efe9c817a834876cdb2cff8dd79c257b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

Cmpe 472 Wireless Internet and M-business

Introduction • Wireless technology turns e-business into m-business, or mobile business • Internet+wireless+e-business = M-Business – Going on-line anywhere at anytime and using multiple devices – New business opportunities • Exponential growth (keeps growing) – No of mobile internet service users: 1 bn by 2004 (the Economist 2001).

Characteristics of M-business • Ubiquitous computing – Anywhere, any time – Conveninet, instant connectivity • Very personal – Device owner has an exclusive access to the contents/ services – Service providers know who the owner is • Varied users, usage contexts – Elementary school students, parents, old people – Location and context-sensitive apps and services – Work-play: business purpoes and personal fun • People seem willing to pay for mobile services

Drivers of M-business • High mobile phone penetration: 18 mm subscribers (Finland: 80%, HK: 90%) • Convergence of the internet and the mobile devices • Improvements in technology (bandwidth, device functionalities): transition to the 3 rd generation • Declining prices: device, service prices • Explosion of e-commerce in general: more opportunities available on-line, i. e. , more opportunities for m-business • M-business based on mobile devices can help developing countries fill the gap of digital divide: – More internet users in China than the US by 2005.

M-business Applications • Current applications – Conduct on-line transactions – Make purchases – Send e-mail • Future applications – A wireless office – In-hand, on-the-go entertainment – Migration from a PC-centric to a multi-device model

Wireless Devices • Wireless development – First-generation wireless technology was the cellular phone – Second generation wireless technology, which includes digital cellular phones, is currently in use worldwide – Third generation (3 G) technology will enable wireless devices to send and receive data as much as seven times faster than a standard 56 K modem (0. 4 to 2 m bps) • Wireless devices – Personal digital assisstants (PDAs) – Digital cellular phones – Two-way pagers, laptops, . . .
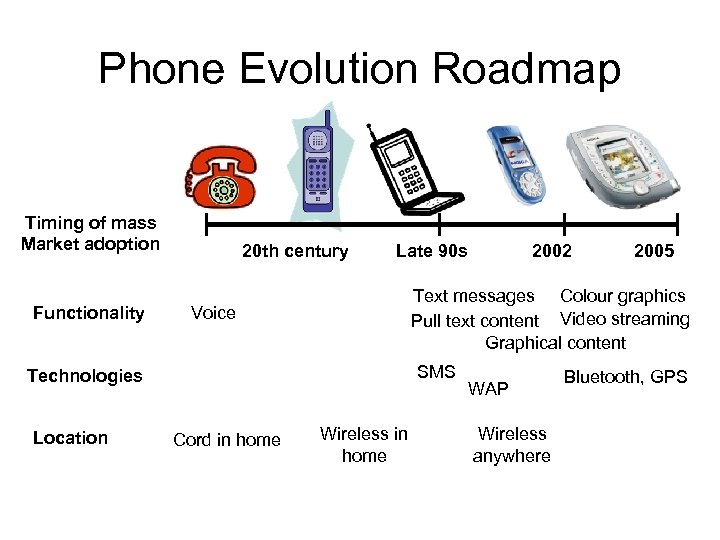
Phone Evolution Roadmap Timing of mass Market adoption Functionality 20 th century Late 90 s Voice SMS Cord in home 2005 Text messages Colour graphics Pull text content Video streaming Graphical content Technologies Location 2002 Wireless in home WAP Wireless anywhere Bluetooth, GPS

Information Appliances • Clear trend for the convergence of several mobile devices including intelligent home appliances • PDA phone: PDA + cell phone • Phones with MP 3 player, voice recorder, digital camera, GPS • Wireless control of refrigerator, TV, DVD through a cell phone

