37d3c9626e9db27785d478d82aa61ddc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Daniel Shouval Liver Unit Hadassah Hospital Hebrew University Jerusalem Israel Liver Unit - Hadassah
Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Daniel Shouval Liver Unit Hadassah Hospital Hebrew University Jerusalem Israel Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Key Concepts Ø Disease is usually insidious and subclinical Ø Persistent HCV infection may progress over decades to chronic hepatitis with fibrosis, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, encephalopathy and hepatocellular ca. Ø HCV is the main indication for liver transplantation Ø Although the liver is the main target for HCV, extrahepatic manifestations are common Ø HCV may complicate the course of other diseases I. e. HIV, HBV, chronic liver disease, hemophilia, Liver Unit - Hadassah renal failure, organ transplantation
Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Key Concepts Ø Disease is usually insidious and subclinical Ø Persistent HCV infection may progress over decades to chronic hepatitis with fibrosis, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, encephalopathy and hepatocellular ca. Ø HCV is the main indication for liver transplantation Ø Although the liver is the main target for HCV, extrahepatic manifestations are common Ø HCV may complicate the course of other diseases I. e. HIV, HBV, chronic liver disease, hemophilia, Liver Unit - Hadassah renal failure, organ transplantation
 Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Background - Pathology • Viral hepatitis is defined as a diffuse necroinflammatory liver disease caused by hepatotropic viruses • The basic morphologic pattern of acute or chronic hepatitis due to different hepatitis viruses are very similar irrespective of causative virus • Despite of the above, there are unique characteristic morphologic patterns in chronic HCV infection incl: lymphoid aggregates(57%), bile duct injury (60%) and steatosis (52%). Unit - Hadassah Liver
Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Background - Pathology • Viral hepatitis is defined as a diffuse necroinflammatory liver disease caused by hepatotropic viruses • The basic morphologic pattern of acute or chronic hepatitis due to different hepatitis viruses are very similar irrespective of causative virus • Despite of the above, there are unique characteristic morphologic patterns in chronic HCV infection incl: lymphoid aggregates(57%), bile duct injury (60%) and steatosis (52%). Unit - Hadassah Liver
 Liver Biopsy in Chronic Hepatitis C – is it still necessary? Background: Little correlation between the inflammatory process observed by microscopy and the clinical or laboratory manifestations The impact of clinical presentation on the rational for performing a biopsy: • Establish diagnosis • Assess grade and stage (Metavir score etc) • Exclude other or additional conditions (i. e alcohol, NASH, CLD, HBV ) • Guide management Liver Unit - Hadassah • Follow-up of therapy
Liver Biopsy in Chronic Hepatitis C – is it still necessary? Background: Little correlation between the inflammatory process observed by microscopy and the clinical or laboratory manifestations The impact of clinical presentation on the rational for performing a biopsy: • Establish diagnosis • Assess grade and stage (Metavir score etc) • Exclude other or additional conditions (i. e alcohol, NASH, CLD, HBV ) • Guide management Liver Unit - Hadassah • Follow-up of therapy
 Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection • Incubation period: Acute hepatitis C 15 -150 days (M 50 d) • Most cases of acute HCV infection (~75%) are not recognized • Clinical symptoms in patients with acute HCV when present, are usually milder as compared to other hepatitis viruses • ~80% of patients who contract acute HCV infection will develop persistent infection which often lasts Liver Unit - Hadassah for decades
Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection • Incubation period: Acute hepatitis C 15 -150 days (M 50 d) • Most cases of acute HCV infection (~75%) are not recognized • Clinical symptoms in patients with acute HCV when present, are usually milder as compared to other hepatitis viruses • ~80% of patients who contract acute HCV infection will develop persistent infection which often lasts Liver Unit - Hadassah for decades
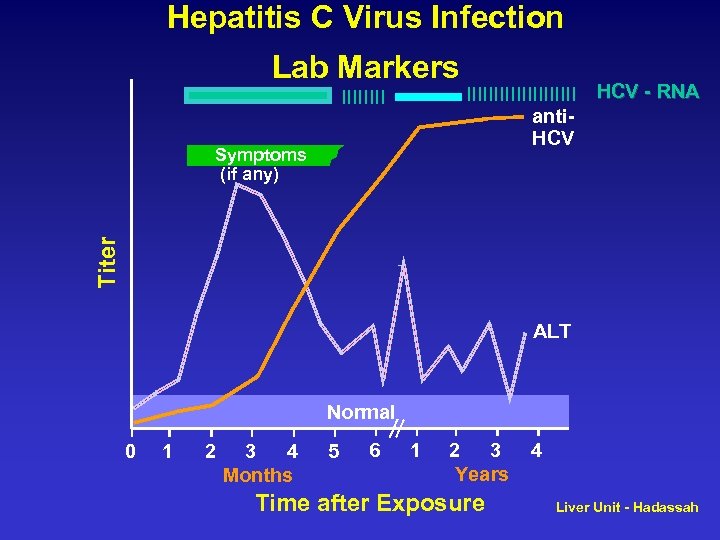 Hepatitis C Virus Infection Lab Markers IIII HCV - RNA Titer Symptoms (if any) IIIIIIIIII anti. HCV ALT Normal 0 1 2 3 4 Months 5 6 1 2 3 Years Time after Exposure 4 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Hepatitis C Virus Infection Lab Markers IIII HCV - RNA Titer Symptoms (if any) IIIIIIIIII anti. HCV ALT Normal 0 1 2 3 4 Months 5 6 1 2 3 Years Time after Exposure 4 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Clinical Presentation of Chronic HCV Infection* Clinical presentation may vary depending on the hos Immune status, the source and duration of infection • Often asymptomatic • Frequently detected during routine lab testing or blood donation Non specific signals: - mild to moderate fatigue - fluctuating ALT levels are *Sharara AL et al. Hepatitis c. Review Ann Int Med 1996; 125: 658 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Clinical Presentation of Chronic HCV Infection* Clinical presentation may vary depending on the hos Immune status, the source and duration of infection • Often asymptomatic • Frequently detected during routine lab testing or blood donation Non specific signals: - mild to moderate fatigue - fluctuating ALT levels are *Sharara AL et al. Hepatitis c. Review Ann Int Med 1996; 125: 658 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Symptoms * Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Fatigue Malaise Nausea Abdominal discomfort* Dark urine and acholic stools Vomitting Jaundice Pruritus Arthralgia Fever * May be present in acute as well as in chronic hepatitis Liver Unit - Hadassah
Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Symptoms * Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø Fatigue Malaise Nausea Abdominal discomfort* Dark urine and acholic stools Vomitting Jaundice Pruritus Arthralgia Fever * May be present in acute as well as in chronic hepatitis Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Clinical Manifestations of HCV o Fatigue o Malaise o Myalgia o Depression o Cognitive dysfunction Liver Unit - Hadassah
Clinical Manifestations of HCV o Fatigue o Malaise o Myalgia o Depression o Cognitive dysfunction Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Musculoskeletal Pain and Fatigue in HCV* Ø 239 patients; age M 46. 7 y; Males 52% Results: ü Musculoskeletal pain – 70% for M of 7 y ü Fatigue – 56% for a M 3. 3 y ü Backache - 54% ü Morning stiffness – 45% ü Arthralgia – 42% ü Myalgia – 38% ü Neck pain – 33% * Barhuizen A et al. Am J Gastroenterology 1999; 94: 1355 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Musculoskeletal Pain and Fatigue in HCV* Ø 239 patients; age M 46. 7 y; Males 52% Results: ü Musculoskeletal pain – 70% for M of 7 y ü Fatigue – 56% for a M 3. 3 y ü Backache - 54% ü Morning stiffness – 45% ü Arthralgia – 42% ü Myalgia – 38% ü Neck pain – 33% * Barhuizen A et al. Am J Gastroenterology 1999; 94: 1355 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Hepatitis C and Cognitive Impairment of Patients with Mild Disease I* Material and Methods Ø 27 HCV patients with biopsy proven mild HCV 17 control patients with resolved HCV Ø Testing through computor based cognitive assessment battery Ø Completing depression, fatigue and quality of life questionnairs *Forton DM et al. Hepatology 2002; 35: 433 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Hepatitis C and Cognitive Impairment of Patients with Mild Disease I* Material and Methods Ø 27 HCV patients with biopsy proven mild HCV 17 control patients with resolved HCV Ø Testing through computor based cognitive assessment battery Ø Completing depression, fatigue and quality of life questionnairs *Forton DM et al. Hepatology 2002; 35: 433 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Hepatitis C and Cognitive Impairment of Patients with Mild Disease II* RESULTS ü HCV patients wereimpaired on more cognitive tasks than patients who cleared HCv ( P < 0. 