ecde8e06dd0ad5270e4c3f9269827619.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 92
 Cloud Computing, CS 596 -015 Amazon EC 2 & Amazon Web Services (AWS) 1
Cloud Computing, CS 596 -015 Amazon EC 2 & Amazon Web Services (AWS) 1
 Outline n Introduction n Amazon Web Services (AWS) Components: q Iaa. S: EC 2, S 3, EBS q Paa. S: Simple. DB, SQS, SNS, Cloud. Front, Relational Data q Saa. S: AWS Web Services q AWS Integration and Management q AWS Billing n AWS Scalability n AWS Application Architecture: Design to Scale using AWS Elastic Features n Summary and Conclusions 2
Outline n Introduction n Amazon Web Services (AWS) Components: q Iaa. S: EC 2, S 3, EBS q Paa. S: Simple. DB, SQS, SNS, Cloud. Front, Relational Data q Saa. S: AWS Web Services q AWS Integration and Management q AWS Billing n AWS Scalability n AWS Application Architecture: Design to Scale using AWS Elastic Features n Summary and Conclusions 2
 Introduction 3
Introduction 3
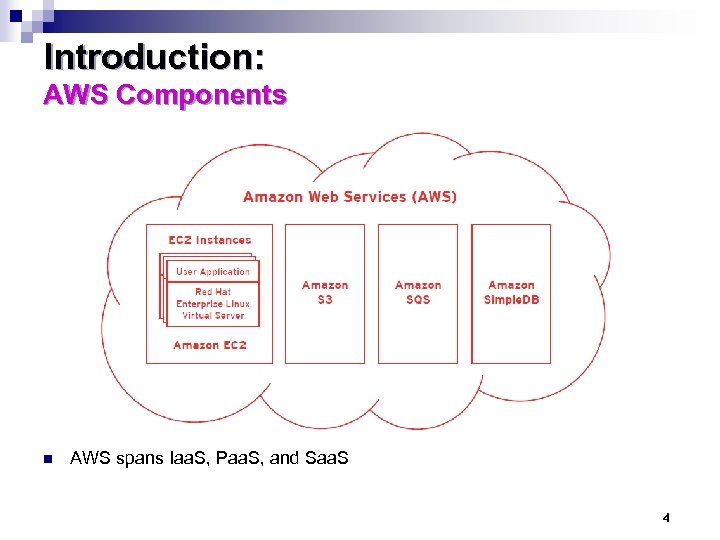 Introduction: AWS Components n AWS spans Iaa. S, Paa. S, and Saa. S 4
Introduction: AWS Components n AWS spans Iaa. S, Paa. S, and Saa. S 4
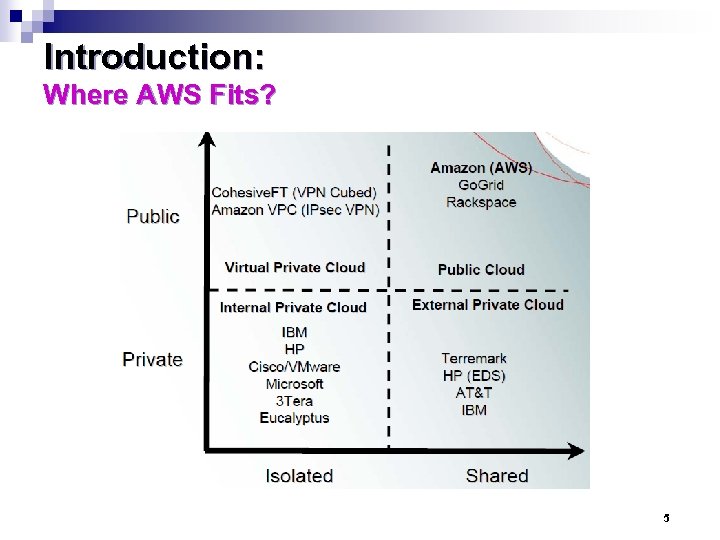 Introduction: Where AWS Fits? 5
Introduction: Where AWS Fits? 5
 Introduction: Issues facing Web Developers n 70% of Web Development Effort is “Muck”: q Data Centers q Bandwidth / Power / Cooling q Operations q Staffing n Scaling is Difficult and Expensive: q Large Up-Front Investment q Invest Ahead of Demand q Load is Unpredictable 6
Introduction: Issues facing Web Developers n 70% of Web Development Effort is “Muck”: q Data Centers q Bandwidth / Power / Cooling q Operations q Staffing n Scaling is Difficult and Expensive: q Large Up-Front Investment q Invest Ahead of Demand q Load is Unpredictable 6
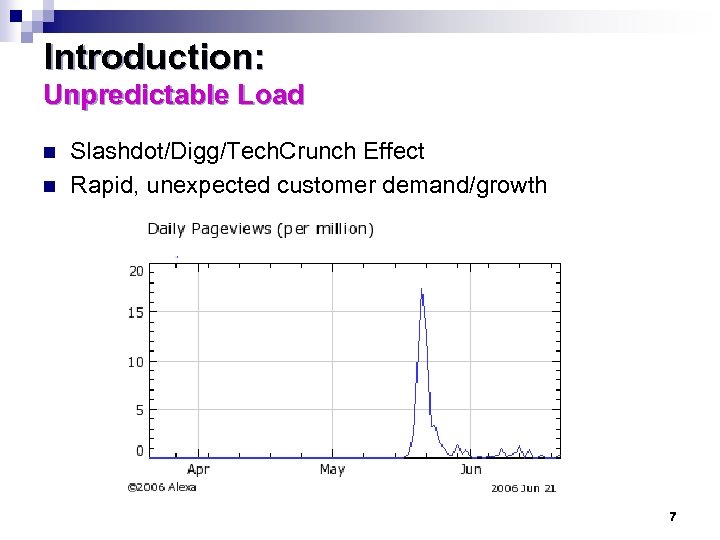 Introduction: Unpredictable Load n n Slashdot/Digg/Tech. Crunch Effect Rapid, unexpected customer demand/growth 7
Introduction: Unpredictable Load n n Slashdot/Digg/Tech. Crunch Effect Rapid, unexpected customer demand/growth 7
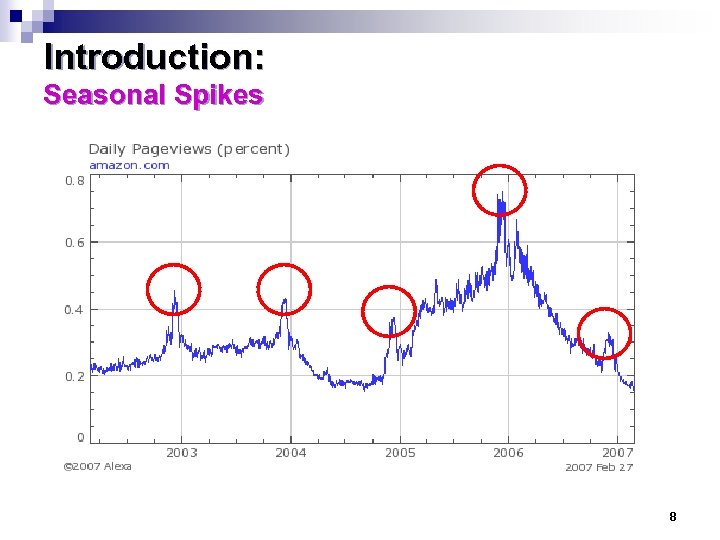 Introduction: Seasonal Spikes 8
Introduction: Seasonal Spikes 8
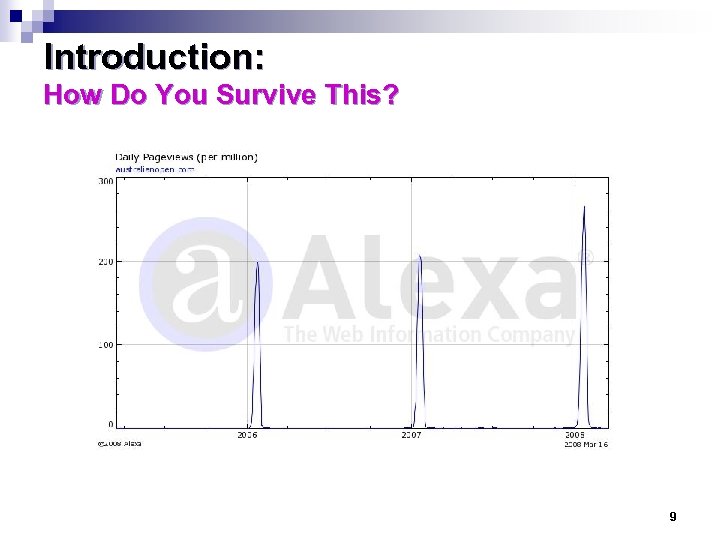 Introduction: How Do You Survive This? 9
Introduction: How Do You Survive This? 9
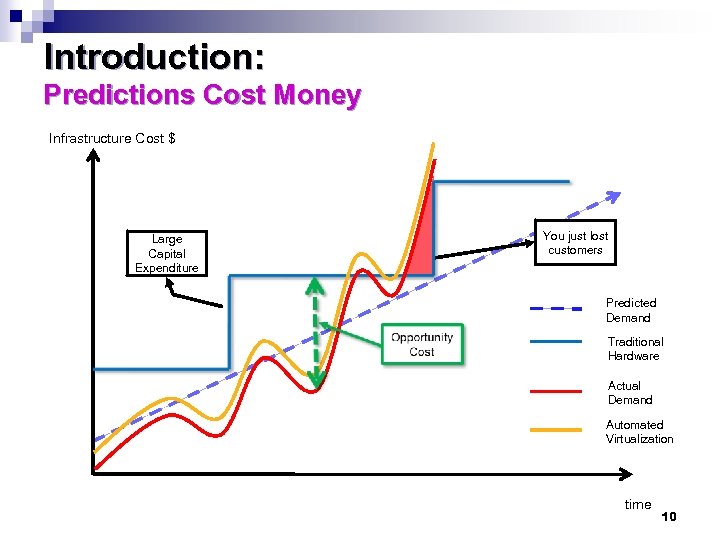 Introduction: Predictions Cost Money Infrastructure Cost $ Large Capital Expenditure You just lost customers Predicted Demand Traditional Hardware Actual Demand Automated Virtualization time 10
Introduction: Predictions Cost Money Infrastructure Cost $ Large Capital Expenditure You just lost customers Predicted Demand Traditional Hardware Actual Demand Automated Virtualization time 10
 Introduction: Solution – Web-Scale Computing n Scale capacity on demand n Turn fixed costs into variable costs n Always available n Rock-solid reliability n Simple APIs and conceptual models n Cost-effective n Reduced time to market n Focus on product & core competencies 11
Introduction: Solution – Web-Scale Computing n Scale capacity on demand n Turn fixed costs into variable costs n Always available n Rock-solid reliability n Simple APIs and conceptual models n Cost-effective n Reduced time to market n Focus on product & core competencies 11
 Amazon Web Services Components 12
Amazon Web Services Components 12
 AWS Services Are: Building block services that allow developers to innovate and make money: Infrastructure As a Service Amazon Simple Storage Service Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud Amazon Simple Queue Service Amazon Simple. DB Commerce As a Service Amazon Flexible Payments Service Fulfillment Web Service Data As A Service Amazon E-Commerce Service Amazon Historical Pricing People As a Service Amazon Mechanical Turk Alexa Web Services Alexa Web Information Service Alexa Top Sites Alexa Site Thumbnail Alexa Web Search Platform Search As A Service Alexa Web Information Service Alexa Top Sites Alexa Site Thumbnail Alexa Web Search Platform 13
AWS Services Are: Building block services that allow developers to innovate and make money: Infrastructure As a Service Amazon Simple Storage Service Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud Amazon Simple Queue Service Amazon Simple. DB Commerce As a Service Amazon Flexible Payments Service Fulfillment Web Service Data As A Service Amazon E-Commerce Service Amazon Historical Pricing People As a Service Amazon Mechanical Turk Alexa Web Services Alexa Web Information Service Alexa Top Sites Alexa Site Thumbnail Alexa Web Search Platform Search As A Service Alexa Web Information Service Alexa Top Sites Alexa Site Thumbnail Alexa Web Search Platform 13
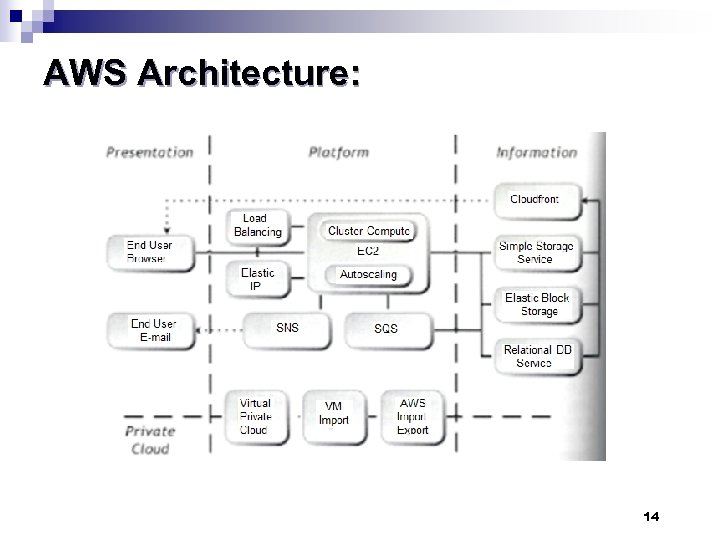 AWS Architecture: 14
AWS Architecture: 14
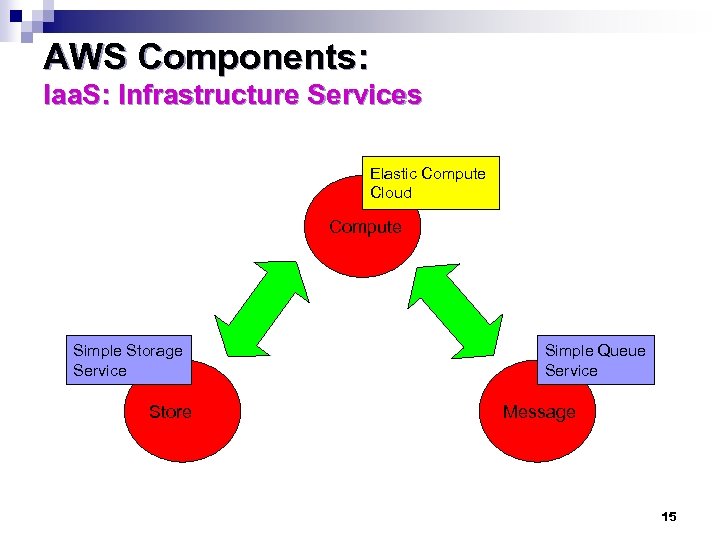 AWS Components: Iaa. S: Infrastructure Services Elastic Compute Cloud Compute Simple Storage Service Store Simple Queue Service Message 15
AWS Components: Iaa. S: Infrastructure Services Elastic Compute Cloud Compute Simple Storage Service Store Simple Queue Service Message 15
 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud – EC 2 16
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud – EC 2 16
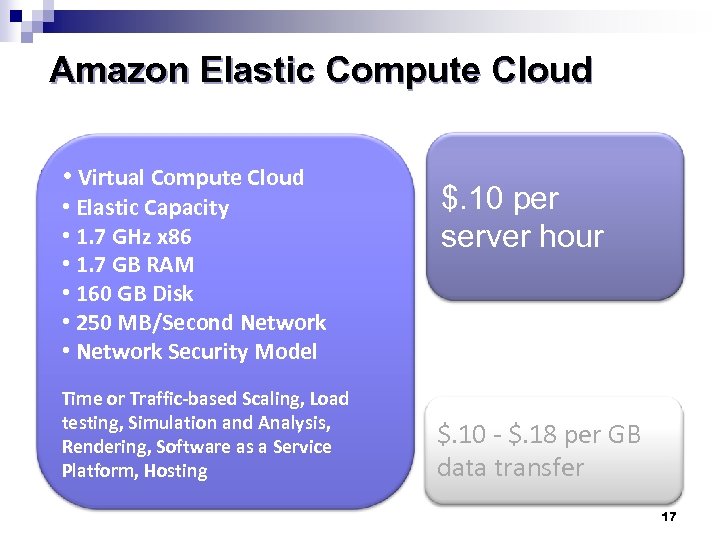 Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud • Virtual Compute Cloud • Elastic Capacity • 1. 7 GHz x 86 • 1. 7 GB RAM • 160 GB Disk • 250 MB/Second Network • Network Security Model Time or Traffic-based Scaling, Load testing, Simulation and Analysis, Rendering, Software as a Service Platform, Hosting $. 10 per server hour $. 10 - $. 18 per GB data transfer 17
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud • Virtual Compute Cloud • Elastic Capacity • 1. 7 GHz x 86 • 1. 7 GB RAM • 160 GB Disk • 250 MB/Second Network • Network Security Model Time or Traffic-based Scaling, Load testing, Simulation and Analysis, Rendering, Software as a Service Platform, Hosting $. 10 per server hour $. 10 - $. 18 per GB data transfer 17
 Amazon EC 2 Concepts q q q n Amazon offers the user a choice of VM template that can be instantiated in shared or virtual environment, called AMI Customer can use pre-packaged AMI or can build their own AMI vary in resources: RAM, Compute units, Local disk and OS Amazon Machine Image (AMI): Bootable root disk Pre-defined or user-built Catalog of user-built AMIs OS: Fedora, Centos, Gentoo, Debian, Ubuntu, Windows Server ¨ App Stack: LAMP, mpi. BLAST, Hadoop ¨ ¨ n Instance: ¨ ¨ ¨ n Network Security Model: ¨ ¨ n Running copy of an AMI Launch in less than 2 minutes Start/stop programmatically Explicit access control Security groups Inter-service bandwidth is free 18
