ca894bac2dcc04add1fa8ab38ff3f632.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

CLINICAL ASPECTS OF BIOCHEMISTRY PROTEINS AND DISEASE HAEMOGLOBIN AND HAPTOGLOBIN Haemoglobin - revision Haemoglobin variants - haemoglobinopathies Haemoglobin S Thalassaemia Haptoglobins

HAEMOGLOBIN - REVISION Myoglobin (Mb) Oxygen binding/storage protein in muscle; may also play a part in local oxygen transport. O 2 binds to haem. Maintenance of haem in Fe 2+ form is necessary for O 2 binding. Mb is a monomeric protein of about 150 aa. Haemoglobin A (Hb. A) O 2 carrier in blood (red cells). Tetramer: 2 2. Quaternary structure allows allostery - cooperative binding of O 2 modulated by p. H (Bohr effect), CO 2 binding, bisphoglycerate (BPG) binding. 3 D structure of each chain is similar to that of Mb.
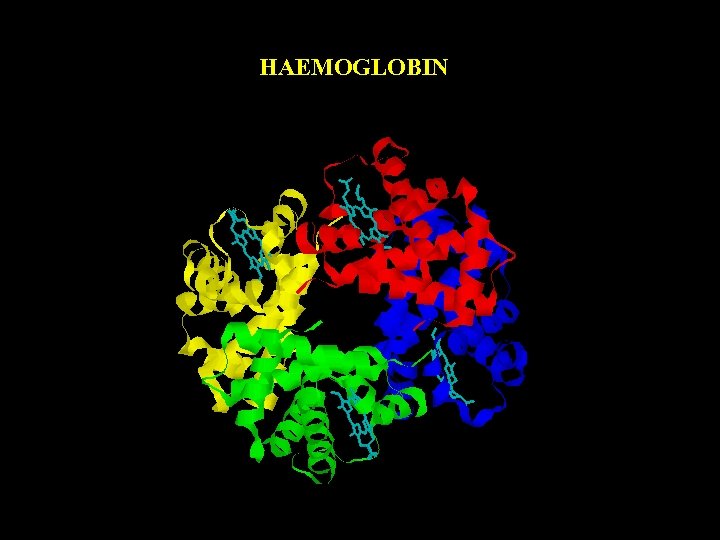
HAEMOGLOBIN
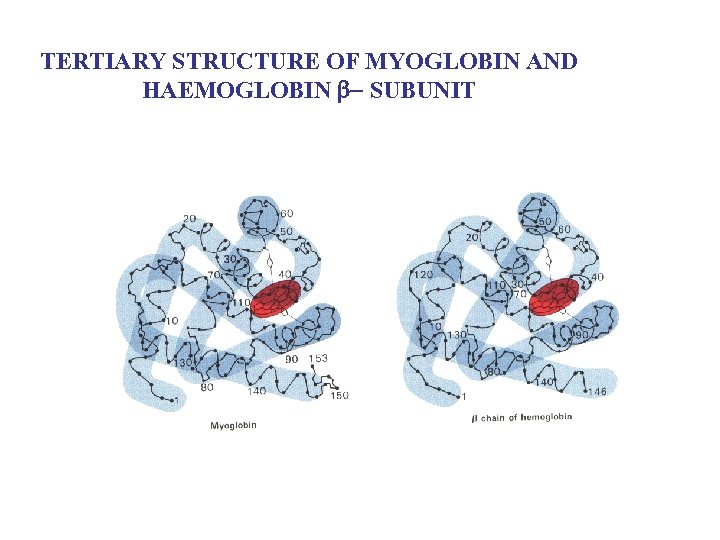
TERTIARY STRUCTURE OF MYOGLOBIN AND HAEMOGLOBIN b SUBUNIT
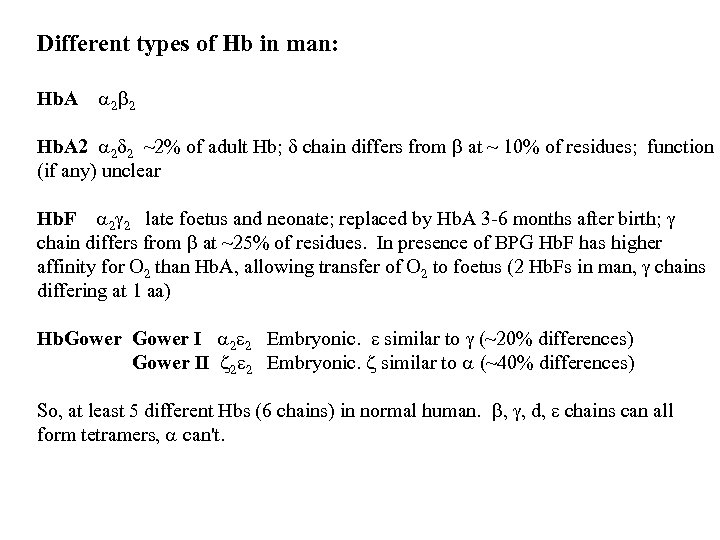
