13f5d1a5fc43cfa2bc8aa8dede853ea5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Clinical Update New & updated guidelines ¡ Significant traffic light updates ¡ Significant safety issues ¡ Other issues ¡ Feedback from practices ¡
Clinical Update New & updated guidelines ¡ Significant traffic light updates ¡ Significant safety issues ¡ Other issues ¡ Feedback from practices ¡
 Clinical Guidelines
Clinical Guidelines
 Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW ¡ ¡ ¡ Categorised as chronic if symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks. Affects around 10% of the population. May occur with or without nasal polyps. Treatment consists of step wise steroid use, aiming for the lowest dose that is most effective for an individual patient. Surgery reserved for resistant cases.
Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW ¡ ¡ ¡ Categorised as chronic if symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks. Affects around 10% of the population. May occur with or without nasal polyps. Treatment consists of step wise steroid use, aiming for the lowest dose that is most effective for an individual patient. Surgery reserved for resistant cases.
 Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW Self-management advice for acute exacerbations: ¡ Simple analgesics such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to reduce pain and fever ¡ Intranasal decongestants used occasionally in adults only (for a maximum of 1 week) – can help if nasal congestion is problematic. Oral decongestants are not recommended. ¡ Many patients find nasal douching with saline prior to administration of topical steroids helpful, e. g. Sinu. Rinse and Sterimar which are OTC preparations ¡ Applying warm (not hot) face packs ¡ Steam inhalation is not recommended
Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW Self-management advice for acute exacerbations: ¡ Simple analgesics such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to reduce pain and fever ¡ Intranasal decongestants used occasionally in adults only (for a maximum of 1 week) – can help if nasal congestion is problematic. Oral decongestants are not recommended. ¡ Many patients find nasal douching with saline prior to administration of topical steroids helpful, e. g. Sinu. Rinse and Sterimar which are OTC preparations ¡ Applying warm (not hot) face packs ¡ Steam inhalation is not recommended
 Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW Antibiotic prescribing: o A short course of antibiotics might be appropriate – as per local antimicrobial guidelines. o Seek specialist advice before prescribing long-term antibiotics, as evidence for this approach is limited
Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW Antibiotic prescribing: o A short course of antibiotics might be appropriate – as per local antimicrobial guidelines. o Seek specialist advice before prescribing long-term antibiotics, as evidence for this approach is limited
 Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW Treatment: ¡ Most idiopathic inflammatory polyps are steroid responsive. ¡ A “ladder” or stepped approach, but ideally patients shouldn’t be left long term on anything other than the 1 st “rung”. ¡ Management is long term, generally not curative. ¡ Consider nasal irrigation with saline solution to relieve congestion and nasal discharge.
Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW Treatment: ¡ Most idiopathic inflammatory polyps are steroid responsive. ¡ A “ladder” or stepped approach, but ideally patients shouldn’t be left long term on anything other than the 1 st “rung”. ¡ Management is long term, generally not curative. ¡ Consider nasal irrigation with saline solution to relieve congestion and nasal discharge.

 Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW
Chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps - NEW
 Children’s asthma guideline 5 to 12 years - UPDATE ¡ Main change is at step 3 a (adding a LABA):
Children’s asthma guideline 5 to 12 years - UPDATE ¡ Main change is at step 3 a (adding a LABA):
 Children’s asthma guideline 5 to 12 years - UPDATE ¡ Included more options to assess control:
Children’s asthma guideline 5 to 12 years - UPDATE ¡ Included more options to assess control:
 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children and young people ¡ ¡ Based on the NICE guideline published in January. GOR (asymptomatic regurgitation of feeds in young babies) is very common and most cases resolve by age 1. Only a small proportion will need to be managed as GORD (GOR causing symptoms e. g. discomfort or pain or complications e. g. oesophagitis). Table of “red flags” included for infants, children and young people with vomiting or regurgitation
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children and young people ¡ ¡ Based on the NICE guideline published in January. GOR (asymptomatic regurgitation of feeds in young babies) is very common and most cases resolve by age 1. Only a small proportion will need to be managed as GORD (GOR causing symptoms e. g. discomfort or pain or complications e. g. oesophagitis). Table of “red flags” included for infants, children and young people with vomiting or regurgitation
 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children and young people When reassuring parents and carers about regurgitation, advise them that they should return for review if any of the following occur: • The regurgitation becomes persistently projectile • There is bile-stained (green or yellow-green) vomiting or haematemesis (blood in vomit) • There are new concerns, such as signs of marked distress, feeding difficulties or faltering growth • There is persistent, frequent regurgitation beyond the first year of life. Advise patients not to use positional management to treat GOR in sleeping infants. Infants should be placed on their back when sleeping.
