df8c3376455a001b4cd071357fcedc67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 CMG Conference Health Identifiers Act Conference 2016 What does the Act mean for your organisation & what major changes should you expect? “Use of Heath Identifier – Case Studies on International Best Practice” Dr Jack Nagle, CEO, Alpha
CMG Conference Health Identifiers Act Conference 2016 What does the Act mean for your organisation & what major changes should you expect? “Use of Heath Identifier – Case Studies on International Best Practice” Dr Jack Nagle, CEO, Alpha
 Learning Aims • Common understanding on IHIs • Ireland’s Journey Ahead • International Best Practice – Learning from International Experience • Looking to the future: – – learning; use; benefits Preventing the pitfalls Challenges Patients / Service Providers
Learning Aims • Common understanding on IHIs • Ireland’s Journey Ahead • International Best Practice – Learning from International Experience • Looking to the future: – – learning; use; benefits Preventing the pitfalls Challenges Patients / Service Providers
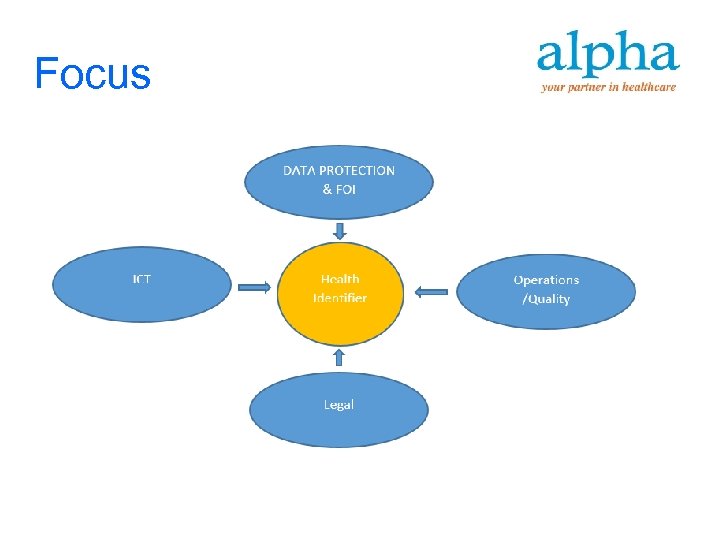 Focus
Focus
 Individual Health Identifier An Individual Number that Uniquely and Safely Identifies Each Person https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. S 2 iwllhbdo
Individual Health Identifier An Individual Number that Uniquely and Safely Identifies Each Person https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. S 2 iwllhbdo
 Health Identifier Source: HSE https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. S 2 iwllhbdo – PIA under way by HSE
Health Identifier Source: HSE https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. S 2 iwllhbdo – PIA under way by HSE
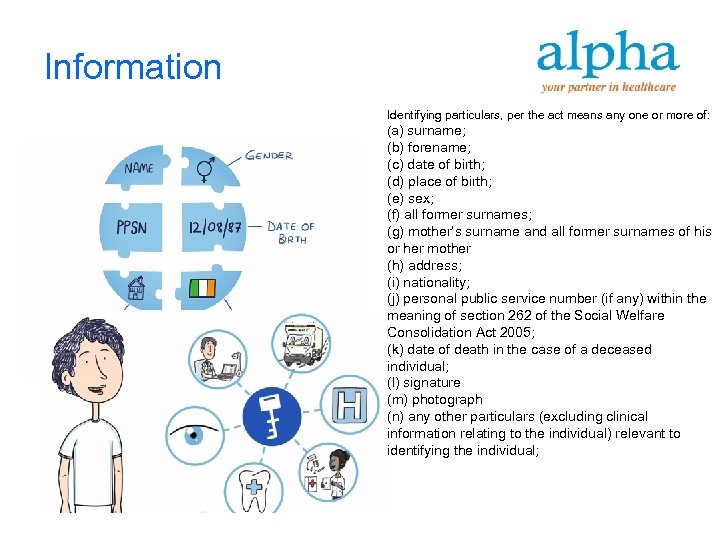 Information Identifying particulars, per the act means any one or more of: (a) surname; (b) forename; (c) date of birth; (d) place of birth; (e) sex; (f) all former surnames; (g) mother’s surname and all former surnames of his or her mother (h) address; (i) nationality; (j) personal public service number (if any) within the meaning of section 262 of the Social Welfare Consolidation Act 2005; (k) date of death in the case of a deceased individual; (l) signature (m) photograph (n) any other particulars (excluding clinical information relating to the individual) relevant to identifying the individual;
Information Identifying particulars, per the act means any one or more of: (a) surname; (b) forename; (c) date of birth; (d) place of birth; (e) sex; (f) all former surnames; (g) mother’s surname and all former surnames of his or her mother (h) address; (i) nationality; (j) personal public service number (if any) within the meaning of section 262 of the Social Welfare Consolidation Act 2005; (k) date of death in the case of a deceased individual; (l) signature (m) photograph (n) any other particulars (excluding clinical information relating to the individual) relevant to identifying the individual;
 International Use of IHI
International Use of IHI
 Research and Studies. • RAND (2008) did a study on the potential implementation of a National Health Information Network in the US. • Study outcomes: – UHI cost ~ $ 11 Bn – Benefits to healthcare system would be greater than this – Easier to safeguard patient privacy with a records system that makes use of a unique health ID, – Social security numbers – poor option as so widely used & pose risk of identity theft.
Research and Studies. • RAND (2008) did a study on the potential implementation of a National Health Information Network in the US. • Study outcomes: – UHI cost ~ $ 11 Bn – Benefits to healthcare system would be greater than this – Easier to safeguard patient privacy with a records system that makes use of a unique health ID, – Social security numbers – poor option as so widely used & pose risk of identity theft.
