10e0ce7b1688455fa3217a434239ed7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 CMM vs. ISO David S. Craft
CMM vs. ISO David S. Craft
 Agenda • Who Am I • EDS • CMM • ISO • Similarities And Differences
Agenda • Who Am I • EDS • CMM • ISO • Similarities And Differences
 Who Am I Managing Consultant Solutions Consulting Engineering and Manufacturing Services Team Leader Industrial Engineer Shift Supervisor Materials Manager Information Specialist, Senior. Volunteer VISTA Consultant Manager Production Planning & Control Chief Industrial Engineer Project Manager Inventory Control Manager
Who Am I Managing Consultant Solutions Consulting Engineering and Manufacturing Services Team Leader Industrial Engineer Shift Supervisor Materials Manager Information Specialist, Senior. Volunteer VISTA Consultant Manager Production Planning & Control Chief Industrial Engineer Project Manager Inventory Control Manager
 Our Vision EDS … the recognized global leader in ensuring clients achieve superior value in the Digital Economy • By delivering the right strategies, solutions and services • Through superior execution on a sustained basis
Our Vision EDS … the recognized global leader in ensuring clients achieve superior value in the Digital Economy • By delivering the right strategies, solutions and services • Through superior execution on a sustained basis
 Some of Our Milestones 1962: EDS founds the IT services industry. 1967: EDS opens its first data center. 1987: EDS completes EDSNET, one of the world’s largest privately owned digital networks. 1995: The Government of South Australia awards EDS the world’s first whole-ofgovernment IT outsourcing contract. 1997: The Commonwealth Bank Group and EDS sign the world’s largest financial sector outsourcing contract. 2000: EDS wins landmark Navy/Marine Corps Intranet project – the largest federal IT contract in history. 2001: EDS becomes the No. 1 provider of global IT infrastructure services to the airline industry. 2002: EDS celebrates its 40 th anniversary.
Some of Our Milestones 1962: EDS founds the IT services industry. 1967: EDS opens its first data center. 1987: EDS completes EDSNET, one of the world’s largest privately owned digital networks. 1995: The Government of South Australia awards EDS the world’s first whole-ofgovernment IT outsourcing contract. 1997: The Commonwealth Bank Group and EDS sign the world’s largest financial sector outsourcing contract. 2000: EDS wins landmark Navy/Marine Corps Intranet project – the largest federal IT contract in history. 2001: EDS becomes the No. 1 provider of global IT infrastructure services to the airline industry. 2002: EDS celebrates its 40 th anniversary.
 SEI & CMM SEI Software Engineering Institute CMM Capability Maturity Model
SEI & CMM SEI Software Engineering Institute CMM Capability Maturity Model
 SEI History • Federal government cannot distinguish between competing bids for software development • Early 1980’s - Federal Government (Congress) awards a contract to establish the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) at Carnegie Mellon University (sponsored by the DOD) • 1988 - SEI begins work on a Process Maturity Framework for judging a company’s capability to produce software • The Process Maturity Framework evolves into the Capability Maturity Model • August 1991 – SW-CMM Version 1 released • SE-CMM developed by the Enterprise Process Improvement Collaboration (EPIC) • 1992 - CMM Version 1. 1 released • 1999 - Begin developing CMMI
SEI History • Federal government cannot distinguish between competing bids for software development • Early 1980’s - Federal Government (Congress) awards a contract to establish the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) at Carnegie Mellon University (sponsored by the DOD) • 1988 - SEI begins work on a Process Maturity Framework for judging a company’s capability to produce software • The Process Maturity Framework evolves into the Capability Maturity Model • August 1991 – SW-CMM Version 1 released • SE-CMM developed by the Enterprise Process Improvement Collaboration (EPIC) • 1992 - CMM Version 1. 1 released • 1999 - Begin developing CMMI
 The SEI's goals in developing CMMs include • Addressing software and disciplines that have an impact on software • Providing integrated process improvement reference models • Building broad community consensus • Harmonizing with standards • Enabling efficient improvement across disciplines Copyright 2002 by Carnegie Mellon University URL: http: //www. sei. cmu. edu/cmms/cmms. html Last Modified: 24 July 2002 The Software Engineering Institute (SEI) is a federally funded research and development center sponsored by the U. S. Department of Defense and operated by Carnegie Mellon University.