Amazon EC 2 Concepts q q q n Amazon offers the user a choice of VM template that can be instantiated in shared or virtual environment, called AMI Customer can use pre-packaged AMI or can build their own AMI vary in resources: RAM, Compute units, Local disk and OS Amazon Machine Image (AMI): Bootable root disk Pre-defined or user-built Catalog of user-built AMIs OS: Fedora, Centos, Gentoo, Debian, Ubuntu, Windows Server ¨ App Stack: LAMP, mpi. BLAST, Hadoop ¨ ¨ n Instance: ¨ ¨ ¨ n Network Security Model: ¨ ¨ n Running copy of an AMI Launch in less than 2 minutes Start/stop programmatically Explicit access control Security groups Inter-service bandwidth is free 18
 Three Flavors of Amazon Machine Images n Public AMIs: Use pre-configured, template AMIs to get up and running immediately. Choose from Fedora, Movable Type, Ubuntu configurations, and more n Private AMIs: Create an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) containing your applications, libraries, data and associated configuration settings n Paid AMIs: Set a price for your AMI and let others purchase and use it (Single payment and/or per hour) 19
Three Flavors of Amazon Machine Images n Public AMIs: Use pre-configured, template AMIs to get up and running immediately. Choose from Fedora, Movable Type, Ubuntu configurations, and more n Private AMIs: Create an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) containing your applications, libraries, data and associated configuration settings n Paid AMIs: Set a price for your AMI and let others purchase and use it (Single payment and/or per hour) 19
 Amazon EC 2 Concepts n Resizable compute capacity in the cloud Obtain and boot new server instances in minutes ¨ Quickly scale capacity, up or down, as your computing requirements change ¨ n n n Full root access to a blank Linux machine Simple Web service management interface Changes the economics of computing 20
Amazon EC 2 Concepts n Resizable compute capacity in the cloud Obtain and boot new server instances in minutes ¨ Quickly scale capacity, up or down, as your computing requirements change ¨ n n n Full root access to a blank Linux machine Simple Web service management interface Changes the economics of computing 20
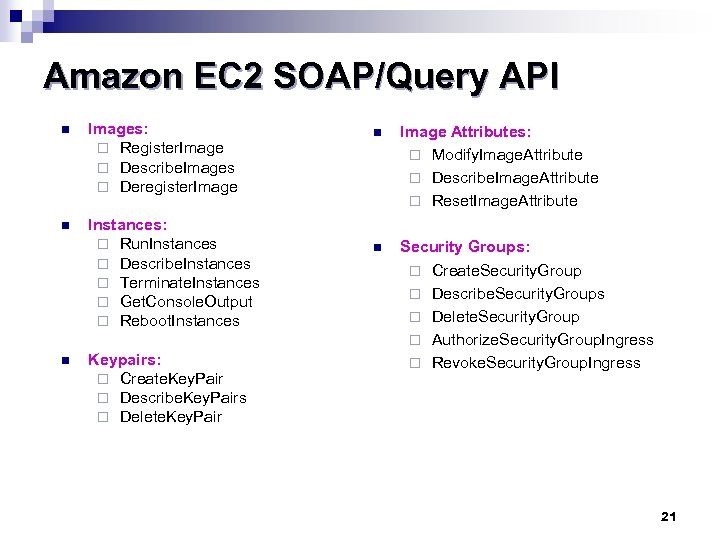 Amazon EC 2 SOAP/Query API n Images: ¨ Register. Image ¨ Describe. Images ¨ Deregister. Image n Instances: ¨ Run. Instances ¨ Describe. Instances ¨ Terminate. Instances ¨ Get. Console. Output ¨ Reboot. Instances n Keypairs: ¨ Create. Key. Pair ¨ Describe. Key. Pairs ¨ Delete. Key. Pair n Image Attributes: ¨ Modify. Image. Attribute ¨ Describe. Image. Attribute ¨ Reset. Image. Attribute n Security Groups: ¨ Create. Security. Group ¨ Describe. Security. Groups ¨ Delete. Security. Group ¨ Authorize. Security. Group. Ingress ¨ Revoke. Security. Group. Ingress 21
Amazon EC 2 SOAP/Query API n Images: ¨ Register. Image ¨ Describe. Images ¨ Deregister. Image n Instances: ¨ Run. Instances ¨ Describe. Instances ¨ Terminate. Instances ¨ Get. Console. Output ¨ Reboot. Instances n Keypairs: ¨ Create. Key. Pair ¨ Describe. Key. Pairs ¨ Delete. Key. Pair n Image Attributes: ¨ Modify. Image. Attribute ¨ Describe. Image. Attribute ¨ Reset. Image. Attribute n Security Groups: ¨ Create. Security. Group ¨ Describe. Security. Groups ¨ Delete. Security. Group ¨ Authorize. Security. Group. Ingress ¨ Revoke. Security. Group. Ingress 21
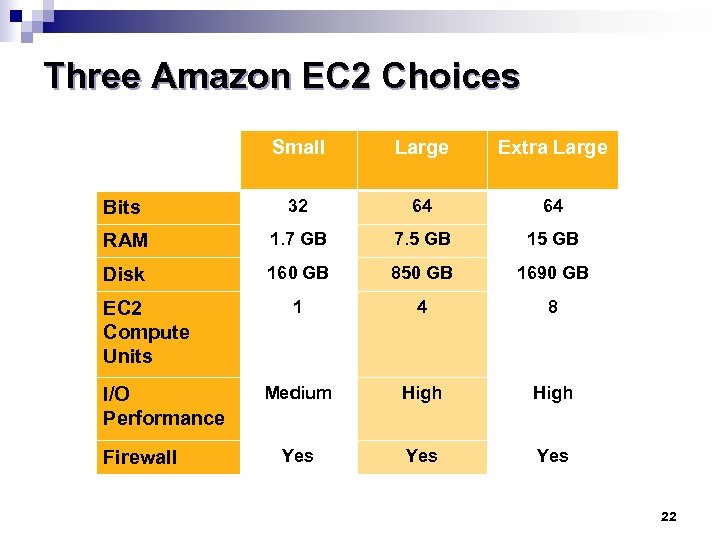 Three Amazon EC 2 Choices Small Large Extra Large Bits 32 64 64 RAM 1. 7 GB 7. 5 GB 15 GB Disk 160 GB 850 GB 1690 GB 1 4 8 Medium High Yes Yes EC 2 Compute Units I/O Performance Firewall 22
Three Amazon EC 2 Choices Small Large Extra Large Bits 32 64 64 RAM 1. 7 GB 7. 5 GB 15 GB Disk 160 GB 850 GB 1690 GB 1 4 8 Medium High Yes Yes EC 2 Compute Units I/O Performance Firewall 22
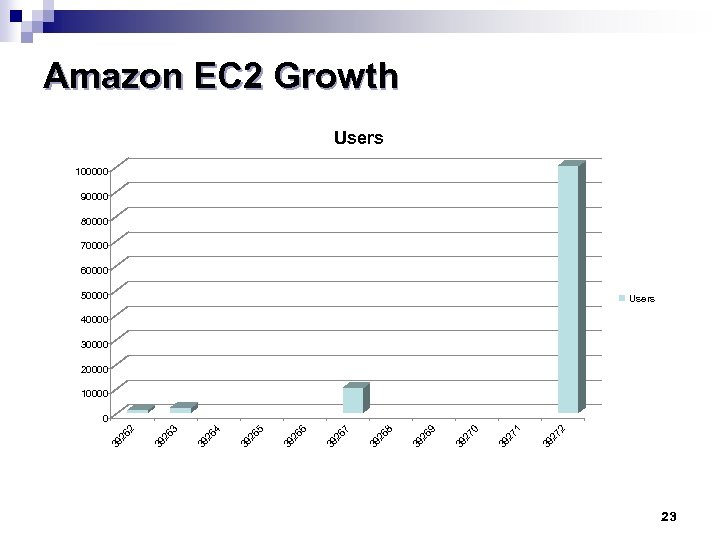 Amazon EC 2 Growth Users 100000 90000 80000 70000 60000 50000 Users 40000 30000 20000 10000 2 39 27 1 39 27 0 39 27 9 39 26 8 39 26 7 39 26 6 39 26 5 39 26 4 39 26 2 0 23
Amazon EC 2 Growth Users 100000 90000 80000 70000 60000 50000 Users 40000 30000 20000 10000 2 39 27 1 39 27 0 39 27 9 39 26 8 39 26 7 39 26 6 39 26 5 39 26 4 39 26 2 0 23
 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service – S 3 24
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service – S 3 24
 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) • Object-Based Storage • 1 B – 5 GB / object • Fast, Reliable, Scalable • Redundant, Dispersed • 99. 99% Availability Goal • Private or Public • Per-object URLs & ACLs • Bit. Torrent Support $. 15 per GB per month storage $. 01 for 1000 to 10000 requests $. 10 - $. 18 per GB data transfer 25
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) • Object-Based Storage • 1 B – 5 GB / object • Fast, Reliable, Scalable • Redundant, Dispersed • 99. 99% Availability Goal • Private or Public • Per-object URLs & ACLs • Bit. Torrent Support $. 15 per GB per month storage $. 01 for 1000 to 10000 requests $. 10 - $. 18 per GB data transfer 25
 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) n S 3 is an opaque storage service n Highly scalable data storage in-the-cloud n Programmatic access via web services API: REST & SOAP n Simple to get going and privdes 1 B – 5 TB and leverage AWS authentication services n Highly available and durable n Offers distributed, redundant buckets replicated using Cloud. Front Content Delivery Network across continents n Pay-as-you-go: ¨ Storage: $0. 15 / GB / month ¨ Data Transfer: starts at $0. 18 / GB ¨ Requests: nominal charges 26
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) n S 3 is an opaque storage service n Highly scalable data storage in-the-cloud n Programmatic access via web services API: REST & SOAP n Simple to get going and privdes 1 B – 5 TB and leverage AWS authentication services n Highly available and durable n Offers distributed, redundant buckets replicated using Cloud. Front Content Delivery Network across continents n Pay-as-you-go: ¨ Storage: $0. 15 / GB / month ¨ Data Transfer: starts at $0. 18 / GB ¨ Requests: nominal charges 26
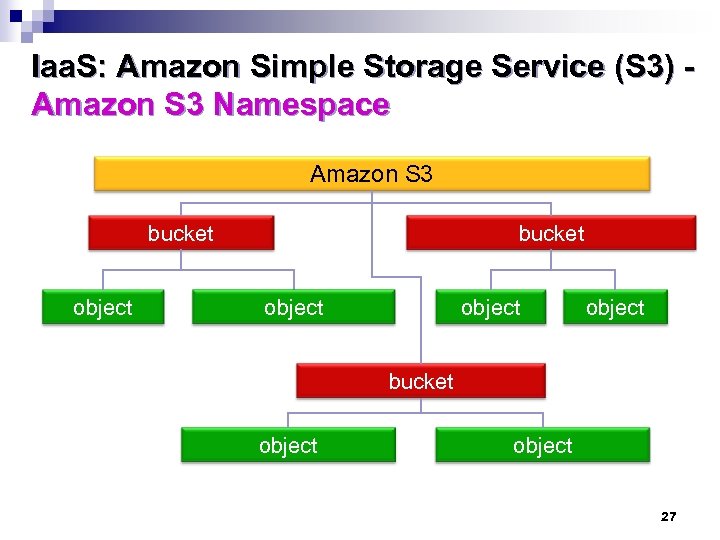 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) Amazon S 3 Namespace Amazon S 3 bucket object bucket object 27
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) Amazon S 3 Namespace Amazon S 3 bucket object bucket object 27
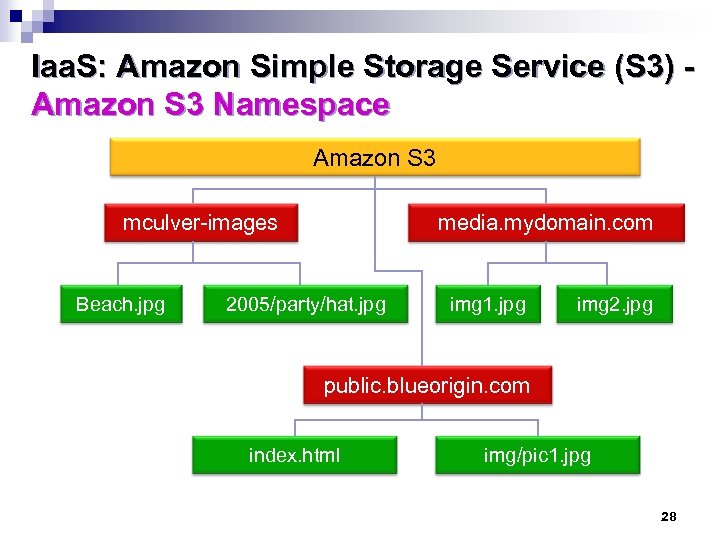 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) Amazon S 3 Namespace Amazon S 3 mculver-images Beach. jpg media. mydomain. com 2005/party/hat. jpg img 1. jpg img 2. jpg public. blueorigin. com index. html img/pic 1. jpg 28
