3ebcdc01e97e4f71e45cacd7d9dbd7de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

CMC/CC A Usability Evaluation Master IK, CIW, MMI L. M. Bosveld-de Smet Course 4; mon. 02/10/06; 16. 00 -18. 00
Usability Evaluation
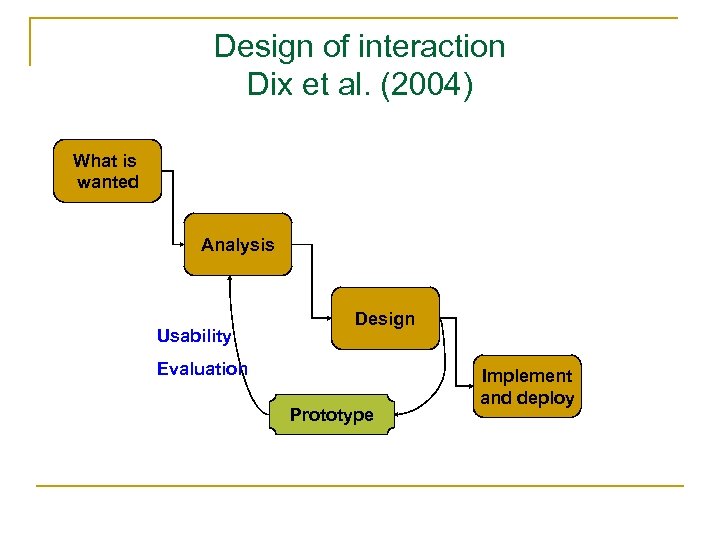
Design of interaction Dix et al. (2004) What is wanted Analysis Usability Design Evaluation Prototype Implement and deploy
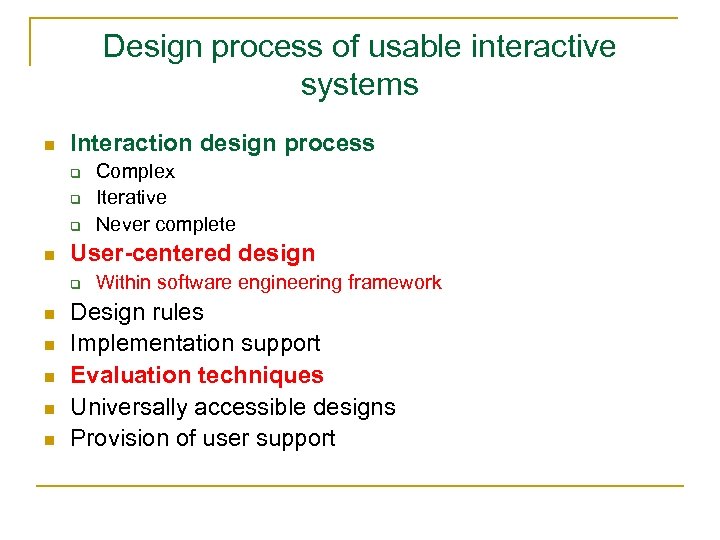
Design process of usable interactive systems n Interaction design process q q q n User-centered design q n n n Complex Iterative Never complete Within software engineering framework Design rules Implementation support Evaluation techniques Universally accessible designs Provision of user support
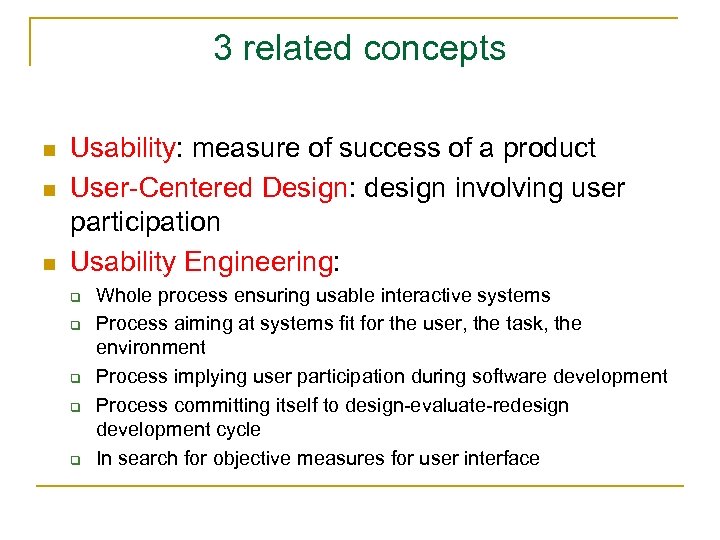
3 related concepts n n n Usability: measure of success of a product User-Centered Design: design involving user participation Usability Engineering: q q q Whole process ensuring usable interactive systems Process aiming at systems fit for the user, the task, the environment Process implying user participation during software development Process committing itself to design-evaluate-redesign development cycle In search for objective measures for user interface