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children and young people When reassuring parents and carers about regurgitation, advise them that they should return for review if any of the following occur: • The regurgitation becomes persistently projectile • There is bile-stained (green or yellow-green) vomiting or haematemesis (blood in vomit) • There are new concerns, such as signs of marked distress, feeding difficulties or faltering growth • There is persistent, frequent regurgitation beyond the first year of life. Advise patients not to use positional management to treat GOR in sleeping infants. Infants should be placed on their back when sleeping.
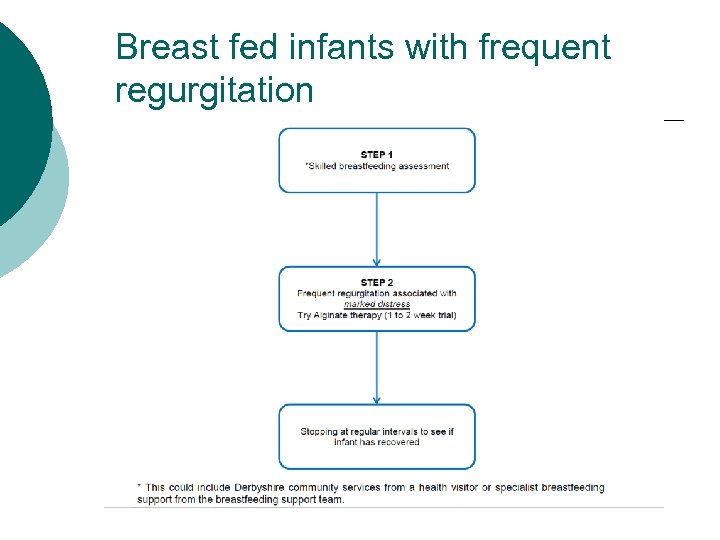 Breast fed infants with frequent regurgitation
Breast fed infants with frequent regurgitation
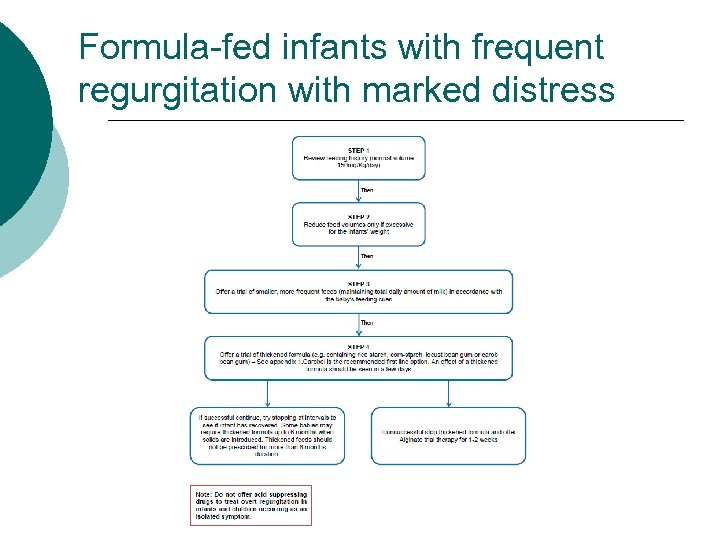 Formula-fed infants with frequent regurgitation with marked distress
Formula-fed infants with frequent regurgitation with marked distress
 Thickened formula information ¡ Carobel first line option (more cost-effective and allows easy review). l l ¡ Needs a wide or vari-flow teat. Endorse ACBS. Powdered “antiregurgitation” formula is an alternative. l l Enfamil AR and SMA Staydown are ACBS approved for significant GOR Not to be used for a period >6 months, Not to be used in conjunction with any other feed thickener or antacid products. Available over the counter for parents to buy special instructions for preparation.