 Research and Studies. • Key Learning: – Massive potential benefits of implementing an IHI, – Huge challenges and hurdles with practical implementation – legal / operational. – Privacy advocates highlighted issues with relevant legislation (HIPAA) – Privacy rules did not cover the full range of organisations that would be involved in collecting, processing and using health records on the NHIN.
Research and Studies. • Key Learning: – Massive potential benefits of implementing an IHI, – Huge challenges and hurdles with practical implementation – legal / operational. – Privacy advocates highlighted issues with relevant legislation (HIPAA) – Privacy rules did not cover the full range of organisations that would be involved in collecting, processing and using health records on the NHIN.
 Implementing a UHI Two issues surrounding the implementation of UHIs that will need to be addressed by all jurisdictions are how UHIs will be governed, managed and audited, and how and whether to apply identifiers to legacy healthcare records. Source: Universal Health Identifiers: Issues and Requirements for Successful Patient Information Exchange, Lorraine Fernandes, RHIA , Scott Schumacher, Ph. D. IBM (2010)
Implementing a UHI Two issues surrounding the implementation of UHIs that will need to be addressed by all jurisdictions are how UHIs will be governed, managed and audited, and how and whether to apply identifiers to legacy healthcare records. Source: Universal Health Identifiers: Issues and Requirements for Successful Patient Information Exchange, Lorraine Fernandes, RHIA , Scott Schumacher, Ph. D. IBM (2010)
 International Best Practice United Kingdom NHS Canada Australia New Zealand
International Best Practice United Kingdom NHS Canada Australia New Zealand
 The UK NHS • NHS Founded 1948 • Principle – good healthcare should be available to all regardless of wealth, • NHS remains free of charge at the point of use for all, • The scale of the NHS: – Employs 1. 7 m people, – 120, 000 hospital doctors, 40, 000 GPs, 400, 000 nurses & 25, 000 ambulance staff – NHS UK – caters for 51 m population – Deals with 1 m patients very 36 hours or 463 patients a second! – In 1948 –budget was £ 437 m ( £ 9 bn equiv); 2010 –budget > £ 110 bn! – Paid for by taxes – in 2008/09 - £ 1980 per head of population,
The UK NHS • NHS Founded 1948 • Principle – good healthcare should be available to all regardless of wealth, • NHS remains free of charge at the point of use for all, • The scale of the NHS: – Employs 1. 7 m people, – 120, 000 hospital doctors, 40, 000 GPs, 400, 000 nurses & 25, 000 ambulance staff – NHS UK – caters for 51 m population – Deals with 1 m patients very 36 hours or 463 patients a second! – In 1948 –budget was £ 437 m ( £ 9 bn equiv); 2010 –budget > £ 110 bn! – Paid for by taxes – in 2008/09 - £ 1980 per head of population,
 NHS – UK - UHI • • The NHS Number in its current format, was developed in 1996 to replace many different numbering systems used in the NHS England. The NHS Operating Framework 2008/9 document mandates the use of the NHS Number as the unique patient identifier in all relevant administrative and clinical systems and in all communications with patients. NHS Number – Unique 10 Digit Number - the first nine digits constitute the identifier and the tenth is a check digit that ensures its validity NHS Number passes majority of the ASTM criteria. Separate to National insurance Number Summary Care Record (SCR) – Linked to NHS Number The infrastructure behind the critical NHS Spine platform has been replaced by The Health and Social Care Information Centre (HSCIC). The nationwide infrastructure – upgraded between 22 and 25 August 2014 – connects clinicians, patients and national applications, as well as storing patient information.
