068ef664e2f3cca75cdd95bb016d8b1d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

CMGT 442 Information Systems Risk Management Philip Robbins – November 21, 2012 (Week 2) University of Phoenix Mililani Campus

Objectives: Week 2 • - Risk Assessment (Part 1) Review Week 1: Concepts LT Activity: Week 1 & Week 2 Article Readings Stuxnet Week 2: Components of Risk Quiz #2 Review Week 2: Questions Assignments: IDV & LT Papers Review Information Sharing Articles
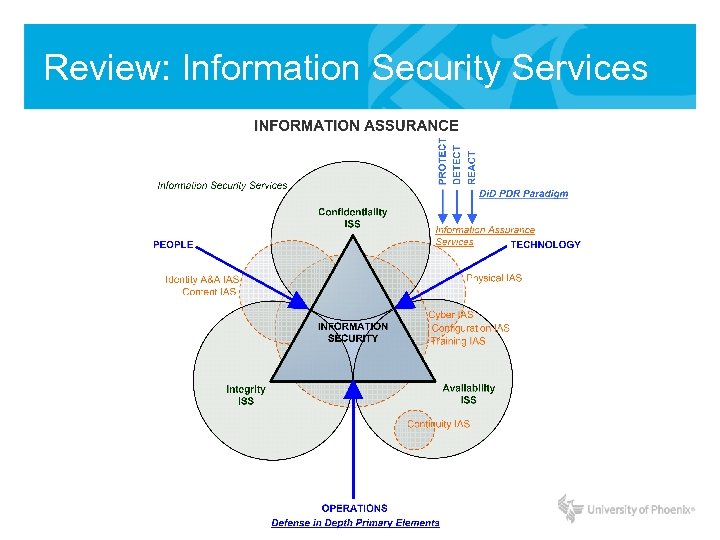
Review: Information Security Services
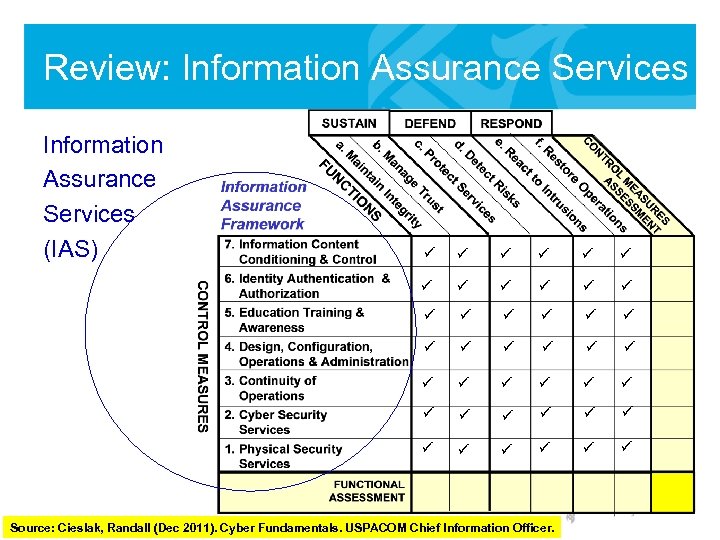
Review: Information Assurance Services (IAS) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Source: Cieslak, Randall (Dec 2011). Cyber Fundamentals. USPACOM Chief Information Officer.
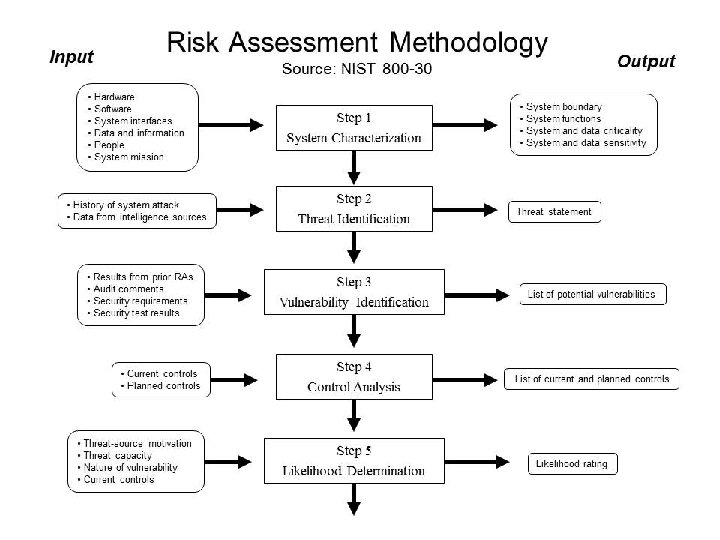
Review: NIST SP 800 -30
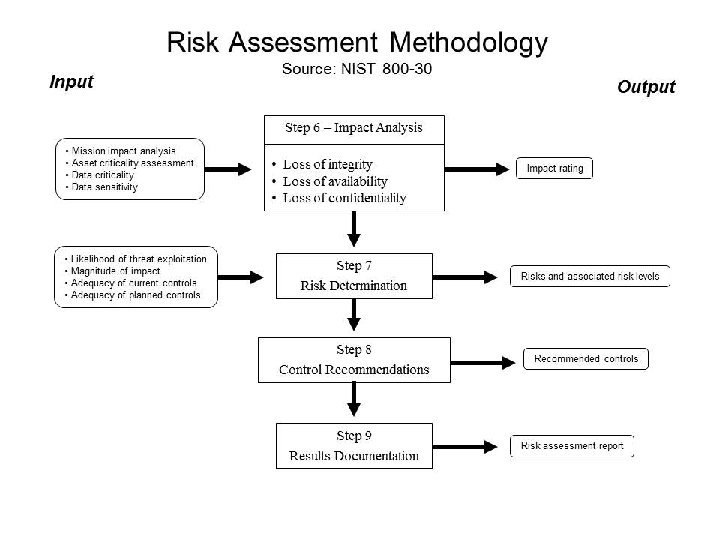
Review: NIST SP 800 -30