Usability: different views n n Same intuitions vs. Different approaches Different views on: q Definition of usability n q q Usability attributes Importance of user-centered design When and how to deal with user participation How to build usable systems How to measure usability

Usability Attributes: Shackel’s view n n n “A usable product is one that users find satisfactory for the tasks for which it was designed. ” “Good design for usability depends upon achieving successful harmony in the dynamic interplay between user, task, system, and environment. ” Usability: 4 usable criteria q q Learnability Effectiveness Attitude Flexibility

Usability Attributes: ISO definition n “Usability is the effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which specified users can achieve specified goals in particular environments. ” q q q Effectiveness: “accuracy and completeness with which users achieve specific goals” Efficiency: “accuracy and completeness of goals in relation to resources expended” Satisfaction: “comfort and acceptability of the system”
An aside: User Interface Standards n Disadvantages: q q n Constrain design Stagnate innovation Describe principles, do not provide solutions Become quickly obsolete Advantages: q q Define ‘good practice’ Affect attitudes w. r. t. ‘software development’
User-Centered Design: Karat’s view n Karat (1996) “UCD: Quality or Quackery? ” n “UCD is an iterative process whose goal is the development of usable systems, achieved through involvement of potential users of a system in system design” n “I suggest we consider UCD a nice fluffy little catch phrase. It captures a commitment that the usability community supports – that you must involve users in system design – while leaving fairly open how this is accomplished”

