a340c06632f99ac9c0620dc900bd3aba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
 Clock Signals § Clock signals are SPEED reference signals that are used in applications where the rate or speed at which data is transferred or output must remain constant. § Clock signals can be used for both analog and digital applications. § In digital audio applications the clock signal is know as Word Clock. § In video applications the clock signal is know as House Sync, or Video Sync, or Black Burst § Clock Signals should not be confused with Timecode. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
Clock Signals § Clock signals are SPEED reference signals that are used in applications where the rate or speed at which data is transferred or output must remain constant. § Clock signals can be used for both analog and digital applications. § In digital audio applications the clock signal is know as Word Clock. § In video applications the clock signal is know as House Sync, or Video Sync, or Black Burst § Clock Signals should not be confused with Timecode. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
 Digital Word Clock • A square wave, clock reference signal for digital audio • Word Clock is a “speed” reference • Sample rate is derived from word clock signal • Allows serial transmission between digital audio devices Typically uses a 75Ω coaxial video cable with BNC termination. "BNC” (British Navy Connector) is a bayonet-type connector, seen on professional video equipment. The male connector, usually mounted on the equipment, appears as a cylinder with a hollow pin in the center. The outer cylinder has two little nubs sticking out on opposite sides. The female connector, normally mounted on the cable, has an outer ring with slots on opposite sides which turns so that it can bayonet onto the nubs of the male connector, and has a smaller center pin which joins to the male's hollow center pin. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
Digital Word Clock • A square wave, clock reference signal for digital audio • Word Clock is a “speed” reference • Sample rate is derived from word clock signal • Allows serial transmission between digital audio devices Typically uses a 75Ω coaxial video cable with BNC termination. "BNC” (British Navy Connector) is a bayonet-type connector, seen on professional video equipment. The male connector, usually mounted on the equipment, appears as a cylinder with a hollow pin in the center. The outer cylinder has two little nubs sticking out on opposite sides. The female connector, normally mounted on the cable, has an outer ring with slots on opposite sides which turns so that it can bayonet onto the nubs of the male connector, and has a smaller center pin which joins to the male's hollow center pin. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
 Video “House Sync” • A video waveform signal without video elements, often referred to as “House” or “Sync” or “Black Burst” or “Video Sync” • House Sync is a “speed” reference signal used as a control track on ALL video tape formats. • “House Sync” is used to synchronize video tape machines and processors to a common speed reference. In video facilities, “House Sync” is sent to all tape machines and video processors. • “House Sync” is embedded into the video signal (from a video camera) during recording. This composite signal creates a control track that defines the speed of the original recording. These camera tapes are called “Source Tapes”. • In post-production video applications, “Master Tapes” are blank tapes that have been formatted by striping them with “House Sync” and a black video signal. This process is called “Blacking”. Video editing is the process of transferring selected “Source Tape” material onto video “Master Tapes”. As with the “Source Tapes”, “House Sync” allows “Master Tapes” to synchronize to the common speed reference from the “House Sync” generator. • House sync DOES NOT CONTAIN TIME CODE! This is a common misconception. • Uses a "BNC" (British Navy Connector) connector. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