Different types of Hb in man: Hb. A 2 2 Hb. A 2 2 2 ~2% of adult Hb; chain differs from at ~ 10% of residues; function (if any) unclear Hb. F 2 2 late foetus and neonate; replaced by Hb. A 3 -6 months after birth; chain differs from at ~ of residues. In presence of BPG Hb. F has higher affinity for O 2 than Hb. A, allowing transfer of O 2 to foetus (2 Hb. Fs in man, chains differing at 1 aa) Hb. Gower I 2 2 Embryonic. similar to (~20% differences) Gower II 2 2 Embryonic. similar to (~40% differences) So, at least 5 different Hbs (6 chains) in normal human. , , d, chains can all form tetramers, can't.
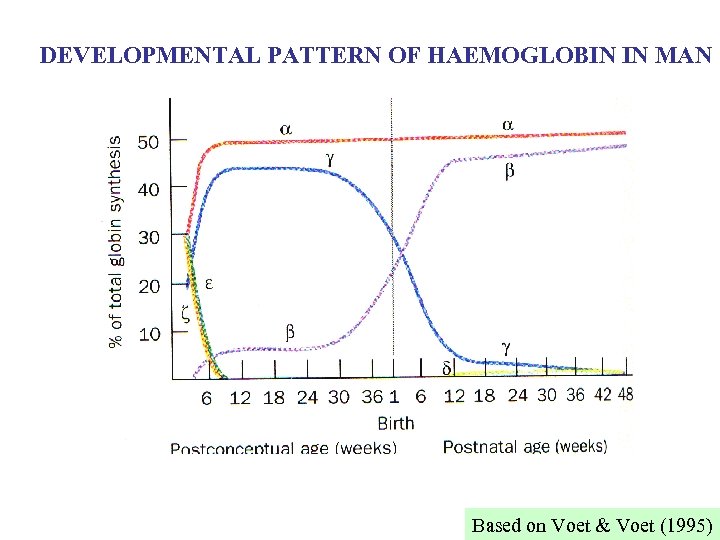
DEVELOPMENTAL PATTERN OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN MAN Based on Voet & Voet (1995)
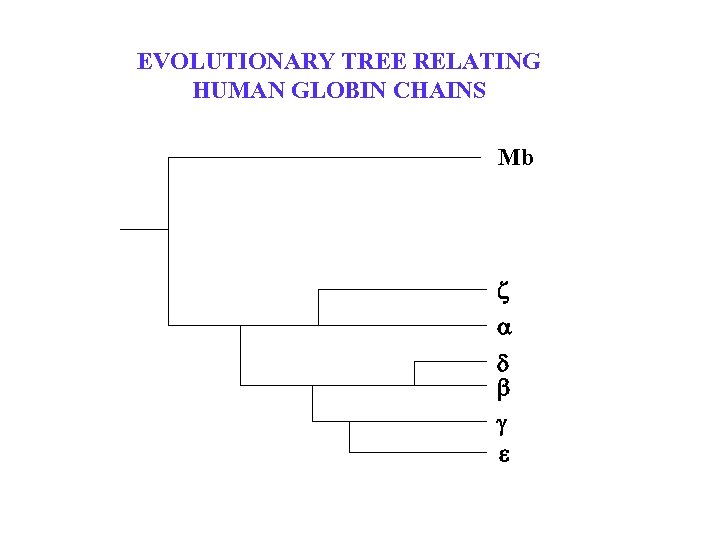
EVOLUTIONARY TREE RELATING HUMAN GLOBIN CHAINS Mb z d b g e
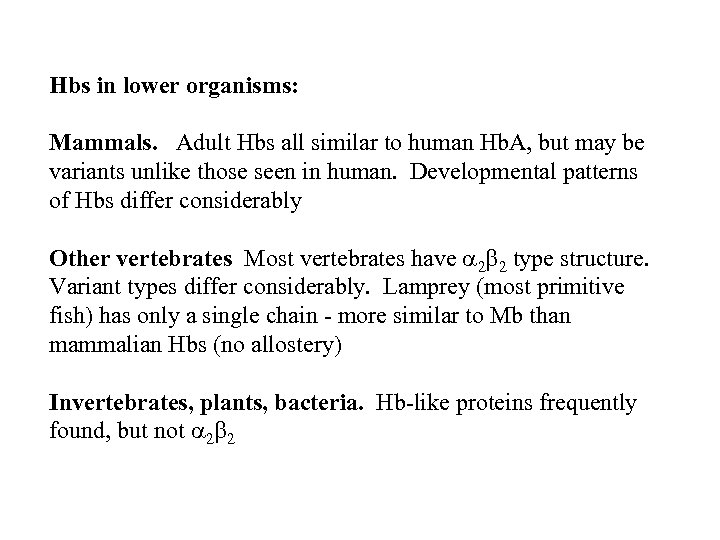
