74372ab5239649db7c32016f8d86cf23.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 CMPE 150 – Winter 09 Lecture 2 January 8, 2009 P. E. Mantey
CMPE 150 – Winter 09 Lecture 2 January 8, 2009 P. E. Mantey
 CMPE 150 -- Introduction to Computer Networks n n n Instructor: Patrick Mantey mantey@soe. ucsc. edu http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/~mantey/ Office: Engr. 2 Room 595 J Office hours: Tuesday 3 -5 PM TA: Anselm Kia akia@soe. ucsc. edu Web site: http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/classes/cmpe 150/Winter 09/ Text: Tannenbaum: Computer Networks (4 th edition – available in bookstore, etc. )
CMPE 150 -- Introduction to Computer Networks n n n Instructor: Patrick Mantey mantey@soe. ucsc. edu http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/~mantey/ Office: Engr. 2 Room 595 J Office hours: Tuesday 3 -5 PM TA: Anselm Kia akia@soe. ucsc. edu Web site: http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/classes/cmpe 150/Winter 09/ Text: Tannenbaum: Computer Networks (4 th edition – available in bookstore, etc. )
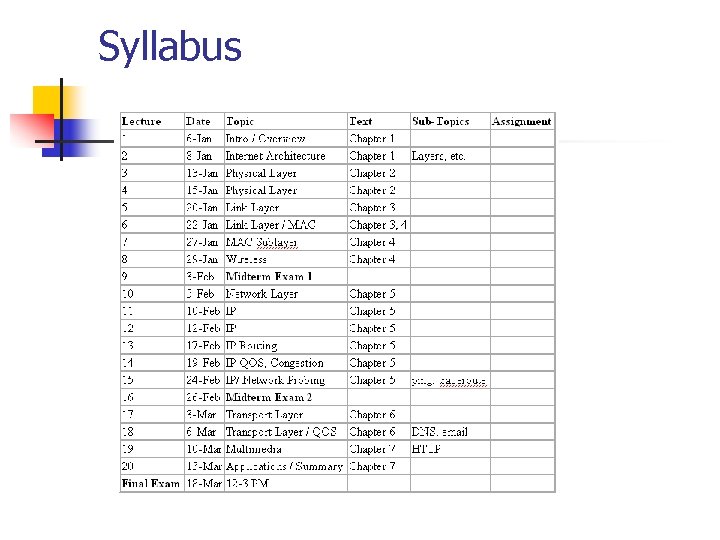 Syllabus
Syllabus
 Assignment #1 Available on the web site: http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/classes/cmpe 150/Winter 09/ Due Thursday January 15, 2009
Assignment #1 Available on the web site: http: //www. soe. ucsc. edu/classes/cmpe 150/Winter 09/ Due Thursday January 15, 2009
 Today’s Agenda n n n n “Big Picture”, terminology Networking Overview (continued) Protocol Concepts Network Software Architecture(s) History (ARPA Net, NSF Net) Networks Today: ATM, Ethernet, etc.
Today’s Agenda n n n n “Big Picture”, terminology Networking Overview (continued) Protocol Concepts Network Software Architecture(s) History (ARPA Net, NSF Net) Networks Today: ATM, Ethernet, etc.
 Network Hardware Local Area Networks n Metropolitan Area Networks n Wide Area Networks n Wireless Networks n Home Networks n Internetworks n
Network Hardware Local Area Networks n Metropolitan Area Networks n Wide Area Networks n Wireless Networks n Home Networks n Internetworks n
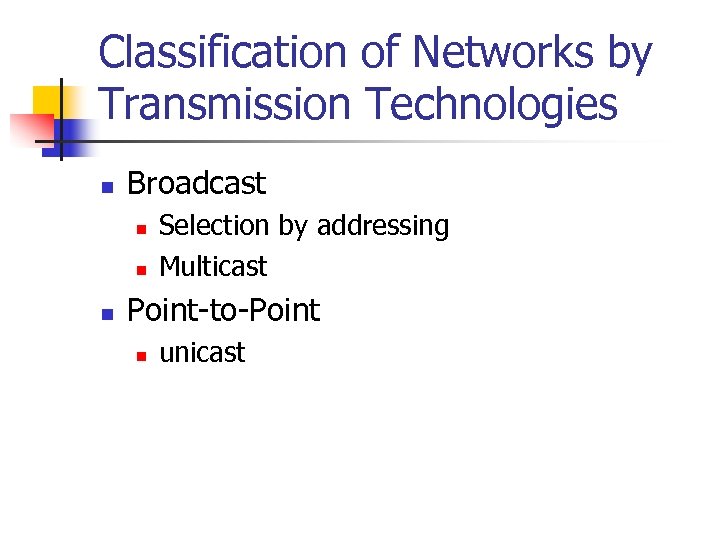 Classification of Networks by Transmission Technologies n Broadcast n n n Selection by addressing Multicast Point-to-Point n unicast
Classification of Networks by Transmission Technologies n Broadcast n n n Selection by addressing Multicast Point-to-Point n unicast
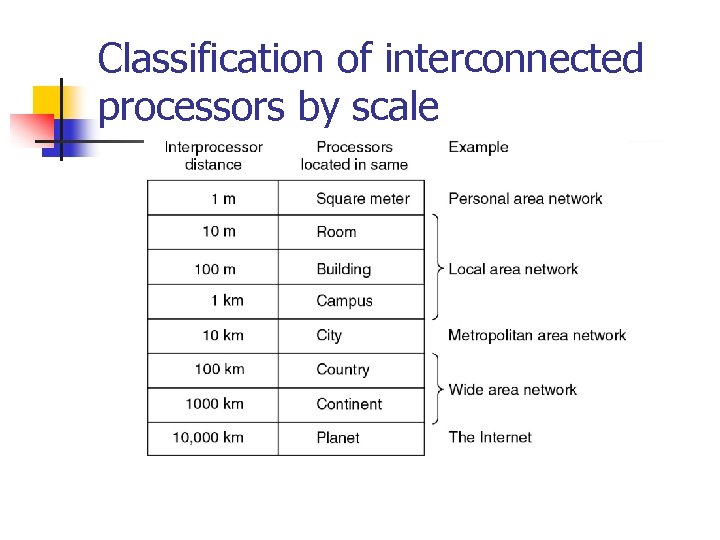 Classification of interconnected processors by scale
Classification of interconnected processors by scale
 Home Network Categories n n n Computers (desktop PC, PDA, shared peripherals Entertainment (TV, DVD, VCR, camera, stereo, MP 3) Telecomm (telephone, cell phone, intercom, fax) Appliances (furnace, air conditioner, oven, clothes dryer, pool pump, lights, microwave, refigerator. . ) Telemetry (utility meter, burglar alarm, babycam).