02) ü HCV patients showed impairment in: - concentration power - speed of working memory (irrespective of fatigue or depression) ü Cerebral proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy showed elevated choline/creatine ratios suggesting a possible organic etiology for cognitive impairment in HCV infection *Forton DM et al. Hepatology 2002; 35: 433 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Hepatitis C and Cognitive Impairment of Patients with Mild Disease II* RESULTS ü HCV patients wereimpaired on more cognitive tasks than patients who cleared HCv ( P < 0. 02) ü HCV patients showed impairment in: - concentration power - speed of working memory (irrespective of fatigue or depression) ü Cerebral proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy showed elevated choline/creatine ratios suggesting a possible organic etiology for cognitive impairment in HCV infection *Forton DM et al. Hepatology 2002; 35: 433 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Complications of Acute HCV Infection (I) • • Fulminant hepatitis – rare Chronic hepatitis - ~80% Cirrhosis* ~20 -35% Hepatocellular carcinom** - ` 1 -4% annually, after prolonged infection * Maybe clinically silent but eventually may lead to portal hypertension, ascites, esophageal and gastric varices which may bleed, or hepatic encephalopathy ** As * with additional extra hepatic manifestations Liver Unit - Hadassah
Complications of Acute HCV Infection (I) • • Fulminant hepatitis – rare Chronic hepatitis - ~80% Cirrhosis* ~20 -35% Hepatocellular carcinom** - ` 1 -4% annually, after prolonged infection * Maybe clinically silent but eventually may lead to portal hypertension, ascites, esophageal and gastric varices which may bleed, or hepatic encephalopathy ** As * with additional extra hepatic manifestations Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Complications of Acute HCV Infection (II)* average time between acute hepatitis c and Ø “Clinically significant” liver disease ~10 years Ø Cirrhosis ~ 21. 2 years Ø Hepatocellular carcinoma ~ 29 years *Sharara AL et al. Hepatitis c. Review Ann Int Med 1996; 125: 658 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Complications of Acute HCV Infection (II)* average time between acute hepatitis c and Ø “Clinically significant” liver disease ~10 years Ø Cirrhosis ~ 21. 2 years Ø Hepatocellular carcinoma ~ 29 years *Sharara AL et al. Hepatitis c. Review Ann Int Med 1996; 125: 658 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Association of HCV infection with other Diseases and Conditions and Impact on Clinical Presentation • Infection with other viruses: HIV, HBV, HTLV, Herpes • Infection of patients with schistosomiasis • IVDA • Hemophilia, Thalassemia, Sickle cell anemia etc. • Hemodialysis and kidney transplantation • Iron overload • Alcoholic liver disease • Autoimmune hepatitis. PBC, PSC Liver Unit - Hadassah
Association of HCV infection with other Diseases and Conditions and Impact on Clinical Presentation • Infection with other viruses: HIV, HBV, HTLV, Herpes • Infection of patients with schistosomiasis • IVDA • Hemophilia, Thalassemia, Sickle cell anemia etc. • Hemodialysis and kidney transplantation • Iron overload • Alcoholic liver disease • Autoimmune hepatitis. PBC, PSC Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection* ü ü ü ü ü Endocrine Salivary Glands (sialadenitis) Ophtalmic ( uveitis, ulcers) Hematologic/lymphoid organs Skin Renal Autoimmune diseases Neurologic and Cognitive impairment Miscellaneous *S. J. Hadziyannis. (Review). J Viral Hepatitis 1997; 4: 9 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection* ü ü ü ü ü Endocrine Salivary Glands (sialadenitis) Ophtalmic ( uveitis, ulcers) Hematologic/lymphoid organs Skin Renal Autoimmune diseases Neurologic and Cognitive impairment