NHS – UK - UHI • • The NHS Number in its current format, was developed in 1996 to replace many different numbering systems used in the NHS England. The NHS Operating Framework 2008/9 document mandates the use of the NHS Number as the unique patient identifier in all relevant administrative and clinical systems and in all communications with patients. NHS Number – Unique 10 Digit Number - the first nine digits constitute the identifier and the tenth is a check digit that ensures its validity NHS Number passes majority of the ASTM criteria. Separate to National insurance Number Summary Care Record (SCR) – Linked to NHS Number The infrastructure behind the critical NHS Spine platform has been replaced by The Health and Social Care Information Centre (HSCIC). The nationwide infrastructure – upgraded between 22 and 25 August 2014 – connects clinicians, patients and national applications, as well as storing patient information.
 UK – UHI – Security & Confidentiality • • Use of 'smart cards' with a Personal Identification Number (PIN). These are individually issued to staff that will be using the NHS Care Records Service and accessing the PDS, following training. Role Based Access – i. e a consultant will see more detail than a receptionist who will only see the information needed to process an appointment, not the full NHS Care record. NHS Care Records will only be accessible in an identifiable form to authorised health care professionals who have a justifiable clinical or legal reason to see the information. For NHS research and management purposes, the data may be used in an anonymised format There will be a log kept of those who use the NHS Care Records Service to access a care record, showing who they are and what they added or changed. The patient can ask to see this information The PDS will not itself hold any clinical information or sensitive data items such as ethnicity or religion
UK – UHI – Security & Confidentiality • • Use of 'smart cards' with a Personal Identification Number (PIN). These are individually issued to staff that will be using the NHS Care Records Service and accessing the PDS, following training. Role Based Access – i. e a consultant will see more detail than a receptionist who will only see the information needed to process an appointment, not the full NHS Care record. NHS Care Records will only be accessible in an identifiable form to authorised health care professionals who have a justifiable clinical or legal reason to see the information. For NHS research and management purposes, the data may be used in an anonymised format There will be a log kept of those who use the NHS Care Records Service to access a care record, showing who they are and what they added or changed. The patient can ask to see this information The PDS will not itself hold any clinical information or sensitive data items such as ethnicity or religion
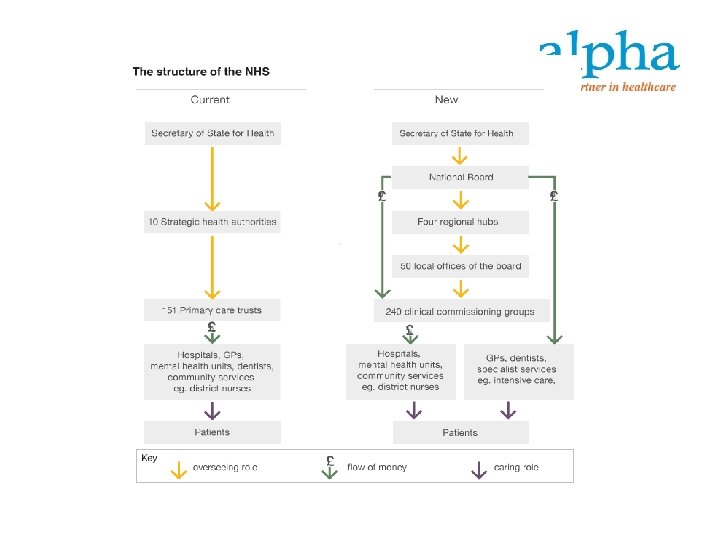
 NHS – UK - Infrastructure
NHS – UK - Infrastructure
 Integrated Digital Record • On a local level some Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs) have started to integrate patients' health and social care records to improve the overall care they provide in their area. • Camden in London is one of the first CCG areas to introduce this.