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) Amazon S 3 Namespace Amazon S 3 mculver-images Beach. jpg media. mydomain. com 2005/party/hat. jpg img 1. jpg img 2. jpg public. blueorigin. com index. html img/pic 1. jpg 28
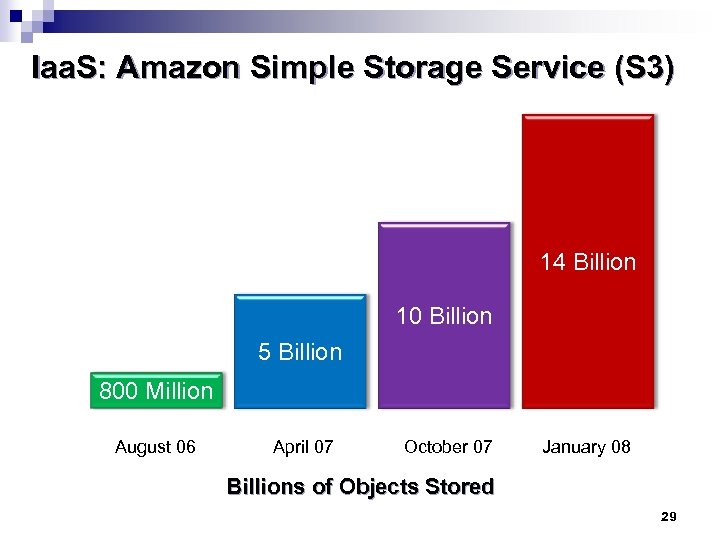 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) 14 Billion 10 Billion 5 Billion 800 Million August 06 April 07 October 07 January 08 Billions of Objects Stored 29
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) 14 Billion 10 Billion 5 Billion 800 Million August 06 April 07 October 07 January 08 Billions of Objects Stored 29
 Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) Open Source Backup 30
Iaa. S: Amazon Simple Storage Service (S 3) Open Source Backup 30
 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage – EBS 31
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage – EBS 31
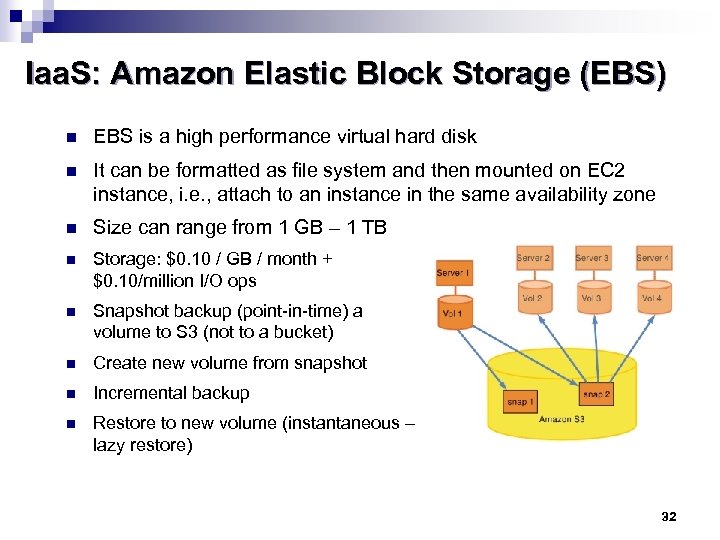 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n EBS is a high performance virtual hard disk n It can be formatted as file system and then mounted on EC 2 instance, i. e. , attach to an instance in the same availability zone n Size can range from 1 GB – 1 TB n Storage: $0. 10 / GB / month + $0. 10/million I/O ops n Snapshot backup (point-in-time) a volume to S 3 (not to a bucket) n Create new volume from snapshot n Incremental backup n Restore to new volume (instantaneous – lazy restore) 32
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n EBS is a high performance virtual hard disk n It can be formatted as file system and then mounted on EC 2 instance, i. e. , attach to an instance in the same availability zone n Size can range from 1 GB – 1 TB n Storage: $0. 10 / GB / month + $0. 10/million I/O ops n Snapshot backup (point-in-time) a volume to S 3 (not to a bucket) n Create new volume from snapshot n Incremental backup n Restore to new volume (instantaneous – lazy restore) 32
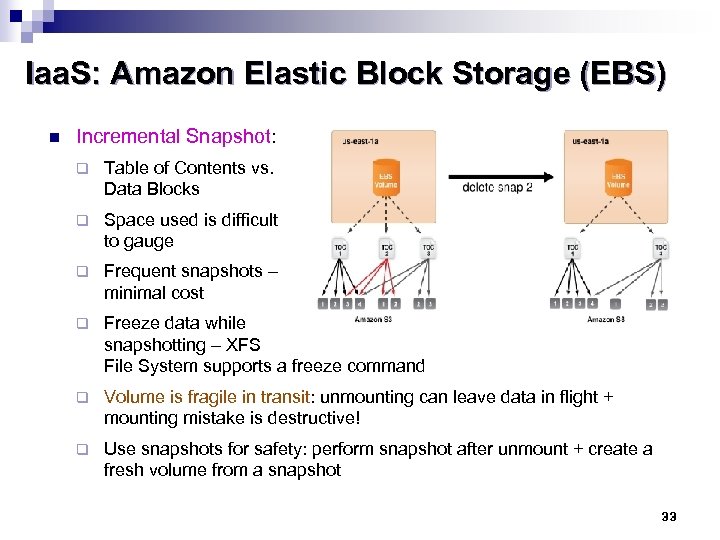 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n Incremental Snapshot: q Table of Contents vs. Data Blocks q Space used is difficult to gauge q Frequent snapshots – minimal cost q Freeze data while snapshotting – XFS File System supports a freeze command q Volume is fragile in transit: unmounting can leave data in flight + mounting mistake is destructive! q Use snapshots for safety: perform snapshot after unmount + create a fresh volume from a snapshot 33
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n Incremental Snapshot: q Table of Contents vs. Data Blocks q Space used is difficult to gauge q Frequent snapshots – minimal cost q Freeze data while snapshotting – XFS File System supports a freeze command q Volume is fragile in transit: unmounting can leave data in flight + mounting mistake is destructive! q Use snapshots for safety: perform snapshot after unmount + create a fresh volume from a snapshot 33
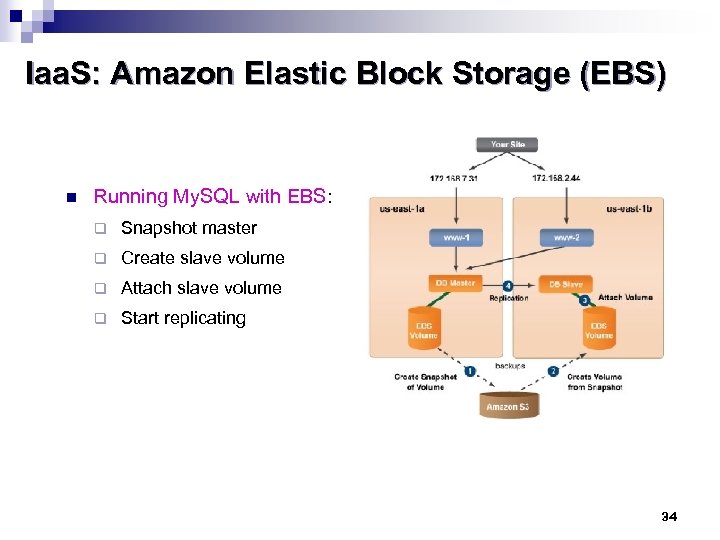 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n Running My. SQL with EBS: q Snapshot master q Create slave volume q Attach slave volume q Start replicating 34
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n Running My. SQL with EBS: q Snapshot master q Create slave volume q Attach slave volume q Start replicating 34
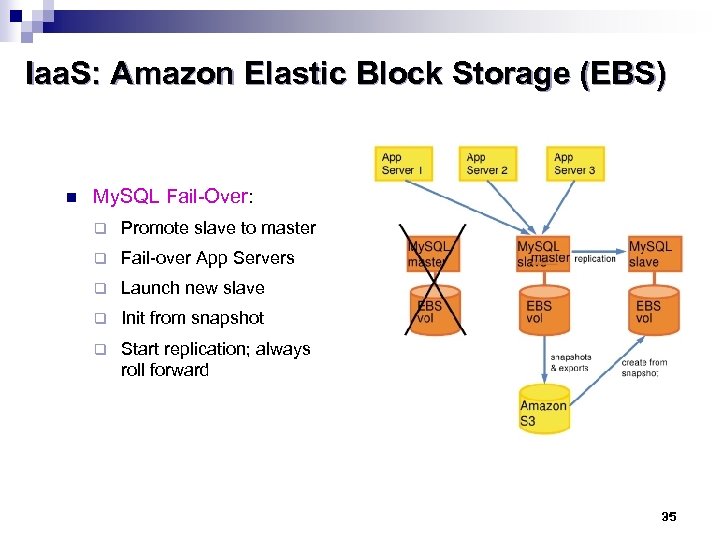 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n My. SQL Fail-Over: q Promote slave to master q Fail-over App Servers q Launch new slave q Init from snapshot q Start replication; always roll forward 35
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n My. SQL Fail-Over: q Promote slave to master q Fail-over App Servers q Launch new slave q Init from snapshot q Start replication; always roll forward 35
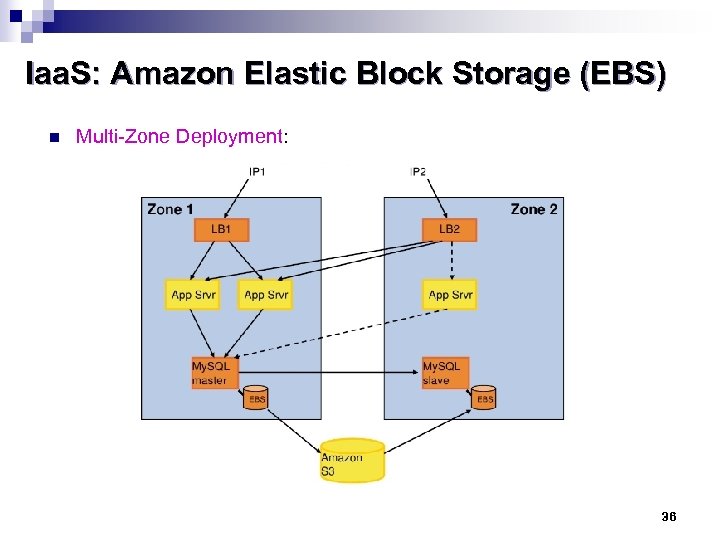 Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n Multi-Zone Deployment: 36
Iaa. S: Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) n Multi-Zone Deployment: 36
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB 37
Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB 37
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n SDB is available for more structured data; it does not support schema but instead defines “Domains” with items that consist of up to 256 attributes/values. A value can be up to 1 KB. SDB supports simple operators such as: =, !=, <, >, <=, >=, STARTS -WITH, AND, OR, NOT, INTERSECTION, and UNION n SDB is a distributed, highly scalable, light-weight, query-able, attribute store – new style of DB for cloud CAP: Consistency: Availability: network-Partitioning Cloud DB needs to sacrifice traditional DB CAP (consistency) properties: client side, Server side, and Eventual n n 38
Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n SDB is available for more structured data; it does not support schema but instead defines “Domains” with items that consist of up to 256 attributes/values. A value can be up to 1 KB. SDB supports simple operators such as: =, !=, <, >, <=, >=, STARTS -WITH, AND, OR, NOT, INTERSECTION, and UNION n SDB is a distributed, highly scalable, light-weight, query-able, attribute store – new style of DB for cloud CAP: Consistency: Availability: network-Partitioning Cloud DB needs to sacrifice traditional DB CAP (consistency) properties: client side, Server side, and Eventual n n 38
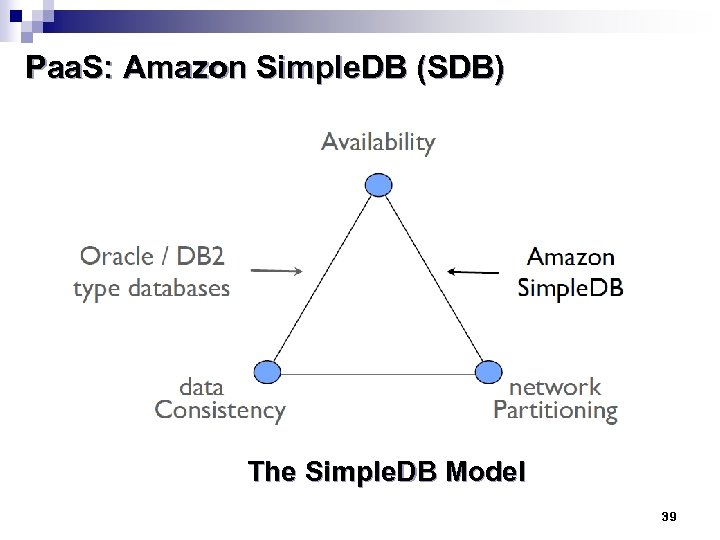 Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) The Simple. DB Model 39
Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) The Simple. DB Model 39
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n Developers want to: Store data q Process data q Query data q n Probably don’t want: Schema management q Index management q Performance tuning q Data access scaling q n n All data is replicated in geographically disbursed data centers (no explicit backup). Requests use HTTPS (security) Complex JOIN applications (DW) are not a good match for Simple. DB 40
Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n Developers want to: Store data q Process data q Query data q n Probably don’t want: Schema management q Index management q Performance tuning q Data access scaling q n n All data is replicated in geographically disbursed data centers (no explicit backup). Requests use HTTPS (security) Complex JOIN applications (DW) are not a good match for Simple. DB 40
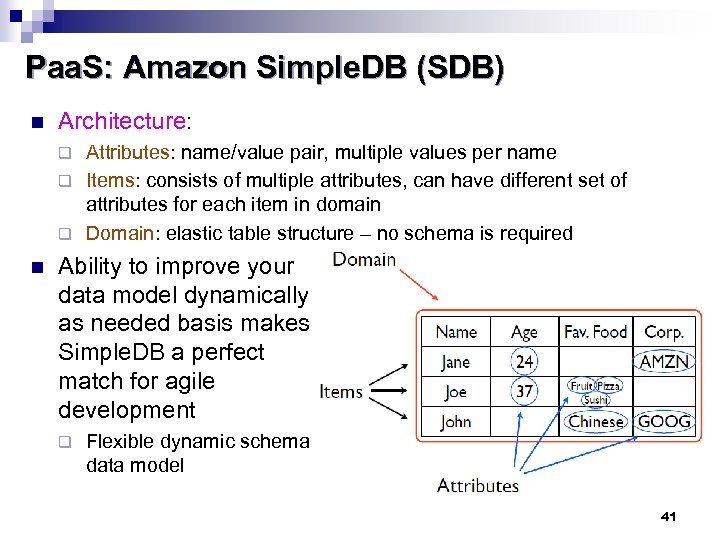 Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n Architecture: Attributes: name/value pair, multiple values per name q Items: consists of multiple attributes, can have different set of attributes for each item in domain q Domain: elastic table structure – no schema is required q n Ability to improve your data model dynamically as needed basis makes Simple. DB a perfect match for agile development q Flexible dynamic schema data model 41
Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n Architecture: Attributes: name/value pair, multiple values per name q Items: consists of multiple attributes, can have different set of attributes for each item in domain q Domain: elastic table structure – no schema is required q n Ability to improve your data model dynamically as needed basis makes Simple. DB a perfect match for agile development q Flexible dynamic schema data model 41
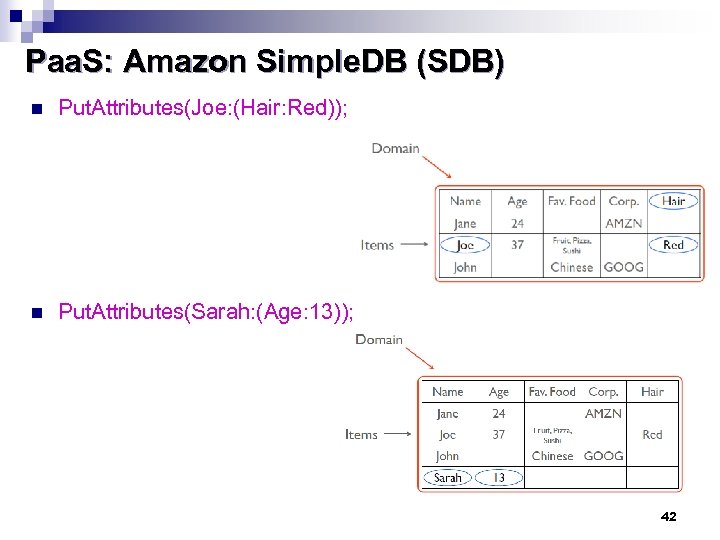 Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n Put. Attributes(Joe: (Hair: Red)); n Put. Attributes(Sarah: (Age: 13)); 42
Paa. S: Amazon Simple. DB (SDB) n Put. Attributes(Joe: (Hair: Red)); n Put. Attributes(Sarah: (Age: 13)); 42
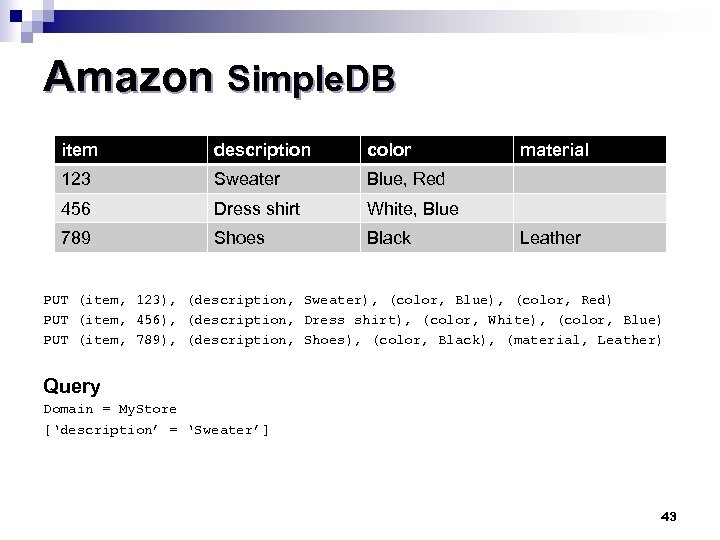 Amazon Simple. DB item description color 123 Sweater Blue, Red 456 Dress shirt White, Blue 789 Shoes Black material Leather PUT (item, 123), (description, Sweater), (color, Blue), (color, Red) PUT (item, 456), (description, Dress shirt), (color, White), (color, Blue) PUT (item, 789), (description, Shoes), (color, Black), (material, Leather) Query Domain = My. Store [‘description’ = ‘Sweater’] 43
Amazon Simple. DB item description color 123 Sweater Blue, Red 456 Dress shirt White, Blue 789 Shoes Black material Leather PUT (item, 123), (description, Sweater), (color, Blue), (color, Red) PUT (item, 456), (description, Dress shirt), (color, White), (color, Blue) PUT (item, 789), (description, Shoes), (color, Black), (material, Leather) Query Domain = My. Store [‘description’ = ‘Sweater’] 43
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service - SQS 44
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service - SQS 44
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) • Scalable Queuing • Elastic Capacity • Reliable, Simple, Secure $. 10 per 1000 messages Inter-process messaging, data buffering, architecture component $. 10 - $. 18 per GB data transfer 45
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) • Scalable Queuing • Elastic Capacity • Reliable, Simple, Secure $. 10 per 1000 messages Inter-process messaging, data buffering, architecture component $. 10 - $. 18 per GB data transfer 45
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Overview n n n A distributed queue in the cloud Used for storing messages traveling between computers Reliable: Runs within Amazon's high-availability data centers ¨ Messages are stored redundantly across multiple servers and locations ¨ n n Scalable to millions of messages a day Simple: Only 6 methods Platform agnostic Provides access control and message locking 46
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Overview n n n A distributed queue in the cloud Used for storing messages traveling between computers Reliable: Runs within Amazon's high-availability data centers ¨ Messages are stored redundantly across multiple servers and locations ¨ n n Scalable to millions of messages a day Simple: Only 6 methods Platform agnostic Provides access control and message locking 46
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Amazon SQS Concepts n Queues: ¨ Named message container ¨ Persistent n Messages: ¨ Up to 256 KB of data per message ¨ Peek / Lock access model n Scalable: ¨ Unlimited number of queues per account ¨ Unlimited number of messages per queue 47
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Amazon SQS Concepts n Queues: ¨ Named message container ¨ Persistent n Messages: ¨ Up to 256 KB of data per message ¨ Peek / Lock access model n Scalable: ¨ Unlimited number of queues per account ¨ Unlimited number of messages per queue 47
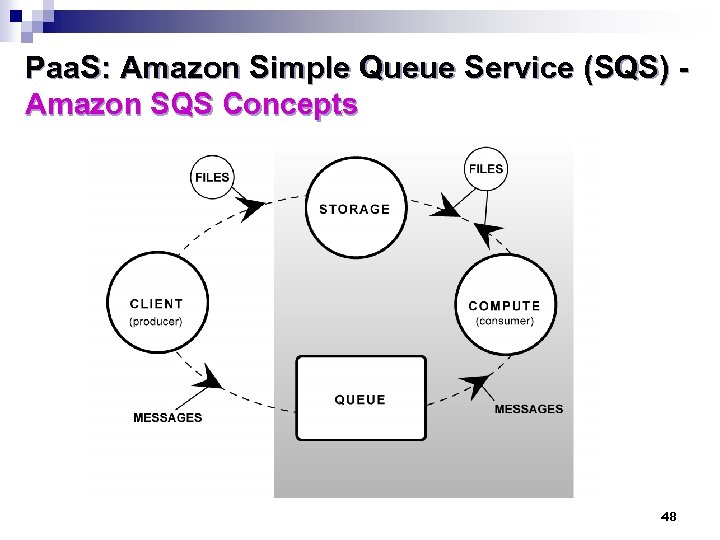 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Amazon SQS Concepts 48
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Amazon SQS Concepts 48
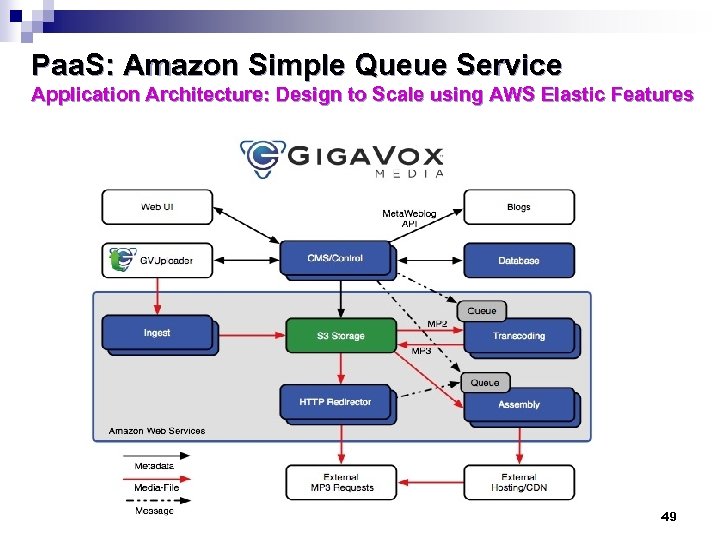 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service Application Architecture: Design to Scale using AWS Elastic Features 49
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service Application Architecture: Design to Scale using AWS Elastic Features 49
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service SQS SOAP / Query API n Queues: ¨ List. Queues ¨ Delete. Queue ¨ Set. Visibility. Timeout ¨ Get. Visibility. Timeout n Messages: ¨ Send. Message ¨ Receive. Message ¨ Delete. Message ¨ Peek. Message n Security: ¨ Add. Grant ¨ List. Grants ¨ Remove. Grant 50
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Queue Service SQS SOAP / Query API n Queues: ¨ List. Queues ¨ Delete. Queue ¨ Set. Visibility. Timeout ¨ Get. Visibility. Timeout n Messages: ¨ Send. Message ¨ Receive. Message ¨ Delete. Message ¨ Peek. Message n Security: ¨ Add. Grant ¨ List. Grants ¨ Remove. Grant 50
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Notification Service - SNS 51
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Notification Service - SNS 51
 Paa. S: Amazon Simple Notification Service - SNS Overview n SNS provides publish/subscribe messaging functionality n SNS is a distributed and redundant service that enables applications, end-user, and devices to send and receive notifications from the cloud n The service works on specified topics, which are Universal Resource Identifier (URIs) that specify communication channels based on content or event types n Any web server, email address, or SQS queue can subscribe to notification messages associated with a particular topic n Authorized publishers can post messages to the channel and they will automatically be delivered to all subscribers 52
Paa. S: Amazon Simple Notification Service - SNS Overview n SNS provides publish/subscribe messaging functionality n SNS is a distributed and redundant service that enables applications, end-user, and devices to send and receive notifications from the cloud n The service works on specified topics, which are Universal Resource Identifier (URIs) that specify communication channels based on content or event types n Any web server, email address, or SQS queue can subscribe to notification messages associated with a particular topic n Authorized publishers can post messages to the channel and they will automatically be delivered to all subscribers 52
 Paa. S: Amazon Cloud. Front 53
Paa. S: Amazon Cloud. Front 53
