675efd8f6792a442545229af2dd07e2a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 CMPE 472 Case in e-commerce infrastructure
CMPE 472 Case in e-commerce infrastructure
 E-commerce Infrastructure • E-commerce is described as a new paradigm – Innovation – Application • It does not happen without the infrastructure electronically linking IS and their users
E-commerce Infrastructure • E-commerce is described as a new paradigm – Innovation – Application • It does not happen without the infrastructure electronically linking IS and their users
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • High. Wired. com provides high school students and teachers a range of free services to enable school interaction on a personalised school website. – – Free unlimited website hosting Publishing tools E-mail and messaging Sports related team management tools • They aim to aggregate the largest community of high school websites in order to attract corporate sponsors and vendors interested in accessing high school market. • The goal was – To reach 30 mm page views up from 10 mm now. – Grow revenues from $5 mm in 2000 to $15 mm and $30 mm in 2001 and 2002 respectively
Case 1: High. Wired. com • High. Wired. com provides high school students and teachers a range of free services to enable school interaction on a personalised school website. – – Free unlimited website hosting Publishing tools E-mail and messaging Sports related team management tools • They aim to aggregate the largest community of high school websites in order to attract corporate sponsors and vendors interested in accessing high school market. • The goal was – To reach 30 mm page views up from 10 mm now. – Grow revenues from $5 mm in 2000 to $15 mm and $30 mm in 2001 and 2002 respectively
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • Capacity issues – Network grew from 1000 member high schools to over 12000 in 50 states and 72 countries in 13 months. • The only company that combined four communities: school, sports, alumni, educators. • Articulate, implement and finance a strategy • Designed to be easy for students and teachers – Point, click and publish • Employed 120 people – 40 engineers • 5 hardware, 35 product development
Case 1: High. Wired. com • Capacity issues – Network grew from 1000 member high schools to over 12000 in 50 states and 72 countries in 13 months. • The only company that combined four communities: school, sports, alumni, educators. • Articulate, implement and finance a strategy • Designed to be easy for students and teachers – Point, click and publish • Employed 120 people – 40 engineers • 5 hardware, 35 product development
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • VP of Product Development: – Directed all technology related initiatives • Development, engineering, QA, network and DB architecture – He was CTO of Softbank and GM of Info Access Centre – His BS is in math • High. Wired Products: – School life: classrooms, guidance offices, newspapers, sports teams, student activities – Simplified publishing tools, unlimited server space, message boards, free e-mail – NYC board of education pilot
Case 1: High. Wired. com • VP of Product Development: – Directed all technology related initiatives • Development, engineering, QA, network and DB architecture – He was CTO of Softbank and GM of Info Access Centre – His BS is in math • High. Wired Products: – School life: classrooms, guidance offices, newspapers, sports teams, student activities – Simplified publishing tools, unlimited server space, message boards, free e-mail – NYC board of education pilot
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • Growth and Venture Capital Financing: – – In 1999: 1000 members from 50 states and 18 foreign countries Launched 2 new website building tools Partnership/ sponsorship agreements with 4 companies Raised $7 mm in venture funding by 2 venture capital firms • Reached 1900 schools in 50 states and 32 countries • Reached 5000 schools in 2000 – Raised 2 nd round of $30 mm in 2000 • Launched sports • By mid 2000 reached 12000 member schools
Case 1: High. Wired. com • Growth and Venture Capital Financing: – – In 1999: 1000 members from 50 states and 18 foreign countries Launched 2 new website building tools Partnership/ sponsorship agreements with 4 companies Raised $7 mm in venture funding by 2 venture capital firms • Reached 1900 schools in 50 states and 32 countries • Reached 5000 schools in 2000 – Raised 2 nd round of $30 mm in 2000 • Launched sports • By mid 2000 reached 12000 member schools