Hbs in lower organisms: Mammals. Adult Hbs all similar to human Hb. A, but may be variants unlike those seen in human. Developmental patterns of Hbs differ considerably Other vertebrates Most vertebrates have 2 2 type structure. Variant types differ considerably. Lamprey (most primitive fish) has only a single chain - more similar to Mb than mammalian Hbs (no allostery) Invertebrates, plants, bacteria. Hb-like proteins frequently found, but not 2 2

HAEMOGLOBIN VARIANTS - HAEMOGLOBINOPATHIES 1. Exterior of molecule e. g. Glu 6 Val [haemoglobin S (Hb. S)] Glu 2. B 8 Lys (harmless? ) Altered tertiary structure Phe [Hb Hammersmith] Gly 3. CD 1 Ser B 6 Arg [Hb Riverdale-Bronx] Altered 'active site’ His F 8 Tyr His 4. [Hb Iwate] (proximal His) ) E 7 Tyr [Hb Boston] (distal His) )(cyanosis; methaemoglobinaemia) Alterations at subunit interfaces Asp Asn G 1 His G 4 Thr [Hb Yakima] ) [Hb Kansas] ) (polycythaemia or cyanosis)
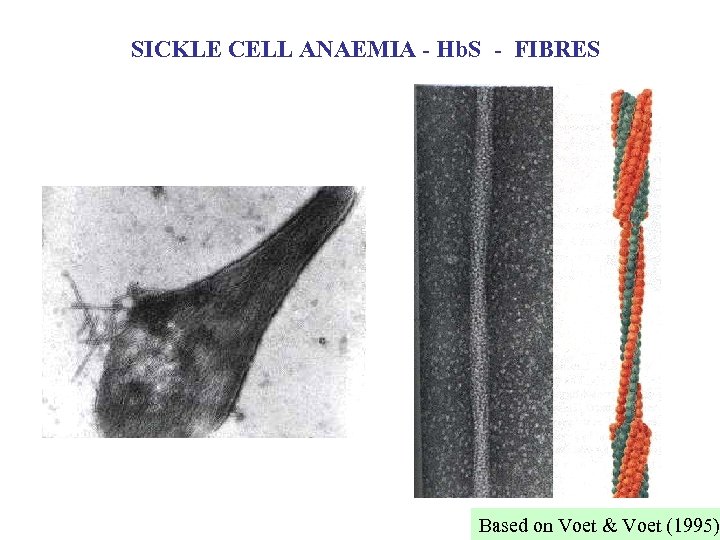
SICKLE CELL ANAEMIA - Hb. S - FIBRES Based on Voet & Voet (1995)