Miscellaneous *S. J. Hadziyannis. (Review). J Viral Hepatitis 1997; 4: 9 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Endocrine v Hyperthyroidism v Hypothyroidism v Hashimoto’s Disease and Thyroiditis v Thyroid antibodies* v Diabetes Mellitus • Higher prevalence of anti-thyroid antibodies; also induced through interferon Rx and leading to hyper and hypothyroidism Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Endocrine v Hyperthyroidism v Hypothyroidism v Hashimoto’s Disease and Thyroiditis v Thyroid antibodies* v Diabetes Mellitus • Higher prevalence of anti-thyroid antibodies; also induced through interferon Rx and leading to hyper and hypothyroidism Liver Unit - Hadassah
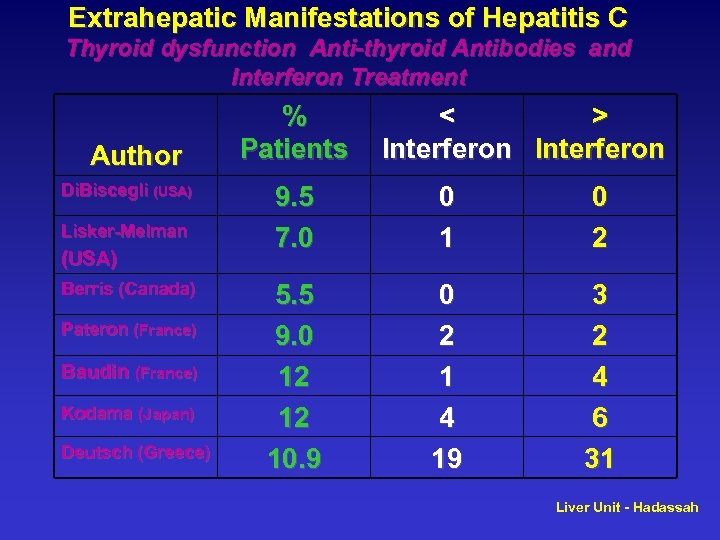 Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Thyroid dysfunction Anti-thyroid Antibodies and Interferon Treatment Author Di. Biscegli (USA) Lisker-Melman (USA) Berris (Canada) Pateron (France) Baudin (France) Kodama (Japan) Deutsch (Greece) % Patients < > Interferon 9. 5 7. 0 0 1 0 2 5. 5 9. 0 12 12 10. 9 0 2 1 4 19 3 2 4 6 31 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Thyroid dysfunction Anti-thyroid Antibodies and Interferon Treatment Author Di. Biscegli (USA) Lisker-Melman (USA) Berris (Canada) Pateron (France) Baudin (France) Kodama (Japan) Deutsch (Greece) % Patients < > Interferon 9. 5 7. 0 0 1 0 2 5. 5 9. 0 12 12 10. 9 0 2 1 4 19 3 2 4 6 31 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Diabetes Mellitus • High prevalence reported in USA, UK, Turkey • UK : DM in 17/34 (50%) in HCV cirrhosis patients • Reports on de-novo appearance of DM post IFN Rx • Putative mechanism linked to destruction of pancreatic islet cells directly by HCV or indirectly via immune response to HCV Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Diabetes Mellitus • High prevalence reported in USA, UK, Turkey • UK : DM in 17/34 (50%) in HCV cirrhosis patients • Reports on de-novo appearance of DM post IFN Rx • Putative mechanism linked to destruction of pancreatic islet cells directly by HCV or indirectly via immune response to HCV Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Salivary Glands § Mild lymphocytic sialadenitis reported in 3 studies in 14 -57% patients § Lymphocytic “capillaritis” reported by Pawlotsky in ~50% of patients while symptomatic lymphocytic sialadenitis reported in 7/49 patients § Clinical presentation - Sjoegren syndr. -rare; antinuclear SSA antibodies are absent § Lacrimal dysfunction reported in 17/34 asymptomatic patients without xerophtalmia Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Salivary Glands § Mild lymphocytic sialadenitis reported in 3 studies in 14 -57% patients § Lymphocytic “capillaritis” reported by Pawlotsky in ~50% of patients while symptomatic lymphocytic sialadenitis reported in 7/49 patients § Clinical presentation - Sjoegren syndr. -rare; antinuclear SSA antibodies are absent § Lacrimal dysfunction reported in 17/34 asymptomatic patients without xerophtalmia Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Ocular Involvement v Peripheral ulcerative keratitis (Mooren ulcers) reported during Interferon therapy and also during post Rx relapse v Challenge with interferon may lead to exacerbation of ulcers v A few cases of Uveitis have been reported Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Ocular Involvement v Peripheral ulcerative keratitis (Mooren ulcers) reported during Interferon therapy and also during post Rx relapse v Challenge with interferon may lead to exacerbation of ulcers v A few cases of Uveitis have been reported Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Renal Involvement • Mild to moderate proteinuria detected in up to 27% of patients with microscopic hematuria • Glomerular deposition of Ig. G, Ig. M and C 3 have been reported in cryoprecipitate conaining HCV-RNA and anti-HCv antibodies • Membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis reported in association with HCV and cryoglobulinemia Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Renal