Home Network Categories n n n Computers (desktop PC, PDA, shared peripherals Entertainment (TV, DVD, VCR, camera, stereo, MP 3) Telecomm (telephone, cell phone, intercom, fax) Appliances (furnace, air conditioner, oven, clothes dryer, pool pump, lights, microwave, refigerator. . ) Telemetry (utility meter, burglar alarm, babycam).
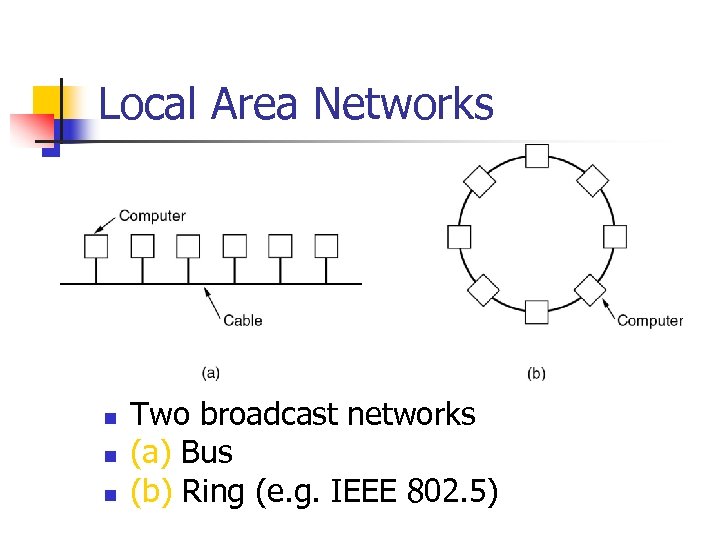 Local Area Networks n n n Two broadcast networks (a) Bus (b) Ring (e. g. IEEE 802. 5)
Local Area Networks n n n Two broadcast networks (a) Bus (b) Ring (e. g. IEEE 802. 5)
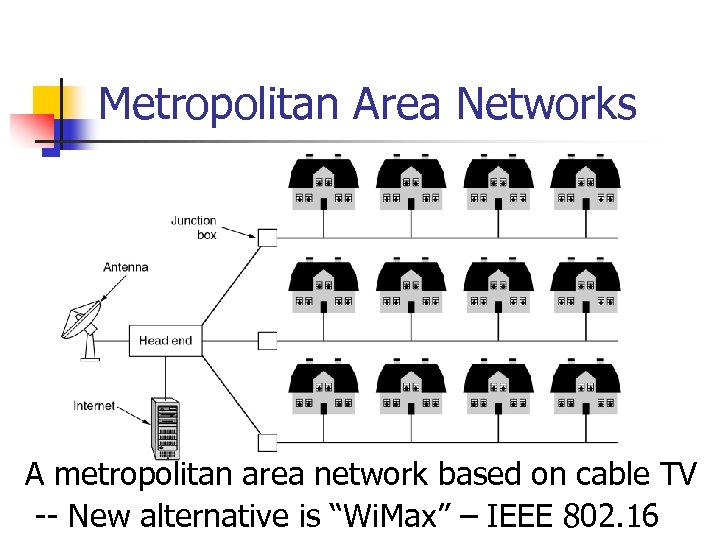 Metropolitan Area Networks A metropolitan area network based on cable TV -- New alternative is “Wi. Max” – IEEE 802. 16
Metropolitan Area Networks A metropolitan area network based on cable TV -- New alternative is “Wi. Max” – IEEE 802. 16
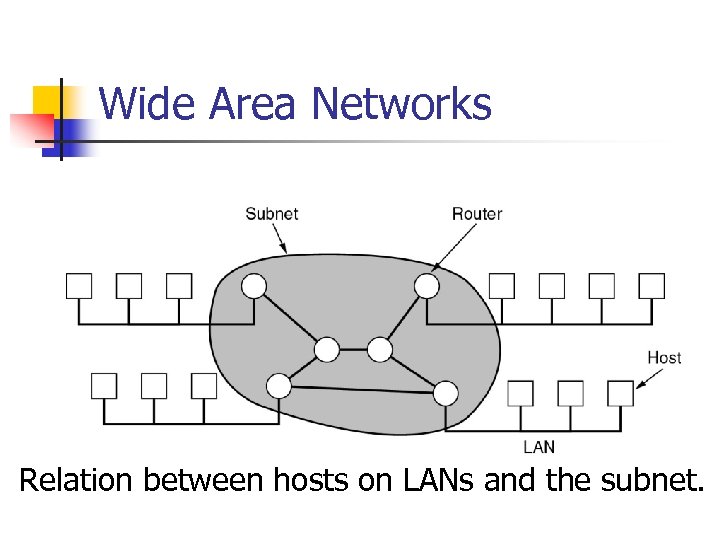 Wide Area Networks Relation between hosts on LANs and the subnet.
Wide Area Networks Relation between hosts on LANs and the subnet.
