Ops team information to make changes and submits updated record to CMR. Scenario 2: Sci. Ops Makes Changes • Sci. Ops team makes necessary changes, notifies the metadata provider, and submits updated record to CMR. 8
Metadata Curation Process: Metadata Changes Scenario 1: Sci. Ops Team Provides Feedback to Metadata Provider • Metadata provider makes necessary changes and resubmits updated record to CMR. OR • Metadata provider sends Sci. Ops team information to make changes and submits updated record to CMR. Scenario 2: Sci. Ops Makes Changes • Sci. Ops team makes necessary changes, notifies the metadata provider, and submits updated record to CMR. 8
 Metadata Curation Tools Bulk QA Tool: Automated QA Validation and Reporting doc. BUILDER: Metadata Editing and Ingest QA OPS: QA Viewer: Metadata Triage Single Record QA and Broken Link Reporting Controlled Vocabulary Adapter: Bulk Loader: Bulk Keyword Change Bulk Ingest of Metadata Keyword Management System (KMS): Keyword Curation and Access 9
Metadata Curation Tools Bulk QA Tool: Automated QA Validation and Reporting doc. BUILDER: Metadata Editing and Ingest QA OPS: QA Viewer: Metadata Triage Single Record QA and Broken Link Reporting Controlled Vocabulary Adapter: Bulk Loader: Bulk Keyword Change Bulk Ingest of Metadata Keyword Management System (KMS): Keyword Curation and Access 9
 Communication with Providers (Now) Metadata Curation • Jira • Email Keyword Changes • Email announcements • Website release notes Curation Software Changes • Email announcements • Website release notes 10
Communication with Providers (Now) Metadata Curation • Jira • Email Keyword Changes • Email announcements • Website release notes Curation Software Changes • Email announcements • Website release notes 10
 Communication with Providers (Future) Metadata Curation • Jira • Email/Kayako • Automated Notification Service (Changes to Records) Keyword Changes • Website release notes • Unified list serve email (focus on curation) • Automated Notification Service (Changes to Keywords) • UTC Telecons • Earthdata Wiki Curation Software Changes • • Website release notes Unified list serve email (focus on curation) UTC Telecons Earthdata Wiki 11
Communication with Providers (Future) Metadata Curation • Jira • Email/Kayako • Automated Notification Service (Changes to Records) Keyword Changes • Website release notes • Unified list serve email (focus on curation) • Automated Notification Service (Changes to Keywords) • UTC Telecons • Earthdata Wiki Curation Software Changes • • Website release notes Unified list serve email (focus on curation) UTC Telecons Earthdata Wiki 11
 Discussion Points • • • Providers that don’t update their internal metadatabase Tools need to keep up with metadata formats When changes to collections affect granules Means to publish and exchange QA rules Additional communication with ESDIS 12
Discussion Points • • • Providers that don’t update their internal metadatabase Tools need to keep up with metadata formats When changes to collections affect granules Means to publish and exchange QA rules Additional communication with ESDIS 12
 Additional Details 13
Additional Details 13
 QA Rules • A QA Rule is a check that is applied to content within a field of a metadata record (across formats) to assess quality. • Rules are objective, transparent, well structured, and available for download. • Checks include • • • GCMD Controlled Vocabulary Use URL Validity Field Lengths Uniqueness Required Fields Populated • Customizable for different providers that require a higherlevel of QA assessment. • QA rules for GES DISC are currently being drafted 14
QA Rules • A QA Rule is a check that is applied to content within a field of a metadata record (across formats) to assess quality. • Rules are objective, transparent, well structured, and available for download. • Checks include • • • GCMD Controlled Vocabulary Use URL Validity Field Lengths Uniqueness Required Fields Populated • Customizable for different providers that require a higherlevel of QA assessment. • QA rules for GES DISC are currently being drafted 14
 Rule Development Rules are driven by: • Metadata Formats (DIF, ECHO, ISO) o Example: ‘Controlled Vocabulary Check’ can check that valid GCMD keywords are being used. • Metadata Models (UMM-C) o Example: ‘Required Field Check’ can check that there is content for a required field, i. e. , required by the UMM-C model or by the metadata format. • System Requirements (GCMD, CMR) o Example: ‘Max Field Length Check’ can check that a string is within a designated character length. • Experience o Example: ‘Non-identical Field Check’ can encourage a metadata author to provide a descriptive title, rather than just repeating the Entry. ID. 15