Learning Team Activity • Activity: Review Week 1 & 2 ‘Article’ Readings - 15 minutes: Read Articles - 10 minutes: Answer article questions - 10 minutes: Present your article to the class - Submit for credit.

LT Activity: Week 1 Article Readings • Barr (2011) - What special issues must be addressed for a risk management strategy that supports user-facing, web-based systems? - What are the risks associated with disruption of these systems? • Ledford (2012) - What special issues must be considered for corporate data which are not fully digitized? - What are the risks associated with the loss of this data? - What recovery procedures do you recommend for these situations?

LT Activity: Week 2 Article Readings • Keston (2008) - How important is enterprise identity management for reducing risk throughout the enterprise? - Explain why a viable risk management strategy must include, at a minimum, a solid enterprise identity management process. • Vosevich (2011) - What software must be considered to provide adequate security management across the enterprise?
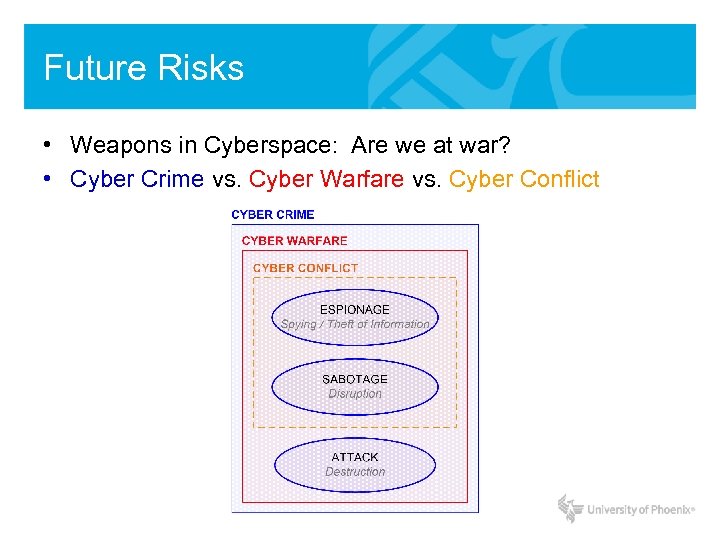
Future Risks • Weapons in Cyberspace: Are we at war? • Cyber Crime vs. Cyber Warfare vs. Cyber Conflict

Break? • This is probably time for a break…

Review: Risk Definition • What is Risk? thus • Units for measurement: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Source: Robbins, P. (Dec, 2011). Security Risk Analysis and Critical Information Systems. Hawaii Pacific University, Honolulu, HI.