UCD: a more objective view n UCD can be accomplished through the application of Usability Engineering n Design should centre on users End-user should be consulted Needs of end-users should be considered n n
HCI in software process n n Software engineering Usability engineering Iterative design practices Design rationale
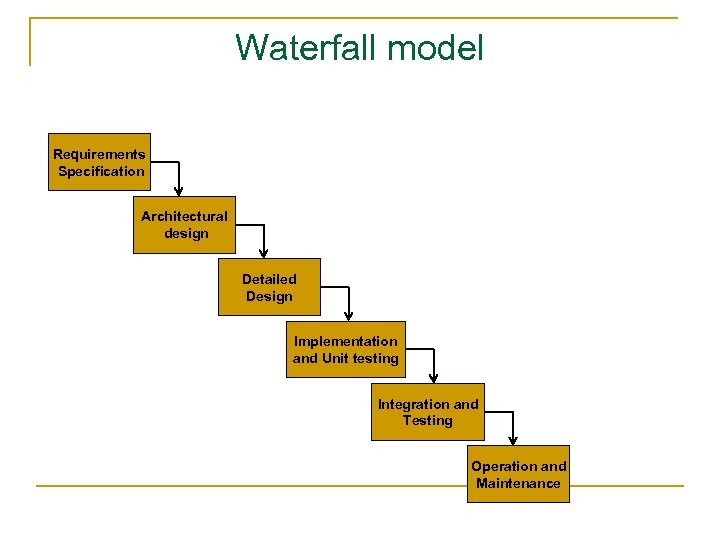
Waterfall model Requirements Specification Architectural design Detailed Design Implementation and Unit testing Integration and Testing Operation and Maintenance
Usability Engineering n n n Usability specification as part of requirements specification Iteration and testing List of usability measurement requirements (Whiteside, Bennett and Holtzblatt, 1988) q q q Time to complete a task Ratio of successes to failures Time spent in errors Number of commands used Frequency of help and documentation use …
Iteration in waterfall model Requirements Specification Architectural design Detailed Design Implementation and Unit testing Integration and Testing Operation and Maintenance
Usability Engineering Lifecycle Faulkner (2000) n n n n n Know the user Know the task User requirements capture Setting usability goals Design process Apply guidelines, heuristics Prototyping Evaluation with users Redesign and evaluation with users Evaluation with users and report
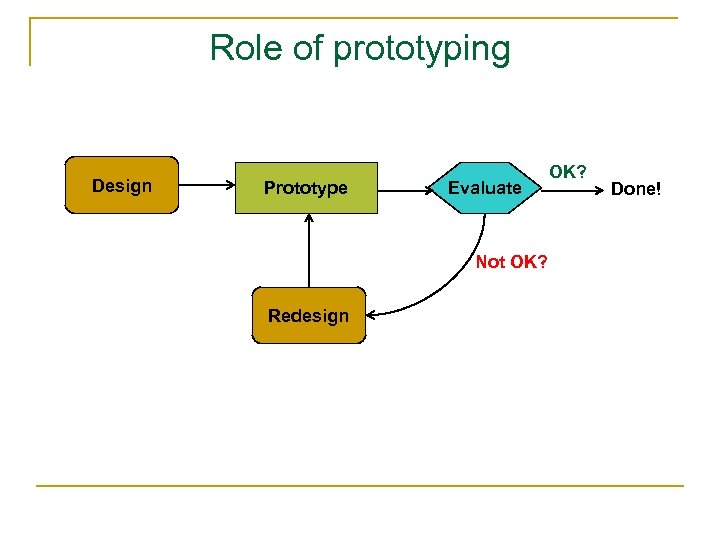
Role of prototyping Design Prototype Evaluate Not OK? Redesign OK? Done!