Key Characteristics of Wireless Device • Ubiquitous interactivity – Personal device: always handy and available at all times on a person – User identity: the device carries its user identity; distinctly personal and the usage can be tracked down to an individual rather than households (e. g. PC) • Location aware – Easy to track down where the user physically is as long as the wireless device is on (using GPS) – Important marketing implications
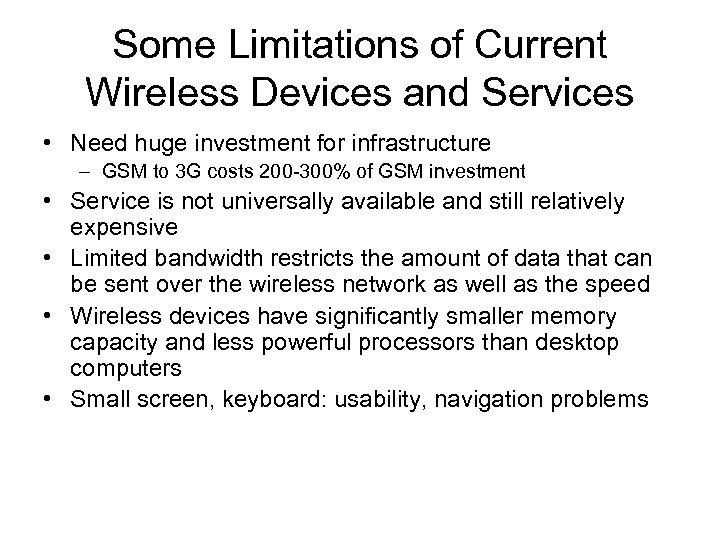
Some Limitations of Current Wireless Devices and Services • Need huge investment for infrastructure – GSM to 3 G costs 200 -300% of GSM investment • Service is not universally available and still relatively expensive • Limited bandwidth restricts the amount of data that can be sent over the wireless network as well as the speed • Wireless devices have significantly smaller memory capacity and less powerful processors than desktop computers • Small screen, keyboard: usability, navigation problems

Some Limitations of Current Wireless Devices and Services (cont’d) • • • Lack of contents Rapidly developing standards Legacy of wire-line internet Security (viruses, tapping, hacking) Safety (radiation, brain cancer? ) However, wireless technology is growing rapidly

Wireless Access • International Telecommunications Union (ITU) definition: – Wireless access is an application of radio technology and personal communication systems. The key characteristic of wireless access is the use of a multiple access radio system instead of wires (e. g. copper or coaxial cables) in the distribution/ access network. – Wireless channel: between users/ terminals and wireless networks.

Limited Wireless Communication Channels • Frequency assigned to wireless communication is limited • Explosive growth of demand • Critical qustion: find more efficient ways of using the assigned frequency band so that multiple users can gain simultaneous accesses • What technology manipulates: three dimensions (space, frequency, time) • SDMA, FDMA, TDMA, CDMA

Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) • Frequency reuse • A covered area (e. g. Bebek) is divided into many small cells • A channel (frequency band) used in one cell to be reused by a different user in another cell as long as there is ENOUGH SEPARATION between the two cells to minimise interference
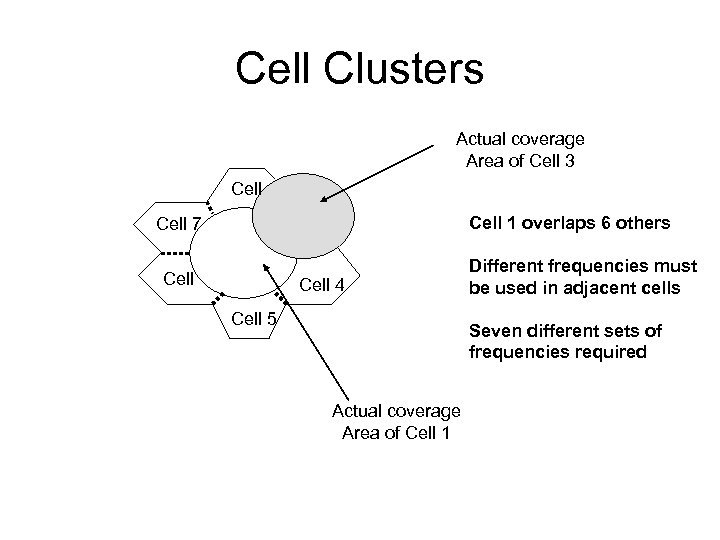
Cell Clusters Actual coverage Area of Cell 3 Cell 1 overlaps 6 others Cell 7 Cell 4 Cell 5 Different frequencies must be used in adjacent cells Seven different sets of frequencies required Actual coverage Area of Cell 1
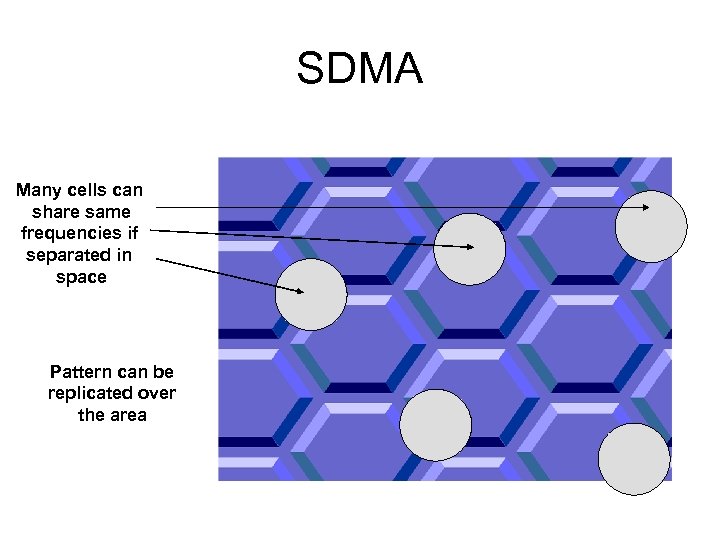
SDMA Many cells can share same frequencies if separated in space Pattern can be replicated over the area
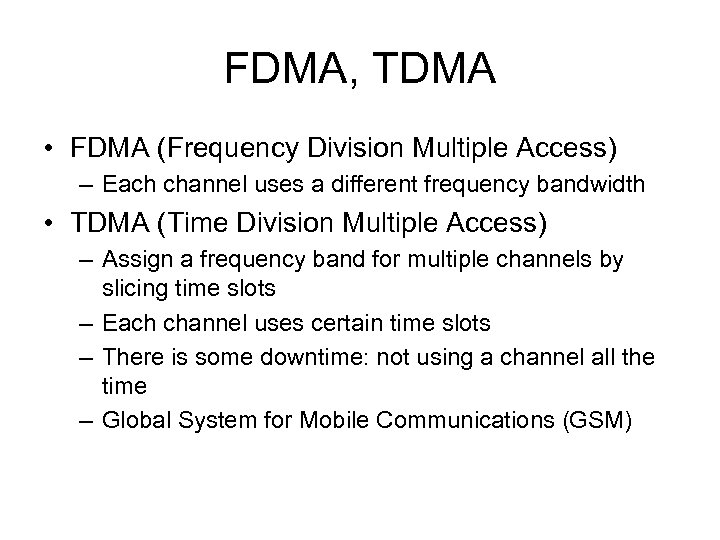
FDMA, TDMA • FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) – Each channel uses a different frequency bandwidth • TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) – Assign a frequency band for multiple channels by slicing time slots – Each channel uses certain time slots – There is some downtime: not using a channel all the time – Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)