 Paa. S: Amazon Cloud. Front (~Akamai) Overview n n n Cloud. Front is a web service for content delivery; both static and streaming content Requests for objects are automatically routed to the nearest edge location Cloud. Front is optimized to work with other Amazon services like S 3, EC 2, but also it works with servers hosted by other providers Cloud. Front objects are organized into distributions. A distribution specified the location of the original version , unique domain name (e. g. , abc 123. cloudfront. net) or map a proprietary domain (e. g. , images. example. com) Distributions can either download definitive content from the origin server (HTTP/HTTPS) or stream the content using RTMP protocol 54
Paa. S: Amazon Cloud. Front (~Akamai) Overview n n n Cloud. Front is a web service for content delivery; both static and streaming content Requests for objects are automatically routed to the nearest edge location Cloud. Front is optimized to work with other Amazon services like S 3, EC 2, but also it works with servers hosted by other providers Cloud. Front objects are organized into distributions. A distribution specified the location of the original version , unique domain name (e. g. , abc 123. cloudfront. net) or map a proprietary domain (e. g. , images. example. com) Distributions can either download definitive content from the origin server (HTTP/HTTPS) or stream the content using RTMP protocol 54
 Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data 55
Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data 55
 Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Overview n n Significant portion of use cases involve data in tabular form and may include cross reference between tables Scalability vs Integrity: SQL supports complex queries for transactional, normalized and uniform data. On the other hand, SQL is not appropriate for unstructured data (e. g. , enforcing schema consistency). In cloud, data is changing fast for SQL engine to manage if all relations/schema need to be fully enforced The above limitation can be summarized as there is a need for systems to manipulate and analyze huge amount of data w/o impacting availability, performance or throughput In other words, SQL is good engine but it is difficult to scale-out to process huge amount of data and with schema-less environment; hence No. SQL initiative like Google Big. Table 56
Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Overview n n Significant portion of use cases involve data in tabular form and may include cross reference between tables Scalability vs Integrity: SQL supports complex queries for transactional, normalized and uniform data. On the other hand, SQL is not appropriate for unstructured data (e. g. , enforcing schema consistency). In cloud, data is changing fast for SQL engine to manage if all relations/schema need to be fully enforced The above limitation can be summarized as there is a need for systems to manipulate and analyze huge amount of data w/o impacting availability, performance or throughput In other words, SQL is good engine but it is difficult to scale-out to process huge amount of data and with schema-less environment; hence No. SQL initiative like Google Big. Table 56
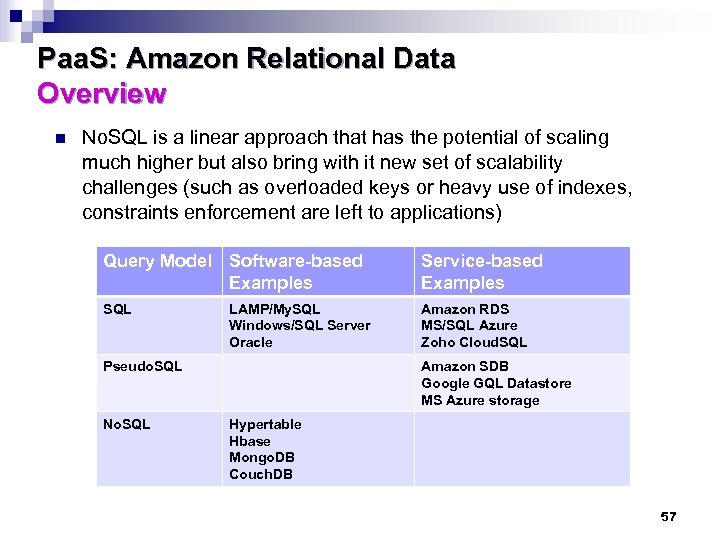 Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Overview n No. SQL is a linear approach that has the potential of scaling much higher but also bring with it new set of scalability challenges (such as overloaded keys or heavy use of indexes, constraints enforcement are left to applications) Query Model Software-based Examples Service-based Examples SQL Amazon RDS MS/SQL Azure Zoho Cloud. SQL LAMP/My. SQL Windows/SQL Server Oracle Pseudo. SQL No. SQL Amazon SDB Google GQL Datastore MS Azure storage Hypertable Hbase Mongo. DB Couch. DB 57
Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Overview n No. SQL is a linear approach that has the potential of scaling much higher but also bring with it new set of scalability challenges (such as overloaded keys or heavy use of indexes, constraints enforcement are left to applications) Query Model Software-based Examples Service-based Examples SQL Amazon RDS MS/SQL Azure Zoho Cloud. SQL LAMP/My. SQL Windows/SQL Server Oracle Pseudo. SQL No. SQL Amazon SDB Google GQL Datastore MS Azure storage Hypertable Hbase Mongo. DB Couch. DB 57
 Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Amazon Relational DB Service (RDS) n n n RDS is a web service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale an RDBMS in the cloud RDS reduces the time-consuming administration tasks RDS gives you compatibility with (access to the capabilities of a familiar) My. SQL, Oracle or MS SQL Server. Applications and tools can be used with RDS automatically patches the database software and backs up your database; storing the backups for a user defined retention period and enable point-in-time recovery IOPS is a new storage option for RDS designed to deliver fast, predictable and consistent IO performance (up to 10, 000 IOPS per DB instance) 58
Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Amazon Relational DB Service (RDS) n n n RDS is a web service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale an RDBMS in the cloud RDS reduces the time-consuming administration tasks RDS gives you compatibility with (access to the capabilities of a familiar) My. SQL, Oracle or MS SQL Server. Applications and tools can be used with RDS automatically patches the database software and backs up your database; storing the backups for a user defined retention period and enable point-in-time recovery IOPS is a new storage option for RDS designed to deliver fast, predictable and consistent IO performance (up to 10, 000 IOPS per DB instance) 58
 Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Amazon Relational DB Service (RDS) n n n RDS DB can be provisioned with either standard storage or IOPS storage RDS makes it easy to use replication to enhance availability and reliability. Multi-AZ (Availability Zones) deployment option allows you to run mission critical workloads with high availability and built-in automated fail-over from your primary database to a synchronously replicated secondary database in case of failure RDS for My. SQL enables you to scale-out beyond the capacity of a single DB deployment for read-heavy DB workloads There is no up-front investment required; pay-per-usage 59
Paa. S: Amazon Relational Data Amazon Relational DB Service (RDS) n n n RDS DB can be provisioned with either standard storage or IOPS storage RDS makes it easy to use replication to enhance availability and reliability. Multi-AZ (Availability Zones) deployment option allows you to run mission critical workloads with high availability and built-in automated fail-over from your primary database to a synchronously replicated secondary database in case of failure RDS for My. SQL enables you to scale-out beyond the capacity of a single DB deployment for read-heavy DB workloads There is no up-front investment required; pay-per-usage 59