Integrated Digital Record • On a local level some Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs) have started to integrate patients' health and social care records to improve the overall care they provide in their area. • Camden in London is one of the first CCG areas to introduce this.
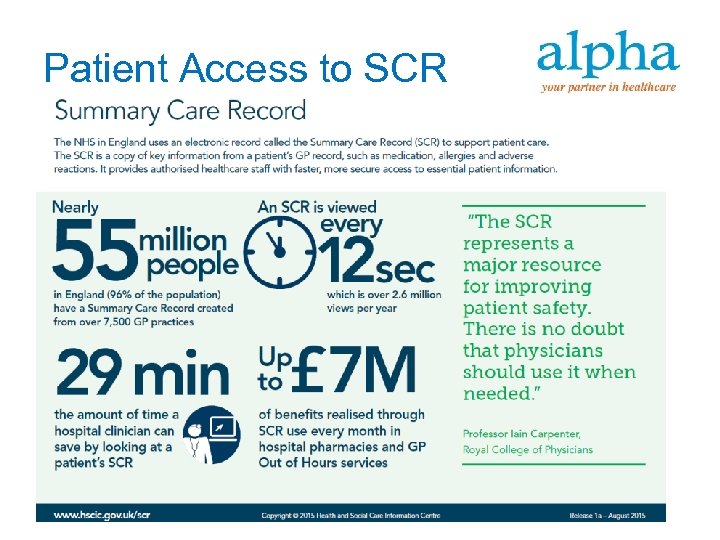 Patient Access to SCR
Patient Access to SCR
 Patient Access to SCR Patient can access their summary care records.
Patient Access to SCR Patient can access their summary care records.
 Patient Access to SCR
Patient Access to SCR
 UK – NHS – Lessons Learnt The following are some of the lessons learned from the NHS experience: • buy-in from the primary care organisations is essential to successful implementation as the majority of secondary care workload is referred from the primary care setting • extensive training is required across all levels of staff to ensure UHI and demographic data integrity as much as possible • full use of the UHI can only be achieved by implementation of a single national system holding a defined standardised dataset • a national health and social care staff and public awareness campaign to explain the benefits of the UHI to individuals is necessary to encourage people to provide their UHI at point of care. • the upgrading of local IT systems so that they are compatible with the UHI system and dataset is necessary • early review of costs aligned to the benefits to patients and clinicians that can be achieved is necessary to ensure cost effectiveness and efficiency. Ref: HIQA – International Review of UHI’s for Individuals (2010)
UK – NHS – Lessons Learnt The following are some of the lessons learned from the NHS experience: • buy-in from the primary care organisations is essential to successful implementation as the majority of secondary care workload is referred from the primary care setting • extensive training is required across all levels of staff to ensure UHI and demographic data integrity as much as possible • full use of the UHI can only be achieved by implementation of a single national system holding a defined standardised dataset • a national health and social care staff and public awareness campaign to explain the benefits of the UHI to individuals is necessary to encourage people to provide their UHI at point of care. • the upgrading of local IT systems so that they are compatible with the UHI system and dataset is necessary • early review of costs aligned to the benefits to patients and clinicians that can be achieved is necessary to ensure cost effectiveness and efficiency. Ref: HIQA – International Review of UHI’s for Individuals (2010)
 e. Health – Australia https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j 6 d 0 Tz 18 u 4 video explain IHI in Australia
e. Health – Australia https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j 6 d 0 Tz 18 u 4 video explain IHI in Australia
 e. Health – Australia • Individual Healthcare Identifier (IHI) Unique 16 digit numbers • Number is generated by ‘medicare’ the national healthcare system. • Allocated IHI – if enrolled in Medicare or hold Dept. of Veterans’ Affairs treatment card • Visitors/students in Australia can apply for an IHI while in the country. • You can view IHI and IHI history online if you are registered for a Medicare online account.
