9c3f15f6b0b5fadb8e6be42cc314c708.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Clinicopathologic Features of Diaphyseal Osteosarcoma Anne N. Normand, MD Patrick P. Lin, MD Norman Jaffe, MD Robert S. Benjamin, MD Shreyaskumar R. Patel, MD Christopher P. Cannon, MD Valerae O. Lewis, MD A. Kevin Raymond, MD Alan W. Yasko, MD, MBA CTOS Meeting November 2005
Clinicopathologic Features of Diaphyseal Osteosarcoma Anne N. Normand, MD Patrick P. Lin, MD Norman Jaffe, MD Robert S. Benjamin, MD Shreyaskumar R. Patel, MD Christopher P. Cannon, MD Valerae O. Lewis, MD A. Kevin Raymond, MD Alan W. Yasko, MD, MBA CTOS Meeting November 2005
 High-grade intramedullary osteosarcoma • Most common in metaphyseal region of long bones • Rare in the diaphyseal region – Previously reported to occur <10% of cases – Site of osteosarcoma variants (eg, periosteal, high-grade surface OS)
High-grade intramedullary osteosarcoma • Most common in metaphyseal region of long bones • Rare in the diaphyseal region – Previously reported to occur <10% of cases – Site of osteosarcoma variants (eg, periosteal, high-grade surface OS)
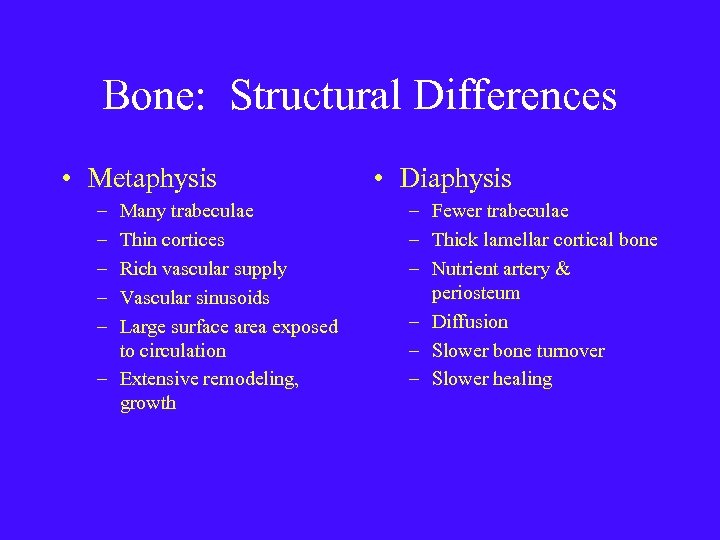 Bone: Structural Differences • Metaphysis – – – Many trabeculae Thin cortices Rich vascular supply Vascular sinusoids Large surface area exposed to circulation – Extensive remodeling, growth • Diaphysis – Fewer trabeculae – Thick lamellar cortical bone – Nutrient artery & periosteum – Diffusion – Slower bone turnover – Slower healing
Bone: Structural Differences • Metaphysis – – – Many trabeculae Thin cortices Rich vascular supply Vascular sinusoids Large surface area exposed to circulation – Extensive remodeling, growth • Diaphysis – Fewer trabeculae – Thick lamellar cortical bone – Nutrient artery & periosteum – Diffusion – Slower bone turnover – Slower healing
 Literature • Sim et al, 1995 – – Mayo Clinic 51 cases 1912 -1979 ~7% of all long bone OS treated during that period – No chemotherapy protocols – 73% (38/51) no chemo – 5 -year survival 29% • Haworth et al, 1981 – Bristol Royal Infirmary – Radiographic review – Heterogeneous presentation, broad DDx – 5 -year survival 23%