Defining Risk • Risk is conditional, NOT independent. Source: Robbins, P. (Dec, 2011). Security Risk Analysis and Critical Information Systems. Hawaii Pacific University, Honolulu, HI.

Defining Risk • Expected Value of Risk = Product of Risks • Risk is never zero: “We can never be 100% confident for protection” • Risk Dimension (units): confidence in the loss of ISS, C-I-A “Risk Loss Confidence” Source: Robbins, P. (Dec, 2011). Security Risk Analysis and Critical Information Systems. Hawaii Pacific University, Honolulu, HI.

Risk Behavior Risk Loss Confidence Increases through interconnections with other network enclaves (risks)! Network Enclave #1 Network Enclave #3 Network Enclave #2
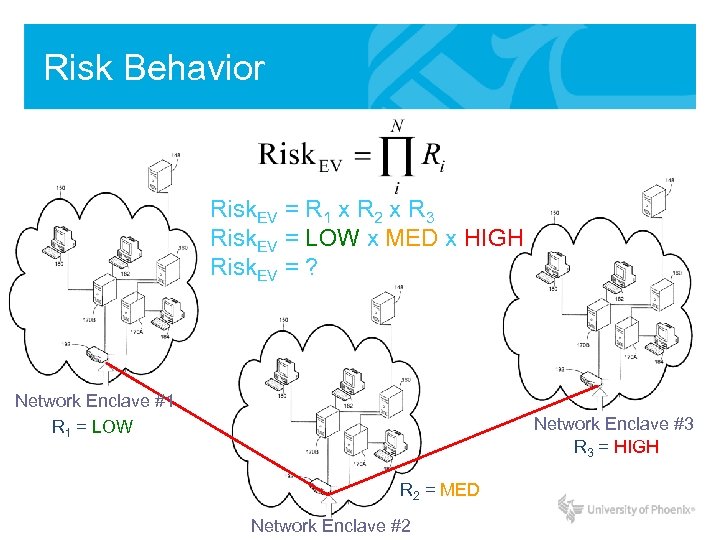
Risk Behavior Risk. EV = R 1 x R 2 x R 3 Risk. EV = LOW x MED x HIGH Risk. EV = ? Network Enclave #1 R 1 = LOW Network Enclave #3 R 3 = HIGH R 2 = MED Network Enclave #2
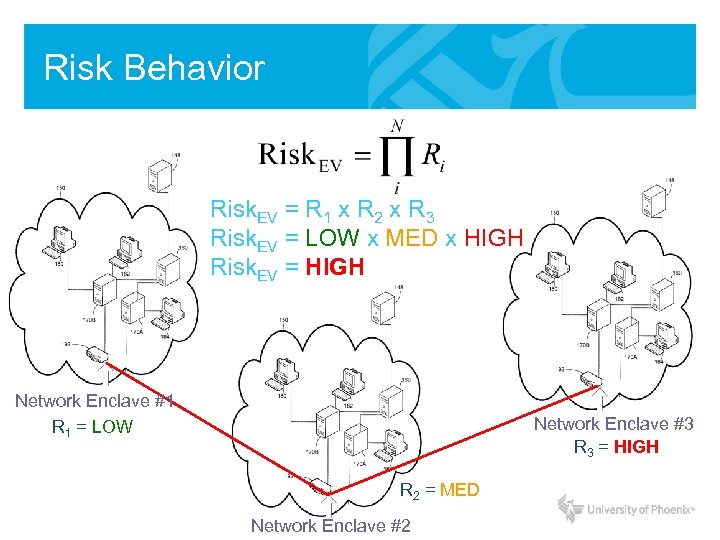
Risk Behavior Risk. EV = R 1 x R 2 x R 3 Risk. EV = LOW x MED x HIGH Risk. EV = HIGH Network Enclave #1 R 1 = LOW Network Enclave #3 R 3 = HIGH R 2 = MED Network Enclave #2
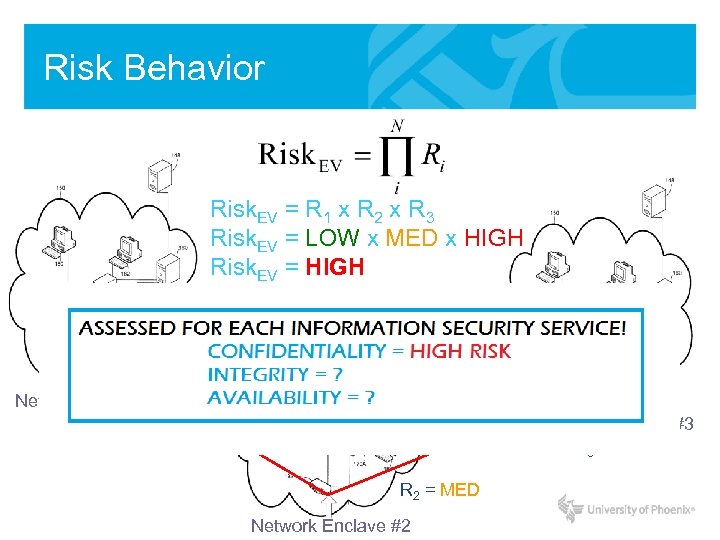
Risk Behavior Risk. EV = R 1 x R 2 x R 3 Risk. EV = LOW x MED x HIGH Risk. EV = HIGH Network Enclave #1 R 1 = LOW Network Enclave #3 R 3 = HIGH R 2 = MED Network Enclave #2
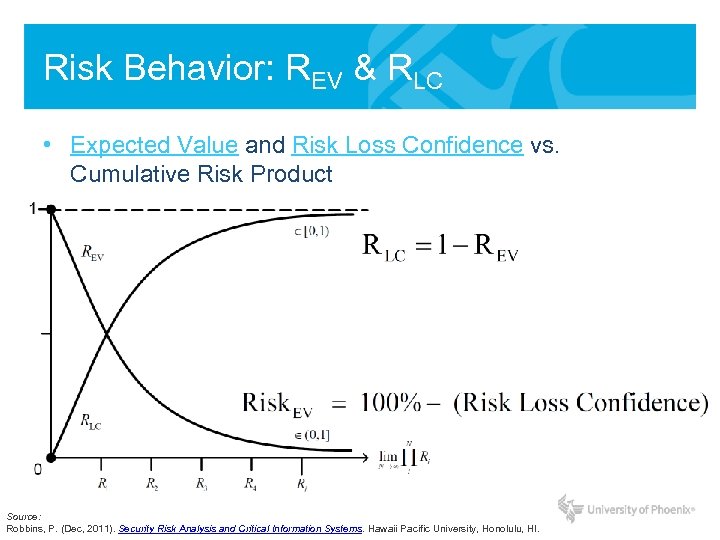
Risk Behavior: REV & RLC • Expected Value and Risk Loss Confidence vs. Cumulative Risk Product Source: Robbins, P. (Dec, 2011). Security Risk Analysis and Critical Information Systems. Hawaii Pacific University, Honolulu, HI.

