6a98b899b12bdbc4ded6af14505e66e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 CMPSC 201 - Spring 2017 Lecture 1 January 9, 2017
CMPSC 201 - Spring 2017 Lecture 1 January 9, 2017
 Welcome to CMPSC 201
Welcome to CMPSC 201
 Instructor Ø Dr. Susan L. Quick Ø Office: 111 J IST building Ø Phone: 865 -9507 Ø e-mail: quick@cse. psu. edu or CANVAS (do not use any other e-mail!) Ø Office hours: M 3: 45 – 5: 30 pm and W 11: 00 am – 1: 30 pm or by appointment (request should be made by noon of the preceding day). Appointments are generally reserved for those students who have classes during my office hours.
Instructor Ø Dr. Susan L. Quick Ø Office: 111 J IST building Ø Phone: 865 -9507 Ø e-mail: quick@cse. psu. edu or CANVAS (do not use any other e-mail!) Ø Office hours: M 3: 45 – 5: 30 pm and W 11: 00 am – 1: 30 pm or by appointment (request should be made by noon of the preceding day). Appointments are generally reserved for those students who have classes during my office hours.
 TAs Ø Yanjun Gao Ø Yu-Tsung Lee Ø Srikumar Sridhar
TAs Ø Yanjun Gao Ø Yu-Tsung Lee Ø Srikumar Sridhar
 Course Expectations Ø No previous programming experience is expected. Ø However, do expect you to be familiar with windows, know how to save files, know how to use folders and subfolders. Ø I will also expect you to read the book, answer the problems in the book (see syllabus), and attend lecture. Ø Take notes. Ø Spend at 6 – 9 (or more) hours per week, reading book, practicing examples, doing problems from book, etc.
Course Expectations Ø No previous programming experience is expected. Ø However, do expect you to be familiar with windows, know how to save files, know how to use folders and subfolders. Ø I will also expect you to read the book, answer the problems in the book (see syllabus), and attend lecture. Ø Take notes. Ø Spend at 6 – 9 (or more) hours per week, reading book, practicing examples, doing problems from book, etc.
 Copies of Lecture Notes Ø Copies of the lectures will usually be posted on CANVAS prior to class. Ø You should be prepared to take additional notes. Ø You should still read the sections in the textbook that pertaining to a lecture before you come to class (refer to the Tentative Schedule posted on CANVAS).
Copies of Lecture Notes Ø Copies of the lectures will usually be posted on CANVAS prior to class. Ø You should be prepared to take additional notes. Ø You should still read the sections in the textbook that pertaining to a lecture before you come to class (refer to the Tentative Schedule posted on CANVAS).
 Computer Use Ø C++ is part Microsoft Visual Studio and is available in this lab or any of the ITS labs across campus. Ø It is recommended that you buy a USB drive (jump drive, flash drive, etc. ) to store your programs.
Computer Use Ø C++ is part Microsoft Visual Studio and is available in this lab or any of the ITS labs across campus. Ø It is recommended that you buy a USB drive (jump drive, flash drive, etc. ) to store your programs.
 Places to Get Visual Studio Ø Two places where you may be able to get a copy of Visual Studio are http: //www. microsoft. com/express/downloads/ http: //dreamspark. com Ø Please note that these versions may not operate exactly the same as the full version. (You will be graded on how your programs run with the full version). Ø I will not provide any support on installing or using these versions.
Places to Get Visual Studio Ø Two places where you may be able to get a copy of Visual Studio are http: //www. microsoft. com/express/downloads/ http: //dreamspark. com Ø Please note that these versions may not operate exactly the same as the full version. (You will be graded on how your programs run with the full version). Ø I will not provide any support on installing or using these versions.
 Grades Ø Labs – short C++ programs that you complete during designated class times. Ø In-class participation – use of iclickers, during M-W lectures. Ø Algorithms – You will create MSword documents defining a problem in your own words. Ø Homework Projects – longer C++ programs that you write to complete a task. Ø Exams – test how well you can read/understand code, know definitions, write code Ø See syllabus for grade breakdown
Grades Ø Labs – short C++ programs that you complete during designated class times. Ø In-class participation – use of iclickers, during M-W lectures. Ø Algorithms – You will create MSword documents defining a problem in your own words. Ø Homework Projects – longer C++ programs that you write to complete a task. Ø Exams – test how well you can read/understand code, know definitions, write code Ø See syllabus for grade breakdown
 In-Class Labs Ø Classes Fridays will be used for completing assignments called labs. Ø Labs submitted after the deadline announced in class will be given a zero. Ø Keep up with the concepts that have been discussed by reading textbook, completing checkpoint exercises and review questions in book. Ø In general these must be completed in the classroom. Ø Do NOT wait until last 10 minutes to ask for help!