 Saa. S: AWS Web Services 60
Saa. S: AWS Web Services 60
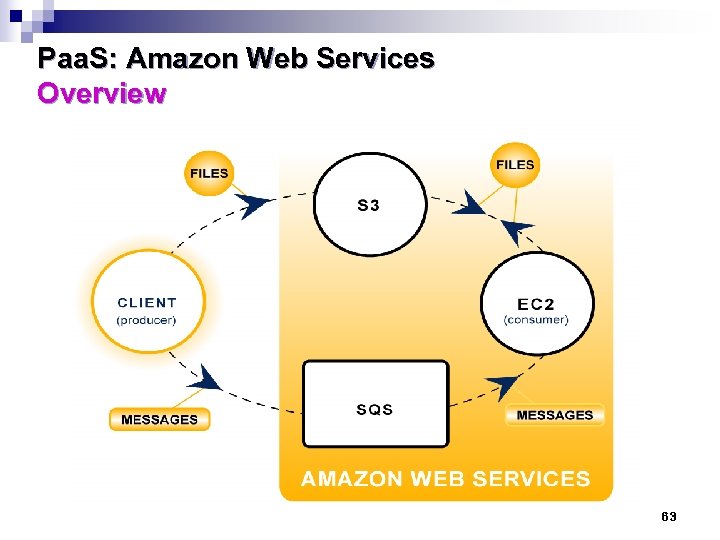
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview n n n AWS began in 2006 to offer IT infrastructure service to businesses in the form of web services – now is called cloud computing With AWS, businesses no longer need to plan for and procure servers and other IT infrastructure weeks or months in advance; instead they can instantly spin up hundreds or thousands of servers in minutes and deliver results faster AWS powers businesses in 190 countries around the world with data center locations around the world. It provides: q Low cost q Agility and Instant Elasticity q Open and Flexible q Secure 61
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview n n n AWS began in 2006 to offer IT infrastructure service to businesses in the form of web services – now is called cloud computing With AWS, businesses no longer need to plan for and procure servers and other IT infrastructure weeks or months in advance; instead they can instantly spin up hundreds or thousands of servers in minutes and deliver results faster AWS powers businesses in 190 countries around the world with data center locations around the world. It provides: q Low cost q Agility and Instant Elasticity q Open and Flexible q Secure 61
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview n AWS Solutions: q Application hosting: reliable, on-demand infrastructure to power your applications, from Iaa. S to Saa. S offerings q Backup and Storage: store data and build dependable backup solutions based on AWS inexpensive storage services q Content Delivery: distribute content to end users worldwide with low cost and high transfer arte q Web hosting: supports dynamic web hosting needs with AWS Elastic infrastructure q Enterprise IT: host internal- or external-facing IT applications in AWS secure environment q Databases: supports variety of scalable DB solutions including SQL or No-SQL databases 62
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview n AWS Solutions: q Application hosting: reliable, on-demand infrastructure to power your applications, from Iaa. S to Saa. S offerings q Backup and Storage: store data and build dependable backup solutions based on AWS inexpensive storage services q Content Delivery: distribute content to end users worldwide with low cost and high transfer arte q Web hosting: supports dynamic web hosting needs with AWS Elastic infrastructure q Enterprise IT: host internal- or external-facing IT applications in AWS secure environment q Databases: supports variety of scalable DB solutions including SQL or No-SQL databases 62
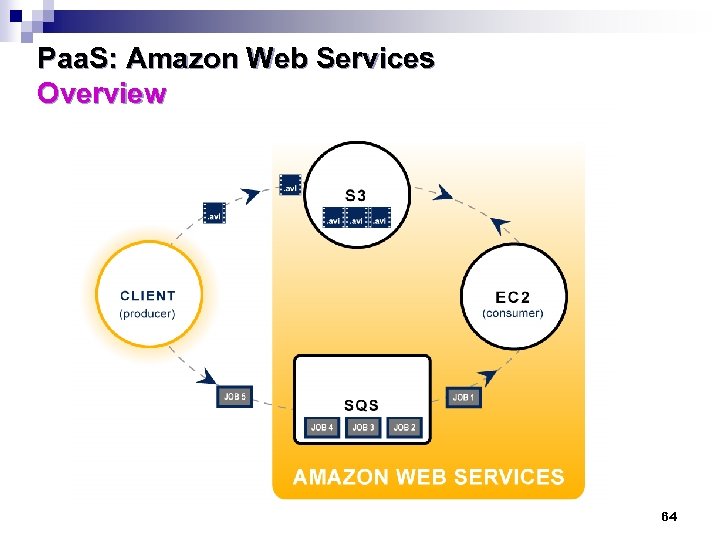
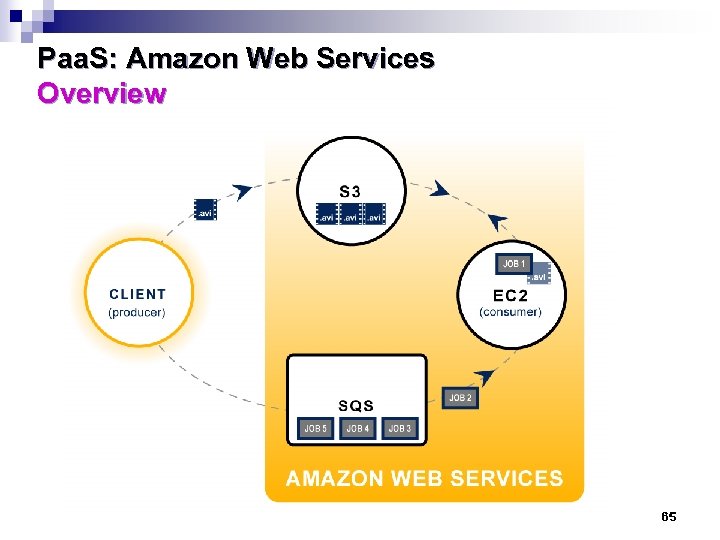
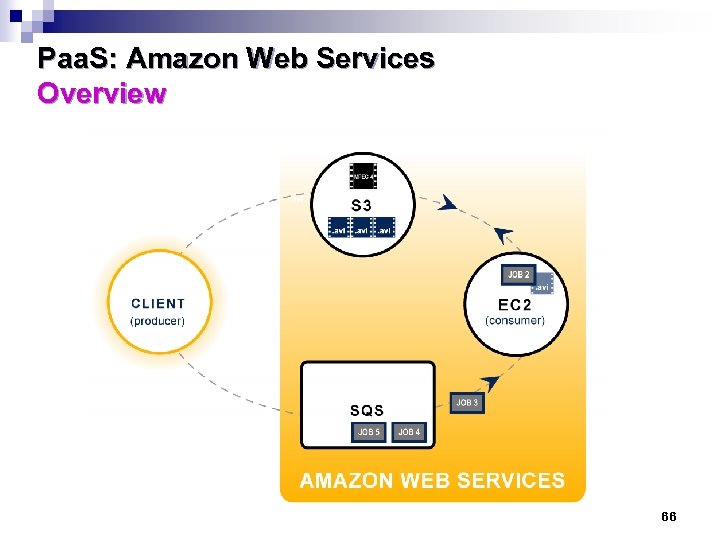
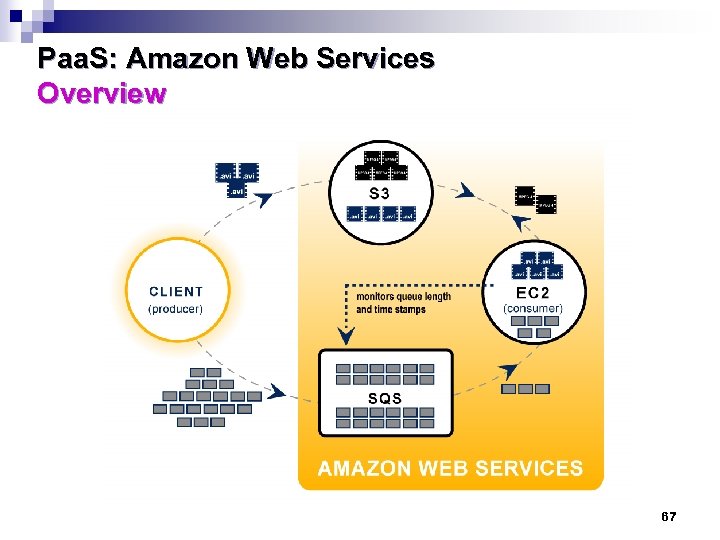
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 63
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 63
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 64
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 64
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 65
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 65
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 66
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 66
 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 67
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 67
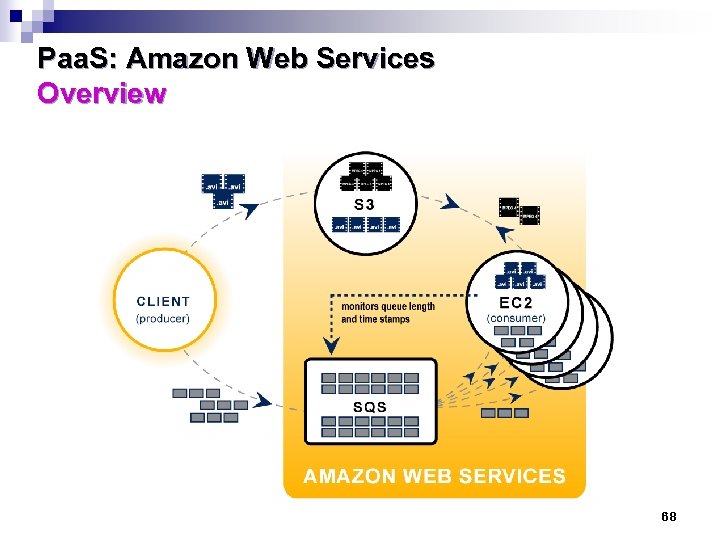 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 68
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 68
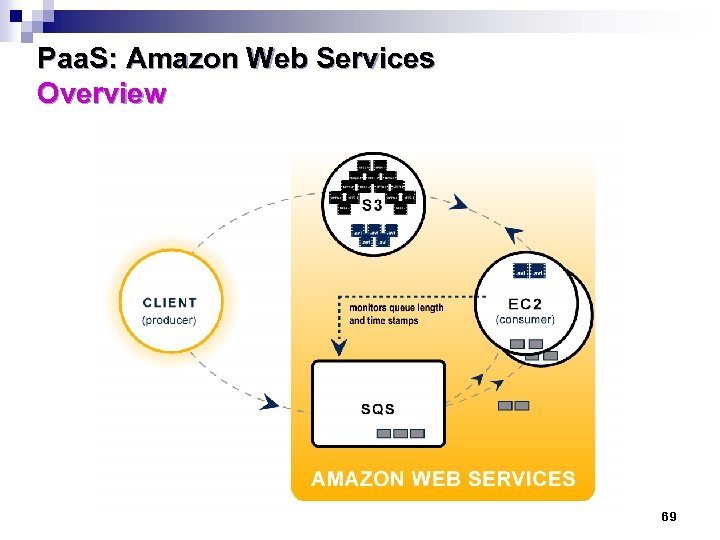 Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 69
Paa. S: Amazon Web Services Overview 69
 AWS Integration and Management 70
AWS Integration and Management 70
 AWS Integration and Management: Integration Overview n AWS has a rich set of integration services: q Elastic IP Addresses: are static IP addresses, associated with an account rather than a particular instance, designed for dynamic cloud computing q Simple Queue Service: provides unlimited # of queues and messages of size up to 8 KB q Simple Notification Service: provides publish/subscribe messaging functionality q Virtual Private Cloud: provides a means for enterprises to extend their private data center into Amazon’s cloud in a secure fashion q VM Import: allow customers to import VM images from their existing environment into Amazon EC 2 q AWS Import/Export: accelerates moving large amount of data into and out of AWS bypassing the Internet with portable storage devices for transport 71
AWS Integration and Management: Integration Overview n AWS has a rich set of integration services: q Elastic IP Addresses: are static IP addresses, associated with an account rather than a particular instance, designed for dynamic cloud computing q Simple Queue Service: provides unlimited # of queues and messages of size up to 8 KB q Simple Notification Service: provides publish/subscribe messaging functionality q Virtual Private Cloud: provides a means for enterprises to extend their private data center into Amazon’s cloud in a secure fashion q VM Import: allow customers to import VM images from their existing environment into Amazon EC 2 q AWS Import/Export: accelerates moving large amount of data into and out of AWS bypassing the Internet with portable storage devices for transport 71
 AWS Integration and Management: Management Overview n n AWS Management Console is the main interface to managing AWS It is also possible to use SSH or HTTP to interact with the instance directly q Cloud. Formation: gives the customer the option to collect related AWS resources in a so-called stack and provision them in an orderly fashion. The stack includes Amazon services such as EC 2, Security groups, SQS queues, RDS instances, load balancers, etc. q Cloud. Watch: is a web service that provides monitoring for AWS cloud resources – can be displayed on the management console as charts in realtime q AWS Ecosysem: AWS services are not enough; hence AWS created an ecosystem of products that fill in any gaps that AWS do not support 72