Thickened formula information ¡ Carobel first line option (more cost-effective and allows easy review). l l ¡ Needs a wide or vari-flow teat. Endorse ACBS. Powdered “antiregurgitation” formula is an alternative. l l Enfamil AR and SMA Staydown are ACBS approved for significant GOR Not to be used for a period >6 months, Not to be used in conjunction with any other feed thickener or antacid products. Available over the counter for parents to buy special instructions for preparation.
 Pharmacological treatment of GORD
Pharmacological treatment of GORD
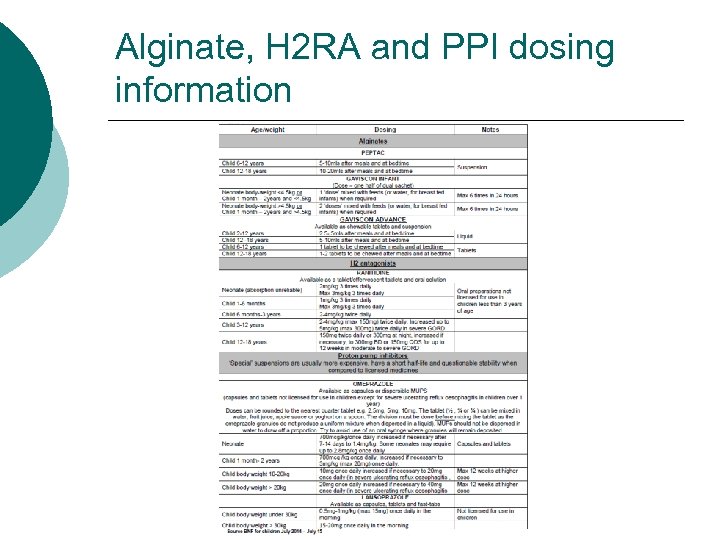 Alginate, H 2 RA and PPI dosing information
Alginate, H 2 RA and PPI dosing information
 AF guideline - UPDATE Now includes a useful algorithm to help guide anticoagulant choice and choice of NOAC if a NOAC is required. ¡ Considers clinical issues (e. g. renal impairment, higher bleeding risk) and practical issues (e. g. need for once daily dose, swallowing difficulties, need for compliance aid) ¡ N. B. no head trials of the NOACs. ¡
AF guideline - UPDATE Now includes a useful algorithm to help guide anticoagulant choice and choice of NOAC if a NOAC is required. ¡ Considers clinical issues (e. g. renal impairment, higher bleeding risk) and practical issues (e. g. need for once daily dose, swallowing difficulties, need for compliance aid) ¡ N. B. no head trials of the NOACs. ¡
 Other guideline updates: Adult asthma: no major changes but table added with assessment options. ¡ Familial hypercholesterolaemia: updated with atorvastatin as preferred statin for new patients (10 to 20 mg initially, increasing to 40 to 80 mg if LDL-C not reduced by 50%) ¡ ACS, NSTEMI and unstable angina antiplatelet flow chart used by CRHFT: no changes. ¡
Other guideline updates: Adult asthma: no major changes but table added with assessment options. ¡ Familial hypercholesterolaemia: updated with atorvastatin as preferred statin for new patients (10 to 20 mg initially, increasing to 40 to 80 mg if LDL-C not reduced by 50%) ¡ ACS, NSTEMI and unstable angina antiplatelet flow chart used by CRHFT: no changes. ¡
 Shared-Care Guidelines
Shared-Care Guidelines
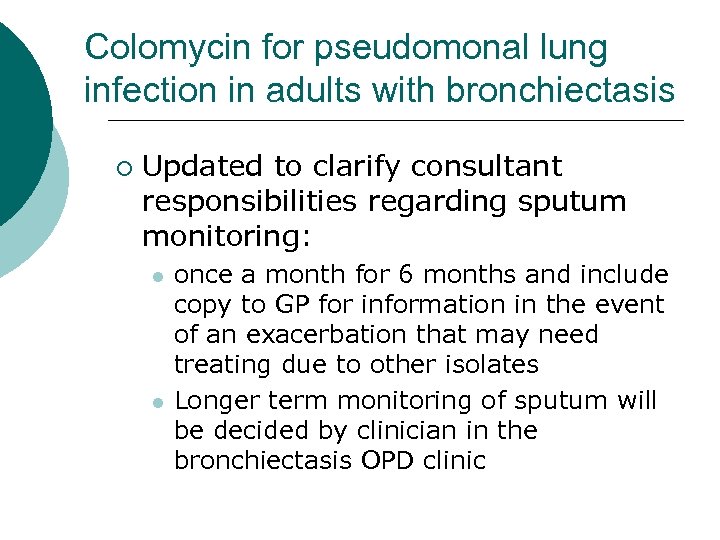 Colomycin for pseudomonal lung infection in adults with bronchiectasis ¡ Updated to clarify consultant responsibilities regarding sputum monitoring: l l once a month for 6 months and include copy to GP for information in the event of an exacerbation that may need treating due to other isolates Longer term monitoring of sputum will be decided by clinician in the bronchiectasis OPD clinic
