c6f14fb7c209772c8869b7e932b07c95.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 CLUSTERING (Segmentation) Saed Sayad www. ismartsoft. com 1
CLUSTERING (Segmentation) Saed Sayad www. ismartsoft. com 1
 Data Mining Steps 1 • Problem Definition 2 • Data Preparation 3 • Data Exploration 4 • Modeling 5 • Evaluation 6 • Deployment www. ismartsoft. com 2
Data Mining Steps 1 • Problem Definition 2 • Data Preparation 3 • Data Exploration 4 • Modeling 5 • Evaluation 6 • Deployment www. ismartsoft. com 2
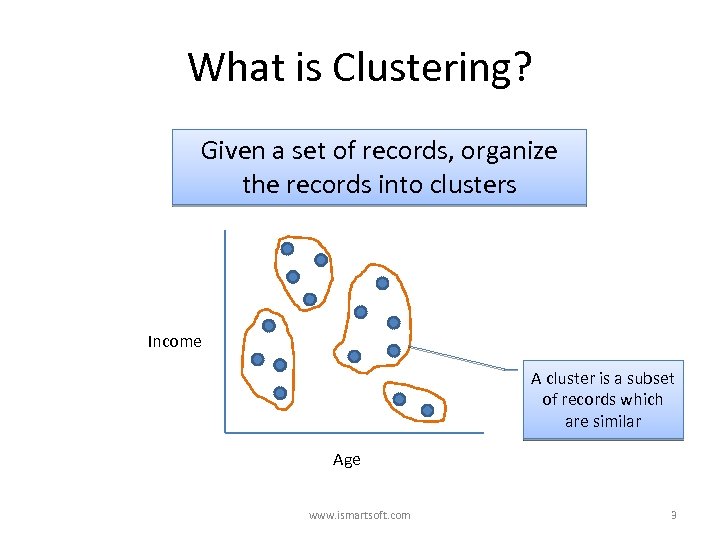 What is Clustering? Given a set of records, organize the records into clusters Income A cluster is a subset of records which are similar Age www. ismartsoft. com 3
What is Clustering? Given a set of records, organize the records into clusters Income A cluster is a subset of records which are similar Age www. ismartsoft. com 3
 Clustering Requirements • The ability to discover some or all of the hidden clusters. • Within-cluster similarity and between-cluster disimilarity. • Ability to deal with various types of attributes. • Can deal with noise and outliers. • Can handle high dimensionality. • Scalability, Interpretability and usability. www. ismartsoft. com 4
Clustering Requirements • The ability to discover some or all of the hidden clusters. • Within-cluster similarity and between-cluster disimilarity. • Ability to deal with various types of attributes. • Can deal with noise and outliers. • Can handle high dimensionality. • Scalability, Interpretability and usability. www. ismartsoft. com 4