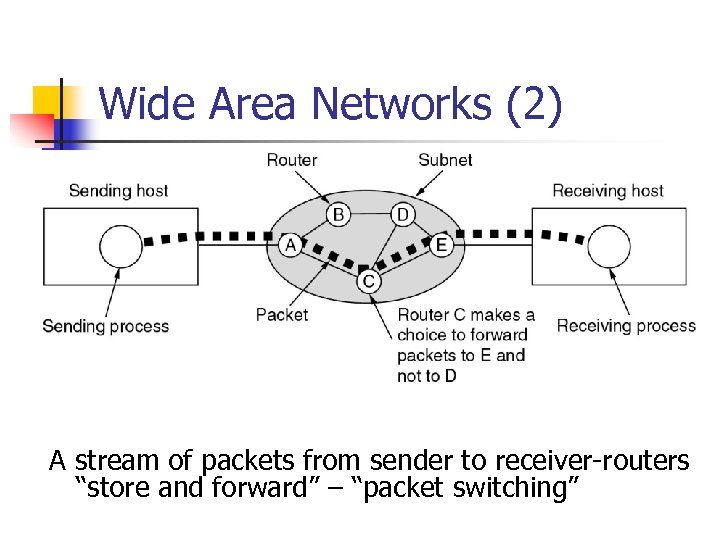 Wide Area Networks (2) A stream of packets from sender to receiver-routers “store and forward” – “packet switching”
Wide Area Networks (2) A stream of packets from sender to receiver-routers “store and forward” – “packet switching”
 Wireless Networks n Categories of wireless networks: n System interconnection n Master/slave Wireless LANs (e. g. 802. 11) n Wireless WANs (e. g. 802. 16) n
Wireless Networks n Categories of wireless networks: n System interconnection n Master/slave Wireless LANs (e. g. 802. 11) n Wireless WANs (e. g. 802. 16) n
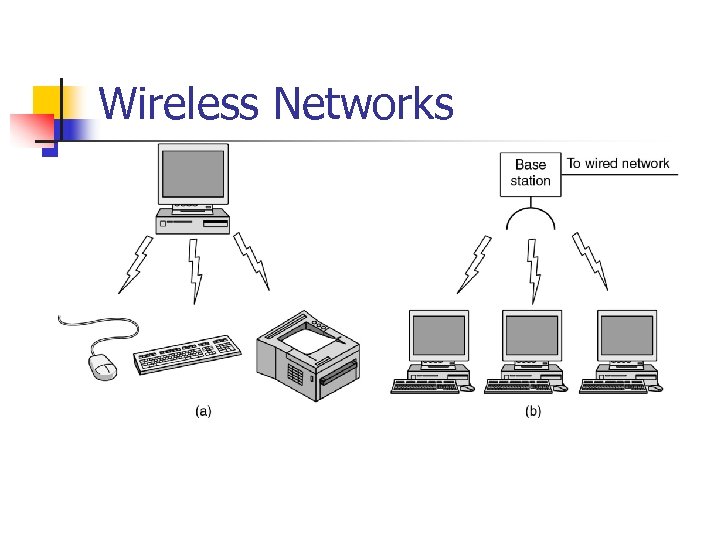 Wireless Networks n n (a) Bluetooth configuration (b) Wireless LAN
Wireless Networks n n (a) Bluetooth configuration (b) Wireless LAN
 Protocols n n Used for communications between entities in a system Must speak the same language Entities n User applications n e-mail facilities n terminals Systems n Computer n Terminal n Remote sensor
Protocols n n Used for communications between entities in a system Must speak the same language Entities n User applications n e-mail facilities n terminals Systems n Computer n Terminal n Remote sensor
 Layered Architecture n n Each layer offers a service Details of how service is offered in hidden Each layer talks to the layer immediatley “above” and the layer “below” “protocol”: communication rules
Layered Architecture n n Each layer offers a service Details of how service is offered in hidden Each layer talks to the layer immediatley “above” and the layer “below” “protocol”: communication rules
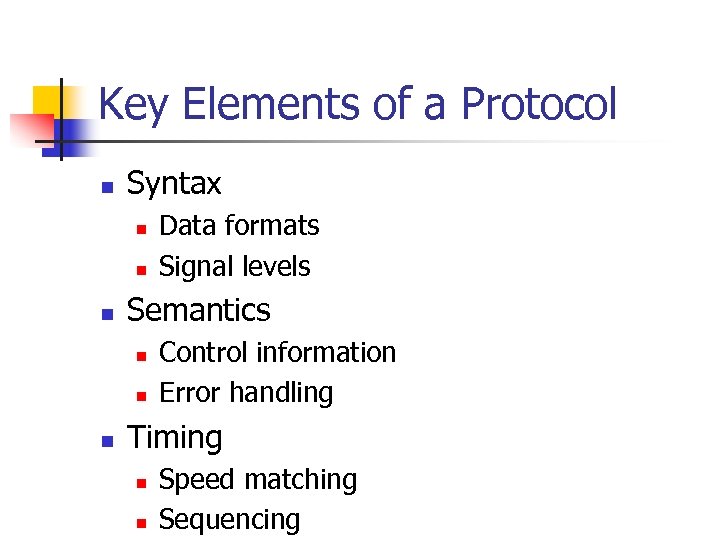 Key Elements of a Protocol n Syntax n n n Semantics n n n Data formats Signal levels Control information Error handling Timing n n Speed matching Sequencing
Key Elements of a Protocol n Syntax n n n Semantics n n n Data formats Signal levels Control information Error handling Timing n n Speed matching Sequencing
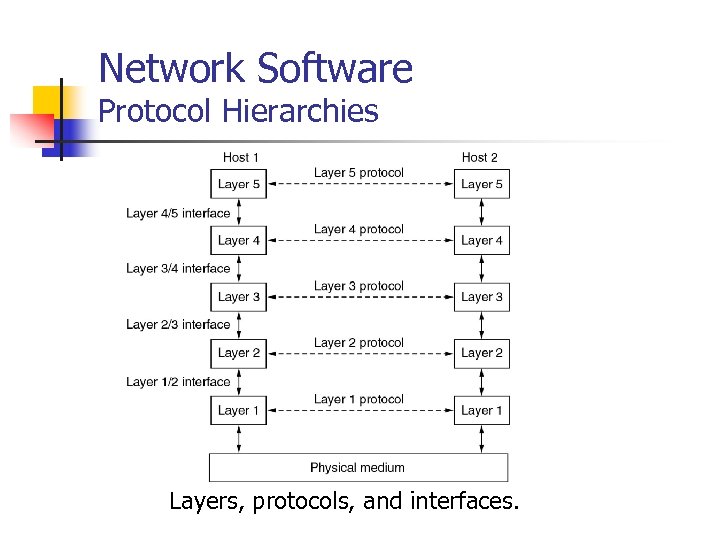 Network Software Protocol Hierarchies Layers, protocols, and interfaces.