Iterative design and prototyping n Three main approaches to prototyping q q q Throw-away prototyping within requirements specification Incremental prototyping within the life cycle Evolutionary prototyping throughout the life cycle
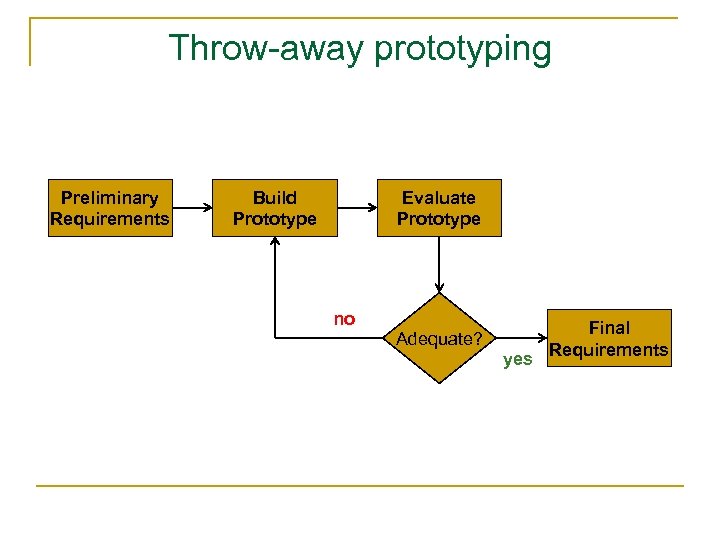
Throw-away prototyping Preliminary Requirements Build Prototype Evaluate Prototype no Adequate? yes Final Requirements
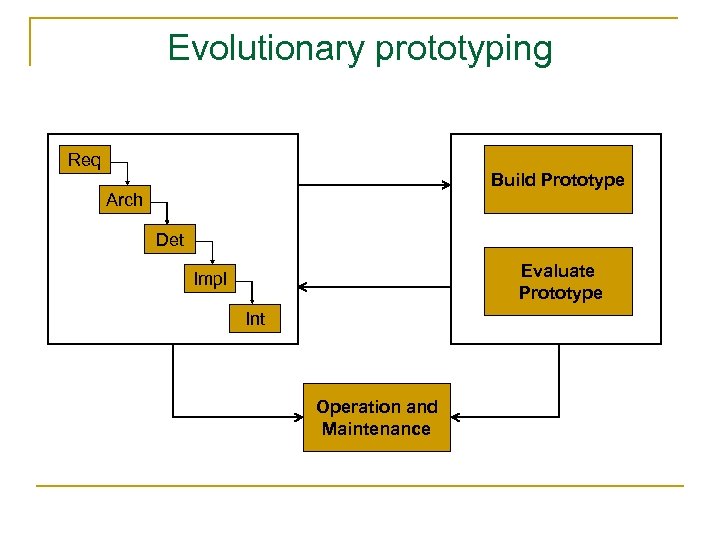
Evolutionary prototyping Req Build Prototype Arch Det Evaluate Prototype Impl Int Operation and Maintenance
Usability Evaluation (UE) n n n Methodologies for measuring usability aspects of system’s user interface and identifying specific problems (Dix et al. 1998; Nielsen 1993) Should occur throughout design life cycle Common activities: q q q n n n Capture Analysis Critic There is a wide range of UE techniques Each technique has its own requirements Different techniques uncover different usability problems
Taxonomies of UE (1) n n n Formative vs. Summative Analytical vs. Empirical Expert analysis vs. User participation Analytic methods q Review methods q Model-based methods vs. q Experimental methods q Observational methods q Query methods q
Taxonomies of UE (2) n n Automated vs. Non-automated Ivory and Hearst (2001): q q q Testing Inspection Inquiry Analytical modeling Simulation