e. Health – Australia • Individual Healthcare Identifier (IHI) Unique 16 digit numbers • Number is generated by ‘medicare’ the national healthcare system. • Allocated IHI – if enrolled in Medicare or hold Dept. of Veterans’ Affairs treatment card • Visitors/students in Australia can apply for an IHI while in the country. • You can view IHI and IHI history online if you are registered for a Medicare online account.
 Background • Introduced in 2010 and legislated for governmental assignment of IHI once a person registers. • 2013 the federal government commissioned a study of the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Record (PCEHR). • After 1. 5 years only 6 percent of the Australian population was using the PCEHR. • The study recommended changes to governance, a switch to an opt-out model by 2015, and the revamping of the board to include representation from clinicians, other healthcare providers, and software vendors
Background • Introduced in 2010 and legislated for governmental assignment of IHI once a person registers. • 2013 the federal government commissioned a study of the Personally Controlled Electronic Health Record (PCEHR). • After 1. 5 years only 6 percent of the Australian population was using the PCEHR. • The study recommended changes to governance, a switch to an opt-out model by 2015, and the revamping of the board to include representation from clinicians, other healthcare providers, and software vendors
 Privacy - Australia • IHI may be given to your healthcare provider or authorised employees of a healthcare organisation. • The system does not allow for browsing of records. • Requests for IHI will only be given when there is an exact match with the patient information given. • Each time your IHI is accessed, the details of who requested your identifier is recorded in your IHI history. • Penalties for the intentional misuse of an IHI are set out in legislation and current privacy laws apply.
Privacy - Australia • IHI may be given to your healthcare provider or authorised employees of a healthcare organisation. • The system does not allow for browsing of records. • Requests for IHI will only be given when there is an exact match with the patient information given. • Each time your IHI is accessed, the details of who requested your identifier is recorded in your IHI history. • Penalties for the intentional misuse of an IHI are set out in legislation and current privacy laws apply.
 Disclosure – Australia • healthcare providers, authorised employees of healthcare providers or contracted service providers so they can communicate or manage a patient’s health information as part of their healthcare • a person to whom you have authorised disclosure of personal information • registration authorities that are responsible under a law for registering members of a particular health profession for the specific purpose of assigning healthcare identifiers to their registrants • the My Health Record system operator • entities that issue security credentials for the specific purpose of authenticating a healthcare provider’s identity in electronic transmissions
Disclosure – Australia • healthcare providers, authorised employees of healthcare providers or contracted service providers so they can communicate or manage a patient’s health information as part of their healthcare • a person to whom you have authorised disclosure of personal information • registration authorities that are responsible under a law for registering members of a particular health profession for the specific purpose of assigning healthcare identifiers to their registrants • the My Health Record system operator • entities that issue security credentials for the specific purpose of authenticating a healthcare provider’s identity in electronic transmissions
 My Health Record System – Australia • A digital health record in the My Health Record system is a secure online summary of your health information. The My Health Record system uses your IHI to create an online health summary.
My Health Record System – Australia • A digital health record in the My Health Record system is a secure online summary of your health information. The My Health Record system uses your IHI to create an online health summary.