Network Software Protocol Hierarchies Layers, protocols, and interfaces.
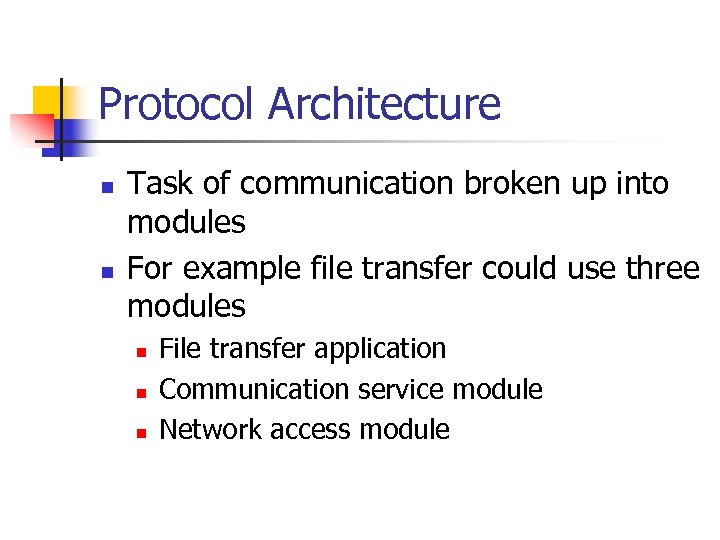 Protocol Architecture n n Task of communication broken up into modules For example file transfer could use three modules n n n File transfer application Communication service module Network access module
Protocol Architecture n n Task of communication broken up into modules For example file transfer could use three modules n n n File transfer application Communication service module Network access module
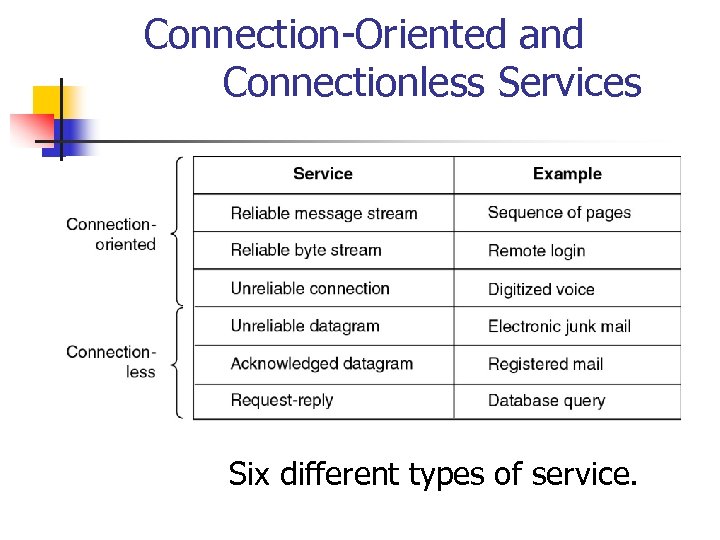 Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Services Six different types of service.
Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Services Six different types of service.
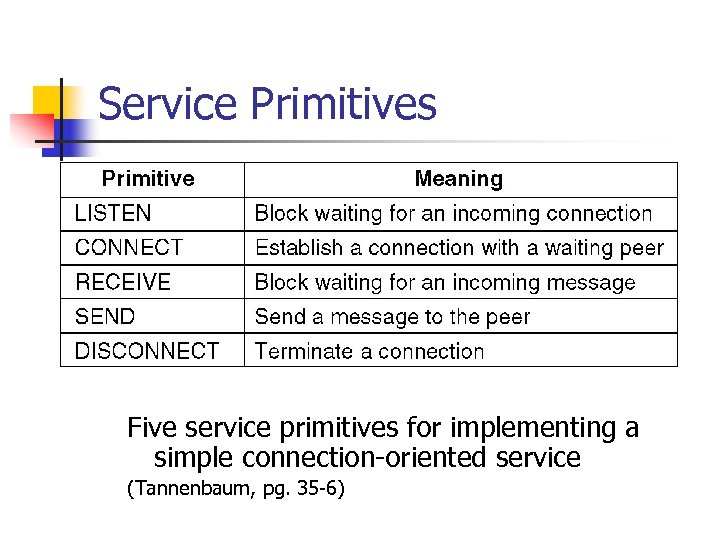 Service Primitives Five service primitives for implementing a simple connection-oriented service (Tannenbaum, pg. 35 -6)
Service Primitives Five service primitives for implementing a simple connection-oriented service (Tannenbaum, pg. 35 -6)
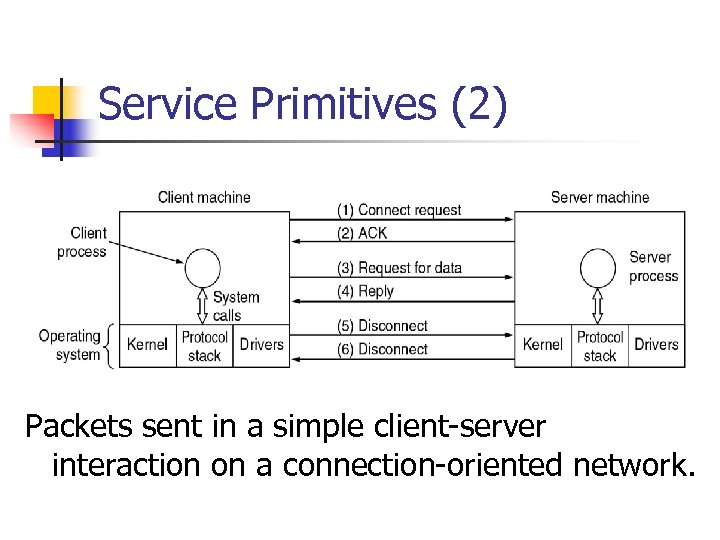 Service Primitives (2) Packets sent in a simple client-server interaction on a connection-oriented network.