Expert Analysis

Controlled Experiment

User participation
Important factors choice UE n n n n Stage in cycle at which UE is carried out Style of UE Level of subjectivity or objectivity of UE technique Type of measures provided Information provided Immediacy of response Level of interference implied Resources required
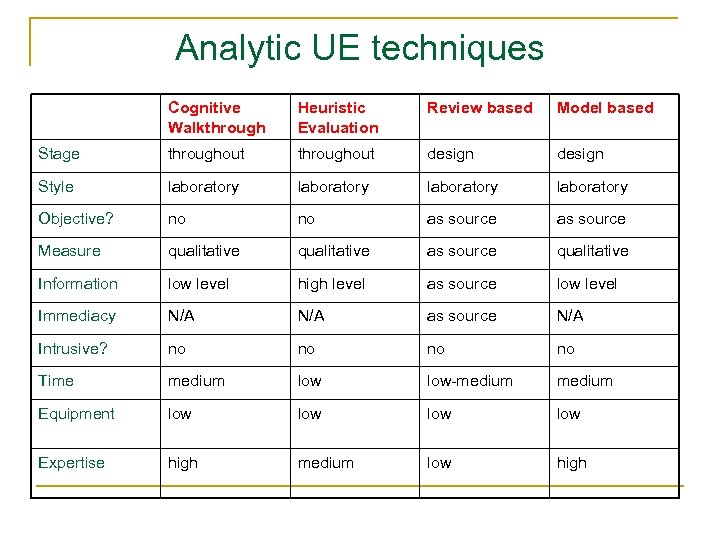
Analytic UE techniques Cognitive Walkthrough Heuristic Evaluation Review based Model based Stage throughout design Style laboratory Objective? no no as source Measure qualitative as source qualitative Information low level high level as source low level Immediacy N/A as source N/A Intrusive? no no Time medium low-medium Equipment low low Expertise high medium low high
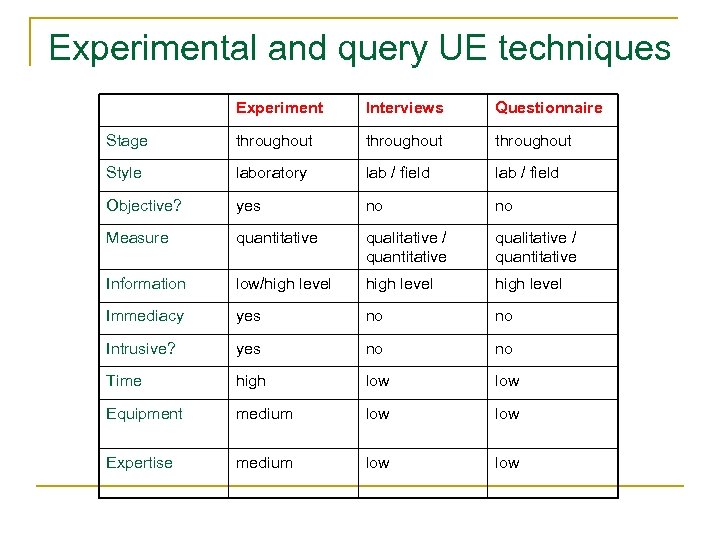
Experimental and query UE techniques Experiment Interviews Questionnaire Stage throughout Style laboratory lab / field Objective? yes no no Measure quantitative qualitative / quantitative Information low/high level Immediacy yes no no Intrusive? yes no no Time high low Equipment medium low Expertise medium low
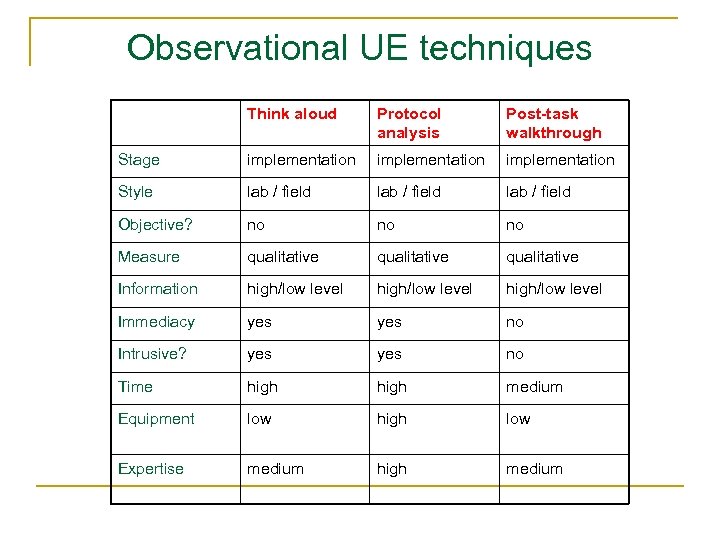
Observational UE techniques Think aloud Protocol analysis Post-task walkthrough Stage implementation Style lab / field Objective? no no no Measure qualitative Information high/low level Immediacy yes no Intrusive? yes no Time high medium Equipment low high low Expertise medium high medium
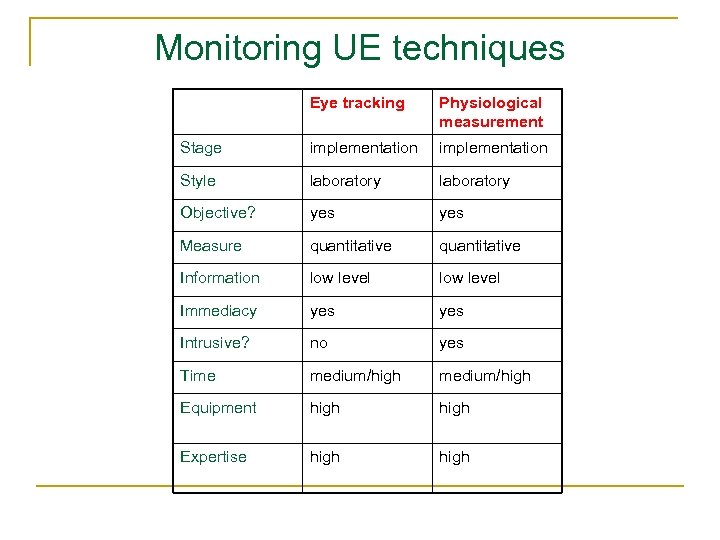
Monitoring UE techniques Eye tracking Physiological measurement Stage implementation Style laboratory Objective? yes Measure quantitative Information low level Immediacy yes Intrusive? no yes Time medium/high Equipment high Expertise high