The SEI's goals in developing CMMs include • Addressing software and disciplines that have an impact on software • Providing integrated process improvement reference models • Building broad community consensus • Harmonizing with standards • Enabling efficient improvement across disciplines Copyright 2002 by Carnegie Mellon University URL: http: //www. sei. cmu. edu/cmms/cmms. html Last Modified: 24 July 2002 The Software Engineering Institute (SEI) is a federally funded research and development center sponsored by the U. S. Department of Defense and operated by Carnegie Mellon University.
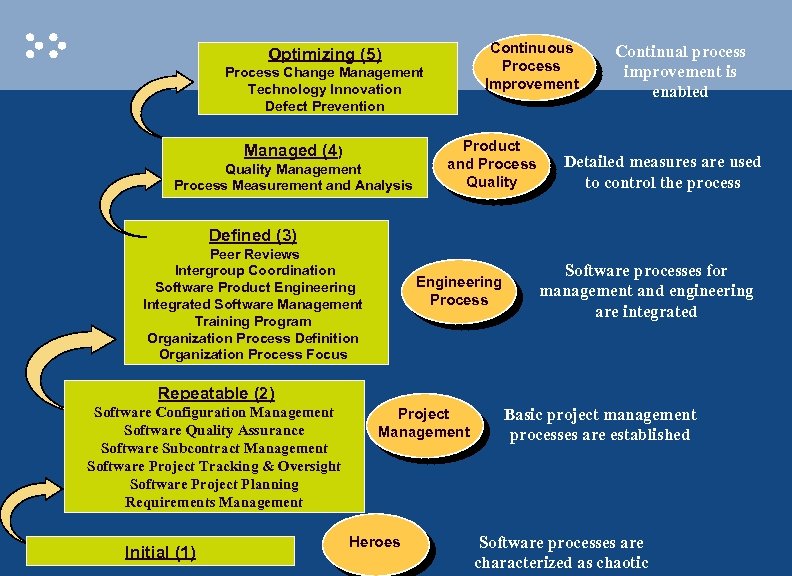 Continuous Process Improvement Optimizing (5) Process Change Management Technology Innovation Defect Prevention Managed (4) Quality Management Process Measurement and Analysis Product and Process Quality Continual process improvement is enabled Detailed measures are used to control the process Defined (3) Peer Reviews Intergroup Coordination Software Product Engineering Integrated Software Management Training Program Organization Process Definition Organization Process Focus Engineering Process Software processes for management and engineering are integrated Repeatable (2) Software Configuration Management Software Quality Assurance Software Subcontract Management Software Project Tracking & Oversight Software Project Planning Requirements Management Initial (1) Project Management Heroes Basic project management processes are established Software processes are characterized as chaotic
Continuous Process Improvement Optimizing (5) Process Change Management Technology Innovation Defect Prevention Managed (4) Quality Management Process Measurement and Analysis Product and Process Quality Continual process improvement is enabled Detailed measures are used to control the process Defined (3) Peer Reviews Intergroup Coordination Software Product Engineering Integrated Software Management Training Program Organization Process Definition Organization Process Focus Engineering Process Software processes for management and engineering are integrated Repeatable (2) Software Configuration Management Software Quality Assurance Software Subcontract Management Software Project Tracking & Oversight Software Project Planning Requirements Management Initial (1) Project Management Heroes Basic project management processes are established Software processes are characterized as chaotic