Involvement • Mild to moderate proteinuria detected in up to 27% of patients with microscopic hematuria • Glomerular deposition of Ig. G, Ig. M and C 3 have been reported in cryoprecipitate conaining HCV-RNA and anti-HCv antibodies • Membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis reported in association with HCV and cryoglobulinemia Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Hematological and Lymphoid Disorders* v Mixed cryoglobulinemia v Non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma (NHL) v Aplastic anemia ( association ? ? ) v Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura *Linked to lymphotropism of HCV to PBLs, dendritic cells, BM, megacariocyte, vascular endothelium and/or chronic antigenic stimulation Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Hematological and Lymphoid Disorders* v Mixed cryoglobulinemia v Non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma (NHL) v Aplastic anemia ( association ? ? ) v Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura *Linked to lymphotropism of HCV to PBLs, dendritic cells, BM, megacariocyte, vascular endothelium and/or chronic antigenic stimulation Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Cryoglobulinemia with or without Vasculitis* Ø Association between HCV and Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCG) established through HCV-RNA testing in cryoprecipitate Ø Often missed due to inadequate handling of blood specimen Ø Cryoglobulinemia may signal a pre-malignant state Ø Affects up to 40% of HCV patients with cirrhosis (mean cryocrit >2%) but only ~10% have symptoms of vasculitis *S. J. Hadziyannis. (Review). J Viral Hepatitis 1997; 4: 9 Dammacco F et al. The cryoglobulins: an overview. Eur J Clin Invest. 2001; 31: 628 Liver Unit - Hadassah
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Cryoglobulinemia with or without Vasculitis* Ø Association between HCV and Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCG) established through HCV-RNA testing in cryoprecipitate Ø Often missed due to inadequate handling of blood specimen Ø Cryoglobulinemia may signal a pre-malignant state Ø Affects up to 40% of HCV patients with cirrhosis (mean cryocrit >2%) but only ~10% have symptoms of vasculitis *S. J. Hadziyannis. (Review). J Viral Hepatitis 1997; 4: 9 Dammacco F et al. The cryoglobulins: an overview. Eur J Clin Invest. 2001; 31: 628 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 HCV Associated Arthritis* v Commonly presents as rheumatoid arthritis like symptoms ( severe morning stiffness and pain) with symmetrical arthritis of small joints v Mono or oligo-arthritis less common v Clinical course usually benign without deformities v Absence of subcutaneous nodules v >70% of patients complain of fatigue * Zuckerman E et al. Bio. Drugs 2001; 15: 573 Liver Unit - Hadassah
HCV Associated Arthritis* v Commonly presents as rheumatoid arthritis like symptoms ( severe morning stiffness and pain) with symmetrical arthritis of small joints v Mono or oligo-arthritis less common v Clinical course usually benign without deformities v Absence of subcutaneous nodules v >70% of patients complain of fatigue * Zuckerman E et al. Bio. Drugs 2001; 15: 573 Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma * v Some evidence suggests that persistent HCV v v v infection leading to lymphoproliferation and cryoglobulinemia may switch over to lymphoma HCV-RNA has repeatedly been demonstrated in lymphoid and BM cells HCV viremia reported in up to 35% of patients with B cell lymphoma and almost 90% of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients with cryoglobulinemia Diagnosis sometime overlooked due to occult presentation and /or similarity of symptoms to chronic HCV infection Liver Unit - Hadassah * Dammacco F. et al. Seminars in Liver-Disease. 2000; 20: 143
