39bd8d29c5e37574e63608a30c31c5b4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Cloud Notation for Users A cloud modelling notation for business users to express requirements concepts Towards a business user driven view of cloud computing Workshop to discuss idea and approach August 26, 2010
Cloud Notation for Users A cloud modelling notation for business users to express requirements concepts Towards a business user driven view of cloud computing Workshop to discuss idea and approach August 26, 2010
 Webex details q q q Meeting Date: Start Time: AUG 26, 2010 5: 00 PM Europe/London BST (British Summer Time) http: //meetingplace. capgemini. co. uk/a/912123364911 0 e 2 c 70928189629 c 5061 UK Number: 01483 788788 International Number: +44 1483 788788 Meeting ID: 0127 Please, go to mute during the first part of the presentation - do not put your phone on hold during the meeting
Webex details q q q Meeting Date: Start Time: AUG 26, 2010 5: 00 PM Europe/London BST (British Summer Time) http: //meetingplace. capgemini. co. uk/a/912123364911 0 e 2 c 70928189629 c 5061 UK Number: 01483 788788 International Number: +44 1483 788788 Meeting ID: 0127 Please, go to mute during the first part of the presentation - do not put your phone on hold during the meeting
 Agenda q q Looking for active volunteers…. A walk through the Cloud Business Notation ideas and concepts - 30 minutes - by Mark Skilton A discuss on the ideas and concepts presented - all Identify advantages and any concerns that need to be addressed - all Identify ideas on how the Cloud Notation may fit with other architecture models - the intention is to work with other stack type models such as NIST, TOGAF for example - to generate different views of cloud models for different types of stakeholders , both technical and business oriented.
Agenda q q Looking for active volunteers…. A walk through the Cloud Business Notation ideas and concepts - 30 minutes - by Mark Skilton A discuss on the ideas and concepts presented - all Identify advantages and any concerns that need to be addressed - all Identify ideas on how the Cloud Notation may fit with other architecture models - the intention is to work with other stack type models such as NIST, TOGAF for example - to generate different views of cloud models for different types of stakeholders , both technical and business oriented.
 Introduction q q The following notes and diagrams are from the meeting attended by a range of participants at the Cloudcamp Boston July 21 The objective was to identify ideas and approaches to define a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture that better defined and represented the evolving nature of the Cloud and how it could be provided and used.
Introduction q q The following notes and diagrams are from the meeting attended by a range of participants at the Cloudcamp Boston July 21 The objective was to identify ideas and approaches to define a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture that better defined and represented the evolving nature of the Cloud and how it could be provided and used.
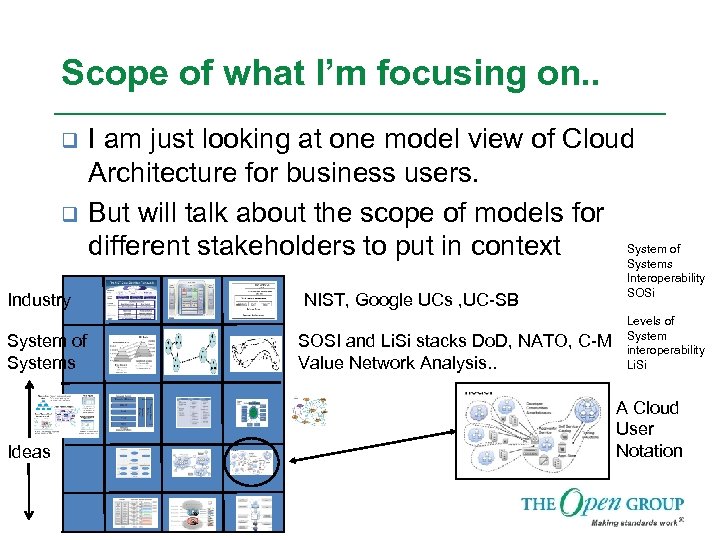 Scope of what I’m focusing on. . q q Industry System of Systems Ideas I am just looking at one model view of Cloud Architecture for business users. But will talk about the scope of models for System of different stakeholders to put in context Systems NIST, Google UCs , UC-SB SOSI and Li. Si stacks Do. D, NATO, C-M Value Network Analysis. . Interoperability SOSi Levels of System interoperability Li. Si A Cloud User Notation
Scope of what I’m focusing on. . q q Industry System of Systems Ideas I am just looking at one model view of Cloud Architecture for business users. But will talk about the scope of models for System of different stakeholders to put in context Systems NIST, Google UCs , UC-SB SOSI and Li. Si stacks Do. D, NATO, C-M Value Network Analysis. . Interoperability SOSi Levels of System interoperability Li. Si A Cloud User Notation
 Why do we need a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA? A range of comments included: q Current reference models are from a seller perspective and don’t fit how cloud “feels” from a User perspective q SOA and Web 2. 0 have provided foundation message and payload standards but need to move to into describing how the service “looks and feels” q Historically the “tiers” approach to describing architecture has originated from the Client-server era; examples seen in 4+1, Zachmann and other concepts have resulted in a perspective of a Provider oriented style “tiers” in Cloud which has limitations q Syntax and semantics have been focused on by community and industry forums but other aspects of behavior interoperability and choreography modelling that could help describe cloud and cloud services is potentially a gap a present q There are many discussions and standards forums on interoperability in the industry but little methodology evolving from an overview of how different parties might work across a cloud service q There are Industry efforts to extend SOA and security standards but these come from a preexisting viewpoint rather than a clean start on cloud descriptions q We are seeing academic research and evidence in Grid computing, agent based technology and some vendors providing examples of how to visualize and potentially represent cloud services more closely relating to the cloud experience. The nature of cloud is emerging continually and the CCRA could help narrate aspects of requirements and how to use Cloud
Why do we need a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA? A range of comments included: q Current reference models are from a seller perspective and don’t fit how cloud “feels” from a User perspective q SOA and Web 2. 0 have provided foundation message and payload standards but need to move to into describing how the service “looks and feels” q Historically the “tiers” approach to describing architecture has originated from the Client-server era; examples seen in 4+1, Zachmann and other concepts have resulted in a perspective of a Provider oriented style “tiers” in Cloud which has limitations q Syntax and semantics have been focused on by community and industry forums but other aspects of behavior interoperability and choreography modelling that could help describe cloud and cloud services is potentially a gap a present q There are many discussions and standards forums on interoperability in the industry but little methodology evolving from an overview of how different parties might work across a cloud service q There are Industry efforts to extend SOA and security standards but these come from a preexisting viewpoint rather than a clean start on cloud descriptions q We are seeing academic research and evidence in Grid computing, agent based technology and some vendors providing examples of how to visualize and potentially represent cloud services more closely relating to the cloud experience. The nature of cloud is emerging continually and the CCRA could help narrate aspects of requirements and how to use Cloud
 The need for a meaningful Cloud Computing Reference Architecture Methodology q q We need to have a methodology that recognizes better how cloud computing experience “looks and feels like in the real world” Considering an analogy; we have seen examples such as virtual reality VR software standards that has attempted to represented a more realistic software representation of the real world – the point is not the VR but that the aim is to create a language and approach that represents how business and technology are working together. Cloud computing is yet another environment / ecosystem combination of tools , assets, people, businesses and experiences that represent aspects of cloud
The need for a meaningful Cloud Computing Reference Architecture Methodology q q We need to have a methodology that recognizes better how cloud computing experience “looks and feels like in the real world” Considering an analogy; we have seen examples such as virtual reality VR software standards that has attempted to represented a more realistic software representation of the real world – the point is not the VR but that the aim is to create a language and approach that represents how business and technology are working together. Cloud computing is yet another environment / ecosystem combination of tools , assets, people, businesses and experiences that represent aspects of cloud
 The current Provider oriented Cloud Computing reference models q q While NIST is arguably the most well known http: //csrc. nist. gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computingv 26. ppt , there are many examples of equally significant and influential models including the Cloud Computing taxonomy from the Google hosted Cloud Computing Use cases Group http: //www. scribd. com/doc/18172802/Cloud-Computing-Use-Cases. Whitepaper and the “Towards a unified Ontology of Cloud Computing” by Lamia Youseff, University of California, Santa Barbara and Maria Butrico and Dilma Da Silva of IBM T. J. Watson Research Center York. Town, New York http: //freedomhui. com/wpcontent/uploads/2010/03/Cloud. Ontology. pdf. All these examples also provide a technology tiered framework of implementation viewpoints for cloud computing.