Total Risk • How do we quantify total risk? - Average the risk to each Information Security Service: Source: Robbins, P. (Dec, 2011). Security Risk Analysis and Critical Information Systems. Hawaii Pacific University, Honolulu, HI.
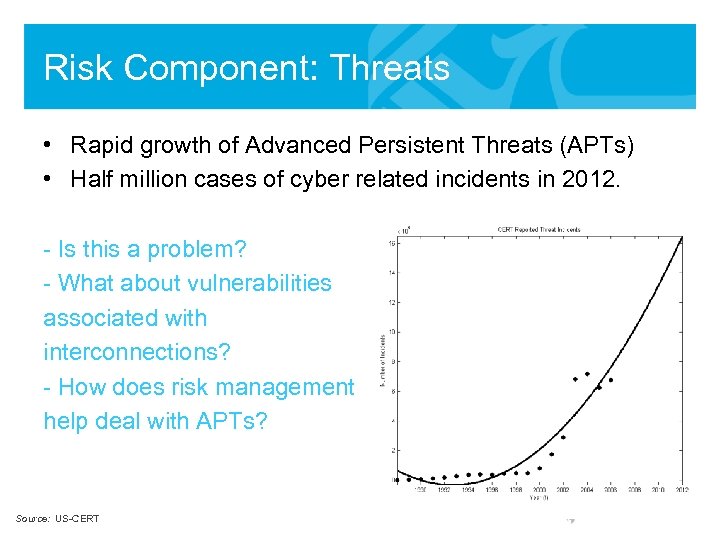
Risk Component: Threats • Rapid growth of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) • Half million cases of cyber related incidents in 2012. - Is this a problem? - What about vulnerabilities associated with interconnections? - How does risk management help deal with APTs? Source: US-CERT