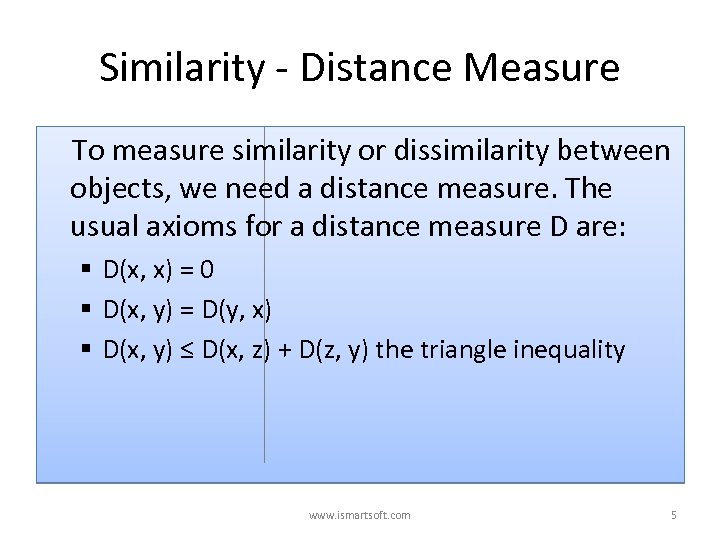 Similarity - Distance Measure To measure similarity or dissimilarity between objects, we need a distance measure. The usual axioms for a distance measure D are: § D(x, x) = 0 § D(x, y) = D(y, x) § D(x, y) ≤ D(x, z) + D(z, y) the triangle inequality www. ismartsoft. com 5
Similarity - Distance Measure To measure similarity or dissimilarity between objects, we need a distance measure. The usual axioms for a distance measure D are: § D(x, x) = 0 § D(x, y) = D(y, x) § D(x, y) ≤ D(x, z) + D(z, y) the triangle inequality www. ismartsoft. com 5
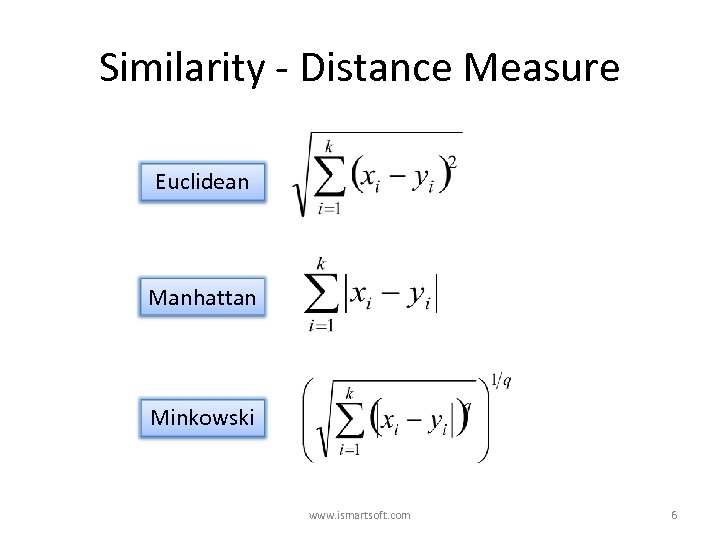 Similarity - Distance Measure Euclidean Manhattan Minkowski www. ismartsoft. com 6
Similarity - Distance Measure Euclidean Manhattan Minkowski www. ismartsoft. com 6
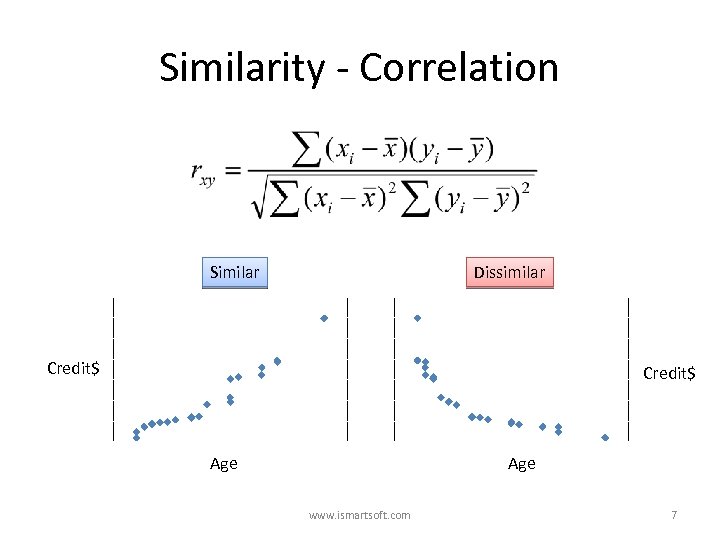 Similarity - Correlation Similar Dissimilar Credit$ Age www. ismartsoft. com 7
Similarity - Correlation Similar Dissimilar Credit$ Age www. ismartsoft. com 7
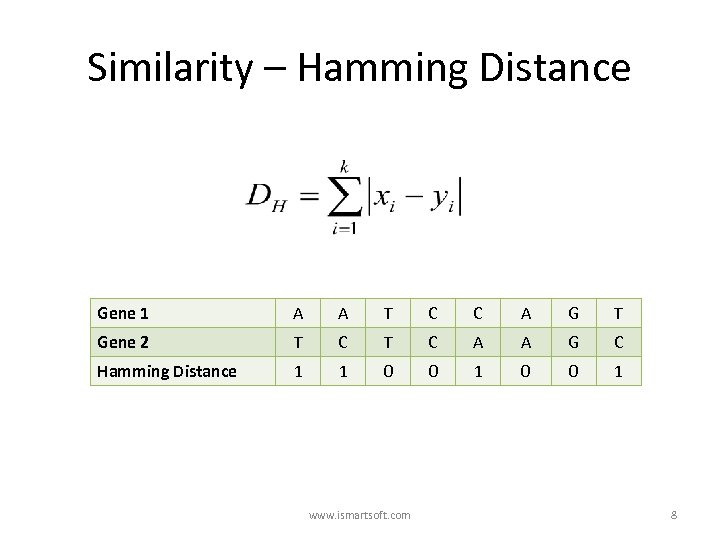 Similarity – Hamming Distance Gene 1 A A T C C A G T Gene 2 T C A A G C Hamming Distance 1 1 0 0 1 www. ismartsoft. com 8
Similarity – Hamming Distance Gene 1 A A T C C A G T Gene 2 T C A A G C Hamming Distance 1 1 0 0 1 www. ismartsoft. com 8
 Clustering Methods • • Exclusive vs. Overlapping Hierarchical vs. Partitive Deterministic vs. Probabilistic Incremental vs. Batch learning www. ismartsoft. com 9