The current Provider oriented Cloud Computing reference models q q While NIST is arguably the most well known http: //csrc. nist. gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computingv 26. ppt , there are many examples of equally significant and influential models including the Cloud Computing taxonomy from the Google hosted Cloud Computing Use cases Group http: //www. scribd. com/doc/18172802/Cloud-Computing-Use-Cases. Whitepaper and the “Towards a unified Ontology of Cloud Computing” by Lamia Youseff, University of California, Santa Barbara and Maria Butrico and Dilma Da Silva of IBM T. J. Watson Research Center York. Town, New York http: //freedomhui. com/wpcontent/uploads/2010/03/Cloud. Ontology. pdf. All these examples also provide a technology tiered framework of implementation viewpoints for cloud computing.
 Building advocacy for a Business User prospective of Cloud Computing q q q But, this has been predominantly from a provider viewpoint of cloud computing and less on how the consumer might see, experience or use the cloud service. These conceptual frameworks represent a description of a technology tiered architecture most meaningful to Enterprise technologies. While this is important it prevents a separation of the concerns most important from the consumer perspective of the service. The customer experience and the business user viewpoint of cloud is quite different from the discussions of design and run time choices for cloud services. A critical goal of cloud computing is to move towards a user ondemand perspective, to use the “cloud” as a service for business.
Building advocacy for a Business User prospective of Cloud Computing q q q But, this has been predominantly from a provider viewpoint of cloud computing and less on how the consumer might see, experience or use the cloud service. These conceptual frameworks represent a description of a technology tiered architecture most meaningful to Enterprise technologies. While this is important it prevents a separation of the concerns most important from the consumer perspective of the service. The customer experience and the business user viewpoint of cloud is quite different from the discussions of design and run time choices for cloud services. A critical goal of cloud computing is to move towards a user ondemand perspective, to use the “cloud” as a service for business.
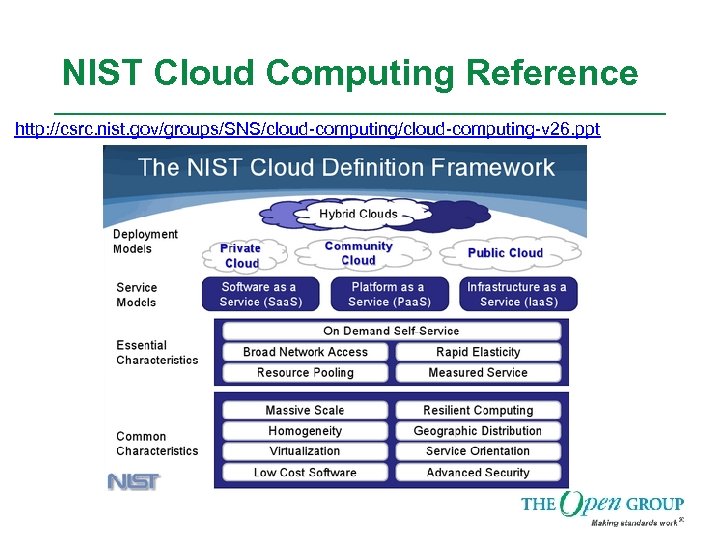 NIST Cloud Computing Reference http: //csrc. nist. gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computing-v 26. ppt
NIST Cloud Computing Reference http: //csrc. nist. gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computing-v 26. ppt
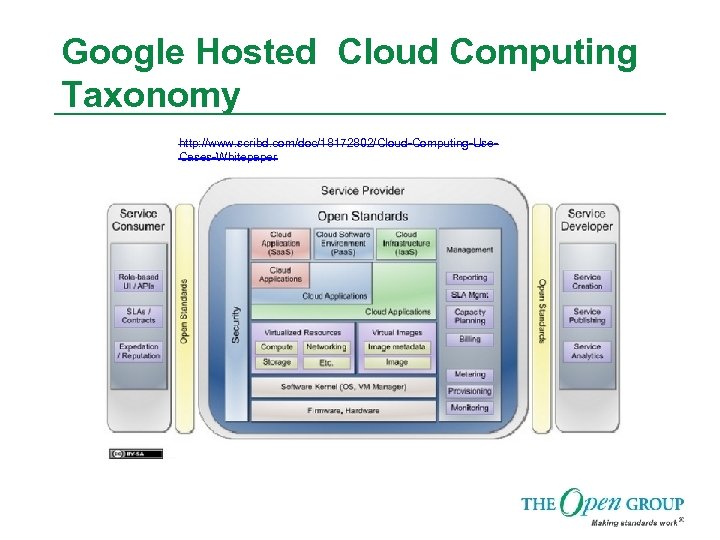 Google Hosted Cloud Computing Taxonomy http: //www. scribd. com/doc/18172802/Cloud-Computing-Use. Cases-Whitepaper
Google Hosted Cloud Computing Taxonomy http: //www. scribd. com/doc/18172802/Cloud-Computing-Use. Cases-Whitepaper
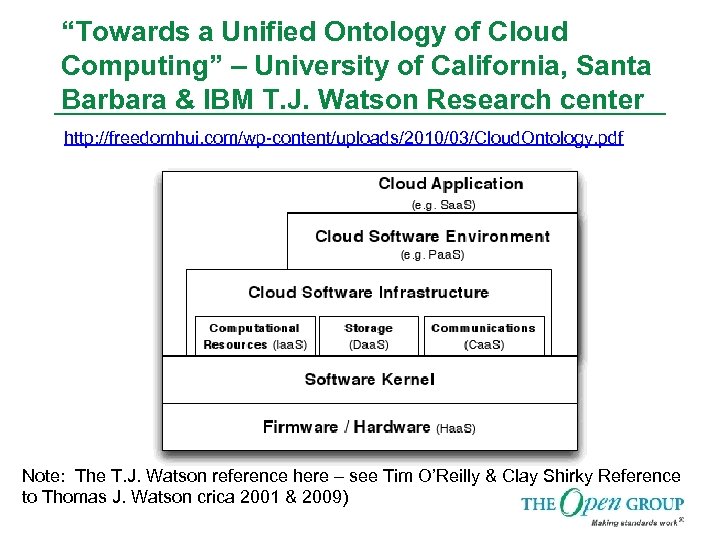 “Towards a Unified Ontology of Cloud Computing” – University of California, Santa Barbara & IBM T. J. Watson Research center http: //freedomhui. com/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Cloud. Ontology. pdf Note: The T. J. Watson reference here – see Tim O’Reilly & Clay Shirky Reference to Thomas J. Watson crica 2001 & 2009)
“Towards a Unified Ontology of Cloud Computing” – University of California, Santa Barbara & IBM T. J. Watson Research center http: //freedomhui. com/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Cloud. Ontology. pdf Note: The T. J. Watson reference here – see Tim O’Reilly & Clay Shirky Reference to Thomas J. Watson crica 2001 & 2009)
 Balancing the Buyer and Seller perspective q We are not advocating a different cloud computing model but a set of models that take into account both the consumer and provider side , the buyer and seller and other intermediate roles that support the types of homogeneous and heterogeneous platforms and subclasses of data and user devices that are found in the real world of IT.
Balancing the Buyer and Seller perspective q We are not advocating a different cloud computing model but a set of models that take into account both the consumer and provider side , the buyer and seller and other intermediate roles that support the types of homogeneous and heterogeneous platforms and subclasses of data and user devices that are found in the real world of IT.
 5 key Business Benefits of a User driven Cloud viewpoint q q Defining a clear Cloud Computing Architecture Modelling approach will help further develop Cloud Computing adoption Defining a common set of standard terminology is key to any new emerging technology trend in helping to raise awareness and express requirements of that technology.