Literature • Sim et al, 1995 – – Mayo Clinic 51 cases 1912 -1979 ~7% of all long bone OS treated during that period – No chemotherapy protocols – 73% (38/51) no chemo – 5 -year survival 29% • Haworth et al, 1981 – Bristol Royal Infirmary – Radiographic review – Heterogeneous presentation, broad DDx – 5 -year survival 23%
 Hypothesis • Diaphyseal and metaphyseal bone differ anatomically and metabolically. – Clinicopathologic features of tumors may differ – Response to treatment may differ
Hypothesis • Diaphyseal and metaphyseal bone differ anatomically and metabolically. – Clinicopathologic features of tumors may differ – Response to treatment may differ
 Purpose • Describe clinicopathologic features of diaphyseal osteosarcoma • Determine differences in outcome between diaphyseal and metaphyseal osteosarcoma with contemporary treatment
Purpose • Describe clinicopathologic features of diaphyseal osteosarcoma • Determine differences in outcome between diaphyseal and metaphyseal osteosarcoma with contemporary treatment
 Materials & Methods
Materials & Methods
 Study Design • • • Retrospective review High-grade intramedullary OS of long bones 1980 to 1999 5 -year potential follow-up 51 diaphyseal, 240 metaphyseal
Study Design • • • Retrospective review High-grade intramedullary OS of long bones 1980 to 1999 5 -year potential follow-up 51 diaphyseal, 240 metaphyseal
 Exclusion criteria • Surface OS • Low- and intermediate-grade OS • Secondary OS
Exclusion criteria • Surface OS • Low- and intermediate-grade OS • Secondary OS
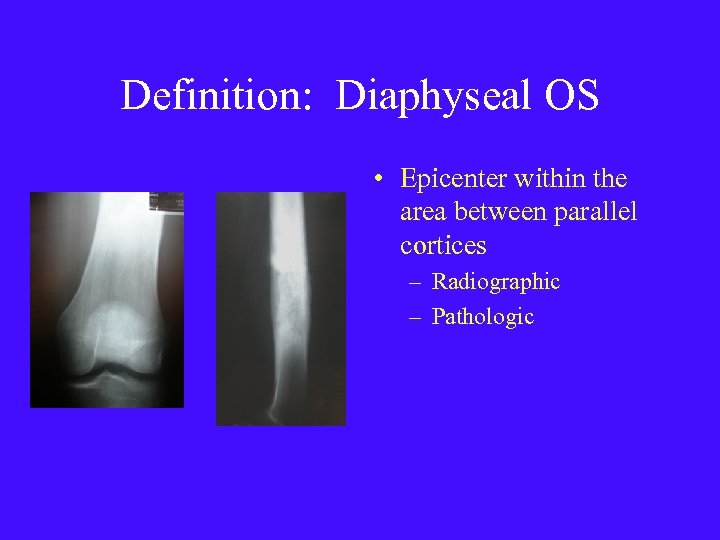 Definition: Diaphyseal OS • Epicenter within the area between parallel cortices – Radiographic – Pathologic
Definition: Diaphyseal OS • Epicenter within the area between parallel cortices – Radiographic – Pathologic
 Treatment algorithm • Pre-operative chemotherapy - 4 cycles • Surgical treatment • Post-operative chemotherapy - tailored – Good responders (≥ 90%) – Poor responders (<90%)
Treatment algorithm • Pre-operative chemotherapy - 4 cycles • Surgical treatment • Post-operative chemotherapy - tailored – Good responders (≥ 90%) – Poor responders (<90%)