AWS Integration and Management: Management Overview n n AWS Management Console is the main interface to managing AWS It is also possible to use SSH or HTTP to interact with the instance directly q Cloud. Formation: gives the customer the option to collect related AWS resources in a so-called stack and provision them in an orderly fashion. The stack includes Amazon services such as EC 2, Security groups, SQS queues, RDS instances, load balancers, etc. q Cloud. Watch: is a web service that provides monitoring for AWS cloud resources – can be displayed on the management console as charts in realtime q AWS Ecosysem: AWS services are not enough; hence AWS created an ecosystem of products that fill in any gaps that AWS do not support 72
 AWS Billing 73
AWS Billing 73
 AWS Billing: Overview n n n Standard licensing terms Commercially usable Aggressive pricing Monthly credit card billing Self-serve model: ¨ Sign up as developer ¨ Choose services ¨ Agree to service licenses ¨ Enter payment info ¨ Start coding 74
AWS Billing: Overview n n n Standard licensing terms Commercially usable Aggressive pricing Monthly credit card billing Self-serve model: ¨ Sign up as developer ¨ Choose services ¨ Agree to service licenses ¨ Enter payment info ¨ Start coding 74
 AWS Billing: Overview n EC 2 support monetization; it exposes set of financial services to its developers: q Flexible Payment Service (FPS): is a service that Amazon created for developers that leverages Amazon’s sophisticated retail billing system. The customer can use the same identity, shipping details and payment information as they would for ordering directly from Amazon q Dev. Pay: is an online billing and account management service supporting application that are built for AWS. It uses Amazon’s authentication and settlement framework to manage customer subscriptions and billing for Amazon EC 2 Machine Images (AMI) or applications that use Amazon S 3 75
AWS Billing: Overview n EC 2 support monetization; it exposes set of financial services to its developers: q Flexible Payment Service (FPS): is a service that Amazon created for developers that leverages Amazon’s sophisticated retail billing system. The customer can use the same identity, shipping details and payment information as they would for ordering directly from Amazon q Dev. Pay: is an online billing and account management service supporting application that are built for AWS. It uses Amazon’s authentication and settlement framework to manage customer subscriptions and billing for Amazon EC 2 Machine Images (AMI) or applications that use Amazon S 3 75
 AWS Scalability 76
AWS Scalability 76
 AWS Scalability: Overview n AWS also caters to enterprise needs for elastic computing with capabilities that scale both vertically and horizontally: q High Performance Computing: The EC 2 cluster Compute and Cluster GPU instance types are designed to combine high compute and networking performance for HPC applications using MPI. Cluster can be up 128 nodes and 10 Gbps bandwidth between them, and you configure up to 128 instances q Elastic Load Balancing: distributes incoming traffic for a given service across multiple EC 2 instances. Customer can enable Elastic Load Balancing within a Single Availability Zone or across zones 77
AWS Scalability: Overview n AWS also caters to enterprise needs for elastic computing with capabilities that scale both vertically and horizontally: q High Performance Computing: The EC 2 cluster Compute and Cluster GPU instance types are designed to combine high compute and networking performance for HPC applications using MPI. Cluster can be up 128 nodes and 10 Gbps bandwidth between them, and you configure up to 128 instances q Elastic Load Balancing: distributes incoming traffic for a given service across multiple EC 2 instances. Customer can enable Elastic Load Balancing within a Single Availability Zone or across zones 77
 AWS Scalability: Overview q Auto Scaling: to support applications that experience hourly, daily, or weekly variability in usage; varies # of EC 2 instances during demand spikes. Amazon provides tools to define triggers (say based on CPU utilization) for adding/removing EC 2 instances q Elastic Map. Reduce: is a web service that enables businesses and developers to process very large amounts of data. It is based on hosted Hadoop running on the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC 2) and Amazon S 3. Amazon Elastic Map. Reduce supports SQL-like tools, such as Hive and Pig as well as many programming languages including C++, Java, Perl, PHP, Python, R, and Ruby 78
AWS Scalability: Overview q Auto Scaling: to support applications that experience hourly, daily, or weekly variability in usage; varies # of EC 2 instances during demand spikes. Amazon provides tools to define triggers (say based on CPU utilization) for adding/removing EC 2 instances q Elastic Map. Reduce: is a web service that enables businesses and developers to process very large amounts of data. It is based on hosted Hadoop running on the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC 2) and Amazon S 3. Amazon Elastic Map. Reduce supports SQL-like tools, such as Hive and Pig as well as many programming languages including C++, Java, Perl, PHP, Python, R, and Ruby 78
 AWS Application Architecture: Design to Scale Using AWS Elastic Features 79
AWS Application Architecture: Design to Scale Using AWS Elastic Features 79
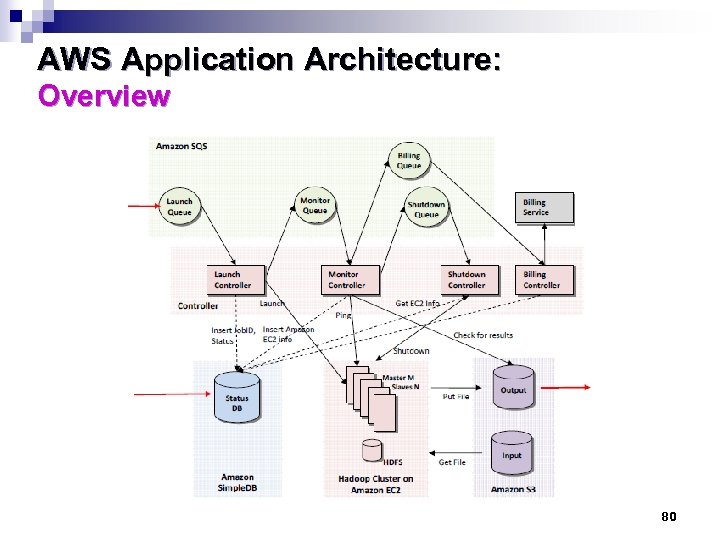 AWS Application Architecture: Overview 80
AWS Application Architecture: Overview 80
 AWS Application Architecture: Cloud Applications Design 10 Best Practices n n n n n Build cloud Apps, not apps in the cloud Virtualize the application stack Design for failures and nothing fails Design for scalability Loose coupling lets you maximize plug & play Design for dynamism Build security into every component Leverage native cloud storage options Leverage best cloud Management Tools Don’t fear cloud constraints 81
AWS Application Architecture: Cloud Applications Design 10 Best Practices n n n n n Build cloud Apps, not apps in the cloud Virtualize the application stack Design for failures and nothing fails Design for scalability Loose coupling lets you maximize plug & play Design for dynamism Build security into every component Leverage native cloud storage options Leverage best cloud Management Tools Don’t fear cloud constraints 81
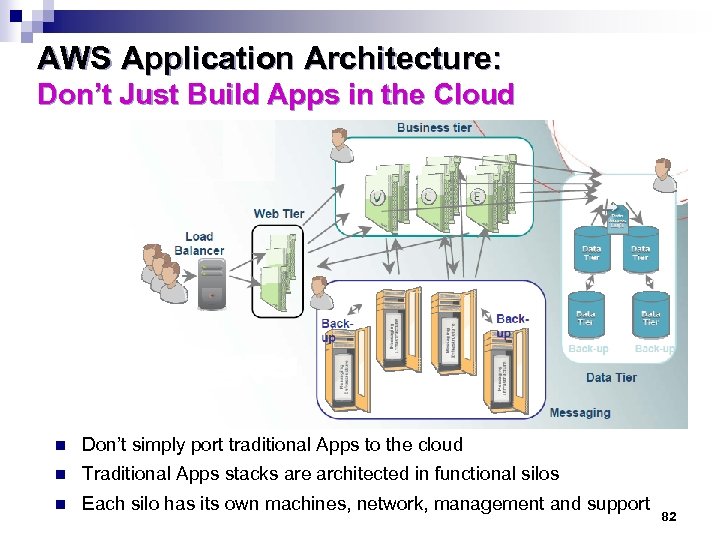 AWS Application Architecture: Don’t Just Build Apps in the Cloud n Don’t simply port traditional Apps to the cloud n Traditional Apps stacks are architected in functional silos n Each silo has its own machines, network, management and support 82
AWS Application Architecture: Don’t Just Build Apps in the Cloud n Don’t simply port traditional Apps to the cloud n Traditional Apps stacks are architected in functional silos n Each silo has its own machines, network, management and support 82