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • History of technolgy decisions: – Initially chose Intel based hw running Windows NT 3 and used Microsoft’s SQL server ($1000) as a DB. – Main application was Vignette Story. Server – Within first few months moved to Sun Solaris hw • Vignette’s sw support personnel was familiar with Sun • Brought on board 2 Sun E 250 servers to run web server and story server with a connection between the 2. • Stable platform • Faster and less expensive altenatives existed (Dell, Intel, Compaq) – Hosting was done by Exodus Communications • Huge data centre, internet bandwidth, fire suppression, high security, redundant power, air-conditioning. • Fixed costs were paid on per sq meter
Case 1: High. Wired. com • History of technolgy decisions: – Initially chose Intel based hw running Windows NT 3 and used Microsoft’s SQL server ($1000) as a DB. – Main application was Vignette Story. Server – Within first few months moved to Sun Solaris hw • Vignette’s sw support personnel was familiar with Sun • Brought on board 2 Sun E 250 servers to run web server and story server with a connection between the 2. • Stable platform • Faster and less expensive altenatives existed (Dell, Intel, Compaq) – Hosting was done by Exodus Communications • Huge data centre, internet bandwidth, fire suppression, high security, redundant power, air-conditioning. • Fixed costs were paid on per sq meter
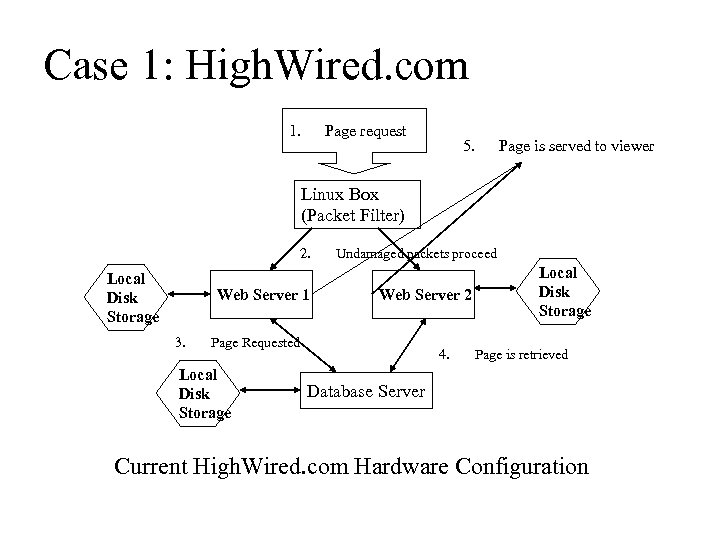 Case 1: High. Wired. com 1. Page request 5. Page is served to viewer Linux Box (Packet Filter) 2. Local Disk Storage Web Server 1 3. Undamaged packets proceed Web Server 2 Page Requested Local Disk Storage 4. Local Disk Storage Page is retrieved Database Server Current High. Wired. com Hardware Configuration
Case 1: High. Wired. com 1. Page request 5. Page is served to viewer Linux Box (Packet Filter) 2. Local Disk Storage Web Server 1 3. Undamaged packets proceed Web Server 2 Page Requested Local Disk Storage 4. Local Disk Storage Page is retrieved Database Server Current High. Wired. com Hardware Configuration
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • History of technolgy decisions: – There were not any non-critical hw components; all linked to one another – Service distinction; internal versus external requests – Bandwidth was the only variable cost • Charged by Exodus for one megabit per second treshold, sampled every 15 minutes • Cost ranged in the hundreds of dollars • Not significant relative to hw costs
Case 1: High. Wired. com • History of technolgy decisions: – There were not any non-critical hw components; all linked to one another – Service distinction; internal versus external requests – Bandwidth was the only variable cost • Charged by Exodus for one megabit per second treshold, sampled every 15 minutes • Cost ranged in the hundreds of dollars • Not significant relative to hw costs
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • Site performance metrics – Response time • • Used a third party performance measurement system: Keynote Noted the amount of time it took for their requests to be filled Played a role of an end-user Results were benchmarked against 40 companies – Down time • • Targeted to be up 99. 8% of the time Scheduled Unscheduled A third party service (Red Alert) monitored the site from a service perspective.
Case 1: High. Wired. com • Site performance metrics – Response time • • Used a third party performance measurement system: Keynote Noted the amount of time it took for their requests to be filled Played a role of an end-user Results were benchmarked against 40 companies – Down time • • Targeted to be up 99. 8% of the time Scheduled Unscheduled A third party service (Red Alert) monitored the site from a service perspective.
 Case 1: High. Wired. com • Server configuration options – To minimise response time and down time: • Utilise sw to make the current complement of servers more efficient • Purchase a ‘big box’ server • Replicate data onto separate servers • Divide data between separate servers • Geographically locate replicated servers, allowing for regional handling of data requests
Case 1: High. Wired. com • Server configuration options – To minimise response time and down time: • Utilise sw to make the current complement of servers more efficient • Purchase a ‘big box’ server • Replicate data onto separate servers • Divide data between separate servers • Geographically locate replicated servers, allowing for regional handling of data requests