Risk Component: Vulnerabilities • What are vulnerabilities? Any flaw or weakness that can be exploited. – Poorly communicated or implemented policy – Improperly configured systems or controls – Inadequately trained personnel
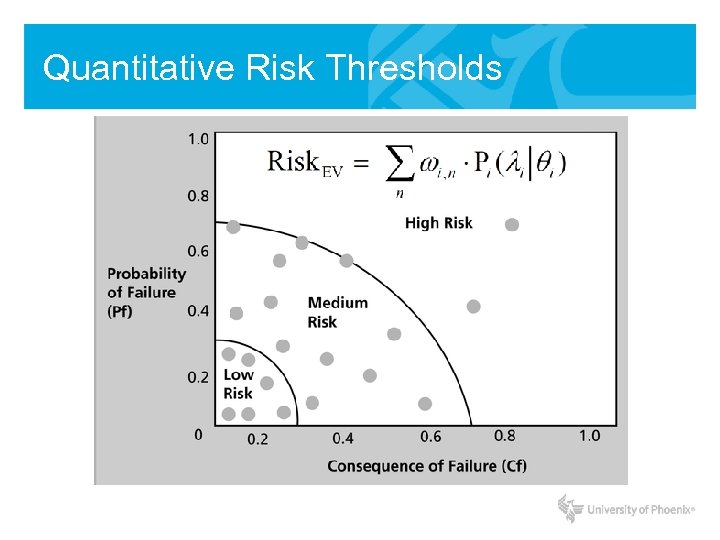
Quantitative Risk Thresholds
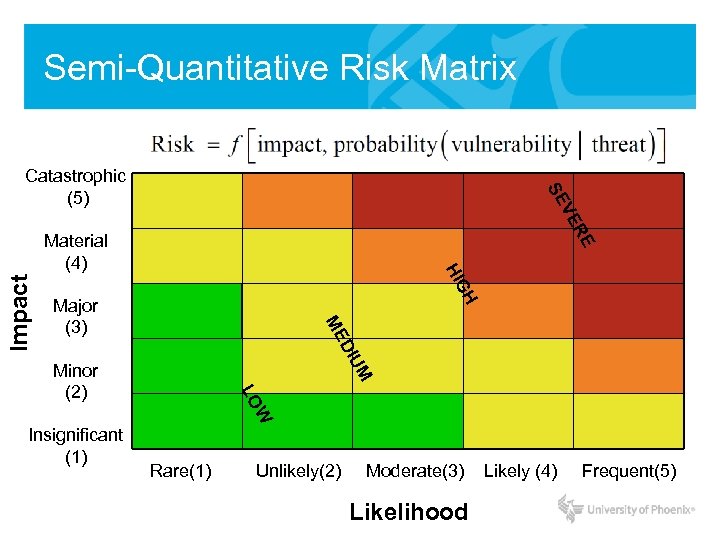
Semi-Quantitative Risk Matrix R VE SE Catastrophic (5) GH HI Major (3) ME UM DI Impact E Material (4) W Insignificant (1) LO Minor (2) Rare(1) Unlikely(2) Moderate(3) Likelihood Likely (4) Frequent(5)
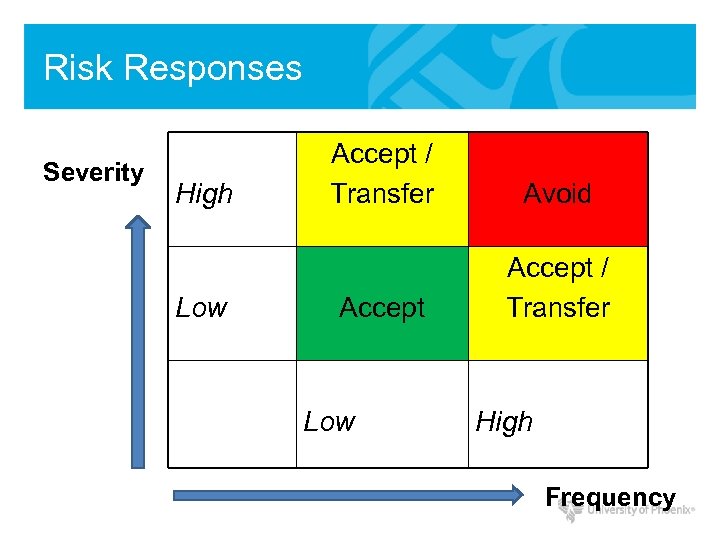
Risk Responses Severity High Low Accept / Transfer Avoid Accept / Transfer Low High Frequency

