3971b36ec5b57d568b32763853e1c0df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Cloud Computing Amazon Web Services - introduction Keke Chen
Infrastructure as a service o o o Elastic Compute Cloud (EC 2) Simple Storage Services (S 3) Cloud. Front Dynamo. DB Simple Queue Service Elastic Mapreduce

EC 2 o A typical example of utility computing o functionality: n launch instances with a variety of operating systems (windows/linux) n load them with your custom application environment (customized AMI) n Full root access to a blank Linux machine n manage your network’s access permissions n run your image using as many or few systems as you desire (scaling up/down)
Backyard… o Powered by Xen – Virtual Machine n Different from Vmware & VPC - high performance n Hardware contributions by Intel (VTx/Vanderpool) and AMD (AMD-V) n Supports “Live Migration” of a virtual machine between hosts We will dedicate one class to Xen. . .

Amazon Machine Images o Public AMIs: Use pre-configured, template AMIs to get up and running immediately. Choose from Fedora, Movable Type, Ubuntu configurations, and more o Private AMIs: Create an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) containing your applications, libraries, data and associated configuration settings o Paid AMIs: Set a price for your AMI and let others purchase and use it (Single payment and/or per hour) n AMIs with commercial DBMS
Normal way to use EC 2 o For web applications n n n Run your base system in minimum # of VMs Monitoring the system load (user traffic) Load is distributed to VMs If over some threshold increase # of VMs If lower than some thresholds decrease # of VMs o For data intensive analysis n Estimate the optimal number of nodes (tricky!) n Load data n Start processing

Tools (most are for web apps) o Elastic Block Store: network-attached persistent storage, can be attached to each VM instance o Elastic IP address: programmatically remap public IP to any instance o Virtual private cloud: bridge private cloud and AWS resources o Cloud. Watch: monitoring EC 2 resouces o Auto Scaling: conditional scaling o Elastic load balancing: automatically distribute incoming traffic across instances
Type of instances o Standard instances (micro, small, large, extra) n E. g. , small: 2 GB Memory, 1 EC 2 Compute Unit (Xeon processor? ), some GBs of instance/EBS storage (i. e. , root volume) o High-CPU instances n More CPU with same amount of memory

AMIs with special software o IBM DB 2, Informix Dynamic Server, Lotus Web Content Management, Web. Sphere Portal Server o MS SQL Server, IIS/Asp. Net o Hadoop o Open MPI o Apache web server o My. SQL o Oracale 11 g o …
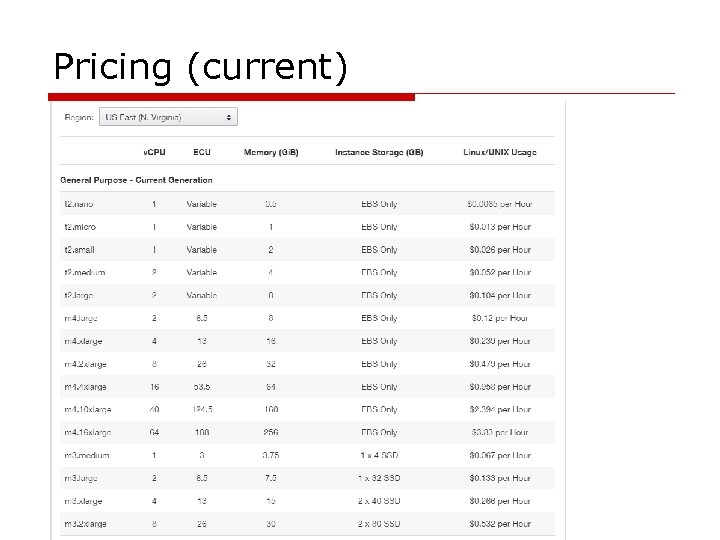
Pricing (current)

Access methods o Web interface o Command line o Programming Interface n E. g. , boto python library