 Pre-op chemotherapy • Intra-arterial cis-platin (120 mg/m 2) • Intravenous doxorubicin (90 mg/m 2) • 4 cycles
Pre-op chemotherapy • Intra-arterial cis-platin (120 mg/m 2) • Intravenous doxorubicin (90 mg/m 2) • 4 cycles
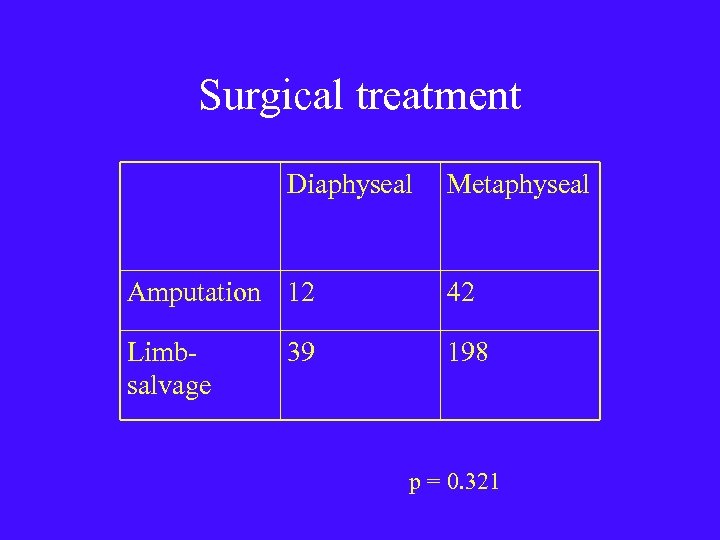 Surgical treatment Diaphyseal Metaphyseal Amputation 12 42 Limbsalvage 198 39 p = 0. 321
Surgical treatment Diaphyseal Metaphyseal Amputation 12 42 Limbsalvage 198 39 p = 0. 321
 Post-operative chemotherapy • Good responders - short course – IV cis-platin – IV doxorubicin • Poor responders - extended course – High-dose methotrexate (12. 5 g/m 2) – High-dose ifosfamide (14 g/m 2)
Post-operative chemotherapy • Good responders - short course – IV cis-platin – IV doxorubicin • Poor responders - extended course – High-dose methotrexate (12. 5 g/m 2) – High-dose ifosfamide (14 g/m 2)
 Statistics • Kaplan-Meier analysis – Disease-specific survival – Log rank test • Chi-square test • Independent student’s t test
Statistics • Kaplan-Meier analysis – Disease-specific survival – Log rank test • Chi-square test • Independent student’s t test
 Results
Results
 Demographics Diaphyseal Metaphyseal p Number 51 240 Age (yrs) Mean Range 22 4 -72 19 4 -75 0. 286 Gender Male Female 31 (61%) 20 (39%) 141 (59%) 99 (41%) 0. 869 F/u (mo. ) Mean Range 106 3 -288 99 1 -283 0. 177 48 (94%) 3 (6%) 225 (94%) 15 (6%) 0. 916 Stage Non-metas Metastatic
Demographics Diaphyseal Metaphyseal p Number 51 240 Age (yrs) Mean Range 22 4 -72 19 4 -75 0. 286 Gender Male Female 31 (61%) 20 (39%) 141 (59%) 99 (41%) 0. 869 F/u (mo. ) Mean Range 106 3 -288 99 1 -283 0. 177 48 (94%) 3 (6%) 225 (94%) 15 (6%) 0. 916 Stage Non-metas Metastatic
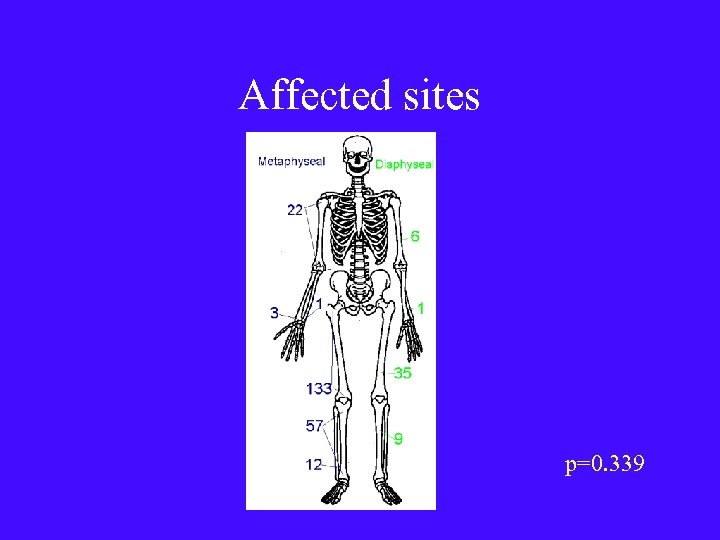 Affected sites p=0. 339
Affected sites p=0. 339
 Presentation • Symptoms – Pain most common – Local swelling, mass • Pathologic fracture – Diaphyseal 9/51 (18%) – Metaphyseal 39/240 (16%) – p = 0. 657
Presentation • Symptoms – Pain most common – Local swelling, mass • Pathologic fracture – Diaphyseal 9/51 (18%) – Metaphyseal 39/240 (16%) – p = 0. 657
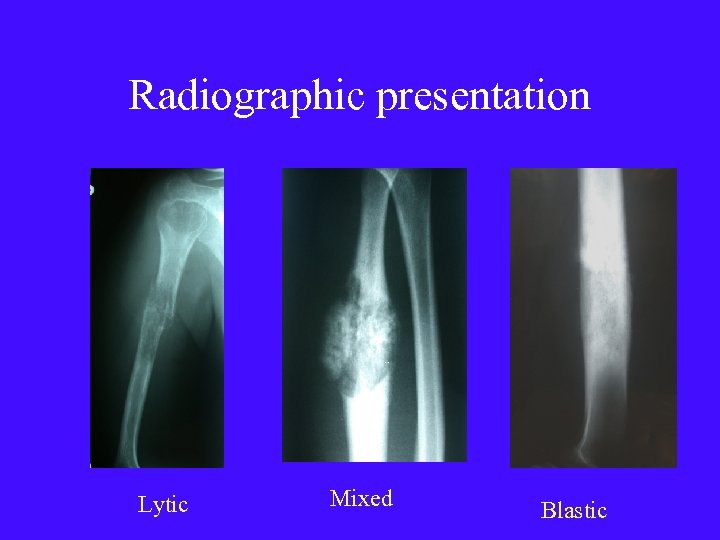 Radiographic presentation Lytic Mixed Blastic