Risk Responses • Risk Avoidance – Halt or stop activity causing risk • Risk Transference – Transfer the risk (i. e. buy insurance) • Risk Mitigation – Reduce impact with controls/safeguards • Risk Acceptance – Understand consequences and accept risk

Information Systems Risk Components • Let’s recap: What are the components of Information Systems Risk? - Threats & Threat Agents - Vulnerabilities (Weakness) - Controls (Safeguards) - Impact How is each component important to understanding and managing risk?
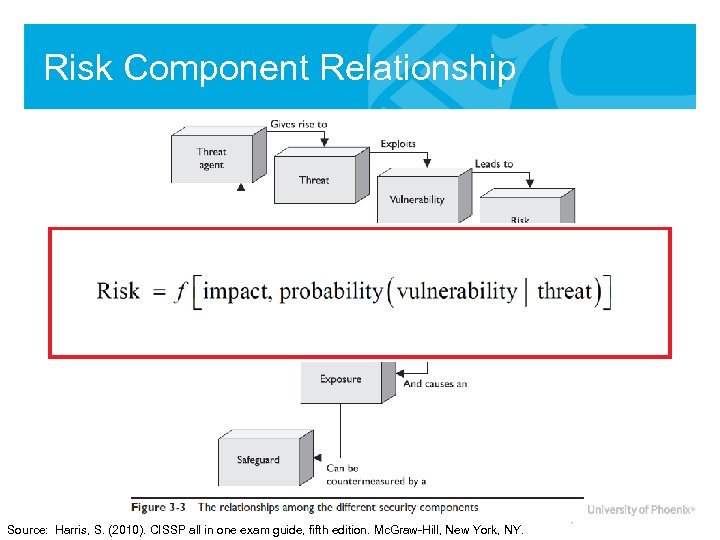
Risk Component Relationship Source: Harris, S. (2010). CISSP all in one exam guide, fifth edition. Mc. Graw-Hill, New York, NY.

Break? • This is probably time for a break…

Quiz: Week 1 • 10 -15 minutes

Week 2 Review Questions

Question #1 What is the likelihood of a threat taking advantage of a vulnerability called? A. B. C. D. A risk A residual risk An exposure A countermeasure

Question #1 What is the likelihood of a threat taking advantage of a vulnerability called? A. B. C. D. A risk A residual risk An exposure A countermeasure

Question #2 Which of the following combinations best defines risk? A. Threat coupled with a breach. B. Threat coupled with a vulnerability. C. Threat coupled with a breach of security. D. Vulnerability coupled with an attack.

Question #2 Which of the following combinations best defines risk? A. Threat coupled with a breach. B. Threat coupled with a vulnerability. C. Threat coupled with a breach of security. D. Vulnerability coupled with an attack.

Question #3 What can be defined as an event that could cause harm to information systems? A. B. C. D. A risk A threat A vulnerability A weakness

Question #3 What can be defined as an event that could cause harm to information systems? A. B. C. D. A risk A threat A vulnerability A weakness

Question #4 What is the definition of a security exposure? A. B. C. D. An instance of being exposed to losses from a threat Any potential danger to information or systems Loss potential due to a threat

Question #4 What is the definition of a security exposure? A. B. C. D. An instance of being exposed to losses from a threat Any potential danger to information or systems Loss potential due to a threat

Question #5 The absence of a safeguard, or a weakness in a system that may possibly be exploited, is called a? A. B. C. D. Threat Exposure Vulnerability Risk

Question #5 The absence of a safeguard, or a weakness in a system that may possibly be exploited, is called a? A. B. C. D. Threat Exposure Vulnerability Risk
068ef664e2f3cca75cdd95bb016d8b1d.ppt