Colomycin for pseudomonal lung infection in adults with bronchiectasis ¡ Updated to clarify consultant responsibilities regarding sputum monitoring: l l once a month for 6 months and include copy to GP for information in the event of an exacerbation that may need treating due to other isolates Longer term monitoring of sputum will be decided by clinician in the bronchiectasis OPD clinic
 ADHD in children and adults Matoride XL included as a costeffective alternative to Concerta XL for new patients. ¡ Bioequivalent and GPs could consider changing existing patients, after a face to face review. ¡
ADHD in children and adults Matoride XL included as a costeffective alternative to Concerta XL for new patients. ¡ Bioequivalent and GPs could consider changing existing patients, after a face to face review. ¡
 Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures ¡ Updated to include men with osteoporosis including the specific sub-set of men with prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy.
Denosumab for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures ¡ Updated to include men with osteoporosis including the specific sub-set of men with prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy.
 Significant Traffic Light Changes
Significant Traffic Light Changes
 Significant traffic light updates: RED ¡ ¡ ¡ Rivaroxaban 2. 5 mg: new strength, licensed for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in patients with ACS in combination with aspirin, aspirin+clopidogrel or ticlodipine. Cardiologists at Chesterfield and Derby still considering its place in the pathway and length of treatment. No immediate plans for use at Chesterfield and will continue with dual antiplatelet therapy as per guidelines.
Significant traffic light updates: RED ¡ ¡ ¡ Rivaroxaban 2. 5 mg: new strength, licensed for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in patients with ACS in combination with aspirin, aspirin+clopidogrel or ticlodipine. Cardiologists at Chesterfield and Derby still considering its place in the pathway and length of treatment. No immediate plans for use at Chesterfield and will continue with dual antiplatelet therapy as per guidelines.
 Significant traffic light updates: GREEN ¡ ¡ ¡ Fluticasone nasules: as per chronic rhinosinusitis guideline. Acetazolamide: for idiopathic intracranial hypertension, after consultant initiation and stabilisation (requested by RDH consultants). Exenatide weekly: reclassified from brown. Now available as a pre-filled pen. Same cost as previous weekly powder and solvent formulation but easier to administer. An option for patients with compliance problems or when nursing staff are required to administer the injection.