Clustering Methods • • Exclusive vs. Overlapping Hierarchical vs. Partitive Deterministic vs. Probabilistic Incremental vs. Batch learning www. ismartsoft. com 9
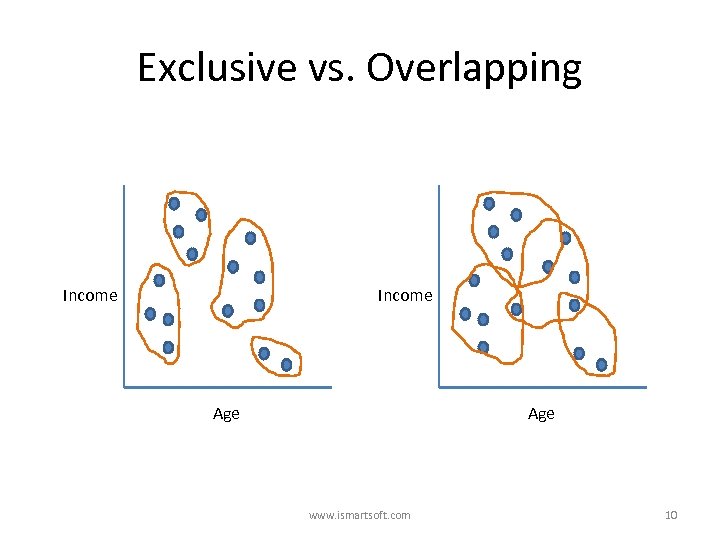 Exclusive vs. Overlapping Income Age www. ismartsoft. com 10
Exclusive vs. Overlapping Income Age www. ismartsoft. com 10
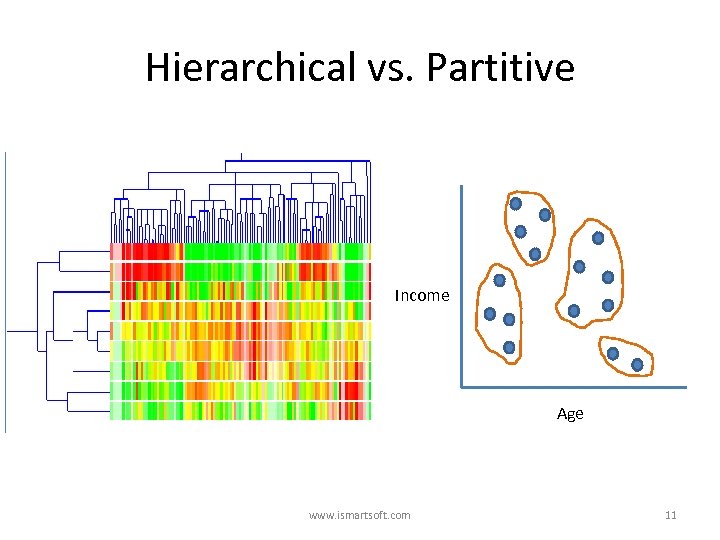 Hierarchical vs. Partitive Income Age www. ismartsoft. com 11
Hierarchical vs. Partitive Income Age www. ismartsoft. com 11
 Hierarchical Clustering • Hierarchical clustering involves creating clusters that have a predetermined ordering from top to bottom. For example, all files and folders on the hard disk are organized in a hierarchy. • There are two types of hierarchical clustering: – Agglomerative – Divisive www. ismartsoft. com 12
Hierarchical Clustering • Hierarchical clustering involves creating clusters that have a predetermined ordering from top to bottom. For example, all files and folders on the hard disk are organized in a hierarchy. • There are two types of hierarchical clustering: – Agglomerative – Divisive www. ismartsoft. com 12
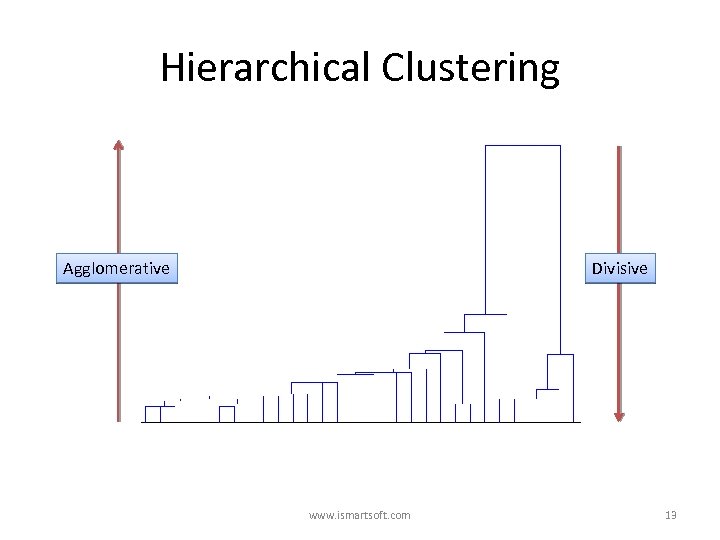 Hierarchical Clustering Agglomerative Divisive www. ismartsoft. com 13
Hierarchical Clustering Agglomerative Divisive www. ismartsoft. com 13
 Hierarchical Clustering - Agglomerative 1. Assign each observation to its own cluster. 2. Compute the similarity (e. g. , distance) between each of the clusters. 3. Join the two most similar clusters. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 until there is only a single cluster left. www. ismartsoft. com 14