5 key Business Benefits of a User driven Cloud viewpoint q q Defining a clear Cloud Computing Architecture Modelling approach will help further develop Cloud Computing adoption Defining a common set of standard terminology is key to any new emerging technology trend in helping to raise awareness and express requirements of that technology.
 5 key Business Benefits of a User driven Cloud viewpoint q Monetizing cloud services § q Visualizing the real cloud § q Probably the biggest affect on everyday lives has been the attention span and impact on people and business through on-demand real-time exchange of messages and content enabled by an increasing social and dynamic network of services that can be described as “the cloud”. Showing this experience and how this changes in a “mash-up”, on-demand world would greatly improve the real world representation of consumer choice , the self-service “menus” and “portfolios” open to business. Describing who has ownership of Security Risk in the cloud § q Cloud is already here, we everyday see the email, video feeds, web sites and tweets. Business needs a way of describing this from that perspective so that we can accelerate the meaning full integration and adoption of cloud into everyday experience. Defining a clear Customer experience § q It is currently an area of adoption question; “how much do cloud services cost my business? ”. Defining a way to show individual services and their common shared service or incremental growth could help accelerate an adoption profile where users understand the cost of service better. The greatest impediment to cloud is probably the risk and security aspects of the data, location and control of services. Defining a user location perspective of security protection points would greatly enhance the provider conditions to address those critical concerns. Defining how to monitoring Quality of Service Qo. S in the cloud § Overall how the service level performance monitoring and disaster recovery aspects of the cloud service needs to be shown in a heterogeneous context. Many enterprise level SLAs need OLAs that are representative of business level Qo. S standards, how multiple service monitoring and management systems need to be position on the provider side and the consumers side. A methodology that helps clarify this “ownership of responsibility” would be a great benefit in definition a clear boundary of service trading and exchange.
5 key Business Benefits of a User driven Cloud viewpoint q Monetizing cloud services § q Visualizing the real cloud § q Probably the biggest affect on everyday lives has been the attention span and impact on people and business through on-demand real-time exchange of messages and content enabled by an increasing social and dynamic network of services that can be described as “the cloud”. Showing this experience and how this changes in a “mash-up”, on-demand world would greatly improve the real world representation of consumer choice , the self-service “menus” and “portfolios” open to business. Describing who has ownership of Security Risk in the cloud § q Cloud is already here, we everyday see the email, video feeds, web sites and tweets. Business needs a way of describing this from that perspective so that we can accelerate the meaning full integration and adoption of cloud into everyday experience. Defining a clear Customer experience § q It is currently an area of adoption question; “how much do cloud services cost my business? ”. Defining a way to show individual services and their common shared service or incremental growth could help accelerate an adoption profile where users understand the cost of service better. The greatest impediment to cloud is probably the risk and security aspects of the data, location and control of services. Defining a user location perspective of security protection points would greatly enhance the provider conditions to address those critical concerns. Defining how to monitoring Quality of Service Qo. S in the cloud § Overall how the service level performance monitoring and disaster recovery aspects of the cloud service needs to be shown in a heterogeneous context. Many enterprise level SLAs need OLAs that are representative of business level Qo. S standards, how multiple service monitoring and management systems need to be position on the provider side and the consumers side. A methodology that helps clarify this “ownership of responsibility” would be a great benefit in definition a clear boundary of service trading and exchange.