CDMA • CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) – Assign a large frequency band for multiple channels – Calls are split into packets and the packets are tagged with identifying codes – Often in the format of FDMA+CDMA – Considered most efficient; creating capacity triple that of comparable TDMA – Generally CDMA>TDMA>FDMA
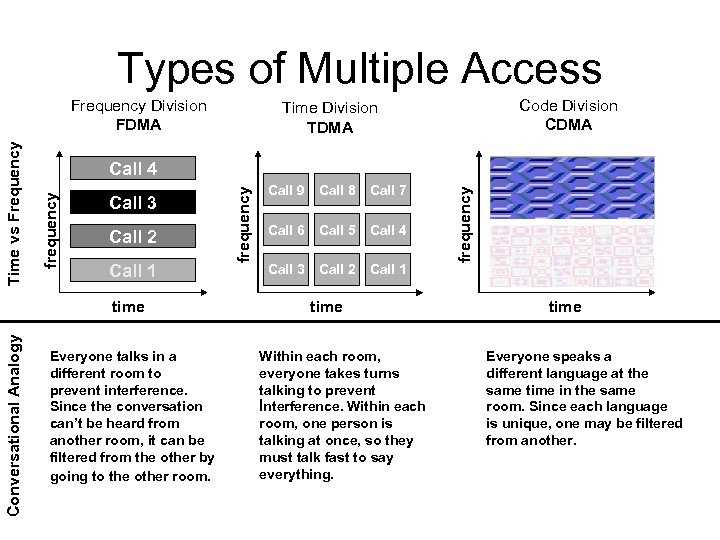
Types of Multiple Access Call 1 Everyone talks in a different room to prevent interference. Since the conversation can’t be heard from another room, it can be filtered from the other by going to the other room. Call 9 Call 8 Call 7 Call 6 Call 5 Call 4 Call 3 Call 2 Call 1 time Within each room, everyone takes turns talking to prevent İnterference. Within each room, one person is talking at once, so they must talk fast to say everything. frequency Call 2 frequency Call 3 time Conversational Analogy Code Division CDMA Time Division TDMA Call 4 frequency Time vs Frequency Division FDMA time Everyone speaks a different language at the same time in the same room. Since each language is unique, one may be filtered from another.
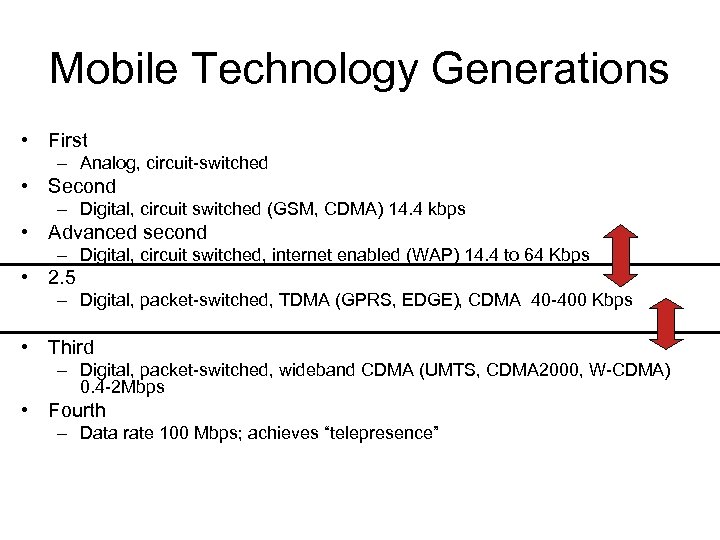
Mobile Technology Generations • First – Analog, circuit-switched • Second – Digital, circuit switched (GSM, CDMA) 14. 4 kbps • Advanced second – Digital, circuit switched, internet enabled (WAP) 14. 4 to 64 Kbps • 2. 5 – Digital, packet-switched, TDMA (GPRS, EDGE), CDMA 40 -400 Kbps • Third – Digital, packet-switched, wideband CDMA (UMTS, CDMA 2000, W-CDMA) 0. 4 -2 Mbps • Fourth – Data rate 100 Mbps; achieves “telepresence”
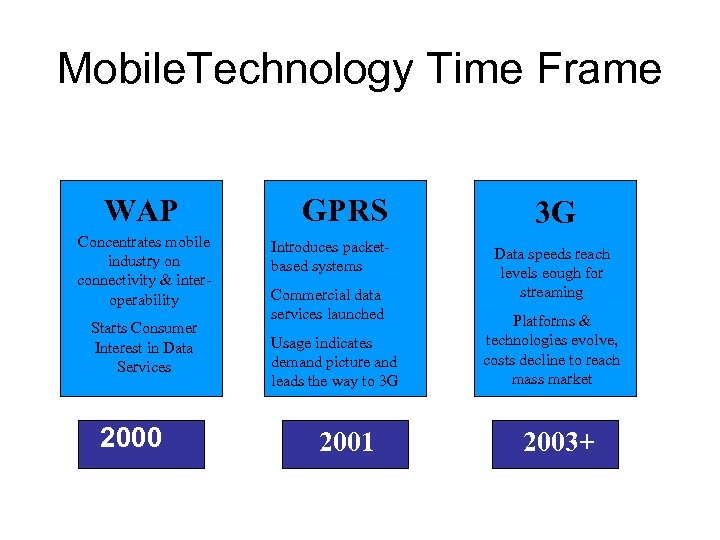
Mobile. Technology Time Frame WAP Concentrates mobile industry on connectivity & interoperability Starts Consumer Interest in Data Services 2000 GPRS Introduces packetbased systems Commercial data services launched Usage indicates demand picture and leads the way to 3 G 2001 3 G Data speeds reach levels eough for streaming Platforms & technologies evolve, costs decline to reach mass market 2003+

Glossary • 2 G: second generation technology category for digital cellular networks • 2. 5 G: umbrella term for technologies designed to add 3 G capabilities to existing cellular networks • 3 G: new digital cellular network technology designed to enable very fast data transmission speeds and delivery of multimedia content.

Glossary (Cont’d) • AMPS: advanced mobile phone service, analog cellular network system used in the US • EDGE: enhanced data rate for GSM evolution, an enhancement to bring the data-transmission rate of TDMA network up to the speed of basic 3 G networks (2. 5 G) • GPRS: general packet radio services, an enhancement designed to introduce packetswitching to GSM networks (2. 5 G).