Hierarchical Clustering - Agglomerative 1. Assign each observation to its own cluster. 2. Compute the similarity (e. g. , distance) between each of the clusters. 3. Join the two most similar clusters. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 until there is only a single cluster left. www. ismartsoft. com 14
 Hierarchical Clustering - Divisive 1. Assign all of the observations to a single cluster. 2. Partition the cluster to two least similar clusters. 3. Proceed recursively on each cluster until there is one cluster for each observation. www. ismartsoft. com 15
Hierarchical Clustering - Divisive 1. Assign all of the observations to a single cluster. 2. Partition the cluster to two least similar clusters. 3. Proceed recursively on each cluster until there is one cluster for each observation. www. ismartsoft. com 15
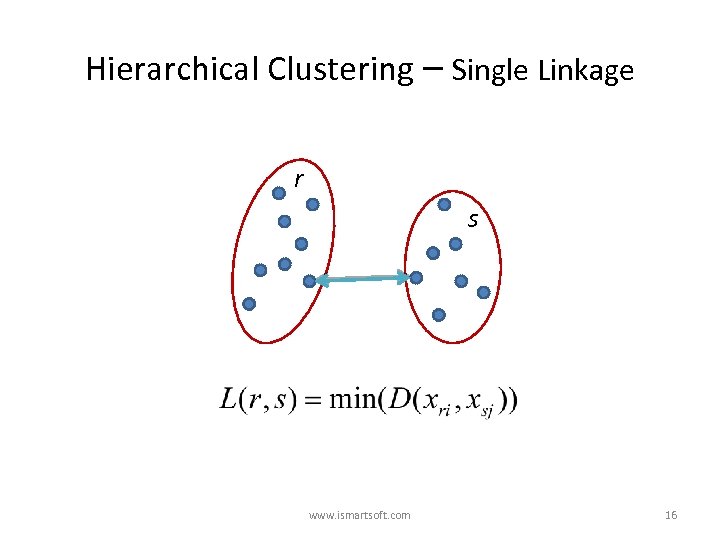 Hierarchical Clustering – Single Linkage r s www. ismartsoft. com 16
Hierarchical Clustering – Single Linkage r s www. ismartsoft. com 16
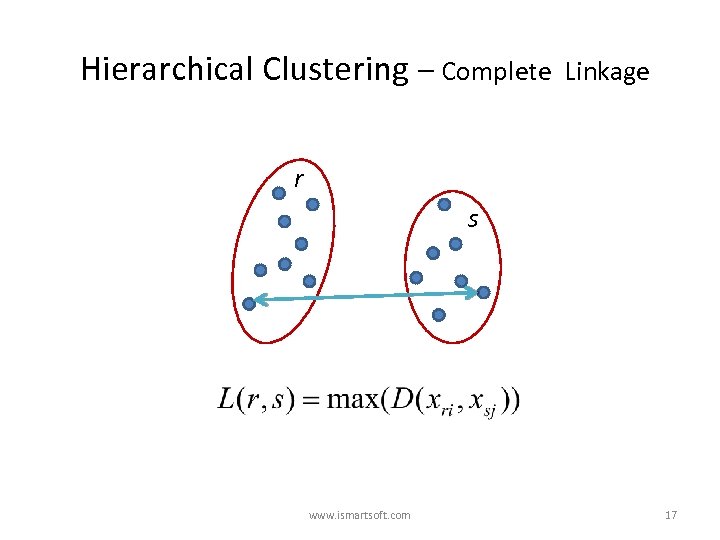 Hierarchical Clustering – Complete Linkage r s www. ismartsoft. com 17
Hierarchical Clustering – Complete Linkage r s www. ismartsoft. com 17
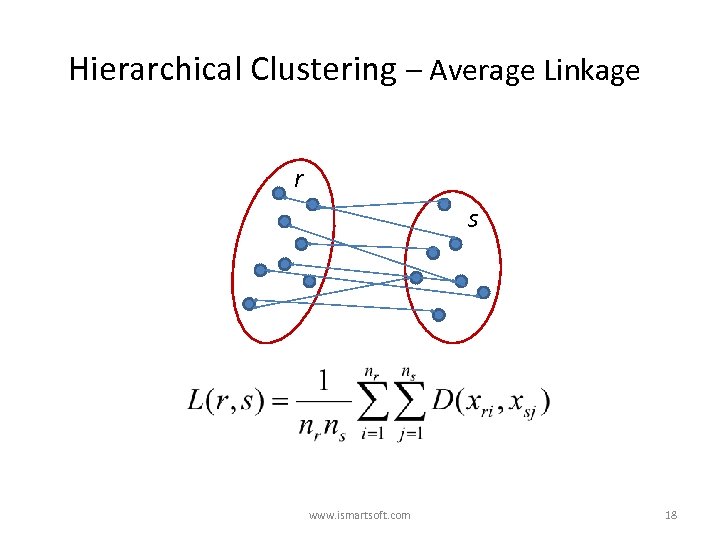 Hierarchical Clustering – Average Linkage r s www. ismartsoft. com 18