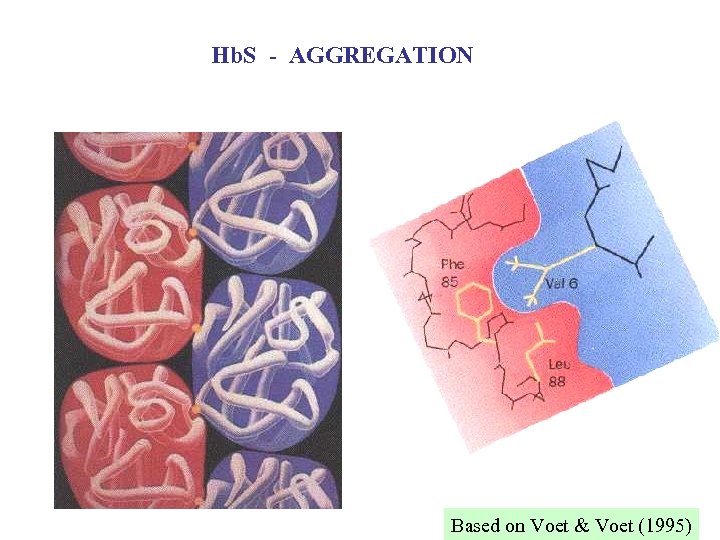
Hb. S - AGGREGATION Based on Voet & Voet (1995)

HAEMOGLOBIN S (Hb. S) Possible therapies: 1. Disruption of intramolecular interactions (peptides? ) 2. Use of agents to increase O 2 binding affinity 3. Lower Hb. S concentration (increase erythrocyte permeability) 4. Keep Hb. F switched on (hydroxyurea) 5. Vasodilators 6. Gene therapy

and b THALASSAEMIAS 0 and 0 thalassaemias- corresponding globin chain missing completely and + thalassaemias - corresponding globin chain produced in reduced amount thalassaemia 1. 2. 3. 4. Silent carrier state: thalassaemia trait: Hb H disease: Hydrops fetalis: [ Hb Barts: excess g 4; 1 (of 4) genes missing 2 genes missing 3 genes missing 4 genes missing [lethal] Hb. H: excess b 4 ] Also thalassaemia due to other causes. E. g. Hb Constant Spring: Mutant stop codon and read-through of 31 aas, but m. RNA degraded, so little protein
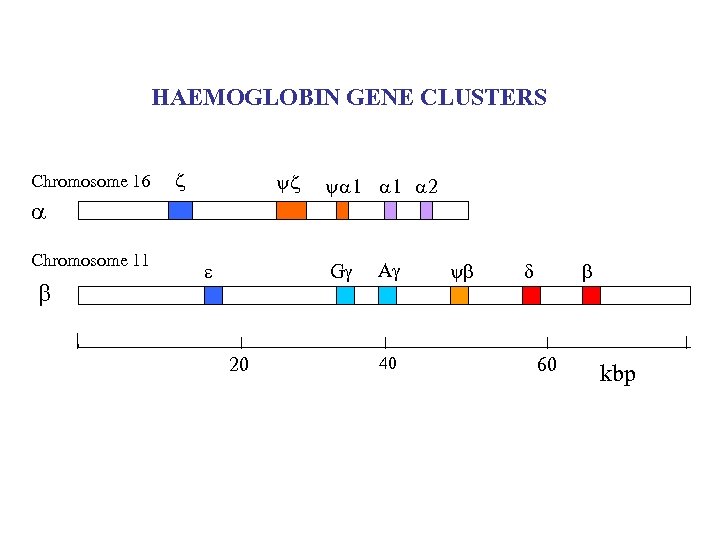