Service Primitives (2) Packets sent in a simple client-server interaction on a connection-oriented network.
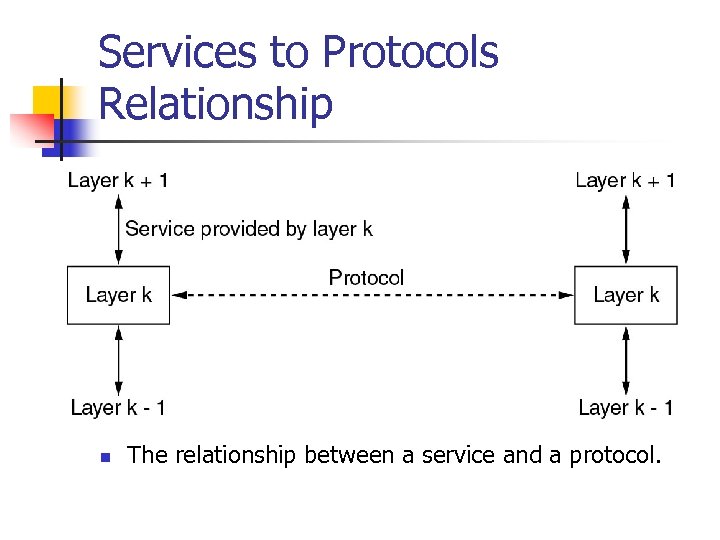 Services to Protocols Relationship n The relationship between a service and a protocol.
Services to Protocols Relationship n The relationship between a service and a protocol.
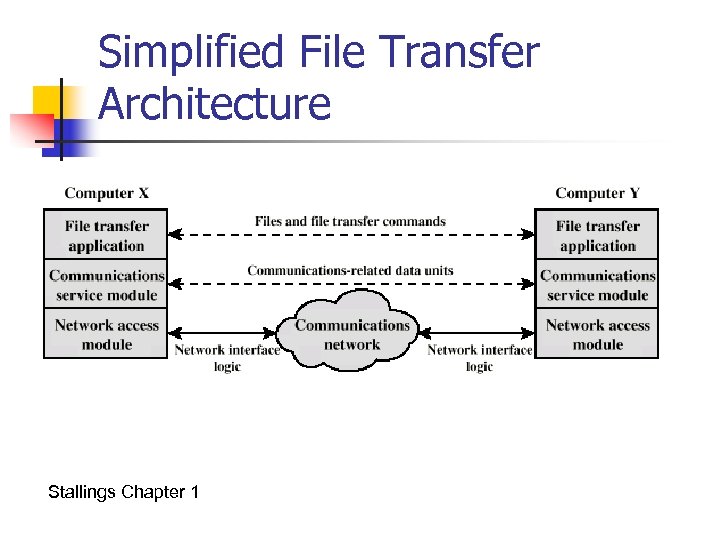 Simplified File Transfer Architecture Stallings Chapter 1
Simplified File Transfer Architecture Stallings Chapter 1
 A Three Layer Model n n n Application Layer Transport Layer Network Access Layer
A Three Layer Model n n n Application Layer Transport Layer Network Access Layer
 Network Access Layer n n Exchange of data between the computer and the network Sending computer provides address of destination May invoke levels of service Dependent on type of network used (LAN, packet switched etc. )
Network Access Layer n n Exchange of data between the computer and the network Sending computer provides address of destination May invoke levels of service Dependent on type of network used (LAN, packet switched etc. )
 Transport Layer n n n Reliable data exchange Independent of network being used Independent of application
Transport Layer n n n Reliable data exchange Independent of network being used Independent of application
 Application Layer n n Support for different user applications e. g. e-mail, file transfer
Application Layer n n Support for different user applications e. g. e-mail, file transfer
 Addressing Requirements n n n Two levels of addressing required Each computer needs unique network address Each application on a (multi-tasking) computer needs a unique address within the computer n The service access point or SAP