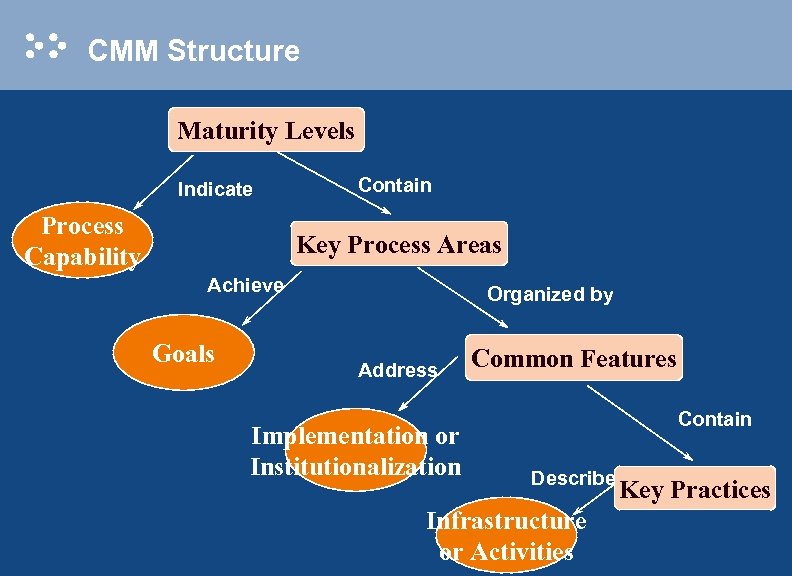 CMM Structure Maturity Levels Indicate Process Capability Contain Key Process Areas Achieve Goals Organized by Address Implementation or Institutionalization Common Features Contain Describe Infrastructure or Activities Key Practices
CMM Structure Maturity Levels Indicate Process Capability Contain Key Process Areas Achieve Goals Organized by Address Implementation or Institutionalization Common Features Contain Describe Infrastructure or Activities Key Practices
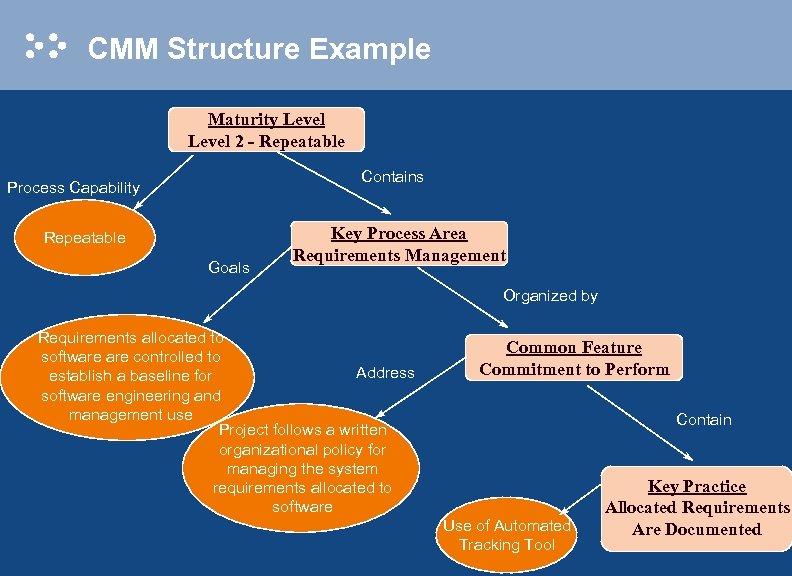 CMM Structure Example Maturity Level 2 - Repeatable Contains Process Capability Repeatable Goals Key Process Area Requirements Management Organized by Requirements allocated to software controlled to Address establish a baseline for software engineering and management use Project follows a written organizational policy for managing the system requirements allocated to software Common Feature Commitment to Perform Contain Use of Automated Tracking Tool Key Practice Allocated Requirements Are Documented
CMM Structure Example Maturity Level 2 - Repeatable Contains Process Capability Repeatable Goals Key Process Area Requirements Management Organized by Requirements allocated to software controlled to Address establish a baseline for software engineering and management use Project follows a written organizational policy for managing the system requirements allocated to software Common Feature Commitment to Perform Contain Use of Automated Tracking Tool Key Practice Allocated Requirements Are Documented
 Different CMM’s • SW-CMM for Software • P-CMM People CMM • SA-CMM Software Acquisition CMM • SE-CMM Systems Engineering CMM • IPD-CMM Integrated Product • CMMI Development Capability Maturity Model Integrated
Different CMM’s • SW-CMM for Software • P-CMM People CMM • SA-CMM Software Acquisition CMM • SE-CMM Systems Engineering CMM • IPD-CMM Integrated Product • CMMI Development Capability Maturity Model Integrated
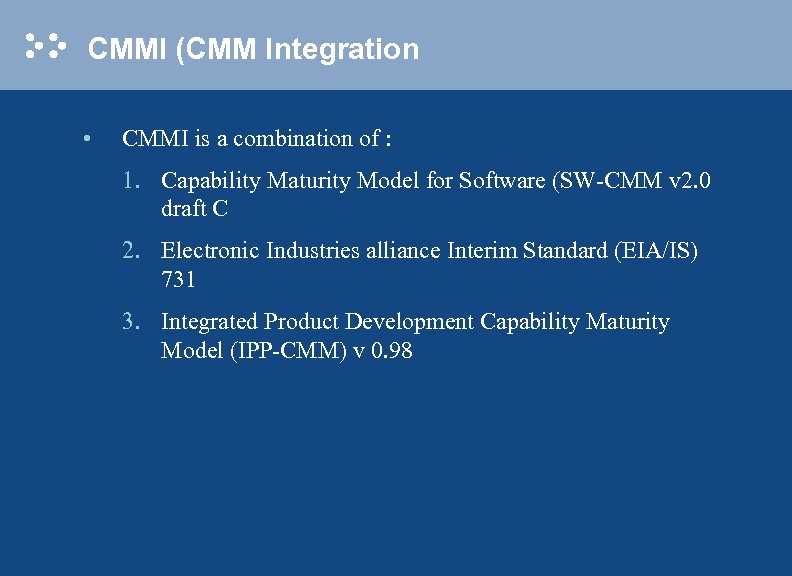 CMMI (CMM Integration • CMMI is a combination of : 1. Capability Maturity Model for Software (SW-CMM v 2. 0 draft C 2. Electronic Industries alliance Interim Standard (EIA/IS) 731 3. Integrated Product Development Capability Maturity Model (IPP-CMM) v 0. 98
CMMI (CMM Integration • CMMI is a combination of : 1. Capability Maturity Model for Software (SW-CMM v 2. 0 draft C 2. Electronic Industries alliance Interim Standard (EIA/IS) 731 3. Integrated Product Development Capability Maturity Model (IPP-CMM) v 0. 98
 ISO International Organization For Standardization Why ISO instead of IOS?