HAEMOGLOBIN GENE CLUSTERS Chromosome 16 y Chromosome 11 y 1 1 2 G 20 A 40 y 60 kbp
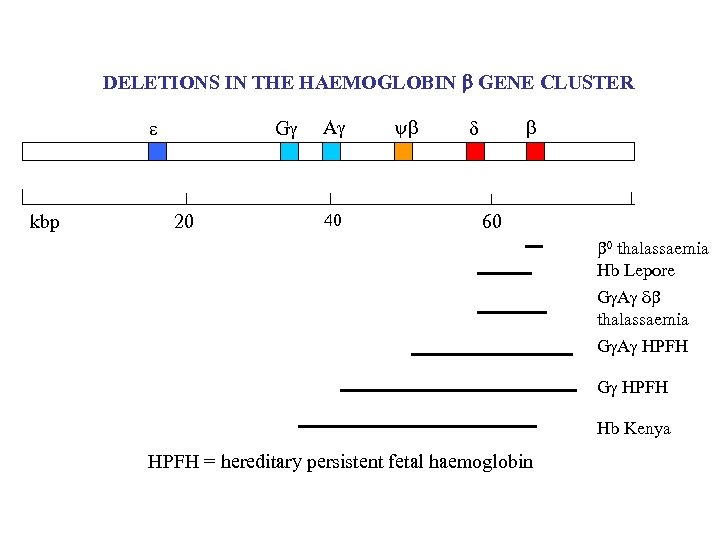
DELETIONS IN THE HAEMOGLOBIN b GENE CLUSTER kbp G 20 A 40 y 60 0 thalassaemia Hb Lepore G A thalassaemia G A HPFH G HPFH Hb Kenya HPFH = hereditary persistent fetal haemoglobin

b thalassaemia Point mutations that can cause thalassaemia: 1. Nonsense mutations 2. Frameshift 3. Point mutation in promoter 4. Point mutations that inactivate or generate splice sites 5. Point mutations of the AATAAA sequence
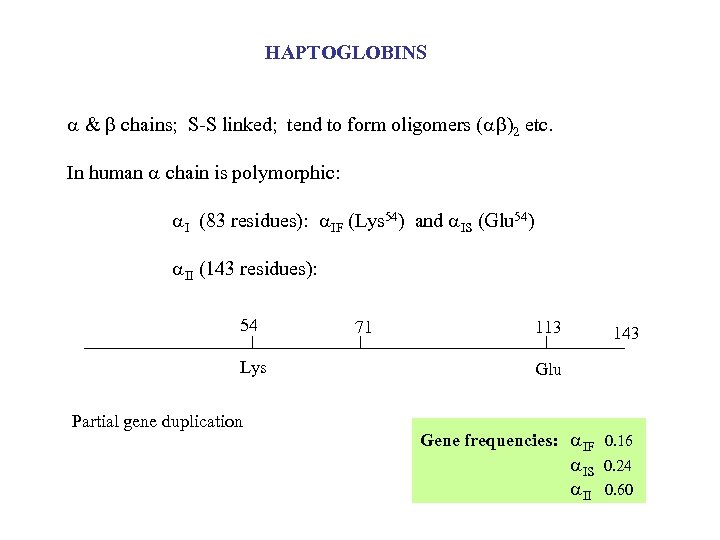
HAPTOGLOBINS & chains; S-S linked; tend to form oligomers ( )2 etc. In human chain is polymorphic: I (83 residues): IF (Lys 54) and IS (Glu 54) II (143 residues): 54 Lys Partial gene duplication 71 113 143 Glu Gene frequencies: IF 0. 16 IS II 0. 24 0. 60
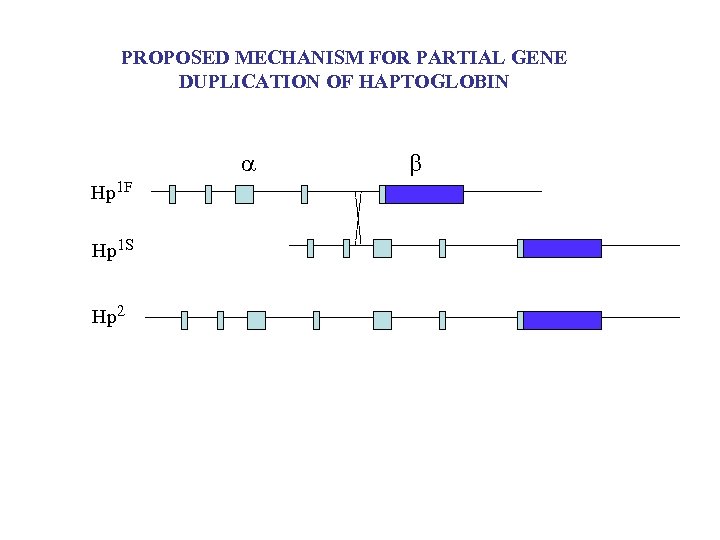
PROPOSED MECHANISM FOR PARTIAL GENE DUPLICATION OF HAPTOGLOBIN Hp 1 F Hp 1 S Hp 2
ca894bac2dcc04add1fa8ab38ff3f632.ppt