S 3 o Write, read, delete objects 1 byte-5 gb o Namespace: buckets, keys, objects o Accessible using URLs
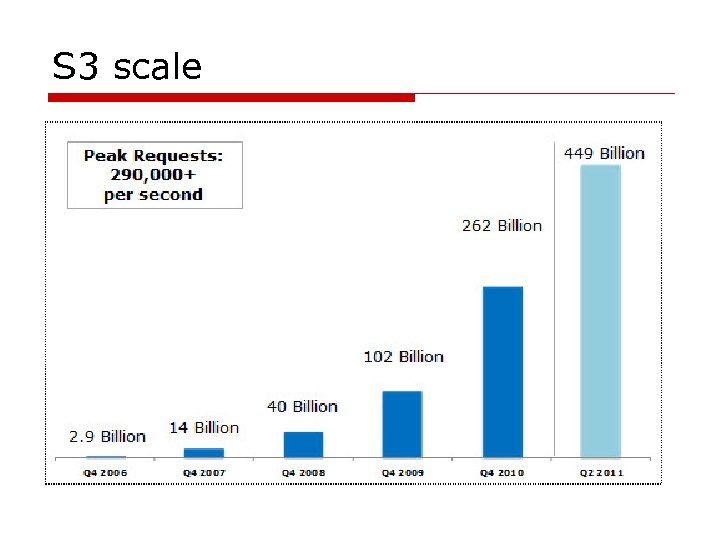
S 3 scale
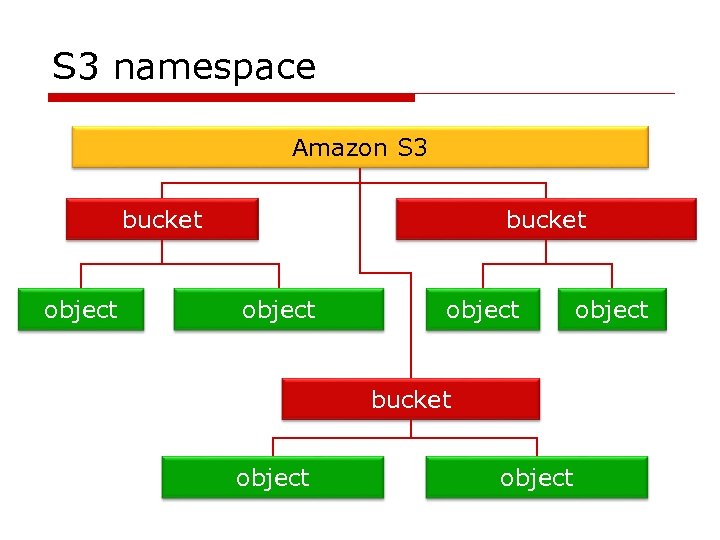
S 3 namespace Amazon S 3 bucket object object
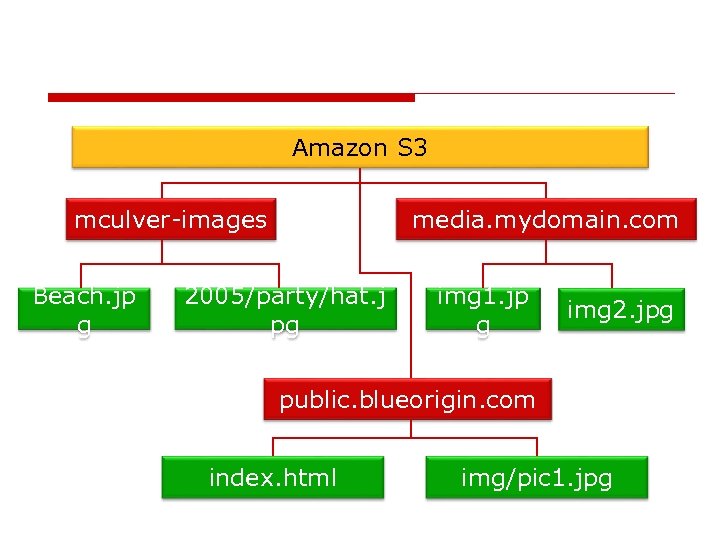
Amazon S 3 mculver-images Beach. jp g media. mydomain. com 2005/party/hat. j pg img 1. jp g img 2. jpg public. blueorigin. com index. html img/pic 1. jpg

Accessing objects o Bucket: keke-images, key: jpg 1, object: a jpg image n accessible with https: //keke-images. s 3. amazonaws. com/jpg 1 o mapping your subdomain to S 3 n with DNS CNAME configuration n e. g. media. yourdomain. com. s 3. amazonaws. com/

Access control o Access log o Objects are private to the user account n Authentication o Authorization n ACL: AWS users, users identified by email, any user … o Digital signature to ensure integrity o Encrypted access: https
Dynamo. DB o Scalable n Dynamo architecture o Reliable n Replicas over multiple data centers o Speed n Fast, single-digit milliseconds o Secure o Weak schema
Data Model o table n Container, similar to a worksheet in excel, n Cannot query across domains o Item name n item name ->(Attribute, value) pairs n An item is stored in a domain (a row in a worksheet. Attributes are column names) o Example n domain: “cars” n Item 1: “car 1”: {“make”: ”BMW”, “year”: ” 2009”}

o Primary key of table n Single key (hash) n Hash-range key o A pair of attributes: first one is hash key, 2 nd one is range key. o Example: Reply(Id, datetime, …) o Data type n Simple: string and number n Multi-valued: string set and number set

example

Access methods o Amazon Dynamo. DB is a web service that uses HTTP and HTTPS as the transport method o Java. Script Object Notation (JSON) as a message serialization format o APIs n Java, PHP, . Net n Boto