Addressing Requirements n n n Two levels of addressing required Each computer needs unique network address Each application on a (multi-tasking) computer needs a unique address within the computer n The service access point or SAP
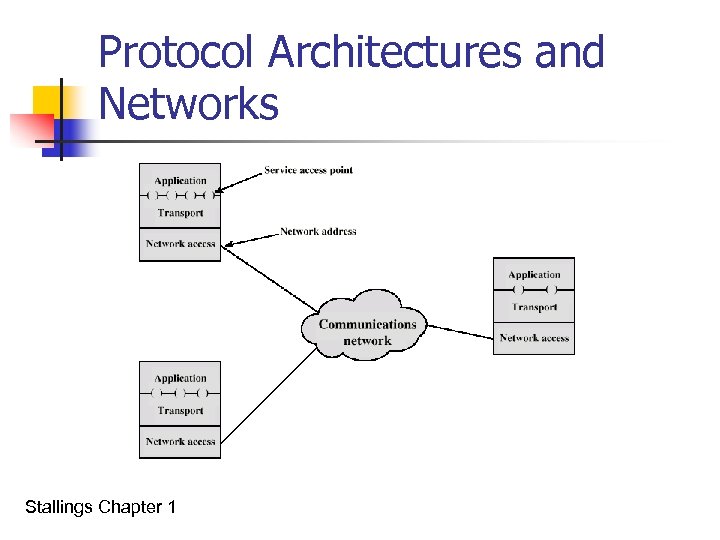 Protocol Architectures and Networks Stallings Chapter 1
Protocol Architectures and Networks Stallings Chapter 1
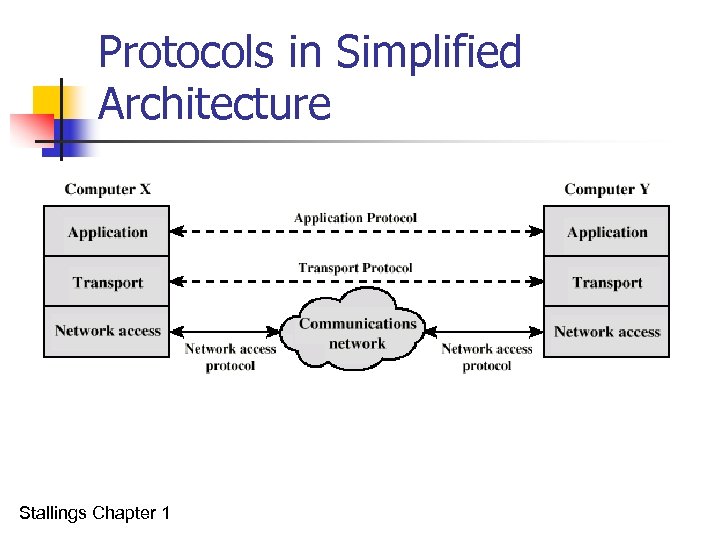 Protocols in Simplified Architecture Stallings Chapter 1
Protocols in Simplified Architecture Stallings Chapter 1
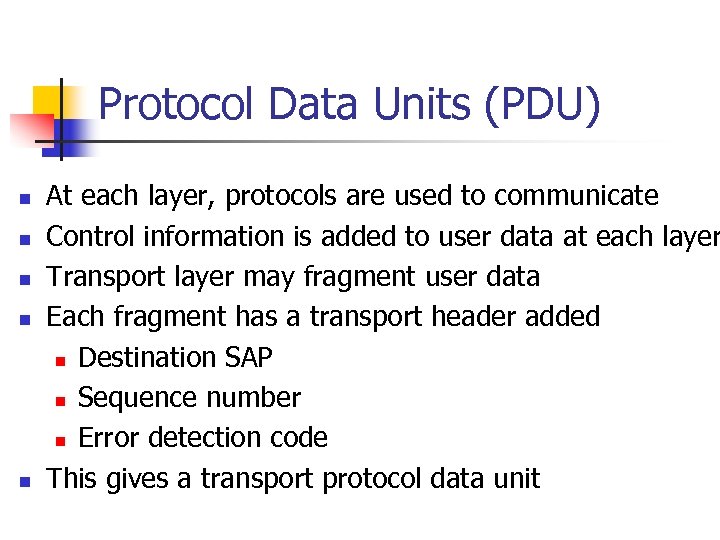 Protocol Data Units (PDU) n n n At each layer, protocols are used to communicate Control information is added to user data at each layer Transport layer may fragment user data Each fragment has a transport header added n Destination SAP n Sequence number n Error detection code This gives a transport protocol data unit
Protocol Data Units (PDU) n n n At each layer, protocols are used to communicate Control information is added to user data at each layer Transport layer may fragment user data Each fragment has a transport header added n Destination SAP n Sequence number n Error detection code This gives a transport protocol data unit
 Network PDU n Adds network header n n network address for destination computer Facilities requests
Network PDU n Adds network header n n network address for destination computer Facilities requests
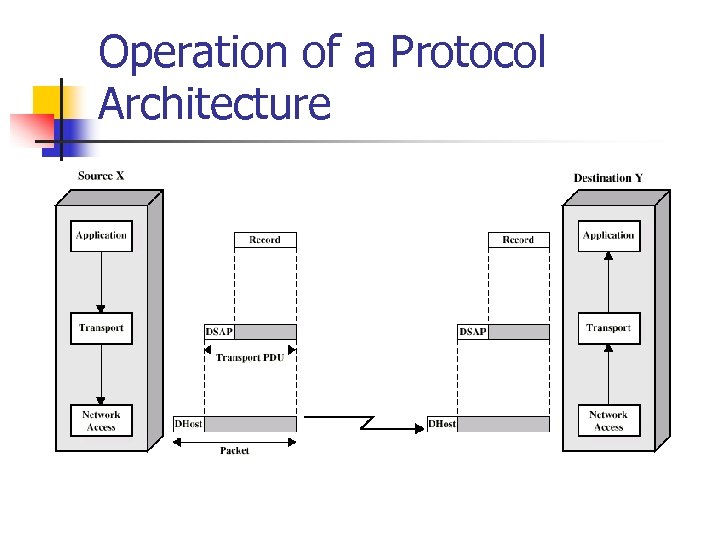 Operation of a Protocol Architecture
Operation of a Protocol Architecture
 TCP/IP Protocol Architecture n n n Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) Used by the global Internet No official model but a working one.
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture n n n Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) Used by the global Internet No official model but a working one.