In-Class Labs Ø Classes Fridays will be used for completing assignments called labs. Ø Labs submitted after the deadline announced in class will be given a zero. Ø Keep up with the concepts that have been discussed by reading textbook, completing checkpoint exercises and review questions in book. Ø In general these must be completed in the classroom. Ø Do NOT wait until last 10 minutes to ask for help!
 Grade Maintenance Ø You should submit your work to assignments on CANVAS. Ø Take the time to confirm your submission. No consideration will be given to submissions of incorrect files.
Grade Maintenance Ø You should submit your work to assignments on CANVAS. Ø Take the time to confirm your submission. No consideration will be given to submissions of incorrect files.
 Academic Honesty Ø You may talk with each other for the in-class labs, but each of you should turn in a completed lab assignment that is unique for you. Ø You may be allowed to work with one other person from your section on some assignments and projects as noted on the writeup. Otherwise your projects should be your own work. Ø Searching the internet for solutions to labs or projects is considered a violation of academic integrity Ø If you receive help from anyone other myself, you should document this help in your program. Ø You are expected to complete the exams on your own.
Academic Honesty Ø You may talk with each other for the in-class labs, but each of you should turn in a completed lab assignment that is unique for you. Ø You may be allowed to work with one other person from your section on some assignments and projects as noted on the writeup. Otherwise your projects should be your own work. Ø Searching the internet for solutions to labs or projects is considered a violation of academic integrity Ø If you receive help from anyone other myself, you should document this help in your program. Ø You are expected to complete the exams on your own.
 "Perhaps the most valuable result of all education is the ability to make yourself do the thing you have to do, when it ought to be done, whether you like it or not. " -Thomas Huxley “Thinking is the hardest work there is, which is the probable reason so few engage in it. ” -Henry Ford “Intelligence is learning from one’s own mistakes, wisdom is learning from mistakes of others. ”
"Perhaps the most valuable result of all education is the ability to make yourself do the thing you have to do, when it ought to be done, whether you like it or not. " -Thomas Huxley “Thinking is the hardest work there is, which is the probable reason so few engage in it. ” -Henry Ford “Intelligence is learning from one’s own mistakes, wisdom is learning from mistakes of others. ”
 Questions About the Class Ø There may not be things as “stupid” questions, but there are “unthinking” questions. Ø Questions for which you can find the answer from the syllabus, tentative schedule, problem writeup, etc are stupid questions. For example, ØWhen are your office hours? ØWhen is the assignment due? ØWhat chapter are we on? Ø Questions about C++ programming are rarely “stupid” or “unthinking” questions as long as you are trying and using the resources you have been given.
Questions About the Class Ø There may not be things as “stupid” questions, but there are “unthinking” questions. Ø Questions for which you can find the answer from the syllabus, tentative schedule, problem writeup, etc are stupid questions. For example, ØWhen are your office hours? ØWhen is the assignment due? ØWhat chapter are we on? Ø Questions about C++ programming are rarely “stupid” or “unthinking” questions as long as you are trying and using the resources you have been given.
 Show Initiative Ø Your programs will build upon and incorporate concepts presented earlier in class, in other assignments, in the book, in demo programs posted on CANVAS. Ø If you forget how to employ concepts that have been covered earlier, try reviewing previous assignments, demo programs, lecture notes, etc. Ø Keep a record of error messages and what you did to correct them so when you encounter them again you have a reference.
Show Initiative Ø Your programs will build upon and incorporate concepts presented earlier in class, in other assignments, in the book, in demo programs posted on CANVAS. Ø If you forget how to employ concepts that have been covered earlier, try reviewing previous assignments, demo programs, lecture notes, etc. Ø Keep a record of error messages and what you did to correct them so when you encounter them again you have a reference.
 Class Attendance Ø Is mandatory on Mondays and Wednesdays Ø During lecture time, you should be listening, taking notes, asking appropriate questions, participating, etc. Ø You are responsible for any and all announcements made during class time, even if they are never posted on CANVAS. Ø After the first lab, labs will be posted by noon the previous day and you will not have to attend class on Friday if you can complete the assignment on your own. (This policy is subject to change. )
Class Attendance Ø Is mandatory on Mondays and Wednesdays Ø During lecture time, you should be listening, taking notes, asking appropriate questions, participating, etc. Ø You are responsible for any and all announcements made during class time, even if they are never posted on CANVAS. Ø After the first lab, labs will be posted by noon the previous day and you will not have to attend class on Friday if you can complete the assignment on your own. (This policy is subject to change. )
 Extra Credit Ø 10 points of easy extra credit. Ø Come to see me in my office during office hours or by appointment before 3/1/17.
Extra Credit Ø 10 points of easy extra credit. Ø Come to see me in my office during office hours or by appointment before 3/1/17.
