c9e8bbcbeb773c2328e78d8c1f6ee9fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

CLOUD COMPUTING & COST MANAGEMENT Presented by S. Gurubalasubramaniyan, MSc IT, MTech
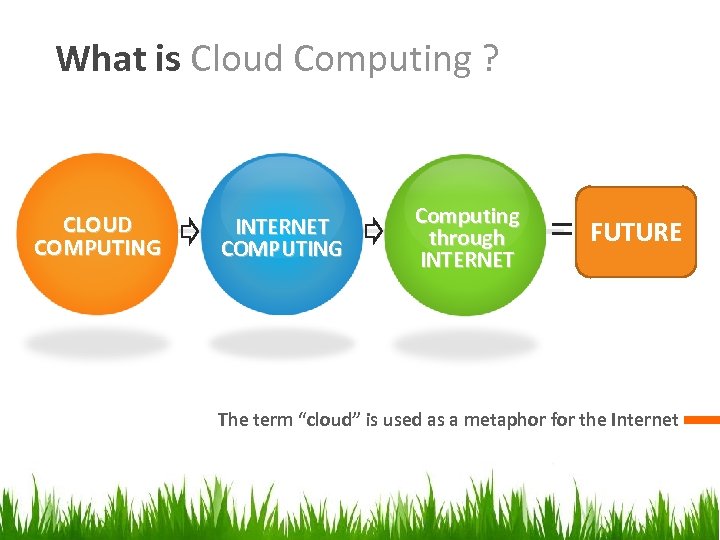
What is Cloud Computing ? CLOUD COMPUTING INTERNET COMPUTING Computing through INTERNET = FUTURE The term “cloud” is used as a metaphor for the Internet

CLOUD COMPUTING ENGINEERING VIEW Providing Services(Saa. S, Paa. S, Iaa. S) through Virtual Machines (VM) on the lap of large Physical machines allocated by the service provider

CLOUD COMPUTING BUSINESS VIEW Cloud computing provides unlimited infrastructure to store and execute customer data and program. As customers they do not need to own the infrastructure, thereby merely accessing or renting, they can forego capital expenditure; and consume resources as a service, paying for what they use. i. e. , Addressing scalability for large scale applications

CLOUD COMPUTING DEFINITION ACCORDING TO NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND TECHNOLOGY (NIST) Cloud Computing is a model for enabling convenient, on demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e. g. , networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction

The cloud model promotes availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, four deployment models, and three service models
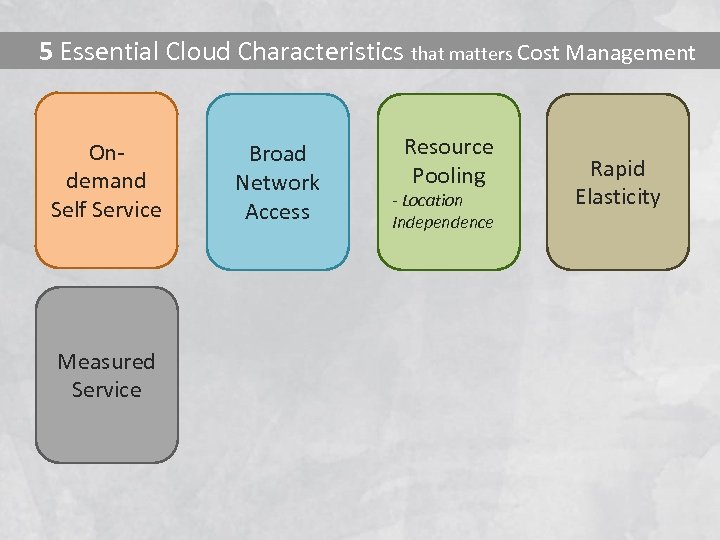
5 Essential Cloud Characteristics that matters Cost Management Ondemand Self Service Measured Service Broad Network Access Resource Pooling - Location Independence Rapid Elasticity
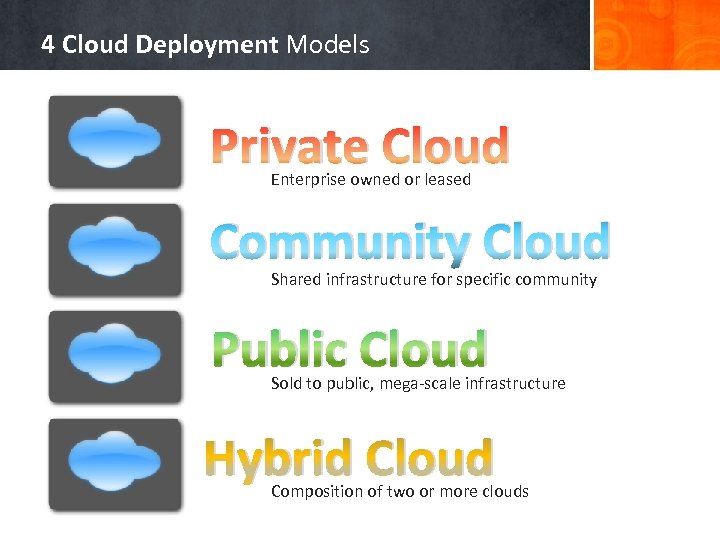
4 Cloud Deployment Models Private Cloud Enterprise owned or leased Community Cloud Shared infrastructure for specific community Public Cloud Sold to public, mega-scale infrastructure Hybrid Cloud Composition of two or more clouds
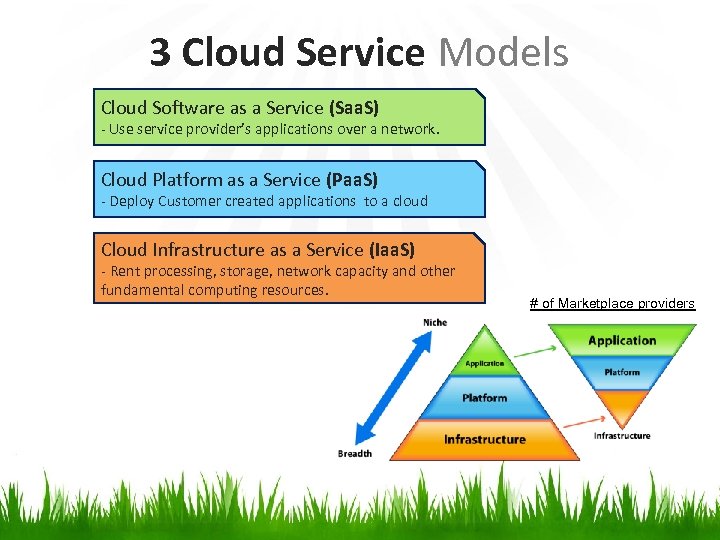
3 Cloud Service Models Cloud Software as a Service (Saa. S) - Use service provider’s applications over a network. Cloud Platform as a Service (Paa. S) - Deploy Customer created applications to a cloud Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (Iaa. S) - Rent processing, storage, network capacity and other fundamental computing resources. # of Marketplace providers