Hierarchical Clustering – Average Linkage r s www. ismartsoft. com 18
 K Means Clustering 1. Clusters the data into k groups where k is predefined. 2. Select k points at random as cluster centers. 3. Assign observations to their closest cluster center according to the Euclidean distance function. 4. Calculate the centroid or mean of all instances in each cluster (this is the mean part) 5. Repeat steps 2, 3 and 4 until the same points are assigned to each cluster in consecutive rounds. www. ismartsoft. com 19
K Means Clustering 1. Clusters the data into k groups where k is predefined. 2. Select k points at random as cluster centers. 3. Assign observations to their closest cluster center according to the Euclidean distance function. 4. Calculate the centroid or mean of all instances in each cluster (this is the mean part) 5. Repeat steps 2, 3 and 4 until the same points are assigned to each cluster in consecutive rounds. www. ismartsoft. com 19
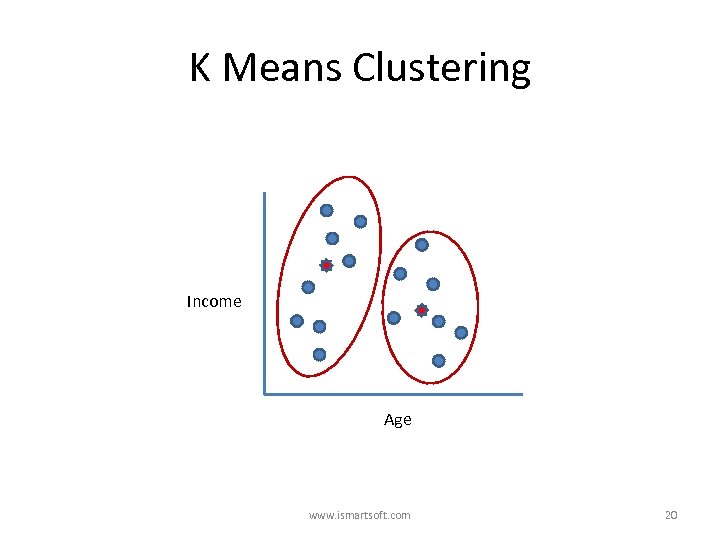 K Means Clustering Income Age www. ismartsoft. com 20
K Means Clustering Income Age www. ismartsoft. com 20
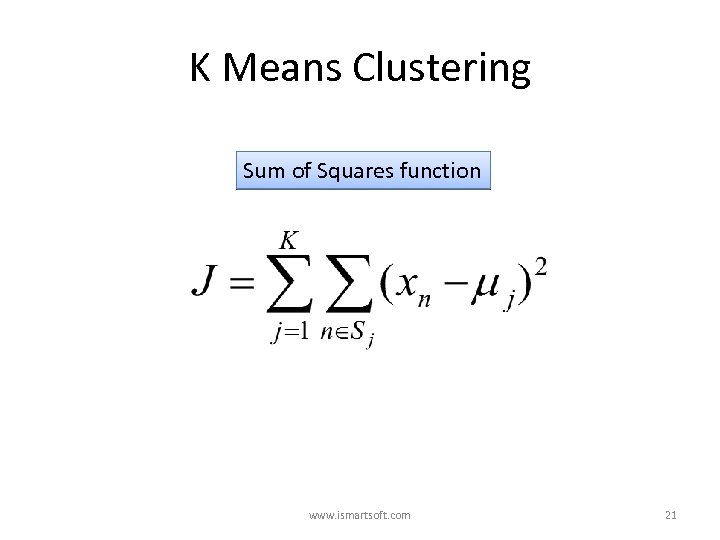 K Means Clustering Sum of Squares function www. ismartsoft. com 21
K Means Clustering Sum of Squares function www. ismartsoft. com 21
 Clustering Evaluation • • • Sarle’s Cubic Clustering Criterion The Pseudo-F Statistic The Pseudo-T 2 Statistic Beale’s F-Type Statistic Target-based www. ismartsoft. com 22