Vocabulary application n Task analysis Feasability study Design representation

Feasibility study n n n Why is system needed? How will system help to improve user task performance? Are there critical processes that need to be supported by system? What are the technical implications? Can system be produced within given budget? Is there a timescale for the development of the system?

Strategies for representing design n n n Storyboards State transition diagrams Simulations Scenarios Rapid prototyping Wizard of Oz …
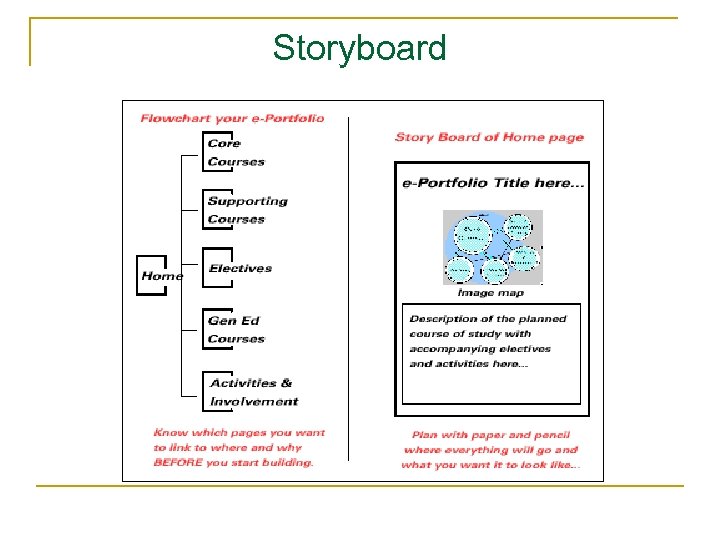
Storyboard
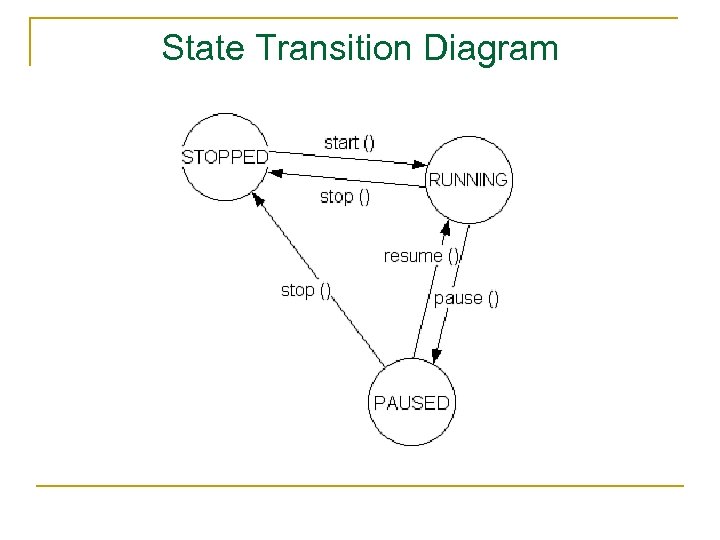
State Transition Diagram
3ebcdc01e97e4f71e45cacd7d9dbd7de.ppt