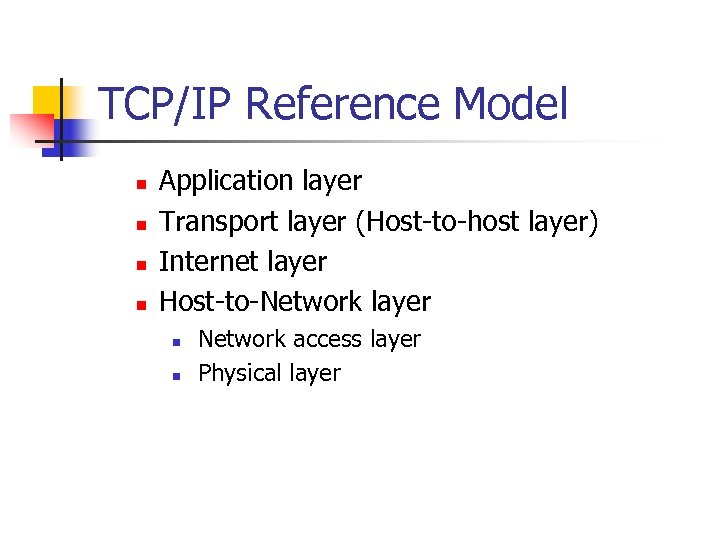 TCP/IP Reference Model n n Application layer Transport layer (Host-to-host layer) Internet layer Host-to-Network layer n n Network access layer Physical layer
TCP/IP Reference Model n n Application layer Transport layer (Host-to-host layer) Internet layer Host-to-Network layer n n Network access layer Physical layer
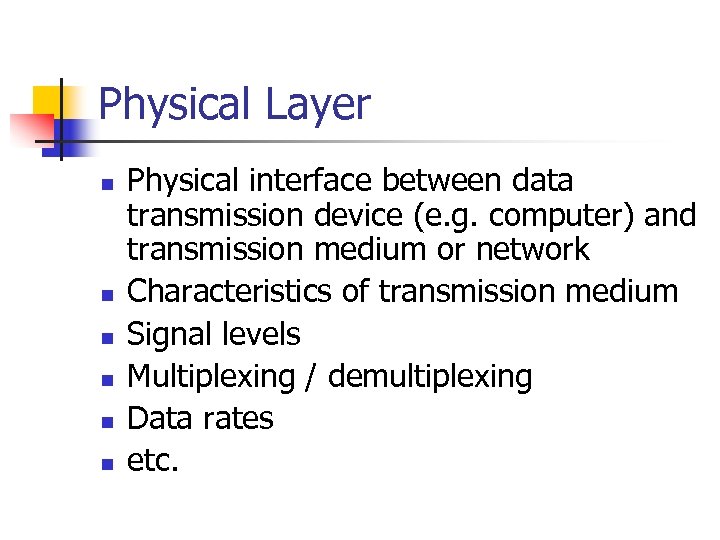 Physical Layer n n n Physical interface between data transmission device (e. g. computer) and transmission medium or network Characteristics of transmission medium Signal levels Multiplexing / demultiplexing Data rates etc.
Physical Layer n n n Physical interface between data transmission device (e. g. computer) and transmission medium or network Characteristics of transmission medium Signal levels Multiplexing / demultiplexing Data rates etc.
 Network Access Layer (Host-to-Network Layer) n n n Exchange of data between end system and network Destination address provision Invoking services like priority
Network Access Layer (Host-to-Network Layer) n n n Exchange of data between end system and network Destination address provision Invoking services like priority
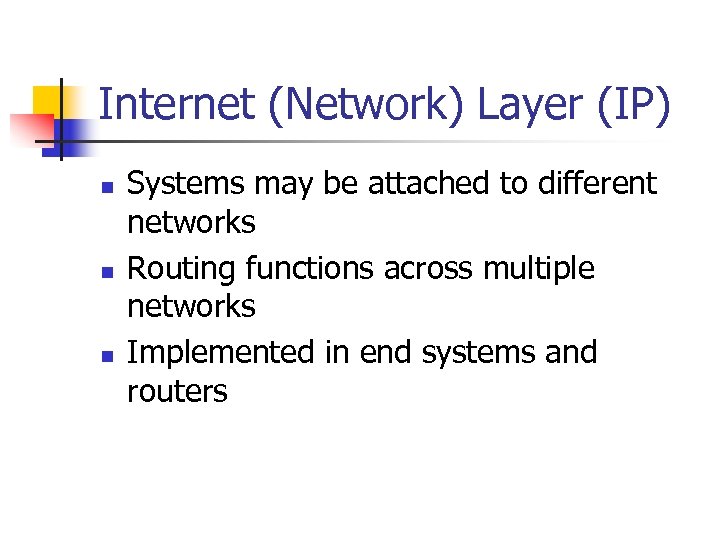 Internet (Network) Layer (IP) n n n Systems may be attached to different networks Routing functions across multiple networks Implemented in end systems and routers
Internet (Network) Layer (IP) n n n Systems may be attached to different networks Routing functions across multiple networks Implemented in end systems and routers
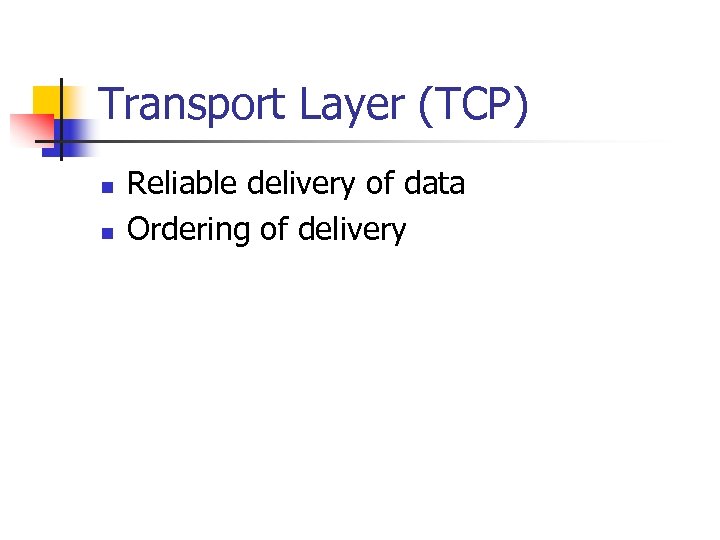 Transport Layer (TCP) n n Reliable delivery of data Ordering of delivery
Transport Layer (TCP) n n Reliable delivery of data Ordering of delivery