Glossary (Cont’d) • ITU: international telecommunication union, the standards body of the telecom industry • IMT-2000: international mobile telecommunications 2000, an ITU initiative aimed at harmonising the various efforts under way to create 3 G networks • CDMA 2000: an implementation of wideband CDMA backed by the US and Korea; a 3 G network type

Glossary (Cont’d) • SMS: short message service, a means of conveying messages upto 160 characters long to and from GSM cell phones • WCDMA: an implementation of wideband CDMA supported by Europe and Japan; a 3 G network type; also known as UMTS (universal mobile telecommunications service) in Europe • Cdma 2000 and WCDMA share basic technology (CDMA). WCDMA marks a break in technology for GSM network operators, whereas cdma 200 isa logical development for CDMA networks.
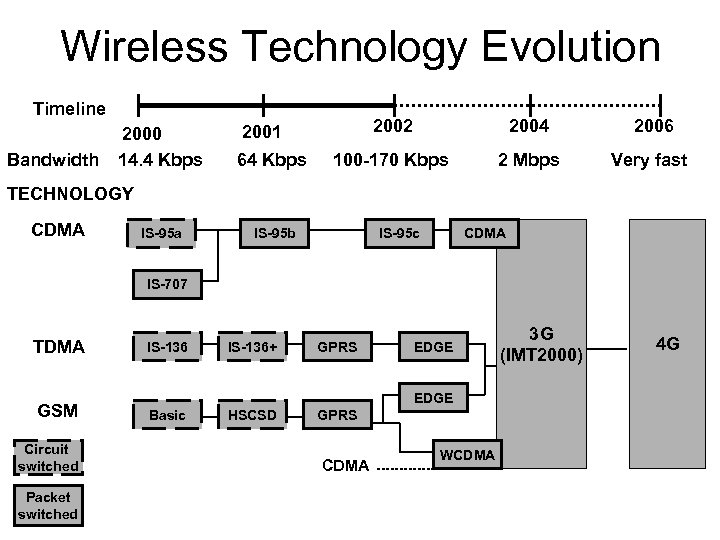
Wireless Technology Evolution Timeline Bandwidth 2000 14. 4 Kbps 2002 2004 2006 100 -170 Kbps 2 Mbps Very fast 2001 64 Kbps TECHNOLOGY CDMA IS-95 a IS-95 b IS-95 c CDMA IS-707 TDMA GSM Circuit switched Packet switched IS-136+ GPRS EDGE Basic HSCSD GPRS CDMA WCDMA 3 G (IMT 2000) 4 G

CDMA 2000 vs WCDMA • WCDMA (Europe and Japan) vs CDMA 2000 (US and Korea) • WCDMA seemed to be the de-facto standard only 2 -3 years ago, but things changed • CDMA 2000 increases its market share fast (50% increase for the last 3 years) • Two representative 3 G services available now – Japan (FOMA: freedom of mobile multimedia access) – Korea: (CDMA 2000 1 x. EV-DO: evolution-data optimised)

M-business • E-business using wireless devices with internet access • New possibilities for commerce beyond internet access • Enormous potential in many areas (B 2 C, B 2 B) • Currently B 2 C wireless apps are more rapidly emerging