 Questions ? ? ?
Questions ? ? ?
 What is an engineer ?
What is an engineer ?
 What is a Computer? Ø A programmable electronic device that canc store, retrieve and process data. Ø Tool that makes a job easier Ø Advantages ØReliable ØFast ØDoes not tire ØFollows instructions (programs) precisely Ø Disadvantages ØNot “smart”– cannot analyze problems ØFollows instructions (programs) precisely
What is a Computer? Ø A programmable electronic device that canc store, retrieve and process data. Ø Tool that makes a job easier Ø Advantages ØReliable ØFast ØDoes not tire ØFollows instructions (programs) precisely Ø Disadvantages ØNot “smart”– cannot analyze problems ØFollows instructions (programs) precisely
 What can a computer do? Ø Simple arithmetic Ø Comparisons/decision making Ø Communication-input, output, transfer of data.
What can a computer do? Ø Simple arithmetic Ø Comparisons/decision making Ø Communication-input, output, transfer of data.
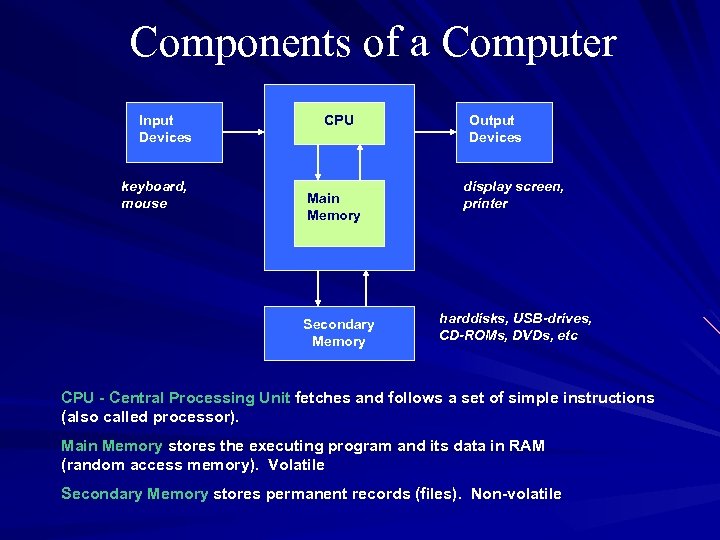 Components of a Computer Input Devices keyboard, mouse CPU Main Memory Secondary Memory Output Devices display screen, printer harddisks, USB-drives, CD-ROMs, DVDs, etc CPU - Central Processing Unit fetches and follows a set of simple instructions (also called processor). Main Memory stores the executing program and its data in RAM (random access memory). Volatile Secondary Memory stores permanent records (files). Non-volatile
Components of a Computer Input Devices keyboard, mouse CPU Main Memory Secondary Memory Output Devices display screen, printer harddisks, USB-drives, CD-ROMs, DVDs, etc CPU - Central Processing Unit fetches and follows a set of simple instructions (also called processor). Main Memory stores the executing program and its data in RAM (random access memory). Volatile Secondary Memory stores permanent records (files). Non-volatile
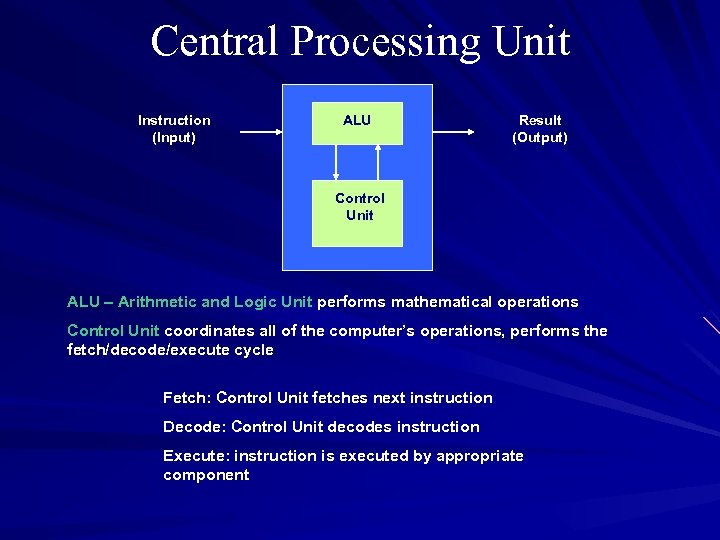 Central Processing Unit Instruction (Input) ALU Result (Output) Control Unit ALU – Arithmetic and Logic Unit performs mathematical operations Control Unit coordinates all of the computer’s operations, performs the fetch/decode/execute cycle Fetch: Control Unit fetches next instruction Decode: Control Unit decodes instruction Execute: instruction is executed by appropriate component
Central Processing Unit Instruction (Input) ALU Result (Output) Control Unit ALU – Arithmetic and Logic Unit performs mathematical operations Control Unit coordinates all of the computer’s operations, performs the fetch/decode/execute cycle Fetch: Control Unit fetches next instruction Decode: Control Unit decodes instruction Execute: instruction is executed by appropriate component
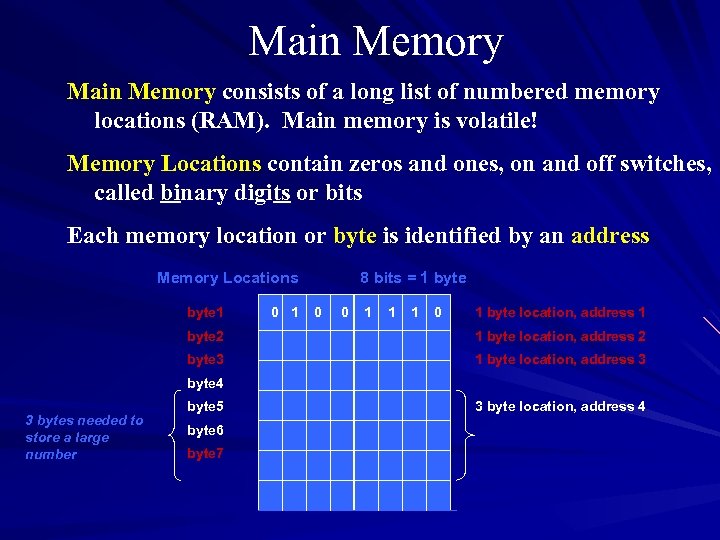 Main Memory consists of a long list of numbered memory locations (RAM). Main memory is volatile! Memory Locations contain zeros and ones, on and off switches, called binary digits or bits Each memory location or byte is identified by an address Memory Locations byte 1 0 1 8 bits = 1 byte 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 byte location, address 1 byte 2 1 byte location, address 2 byte 3 1 byte location, address 3 byte 4 3 bytes needed to store a large number byte 5 byte 6 byte 7 3 byte location, address 4