ISO International Organization For Standardization Why ISO instead of IOS?
 ISO History X Began with British Military standards X ISO organization was established in 1947 X Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland X Currently composed of 133 National Standard Bodies X As of 12/31/00 there are 13, 544 International Standards embodied in 430, 608 pages of English text
ISO History X Began with British Military standards X ISO organization was established in 1947 X Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland X Currently composed of 133 National Standard Bodies X As of 12/31/00 there are 13, 544 International Standards embodied in 430, 608 pages of English text
 What are standards? Standards are documented agreements containing technical specifications or other precise criteria to be used consistently as rules, guidelines, or definitions of characteristics, to ensure that materials, products, processes and services are fit for their purpose. For example, the format of the credit cards, phone cards, and "smart" cards that have become commonplace is derived from an ISO International Standard. Adhering to the standard, which defines such features as an optimal thickness (0, 76 mm), means that the cards can be used worldwide. International Standards thus contribute to making life simpler, and to increasing the reliability and effectiveness of the goods and services we use. Last modified 2002 -07 -17
What are standards? Standards are documented agreements containing technical specifications or other precise criteria to be used consistently as rules, guidelines, or definitions of characteristics, to ensure that materials, products, processes and services are fit for their purpose. For example, the format of the credit cards, phone cards, and "smart" cards that have become commonplace is derived from an ISO International Standard. Adhering to the standard, which defines such features as an optimal thickness (0, 76 mm), means that the cards can be used worldwide. International Standards thus contribute to making life simpler, and to increasing the reliability and effectiveness of the goods and services we use. Last modified 2002 -07 -17
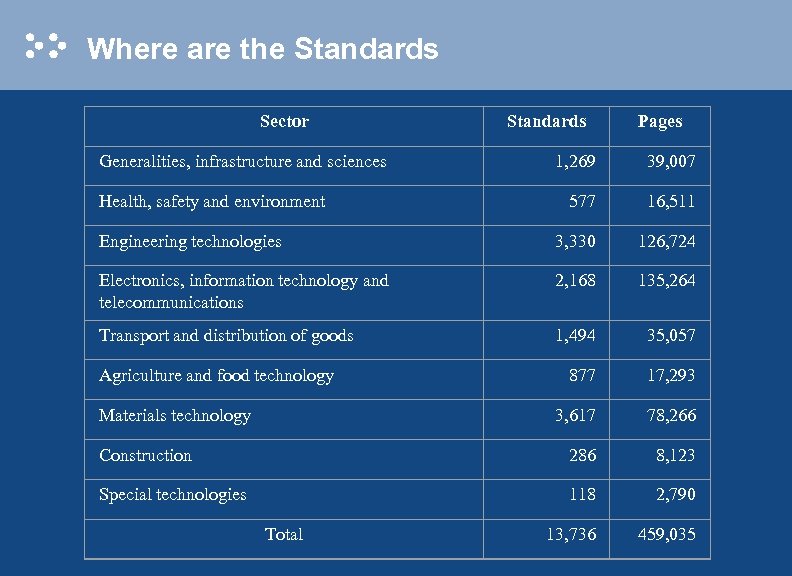 Where are the Standards Sector Generalities, infrastructure and sciences Standards Pages 1, 269 39, 007 577 16, 511 Engineering technologies 3, 330 126, 724 Electronics, information technology and telecommunications 2, 168 135, 264 Transport and distribution of goods 1, 494 35, 057 877 17, 293 3, 617 78, 266 Construction 286 8, 123 Special technologies 118 2, 790 13, 736 459, 035 Health, safety and environment Agriculture and food technology Materials technology Total