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma * v Some evidence suggests that persistent HCV v v v infection leading to lymphoproliferation and cryoglobulinemia may switch over to lymphoma HCV-RNA has repeatedly been demonstrated in lymphoid and BM cells HCV viremia reported in up to 35% of patients with B cell lymphoma and almost 90% of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients with cryoglobulinemia Diagnosis sometime overlooked due to occult presentation and /or similarity of symptoms to chronic HCV infection Liver Unit - Hadassah * Dammacco F. et al. Seminars in Liver-Disease. 2000; 20: 143
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Neurological and Musculoskeletal Involvement v Peripheral neuropathy reported but rare v Muscle weakness and myopathy are frequent complaints in fatigued HCV patients , often with cryoglobulinemia v Some rare. latent muscle disorders may exacerbate in HCV patients receiving interferon treatment v Myasthenia Gravis rarely observed in Liver Unit - Hadassah interfeon treated patients
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Neurological and Musculoskeletal Involvement v Peripheral neuropathy reported but rare v Muscle weakness and myopathy are frequent complaints in fatigued HCV patients , often with cryoglobulinemia v Some rare. latent muscle disorders may exacerbate in HCV patients receiving interferon treatment v Myasthenia Gravis rarely observed in Liver Unit - Hadassah interfeon treated patients
 Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Dermatologic Involvement* • • Pruritus – Non specific Leukocytoclastic-cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis with cryoglobulinemia Lichen Planus Erythema Multiforme Erythema Nodosum Urticaria Porphyria Cutanea Tarda Malaplakia *S. J. Hadziyannis. (Review). Liver Unit - Hadassah J Viral Hepatitis 1997; 4: 9
Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV Dermatologic Involvement* • • Pruritus – Non specific Leukocytoclastic-cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis with cryoglobulinemia Lichen Planus Erythema Multiforme Erythema Nodosum Urticaria Porphyria Cutanea Tarda Malaplakia *S. J. Hadziyannis. (Review). Liver Unit - Hadassah J Viral Hepatitis 1997; 4: 9
 Rare (anecdotal? ) Association with HCV § Behcet Syndrome § Generalized vasculitis in polyarteritis nodosa § Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vasculitis § Anti-phospholipid syndrome § Auto-antibodies in autoimmune hepatitis Liver Unit - Hadassah
Rare (anecdotal? ) Association with HCV § Behcet Syndrome § Generalized vasculitis in polyarteritis nodosa § Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vasculitis § Anti-phospholipid syndrome § Auto-antibodies in autoimmune hepatitis Liver Unit - Hadassah
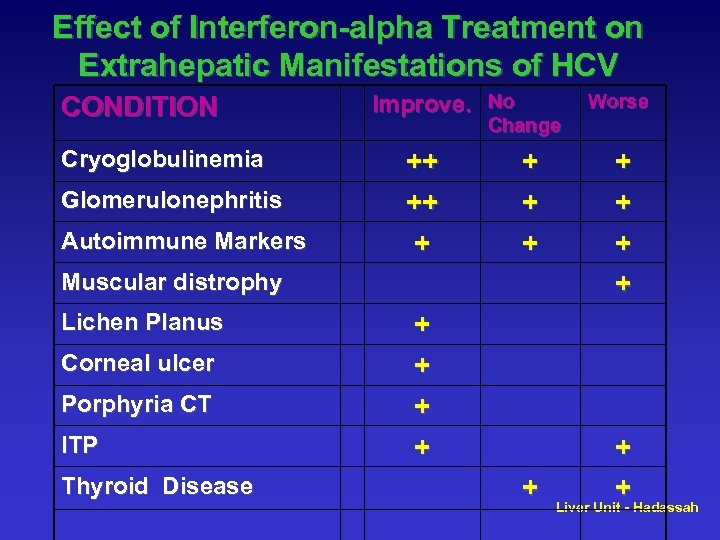 Effect of Interferon-alpha Treatment on Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV CONDITION Cryoglobulinemia Glomerulonephritis Autoimmune Markers Improve. No Change ++ ++ + Muscular distrophy Lichen Planus Corneal ulcer Porphyria CT ITP Thyroid Disease Worse + + + + Liver Unit - Hadassah
Effect of Interferon-alpha Treatment on Extrahepatic Manifestations of HCV CONDITION Cryoglobulinemia Glomerulonephritis Autoimmune Markers Improve. No Change ++ ++ + Muscular distrophy Lichen Planus Corneal ulcer Porphyria CT ITP Thyroid Disease Worse + + + + Liver Unit - Hadassah
 Clinical Presentation of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Summary ü The liver is the primary target for the hepatotropic HCV ü Yet infection with HCV is a systemic disease and can involve most organs ü Clinicians taking care of patients with HCV must pay attention to the multisystemic nature of the disease including the effects on general well being and quality Liver Unit - Hadassah of life
Clinical Presentation of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Summary ü The liver is the primary target for the hepatotropic HCV ü Yet infection with HCV is a systemic disease and can involve most organs ü Clinicians taking care of patients with HCV must pay attention to the multisystemic nature of the disease including the effects on general well being and quality Liver Unit - Hadassah of life