Video “House Sync” • A video waveform signal without video elements, often referred to as “House” or “Sync” or “Black Burst” or “Video Sync” • House Sync is a “speed” reference signal used as a control track on ALL video tape formats. • “House Sync” is used to synchronize video tape machines and processors to a common speed reference. In video facilities, “House Sync” is sent to all tape machines and video processors. • “House Sync” is embedded into the video signal (from a video camera) during recording. This composite signal creates a control track that defines the speed of the original recording. These camera tapes are called “Source Tapes”. • In post-production video applications, “Master Tapes” are blank tapes that have been formatted by striping them with “House Sync” and a black video signal. This process is called “Blacking”. Video editing is the process of transferring selected “Source Tape” material onto video “Master Tapes”. As with the “Source Tapes”, “House Sync” allows “Master Tapes” to synchronize to the common speed reference from the “House Sync” generator. • House sync DOES NOT CONTAIN TIME CODE! This is a common misconception. • Uses a "BNC" (British Navy Connector) connector. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
 House Sync & Word Clock Both are speed reference signals. They do not contain timing information such as Time Code or Sample Rate, rather they provide the basic speed reference to generate a timing signal. Sample Rate is derived from Word Clock. Frame Rate is derived from House Sync. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
House Sync & Word Clock Both are speed reference signals. They do not contain timing information such as Time Code or Sample Rate, rather they provide the basic speed reference to generate a timing signal. Sample Rate is derived from Word Clock. Frame Rate is derived from House Sync. Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
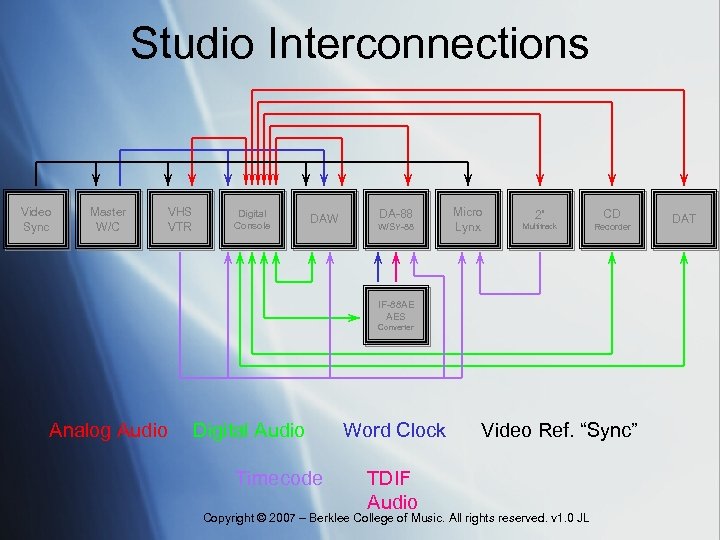 Studio Interconnections Video Sync Master W/C VHS VTR Digital Console DAW DA-88 W/SY-88 Micro Lynx 2” CD Multitrack Recorder IF-88 AE AES Converter Analog Audio Digital Audio Timecode Word Clock TDIF Audio Video Ref. “Sync” Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL DAT
Studio Interconnections Video Sync Master W/C VHS VTR Digital Console DAW DA-88 W/SY-88 Micro Lynx 2” CD Multitrack Recorder IF-88 AE AES Converter Analog Audio Digital Audio Timecode Word Clock TDIF Audio Video Ref. “Sync” Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL DAT
 M 27 Digital Connections Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
M 27 Digital Connections Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
 Common delivery formats • Audio CD • 44. 1 k. Hz / 16 bit • Digital Audio for Video • 48 k. Hz / 16 & 24 bit (mostly 16 bit!! Sometimes 32 k. Hz!!!) • DAT, DA-88, ADAT • 44. 1 k. Hz, 48 k. Hz /16 bit • Some models can record 24 bit audio • DVD-V • 48 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz /16 & 24 bit • DVD-A • 44. 1 k. Hz, 48 k. Hz, 88. 2 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz, 176. 4 k. Hz, 192 k. Hz / 16 & 24 bit Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
Common delivery formats • Audio CD • 44. 1 k. Hz / 16 bit • Digital Audio for Video • 48 k. Hz / 16 & 24 bit (mostly 16 bit!! Sometimes 32 k. Hz!!!) • DAT, DA-88, ADAT • 44. 1 k. Hz, 48 k. Hz /16 bit • Some models can record 24 bit audio • DVD-V • 48 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz /16 & 24 bit • DVD-A • 44. 1 k. Hz, 48 k. Hz, 88. 2 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz, 176. 4 k. Hz, 192 k. Hz / 16 & 24 bit Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
 High Resolution Audio • DVD-V • 48 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz /16 & 24 bit • DVD-A • 44. 1 k. Hz, 48 k. Hz, 88. 2 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz, 176. 4 k. Hz, 192 k. Hz / 16 & 24 bit Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
High Resolution Audio • DVD-V • 48 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz /16 & 24 bit • DVD-A • 44. 1 k. Hz, 48 k. Hz, 88. 2 k. Hz, 96 k. Hz, 176. 4 k. Hz, 192 k. Hz / 16 & 24 bit Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
 Digital Audio Interconnects & Transmission Formats • SDIF • AES/EBU • S/PDIF • ADAT Optical (lightpipe) • TOSlink Optical (lightpipe) • TDIF Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL
Digital Audio Interconnects & Transmission Formats • SDIF • AES/EBU • S/PDIF • ADAT Optical (lightpipe) • TOSlink Optical (lightpipe) • TDIF Copyright © 2007 – Berklee College of Music. All rights reserved. v 1. 0 JL