Clustering Evaluation • • • Sarle’s Cubic Clustering Criterion The Pseudo-F Statistic The Pseudo-T 2 Statistic Beale’s F-Type Statistic Target-based www. ismartsoft. com 22
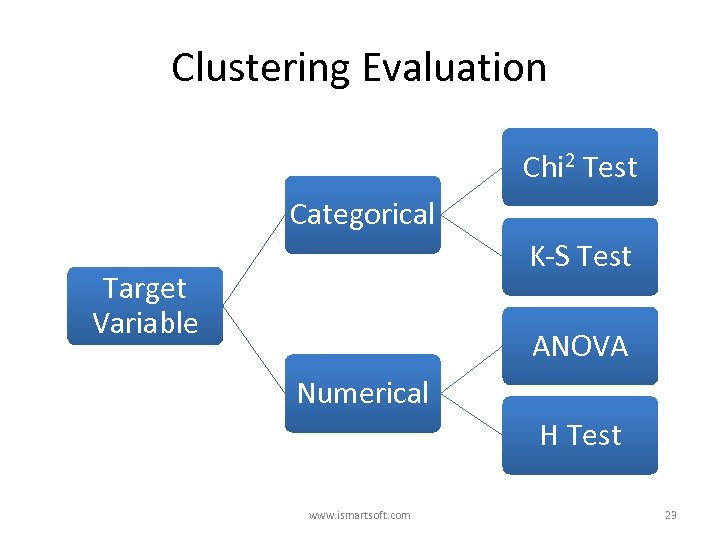 Clustering Evaluation Chi 2 Test Categorical K-S Test Target Variable ANOVA Numerical H Test www. ismartsoft. com 23
Clustering Evaluation Chi 2 Test Categorical K-S Test Target Variable ANOVA Numerical H Test www. ismartsoft. com 23
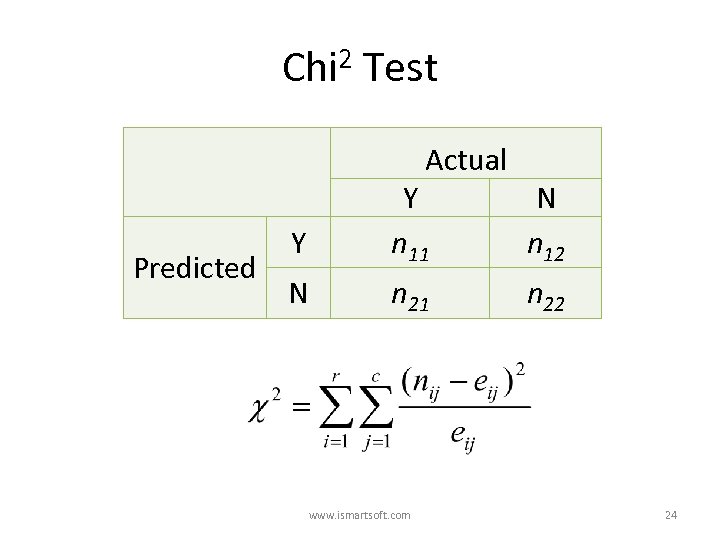 Chi 2 Test Actual Predicted Y Y n 11 N n 12 N n 21 n 22 www. ismartsoft. com 24
Chi 2 Test Actual Predicted Y Y n 11 N n 12 N n 21 n 22 www. ismartsoft. com 24
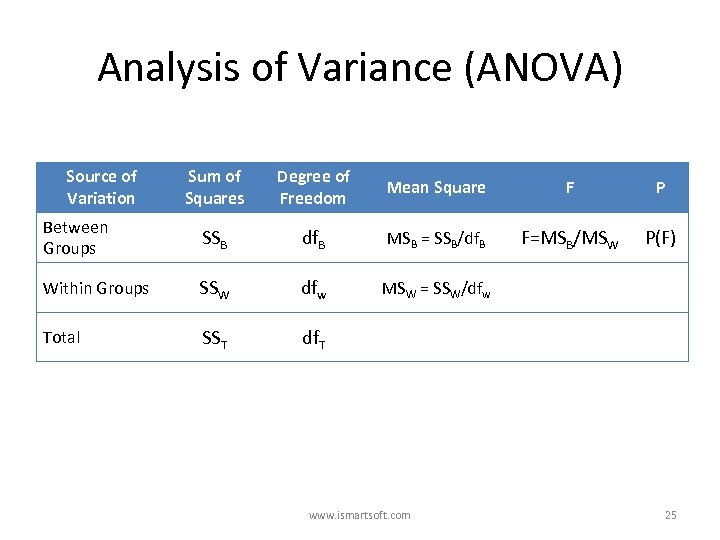 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Source of Variation Sum of Squares Degree of Freedom Mean Square F P Between Groups SSB df. B MSB = SSB/df. B F=MSB/MSW P(F) Within Groups SSW dfw MSW = SSW/dfw Total SST df. T www. ismartsoft. com 25
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Source of Variation Sum of Squares Degree of Freedom Mean Square F P Between Groups SSB df. B MSB = SSB/df. B F=MSB/MSW P(F) Within Groups SSW dfw MSW = SSW/dfw Total SST df. T www. ismartsoft. com 25
 Clustering - Applications • Marketing: finding groups of customers with similar behavior. • Insurance & Banking: identifying frauds. • Biology: classification of plants and animals given their features. • Libraries: book ordering. • City-planning: identifying groups of houses according to their house type, value and geographical location. • World Wide Web: document classification; clustering weblog data to discover groups with similar access patterns. www. ismartsoft. com 26
Clustering - Applications • Marketing: finding groups of customers with similar behavior. • Insurance & Banking: identifying frauds. • Biology: classification of plants and animals given their features. • Libraries: book ordering. • City-planning: identifying groups of houses according to their house type, value and geographical location. • World Wide Web: document classification; clustering weblog data to discover groups with similar access patterns. www. ismartsoft. com 26
 Summary • Clustering is the process of organizing objects (records or variables) into groups whose members are similar in some way. • Hierarchical and K-Means are the two most used clustering techniques. • The effectiveness of the clustering method depends on the similarity function. • The result of the clustering algorithm can be interpreted and evaluated in different ways. www. ismartsoft. com 27
Summary • Clustering is the process of organizing objects (records or variables) into groups whose members are similar in some way. • Hierarchical and K-Means are the two most used clustering techniques. • The effectiveness of the clustering method depends on the similarity function. • The result of the clustering algorithm can be interpreted and evaluated in different ways. www. ismartsoft. com 27
 Questions? www. ismartsoft. com 28
Questions? www. ismartsoft. com 28