 Why this helps monetize Cloud q q Because it is a middle-out not a outward-in approach – it drives the user journey through using the cloud You look at cloud from the viewpoint of using one to many cloud services which can be used and built on incrementally. This matches the incremental cashflow and elastic growth we so often see in cloud service use
Why this helps monetize Cloud q q Because it is a middle-out not a outward-in approach – it drives the user journey through using the cloud You look at cloud from the viewpoint of using one to many cloud services which can be used and built on incrementally. This matches the incremental cashflow and elastic growth we so often see in cloud service use
 Defining Models for Cloud Computing that considered the Business User viewpoint
Defining Models for Cloud Computing that considered the Business User viewpoint
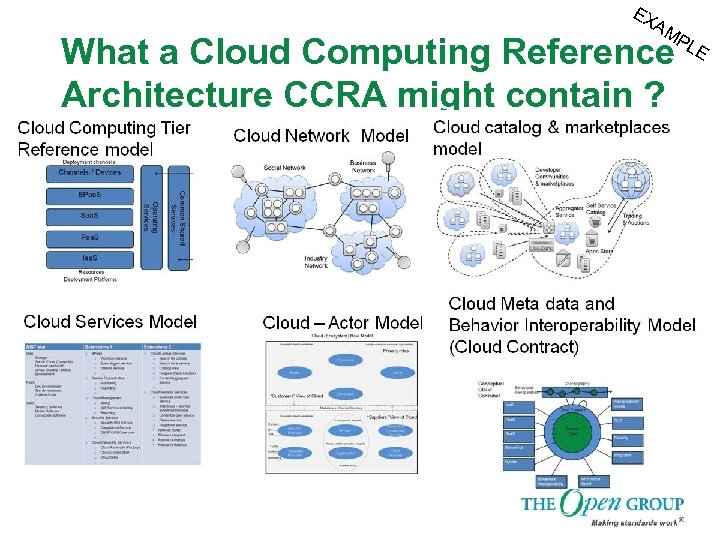
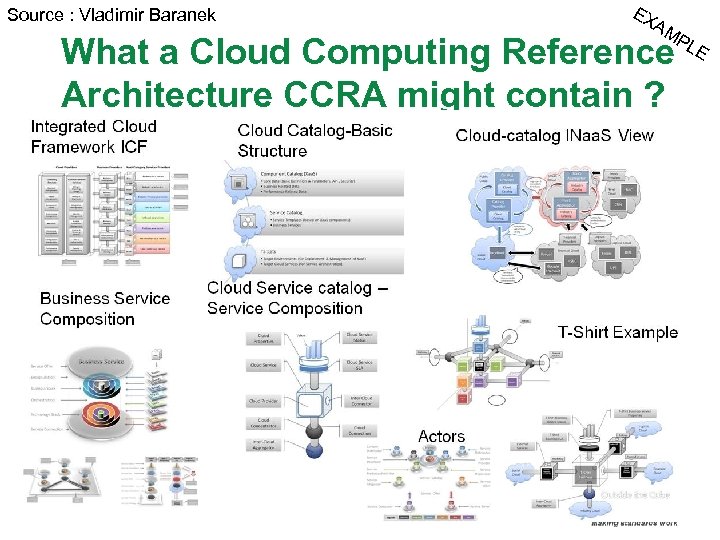
 At Cloudcamp we discussed… What a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA might contain ? q Cloud Computing Technology reference model § q Cloud services model § § q How the overall flow of a Cloud service transaction might flow How the cloud service “communities” might look and interact How trading and marketplaces might interoperate Integrated Cloud Framework § § q The types if actors that might participate in a cloud service from all perspectives Cloud network (Choreography) Model § § § q A description of the types of services we see in cloud computing – more from the perspective of the type of “operations” and services that cloud might support. Examples. This is not Web services or BPEL style protocols and workflow styles How the service meta data might be defined Cloud Actor Model § q This is arguably already covered in the many technology stack reference models: NIST etal. They provide a provider technology perspective of the cloud solution How to design Cloud Components How to define a Cloud Service Lifecycle Cloud catalog and user experience model § § How a catalog or catalogs of business and IT services might be represented in the cloud How the services might be visualized , discovered and used q Cloud Meta data and Behavior (Cloud Contract) Model q § A description of the service exchange meta data model Others……. . Some of these relate to CCA, SOCCI etc
At Cloudcamp we discussed… What a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA might contain ? q Cloud Computing Technology reference model § q Cloud services model § § q How the overall flow of a Cloud service transaction might flow How the cloud service “communities” might look and interact How trading and marketplaces might interoperate Integrated Cloud Framework § § q The types if actors that might participate in a cloud service from all perspectives Cloud network (Choreography) Model § § § q A description of the types of services we see in cloud computing – more from the perspective of the type of “operations” and services that cloud might support. Examples. This is not Web services or BPEL style protocols and workflow styles How the service meta data might be defined Cloud Actor Model § q This is arguably already covered in the many technology stack reference models: NIST etal. They provide a provider technology perspective of the cloud solution How to design Cloud Components How to define a Cloud Service Lifecycle Cloud catalog and user experience model § § How a catalog or catalogs of business and IT services might be represented in the cloud How the services might be visualized , discovered and used q Cloud Meta data and Behavior (Cloud Contract) Model q § A description of the service exchange meta data model Others……. . Some of these relate to CCA, SOCCI etc
 Why do we need Cloud Model Symbols ? Reasons for using the “Symbology”: Marketplace Visualization Visualizing Behavior Cloud Network Nomenclature
Why do we need Cloud Model Symbols ? Reasons for using the “Symbology”: Marketplace Visualization Visualizing Behavior Cloud Network Nomenclature
 EX AM What a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA might contain ? PL E
EX AM What a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA might contain ? PL E
 Source : Vladimir Baranek EX AM What a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA might contain ? PL E