Main Memory consists of a long list of numbered memory locations (RAM). Main memory is volatile! Memory Locations contain zeros and ones, on and off switches, called binary digits or bits Each memory location or byte is identified by an address Memory Locations byte 1 0 1 8 bits = 1 byte 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 byte location, address 1 byte 2 1 byte location, address 2 byte 3 1 byte location, address 3 byte 4 3 bytes needed to store a large number byte 5 byte 6 byte 7 3 byte location, address 4
 Secondary Memory Ø Uses same idea of bits and bytes Ø Programs/data stored in units called files. Ø Stores files when they are not in use Ø Non-volatile Ø Examples: ØHard drives ØCDs & DVDs ØUSB drives (jump, flash, thumb, stick, etc. )
Secondary Memory Ø Uses same idea of bits and bytes Ø Programs/data stored in units called files. Ø Stores files when they are not in use Ø Non-volatile Ø Examples: ØHard drives ØCDs & DVDs ØUSB drives (jump, flash, thumb, stick, etc. )
 Software Ø Operating Systems – allocates computer’s resources and allows communication between user and computer. ØUNIX, DOS, Linux, Windows, VMS, etc. Ø Programs – set of instructions to perform specific tasks. Program Data Computer Output - Information
Software Ø Operating Systems – allocates computer’s resources and allows communication between user and computer. ØUNIX, DOS, Linux, Windows, VMS, etc. Ø Programs – set of instructions to perform specific tasks. Program Data Computer Output - Information
 Algorithm vs. Program Ø Algorithm - set of well-defined steps for performing a task or solving a problem Ø Program – A set of instructions a computer follows to perform a task. An algorithm that has been translated into a programming language so the computer can “understand” and perform the steps. Ø Programming Language – special language used to write programs.
Algorithm vs. Program Ø Algorithm - set of well-defined steps for performing a task or solving a problem Ø Program – A set of instructions a computer follows to perform a task. An algorithm that has been translated into a programming language so the computer can “understand” and perform the steps. Ø Programming Language – special language used to write programs.
 Questions Ø Read Chapter 1 in the book Ø Work through the Checkpoint problems, throughout the chapters, the Review Questions and Exercises at the end of the chapter. (Please note answers to Checkpoint and some Review Questions are given on-line. ) Ø Read material posted on CANVAS (Course Description, Tentative Schedule, etc. )
Questions Ø Read Chapter 1 in the book Ø Work through the Checkpoint problems, throughout the chapters, the Review Questions and Exercises at the end of the chapter. (Please note answers to Checkpoint and some Review Questions are given on-line. ) Ø Read material posted on CANVAS (Course Description, Tentative Schedule, etc. )