Where are the Standards Sector Generalities, infrastructure and sciences Standards Pages 1, 269 39, 007 577 16, 511 Engineering technologies 3, 330 126, 724 Electronics, information technology and telecommunications 2, 168 135, 264 Transport and distribution of goods 1, 494 35, 057 877 17, 293 3, 617 78, 266 Construction 286 8, 123 Special technologies 118 2, 790 13, 736 459, 035 Health, safety and environment Agriculture and food technology Materials technology Total
 Which ISO Standards • The ISO family includes: – 9000: 1994 – Guidelines for selection and use – 9001: 1994 – Quality assurance in design/development, production, installation and servicing – 9002: 1994 – Quality assurance in production, installation, and servicing – 9003: 1994 – Quality assurance in final inspection and test – 9004: 1994 – Quality management and quality system elements • Which Standards Are We Dealing With – Specifically 9001 & 9002:
Which ISO Standards • The ISO family includes: – 9000: 1994 – Guidelines for selection and use – 9001: 1994 – Quality assurance in design/development, production, installation and servicing – 9002: 1994 – Quality assurance in production, installation, and servicing – 9003: 1994 – Quality assurance in final inspection and test – 9004: 1994 – Quality management and quality system elements • Which Standards Are We Dealing With – Specifically 9001 & 9002:
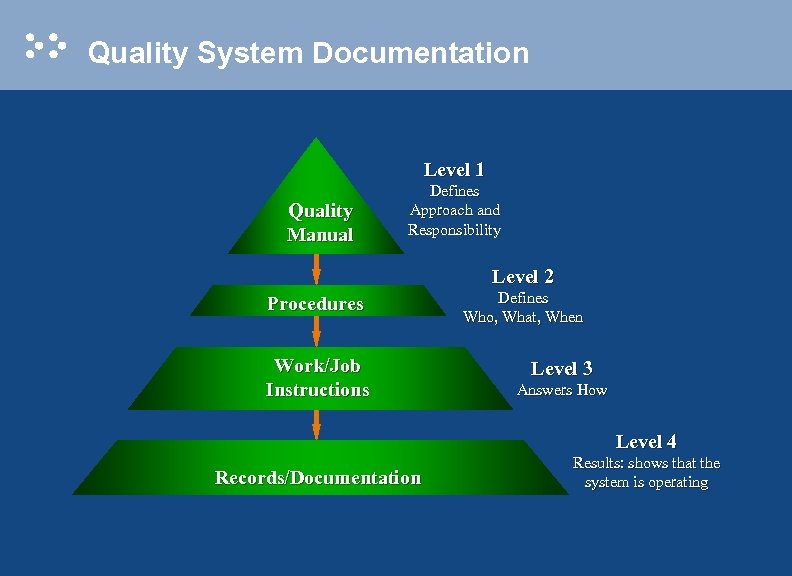 Quality System Documentation Level 1 Quality Manual Defines Approach and Responsibility Level 2 Procedures Work/Job Instructions Defines Who, What, When Level 3 Answers How Level 4 Records/Documentation Results: shows that the system is operating
Quality System Documentation Level 1 Quality Manual Defines Approach and Responsibility Level 2 Procedures Work/Job Instructions Defines Who, What, When Level 3 Answers How Level 4 Records/Documentation Results: shows that the system is operating
 ISO 9001: 2000 Structure 4. 5. Quality Management System 4. 1 General requirements 4. 2 Document requirements Management Responsibility 5. 1 Management commitment 5. 2 Customer focus 5. 3 Quality policy 5. 4 Planning 5. 5 Responsibility, authority, communication 5. 6 Management review Resource Management 6. 1 Provision of resources 6. 2 Human resources 6. 3 Infrastructure 6. 4 Work environment Product realization 7. 1 Planning of product realization 7. 2 Customer-related processes 7. 3 Design and development 7. 4 Purchasing 7. 5 Production and service provision 7. 6 Control of monitoring and measuring devices 8. 6. 7. Measurement, Analysis & Improvement 8. 1 General 8. 2 Monitoring and measurement 8. 3 Control of nonconforming product 8. 4 Analysis of data 8. 5 Improvement