Source : Vladimir Baranek EX AM What a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture CCRA might contain ? PL E
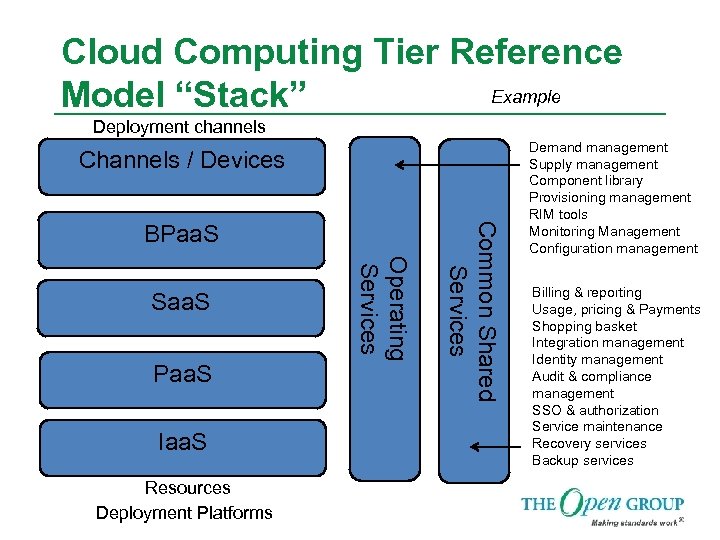 Cloud Computing Tier Reference Example Model “Stack” Deployment channels Channels / Devices Paa. S Iaa. S Resources Deployment Platforms Operating Services Saa. S Common Shared Services BPaa. S Demand management Supply management Component library Provisioning management RIM tools Monitoring Management Configuration management Billing & reporting Usage, pricing & Payments Shopping basket Integration management Identity management Audit & compliance management SSO & authorization Service maintenance Recovery services Backup services
Cloud Computing Tier Reference Example Model “Stack” Deployment channels Channels / Devices Paa. S Iaa. S Resources Deployment Platforms Operating Services Saa. S Common Shared Services BPaa. S Demand management Supply management Component library Provisioning management RIM tools Monitoring Management Configuration management Billing & reporting Usage, pricing & Payments Shopping basket Integration management Identity management Audit & compliance management SSO & authorization Service maintenance Recovery services Backup services
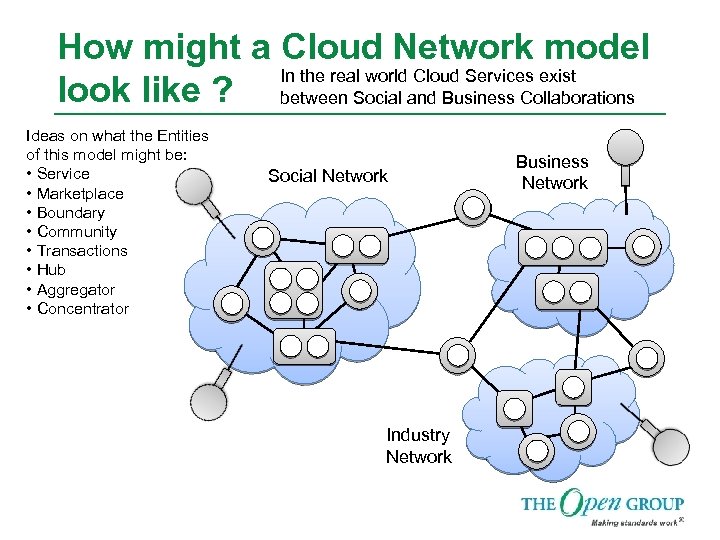 How might a Cloud Network model In the real world Cloud Services exist look like ? between Social and Business Collaborations Ideas on what the Entities of this model might be: • Service • Marketplace • Boundary • Community • Transactions • Hub • Aggregator • Concentrator Social Network Industry Network Business Network
How might a Cloud Network model In the real world Cloud Services exist look like ? between Social and Business Collaborations Ideas on what the Entities of this model might be: • Service • Marketplace • Boundary • Community • Transactions • Hub • Aggregator • Concentrator Social Network Industry Network Business Network
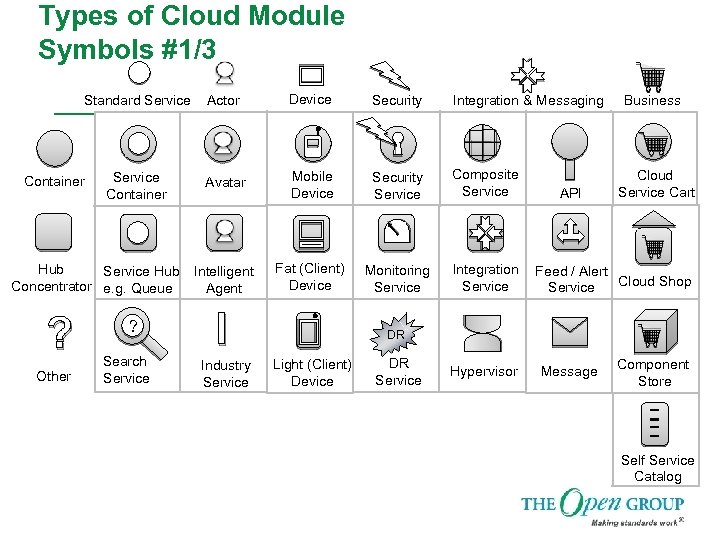 Types of Cloud Module Symbols #1/3 Standard Service Actor Device Security Integration & Messaging Service Container Avatar Mobile Device Security Service Composite Service Intelligent Agent Fat (Client) Device Monitoring Service Integration Service Container Hub Service Hub Concentrator e. g. Queue ? Other ? Search Service I Industry Service API Business Cloud Service Cart Feed / Alert Cloud Shop Service DR Light (Client) Device DR Service Hypervisor Message Component Store Self Service Catalog
Types of Cloud Module Symbols #1/3 Standard Service Actor Device Security Integration & Messaging Service Container Avatar Mobile Device Security Service Composite Service Intelligent Agent Fat (Client) Device Monitoring Service Integration Service Container Hub Service Hub Concentrator e. g. Queue ? Other ? Search Service I Industry Service API Business Cloud Service Cart Feed / Alert Cloud Shop Service DR Light (Client) Device DR Service Hypervisor Message Component Store Self Service Catalog
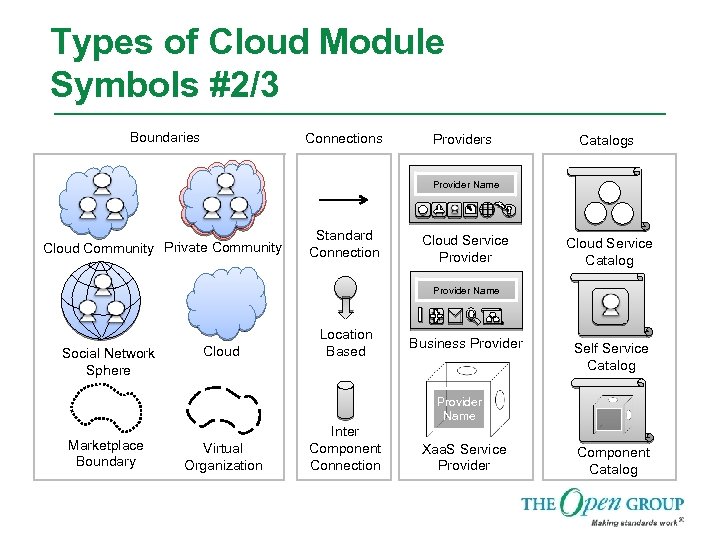 Types of Cloud Module Symbols #2/3 Boundaries Connections Providers Catalogs Provider Name Cloud Community Private Community Standard Connection Cloud Service Provider Cloud Service Catalog Provider Name Social Network Sphere Cloud Location Based I Business Provider Self Service Catalog Provider Name Marketplace Boundary Virtual Organization Inter Component Connection Xaa. S Service Provider Component Catalog
Types of Cloud Module Symbols #2/3 Boundaries Connections Providers Catalogs Provider Name Cloud Community Private Community Standard Connection Cloud Service Provider Cloud Service Catalog Provider Name Social Network Sphere Cloud Location Based I Business Provider Self Service Catalog Provider Name Marketplace Boundary Virtual Organization Inter Component Connection Xaa. S Service Provider Component Catalog
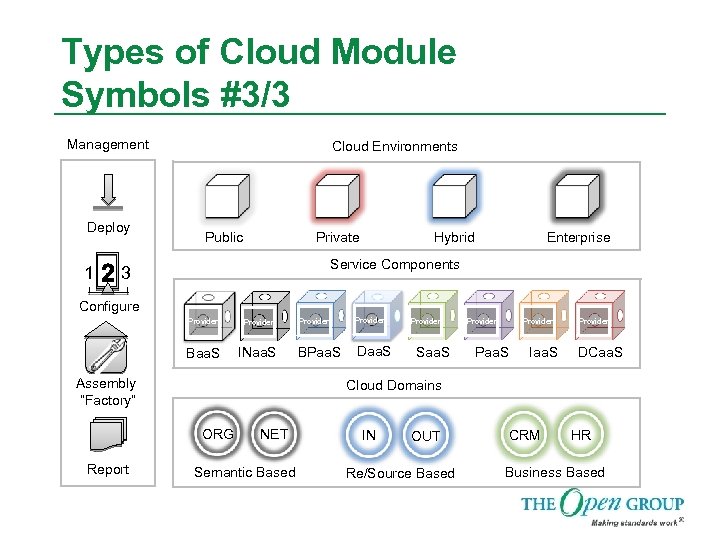 Types of Cloud Module Symbols #3/3 Management Deploy 1 Cloud Environments Public Private Hybrid Enterprise Service Components 3 Configure Provider Baa. S INaa. S Assembly “Factory” Provider BPaa. S Daa. S Provider Saa. S Provider Paa. S Iaa. S Provider DCaa. S Cloud Domains ORG Report Provider NET Semantic Based IN OUT Re/Source Based CRM HR Business Based