New Competition, New Opportunities • Wireless technology is attracting interest from virtually every industry, creating interesting competitive and partnership opportunities – Mobile service providers vs banks – Automotive multimedia m-commerce apps
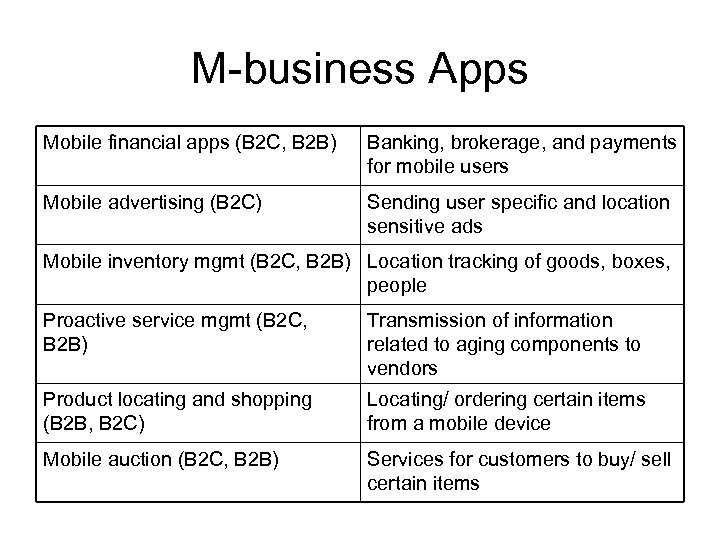
M-business Apps Mobile financial apps (B 2 C, B 2 B) Banking, brokerage, and payments for mobile users Mobile advertising (B 2 C) Sending user specific and location sensitive ads Mobile inventory mgmt (B 2 C, B 2 B) Location tracking of goods, boxes, people Proactive service mgmt (B 2 C, B 2 B) Transmission of information related to aging components to vendors Product locating and shopping (B 2 B, B 2 C) Locating/ ordering certain items from a mobile device Mobile auction (B 2 C, B 2 B) Services for customers to buy/ sell certain items
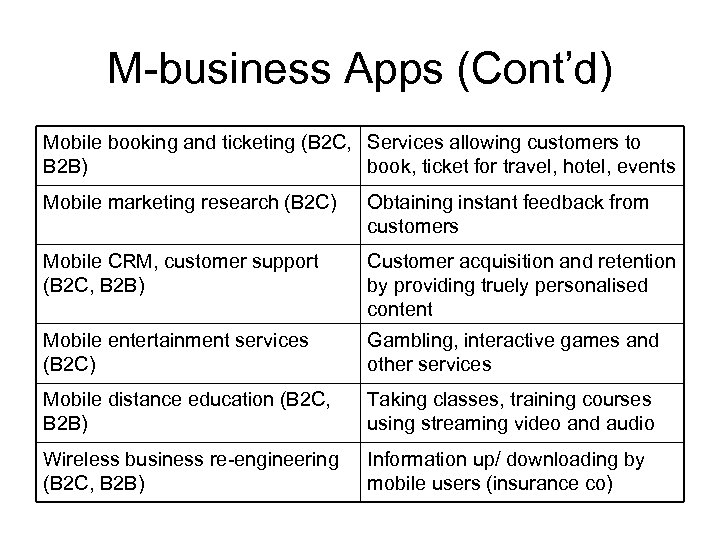
M-business Apps (Cont’d) Mobile booking and ticketing (B 2 C, Services allowing customers to B 2 B) book, ticket for travel, hotel, events Mobile marketing research (B 2 C) Obtaining instant feedback from customers Mobile CRM, customer support (B 2 C, B 2 B) Customer acquisition and retention by providing truely personalised content Mobile entertainment services (B 2 C) Gambling, interactive games and other services Mobile distance education (B 2 C, B 2 B) Taking classes, training courses using streaming video and audio Wireless business re-engineering (B 2 C, B 2 B) Information up/ downloading by mobile users (insurance co)

Location-aware Apps • Vehicle tracking – Automatic vehicle location (AVL): using GPS device installed in a vehicle – Can be used for rapidly dispatching taxis, ambulances, police vehicles, trucks – Can be used for navigating optimal routing in unfamiliar geographical areas or heavy traffic – Can also be used for tracking cargo, delivery, baggege, giving customers more accurate info
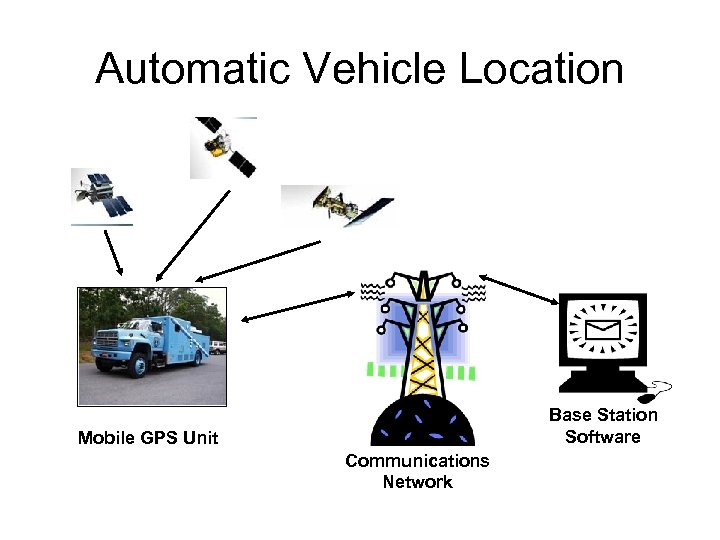
Automatic Vehicle Location Base Station Software Mobile GPS Unit Communications Network