Software as a Service (Saa. S) It is a Software Delivery Model q Service is delivered through a browser. q No Hardware or Software to manage. q Increasingly popular with Small and Medium sized Enterprises (SME). q Examples of usage: Ø Your email is hosted on an exchange server in your office and it is very slow. You may outsource this with services like Hosted exchange. Ø Your current Customer Relationship Management (CRM) package is not managing the load or you simply don’t want to host it in-house. You may use Saa. S provider such as salesforce. com. Ø Enterprise Fraud Management through Saa. S.

Platform as a Service (Paa. S) » It is a Platform delivery model which deploys customer created applications to a cloud. » Plat forms which are built upon Infrastructures are expensive, hence it is cost efficient to go for platforms as a service. » The Platform management is also cumbersome when compared to using a platform as a service. » Estimating the demand in a platform is highly unpredictable, hence the platform as a service can take care of the demand. » Examples of usage: » You need to host a large file (10 MB) on your website and making it available for 35, 000 users for only two months duration. You may use Cloud Front from amazon. » You want to start Storage Services on your network for a large number of files and you do not have the storage capacity. You may use Amazon S 3.

Infrastructure as a Service (Iaa. S) ‼ It is a Computer Infrastructure delivery model. Hiring fundamental Computing Resources. ‼ Access to → Infrastructure stack. → Full Operating System access. → Firewalls. → Routers. → Load Balancing. ‼ Example of usage: → You want to host a website but only for a few days. You may use Flexi Scale. → You want to run a batch job but you do not have the infrastructure necessary to run it in a timely manner. You may use Amazon EC 2.
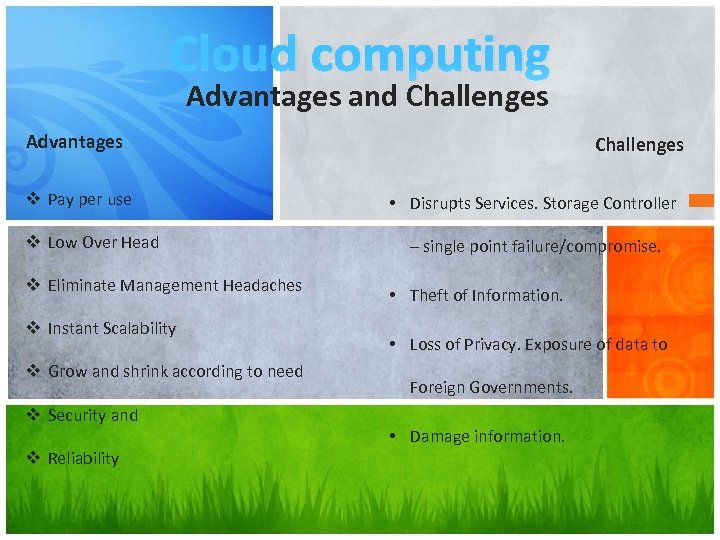
Cloud computing Advantages and Challenges Advantages v Pay per use v Low Over Head v Eliminate Management Headaches v Instant Scalability v Grow and shrink according to need v Security and v Reliability Challenges • Disrupts Services. Storage Controller – single point failure/compromise. • Theft of Information. • Loss of Privacy. Exposure of data to Foreign Governments. • Damage information.

CONCLUSION ü Small, Medium and Large Enterprises can use the services of cloud computing by using cost effective public clouds for specific needs. ü Any change in the business process causes drastic effect on cost management. These costs can be effectively reduced by using service based utilization of cloud computing.

c9e8bbcbeb773c2328e78d8c1f6ee9fb.ppt