Radiographic presentation Lytic Mixed Blastic
 Histology
Histology
 Tumor necrosis Diaphysis Metaphysis Good 16 134 Poor 32 96 p = 0. 0016
Tumor necrosis Diaphysis Metaphysis Good 16 134 Poor 32 96 p = 0. 0016
 Disease-specific survival
Disease-specific survival
 Disease-specific survival Diaphyseal Metaphyseal 5 years 62% 69% 10 years 59% 60% 20 years 56% 60%
Disease-specific survival Diaphyseal Metaphyseal 5 years 62% 69% 10 years 59% 60% 20 years 56% 60%
 DSS & Tumor Necrosis
DSS & Tumor Necrosis
 Impact of metastatic disease
Impact of metastatic disease
 Discussion
Discussion
 Similarities • Diaphyseal & metaphyseal OS share many features – Age – Gender – Sites – Presentation – Histological subtypes
Similarities • Diaphyseal & metaphyseal OS share many features – Age – Gender – Sites – Presentation – Histological subtypes
 Key Difference Response to pre-op chemotherapy • Diaphyseal OS less sensitive than metaphyseal OS to doxorubicin & IAcisplatin – ? Anatomical/vascular/structural differences
Key Difference Response to pre-op chemotherapy • Diaphyseal OS less sensitive than metaphyseal OS to doxorubicin & IAcisplatin – ? Anatomical/vascular/structural differences
 Similar outcomes • Disease-specific survival same • Supports tailoring of post-op chemotherapy – Switch to HD-MTX & HD-IFX – Historical data • survival w/ poor response to pre-op chemo significantly worse
Similar outcomes • Disease-specific survival same • Supports tailoring of post-op chemotherapy – Switch to HD-MTX & HD-IFX – Historical data • survival w/ poor response to pre-op chemo significantly worse
 Conclusion • Clinicopathological characteristics of diaphyseal OS are similar to metaphyseal OS • Diaphyseal OS responds less well to pre-op chemo • Tailoring of post-op chemo for poor responders to include HD-MTX & HD-IFX may be important to achieve good survival
Conclusion • Clinicopathological characteristics of diaphyseal OS are similar to metaphyseal OS • Diaphyseal OS responds less well to pre-op chemo • Tailoring of post-op chemo for poor responders to include HD-MTX & HD-IFX may be important to achieve good survival
 Thank you
Thank you