Types of Cloud Module Symbols #3/3 Management Deploy 1 Cloud Environments Public Private Hybrid Enterprise Service Components 3 Configure Provider Baa. S INaa. S Assembly “Factory” Provider BPaa. S Daa. S Provider Saa. S Provider Paa. S Iaa. S Provider DCaa. S Cloud Domains ORG Report Provider NET Semantic Based IN OUT Re/Source Based CRM HR Business Based
 My focus here is just on a Business Notation for describing Cloud requirements
My focus here is just on a Business Notation for describing Cloud requirements
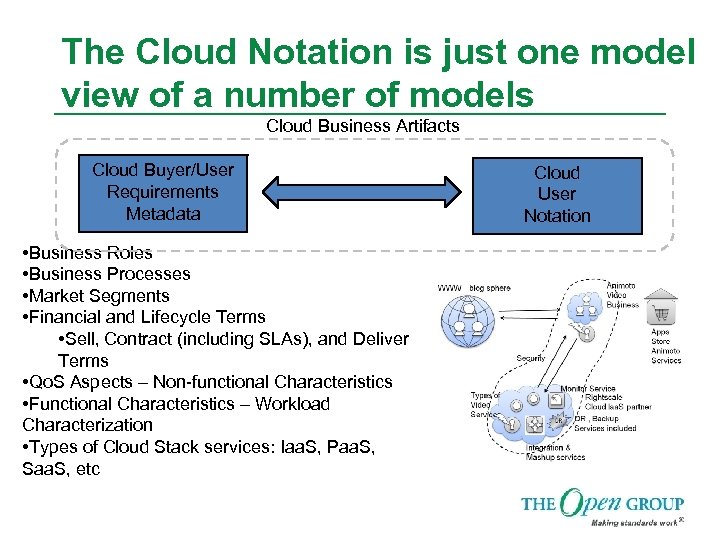 The Cloud Notation is just one model view of a number of models Cloud Business Artifacts Cloud Buyer/User Requirements Metadata • Business Roles • Business Processes • Market Segments • Financial and Lifecycle Terms • Sell, Contract (including SLAs), and Deliver Terms • Qo. S Aspects – Non-functional Characteristics • Functional Characteristics – Workload Characterization • Types of Cloud Stack services: Iaa. S, Paa. S, Saa. S, etc Cloud User Notation
The Cloud Notation is just one model view of a number of models Cloud Business Artifacts Cloud Buyer/User Requirements Metadata • Business Roles • Business Processes • Market Segments • Financial and Lifecycle Terms • Sell, Contract (including SLAs), and Deliver Terms • Qo. S Aspects – Non-functional Characteristics • Functional Characteristics – Workload Characterization • Types of Cloud Stack services: Iaa. S, Paa. S, Saa. S, etc Cloud User Notation
 Some examples using the Cloud notation q The following uses examples from Kevin Jackson, Leading Cloud evangelist , Cloud. Computing. Journal http: //cloudcomputing. sys-con. com/ recent blog publications to illustrate the point. http: //www. xmind. net/share/_embed/kvjacksn/ cloud-computing-training/
Some examples using the Cloud notation q The following uses examples from Kevin Jackson, Leading Cloud evangelist , Cloud. Computing. Journal http: //cloudcomputing. sys-con. com/ recent blog publications to illustrate the point. http: //www. xmind. net/share/_embed/kvjacksn/ cloud-computing-training/
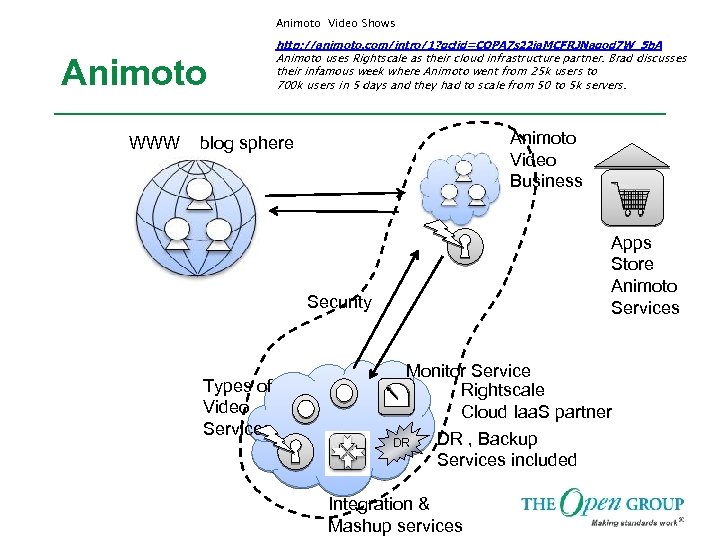 Animoto Video Shows Animoto WWW http: //animoto. com/intro/1? gclid=COPA 7 s 22 ia. MCFRJNagod 7 W_5 b. A Animoto uses Rightscale as their cloud infrastructure partner. Brad discusses their infamous week where Animoto went from 25 k users to 700 k users in 5 days and they had to scale from 50 to 5 k servers. Animoto Video Business blog sphere Apps Store Animoto Services Security Types of Video Services Monitor Service Rightscale Cloud Iaa. S partner DR DR , Backup Services included Integration & Mashup services
Animoto Video Shows Animoto WWW http: //animoto. com/intro/1? gclid=COPA 7 s 22 ia. MCFRJNagod 7 W_5 b. A Animoto uses Rightscale as their cloud infrastructure partner. Brad discusses their infamous week where Animoto went from 25 k users to 700 k users in 5 days and they had to scale from 50 to 5 k servers. Animoto Video Business blog sphere Apps Store Animoto Services Security Types of Video Services Monitor Service Rightscale Cloud Iaa. S partner DR DR , Backup Services included Integration & Mashup services
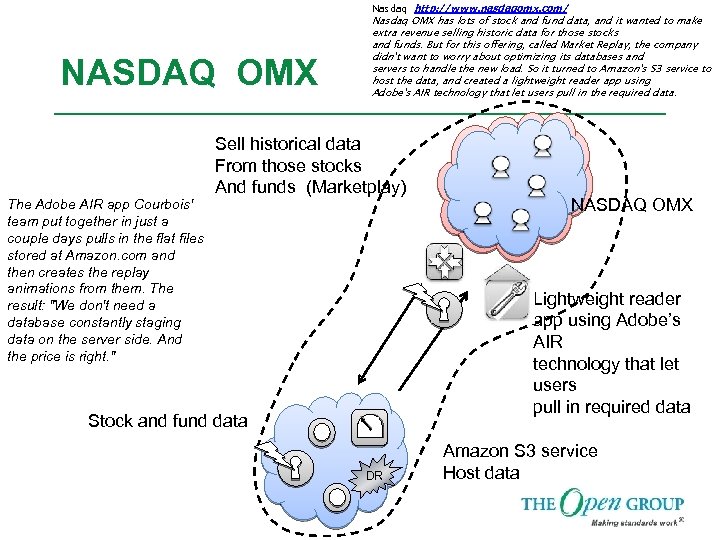 Nasdaq http: //www. nasdaqomx. com/ NASDAQ OMX The Adobe AIR app Courbois' team put together in just a couple days pulls in the flat files stored at Amazon. com and then creates the replay animations from them. The result: "We don't need a database constantly staging data on the server side. And the price is right. " Nasdaq OMX has lots of stock and fund data, and it wanted to make extra revenue selling historic data for those stocks and funds. But for this offering, called Market Replay, the company didn't want to worry about optimizing its databases and servers to handle the new load. So it turned to Amazon's S 3 service to host the data, and created a lightweight reader app using Adobe's AIR technology that let users pull in the required data. Sell historical data From those stocks And funds (Marketplay) NASDAQ OMX Lightweight reader app using Adobe’s AIR technology that let users pull in required data Stock and fund data DR Amazon S 3 service Host data