Location-aware Apps • Shopper assisstance, product location, and shopping – Provide shoppers ads, promotional events, price alerts at a shopping mall – Allowing shoppers to locate and compare products using a. DB containing info on products, locations of stores, and distance from the users’ current location, alleviating the need to visit several stores in a particular area – Allowing shoppers to buy on-line using a mobile device – Can be applied to mobile retailing, ticketing and reservation
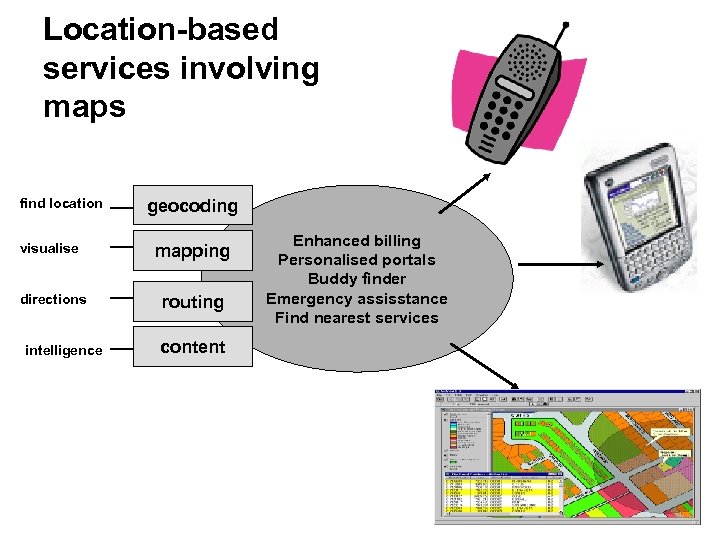
Location-based services involving maps find location geocoding visualise mapping directions routing intelligence content Enhanced billing Personalised portals Buddy finder Emergency assisstance Find nearest services

Location-aware Apps • E-911 (Enhanced 911) – Mandates wireless carriers to provide location-identification capabilities that enable rescuers to locate 911 callers – Designed to improve emergency response time – Interest increased after 9/11, earthquakes, etc. – Can be used for rescuing people in a disaster area • Firemen, emergency crew, doctors, patients assistance – Firemen in a building under fire (automatic warning signal for oxygen remaining) – Sending doctors vital signs of patients in critical situations – Patients with Alzheimer’s: exact location, the location of the nearest police station and contact information for family members

Telematics (or Telemetry) • Integration of – Wireless communications – Vehicle monitoring systems – Vehicle location devices • Diverse apps for cars – Remote vehicle diognostics • Install GSM chip sets in cars to monitor performance and to provide an early warning message to the manufacturer indicating what problem is occuring – Emergency breakdown service (Mercedes Benz) – Multimedia services and m-commerce right on the dashboard – Smart traffic products: • Nokia: by 2010 every vehicle will have its IP address

Mobile Financial Apps • Likely to be one of the most important components of m-business • Involve a variety of apps – Mobile banking, brokerage, money transfer – Can turn a mobile device into business tool, replacing bank, ATM – Easy identification and authentication both for restricted access and for payment purposes, even replacing credit cards

Mobile Financial Apps • Micro-payment: small purchases such as vending through a wireless network – Can be implemented in several ways • Per minute phone call charge equal to the cost of vending item (Sonera for Pepsi) • Pre-paid numbers purchased from a service provider, bank, or credit-card co • To support financial transactions including micropayments, amobile service provider could act as a bank, competing with a bank

A wearable bank • Cell phone • Pager • PDA • PC • TV • Card • ATM
Mobile Financial Apps

Mobile Financial Apps

Mobile Financial Apps

Mobile Inventory Management (MIM) • Involves location tracking of goods, services, and possibly inventory • Rolling inventory – Involves multiple trucks carrying a large amount of inventory while on the move – Whenever a store needs certain items, it can locate a truck and JIT can be performed • JIT delivery of components in an assembly plant – New components required can be moved by a supplier at a certain speed after receiving a signal from the components reaching the assembly line or from the assembly line itself – Possible adjustment of assembly speed to match the arrival time of components

i. Button • Java-enabled i. Button • Communicates by contact at 142 Kbps • Small memory chips (ROM, RAM) in a stainless steel can • Uses: authentication, e-payment, access

Mobile Security System • Remote surveillance • Remote alarm verification • Monitor from work, abroad