 New Zealand • The Minister of Health in New Zealand has overall responsibility for the health and disability system • New Zealand has a reputation for leadership in national health information systems- national unique identifier in place 1970 s , fully specified NHI system since 1992. Lessons learned were highlighted in a review of the NHI undertaken in 2006: • the use of the unique identifier must span all levels of health and social care, particularly primary care, in order to be truly effective in accurately identifying and tracking the care of individuals. • privacy concerns around the accuracy of data held on individuals should be addressed and prevented if possible by avoiding manual transcription of the identifier and minimising duplicate numbers and records in the central repository • real time assignability of the UHI. • the ability for authorised users to update individual demographics on the UHI system in real time
New Zealand • The Minister of Health in New Zealand has overall responsibility for the health and disability system • New Zealand has a reputation for leadership in national health information systems- national unique identifier in place 1970 s , fully specified NHI system since 1992. Lessons learned were highlighted in a review of the NHI undertaken in 2006: • the use of the unique identifier must span all levels of health and social care, particularly primary care, in order to be truly effective in accurately identifying and tracking the care of individuals. • privacy concerns around the accuracy of data held on individuals should be addressed and prevented if possible by avoiding manual transcription of the identifier and minimising duplicate numbers and records in the central repository • real time assignability of the UHI. • the ability for authorised users to update individual demographics on the UHI system in real time
 Canada (Newfoundland Labrador) – Lessons Learnt They defined the purpose of the UPI /Client Registry (CR) as: • provide a central database of clients of the health and community services system • identify accurately an individual during an encounter with the health system • confirm an individual’s eligibility for free medical care coverage • maintain the accuracy of client indexes in users’ local systems • identify newborns for metabolic screening • provide for the linking of health information in the proposed Electronic Health Records (EHR) Ref: HIQA – International Review of UHI’s for Individuals (2010)
Canada (Newfoundland Labrador) – Lessons Learnt They defined the purpose of the UPI /Client Registry (CR) as: • provide a central database of clients of the health and community services system • identify accurately an individual during an encounter with the health system • confirm an individual’s eligibility for free medical care coverage • maintain the accuracy of client indexes in users’ local systems • identify newborns for metabolic screening • provide for the linking of health information in the proposed Electronic Health Records (EHR) Ref: HIQA – International Review of UHI’s for Individuals (2010)
 Canada (Newfoundland Labrador) – Lessons Learnt • Audit business processes regularly. • Anticipate additional resource requirements – support change/implementation & ‘routine work’ • Education and training of staff is essential. Incomplete education of all front-line workers had an impact on implementation Ref: HIQA – International Review of UHI’s for Individuals (2010)
Canada (Newfoundland Labrador) – Lessons Learnt • Audit business processes regularly. • Anticipate additional resource requirements – support change/implementation & ‘routine work’ • Education and training of staff is essential. Incomplete education of all front-line workers had an impact on implementation Ref: HIQA – International Review of UHI’s for Individuals (2010)
 IHI Implementation Journey. .
IHI Implementation Journey. .
 Key Lessons Learnt - Summary • Privacy and the protection of individual confidentiality is recognised as overarching the success of an IHI. • Strong governance controls must be in place with clear lines of accountability prior to any implementation of an IHI • A central trusted authority is necessary in driving the project forward and ensuring consistency across providers. • Broad ranging stakeholder engagement is required early on in the project to ensure representation from all parties involved • Change management processes must be developed prior to implementation in order to minimise the impact on front line staff and consequently the delivery of care to the individual • Monitor business processes • IHI – satisfy fundamental Criteria for Selection (ASTM guides)
Key Lessons Learnt - Summary • Privacy and the protection of individual confidentiality is recognised as overarching the success of an IHI. • Strong governance controls must be in place with clear lines of accountability prior to any implementation of an IHI • A central trusted authority is necessary in driving the project forward and ensuring consistency across providers. • Broad ranging stakeholder engagement is required early on in the project to ensure representation from all parties involved • Change management processes must be developed prior to implementation in order to minimise the impact on front line staff and consequently the delivery of care to the individual • Monitor business processes • IHI – satisfy fundamental Criteria for Selection (ASTM guides)
 Thank you for listening Q & A Contact & References: • jnagle@alphaprimarycare. com • www. alphaprimarycare. com • www. alphaprimarycare. co. uk • www. healthmanagementplus. co. uk AHC at : www. alphahealthcare. com
Thank you for listening Q & A Contact & References: • jnagle@alphaprimarycare. com • www. alphaprimarycare. com • www. alphaprimarycare. co. uk • www. healthmanagementplus. co. uk AHC at : www. alphahealthcare. com