Cloud. Front o For content delivery: distribute content to end users with a global network of edge locations. n “Edges”: servers close to user’s geographical location o Objects are organized into distributions n Each distribution has a domain name o Distributions are stored in a S 3 bucket

Edge servers o US o EU n US and EU are partitioned to different regions o Hongkong o Japan

Use cases o Hosting your most frequently accessed website components n Small pieces of your website are cached in the edge locations, and are ideal for Amazon Cloud. Front. o Distributing software n distribute applications, updates or other downloadable software to end users. o Publishing popular media files n If your application involves rich media – audio or video – that is frequently accessed

Simple Queue Service o Store messages traveling between computers o Make it easy to build automated workflows o Implemented as a web service n read/add messages easily o Scalable to millions of messages a day

Some features o Message body : <8 Kb in any format o Message is retained in queues for up to 4 days o Messages can be sent and read simultaneously n Can be “locked”, keeping from simultaneous processing o Accessible with SOAP/REST n Simple: Only a few methods o Secure sharing
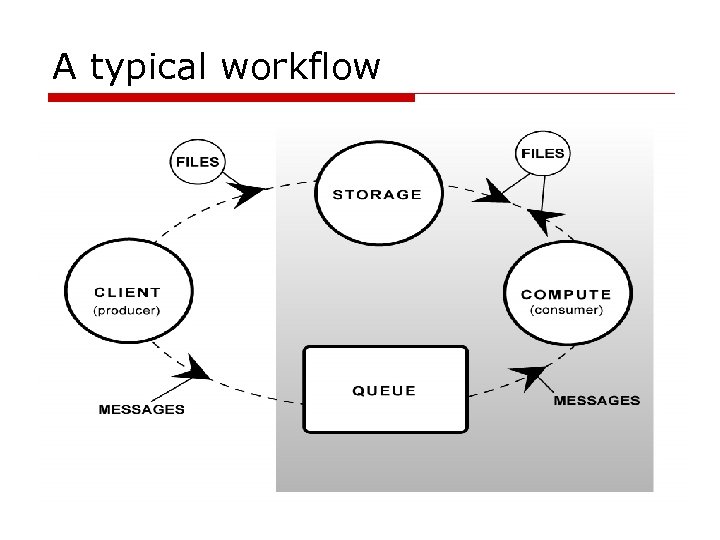
A typical workflow
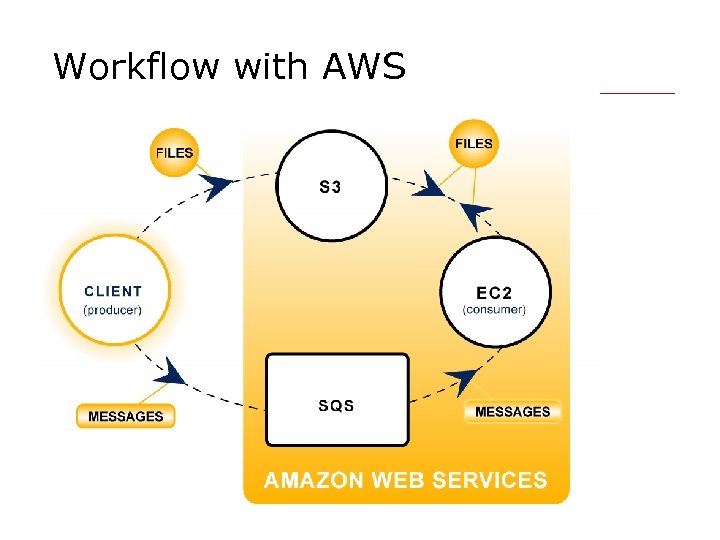
Workflow with AWS

Elastic Mapreduce o Based on hadoop AMI o Data stored on S 3 o “job flow”

Example elastic-mapreduce --create --stream --mapper s 3: //elasticmapreduce/samples/wordcou nt/word. Splitter. py --input s 3: //elasticmapreduce/samples/wordcount /input --output s 3: //my-bucket/output --reducer aggregate
3971b36ec5b57d568b32763853e1c0df.ppt