Bluetooth • A wireless technology that provides short-range, high-speed voice and data communication between a variety of mobile digital devices • Conceived by Ericsson in 1994 • Bluetooth Special Interest Group (1998) – Initially comprising Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Toshiba and Nokia – Developed an open specification for the technology and to encourage cross-platform capabilities for the different wireless devices – Currently over 2000 companies are supporting the standard and Bluetooth-enabled devices

Bluetooth Apps • Can create a personal area network (PAN) – Can be used to create wireless offices – Can remote control digital appliances at home • Mobile transactions between users and fixed points such as cash registers, vending machines, ticket readers • Ad hoc conferences among business users by establishing a temporary wireless LAN – Face-to-face meetings with shared computing resources allowing temporary documents and apps sharing • Advertising, conveying info

BLIP Zone • Bluetooth Local Infotainment Point • A small hub unit, with a 10 -meter radius, and with Bluetooth connectivity • ınstalled at strategic places, providing people with info depending on their immediate situation and location • Shopping malls, buses, bars, restaurants will use BLIP as an infrastructure element to distribute info relevant to their businesses

Bluetooth Chracteristics • Packet switched • Uses radio frequency band (2. 4 GHz) available worldwide, allowing for global compatibility • Lower power (1 milliwatt) making it suitable for small, battery-operated devices • Data transfer capability between devices: 10 – 100 meter range, bandwidth 1 -2 mbps • Supports upto 8 devices in a network • Built-in security (encryption, authentication) • Non line-of-sight: penetrating walls and avoiding obstacles

Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) • Increasingly popular networking standard used to create wireless LANs in homes/ offices – Provides broadband internet access to PCs and laptops within a few hundred feet (300 ft) of a Wi-Fi base stationin hot-spots where people can log onto wireless networks • Technical standard IEEE 802. 11 – 802. 11 b: popular standard for wireless LAN, speed up to 11 Mbps at 2. 4 GHz band, typically 500 k-1 M – 802. 11 a: just start to be introduced, speed up to 54 Mbps at 5 GHz band (less conjested, less inteference) – 802. 11 g: new standard being developed, up to 225 Mbps at 2. 4 GHz band (extension of 802. 11 b)

Wi-Fi (Cont’d) • Why attractive? – Cheap, fast (both set-up and use) broadband connection – Especially for small businesses or frequently moving companies – Wireless home networking • Some concerns – Security, interference (micro-wave owenns, garage doors), network slow-down – Network hopping: can share a connection with other people (free -riders), hard to monitor unauthorised uses – Can not maintain a connection outside the range of the hot spot • Could be complementary to 3 G wireless – Seamless roaming between Wi-Fi hot spots and cellular network
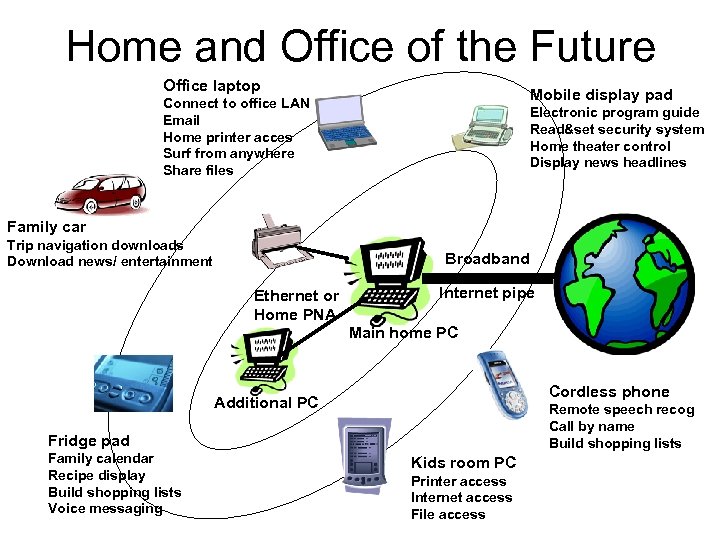
Home and Office of the Future Office laptop Mobile display pad Connect to office LAN Email Home printer acces Surf from anywhere Share files Electronic program guide Read&set security system Home theater control Display news headlines Family car Trip navigation downloads Download news/ entertainment Broadband Ethernet or Home PNA Internet pipe Main home PC Cordless phone Additional PC Remote speech recog Call by name Build shopping lists Fridge pad Family calendar Recipe display Build shopping lists Voice messaging Kids room PC Printer access Internet access File access
efe9c817a834876cdb2cff8dd79c257b.ppt