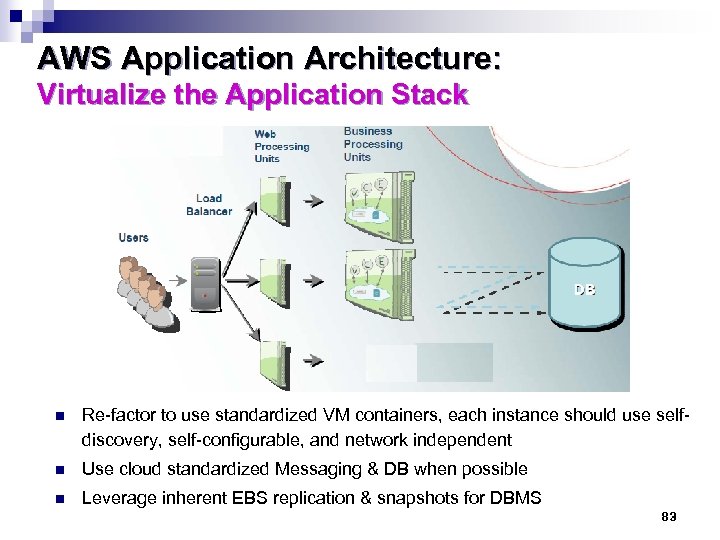 AWS Application Architecture: Virtualize the Application Stack n Re-factor to use standardized VM containers, each instance should use selfdiscovery, self-configurable, and network independent n Use cloud standardized Messaging & DB when possible n Leverage inherent EBS replication & snapshots for DBMS 83
AWS Application Architecture: Virtualize the Application Stack n Re-factor to use standardized VM containers, each instance should use selfdiscovery, self-configurable, and network independent n Use cloud standardized Messaging & DB when possible n Leverage inherent EBS replication & snapshots for DBMS 83
 AWS Application Architecture: Compensate for Ephemeral Storage n n n EC 2 instance default storage can only be used for transient data and not for archival data logs; consider using SDB to store persistent archival data records that can be associated with a key (timestamp) If possible recover only from the most recent backup; consider restoring data from S 3 at boot-up and backing-up current data to S 3 at shutdown If not OK, use EBS attached volumes for all persistent file data DBMS should always use EBS volumes Consider using soft-links (Linux) to map portions of the default storage to persistent EBS volume Consider using EBS volumes exported on EC 2 NFS server if small chunks of persistent storage are needed 84
AWS Application Architecture: Compensate for Ephemeral Storage n n n EC 2 instance default storage can only be used for transient data and not for archival data logs; consider using SDB to store persistent archival data records that can be associated with a key (timestamp) If possible recover only from the most recent backup; consider restoring data from S 3 at boot-up and backing-up current data to S 3 at shutdown If not OK, use EBS attached volumes for all persistent file data DBMS should always use EBS volumes Consider using soft-links (Linux) to map portions of the default storage to persistent EBS volume Consider using EBS volumes exported on EC 2 NFS server if small chunks of persistent storage are needed 84
 AWS Application Architecture: Compensate for Dynamic IP Addresses n Attach Elastic. IP for Internet-facing EC 2 instances (e. g. , HA Proxy Load-balancer instance) n Use dynamic DNS registration of EC 2 instance’s internal IP address or use SDB n EC 2 instances should only use the internal IP address for communicating with each other (free!) 85
AWS Application Architecture: Compensate for Dynamic IP Addresses n Attach Elastic. IP for Internet-facing EC 2 instances (e. g. , HA Proxy Load-balancer instance) n Use dynamic DNS registration of EC 2 instance’s internal IP address or use SDB n EC 2 instances should only use the internal IP address for communicating with each other (free!) 85
 AWS Application Architecture: Design for Failure n n n Everything fails all the time Avoid single points of failure Assume everything fails, and design backwards Design for failure and your application won’t fail What can fail: q EC 2 instance may crash q Portion of zone may not be accessible due to network failure q AWS Services in a Region may not be accessible 86
AWS Application Architecture: Design for Failure n n n Everything fails all the time Avoid single points of failure Assume everything fails, and design backwards Design for failure and your application won’t fail What can fail: q EC 2 instance may crash q Portion of zone may not be accessible due to network failure q AWS Services in a Region may not be accessible 86
 AWS Application Architecture: Design for Scalability n n Use Load Balancing on multiple layers; use your own or AWS Elastic Load Balancing Use Cloud monitoring systems: either your own or AWS Cloud. Watch Use Auto-scaling technology (free with Cloud. Watch) Build Lossely Coupled Systems: q Use independent components q Design everything as a Black Box with well defined inputs & outputs q Use subsystems de-coupling for hybrid models q Use Load-balanced clusters of Black Boxes to maximize plug & play 87
AWS Application Architecture: Design for Scalability n n Use Load Balancing on multiple layers; use your own or AWS Elastic Load Balancing Use Cloud monitoring systems: either your own or AWS Cloud. Watch Use Auto-scaling technology (free with Cloud. Watch) Build Lossely Coupled Systems: q Use independent components q Design everything as a Black Box with well defined inputs & outputs q Use subsystems de-coupling for hybrid models q Use Load-balanced clusters of Black Boxes to maximize plug & play 87
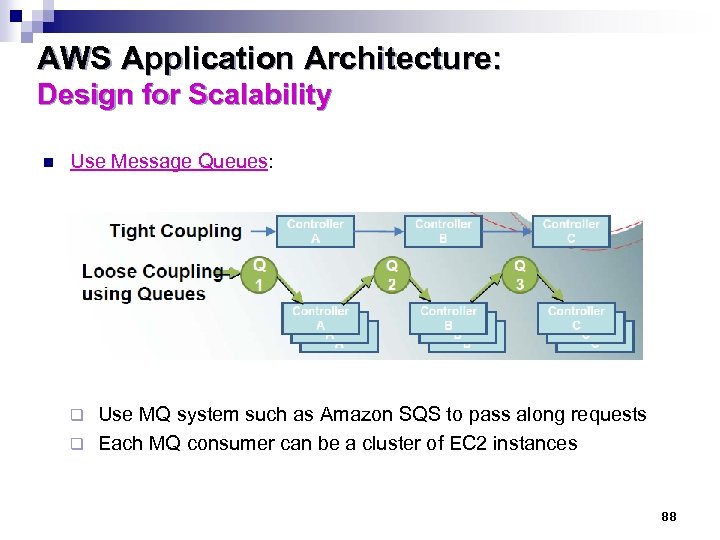 AWS Application Architecture: Design for Scalability n Use Message Queues: Use MQ system such as Amazon SQS to pass along requests q Each MQ consumer can be a cluster of EC 2 instances q 88
AWS Application Architecture: Design for Scalability n Use Message Queues: Use MQ system such as Amazon SQS to pass along requests q Each MQ consumer can be a cluster of EC 2 instances q 88
 AWS Application Architecture: Design for Scalability n Leverage Amazon Storage Solutions: q q q Amazon S 3: large static objects Amazon Cloud. Front: content distribution Amazon Simple. DB: simple data indexing/querying Amazon EC 2 local disc drive: transient data Amazon EBS: RDBMS persistent storage + S 3 snapshots 89
AWS Application Architecture: Design for Scalability n Leverage Amazon Storage Solutions: q q q Amazon S 3: large static objects Amazon Cloud. Front: content distribution Amazon Simple. DB: simple data indexing/querying Amazon EC 2 local disc drive: transient data Amazon EBS: RDBMS persistent storage + S 3 snapshots 89
 Summary and Conclusions 90
Summary and Conclusions 90
 AWS: Summary and Conclusions n n AWS is the leading Solution in the public cloud offering AWS supports both Iaa. S, Paa. S, and Saa. S. It also has a comprehensive integration and management story in addition to billing q Iaa. S offering includes EC 2, S 3, and EBS q Paa. S offering includes SDB, SQS, SNS, Cloud. Front, and RDS q Saa. S include AWS web services AWS supports scalability via elastic computing AWS applications can be designed to scale leveraging AWS Elastic featured 91
AWS: Summary and Conclusions n n AWS is the leading Solution in the public cloud offering AWS supports both Iaa. S, Paa. S, and Saa. S. It also has a comprehensive integration and management story in addition to billing q Iaa. S offering includes EC 2, S 3, and EBS q Paa. S offering includes SDB, SQS, SNS, Cloud. Front, and RDS q Saa. S include AWS web services AWS supports scalability via elastic computing AWS applications can be designed to scale leveraging AWS Elastic featured 91
 END 92
END 92