Significant traffic light updates: GREEN ¡ ¡ ¡ Fluticasone nasules: as per chronic rhinosinusitis guideline. Acetazolamide: for idiopathic intracranial hypertension, after consultant initiation and stabilisation (requested by RDH consultants). Exenatide weekly: reclassified from brown. Now available as a pre-filled pen. Same cost as previous weekly powder and solvent formulation but easier to administer. An option for patients with compliance problems or when nursing staff are required to administer the injection.
 Significant traffic light updates: GREEN ¡ Lamotrigine: after specialist initiation for indications in addition to epilepsy e. g. bipolar disorder.
Significant traffic light updates: GREEN ¡ Lamotrigine: after specialist initiation for indications in addition to epilepsy e. g. bipolar disorder.
 Significant traffic light updates: BROWN ¡ ¡ ¡ Levocetirizine, desloratidine and esomeprazole reclassified from black due to significant reduction in cost. Silica gel/sheets reclassified from black for patients under specialist burns units. Dapagliflozin + metformin. Cheaper to use combination product if patient on both, but does not allow metformin dose to be increased to UKPDS target dose (around 2. 5 g/day). Dapagliflozin specialist initiation.
Significant traffic light updates: BROWN ¡ ¡ ¡ Levocetirizine, desloratidine and esomeprazole reclassified from black due to significant reduction in cost. Silica gel/sheets reclassified from black for patients under specialist burns units. Dapagliflozin + metformin. Cheaper to use combination product if patient on both, but does not allow metformin dose to be increased to UKPDS target dose (around 2. 5 g/day). Dapagliflozin specialist initiation.
 Significant traffic light updates: BROWN Escitalopram: reclassified from black due to reduction in cost. For continued use in those responding to treatment or who have had a good response previously, after trying formulary choices. ¡ Empagliflozin: following specialist initiation when a gliptin considered inappropriate. ¡
Significant traffic light updates: BROWN Escitalopram: reclassified from black due to reduction in cost. For continued use in those responding to treatment or who have had a good response previously, after trying formulary choices. ¡ Empagliflozin: following specialist initiation when a gliptin considered inappropriate. ¡
 Significant traffic light updates: BROWN Aclidinium + formoterol (Duaklir Genuair): reclassified from black in line with other LABA/LAMA combination inhalers. ¡ Limited place of LABA/LAMA in COPD and weak evidence but if patient deriving benefit from separate consituents, the combination inhaler is more costeffective. ¡
Significant traffic light updates: BROWN Aclidinium + formoterol (Duaklir Genuair): reclassified from black in line with other LABA/LAMA combination inhalers. ¡ Limited place of LABA/LAMA in COPD and weak evidence but if patient deriving benefit from separate consituents, the combination inhaler is more costeffective. ¡
 Significant traffic light updates: BLACK ¡ Olodaterol. Once daily LABA for COPD but less cost-effective formulary choice, formoterol Easyhaler.
Significant traffic light updates: BLACK ¡ Olodaterol. Once daily LABA for COPD but less cost-effective formulary choice, formoterol Easyhaler.
 Significant Safety Updates
Significant Safety Updates
 Drug safety Update – March 15 ¡ ¡ ¡ Dimethyl fumarate: fatal progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in an MS patient. Ferumoxytol (IV iron): no longer available. Cortocosteroid e-learning module launched: interactive module for clinical practitioners covering: l l Commonly used corticosteroids. Adverse effects. Reducing risks. Specific treatment of adverse effects.
Drug safety Update – March 15 ¡ ¡ ¡ Dimethyl fumarate: fatal progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in an MS patient. Ferumoxytol (IV iron): no longer available. Cortocosteroid e-learning module launched: interactive module for clinical practitioners covering: l l Commonly used corticosteroids. Adverse effects. Reducing risks. Specific treatment of adverse effects.