 Application Layer n n Support for user applications e. g. http, SMPT
Application Layer n n Support for user applications e. g. http, SMPT
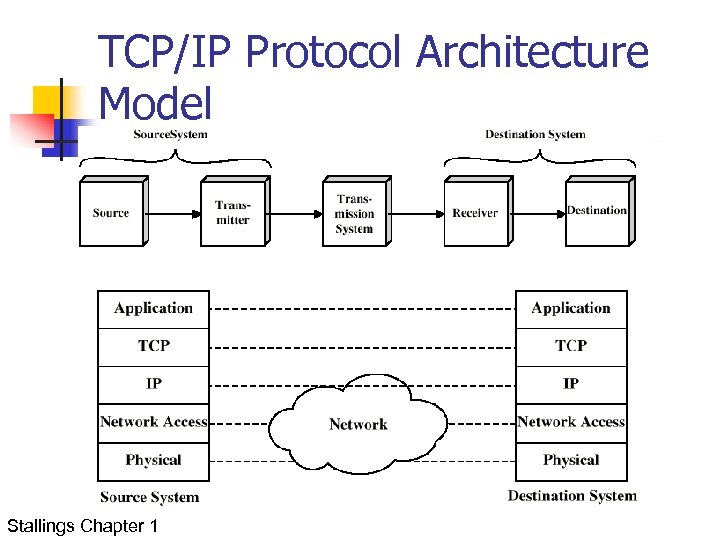 TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model Stallings Chapter 1
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model Stallings Chapter 1
 OSI Model n n n Open Systems Interconnection Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Seven layers A theoretical system delivered too late! TCP/IP is the de facto standard
OSI Model n n n Open Systems Interconnection Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Seven layers A theoretical system delivered too late! TCP/IP is the de facto standard
 OSI Layers n n n n Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical
OSI Layers n n n n Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical
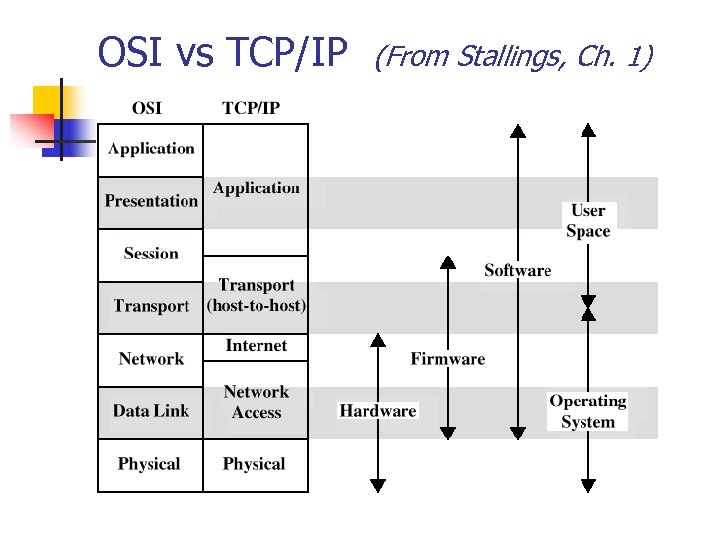 OSI vs TCP/IP (From Stallings, Ch. 1)
OSI vs TCP/IP (From Stallings, Ch. 1)
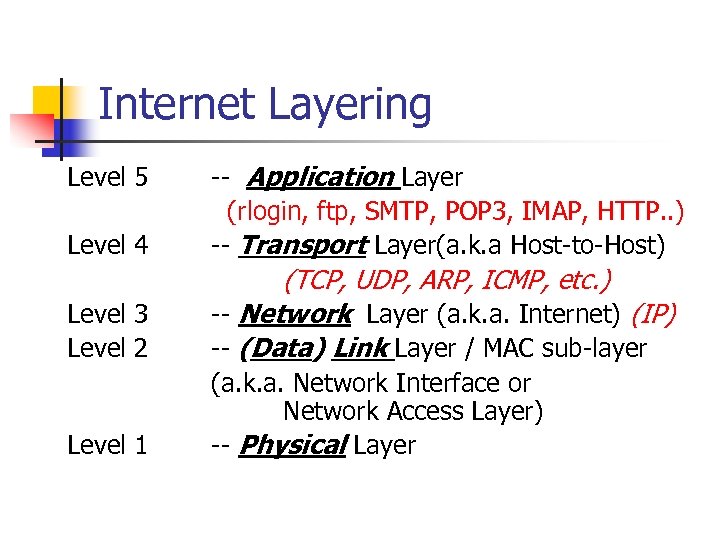 Internet Layering Level 4 -- Application Layer (rlogin, ftp, SMTP, POP 3, IMAP, HTTP. . ) -- Transport Layer(a. k. a Host-to-Host) Level 3 Level 2 (TCP, UDP, ARP, ICMP, etc. ) -- Network Layer (a. k. a. Internet) (IP) -- (Data) Link Layer / MAC sub-layer Level 1 (a. k. a. Network Interface or Network Access Layer) -- Physical Layer Level 5
Internet Layering Level 4 -- Application Layer (rlogin, ftp, SMTP, POP 3, IMAP, HTTP. . ) -- Transport Layer(a. k. a Host-to-Host) Level 3 Level 2 (TCP, UDP, ARP, ICMP, etc. ) -- Network Layer (a. k. a. Internet) (IP) -- (Data) Link Layer / MAC sub-layer Level 1 (a. k. a. Network Interface or Network Access Layer) -- Physical Layer Level 5