Nasdaq http: //www. nasdaqomx. com/ NASDAQ OMX The Adobe AIR app Courbois' team put together in just a couple days pulls in the flat files stored at Amazon. com and then creates the replay animations from them. The result: "We don't need a database constantly staging data on the server side. And the price is right. " Nasdaq OMX has lots of stock and fund data, and it wanted to make extra revenue selling historic data for those stocks and funds. But for this offering, called Market Replay, the company didn't want to worry about optimizing its databases and servers to handle the new load. So it turned to Amazon's S 3 service to host the data, and created a lightweight reader app using Adobe's AIR technology that let users pull in the required data. Sell historical data From those stocks And funds (Marketplay) NASDAQ OMX Lightweight reader app using Adobe’s AIR technology that let users pull in required data Stock and fund data DR Amazon S 3 service Host data
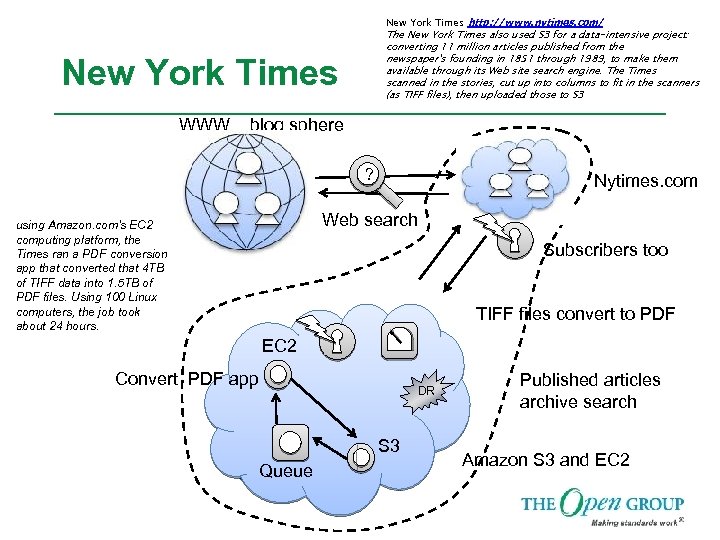 New York Times http: //www. nytimes. com/ The New York Times also used S 3 for a data-intensive project: converting 11 million articles published from the newspaper's founding in 1851 through 1989, to make them available through its Web site search engine. The Times scanned in the stories, cut up into columns to fit in the scanners (as TIFF files), then uploaded those to S 3 New York Times WWW blog sphere ? Nytimes. com Web search using Amazon. com's EC 2 computing platform, the Times ran a PDF conversion app that converted that 4 TB of TIFF data into 1. 5 TB of PDF files. Using 100 Linux computers, the job took about 24 hours. Subscribers too TIFF files convert to PDF EC 2 Convert PDF app DR S 3 Queue Published articles archive search Amazon S 3 and EC 2
New York Times http: //www. nytimes. com/ The New York Times also used S 3 for a data-intensive project: converting 11 million articles published from the newspaper's founding in 1851 through 1989, to make them available through its Web site search engine. The Times scanned in the stories, cut up into columns to fit in the scanners (as TIFF files), then uploaded those to S 3 New York Times WWW blog sphere ? Nytimes. com Web search using Amazon. com's EC 2 computing platform, the Times ran a PDF conversion app that converted that 4 TB of TIFF data into 1. 5 TB of PDF files. Using 100 Linux computers, the job took about 24 hours. Subscribers too TIFF files convert to PDF EC 2 Convert PDF app DR S 3 Queue Published articles archive search Amazon S 3 and EC 2
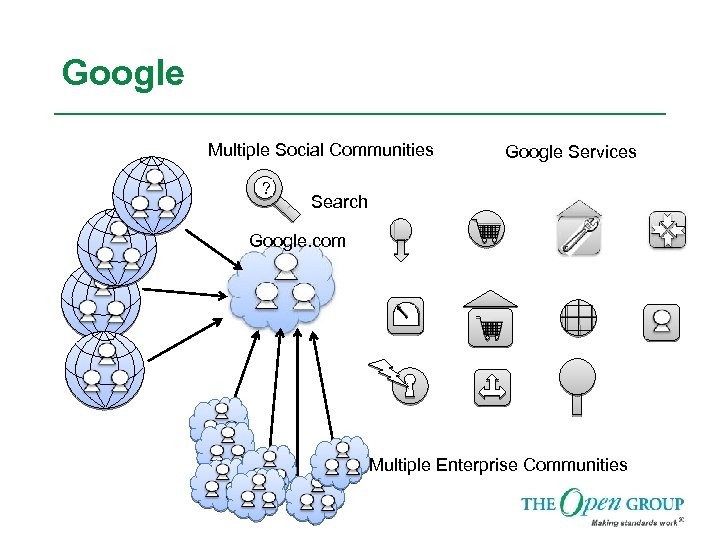 Google Multiple Social Communities ? Google Services Search Google. com Multiple Enterprise Communities
Google Multiple Social Communities ? Google Services Search Google. com Multiple Enterprise Communities
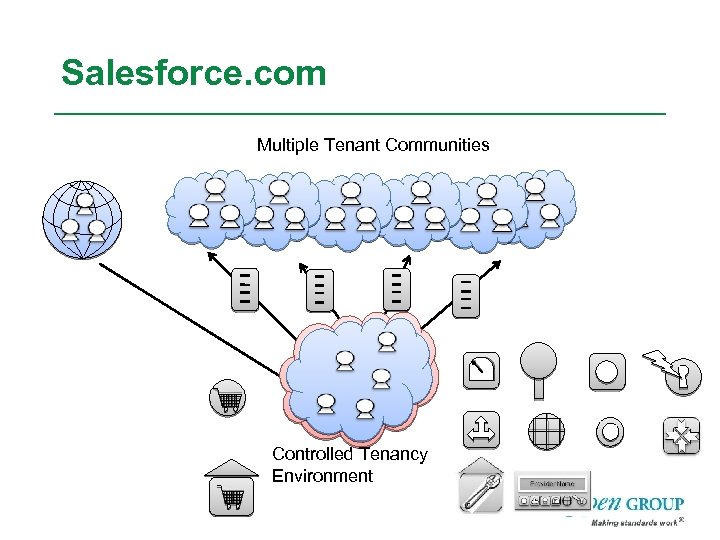 Salesforce. com Multiple Tenant Communities Controlled Tenancy Environment
Salesforce. com Multiple Tenant Communities Controlled Tenancy Environment
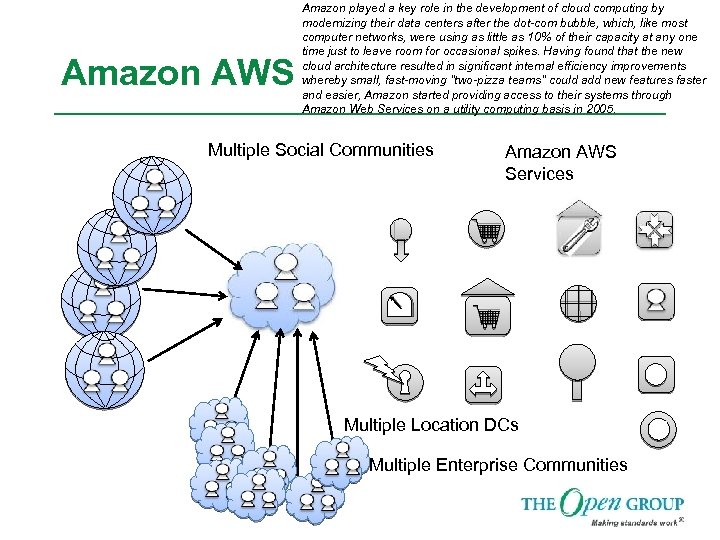 Amazon AWS Amazon played a key role in the development of cloud computing by modernizing their data centers after the dot-com bubble, which, like most computer networks, were using as little as 10% of their capacity at any one time just to leave room for occasional spikes. Having found that the new cloud architecture resulted in significant internal efficiency improvements whereby small, fast-moving "two-pizza teams" could add new features faster and easier, Amazon started providing access to their systems through Amazon Web Services on a utility computing basis in 2005. Multiple Social Communities Amazon AWS Services Multiple Location DCs Multiple Enterprise Communities
Amazon AWS Amazon played a key role in the development of cloud computing by modernizing their data centers after the dot-com bubble, which, like most computer networks, were using as little as 10% of their capacity at any one time just to leave room for occasional spikes. Having found that the new cloud architecture resulted in significant internal efficiency improvements whereby small, fast-moving "two-pizza teams" could add new features faster and easier, Amazon started providing access to their systems through Amazon Web Services on a utility computing basis in 2005. Multiple Social Communities Amazon AWS Services Multiple Location DCs Multiple Enterprise Communities
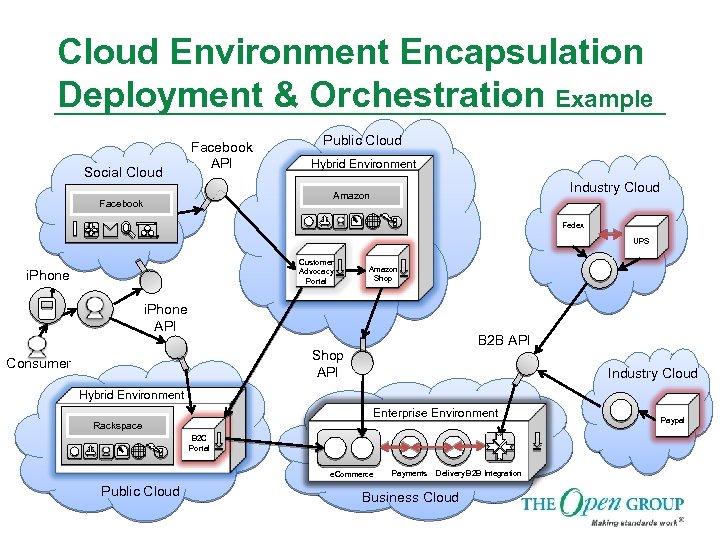 Cloud Environment Encapsulation Deployment & Orchestration Example Social Cloud Facebook API Public Cloud Hybrid Environment Industry Cloud Amazon Facebook I Fedex UPS Customer Advocacy Portal i. Phone Amazon Shop i. Phone API B 2 B API Shop API Consumer Industry Cloud Hybrid Environment Enterprise Environment Rackspace B 2 C Portal e. Commerce Public Cloud Payments Delivery B 2 B Integration Business Cloud Paypal