 Drug safety Update – April 15 ¡ Hydroxyzine: risk of QT interval prolongation and Torsade de Pointes. l l l Do not prescribe with known prolonged QT interval or risk factors (other medicines, CV disease, family history sudden cardiac death, significant electrolyte imbalance - low K or Mg, significant bradycardia). Avoid in the elderly. Consider risks if patient taking medicines that lower heart rate or potassium levels. Maximum adult daily dose 100 mg (50 mg for elderly if use cannot be avoided); 2 mg/kg for children up to 40 kg. Lowest effective dose for shortest period of time.
Drug safety Update – April 15 ¡ Hydroxyzine: risk of QT interval prolongation and Torsade de Pointes. l l l Do not prescribe with known prolonged QT interval or risk factors (other medicines, CV disease, family history sudden cardiac death, significant electrolyte imbalance - low K or Mg, significant bradycardia). Avoid in the elderly. Consider risks if patient taking medicines that lower heart rate or potassium levels. Maximum adult daily dose 100 mg (50 mg for elderly if use cannot be avoided); 2 mg/kg for children up to 40 kg. Lowest effective dose for shortest period of time.
 Drug safety Update – April 15 ¡ ¡ ¡ Codeine for cough and cold: do not use in children under 12 due to respiratory side effects related opiate toxicity. Not recommended in adolescents who have problems with breathing. Brings advice in line with 2013 warning to avoid codeine for analgesia in under 12 s and only use in over 12 s if ibuprofen or paracetamol not effective; avoid completely after tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy.
Drug safety Update – April 15 ¡ ¡ ¡ Codeine for cough and cold: do not use in children under 12 due to respiratory side effects related opiate toxicity. Not recommended in adolescents who have problems with breathing. Brings advice in line with 2013 warning to avoid codeine for analgesia in under 12 s and only use in over 12 s if ibuprofen or paracetamol not effective; avoid completely after tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy.
 Drug safety Update – April 15 ¡ Ketoprofen gel: letter sent to HCPs to remind about risk of photosensitivity reactions: l l l protect from sunlight during the whole period of topical ketoprofen treatment and for 2 weeks after stopping treatment; wash hands after every application; stop treatment immediately if they develop any skin reaction
Drug safety Update – April 15 ¡ Ketoprofen gel: letter sent to HCPs to remind about risk of photosensitivity reactions: l l l protect from sunlight during the whole period of topical ketoprofen treatment and for 2 weeks after stopping treatment; wash hands after every application; stop treatment immediately if they develop any skin reaction
 Drug safety Update – May 15 Sofosbuvir with daclatasvir; sofasbuvir with ledipasvir (for hepatitis C): risk of severe bradycardia and heart block if taken with amiodarone. ¡ Pomalidomide (for multiple myeloma): risk of cardiac failure, interstitial lung disease and hepatotoxity. ¡ Epoetin beta (Neo. Recormin): increased risk of retinopathy in pre-term infants) ¡
Drug safety Update – May 15 Sofosbuvir with daclatasvir; sofasbuvir with ledipasvir (for hepatitis C): risk of severe bradycardia and heart block if taken with amiodarone. ¡ Pomalidomide (for multiple myeloma): risk of cardiac failure, interstitial lung disease and hepatotoxity. ¡ Epoetin beta (Neo. Recormin): increased risk of retinopathy in pre-term infants) ¡
 Other issues
Other issues
 Bimatoprost eye drops 300 mcg 3 ml bottles discontinued April 15. ¡ CRHFT ophthalmologists generally use the 100 mcg strength and have advised that patients on the 300 mcg strength can be changed to the 100 mcg strength in primary care. ¡ Intra-ocular pressure to be checked at next routine appointment (unless other issues) ¡
Bimatoprost eye drops 300 mcg 3 ml bottles discontinued April 15. ¡ CRHFT ophthalmologists generally use the 100 mcg strength and have advised that patients on the 300 mcg strength can be changed to the 100 mcg strength in primary care. ¡ Intra-ocular pressure to be checked at next routine appointment (unless other issues) ¡