ISO 9001: 2000 Structure 4. 5. Quality Management System 4. 1 General requirements 4. 2 Document requirements Management Responsibility 5. 1 Management commitment 5. 2 Customer focus 5. 3 Quality policy 5. 4 Planning 5. 5 Responsibility, authority, communication 5. 6 Management review Resource Management 6. 1 Provision of resources 6. 2 Human resources 6. 3 Infrastructure 6. 4 Work environment Product realization 7. 1 Planning of product realization 7. 2 Customer-related processes 7. 3 Design and development 7. 4 Purchasing 7. 5 Production and service provision 7. 6 Control of monitoring and measuring devices 8. 6. 7. Measurement, Analysis & Improvement 8. 1 General 8. 2 Monitoring and measurement 8. 3 Control of nonconforming product 8. 4 Analysis of data 8. 5 Improvement
 Similarities • Both are based on processes • Say what you do; do what you say • Record information for later use and analysis • Require strong management support to succeed • Provide a structured approach to improvement • Require an outside audit for “certification” • Both are refined/improved over time
Similarities • Both are based on processes • Say what you do; do what you say • Record information for later use and analysis • Require strong management support to succeed • Provide a structured approach to improvement • Require an outside audit for “certification” • Both are refined/improved over time
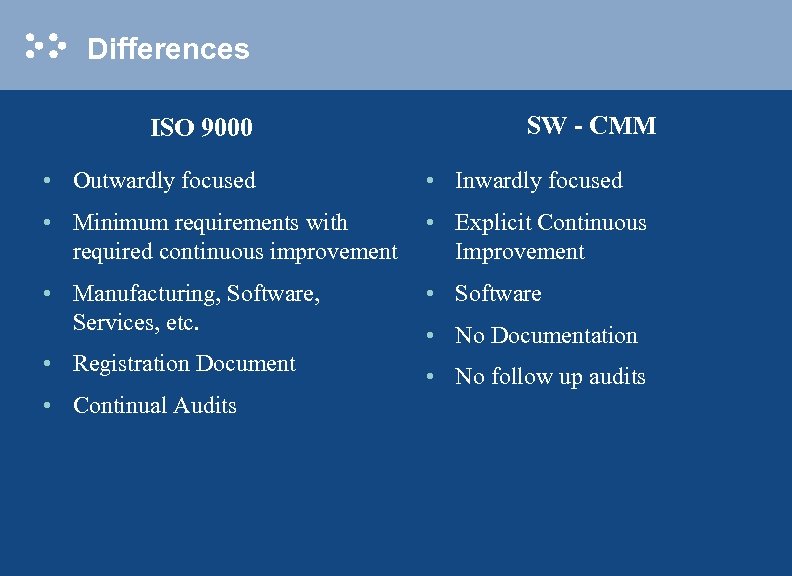 Differences ISO 9000 SW - CMM • Outwardly focused • Inwardly focused • Minimum requirements with required continuous improvement • Explicit Continuous Improvement • Manufacturing, Software, Services, etc. • Software • Registration Document • Continual Audits • No Documentation • No follow up audits
Differences ISO 9000 SW - CMM • Outwardly focused • Inwardly focused • Minimum requirements with required continuous improvement • Explicit Continuous Improvement • Manufacturing, Software, Services, etc. • Software • Registration Document • Continual Audits • No Documentation • No follow up audits
 What’s The Future X CMM - Continued revisions to basic model and move to more integrated models X ISO - ISO 2000 replaces the 9000 series X Companies are demanding ISO registration X More companies are demanding CMM certification, especially the government
What’s The Future X CMM - Continued revisions to basic model and move to more integrated models X ISO - ISO 2000 replaces the 9000 series X Companies are demanding ISO registration X More companies are demanding CMM certification, especially the government
 So What!! Why should you care about CMM or ISO? Why is it important? How might it impact your personally?
So What!! Why should you care about CMM or ISO? Why is it important? How might it impact your personally?
 Status Reports CMM 2002 aug. pdf ISO survey 10 thcycle. pdf
Status Reports CMM 2002 aug. pdf ISO survey 10 thcycle. pdf
 Additional Information • For CMM www. sei. cmu. edu/cmms/cmms. html • For ISO www. iso. ch/iso/en/isoonline. frontpage
Additional Information • For CMM www. sei. cmu. edu/cmms/cmms. html • For ISO www. iso. ch/iso/en/isoonline. frontpage
 eds. com
eds. com