Cloud Environment Encapsulation Deployment & Orchestration Example Social Cloud Facebook API Public Cloud Hybrid Environment Industry Cloud Amazon Facebook I Fedex UPS Customer Advocacy Portal i. Phone Amazon Shop i. Phone API B 2 B API Shop API Consumer Industry Cloud Hybrid Environment Enterprise Environment Rackspace B 2 C Portal e. Commerce Public Cloud Payments Delivery B 2 B Integration Business Cloud Paypal
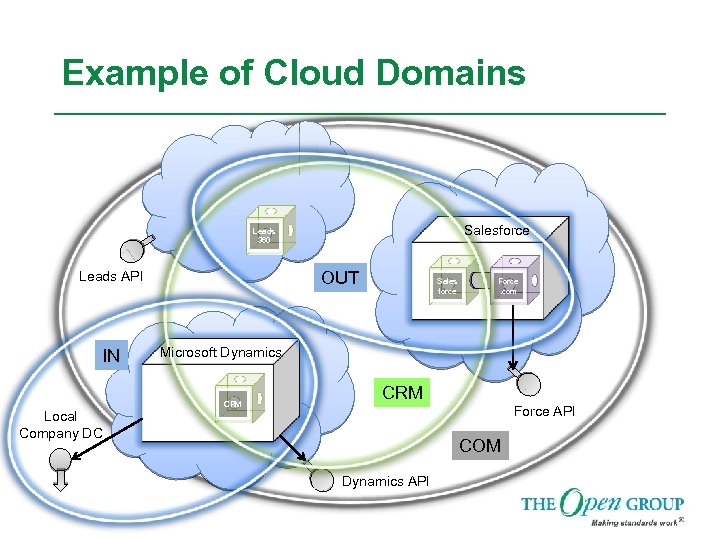 Example of Cloud Domains Salesforce Leads 360 OUT Leads API IN Local Company DC Sales force Force. com Microsoft Dynamics CRM Force API COM Dynamics API
Example of Cloud Domains Salesforce Leads 360 OUT Leads API IN Local Company DC Sales force Force. com Microsoft Dynamics CRM Force API COM Dynamics API
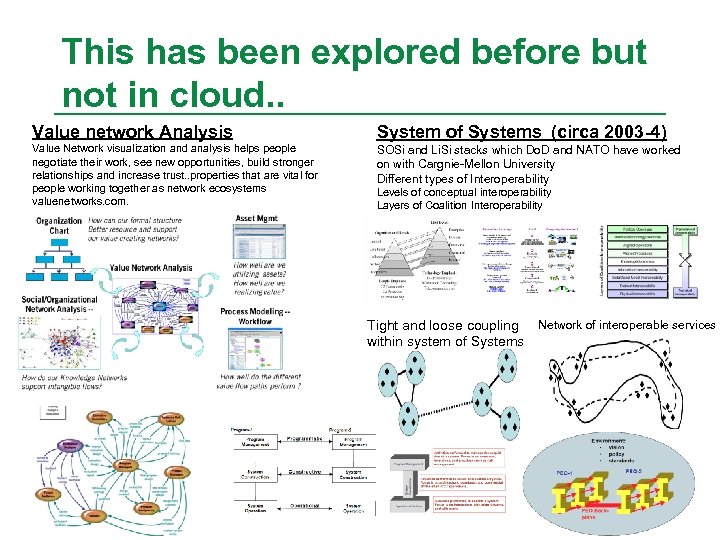 This has been explored before but not in cloud. . Value network Analysis System of Systems (circa 2003 -4) Value Network visualization and analysis helps people negotiate their work, see new opportunities, build stronger relationships and increase trust. . properties that are vital for people working together as network ecosystems valuenetworks. com. SOSi and Li. Si stacks which Do. D and NATO have worked on with Cargnie-Mellon University Different types of Interoperability Levels of conceptual interoperability Layers of Coalition Interoperability Tight and loose coupling within system of Systems Network of interoperable services
This has been explored before but not in cloud. . Value network Analysis System of Systems (circa 2003 -4) Value Network visualization and analysis helps people negotiate their work, see new opportunities, build stronger relationships and increase trust. . properties that are vital for people working together as network ecosystems valuenetworks. com. SOSi and Li. Si stacks which Do. D and NATO have worked on with Cargnie-Mellon University Different types of Interoperability Levels of conceptual interoperability Layers of Coalition Interoperability Tight and loose coupling within system of Systems Network of interoperable services
 Next steps q q Is this notation something that The Open Group Cloud Work Group think has merit and should be carried forward ? Should this be a set up as a separate Project within the Cloud Work Group with new chairs and a Charter ? Should this be kept within the current CBA Project as it has links with the metadata work in CBA ? How should this be linked with the CCA and SOCCI project teams - the intention is to position CBAN as separate to other projects and to be business oriented notation
Next steps q q Is this notation something that The Open Group Cloud Work Group think has merit and should be carried forward ? Should this be a set up as a separate Project within the Cloud Work Group with new chairs and a Charter ? Should this be kept within the current CBA Project as it has links with the metadata work in CBA ? How should this be linked with the CCA and SOCCI project teams - the intention is to position CBAN as separate to other projects and to be business oriented notation
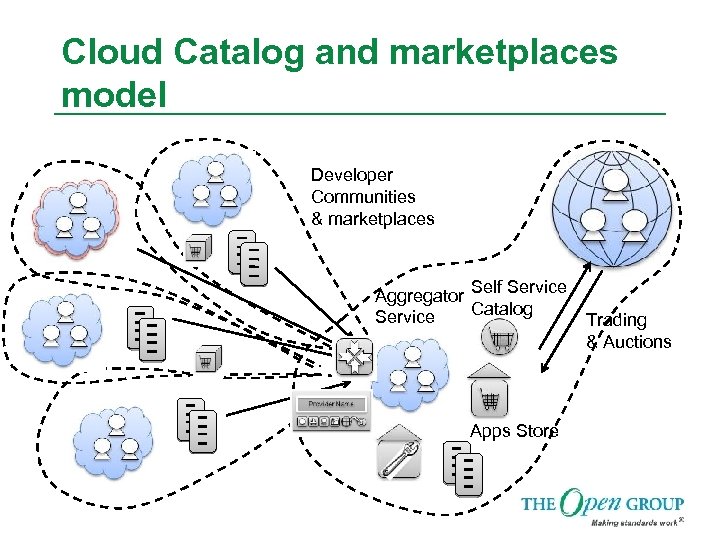 Cloud Catalog and marketplaces model Developer Communities & marketplaces Aggregator Self Service Catalog Service Apps Store Trading & Auctions
Cloud Catalog and marketplaces model Developer Communities & marketplaces Aggregator Self Service Catalog Service Apps Store Trading & Auctions
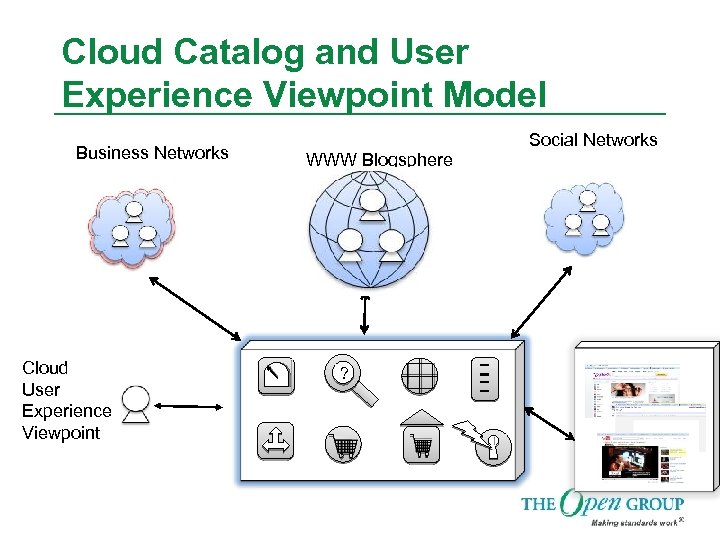 Cloud Catalog and User Experience Viewpoint Model Business Networks Cloud User Experience Viewpoint WWW Blogsphere ? Social Networks
Cloud Catalog and User Experience Viewpoint Model Business Networks Cloud User Experience Viewpoint WWW Blogsphere ? Social Networks
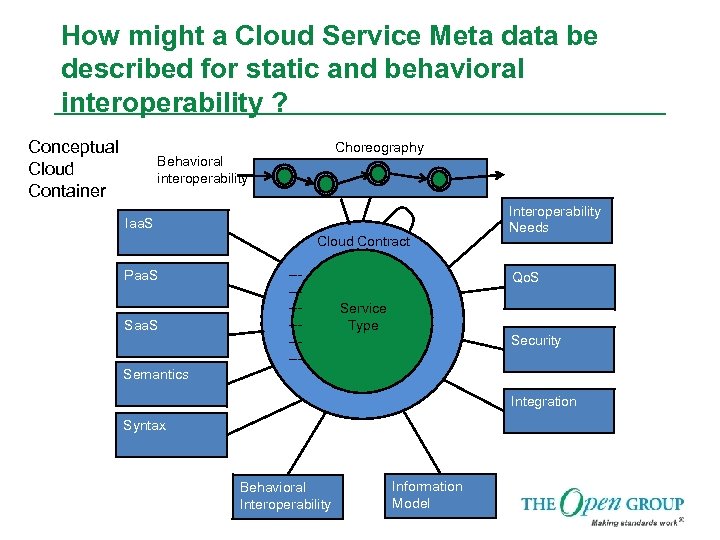 How might a Cloud Service Meta data be described for static and behavioral interoperability ? Conceptual Cloud Container Choreography Behavioral interoperability Iaa. S Cloud Contract Paa. S Saa. S ------- Interoperability Needs Qo. S Service Type Security Semantics Integration Syntax Behavioral Interoperability Information Model
How might a Cloud Service Meta data be described for static and behavioral interoperability ? Conceptual Cloud Container Choreography Behavioral interoperability Iaa. S Cloud Contract Paa. S Saa. S ------- Interoperability Needs Qo. S Service Type Security Semantics Integration Syntax Behavioral Interoperability Information Model