Rule Development Rules are driven by: • Metadata Formats (DIF, ECHO, ISO) o Example: ‘Controlled Vocabulary Check’ can check that valid GCMD keywords are being used. • Metadata Models (UMM-C) o Example: ‘Required Field Check’ can check that there is content for a required field, i. e. , required by the UMM-C model or by the metadata format. • System Requirements (GCMD, CMR) o Example: ‘Max Field Length Check’ can check that a string is within a designated character length. • Experience o Example: ‘Non-identical Field Check’ can encourage a metadata author to provide a descriptive title, rather than just repeating the Entry. ID. 15
 Rule Categories • Link Rules: Applied to fields that are or may contain links to an external source in the metadata. • Character Rules: Applied to the number, type, or pattern of characters that are allowed within a field. • Date Rules: Applied to date fields to check that dates are in the proper format. • Numeric Rules: Applied to fields where the content should be or include a numeric value. • Controlled Vocabulary Rules: Applied to content of the field to check that it matches a valid keyword, either by comparing to an author-provided list or to an external source (i. e. KMS). Miscellaneous Rules: Applies other various rules such as exists checks and suffix checks. 16
Rule Categories • Link Rules: Applied to fields that are or may contain links to an external source in the metadata. • Character Rules: Applied to the number, type, or pattern of characters that are allowed within a field. • Date Rules: Applied to date fields to check that dates are in the proper format. • Numeric Rules: Applied to fields where the content should be or include a numeric value. • Controlled Vocabulary Rules: Applied to content of the field to check that it matches a valid keyword, either by comparing to an author-provided list or to an external source (i. e. KMS). Miscellaneous Rules: Applies other various rules such as exists checks and suffix checks. 16
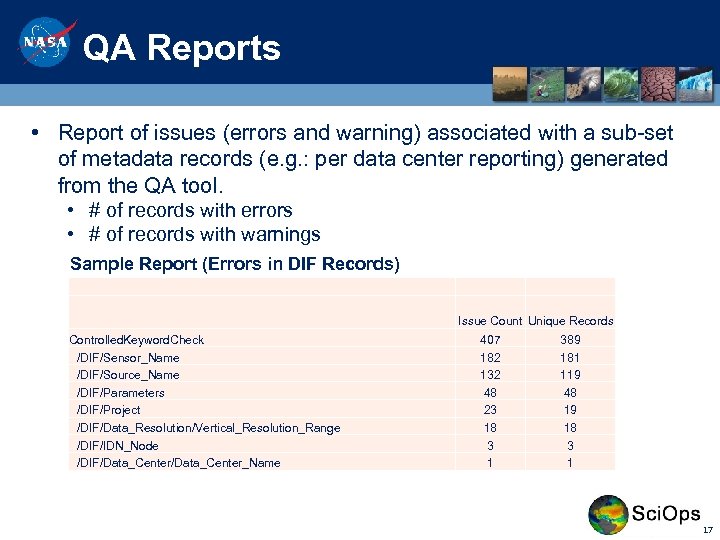 QA Reports • Report of issues (errors and warning) associated with a sub-set of metadata records (e. g. : per data center reporting) generated from the QA tool. • # of records with errors • # of records with warnings Sample Report (Errors in DIF Records) Issue Count Unique Records Controlled. Keyword. Check /DIF/Sensor_Name /DIF/Source_Name /DIF/Parameters /DIF/Project /DIF/Data_Resolution/Vertical_Resolution_Range /DIF/IDN_Node /DIF/Data_Center_Name 407 182 132 48 23 18 3 1 389 181 119 48 19 18 3 1 17
QA Reports • Report of issues (errors and warning) associated with a sub-set of metadata records (e. g. : per data center reporting) generated from the QA tool. • # of records with errors • # of records with warnings Sample Report (Errors in DIF Records) Issue Count Unique Records Controlled. Keyword. Check /DIF/Sensor_Name /DIF/Source_Name /DIF/Parameters /DIF/Project /DIF/Data_Resolution/Vertical_Resolution_Range /DIF/IDN_Node /DIF/Data_Center_Name 407 182 132 48 23 18 3 1 389 181 119 48 19 18 3 1 17
 Reference Links • Metadata Curation Con. Ops ‘Draft’ (2015 -01 -12) • https: //wiki. earthdata. nasa. gov/download/attachments/41615882/Metadata%20 Quality%20 Revi ew%20 Life%20 Cycle%20 Doc%20%2012%20 Jan%202015. docx? version=1&modification. Date=1421090966604&api=v 2 • Keyword Community Guide Document ‘Draft’ (2015 -07 -23) • https: //wiki. earthdata. nasa. gov/display/CMR/GCMD+Keyword+Documents • doc. BUILDER • http: //gcmd. nasa. gov/collaborate/docbuilder • QA Viewer • http: //gcmddemo. gsfc. nasa. gov/qaviewer/QAViewer 18
Reference Links • Metadata Curation Con. Ops ‘Draft’ (2015 -01 -12) • https: //wiki. earthdata. nasa. gov/download/attachments/41615882/Metadata%20 Quality%20 Revi ew%20 Life%20 Cycle%20 Doc%20%2012%20 Jan%202015. docx? version=1&modification. Date=1421090966604&api=v 2 • Keyword Community Guide Document ‘Draft’ (2015 -07 -23) • https: //wiki. earthdata. nasa. gov/display/CMR/GCMD+Keyword+Documents • doc. BUILDER • http: //gcmd. nasa. gov/collaborate/docbuilder • QA Viewer • http: //gcmddemo. gsfc. nasa. gov/qaviewer/QAViewer 18


